Provinces of Indonesia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Provinces are the first-level
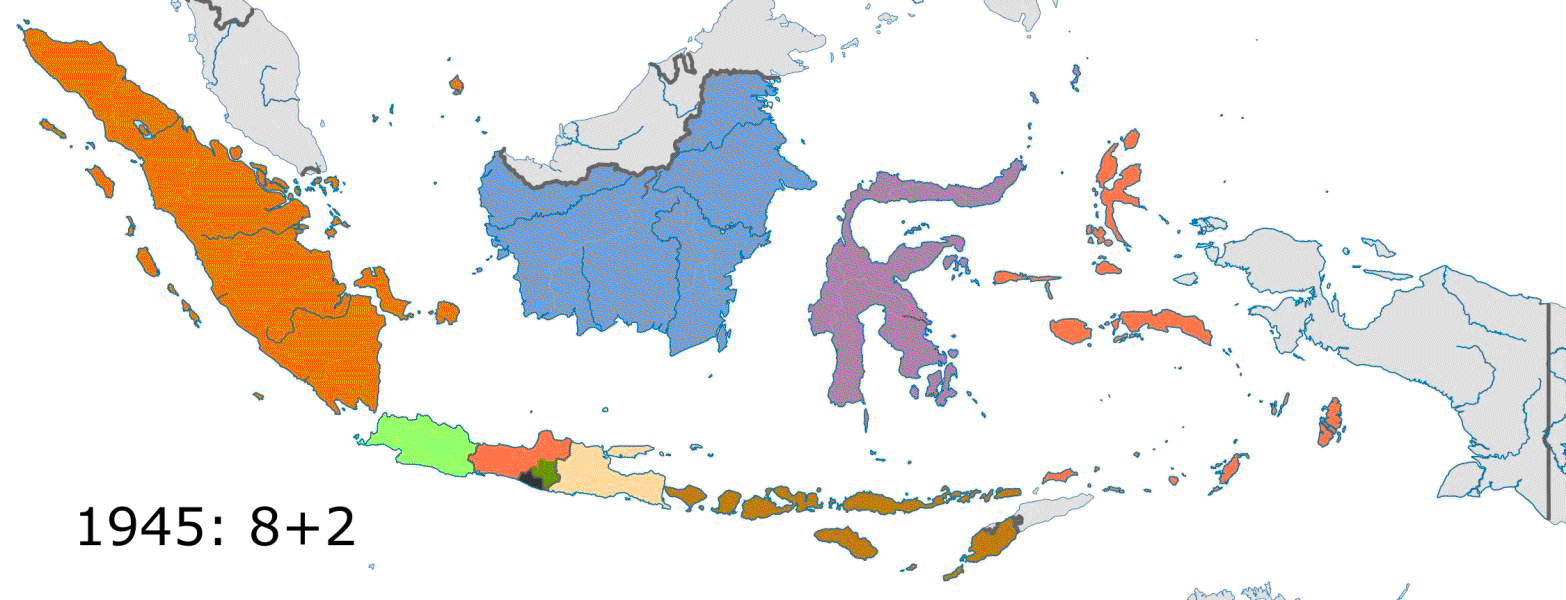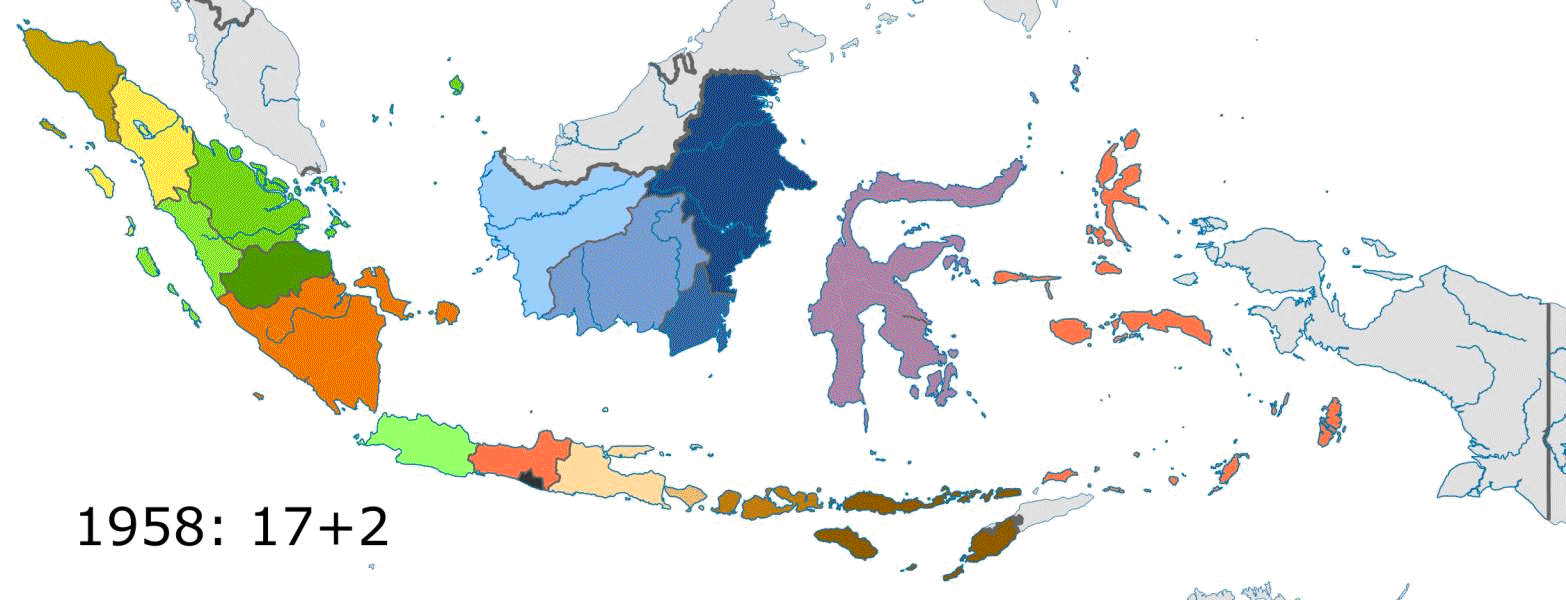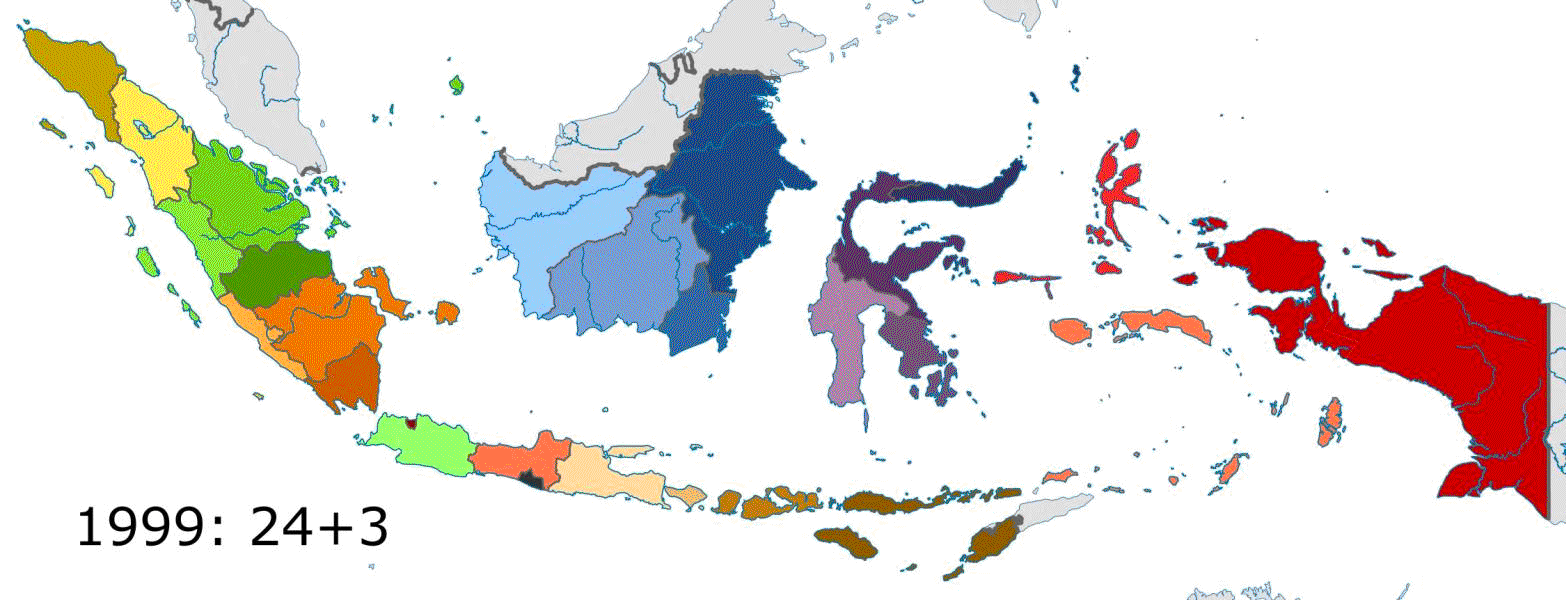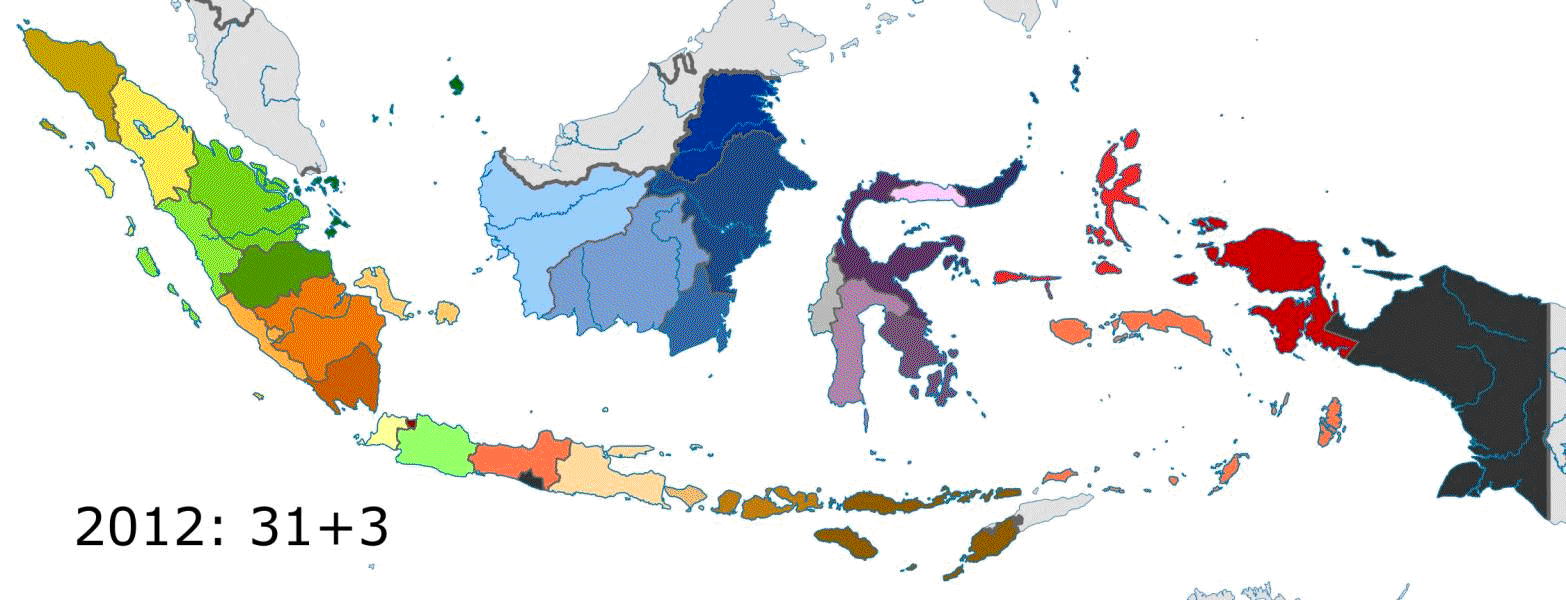 Upon the independence of Indonesia, eight provinces were established.
Upon the independence of Indonesia, eight provinces were established.
administrative division
Administrative divisions (also administrative units, administrative regions, subnational entities, or constituent states, as well as many similar generic terms) are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divi ...
s of Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
. They were formerly called first-level provincial regions (), before the Reform era. Provinces have a local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of a higher-level political or administrative unit, such a ...
, consisting of a
governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
() and a regional legislative body (). The governor and members of local representative bodies are elected by popular vote for five-year terms, but governors can only serve for two terms. Provincial governments have the authority to regulate and manage their own government affairs, subject to the limits of the central government. The average land area of all 38 provinces in Indonesia is about , and they had an average population of 7,410,626 people in mid-2024.
Indonesia is divided into 38 provinces, nine of which have special autonomous status. The terms for special status are "" and "", which translate to "special", or "designated". Provinces are further divided into regencies and cities (formerly called second-level region regencies/cities, or ), which are in turn subdivided into districts (). Proposals for the creation of additional provinces (by the splitting of existing ones) have been considered by the Indonesian government, but further action has been suspended since 2013 under a moratorium. However, in 2022, nine years later, Central Papua, Highland Papua
Highland Papua () is a provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of the Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago (often shortened to La Pago). It covers an area of and had a population of 1,467,050 according to ...
, South Papua, and Southwest Papua were created and became the youngest provinces in the country. The enactment of the Law on State Capital in 2022 established a future provincial-level city, Nusantara, which would officially become the 39th province after a presidential decree on relocating the state capital is issued, and it would replace Jakarta as the nation's capital city.
Background
Article 18 paragraph 1 of the 1945 Constitution states that "the Unitary State of the Republic of Indonesia is divided into provincial regions and those provincial regions are divided into regencies and city, whereby every one of those provinces, regencies, and municipalities has its regional government, which shall be regulated by laws." According to the Law on Regional Government (UU 23/2014) the authority of the Provincial Government includes: # Development planning and control; # Planning, utilization, and community peace; # Implementation of public order and public peace; # Provision of public facilities and infrastructure; # Handling the health sector; # Education and allocation of potential human resources; # Handling social problems across regencies/cities; # Services in the field of manpower across regencies/cities; # Facilitating the development of cooperatives, small and medium enterprises, including across districts/cities; # Environmental control; # Defense services, including across regencies/cities; # Population and civil registration services; # Government general administration services; # Investment administration services, including across regencies/cities; # The implementation of other basic services that cannot be carried out by regencies/cities; and # Other mandatory affairs mandated by laws and regulations. The authority of the provincial government are government affairs which are located across regencies/municipalities, government affairs whose users are across regencies/municipalities, government affairs whose benefits or negative impacts lie across regencies/municipalities, government affairs which use more resources. efficient if carried out by the province. Each province has alocal government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of a higher-level political or administrative unit, such a ...
, headed by a governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
and a legislative body (DPRD). The governor and members of local representative bodies are elected by popular vote for five-year terms, but governors can only serve for two terms. The general election to elect members of the DPRDs is conducted simultaneously with the national general election. Previously, the general elections for Governor and Vice Governor were not held simultaneously. However, since 2015 regional head elections have been held simultaneously. Under the plan, simultaneous partial local elections were held in February 2017, June 2018 and December 2020, culminating in simultaneous elections for all local executive posts in November 2024 and then every five years.
Current provinces
Special autonomy
The decentralization of some power and autonomy to provinces is called for by Article 18 of the Constitution of Indonesia, and this article was expanded through amendments in October 1999 in the period following the fall of Suharto. Some provinces have been granted additional autonomy beyond this, although Indonesia is not afederated state
A federated state (also State (polity), state, province, region, Canton (administrative division), canton, Länder, land, governorate, oblast, emirate, or country) is a territorial and constitutional community forming part of a federation ...
. The form this special autonomy takes is not standardized, with provinces gaining different formulations of specific autonomy based on particular political imperatives.
* The Special Region of Yogyakarta, which was autonomous under Dutch rule, was (along with Surakarta
Surakarta (Javanese script, Javanese: , Pegon script, Pegon: ), known colloquially as Solo (Javanese script, Javanese: ; ), is a major List of regencies and cities of Indonesia, city in Central Java, Indonesia. The city adjoins Karanganyar Reg ...
) given consideration for autonomy as part of Law no. 1 of 1945. Autonomy for Yogyakarta was confirmed directly through Law no. 3 of 1950, the first granting of special autonomy to a province. This status has been maintained until the present, with some tweaks from additional laws. Sultan Hamengkubuwono serves as a hereditary governor and Adipati Paku Alam as a hereditary vice-governor.
* Rebellion
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
in Aceh
Aceh ( , ; , Jawi script, Jawoë: ; Van Ophuijsen Spelling System, Old Spelling: ''Atjeh'') is the westernmost Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is located on the northern end of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capit ...
due to demands for a stricter implementation of Islamic law has led to several shifts in political status. Specific autonomy was initially granted to the province through Law no. 24 of 1956. Further autonomy was given through the declaration that Aceh was a "special region" on 23 May 1959, later formalized through Law no. 18 of 1965. Following the fall of Suharto, Law no. 44 of 1999 and Law no. 18 of 2001 created a new framework that was adopted by both parties through Law no. 11 of 2006. This law provides privileged status regarding implementation of Islamic law in religious life for Muslim citizens, customary life, and education. Aceh also received its own development fund for a period of 20 years.
* The province of Papua was granted special autonomy through Law no. 21 of 2001. This was a response to independence movements that had been present in the province since it became part of Indonesia, and occurred alongside the renaming of the province from Irian Jaya to Papua. This gave Papua a greater portion of revenue, autonomy outside reserved areas maintained by the central government, and 20 years of a special development fund. Before special autonomy was implemented, West Papua was split from Papua in 2003, although both kept special autonomy. The special autonomy for both provinces was renewed in 2021, including a renewal and increase of the special autonomy fund. Included in this new legislation was the provision to create new provinces, and in July 2022 new national legislation split South Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua
Highland Papua () is a provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of the Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago (often shortened to La Pago). It covers an area of and had a population of 1,467,050 according to ...
from Papua through Law Number 14 of 2022, Law Number 15 of 2022, and Law Number 16 of 2022 respectively. Law No. 29 of 2022 was enacted in December 2022 splitting Southwest Papua from West Papua. All the split provinces retained their autonomous status.
* The Special Capital Region of Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
has its own status, due to it being the country's capital and largest city.
Geographical units
The provinces are officially grouped into seven geographical units for statistical and national planning purposes, but without administrative function. ISO 3166-2:IDFormer provinces
 Upon the independence of Indonesia, eight provinces were established.
Upon the independence of Indonesia, eight provinces were established. West Java
West Java (, ) is an Indonesian Provinces of Indonesia, province on the western part of the island of Java, with its provincial capital in Bandung. West Java is bordered by the province of Banten and the country's capital region of Jakarta to t ...
, Central Java, East Java, and Maluku still exist as of today despite later divisions, while Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
, Kalimantan
Kalimantan (; ) is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area, and consists of the provinces of Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan, North Kalimantan, South Kalimantan, and West Kalimantan. The non-Ind ...
, Sulawesi
Sulawesi ( ), also known as Celebes ( ), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the List of islands by area, world's 11th-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Min ...
, and Nusa Tenggara
The Lesser Sunda Islands (, , ), now known as Nusa Tenggara Islands (, or "Southeast Islands"), are an archipelago in the Indonesian archipelago. Most of the Lesser Sunda Islands are located within the Wallacea region, except for the Bali pr ...
, formerly Lesser Sunda (''Sunda Kecil'') were fully liquidated by dividing them into new provinces. The province of Central Sumatra existed from 1948 to 1957, while East Timor
Timor-Leste, also known as East Timor, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is a country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the coastal exclave of Oecusse in the island's northwest, and ...
was annexed as a province from 1976 until its power transfer to UNTAET in 1999 prior to its independence as a country in 2002.
New provinces made from currently-existing provinces
Renamed provinces
Former provincial capitals
* Tanjungpinang to Pekanbaru, Riau (until 1959) *Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
to Bandung
Bandung is the capital city of the West Java province of Indonesia. Located on the island of Java, the city is the List of Indonesian cities by population, fourth-most populous city and fourth largest city in Indonesia after Jakarta, Surabay ...
, West Java (until 1960)
* Singaraja to Denpasar, Bali (until 1960)
* Soasio to Sukarnopura, West Irian (1956–1963)
* Dili, East Timor (1975–1999), later became the capital of Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste
*Ternate
Ternate (), also known as the City of Ternate (; ), is the
List of regencies and cities of Indonesia, city with the largest population in the province of North Maluku and an island in the Maluku Islands, Indonesia. It was the ''de facto'' provi ...
to Sofifi, North Maluku (until 2010)
* Banjarmasin to Banjarbaru, South Kalimantan (until 2022)
See also
*List of regencies and cities of Indonesia
Regency (Indonesia), Regencies () and City status in Indonesia#Kota, cities (''kota'') are the second-level subdivisions of Indonesia, administrative subdivision in Indonesia, immediately below the Provinces of Indonesia, provinces, and above th ...
* Subdivisions of Indonesia
Notes
References
{{Authority controlIndonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
Subdivisions of Indonesia
Provinces
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ...