Photoreceptor cell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the
 Each photoreceptor absorbs light according to its
Each photoreceptor absorbs light according to its
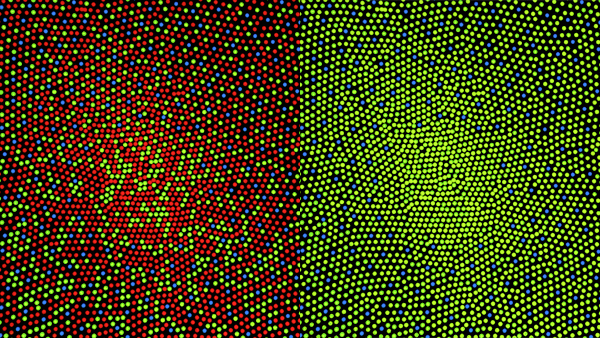 Most vertebrate photoreceptors are located in the retina. The distribution of rods and cones (and classes thereof) in the retina is called the retinal mosaic. Each human
Most vertebrate photoreceptors are located in the retina. The distribution of rods and cones (and classes thereof) in the retina is called the retinal mosaic. Each human
 The path of a visual signal is described by the phototransduction cascade, the mechanism by which the energy of a photon signals a mechanism in the cell that leads to its electrical polarization. This polarization ultimately leads to either the transmittance or inhibition of a neural signal that will be fed to the brain via the
The path of a visual signal is described by the phototransduction cascade, the mechanism by which the energy of a photon signals a mechanism in the cell that leads to its electrical polarization. This polarization ultimately leads to either the transmittance or inhibition of a neural signal that will be fed to the brain via the
Blind people 'see' sunrise and sunset
New Scientist, 26 December 2007, issue 2635.Medical News Today
Normal Responses To Non-visual Effects Of Light Retained By Blind Humans Lacking Rods And Cones
. 14 December 2007. As had been found in other mammals, the identity of the non-rod non-cone photoreceptor in humans was found to be a ganglion cell in the inner retina. The researchers had tracked down patients with rare diseases wiping out classic rod and cone photoreceptor function but preserving ganglion cell function. Despite having no rods or cones the patients continued to exhibit circadian photoentrainment, circadian behavioural patterns, melanopsin suppression, and pupil reactions, with peak spectral sensitivities to environmental and experimental light matching that for the melanopsin photopigment. Their brains could also associate vision with light of this frequency.
NIF Search – Photoreceptor Cell
via the
retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
that is capable of visual phototransduction
Visual phototransduction is the sensory transduction process of the visual system by which light is detected by photoreceptor cells ( rods and cones) in the vertebrate retina. A photon is absorbed by a retinal chromophore (each bound to an op ...
. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. It equals the interior potential minus the exterior potential. This is th ...
.
There are currently three known types of photoreceptor cells in mammalian eyes: rods, cones, and intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells. The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system
The visual system is the physiological basis of visual perception (the ability to perception, detect and process light). The system detects, phototransduction, transduces and interprets information concerning light within the visible range to ...
to form an image of the environment, sight
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual percept ...
. Rods primarily mediate scotopic vision (dim conditions) whereas cones primarily mediate photopic vision
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under well-lit conditions (luminance levels from 10 to 108 cd/m2). In humans and many other animals, photopic vision allows color perception, mediated by cone cells, and a significantly higher vis ...
(bright conditions), but the processes in each that supports phototransduction is similar. The intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells were discovered during the 1990s. These cells are thought not to contribute to sight directly, but have a role in the entrainment of the circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
and the pupillary reflex.
Photosensitivity
spectral sensitivity
Spectral sensitivity is the relative efficiency of detection, of light or other signal, as a function of the frequency or wavelength of the signal.
In visual neuroscience, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics ...
(absorptance), which is determined by the photoreceptor proteins expressed in that cell. Humans have three classes of cones (L, M, S) that each differ in spectral sensitivity and 'prefer' photons of different wavelengths (see graph). For example, the peak wavelength of the S-cone's spectral sensitivity is approximately 420 nm (nanometers, a measure of wavelength), so it is more likely to absorb a photon at 420 nm than at any other wavelength. Light of a longer wavelength can also produce the same response from an S-cone, but it would have to be brighter to do so.
In accordance with the principle of univariance, a photoreceptor's output signal is proportional only to the number of photons absorbed. The photoreceptors can not measure the wavelength of light that it absorbs and therefore does not detect color on its own. Rather, it is the ratios of responses of the three types of cone cells that can estimate wavelength, and therefore enable color vision.
Histology
Rod andcone
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the '' apex'' or '' vertex''.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines ...
photoreceptors are found on the outermost layer of the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
; they both have the same basic structure. Closest to the visual field (and farthest from the brain) is the axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, ...
terminal, which releases a neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
called glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
to bipolar cells. Farther back is the cell body, which contains the cell's organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
s. Farther back still is the inner segment, a specialized part of the cell full of mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
. The chief function of the inner segment is to provide ATP (energy) for the sodium-potassium pump. Finally, closest to the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
(and farthest from the field of view) is the outer segment, the part of the photoreceptor that absorbs light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
. Outer segments are actually modified cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
that contain disks filled with opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most pro ...
, the molecule that absorbs photons, as well as voltage-gated sodium channels.
The membranous photoreceptor protein ''opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most pro ...
'' contains a pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
molecule called ''retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use ret ...
''. In rod cells, these together are called rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the ''RHO'' gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction in rod cells. Rhodopsin mediates dim ...
. In cone cells, there are different types of opsins that combine with retinal to form pigments called photopsins. Three different classes of photopsins in the cones react to different ranges of light frequency, a selectivity that allows the visual system to transduce color
Color (or colour in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though co ...
. The function of the photoreceptor cell is to convert the light information of the photon into a form of information communicable to the nervous system and readily usable to the organism: This conversion is called signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
.
The opsin found in the intrinsically photosensitive ganglion cells of the retina is called melanopsin
Melanopsin is a type of photopigment belonging to a larger family of light-sensitive retinylidene protein, retinal proteins called opsins and encoded by the gene ''Opn4''. In the mammalian retina, there are two additional categories of opsins, b ...
. These cells are involved in various reflexive responses of the brain and body to the presence of (day)light, such as the regulation of circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
s, pupillary reflex and other non-visual responses to light. Melanopsin functionally resembles invertebrate opsins.
Retinal mosaic
 Most vertebrate photoreceptors are located in the retina. The distribution of rods and cones (and classes thereof) in the retina is called the retinal mosaic. Each human
Most vertebrate photoreceptors are located in the retina. The distribution of rods and cones (and classes thereof) in the retina is called the retinal mosaic. Each human retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
has approximately 6 million cones and 120 million rods. At the "center" of the retina (the point directly behind the lens) lies the fovea (or fovea centralis), which contains only cone cells; and is the region capable of producing the highest visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye ...
or highest resolution. Across the rest of the retina, rods and cones are intermingled. No photoreceptors are found at the blind spot, the area where ganglion cell fibers are collected into the optic nerve and leave the eye. The distribution of cone classes (L, M, S) are also nonhomogenous, with no S-cones in the fovea, and the ratio of L-cones to M-cones differing between individuals.
The number and ratio of rods to cones varies among species, dependent on whether an animal is primarily diurnal or nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatur ...
. Certain owls, such as the nocturnal tawny owl
The tawny owl (''Strix aluco''), also called the brown owl, is a stocky, medium-sized owl in the family Strigidae. It is commonly found in woodlands across Europe, as well as western Siberia, and has seven recognized subspecies. The tawny owl' ...
, have a tremendous number of rods in their retinae. Other vertebrates will also have a different number of cone classes, ranging from monochromats to pentachromats.
Signaling
 The path of a visual signal is described by the phototransduction cascade, the mechanism by which the energy of a photon signals a mechanism in the cell that leads to its electrical polarization. This polarization ultimately leads to either the transmittance or inhibition of a neural signal that will be fed to the brain via the
The path of a visual signal is described by the phototransduction cascade, the mechanism by which the energy of a photon signals a mechanism in the cell that leads to its electrical polarization. This polarization ultimately leads to either the transmittance or inhibition of a neural signal that will be fed to the brain via the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
. The steps that apply to the phototransduction pathway from vertebrate rod/cone photoreceptors are:
#The Vertebrate visual opsin in the disc membrane of the outer segment absorbs a photon, changing the configuration of a retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use ret ...
Schiff base cofactor inside the protein from the cis-form to the trans-form, causing the retinal to change shape.
#This results in a series of unstable intermediates, the last of which binds stronger to a G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a Protein family, family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell (biology), ...
in the membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Bi ...
, called transducin
Transducin (Gt) is a protein naturally expressed in vertebrate retina rods and cones and it is very important in vertebrate phototransduction. It is a type of heterotrimeric G-protein with different α subunits in rod and cone photoreceptors.
...
, and activates it. This is the first amplification step – each photoactivated opsin triggers activation of about 100 transducins.
#Each transducin then activates the enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE).
#PDE then catalyzes the hydrolysis of cGMP to 5' GMP. This is the second amplification step, where a single PDE hydrolyses about 1000 cGMP molecules.
#The net concentration of intracellular cGMP is reduced (due to its conversion to 5' GMP via PDE), resulting in the closure of cyclic nucleotide-gated Na+ ion channels located in the photoreceptor outer segment membrane.
#As a result, sodium ions can no longer enter the cell, and the photoreceptor outer segment membrane becomes hyperpolarized, due to the charge inside the membrane becoming more negative.
#This change in the cell's membrane potential causes voltage-gated calcium channels to close. This leads to a decrease in the influx of calcium ions into the cell and thus the intracellular calcium ion concentration falls.
#A decrease in the intracellular calcium concentration means that less glutamate is released via calcium-induced exocytosis to the bipolar cell (see below). (The decreased calcium level slows the release of the neurotransmitter glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
, which excites the postsynaptic bipolar cells and horizontal cells.)
#ATP provided by the inner segment powers the sodium-potassium pump. This pump is necessary to reset the initial state of the outer segment by taking the sodium ions that are entering the cell and pumping them back out.
Hyperpolarization
Unlike most sensory receptor cells, photoreceptors actually become hyperpolarized when stimulated; and conversely are depolarized when not stimulated. This means that glutamate is released continuously when the cell is unstimulated, and stimulus causes release to stop. In the dark, cells have a relatively high concentration of cyclic guanosine 3'-5' monophosphate (cGMP), which opens cGMP-gated ion channels. These channels are nonspecific, allowing movement of both sodium and calcium ions when open. The movement of these positively charged ions into the cell (driven by their respectiveelectrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts:
* The chemical gradient, or difference in Concentration, solute concentration across ...
) depolarizes the membrane, and leads to the release of the neurotransmitter glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
.
Unstimulated (in the dark), cyclic-nucleotide gated channels in the outer segment are open because cyclic GMP (cGMP) is bound to them. Hence, positively charged ions (namely sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
ions) enter the photoreceptor, depolarizing it to about −40 mV ( resting potential in other nerve cells is usually −65 mV). This depolarization current is often known as dark current.
Bipolar cells
The photoreceptors (''rods'' and ''cones'') transmit to the bipolar cells, which transmit then to the retinal ganglion cells. Retinal ganglion cell axons collectively form theoptic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
, via which they project to the brain.
The rod and cone photoreceptors signal their absorption of photons via a decrease in the release of the neurotransmitter glutamate to bipolar cells at its axon terminal. Since the photoreceptor is depolarized in the dark, a high amount of glutamate is being released to bipolar cells in the dark. Absorption of a photon will hyperpolarize the photoreceptor and therefore result in the release of ''less'' glutamate at the presynaptic terminal to the bipolar cell.
Every rod or cone photoreceptor releases the same neurotransmitter, glutamate. However, the effect of glutamate differs in the bipolar cells, depending upon the type of receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
imbedded in that cell's membrane. When glutamate binds to an ionotropic receptor, the bipolar cell will depolarize (and therefore will hyperpolarize with light as less glutamate is released). On the other hand, binding of glutamate to a metabotropic receptor results in a hyperpolarization, so this bipolar cell will depolarize to light as less glutamate is released.
In essence, this property allows for one population of bipolar cells that gets excited by light and another population that gets inhibited by it, even though all photoreceptors show the same response to light. This complexity becomes both important and necessary for detecting color, contrast, edges, etc.
Advantages
Phototransduction in rods and cones is somewhat unusual in that the stimulus (in this case, light) reduces the cell's response or firing rate, different from most other sensory systems in which a stimulus increases the cell's response or firing rate. This difference has important functional consequences: # the classic (rod or cone) photoreceptor is depolarized in the dark, which means many sodium ions are flowing into the cell. Thus, the random opening or closing of sodium channels will not affect the membrane potential of the cell; only the closing of a large number of channels, through absorption of a photon, will affect it and signal that light is in the visual field. This system may have less noise relative to sensory transduction schema that increase rate of neural firing in response to stimulus, liketouch
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of bo ...
and olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, ...
.
# there is a lot of amplification in two stages of classic phototransduction: one pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
will activate many molecules of transducin
Transducin (Gt) is a protein naturally expressed in vertebrate retina rods and cones and it is very important in vertebrate phototransduction. It is a type of heterotrimeric G-protein with different α subunits in rod and cone photoreceptors.
...
, and one PDE will cleave many cGMPs. This amplification means that even the absorption of one photon will affect membrane potential and signal to the brain that light is in the visual field. This is the main feature that differentiates rod photoreceptors from cone photoreceptors. Rods are extremely sensitive and have the capacity of registering a single photon of light, unlike cones. On the other hand, cones are known to have very fast kinetics in terms of rate of amplification of phototransduction, unlike rods.
Difference between rods and cones
Comparison of human rod and cone cells, from Eric Kandel et al. in '' Principles of Neural Science''.Development
The key events mediating rod versus S cone versus M cone differentiation are induced by several transcription factors, including RORbeta, OTX2, NRL, CRX, NR2E3 and TRbeta2. The S cone fate represents the default photoreceptor program; however, differential transcriptional activity can bring about rod or M cone generation. L cones are present in primates, however there is not much known for their developmental program due to use of rodents in research. There are five steps to developing photoreceptors: proliferation of multi-potent retinal progenitor cells (RPCs); restriction of competence of RPCs; cell fate specification; photoreceptor gene expression; and lastly axonal growth, synapse formation and outer segment growth. Early Notch signaling maintains progenitor cycling. Photoreceptor precursors come about through inhibition of Notch signaling and increased activity of various factors including achaete-scute homologue 1. OTX2 activity commits cells to the photoreceptor fate. CRX further defines the photoreceptor specific panel of genes being expressed. NRL expression leads to the rod fate. NR2E3 further restricts cells to the rod fate by repressing cone genes. RORbeta is needed for both rod and cone development. TRbeta2 mediates the M cone fate. If any of the previously mentioned factors' functions are ablated, the default photoreceptor is a S cone. These events take place at different time periods for different species and include a complex pattern of activities that bring about a spectrum of phenotypes. If these regulatory networks are disrupted, retinitis pigmentosa, macular degeneration or other visual deficits may result.Ganglion cell photoreceptors
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) are a subset (≈1–3%) ofretinal ganglion cell
A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptor cell, photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: Bipolar ...
s, unlike other retinal ganglion cells, are intrinsically photosensitive due to the presence of melanopsin
Melanopsin is a type of photopigment belonging to a larger family of light-sensitive retinylidene protein, retinal proteins called opsins and encoded by the gene ''Opn4''. In the mammalian retina, there are two additional categories of opsins, b ...
, a light-sensitive protein. Therefore they constitute a third class of photoreceptors, in addition to rod and cone cells.
In human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s the ipRGCs contribute to non-image-forming functions like circadian rhythms, behavior and pupillary light reflex
The pupillary light reflex (PLR) or photopupillary reflex is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity ( luminance) of light that falls on the retinal ganglion cells of the retina in the back of the eye, t ...
. Peak spectral sensitivity
Spectral sensitivity is the relative efficiency of detection, of light or other signal, as a function of the frequency or wavelength of the signal.
In visual neuroscience, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics ...
of the receptor is between 460 and 482 nm. However, they may also contribute to a rudimentary visual pathway enabling conscious
Consciousness, at its simplest, is awareness of a state or object, either internal to oneself or in one's external environment. However, its nature has led to millennia of analyses, explanations, and debate among philosophers, scientists, a ...
sight and brightness detection. Classic photoreceptors (rods and cones) also feed into the novel visual system, which may contribute to color constancy. ipRGCs could be instrumental in understanding many diseases including major causes of blindness worldwide like glaucoma, a disease that affects ganglion cells, and the study of the receptor offered potential as a new avenue to explore in trying to find treatments for blindness.
ipRGCs were only definitively detected ipRGCs in humans during landmark experiments in 2007 on rodless, coneless humans.Coghlan ABlind people 'see' sunrise and sunset
New Scientist, 26 December 2007, issue 2635.Medical News Today
Normal Responses To Non-visual Effects Of Light Retained By Blind Humans Lacking Rods And Cones
. 14 December 2007. As had been found in other mammals, the identity of the non-rod non-cone photoreceptor in humans was found to be a ganglion cell in the inner retina. The researchers had tracked down patients with rare diseases wiping out classic rod and cone photoreceptor function but preserving ganglion cell function. Despite having no rods or cones the patients continued to exhibit circadian photoentrainment, circadian behavioural patterns, melanopsin suppression, and pupil reactions, with peak spectral sensitivities to environmental and experimental light matching that for the melanopsin photopigment. Their brains could also associate vision with light of this frequency.
Non-human photoreceptors
Rod and cone photoreceptors are common to almost all vertebrates. The pineal and parapineal glands are photoreceptive in non-mammalian vertebrates, but not in mammals. Birds have photoactive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons within the paraventricular organ that respond to light in the absence of input from the eyes or neurotransmitters. Invertebrate photoreceptors in organisms such asinsect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s and mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s are different in both their morphological organization and their underlying biochemical pathways. This article describes human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
photoreceptors.
See also
*Visual phototransduction
Visual phototransduction is the sensory transduction process of the visual system by which light is detected by photoreceptor cells ( rods and cones) in the vertebrate retina. A photon is absorbed by a retinal chromophore (each bound to an op ...
*G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...
*Sensory system
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved ...
* Photosensitive
*Photosensitive ganglion cell
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence ...
* Horizontal cell
* Bipolar cell
* Amacrine cell
References
Bibliography
* *External links
*NIF Search – Photoreceptor Cell
via the
Neuroscience Information Framework
The Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/ genomic resources and provides many aut ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Photoreceptor Cell
Human eye anatomy
Histology