Phyllosilicates on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Silicate minerals are rock-forming
Silicate minerals are rock-forming  Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of
Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of
 Nesosilicates (from Greek 'island'), or orthosilicates, have the orthosilicate ion, present as isolated (insular) tetrahedra connected only by interstitial
Nesosilicates (from Greek 'island'), or orthosilicates, have the orthosilicate ion, present as isolated (insular) tetrahedra connected only by interstitial
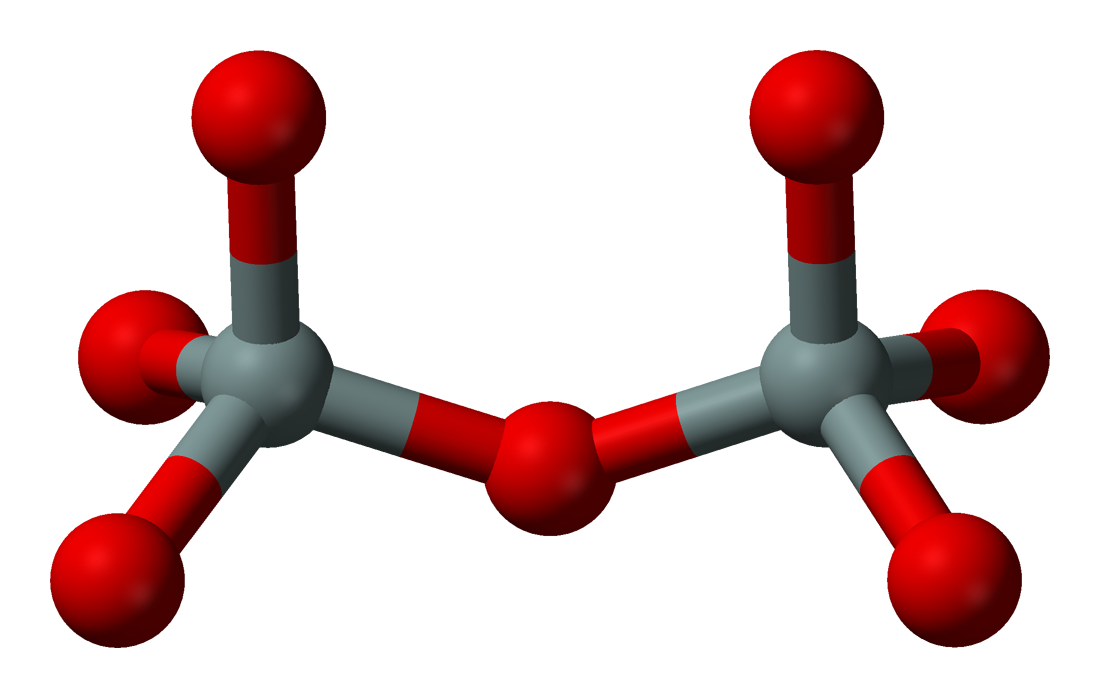 Sorosilicates (from Greek 'heap, mound') have isolated pyrosilicate anions , consisting of double tetrahedra with a shared oxygen vertex—a silicon:oxygen ratio of 2:7. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.B. Examples include:
* Thortveitite –
* Hemimorphite (
Sorosilicates (from Greek 'heap, mound') have isolated pyrosilicate anions , consisting of double tetrahedra with a shared oxygen vertex—a silicon:oxygen ratio of 2:7. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.B. Examples include:
* Thortveitite –
* Hemimorphite (
File:Beryll.ring.combined.png, 6 units ,
Some example minerals are:
* 3-member single ring
** Benitoite –
* 4-member single ring
** Papagoite – .
* 6-member single ring
**
File:Pyroxen-chain.png, Inosilicate, pyroxene family, with 2-periodic single chain , diopside
File:Tremolite-chain.png, Inosilicate, clinoamphibole, with 2-periodic double chains , tremolite
File:Wollastonite-chain.png, Inosilicate, unbranched 3-periodic single chain of
File:Muskovite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, mica group, muscovite (red: Si, blue: O)
File:Apophyllite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, single net of tetrahedra with 4-membered rings, apophyllite-(KF)-apophyllite-(KOH) series
File:Pyrosmalite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, single tetrahedral nets of 6-membered rings, pyrosmalite-(Fe)-pyrosmalite-(Mn) series
File:Zeophyllite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, single tetrahedral nets of 6-membered rings, zeophyllite
File:Carletonite.sheet.png, Phyllosilicate, double nets with 4- and 6-membered rings, carletonite

 Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate tetrahedra with in a 1:2 ratio. This group comprises nearly 75% of the crust of the
Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate tetrahedra with in a 1:2 ratio. This group comprises nearly 75% of the crust of the
 Silicate minerals are rock-forming
Silicate minerals are rock-forming mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s made up of silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
.
In mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical mineralogy, optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifact (archaeology), artifacts. Specific s ...
, the crystalline forms of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
(silicon dioxide, ) are usually considered to be tectosilicates
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, the crystalline forms of silica (silicon dio ...
, and they are classified as such in the Dana system (75.1). However, the Nickel-Strunz system classifies them as oxide mineral
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. Minerals with complex anion groups such as the sil ...
s (4.DA). Silica is found in nature as the mineral quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
, and its polymorphs.
On Earth, a wide variety of silicate minerals occur in an even wider range of combinations as a result of the processes that have been forming and re-working the crust for billions of years. These processes include partial melting
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which inc ...
, crystallization
Crystallization is a process that leads to solids with highly organized Atom, atoms or Molecule, molecules, i.e. a crystal. The ordered nature of a crystalline solid can be contrasted with amorphous solids in which atoms or molecules lack regu ...
, fractionation
Fractionation is a separation process in which a certain quantity of a mixture (of gasses, solids, liquids, enzymes, or isotopes, or a suspension) is divided during a phase transition, into a number of smaller quantities (fractions) in which t ...
, metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated ...
, weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals (as well as wood and artificial materials) through contact with water, atmospheric gases, sunlight, and biological organisms. It occurs '' in situ'' (on-site, with little or no move ...
, and diagenesis.
 Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of
Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
known as diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's B ...
s construct their exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
s ("frustules") from silica extracted from seawater
Seawater, or sea water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximat ...
. The frustules of dead diatoms are a major constituent of deep ocean
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low tempe ...
sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
, and of diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth ( ), also known as diatomite ( ), celite, or kieselguhr, is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous rock, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging fr ...
.
General structure
A silicate mineral is generally aninorganic compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''.
Inorgan ...
consisting of subunits with the formula iO2+''n''sup>2''n''−. Although depicted as such, the description of silicates as anions is a simplification. Balancing the charges of the silicate anions are metal cations, M''x''+. Typical cations are Mg2+, Fe2+, and Na+. The Si-O-M linkage between the silicates and the metals are strong, polar-covalent bonds. Silicate anions ( iO2+''n''sup>2''n''−) are invariably colorless, or when crushed to a fine powder, white. The colors of silicate minerals arise from the metal component, commonly iron.
In most silicate minerals, silicon is tetrahedral, being surrounded by four oxides. The coordination number
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central ion ...
of the oxides is variable except when it bridges two silicon centers, in which case the oxide has a coordination number of two.
Some silicon centers may be replaced by atoms of other elements, still bound to the four corner oxygen corners. If the substituted atom is not normally tetravalent, it usually contributes extra charge to the anion, which then requires extra cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s. For example, in the mineral orthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture", because its two cleavage planes are at right angles ...
, the anion is a tridimensional network of tetrahedra in which all oxygen corners are shared. If all tetrahedra had silicon centers, the anion would be just neutral silica . Replacement of one in every four silicon atoms by an aluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
atom results in the anion , whose charge is neutralized by the potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
cations .
Main groups
Inmineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical mineralogy, optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifact (archaeology), artifacts. Specific s ...
, silicate minerals are classified into seven major groups according to the structure of their silicate anion:
Tectosilicates can only have additional cations if some of the silicon is replaced by an atom of lower valence such as aluminum. Al for Si substitution is common.
Nesosilicates or orthosilicates
 Nesosilicates (from Greek 'island'), or orthosilicates, have the orthosilicate ion, present as isolated (insular) tetrahedra connected only by interstitial
Nesosilicates (from Greek 'island'), or orthosilicates, have the orthosilicate ion, present as isolated (insular) tetrahedra connected only by interstitial cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.A –examples include:
*Phenakite group
** Phenakite –
** Willemite –
*Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron Silicate minerals, silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of Nesosilicates, nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle, it is a com ...
group
**Forsterite
Forsterite (Mg2SiO4; commonly abbreviated as Fo; also known as white olivine) is the magnesium-rich Endmember, end-member of the olivine solid solution series. It is Isomorphism (crystallography), isomorphous with the iron-rich end-member, fayalit ...
–
**Fayalite
Fayalite (, commonly abbreviated to Fa) is the iron-rich endmember, end-member of the olivine solid solution, solid-solution series. In common with all minerals in the olivine, olivine group, fayalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (spac ...
–
** Tephroite –
*Garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
Garnet minerals, while sharing similar physical and crystallographic properties, exhibit a wide range of chemical compositions, de ...
group
** Pyrope –
** Almandine –
** Spessartine –
** Grossular –
** Andradite –
** Uvarovite –
** Hydrogrossular –
*Zircon group
** Zircon –
** Thorite –
** Hafnon –
* group
** Andalusite –
** Kyanite –
** Sillimanite –
** Dumortierite –
** Topaz –
** Staurolite –
* Humite group –
** Norbergite –
** Chondrodite –
** Humite –
** Clinohumite –
* Datolite –
* Titanite –
* Chloritoid –
* Mullite (aka Porcelainite) –
Sorosilicates
 Sorosilicates (from Greek 'heap, mound') have isolated pyrosilicate anions , consisting of double tetrahedra with a shared oxygen vertex—a silicon:oxygen ratio of 2:7. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.B. Examples include:
* Thortveitite –
* Hemimorphite (
Sorosilicates (from Greek 'heap, mound') have isolated pyrosilicate anions , consisting of double tetrahedra with a shared oxygen vertex—a silicon:oxygen ratio of 2:7. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.B. Examples include:
* Thortveitite –
* Hemimorphite (calamine
Calamine, also known as calamine lotion, is a medication made from powdered calamine (mineral), calamine mineral that is used to treat mild itchiness. Conditions treated include sunburn, insect bites, Toxicodendron radicans, poison ivy, poiso ...
) –
* Lawsonite –
* Axinite –
* Ilvaite –
*Epidote group (has both and groups}
** Epidote –
** Zoisite –
*** Tanzanite –
** Clinozoisite –
** Allanite –
** Dollaseite-(Ce) –
* Vesuvianite ( idocrase) –
Cyclosilicates
Cyclosilicates (from Greek 'circle'), or ring silicates, have three or more tetrahedra linked in a ring. The general formula is (Si''x''O3''x'')2''x''−, where one or more silicon atoms can be replaced by other 4-coordinated atom(s). The silicon:oxygen ratio is 1:3. Double rings have the formula (Si2''x''O5''x'')2''x''− or a 2:5 ratio. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.C. Possible ring sizes include:beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
(red: Si, blue: O)
File:Benitoid.2200.png, 3 units , benitoite
File:Papagoite.2200.png, 4 units , papagoite
File:Eudialyte.2200.png, 9 units , eudialyte
File:Milarite.png, 12 units, double ring , milarite
Beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
–
** Bazzite –
** Sugilite –
**Tourmaline
Tourmaline ( ) is a crystalline silicate mineral, silicate mineral group in which boron is chemical compound, compounded with chemical element, elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. This gemstone comes in a ...
–
** Pezzottaite –
** Osumilite –
** Cordierite –
** Sekaninaite –
* 9-member single ring
** Eudialyte –
* 6-member double ring
** Milarite –
The ring in axinite contains two B and four Si tetrahedra and is highly distorted compared to the other 6-member ring cyclosilicates.
Inosilicates
Inosilicates (from Greek enitive: 'fibre'), or chain silicates, have interlocking chains ofsilicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
tetrahedra with either , 1:3 ratio, for single chains or , 4:11 ratio, for double chains. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.D – examples include:
Single chain inosilicates
*Pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated Px) are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents ions of calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron ( ...
group
**Enstatite – orthoferrosilite series
*** Enstatite –
*** Ferrosilite –
** Pigeonite –
**Diopside – hedenbergite series
*** Diopside –
*** Hedenbergite –
*** Augite –
**Sodium pyroxene series
*** Jadeite –
*** Aegirine (or acmite) –
** Spodumene –
** Pyroxferroite -
*Pyroxenoid group
**Wollastonite
Wollastonite is a calcium Silicate minerals, inosilicate mineral (calcium, Casilicon, Sioxygen, O3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone or D ...
–
** Rhodonite –
** Pectolite –
Double chain inosilicates
*Amphibole
Amphibole ( ) is a group of inosilicate minerals, forming prism or needlelike crystals, composed of double chain tetrahedra, linked at the vertices and generally containing ions of iron and/or magnesium in their structures. Its IMA symbol is ...
group
** Anthophyllite –
**Cummingtonite series
*** Cummingtonite –
*** Grunerite –
**Tremolite series
*** Tremolite –
*** Actinolite –
**Hornblende
Hornblende is a complex silicate minerals#Inosilicates, inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common ...
–
**Sodium amphibole group
*** Glaucophane –
*** Riebeckite (asbestos
Asbestos ( ) is a group of naturally occurring, Toxicity, toxic, carcinogenic and fibrous silicate minerals. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous Crystal habit, crystals, each fibre (particulate with length su ...
) –
*** Arfvedsonite –
wollastonite
Wollastonite is a calcium Silicate minerals, inosilicate mineral (calcium, Casilicon, Sioxygen, O3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone or D ...
File:Rhodonite-chain.png, Inosilicate with 5-periodic single chain, rhodonite
File:Pellyite-chain.png, Inosilicate with cyclic branched 8-periodic chain, pellyite
Phyllosilicates
Phyllosilicates (from Greek 'leaf'), or sheet silicates, form parallel sheets of silicate tetrahedra with or a 2:5 ratio. The Nickel–Strunz classification is 09.E. All phyllosilicate minerals arehydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understo ...
d, with either water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
or hydroxyl groups attached.
Examples include:
* Serpentine subgroup
** Antigorite –
** Chrysotile –
** Lizardite –
* Clay minerals group
**1:1 clay minerals (TO)
***Halloysite
Halloysite is an aluminosilicate clay mineral with the empirical formula Al2Si2O5(OH)4. Its main constituents are oxygen (55.78%), silicon (21.76%), aluminium (20.90%), and hydrogen (1.56%). It is a member of the kaolinite group. Halloysite typic ...
–
***Kaolinite
Kaolinite ( ; also called kaolin) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina () ...
–
**2:1 clay minerals (TOT)
*** Pyrophyllite –
***Talc
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate, with the chemical formula . Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent and lubricant ...
–
*** Illite –
***Montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite grou ...
(smectite) –
***Chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite (oxyanion), halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as s ...
–
*** Vermiculite –
**Other clay minerals
*** Sepiolite –
*** Palygorskite (or attapulgite) –
*Mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into fragile elastic plates. This characteristic is described as ''perfect basal cleavage''. Mica is co ...
group
**Brittle mica group
*** Anandite –
*** Bityite –
*** Clintonite –
*** Margarite –
**Dioctahedral mica group
***Celadonite subgroup
**** Celadonite –
**** Aluminoceladonite –
*** Glauconite –
*** Muscovite –
**** Fuchsite – (Cr replaces Al in muscovite)
**** Illite – (K-deficient muscovite)
**** Mariposite – (Cr-bearing muscovite)
**** Phengite – (Fe/Mg-bearing muscovite)
*** Paragonite –
*** Roscoelite –
**Trioctahedral mica group
*** Aspidolite –
*** Biotite subgroup –
**** Annite –
**** Phlogopite –
*** Hendricksite –
*** Lepidolite (polylithionite-trilithionite series) –
*** Zinnwaldite series –
Tectosilicates

 Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate tetrahedra with in a 1:2 ratio. This group comprises nearly 75% of the crust of the
Tectosilicates, or "framework silicates," have a three-dimensional framework of silicate tetrahedra with in a 1:2 ratio. This group comprises nearly 75% of the crust of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. Tectosilicates, with the exception of the quartz group, are aluminosilicates. The Nickel–Strunz classifications are 9.F (tectosilicates without zeolitic ), 9.G (tectosilicates with zeolitic ), and 4.DA (quartz/silica group). Below is a list of tectosilicate minerals and their chemical formulas, organized by groups and series:
*Quartz group (silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
)
**Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
–
**Tridymite
Tridymite is a high-temperature polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of silica and usually occurs as minute tabular white or colorless pseudo-hexagonal crystals, or scales, in cavities in felsic volcanic rocks. Its chemical formula is sili ...
–
**Cristobalite
Cristobalite ( ) is a mineral polymorph of silica that is formed at very high temperatures. It has the same chemical formula as quartz, Si O2, but a distinct crystal structure. Both quartz and cristobalite are polymorphs with all the members o ...
–
**Coesite
Coesite () is a form (polymorphism (materials science), polymorph) of silicon dioxide (silicon, Sioxide, O2) that is formed when very high pressure (2–3 gigapascals), and moderately high temperature (), are applied to quartz. Coesite was first ...
–
**Stishovite
Stishovite is an extremely hard, dense tetragonal form ( polymorph) of silicon dioxide. It is very rare on the Earth's surface; however, it may be a predominant form of silicon dioxide in the Earth, especially in the lower mantle.
Stishovite w ...
–
** Moganite –
** Chalcedony –
*Feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagiocl ...
group
**Alkali feldspar series (potassium feldspars or K-spar)
*** Microcline –
****Amazonite
Amazonite, also known as amazonstone, is a green tectosilicate mineral, a variety of the potassium feldspar called microcline. Its chemical formula is KAlSi3O8, which is Polymorphism (materials science), polymorphic to orthoclase.
Its name is ta ...
– green variety of microcline
***Orthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture", because its two cleavage planes are at right angles ...
–
**** Moonstone – opalescent variety of orthoclase
*** Anorthoclase –
***Sanidine
Sanidine is the high temperature form of potassium feldspar with a general formula K(AlSi3O8). Sanidine is found most typically in felsic volcanic rocks such as obsidian, rhyolite and trachyte. Sanidine crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal sys ...
–
**Plagioclase
Plagioclase ( ) is a series of Silicate minerals#Tectosilicates, tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continu ...
feldspar series
***Albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilicat ...
(sodium endmember) –
*** Oligoclase – (Na:Ca 90:10 to 70:30)
*** Andesine – (Na:Ca 50:50 to 70:30)
*** Labradorite – (Na:Ca 30:70 to 50:50)
*** Bytownite – (Na:Ca 10:90 to 30:70)
***Anorthite
Anorthite (< ''an'' 'not' + ''ortho'' 'straight') is the
Buddingtonite —
***
Mindat.org, Dana classification
Webmineral : Dana's New Silicate Classification
{{Authority control pl:Krzemiany
Celsian
Celsian is an uncommon feldspar mineral, barium aluminosilicate, Barium, BaAluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O8. The mineral occurs in contact metamorphic rocks with significant barium content. Its crystal system is monoclinic, and it is white, ...
–
***Hyalophane
Hyalophane or jaloallofane is a crystalline mineral, part of the feldspar group of tectosilicates. It is considered a barium-rich potassium feldspar. Its chemical formula is , and it has a hardness of 6 to . The name ''hyalophane'' comes from the ...
–
*** Rubicline –
*Feldspathoid
The feldspathoids are a group of tectosilicate minerals which resemble feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, pota ...
group
**Cancrinite subgroup
*** Cancrinite –
*** Afghanite –
*** Alloriite –
*** Bystrite –
*** Farneseite –
*** Sacrofanite –
*** Vishnevite –
** Danalite –
** Kalsilite –
** Leucite –
**Nepheline subgroup
***Nepheline
Nepheline, also called nephelite (), is a rock-forming mineral in the feldspathoid groupa silica-undersaturated aluminosilicate, Na3 K Al4 Si4 O16, that occurs in intrusive and volcanic rocks with low silica, and in their associated pegmatit ...
–
*** Davidsmithite –
**Sodalite subgroup
*** Sodalite –
*** Hauyne –
*** Lazurite –
*** Nosean –
*** Tugtupite –
* Scapolite group
** Marialite –
** Meionite –
* Zeolite group
** Amicite –
** Analcime –
** Brewsterite subgroup –
**Chabazite-Lévyne subgroup
*** Chabazite –
*** Lévyne –
** Clinoptilolite subgroup –
** Cowlesite –
** Dachiardite-K –
** Edingtonite –
** Erionite subgroup –
** Faujasite subgroup –
** Ferrierite subgroup – (Ferrierite-Mg)
** Garronite-Ca –
** Gismondine – (Gismondine-Ca)
** Gmelinite subgroup – (Gmelinite-Na)
** Heulandite subgroup –
** Hsianghualite –
** Laumontite –
** Mordenite –
** Nabesite –
**Natrolite subgroup
*** Natrolite –
*** Gonnardite –
*** Mesolite –
*** Scolecite –
** Paulingite subgroup – (Paulingite-K)
**Phillipsite subgroup
*** Phillipsite – (Phillipsite-Ca)
*** Harmotome –
** Pollucite –
**Stilbite subgroup
*** Stilbite –
*** Barrerite –
*** Stellerite –
** Thomsonite subgroup – (Thomsonite-Ca)
** Wairakite –
** Yugawaralite –
See also
* * *References
External links
Mindat.org, Dana classification
Webmineral : Dana's New Silicate Classification
{{Authority control pl:Krzemiany