Parallel Robots on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
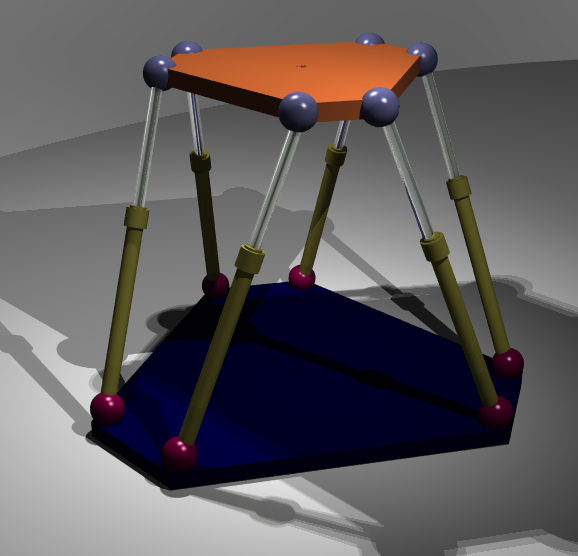 A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or
A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or  Also known as parallel robots, or generalized Stewart platforms (in the
Also known as parallel robots, or generalized Stewart platforms (in the
 Most robot applications require rigidity. Serial robots may achieve this by using high-quality rotary joints that permit movement in one axis but are rigid against movement outside this. Any joint permitting movement ''must'' also have this movement under deliberate control by an actuator. A movement requiring several axes thus requires a number of such joints. Unwanted flexibility or sloppiness in one joint causes a similar sloppiness in the arm, which may be amplified by the distance between the joint and the end-effectuor: there is no opportunity to brace one joint's movement against another. Their inevitable
Most robot applications require rigidity. Serial robots may achieve this by using high-quality rotary joints that permit movement in one axis but are rigid against movement outside this. Any joint permitting movement ''must'' also have this movement under deliberate control by an actuator. A movement requiring several axes thus requires a number of such joints. Unwanted flexibility or sloppiness in one joint causes a similar sloppiness in the arm, which may be amplified by the distance between the joint and the end-effectuor: there is no opportunity to brace one joint's movement against another. Their inevitable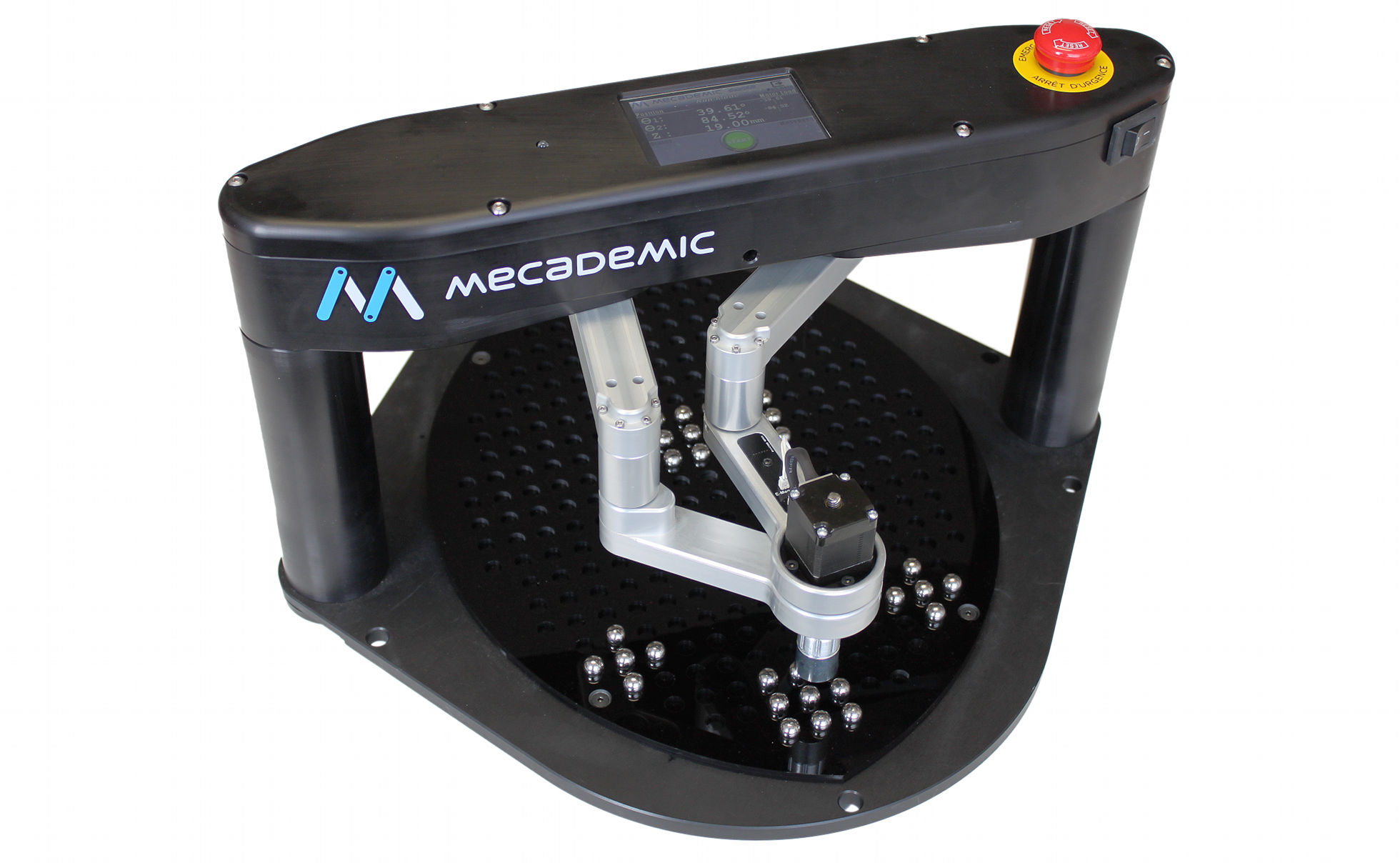 
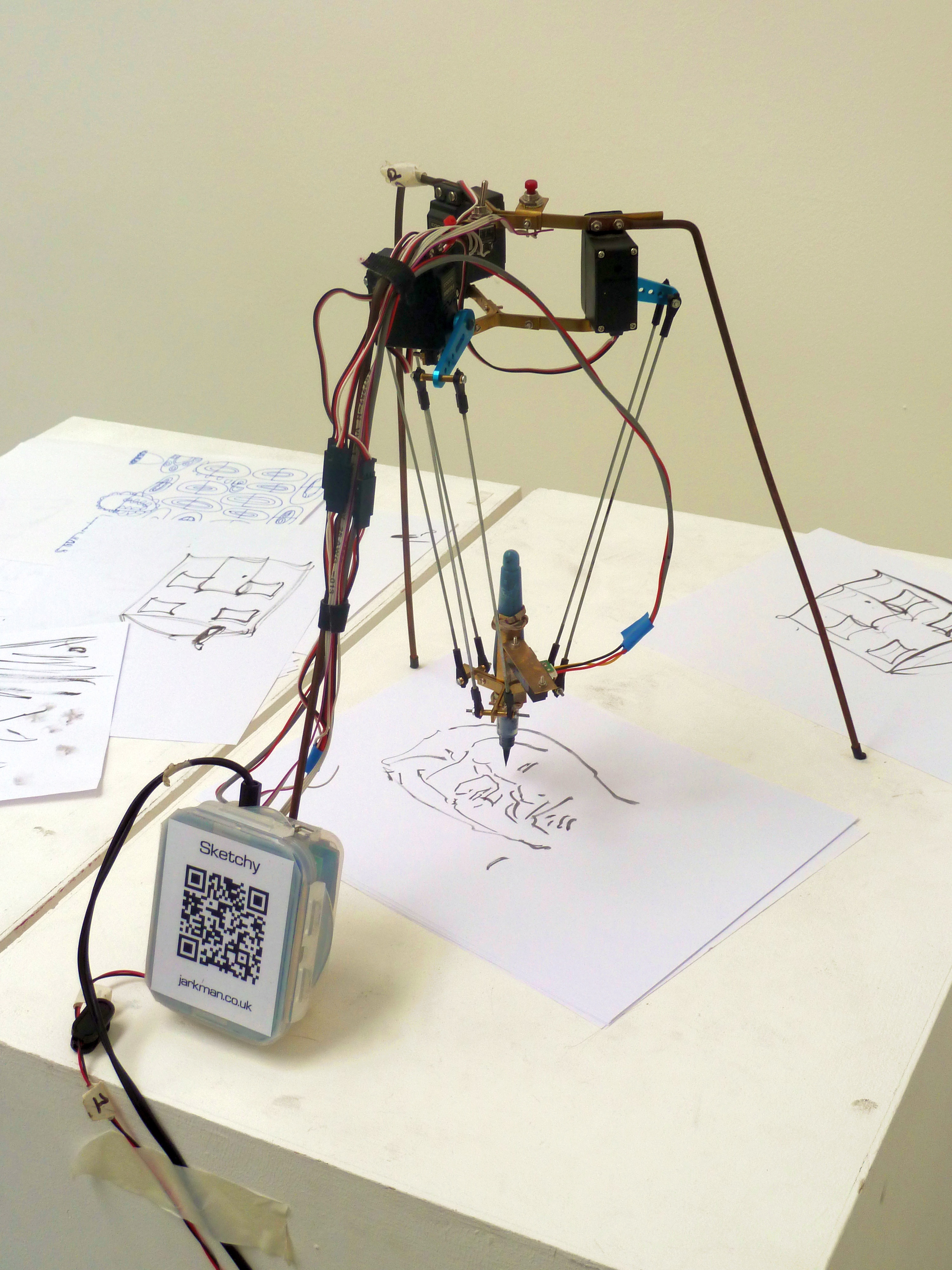 A drawback of parallel manipulators, in comparison to serial manipulators, is their limited workspace. As for serial manipulators, the workspace is limited by the geometrical and mechanical limits of the design (collisions between legs maximal and minimal lengths of the legs). The workspace is also limited by the existence of ''singularities'', which are positions where, for some trajectories of the movement, the variation of the lengths of the legs is infinitely smaller than the variation of the position. Conversely, at a singular position, a force (like gravity) applied on the end-effector induce infinitely large constraints on the legs, which may result in a kind of "explosion" of the manipulator. The determination of the singular positions is difficult (for a general parallel manipulator, this is an open problem). This implies that the workspaces of the parallel manipulators are, usually, artificially limited to a small region where one knows that there is no singularity.
Another drawback of parallel manipulators is their
A drawback of parallel manipulators, in comparison to serial manipulators, is their limited workspace. As for serial manipulators, the workspace is limited by the geometrical and mechanical limits of the design (collisions between legs maximal and minimal lengths of the legs). The workspace is also limited by the existence of ''singularities'', which are positions where, for some trajectories of the movement, the variation of the lengths of the legs is infinitely smaller than the variation of the position. Conversely, at a singular position, a force (like gravity) applied on the end-effector induce infinitely large constraints on the legs, which may result in a kind of "explosion" of the manipulator. The determination of the singular positions is difficult (for a general parallel manipulator, this is an open problem). This implies that the workspaces of the parallel manipulators are, usually, artificially limited to a small region where one knows that there is no singularity.
Another drawback of parallel manipulators is their
 Two examples of popular parallel robots are the
Two examples of popular parallel robots are the
 *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Parallel Mechanisms Information Center
{{Authority control Parallel robots Articulated robotics
 A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or
A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or end-effector
In robotics, an end effector is the device at the end of a robotic arm, designed to interact with the environment. The exact nature of this device depends on the application of the robot.
In the strict definition, which originates from serial ro ...
. Perhaps, the best known parallel manipulator is formed from six linear actuators that support a movable base for devices such as flight simulators. This device is called a Stewart platform
A Stewart platform is a type of parallel manipulator that has six prismatic actuators, commonly hydraulic jacks or electric linear actuators, attached in pairs to three positions on the platform's baseplate, crossing over to three mounting poi ...
or the Gough-Stewart platform in recognition of the engineers who first designed and used them.
 Also known as parallel robots, or generalized Stewart platforms (in the
Also known as parallel robots, or generalized Stewart platforms (in the Stewart platform
A Stewart platform is a type of parallel manipulator that has six prismatic actuators, commonly hydraulic jacks or electric linear actuators, attached in pairs to three positions on the platform's baseplate, crossing over to three mounting poi ...
, the actuators are paired together on both the basis and the platform), these systems are articulated robot
An articulated robot is a robot with rotary joints (e.g. a legged robot or an industrial robot). Articulated robots can range from simple two-jointed structures to systems with 10 or more interacting joints and materials.
They are powered by a ...
s that use similar mechanisms for the movement of either the robot on its base, or one or more manipulator arms. Their 'parallel' distinction, as opposed to a serial manipulator Serial manipulators are the most common industrial robots and they are designed as a series of links connected by motor-actuated joints that extend from a base to an end-effector. Often they have an anthropomorphic arm structure described as having ...
, is that the end effector (or 'hand') of this linkage (or 'arm') is directly connected to its base by a number of (usually three or six) separate and independent linkages working simultaneously. No geometrical parallelism is implied.
Design features
A parallel manipulator is designed so that each chain is usually short, simple and can thus be rigid against unwanted movement, compared to aserial manipulator Serial manipulators are the most common industrial robots and they are designed as a series of links connected by motor-actuated joints that extend from a base to an end-effector. Often they have an anthropomorphic arm structure described as having ...
. Errors in one chain's positioning are averaged in conjunction with the others, rather than being cumulative. Each actuator must still move within its own degree of freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or ...
, as for a serial robot; however in the parallel robot the off-axis flexibility of a joint is also constrained by the effect of the other chains. It is this closed-loop
A control loop is the fundamental building block of industrial control systems. It consists of all the physical components and control functions necessary to automatically adjust the value of a measured process variable (PV) to equal the value of ...
stiffness that makes the overall parallel manipulator stiff relative to its components, unlike the serial chain that becomes progressively less rigid with more components.
This mutual stiffening also permits simple construction: Stewart platform
A Stewart platform is a type of parallel manipulator that has six prismatic actuators, commonly hydraulic jacks or electric linear actuators, attached in pairs to three positions on the platform's baseplate, crossing over to three mounting poi ...
hexapods chains use prismatic joint
A prismatic joint is a one- degree-of-freedom kinematic pair which constrains the motion of two bodies to sliding along a common axis, without rotation; for this reason it is often called a slider (as in the slider-crank linkage) or a sliding ...
linear actuator
A linear actuator is an actuator that creates motion in a straight line, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer peripherals such as ...
s between any-axis universal ball joint
In an automobile, ball joints are spherical bearings that connect the control arms to the steering knuckles, and are used on virtually every automobile made. They bionically resemble the ball-and-socket joints found in most tetrapod an ...
s. The ball joints are passive: simply free to move, without actuators or brakes; their position is constrained solely by the other chains. Delta robot
A delta robot is a type of parallel robot that consists of three arms connected to universal joints at the base. The key design feature is the use of parallelograms in the arms, which maintains the orientation of the end effector. In contrast, ...
s have base-mounted rotary actuator
A rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque.
The simplest actuator is purely mechanical, where linear motion in one direction gives rise to rotation. The most common actuators are electrically powered; others may be p ...
s that move a light, stiff, parallelogram arm. The effector is mounted between the tips of three of these arms and again, it may be mounted with simple ball-joints. Static representation of a parallel robot is often akin to that of a pin-jointed truss: the links and their actuators feel only tension or compression, without any bending or torque, which again reduces the effects of any flexibility to off-axis forces.
A further advantage of the parallel manipulator is that the heavy actuators may often be centrally mounted on a single base platform, the movement of the arm taking place through struts and joints alone. This reduction in mass along the arm permits a lighter arm construction, thus lighter actuators and faster movements. This centralisation of mass also reduces the robot's overall moment of inertia
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular accele ...
, which may be an advantage for a mobile or walking robot
Walking (also known as ambulation) is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legged animals. Walking is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined by an 'inverted pendulum' gait in which the body vaults ov ...
.
All these features result in manipulators with a wide range of motion capability. As their speed of action is often constrained by their rigidity rather than sheer power, they can be fast-acting, in comparison to serial manipulators.
Lower mobility
A manipulator can move an object with up to 6degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or ...
(DoF), determined by 3 translation ''3T'' and 3 rotation ''3R'' coordinates for full ''3T3R m''obility. However, when a manipulation task requires less than 6 DoF, the use of lower mobility manipulators, with fewer than 6 DoF, may bring advantages in terms of simpler architecture, easier control, faster motion and lower cost. For example, the 3 DoF Delta robot has lower ''3T'' mobility and has proven to be very successful for rapid pick-and-place translational positioning applications. The workspace of lower mobility manipulators may be decomposed into `motion’ and `constraint’ subspaces. For example, 3 position coordinates constitute the motion subspace of the 3 DoF Delta robot and the 3 orientation coordinates are in the constraint subspace. The motion subspace of lower mobility manipulators may be further decomposed into independent (desired) and dependent subspaces: consisting of `concomitant’ or `parasitic’ motion which is undesired motion of the manipulator. The debilitating effects of parasitic motion should be mitigated or eliminated in the successful design of lower mobility manipulators. For example, the Delta robot does not have parasitic motion since its end effector does not rotate.
Comparison to serial manipulators
 Most robot applications require rigidity. Serial robots may achieve this by using high-quality rotary joints that permit movement in one axis but are rigid against movement outside this. Any joint permitting movement ''must'' also have this movement under deliberate control by an actuator. A movement requiring several axes thus requires a number of such joints. Unwanted flexibility or sloppiness in one joint causes a similar sloppiness in the arm, which may be amplified by the distance between the joint and the end-effectuor: there is no opportunity to brace one joint's movement against another. Their inevitable
Most robot applications require rigidity. Serial robots may achieve this by using high-quality rotary joints that permit movement in one axis but are rigid against movement outside this. Any joint permitting movement ''must'' also have this movement under deliberate control by an actuator. A movement requiring several axes thus requires a number of such joints. Unwanted flexibility or sloppiness in one joint causes a similar sloppiness in the arm, which may be amplified by the distance between the joint and the end-effectuor: there is no opportunity to brace one joint's movement against another. Their inevitable hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of ...
and off-axis flexibility accumulates along the arm's kinematic chain
In mechanical engineering, a kinematic chain is an assembly of rigid bodies connected by joints to provide constrained (or desired) motion that is the mathematical model for a mechanical system. Reuleaux, F., 187''The Kinematics of Machine ...
; a precision serial manipulator is a compromise between precision, complexity, mass (of the manipulator and of the manipulated objects) and cost. On the other hand, with parallel manipulators, a high rigidity may be obtained with a small mass of the manipulator (relatively to the charge being manipulated). This allows high precision and high speed of movements, and motivates the use of parallel manipulators in flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they rea ...
s (high speed with rather large masses) and electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest (static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for am ...
or magnetic lenses in particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams.
Large accelerators are used for fun ...
s (very high precision in positioning large masses).

 A drawback of parallel manipulators, in comparison to serial manipulators, is their limited workspace. As for serial manipulators, the workspace is limited by the geometrical and mechanical limits of the design (collisions between legs maximal and minimal lengths of the legs). The workspace is also limited by the existence of ''singularities'', which are positions where, for some trajectories of the movement, the variation of the lengths of the legs is infinitely smaller than the variation of the position. Conversely, at a singular position, a force (like gravity) applied on the end-effector induce infinitely large constraints on the legs, which may result in a kind of "explosion" of the manipulator. The determination of the singular positions is difficult (for a general parallel manipulator, this is an open problem). This implies that the workspaces of the parallel manipulators are, usually, artificially limited to a small region where one knows that there is no singularity.
Another drawback of parallel manipulators is their
A drawback of parallel manipulators, in comparison to serial manipulators, is their limited workspace. As for serial manipulators, the workspace is limited by the geometrical and mechanical limits of the design (collisions between legs maximal and minimal lengths of the legs). The workspace is also limited by the existence of ''singularities'', which are positions where, for some trajectories of the movement, the variation of the lengths of the legs is infinitely smaller than the variation of the position. Conversely, at a singular position, a force (like gravity) applied on the end-effector induce infinitely large constraints on the legs, which may result in a kind of "explosion" of the manipulator. The determination of the singular positions is difficult (for a general parallel manipulator, this is an open problem). This implies that the workspaces of the parallel manipulators are, usually, artificially limited to a small region where one knows that there is no singularity.
Another drawback of parallel manipulators is their nonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other ...
behavior: the command which is needed for getting a linear or a circular movement of the end-effector depends dramatically on the location in the workspace and does not vary linearly during the movement.
Applications
Major industrial applications of these devices are: *flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they rea ...
s
* automobile simulators
* in work processes
* photonics
Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. Though ...
/ optical fiber
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparency and translucency, transparent fiber made by Drawing (manufacturing), drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a Hair ...
alignment
They have also become more popular:
* in high speed, high-accuracy positioning with limited workspace, such as in assembly of PCBs
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act in 1979 and internationally by ...
* as micro manipulators mounted on the end effector of larger but slower serial manipulator Serial manipulators are the most common industrial robots and they are designed as a series of links connected by motor-actuated joints that extend from a base to an end-effector. Often they have an anthropomorphic arm structure described as having ...
s
* as high speed/high-precision milling machine
Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done by varying direction on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling covers a wide variety of d ...
s
Parallel robots are usually more limited in the workspace; for instance, they generally cannot reach around obstacles. The calculations involved in performing a desired manipulation (forward kinematics) are also usually more difficult and can lead to multiple solutions.
 Two examples of popular parallel robots are the
Two examples of popular parallel robots are the Stewart platform
A Stewart platform is a type of parallel manipulator that has six prismatic actuators, commonly hydraulic jacks or electric linear actuators, attached in pairs to three positions on the platform's baseplate, crossing over to three mounting poi ...
and the Delta robot
A delta robot is a type of parallel robot that consists of three arms connected to universal joints at the base. The key design feature is the use of parallelograms in the arms, which maintains the orientation of the end effector. In contrast, ...
.
See also
*Robot kinematics
In robotics, robot kinematics applies geometry to the study of the movement of multi-degree of freedom kinematic chains that form the structure of robotic systems. The emphasis on geometry means that the links of the robot are modeled as rigid ...
*Cartesian parallel manipulators
In robotics, Cartesian parallel manipulators are manipulators that move a platform using parallel-connected kinematic linkages (`limbs') lined up with a Cartesian coordinate system. Multiple limbs connect the moving platform to a base. Each lim ...
References
Further reading
* *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Parallel Mechanisms Information Center
{{Authority control Parallel robots Articulated robotics