Palm tree on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Arecaceae () is a
 Like all
Like all
 Most palms are native to tropical and subtropical climates. Palms thrive in moist and hot climates but can be found in a variety of different habitats. Their diversity is highest in wet, lowland forests.
Most palms are native to tropical and subtropical climates. Palms thrive in moist and hot climates but can be found in a variety of different habitats. Their diversity is highest in wet, lowland forests.
 Palms are a
Palms are a





 * '' Archontophoenix''— Bangalow palm
* ''
* '' Archontophoenix''— Bangalow palm
* ''

 Evidence for cultivation of the date palm by
Evidence for cultivation of the date palm by
Image:Dates on date palm.jpg, Fruit of the date palm ''
 The palm branch was a symbol of triumph and victory in
The palm branch was a symbol of triumph and victory in 
''Natürliches System des Pflanzenreichs...''
p
317
Berlin, Germany.
Palmpedia
��A wiki-based site dedicated to high quality images and information on palm trees.
Fairchild Guide to Palms
��A collection of palm images, scientific data, and horticultural information hosted by Fairchild Tropical Botanic Garden, Miami.
Kew Botanic Garden's Palm Genera list
��A list of the currently acknowledged genera by Kew Royal Botanic Gardens in London, England (archived 2007)
Palm species listing with images
��Palm and Cycad Societies of Australia (PACSOA)
Palm & Cycad Societies of Florida, Inc. (PACSOF)
which includes pages o
and
*
in th
* Wallace, A. R. (1853),
Palm trees of the Amazon and their uses
'. {{Authority control Arecales Commelinid families Extant Campanian first appearances Tropical agriculture
family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
of perennial
In horticulture, the term perennial ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the year") is used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. It has thus been defined as a plant that lives more than 2 years. The term is also ...
, flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s in the monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are flowering plants whose seeds contain only one Embryo#Plant embryos, embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. A monocot taxon has been in use for several decades, but ...
order Arecales. Their growth form can be climbers, shrub
A shrub or bush is a small to medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple ...
s, tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
-like and stemless plants, all commonly known as palms. Those having a tree-like form are colloquially called palm trees. Currently, 181 genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
with around 2,600 species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
are known, most of which are restricted to tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
and subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
climates. Most palms are distinguished by their large, compound, evergreen
In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has Leaf, foliage that remains green and functional throughout the year. This contrasts with deciduous plants, which lose their foliage completely during the winter or dry season. Consisting of many diffe ...
leaves, known as fronds, arranged at the top of an unbranched stem, except for the Hyphaene genus, who has branched palms. However, palms exhibit an enormous diversity in physical characteristics and inhabit nearly every type of habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
within their range, from rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropi ...
s to desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
s.
Palms are among the best known and most extensively cultivated plant families. They have been important to humans throughout much of history, especially in regions like the Middle East and North Africa. A wide range of common products and foods are derived from palms. In contemporary times, palms are also widely used in landscaping. In many historical cultures, because of their importance as food, palms were symbols
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise different concep ...
for such ideas as victory, peace, and fertility.
Etymology
The word ''Arecaceae'' is derived from the word ''areca
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of Arecaceae, palms in the family (biology), family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines and Malaysia, India, and across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ' ...
'' with the suffix "-aceae". ''Areca'' is derived from Portuguese, via Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
അടയ്ക്ക (''aṭaykka''), which is from Dravidian ''*aṭ-ay-kkāy'' ("areca nut"). The suffix ''-aceae'' is the feminine plural of the Latin ''-āceus'' ("resembling").
''Palm'' originates from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''palma'' semantically overlapping with sense of " hand front" (due to similar splayed shape) ultimately from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
*''pl̥h₂meh₂'', a direct descendant once existed in Old English.
Morphology
Whether as shrubs, tree-like, or vines, palms have two methods of growth: solitary or clustered. The common representation is that of a solitary shoot ending in a crown of leaves. Thismonopodial
Vascular plants with monopodial growth habits grow upward from a single point. They add leaves to the apex each year and the stem grows longer accordingly. The word ''Monopodial'' is derived from Greek language, Greek '', ''one'' and '', "foot", in ...
character may be exhibited by prostrate, trunkless, and trunk-forming members. Some common palms restricted to solitary growth include '' Washingtonia'' and '' Roystonea''. Palms may instead grow in sparse though dense clusters. The trunk develops an axillary bud at a leaf node, usually near the base, from which a new shoot emerges. The new shoot, in turn, produces an axillary bud and a clustering habit results. Exclusively sympodial
In botany, sympodial growth is a bifurcating branching pattern where one branch develops more strongly than the other, resulting in the stronger branches forming the primary shoot and the weaker branches appearing laterally. A sympodium, als ...
genera include many of the rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan (from Malay language, Malay: ''rotan''), is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the clos ...
s, '' Guihaia'', and '' Rhapis''. Several palm genera have both solitary and clustering members. Palms which are usually solitary may grow in clusters and vice versa.
Palms have large, evergreen leaves that are either palmately ('fan-leaved') or pinnately ('feather-leaved') compound and spirally (-alternately) arranged at the top of the stem, with the sole exception of the King Raphia ('' Raphia vinifera'' variety ''nigerica'') which has opposite pairs of fronds). The leaves have a tubular sheath at the base that usually splits open on one side at maturity. The inflorescence
In botany, an inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a plant's Plant stem, stem that is composed of a main branch or a system of branches. An inflorescence is categorized on the basis of the arrangement of flowers on a mai ...
is a spadix or spike surrounded by one or more bract
In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale.
Bracts are usually different from foliage leaves in size, color, shape or texture. They also lo ...
s or spathes that become woody at maturity. The flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
s are generally small and white, radially symmetric, and can be either uni- or bisexual. The sepals and petals usually number three each and may be distinct or joined at the base. The stamens generally number six, with filaments that may be separate, attached to each other, or attached to the pistil at the base. The fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
is usually a single-seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
ed drupe
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is a type of fruit in which an outer fleshy part (exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pip'' (UK), ''pit'' (US), ''stone'', or ''pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed ...
(sometimes berry-like) but some genera (e.g., '' Salacca'') may contain two or more seeds in each fruit.
monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are flowering plants whose seeds contain only one Embryo#Plant embryos, embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. A monocot taxon has been in use for several decades, but ...
s, palms do not have the ability to increase the width of a stem ( secondary growth) via the same kind of vascular cambium
The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants exhibiting secondary growth, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular ...
found in non-monocot woody plant
A woody plant is a plant that produces wood as its structural tissue and thus has a hard stem. In cold climates, woody plants further survive winter or dry season above ground, as opposed to Herbaceous plant, herbaceous plants that die back to t ...
s. This explains the cylindrical shape of the trunk (almost constant diameter) that is often seen in palms, unlike in ring-forming trees. However, many palms, like some other monocots, do have secondary growth, although because it does not arise from a single vascular cambium producing xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue (biology), tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem; both of these are part of the vascular bundle. The basic function of the xylem is to transport water upward from the roots to parts o ...
inwards and phloem outwards, it is often called "anomalous secondary growth".
The Arecaceae are notable among monocots for their height and for the size of their seeds, leaves, and inflorescences. '' Ceroxylon quindiuense'', Colombia's national "tree", is the tallest monocot in the world, reaching up to tall. The '' coco de mer'' (''Lodoicea maldivica'') has the largest seeds of any plant, in diameter and weighing each ( coconuts are the second largest). Raffia palms ('' Raphia'' spp.) have the largest leaves of any plant, up to long and wide. The '' Corypha'' species have the largest inflorescence of any plant, up to tall and containing millions of small flowers. '' Calamus'' stems can reach in length.
Range and habitat
 Most palms are native to tropical and subtropical climates. Palms thrive in moist and hot climates but can be found in a variety of different habitats. Their diversity is highest in wet, lowland forests.
Most palms are native to tropical and subtropical climates. Palms thrive in moist and hot climates but can be found in a variety of different habitats. Their diversity is highest in wet, lowland forests. South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, and areas of the South Pacific and southern Asia are regions of concentration. Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
may have the highest number of palm species in one country. There are some palms that are also native to desert areas such as the Arabian Peninsula and parts of northwestern Mexico. Only about 130 palm species naturally grow entirely beyond the tropics, mostly in humid lowland subtropical climates, in highlands in southern Asia, and along the rim lands of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. The northernmost native palm is '' Chamaerops humilis'', which reaches 44°N latitude along the coast of Liguria
Liguria (; ; , ) is a Regions of Italy, region of north-western Italy; its Capital city, capital is Genoa. Its territory is crossed by the Alps and the Apennine Mountains, Apennines Mountain chain, mountain range and is roughly coextensive with ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
. In the southern hemisphere, the southernmost palm is the '' Rhopalostylis sapida'' (nīkau), which reaches 44°S on the Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands ( ; Moriori language, Moriori: , 'Misty Sun'; ) are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about east of New Zealand's South Island, administered as part of New Zealand, and consisting of about 10 islands within an approxima ...
where an oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
prevails. Cultivation of palms is possible north of subtropical climates, and some higher latitude locales such as Ireland, Scotland, England, and the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common ...
feature a few palms in protected locations and microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often slightly but sometimes substantially. The term may refer to areas as small as a few square m ...
s. In the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, there are at least 12 native palm species, mostly occurring in the states of the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
and Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
.
Palms inhabit a variety of ecosystems. More than two-thirds of palm species live in humid moist forests, where some species grow tall enough to form part of the canopy and shorter ones form part of the understory
In forestry and ecology, understory (American English), or understorey (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English), also known as underbrush or undergrowth, includes plant life growing beneath the Canopy (biology), forest ca ...
. Some species form pure stands in areas with poor drainage or regular flooding, including '' Raphia hookeri'' which is common in coastal freshwater swamps in West Africa. Other palms live in tropical mountain habitats above , such as those in the genus '' Ceroxylon'' native to the Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
. Palms may also live in grasslands and scrublands, usually associated with a water source, and in desert oases such as the date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as the date palm, is a flowering-plant species in the palm family Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet #Fruits, fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across North Africa, northern A ...
. A few palms are adapted to extremely basic
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
lime soils, while others are similarly adapted to extreme potassium deficiency and toxicity of heavy metals in serpentine soils.
Taxonomy
 Palms are a
Palms are a monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
group of plants, meaning the group consists of a common ancestor and all its descendants. Extensive taxonomic research on palms began with botanist H.E. Moore, who organized palms into 15 major groups based mostly on general morphological characteristics. The following classification, proposed by N.W. Uhl and J. Dransfield in 1987, is a revision of Moore's classification that organizes palms into 6 subfamilies. A few general traits of each subfamily are listed below.
* Subfamily are the largest subfamily with 14 tribes and containing over 100 genera. All tribes have pinnate or bipinnate leaves and flowers arranged in groups of three, with a central pistillate and two staminate flowers.
* Subfamily includes the climbing palms, such as rattans. The leaves are usually pinnate; derived characters ( synapomorphies) include spines on various organs, organs specialized for climbing, an extension of the main stem of the leaf-bearing reflexed spines, and overlapping scales covering the fruit and ovary.
* Subfamily has small to medium-sized flowers, spirally arranged, with a gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl (botany), whorl of a flower; it consists ...
of three joined carpels.
* Subfamily are the second-largest subfamily with 8 tribes. Most palms in this subfamily have palmately lobed leaves and solitary flowers with three, or sometimes four carpel
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more ...
s. The fruit normally develops from only one carpel.
* Subfamily contains only one species, ''Nypa fruticans
''Nypa fruticans'', commonly known as the nipa palm (or simply nipa, from ) or mangrove palm, is a species of palm native to the coastlines and estuarine habitats of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the only palm considered adapted to the ...
'', which has large, pinnate leaves. The fruit is unusual in that it floats, and the stem is underground and dichotomously branched, also unusual in palms.
The is the sixth subfamily of Arecaceae in N.W. Uhl and J. Dransfield's 1987 classification. Members of this group have distinct monopodial flower clusters. Other distinct features include a gynoecium with five to 10 joined carpels, and flowers with more than three parts per whorl. Fruits are multiple-seeded and have multiple parts. From the modern phylogenomic data, the Phytelephantoideae are tribe in the Ceroxyloideae subfamily.
Currently, few extensive phylogenetic studies of the Arecaceae exist. In 1997, Baker ''et al.'' explored subfamily and tribe relationships using chloroplast DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
from 60 genera from all subfamilies and tribes. The results strongly showed the Calamoideae are monophyletic, and Ceroxyloideae and Coryphoideae are paraphyletic. The relationships of Arecoideae are uncertain, but they are possibly related to the Ceroxyloideae and Phytelephantoideae. Studies have suggested the lack of a fully resolved hypothesis for the relationships within the family is due to a variety of factors, including difficulties in selecting appropriate outgroups, homoplasy in morphological character states, slow rates of molecular evolution important for the use of standard DNA markers, and character polarization. However, hybridization has been observed among ''Orbignya'' and ''Phoenix'' species, and using chloroplast DNA in cladistic studies may produce inaccurate results due to maternal inheritance of the chloroplast DNA. Chemical and molecular data from non-organelle DNA, for example, could be more effective for studying palm phylogeny.
Recently, nuclear genomes and transcriptomes have been used to reconstruct the phylogeny of palms. This has revealed, for example, that a whole-genome duplication event occurred early in the evolution of the Arecaceae lineage, that was not experienced by its sister clade, the Dasypogonaceae.
For a phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
of the family, see the list of Arecaceae genera.
Selected genera





 * '' Archontophoenix''— Bangalow palm
* ''
* '' Archontophoenix''— Bangalow palm
* ''Areca
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of Arecaceae, palms in the family (biology), family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines and Malaysia, India, and across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ' ...
''— Betel palm
* '' Astrocaryum''
* '' Attalea''
* '' Bactris''— Pupunha
* '' Beccariophoenix''— Beccariophoenix alfredii
* '' Bismarckia''—Bismarck palm
* '' Borassus''—Palmyra palm, sugar palm, toddy palm
* '' Butia''
* '' Calamus''—Rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan (from Malay language, Malay: ''rotan''), is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the clos ...
palm
* '' Ceroxylon''
* '' Cocos''—Coconut
* '' Coccothrinax''
* '' Copernicia''— Carnauba wax palm
* '' Corypha''—Gebang palm, Buri palm or Talipot palm
* '' Elaeis''—Oil palm
* '' Euterpe''—Cabbage heart palm, açaí palm
* '' Hyphaene''— Doum palm
* '' Jubaea''—Chilean wine palm, Coquito palm
* '' Latania''—Latan palm
* '' Licuala''
* '' Livistona''—Cabbage palm
* '' Mauritia''— Moriche palm
* '' Metroxylon''— Sago palm
* '' Nypa''— Nipa palm
* '' Parajubaea''—Bolivian coconut palms
* '' Phoenix''—Date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as the date palm, is a flowering-plant species in the palm family Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet #Fruits, fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across North Africa, northern A ...
* '' Pritchardia''
* '' Raphia''—Raffia palm
* '' Rhapidophyllum''
* '' Rhapis''
* '' Roystonea''—Royal palm
* '' Sabal''—Palmettos
* '' Salacca''— Salak
* '' Syagrus''— Queen palm
* '' Thrinax''
* ''Trachycarpus
''Trachycarpus'' is a genus of ten species of Arecaceae, palms native to Asia, from the Himalaya east to eastern China. They are fan palms (subfamily Coryphoideae), with the leaf, leaves with a bare petiole terminating in a rounded fan of numerou ...
''— Windmill palm, Kumaon palm
* '' Trithrinax''
* '' Veitchia''— Manila palm, Joannis palm
* '' Washingtonia''—Fan palm
Evolution
The Arecaceae were the first modern family of monocots to appear in the fossil record around 80 million years ago (Mya), during the lateCretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
period. The first modern species, such as ''Nypa fruticans
''Nypa fruticans'', commonly known as the nipa palm (or simply nipa, from ) or mangrove palm, is a species of palm native to the coastlines and estuarine habitats of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the only palm considered adapted to the ...
'' and '' Acrocomia aculeata'', appeared 69 Mya, as evidenced by fossil ''Nypa'' pollen. Palms appear to have undergone an early period of adaptive radiation. By 60 Mya, many of the modern, specialized genera of palms appeared and became widespread and common, much more widespread than their range today. Because palms separated from the monocots earlier than other families, they developed more intrafamilial specialization and diversity. By tracing back these diverse characteristics of palms to the basic structures of monocots, palms may be valuable in studying monocot evolution. Several species of palms have been identified from flowers preserved in amber, including '' Palaeoraphe dominicana'' and '' Roystonea palaea''. Fossil evidence of them can also be found in samples of petrified palmwood.
The relationship between the subfamilies is shown in the following cladogram:
Uses

 Evidence for cultivation of the date palm by
Evidence for cultivation of the date palm by Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
ns and other Middle Eastern peoples exists from more than 5,000 years ago, in the form of date wood, pits for storing dates, and other remains of the date palm in Mesopotamian sites. The date palm had a significant effect on the history of the Middle East and North Africa. In the text "Date Palm Products" (1993), W.H. Barreveld wrote:
An indication of the importance of palms in ancient times is that they are mentioned more than 30 times in the Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
, and at least 22 times in the Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
. The Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
also references the "70 date palm trees", which symbolize the 70 aspects of Torah that are revealed to those who "eat of its fruit."
Arecaceae have great economic importance, including coconut products, oils, dates, palm syrup, ivory nuts, carnauba wax, rattan cane, raffia, and palm wood. This family supplies a large amount of the human diet and several other human uses, both by absolute amount produced and by number of species domesticated. This is far higher than almost any other plant family, sixth out of domesticated crops in the human diet, and first in total economic value produced sharing the top spot with the Poaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivate ...
and Fabaceae
Fabaceae () or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomen ...
. These human uses have also spread many Arecaceae species around the world.
Along with dates mentioned above, members of the palm family with human uses are numerous:
* The type member of Arecaceae is the areca palm ('' Areca catechu''), the fruit of which, the areca nut, is chewed with the betel leaf for intoxicating effects.
* Carnauba
Carnauba (; ), also called Brazil wax and palm wax, is a wax of the leaves of the carnauba palm '' Copernicia prunifera'' (synonym: ''Copernicia cerifera''), a plant native to and grown only in the northeastern Brazilian states of Ceará, Pia ...
wax is harvested from the leaves of South American palms of the genus ''Copernicia''.
* Rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan (from Malay language, Malay: ''rotan''), is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the clos ...
s, whose stems are used extensively in furniture
Furniture refers to objects intended to support various human activities such as seating (e.g., Stool (seat), stools, chairs, and sofas), eating (table (furniture), tables), storing items, working, and sleeping (e.g., beds and hammocks). Furnitur ...
and basket
A basket is a container that is traditionally constructed from stiff Fiber, fibers, and can be made from a range of materials, including wood splints, Stolon, runners, and cane. While most baskets are made from plant materials, other materials ...
s, are in the genus ''Calamus''.
* Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil produced by the oil palm
''Elaeis'' () is a genus of palms, called oil palms, containing two species, native to Africa and the Americas. They are used in commercial agriculture in the production of palm oil.
Description
Mature palms are single-stemmed, and can gro ...
s in the genus '' Elaeis''.
* Several species are harvested for heart of palm, a vegetable eaten in salads.
* Sap of the nipa palm, ''Nypa fruticans
''Nypa fruticans'', commonly known as the nipa palm (or simply nipa, from ) or mangrove palm, is a species of palm native to the coastlines and estuarine habitats of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the only palm considered adapted to the ...
'', is used to make vinegar.
* Palm sap is sometimes fermented to produce palm wine or toddy, an alcoholic beverage
Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-al ...
common in parts of Africa, India, and the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
. The sap may be drunk fresh, but fermentation is rapid, reaching up to 4% alcohol content within an hour, and turning vinegary in a day.
* Palmyra and date palm sap is harvested in Bengal, India, to process into ''gur'' and ''jaggery
Jaggery is a List of unrefined sweeteners, traditional non-centrifugal cane sugar consumed in the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, North America, Central America, Brazil and Africa. It is a concentrated product of Sugarcane juice, cane jui ...
''.
* Coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
is the partially edible seed of the fruit of the coconut palm (''Cocos nucifera'').
* Coir is a coarse, water-resistant fiber extracted from the outer shell of coconuts, used in doormats, brushes, mattresses, and ropes.
* Some indigenous groups living in palm-rich areas use palms to make many of their necessary items and food. Sago
Sago () is a starch extracted from the pith, or spongy core tissue, of various tropical palm stems, especially those of ''Metroxylon sagu''. It is a major staple food for the lowland peoples of New Guinea and the Maluku Islands, where it is c ...
, for example, a starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
made from the pith of the trunk of the sago palm '' Metroxylon sagu'', is a major staple food
A staple food, food staple, or simply staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for an individual or a population group, supplying a large fraction of energy needs an ...
for lowland peoples of New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
and the Moluccas.
* Palm wine is made from '' Jubaea'' also called Chilean wine palm, or coquito palm.
* Recently, the fruit of the açaí palm '' Euterpe'' has been used for its reputed health benefits.
* Saw palmetto ('' Serenoa repens'') is being investigated as a drug for treating enlarged prostates.
* Palm leaves are also valuable to some peoples as a material for thatching, basketry, clothing, and in religious ceremonies (see "Symbolism" below).
* Ornamental uses: Today, palms are valuable as ornamental plant
Ornamental plants or ''garden plants'' are plants that are primarily grown for their beauty but also for qualities such as scent or how they shape physical space. Many flowering plants and garden varieties tend to be specially bred cultivars th ...
s and are often grown along streets in tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
and subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
cities. '' Chamaedorea elegans'' is a popular houseplant
A houseplant, also known as a pot plant, potted plant, or indoor plant, is an ornamental plant cultivated indoors. for aesthetic or practical purposes. These plants are commonly found in House, homes, Office, offices, and various indoor spaces, w ...
and is grown indoors for its low maintenance. Farther north, palms are a common feature in botanical gardens or as indoor plants. Few palms tolerate severe cold and the majority of the species are tropical or subtropical. The three most cold-tolerant species are '' Trachycarpus fortunei'', native to eastern Asia, and ''Rhapidophyllum hystrix
''Rhapidophyllum hystrix'', the needle palm, is a Arecaceae, palm native to coastal margins of the Subtropics, subtropical eastern Gulf and south Atlantic states of the United States. Populations can be found from coastal southeast South Carolin ...
'' and ''Sabal minor
''Sabal minor'', commonly known as the dwarf palmetto, is a small species of Arecaceae, palm. It is native to the deep southeastern and south-central United States and northeastern Mexico. It is naturally found in a diversity of habitats, includi ...
'', both native to the southeastern United States.
* The southeastern U.S. state of South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
is nicknamed the Palmetto State after the sabal palmetto
''Sabal palmetto'' (, ''Help:Pronunciation respelling key, SAY-bəl''), also known as cabbage palm, cabbage palmetto, sabal palm, blue palmetto, Carolina palmetto, common palmetto, Garfield's tree, and swamp cabbage, is one of 15 species of Saba ...
(cabbage palmetto), logs from which were used to build the fort at Fort Moultrie
Fort Moultrie is a series of fortifications on Sullivan's Island, South Carolina, built to protect the city of Charleston, South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina. The first fort, formerly named Fort Sullivan, built of Cabbage Pal ...
. During the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, they were invaluable to those defending the fort, because their spongy wood absorbed or deflected the British cannonballs.
* Singaporean politician Tan Cheng Bock uses a palm tree-like symbol similar to a '' Ravenala'' to represent him in the 2011 Singaporean presidential election. The symbol of a party he founded, Progress Singapore Party
The Progress Singapore Party (abbreviation: PSP) is a political party in Singapore. It was one of the three political parties represented in 14th Parliament, alongside the governing People's Action Party (PAP) and the other opposition Workers' ...
, was also based on a palm tree.
* On Ash Wednesday
Ash Wednesday is a holy day of prayer and fasting in many Western Christian denominations. It is preceded by Shrove Tuesday and marks the first day of Lent: the seven weeks of Christian prayer, prayer, Religious fasting#Christianity, fasting and ...
, Catholics receive a cross on their forehead made of palm ashes as a reminder of the Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
belief that everyone and everything eventually returns to where it came from, commonly expressed by the saying "ashes to ashes and dust to dust."
* Lately the Fujairah Research Centre reported the use of date palm leaves to help restore coral reefs as it merged ancient Emerati techniques with modern science.
Phoenix dactylifera
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as the date palm, is a flowering-plant species in the palm family Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet #Fruits, fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across North Africa, northern A ...
''
Image:Santa Monica Palm Trees.jpg, '' Washingtonia robusta'' palms line Ocean Avenue in Santa Monica, California
Santa Monica (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast (California), South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 United Sta ...
.
Image:Rodeo Palms -- Manvel, Texas.jpg, Rodeo Palms, a subdivision in Manvel, Texas
File:Palm tree CANA.JPG, Sabal palm in the Canaveral National Seashore
File:Coconut Palm flowers.jpg, Coconut flowers
File:Palm tree top, Georgia, US.jpg, Close-up of the top, Atlantic Ocean, Georgia, U.S.
File:Thumbnail 0EABDEB1-4CA9-4B26-9C05-035B8F9C1221.jpg, Palm Tree Orlando Florida
Endangered species
Like many other plants, palms have been threatened by human intervention and exploitation. The greatest risk to palms is destruction of habitat, especially in thetropical forest
Tropical forests are forested ecoregions with tropical climates – that is, land areas approximately bounded by the Tropic of Cancer, tropics of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, Capricorn, but possibly affected by other factors such as prevailing ...
s, due to urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
, wood-chipping, mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
, and conversion to farmland. Palms rarely reproduce after such great changes in the habitat, and those with small habitat ranges are most vulnerable to them. The harvesting of heart of palm, a delicacy in salads, also poses a threat because it is derived from the palm's apical meristem, a vital part of the palm that cannot be regrown (except in domesticated varieties, e.g. of peach palm). The use of rattan palms in furniture has caused a major population decrease in these species that has negatively affected local and international markets, as well as biodiversity in the area. The sale of seeds to nurseries and collectors is another threat, as the seeds of popular palms are sometimes harvested directly from the wild. In 2006, at least 100 palm species were considered endangered, and nine species have been reported as recently extinct.
However, several factors make palm conservation more difficult. Palms live in almost every type of warm habitat and have tremendous morphological diversity. Most palm seeds lose viability quickly, and they cannot be preserved in low temperatures because the cold kills the embryo. Using botanical gardens for conservation also presents problems, since they can rarely house more than a few plants of any species or truly imitate the natural setting. There is also the risk that cross-pollination can lead to hybrid species.
The Palm Specialist Group of the World Conservation Union (IUCN) began in 1984, and has performed a series of three studies to find basic information on the status of palms in the wild, use of wild palms, and palms under cultivation. Two projects on palm conservation and use supported by the World Wildlife Fund
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) is a Swiss-based international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the ...
took place from 1985 to 1990 and 1986–1991, in the American tropics and southeast Asia, respectively. Both studies produced copious new data and publications on palms. Preparation of a global action plan for palm conservation began in 1991, supported by the IUCN, and was published in 1996.
The rarest palm known is '' Hyophorbe amaricaulis''. The only living individual remains at the Botanic Gardens of Curepipe in Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
.
Arthropod pests
Some pests are specialists to particulartaxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
. Pests that attack a ''variety'' of species of palms include:
* '' Raoiella indica'', the red palm mite
* '' Caryobruchus gleditsiae'', the palm seed beetle or palm seed weevil
* '' Rhynchophorus ferrugineus'', the red palm weevil, recently introduced to Europe
* '' Rhynchophorus palmarum'', the South American palm weevil
Symbolism
 The palm branch was a symbol of triumph and victory in
The palm branch was a symbol of triumph and victory in classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
. The Romans rewarded champions of the games and celebrated military successes with palm branches. Early Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
used the palm branch to symbolize the victory of the faithful over enemies of the soul, as in the Palm Sunday
Palm Sunday is the Christian moveable feast that falls on the Sunday before Easter. The feast commemorates Christ's triumphal entry into Jerusalem, an event mentioned in each of the four canonical Gospels. Its name originates from the palm bran ...
festival celebrating the triumphal entry of Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
into Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
. In Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, the palm represents peace and plenty, and is one of the Four Species of Sukkot
Sukkot, also known as the Feast of Tabernacles or Feast of Booths, is a Torah-commanded Jewish holiday celebrated for seven days, beginning on the 15th day of the month of Tishrei. It is one of the Three Pilgrimage Festivals on which Israelite ...
; the palm may also symbolize the Tree of Life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythology, mythological, religion, religious, and philosophy, philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The ...
in Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ...
.
The canopies of the Rathayatra carts which carry the deities of Krishna and his family members in the cart festival of Jagganath Puri in India are marked with the emblem of a palm tree. Specifically it is the symbol of Krishna's brother, Baladeva.
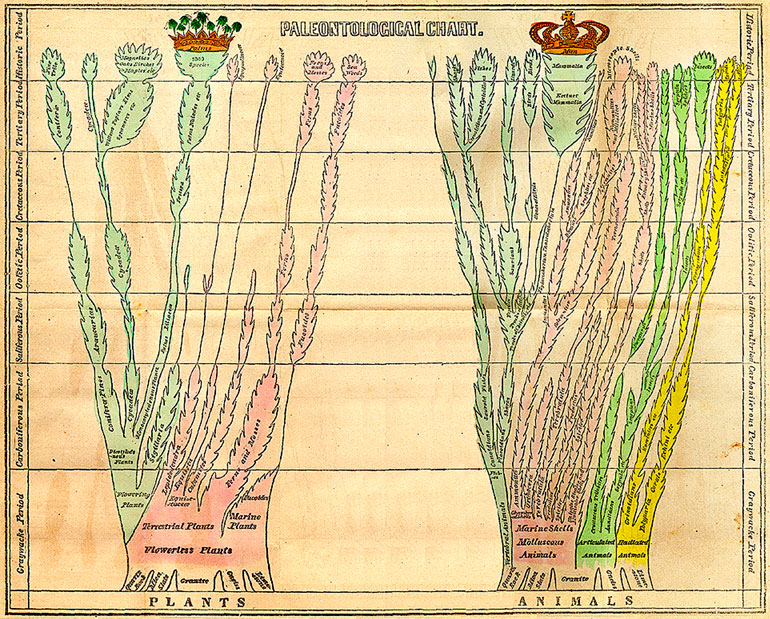
In 1840, the American geologist Edward Hitchcock (1793–1864) published the first tree-like paleontology chart in his ''Elementary Geology'', with two separate trees of life for the plants and the animals. These are crowned (graphically) with the Palms and with Man.
Today, the palm, especially the coconut palm, remains a symbol of the tropical island paradise
In religion and folklore, paradise is a place of everlasting happiness, delight, and bliss. Paradisiacal notions are often laden with pastoral imagery, and may be cosmogonical, eschatological, or both, often contrasted with the miseries of human ...
.
Palms appear on the flags and seals of several places where they are native, including those of Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
, Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
, Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, and South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
.

Other plants
Some species commonly called palms, though they are not true palms, include: * ''Ailanthus altissima
''Ailanthus altissima'' ( ), commonly known as tree of heaven or ailanthus tree, is a deciduous tree in the quassia family. It is native to northeast and central China, and Taiwan. Unlike other members of the genus ''Ailanthus'', it is found ...
'' (Ghetto palm), a tree in the flowering plant family Simaroubaceae
* '' Alocasia odora x gageana'' 'Calidora' (Persian palm), a flowering plant in the family Araceae
The Araceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in which flowers are borne on a type of inflorescence called a spadix. The spadix is usually accompanied by, and sometimes partially enclosed in, a spathe (or leaf-like bract). Also ...
* '' Aloe thraskii'' (Palm aloe), a flowering plant in the family Asphodelaceae
* '' Amorphophallus konjac'' (Snake palm), a flowering plant in the family Araceae
* '' Beaucarnea recurvata'' (Ponytail palm), a flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae
Asparagaceae (), known as the asparagus family, is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. The family name is based on the edible garden asparagus, '' Asparagus officinalis''. This family includes both ...
* '' Begonia luxurians'' (Palm leaf begonia), a flowering plant in the family Begoniaceae
* '' Biophytum umbraculum'' (South Pacific palm), a flowering plant in the family Oxalidaceae
* '' Blechnum appendiculatum'' (Palm fern), a fern in the family Aspleniaceae
* ''Brassica oleracea
''Brassica oleracea'', also known as wild cabbage in its uncultivated form, is a plant of the family Brassicaceae. The species originated from feral populations of related plants in the Eastern Mediterranean, where it was most likely first cultiv ...
'' ' Lacinato kale' (Black Tuscan palm), a flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae
Brassicaceae () or (the older but equally valid) Cruciferae () is a medium-sized and economically important Family (biology), family of flowering plants commonly known as the mustards, the crucifers, or the cabbage family. Most are herbaceous pla ...
* '' Brighamia insignis'' (Vulcan palm), a flowering plant in the family Campanulaceae
The family Campanulaceae (also bellflower family), of the order Asterales, contains nearly 2400 species in 84 genera of herbaceous plants, shrubs, and rarely small trees, often with milky sap. Among them are several familiar garden plants bel ...
* '' Carludovica palmata'' (Panama hat palm) and perhaps other members in the family Cyclanthaceae.
* '' Cordyline australis'' (Cabbage palm, Torbay palm, ti palm) or palm lily (family Asparagaceae) and other representatives in the genus '' Cordyline''.
* '' Cyathea cunninghamii'' (Palm fern) and other tree ferns (families Cyatheaceae and Dicksoniaceae) that may be confused with palms.
* '' Cycas revoluta'' (Sago palm) and the rest of the order Cycadales.
* '' Cyperus alternifolius'' (Umbrella palm), a sedge in the family Cyperaceae
The Cyperaceae () are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as wikt:sedge, sedges. The family (biology), family is large; botanists have species description, described some 5,500 known species in about 90 ...
* '' Dasylirion longissimum'' (Grass palm), a flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae and other plants in the genus ''Dasylirion
''Dasylirion'' is a genus of succulent, rosette-forming plants in the Asparagaceae family (where it is included in the Nolinoideae subfamily). Most species are native to mountainous arid regions of Mexico, with some species also native to the Sou ...
''
* '' Dioon spinulosum'' (Gum palm), a cycad in the family Zamiaceae
* '' Dracaena marginata'' (Dragon palm) a flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae
* '' Eisenia arborea'' (Southern sea palm), a species of brown alga in the family Lessoniaceae
Lessoniaceae are a family of kelp. Species of this family have a transition zone with the intercalary meristem subdivided so that there are a number of secondary stipes in addition to the primary Stipe (botany), stipe.
Genera and species
*''Eckl ...
* '' Fatsia japonica'' (Figleaf palm), a flowering plant in the family Araliaceae
The Araliaceae are a family of flowering plants composed of about 43 genera and around 1500 species consisting of primarily woody plants and some herbaceous plants commonly called the ginseng family. The morphology of Araliaceae varies widely ...
* '' Heracleum persicum'' (Tromsø palm), a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae
Apiaceae () or Umbelliferae is a family of mostly aromatic flowering plants named after the type genus ''Apium,'' and commonly known as the celery, carrot, or parsley family, or simply as umbellifers. It is the 16th-largest family of flowering p ...
* '' Hypnodendron comosum'' (Palm tree moss or palm moss), a moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryo ...
in the family Hypnodendraceae
* '' Musa'' species (Banana palm), a flowering plant in the family Musaceae
* '' Pachypodium lamerei'' (Madagascar palm), a flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae
Apocynaceae (, from '' Apocynum'', Greek for "dog-away") is a family of flowering plants that includes trees, shrubs, herbs, stem succulents, and vines, commonly known as the dogbane family, because some taxa were used as dog poison. Notable mem ...
* '' Pandanus spiralis'' (Screw palm), a flowering plant in the family PandanaceaeFAO 1995. ''Tropical Palms.''. Introduction. ''Non-Wood Forest Products'' 10. FAO – Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. and perhaps other '' Pandanus'' spp.
* '' Ravenala'' (Traveller's palm), a flowering plant in the family Strelitziaceae
* '' Setaria palmifolia'' (Palm grass), a grass in the family Poaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivate ...
* ''Yucca brevifolia
''Yucca brevifolia'' (also known as the Joshua tree, yucca palm, tree yucca, and palm tree yucca) is a plant species belonging to the genus ''Yucca''. It is tree-like in habit, which is reflected in its common names.
This monocotyledonous tree ...
'' (Yucca palm or palm tree yucca)
* '' Yucca filamentosa'' (Needle palm) and '' Yucca filifera'' (St. Peter's palm), flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae
* '' Zamia furfuracea'' (Cardboard palm), a cycad in the family Zamiaceae
* ''Zamioculcas zamiifolia
''Zamioculcas'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, containing the single species ''Zamioculcas zamiifolia.'' It is a tropical herbaceous perennial plant, and is native to eastern Africa, including Kenya, KwaZulu-Natal, Malawi ...
'' (Emerald palm or aroid palm), a flowering plant in the family Araceae
See also
*Coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
* Fan palm—genera with palmate leaves
* List of Arecaceae genera
* List of foliage plant diseases (Arecaceae)
* List of hardy palms—palms able to withstand colder temperatures
* '' Postelsia''—called the "sea palm" (a brown alga)
References
Citations
General sources
* (Latest Arecaceae or Palmae classification.) * * Schultz-Schultzenstein, C. H. (1832)''Natürliches System des Pflanzenreichs...''
p
317
Berlin, Germany.
External links
Palmpedia
��A wiki-based site dedicated to high quality images and information on palm trees.
Fairchild Guide to Palms
��A collection of palm images, scientific data, and horticultural information hosted by Fairchild Tropical Botanic Garden, Miami.
Kew Botanic Garden's Palm Genera list
��A list of the currently acknowledged genera by Kew Royal Botanic Gardens in London, England (archived 2007)
Palm species listing with images
��Palm and Cycad Societies of Australia (PACSOA)
Palm & Cycad Societies of Florida, Inc. (PACSOF)
which includes pages o
and
*
in th
* Wallace, A. R. (1853),
Palm trees of the Amazon and their uses
'. {{Authority control Arecales Commelinid families Extant Campanian first appearances Tropical agriculture