Orion (constellation) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Orion is a prominent set of stars visible during winter in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer
 Orion is bordered by Taurus to the northwest, Eridanus to the southwest, Lepus to the south,
Orion is bordered by Taurus to the northwest, Eridanus to the southwest, Lepus to the south,
 Orion is very useful as an aid to locating other stars. By extending the line of the Belt southeastward, Sirius (α CMa) can be found; northwestward, Aldebaran (α
Orion is very useful as an aid to locating other stars. By extending the line of the Belt southeastward, Sirius (α CMa) can be found; northwestward, Aldebaran (α
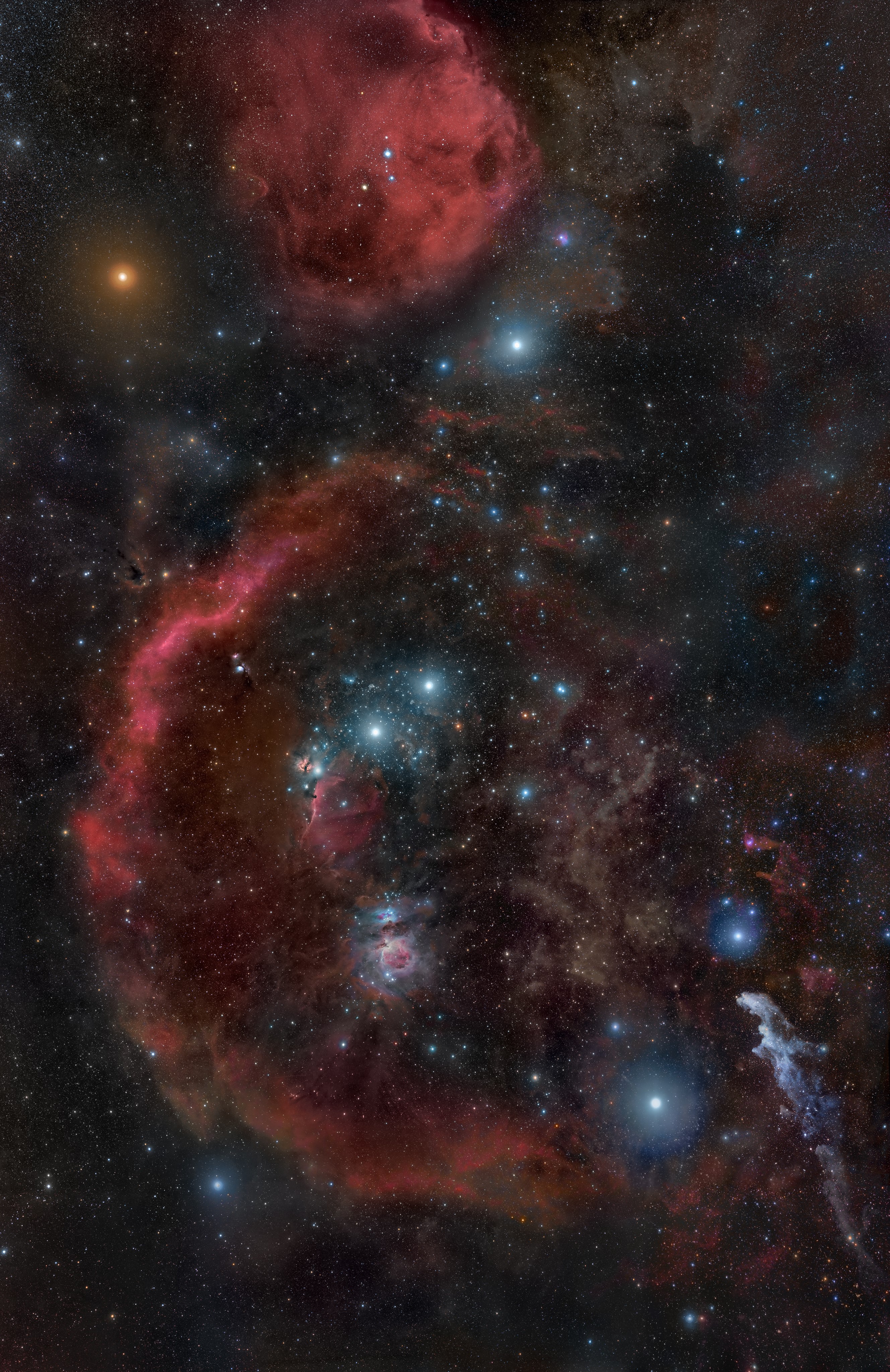
 Hanging from Orion's belt is his sword, consisting of the multiple stars θ1 and θ2 Orionis, called the Trapezium and the Orion Nebula (M42). This is a spectacular object that can be clearly identified with the naked eye as something other than a star. Using binoculars, its clouds of nascent stars, luminous gas, and dust can be observed. The Trapezium cluster has many newborn stars, including several brown dwarfs, all of which are at an approximate distance of 1,500 light-years. Named for the four bright stars that form a
Hanging from Orion's belt is his sword, consisting of the multiple stars θ1 and θ2 Orionis, called the Trapezium and the Orion Nebula (M42). This is a spectacular object that can be clearly identified with the naked eye as something other than a star. Using binoculars, its clouds of nascent stars, luminous gas, and dust can be observed. The Trapezium cluster has many newborn stars, including several brown dwarfs, all of which are at an approximate distance of 1,500 light-years. Named for the four bright stars that form a
 In medieval Muslim astronomy, Orion was known as ''al-jabbar'', "the giant". Orion's sixth brightest star, Saiph, is named from the Arabic, ''saif al-jabbar'', meaning "sword of the giant".
In medieval Muslim astronomy, Orion was known as ''al-jabbar'', "the giant". Orion's sixth brightest star, Saiph, is named from the Arabic, ''saif al-jabbar'', meaning "sword of the giant".
 In artistic renderings, the surrounding constellations are sometimes related to Orion: he is depicted standing next to the river Eridanus with his two hunting dogs
In artistic renderings, the surrounding constellations are sometimes related to Orion: he is depicted standing next to the river Eridanus with his two hunting dogs
 Orion is located on the celestial equator, but it will not always be so located due to the effects of
Orion is located on the celestial equator, but it will not always be so located due to the effects of
The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Orion
Melbourne Planetarium: Orion Sky Tour
*
Beautiful Astrophoto: Zoom Into Orion
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (medieval and early modern images of Orion)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Orion (Constellation) Constellations Constellations listed by Ptolemy Equatorial constellations
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
. It is named after a hunter in Greek mythology.
Orion is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Orion's two brightest stars, Rigel (β) and Betelgeuse (α), are both among the brightest stars in the night sky; both are supergiants and slightly variable. There are a further six stars brighter than magnitude 3.0, including three making the short straight line of the Orion's Belt asterism. Orion also hosts the radiant of the annual Orionids
The Orionids meteor shower, often shortened to the Orionids, is one of two meteor showers associated with Halley's Comet. The Orionids are so-called because the point they appear to come from, called the radiant, lies in the constellation
...
, the strongest meteor shower associated with Halley's Comet
Halley's Comet is the only known List of periodic comets, short-period comet that is consistently visible to the naked eye from Earth, appearing every 72–80 years, though with the majority of recorded apparitions (25 of 30) occurring after ...
, and the Orion Nebula, one of the brightest nebula
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in ...
e in the sky.
Characteristics
 Orion is bordered by Taurus to the northwest, Eridanus to the southwest, Lepus to the south,
Orion is bordered by Taurus to the northwest, Eridanus to the southwest, Lepus to the south, Monoceros
Monoceros ( Greek: , "unicorn") is a faint constellation on the celestial equator. Its definition is attributed to the 17th-century cartographer Petrus Plancius. It is bordered by Orion to the west, Gemini to the north, Canis Major to the s ...
to the east, and Gemini to the northeast. Covering 594 square degrees, Orion ranks twenty-sixth of the 88 constellations in size. The constellation boundaries, as set by Belgian astronomer Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined by a polygon of 26 sides. In the equatorial coordinate system
The equatorial coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system widely used to specify the positions of astronomical object, celestial objects. It may be implemented in spherical coordinate system, spherical or Cartesian coordinate system, rect ...
, the right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in questio ...
coordinates of these borders lie between and , while the declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
coordinates are between and . The constellation's three-letter abbreviation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
in 1922, is "Ori".
Orion is most visible in the evening sky from January to April, winter in the Northern Hemisphere, and summer in the Southern Hemisphere. In the tropics (less than about 8° from the equator), the constellation transits at the zenith
The zenith (, ) is the imaginary point on the celestial sphere directly "above" a particular location. "Above" means in the vertical direction (Vertical and horizontal, plumb line) opposite to the gravity direction at that location (nadir). The z ...
.
In the period May–July (summer in the Northern Hemisphere, winter in the Southern Hemisphere), Orion is in the daytime sky and thus invisible at most latitudes. However, for much of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
in the Southern Hemisphere's winter months, the Sun is below the horizon
The horizon is the apparent curve that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This curve divides all viewing directions based on whethe ...
even at midday. Stars (and thus Orion, but only the brightest stars) are then visible at twilight for a few hours around local noon, just in the brightest section of the sky low in the North where the Sun is just below the horizon. At the same time of day at the South Pole itself ( Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station), Rigel is only 8° above the horizon, and the Belt sweeps just along it. In the Southern Hemisphere's summer months, when Orion is normally visible in the night sky, the constellation is actually not visible in Antarctica because the sun does not set at that time of year south of the Antarctic Circle.
In countries close to the equator (e.g., Kenya, Indonesia, Colombia, Ecuador), Orion appears overhead in December around midnight and in the February evening sky.
Navigational aid
Tau
Tau (; uppercase Τ, lowercase τ or \boldsymbol\tau; ) is the nineteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless alveolar plosive, voiceless dental or alveolar plosive . In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 300 ...
). A line eastward across the two shoulders indicates the direction of Procyon
Procyon () is the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Minor and usually the list of brightest stars, eighth-brightest star in the night sky, with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.34. It has the Bayer designation α Canis Min ...
(α CMi). A line from Rigel through Betelgeuse points to Castor and Pollux (α Gem and β Gem). Additionally, Rigel is part of the Winter Circle asterism. Sirius and Procyon
Procyon () is the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Minor and usually the list of brightest stars, eighth-brightest star in the night sky, with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.34. It has the Bayer designation α Canis Min ...
, which may be located from Orion by following imaginary lines (see map), also are points in both the Winter Triangle and the Circle.
Features
Orion's seven brightest stars form a distinctive hourglass-shaped asterism, or pattern, in the night sky. Four stars—Rigel, Betelgeuse, Bellatrix, and Saiph—form a large roughly rectangular shape, at the center of which lie the three stars of Orion's Belt— Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. His head is marked by an additional 8th star called Meissa, which is fairly bright to the observer. Descending from the "belt" is a smaller line of three stars, Orion's Sword (the middle of which is in fact not a star but the Orion Nebula), also known as the hunter's sword. Many of the stars are luminous hot blue supergiants, with the stars of the belt and sword forming the Orion OB1 association. Standing out by its red hue, Betelgeuse may nevertheless be a runaway member of the same group.
Bright stars
* Betelgeuse, also designated Alpha Orionis, is a massive M-type red supergiant star nearing the end of its life. It is the second brightest star in Orion, and is a semiregular variable star. It serves as the "right shoulder" of the hunter (assuming that he is facing the observer). It is generally the eleventh brightest star in the night sky, but this has varied between being the tenth brightest to the 23rd brightest by the end of 2019. The end of its life is expected to result in a supernova explosion that will be highly visible from Earth, possibly outshining the Moon and being visible during the day. This is most likely to occur within the next 100,000 years. * Rigel, also known as Beta Orionis, is a B-type blue supergiant that is the seventh brightest star in the night sky. Similar to Betelgeuse, Rigel is fusing heavy elements in its core and will pass its supergiant stage soon (on an astronomical timescale), either collapsing in the case of asupernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
or shedding its outer layers and turning into a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place i ...
. It serves as the left foot of the hunter.
* Bellatrix is designated Gamma Orionis by Johann Bayer. It is the twenty-seventh brightest star in the night sky. Bellatrix is considered a B-type blue giant, though it is too small to explode in a supernova. Bellatrix's luminosity is derived from its high temperature rather than a large radius. Bellatrix marks Orion's left shoulder and it means the "female warrior", and is sometimes known colloquially as the "Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
Star". It is the closest major star in Orion at only 244.6 light years from the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
.
* Mintaka is designated Delta Orionis, despite being the faintest of the three stars in Orion's Belt. Its name means "the belt". It is a multiple star system, composed of a large B-type blue giant and a more massive O-type main-sequence star. The Mintaka system constitutes an eclipsing binary variable star, where the eclipse of one star over the other creates a dip in brightness. Mintaka is the westernmost of the three stars of Orion's Belt, as well as the northernmost.
* Alnilam is designated Epsilon Orionis and is named for the Arabic phrase meaning "string of pearls". It is the middle and brightest of the three stars of Orion's Belt. Alnilam is a B-type blue supergiant; despite being nearly twice as far from the Sun as the other two belt stars, its luminosity makes it nearly equal in magnitude. Alnilam is losing mass quickly, a consequence of its size. It is the farthest major star in Orion at 1,344 light years.
* Alnitak, meaning "the girdle", is designated Zeta Orionis, and is the easternmost star in Orion's Belt. It is a triple star system, with the primary star being a hot blue supergiant and the brightest class O star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
in the night sky.
* Saiph is designated Kappa Orionis by Bayer, and serves as Orion's right foot. It is of a similar distance and size to Rigel, but appears much fainter. It means the "sword of the giant"
* Meissa is designated Lambda Orionis, forms Orion's head, and is a multiple star with a combined apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
of 3.33. Its name means the "shining one".
Belt
Orion's Belt or The Belt of Orion is an asterism within the constellation. It consists of the three bright starsZeta
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ζ, lowercase ζ; , , classical or ''zē̂ta''; ''zíta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter zay ...
(Alnitak), Epsilon
Epsilon (, ; uppercase , lowercase or ; ) is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a mid front unrounded vowel or . In the system of Greek numerals it also has the value five. It was derived from the Phoenic ...
(Alnilam), and Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
(Mintaka). Alnitak is around 800 light years away from Earth and is 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun and shines with magnitude 1.8; much of its radiation is in the ultraviolet range, which the human eye cannot see. Alnilam is approximately 2,000 light years away from Earth, shines with magnitude 1.70, and with ultraviolet light is 375,000 times more luminous than the Sun. Mintaka is 915 light years away and shines with magnitude 2.21. It is 90,000 times more luminous than the Sun and is a double star: the two orbit each other every 5.73 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, Orion's Belt is best visible in the night sky during the month of January around 9:00 pm, when it is approximately around the local meridian.
Just southwest of Alnitak lies Sigma Orionis, a multiple star system composed of five stars that have a combined apparent magnitude of 3.7 and lying 1150 light years distant. Southwest of Mintaka lies the quadruple star Eta Orionis.
Sword
Orion's Sword contains the Orion Nebula, the Messier 43 nebula, the Running Man Nebula, and the stars Theta Orionis, Iota Orionis, and 42 Orionis.Head
Three stars comprise a small triangle that marks the head. The apex is marked by Meissa (Lambda Orionis), a hot blue giant of spectral type O8 III and apparent magnitude 3.54, which lies some 1100 light years distant. Phi-1 and Phi-2 Orionis make up the base. Also nearby is the very young star FU Orionis.Club
Stretching north from Betelgeuse are the stars that make up Orion's club. Mu Orionis marks the elbow, Nu and Xi mark the handle of the club, and Chi1 and Chi2 mark the end of the club. Just east of Chi1 is the Mira-type variable red giant U Orionis.Shield
West from Bellatrix lie six stars all designated Pi Orionis ( π1 Ori, π2 Ori, π3 Ori, π4 Ori, π5 Ori and π6 Ori) which make up Orion's shield.Meteor showers
Around 20 October each year the Orionid meteor shower (Orionids) reaches its peak. Coming from the border with the constellation Gemini as many as 20 meteors per hour can be seen. The shower's parent body isHalley's Comet
Halley's Comet is the only known List of periodic comets, short-period comet that is consistently visible to the naked eye from Earth, appearing every 72–80 years, though with the majority of recorded apparitions (25 of 30) occurring after ...
.
Deep-sky objects
 Hanging from Orion's belt is his sword, consisting of the multiple stars θ1 and θ2 Orionis, called the Trapezium and the Orion Nebula (M42). This is a spectacular object that can be clearly identified with the naked eye as something other than a star. Using binoculars, its clouds of nascent stars, luminous gas, and dust can be observed. The Trapezium cluster has many newborn stars, including several brown dwarfs, all of which are at an approximate distance of 1,500 light-years. Named for the four bright stars that form a
Hanging from Orion's belt is his sword, consisting of the multiple stars θ1 and θ2 Orionis, called the Trapezium and the Orion Nebula (M42). This is a spectacular object that can be clearly identified with the naked eye as something other than a star. Using binoculars, its clouds of nascent stars, luminous gas, and dust can be observed. The Trapezium cluster has many newborn stars, including several brown dwarfs, all of which are at an approximate distance of 1,500 light-years. Named for the four bright stars that form a trapezoid
In geometry, a trapezoid () in North American English, or trapezium () in British English, is a quadrilateral that has at least one pair of parallel sides.
The parallel sides are called the ''bases'' of the trapezoid. The other two sides are ...
, it is largely illuminated by the brightest stars, which are only a few hundred thousand years old. Observations by the Chandra X-ray Observatory show both the extreme temperatures of the main stars—up to 60,000 kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By de ...
s—and the star forming regions still extant in the surrounding nebula.
M78 (NGC 2068) is a nebula in Orion. With an overall magnitude of 8.0, it is significantly dimmer than the Great Orion Nebula that lies to its south; however, it is at approximately the same distance, at 1600 light-years from Earth. It can easily be mistaken for a comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
in the eyepiece of a telescope. M78 is associated with the variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
V351 Orionis, whose magnitude changes are visible in very short periods of time. Another fairly bright nebula in Orion is NGC 1999, also close to the Great Orion Nebula. It has an integrated magnitude of 10.5 and is 1500 light-years from Earth. The variable star V380 Orionis is embedded in NGC 1999.
Another famous nebula
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in ...
is IC 434, the Horsehead Nebula, near ζ Orionis. It contains a dark dust cloud whose shape gives the nebula its name.
NGC 2174 is an emission nebula located 6400 light-years from Earth.
Besides these nebulae, surveying Orion with a small telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
will reveal a wealth of interesting deep-sky objects, including M43, M78, as well as multiple stars including Iota Orionis and Sigma Orionis. A larger telescope may reveal objects such as the Flame Nebula (NGC 2024), as well as fainter and tighter multiple stars and nebulae. Barnard's Loop can be seen on very dark nights or using long-exposure photography.
All of these nebulae are part of the larger Orion molecular cloud complex, which is located approximately 1,500 light-years away and is hundreds of light-years across. It is one of the most intense regions of stellar formation visible within the Milky Way Galaxy.
History and mythology
The distinctive pattern of Orion is recognized in numerous cultures around the world, and many myths are associated with it. Orion is used as a symbol in the modern world.Ancient Near East
The Babylonian star catalogues of the Late Bronze Age name Orion ',The determiner glyph for "constellation" or "star" in these lists is MUL (). See Babylonian star catalogues. "The Heavenly Shepherd" or "True Shepherd of Anu" – Anu being the chief god of the heavenly realms. The Babylonian constellation is sacred to Papshukal and Ninshubur, both minor gods fulfilling the role of 'messenger to the gods'. Papshukal is closely associated with the figure of a walkingbird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
on Babylonian boundary stones, and on the star map the figure of the Rooster is located below and behind the figure of the True Shepherd—both constellations represent the herald of the gods, in his bird and human forms respectively.
In ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
, the stars of Orion were regarded as a god
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
, called Sah. Because Orion rises before Sirius, the star whose heliacal rising
The heliacal rising ( ) of a star or a planet occurs annually when it becomes visible above the eastern horizon at dawn just before sunrise (thus becoming "the Morning Star (disambiguation)#Astronomy, morning star"). A heliacal rising marks the ti ...
was the basis for the Solar Egyptian calendar
The ancient Egyptian calendar – a civil calendar – was a solar calendar with a 365-day year. The year consisted of three seasons of 120 days each, plus an Egyptian intercalary month, intercalary month of five epagomenal days treated as outs ...
, Sah was closely linked with Sopdet, the goddess who personified Sirius. The god Sopdu is said to be the son of Sah and Sopdet. Sah is syncretized with Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wikt:wsjr, wsjr'') was the ancient Egyptian deities, god of fertility, agriculture, the Ancient Egyptian religion#Afterlife, afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was ...
, while Sopdet is syncretized with Osiris' mythological wife, Isis
Isis was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her sla ...
. In the Pyramid Texts, from the 24th and 23rd centuries BC, Sah is one of many gods whose form the dead pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty ( ...
is said to take in the afterlife.
The Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
identified their legendary patriarch and founder Hayk with Orion. ''Hayk'' is also the name of the Orion constellation in the Armenian translation of the Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
.
The Bible mentions Orion three times, naming it "Kesil" (כסיל, literally – fool). Though, this name perhaps is etymologically connected with "Kislev", the name for the ninth month of the Hebrew calendar (i.e. November–December), which, in turn, may derive from the Hebrew root K-S-L as in the words "kesel, kisla" (כֵּסֶל, כִּסְלָה, hope, positiveness), i.e. hope for winter rains.: Job 9:9 ("He is the maker of the Bear and Orion"), Job 38:31 ("Can you loosen Orion's belt?"), and Amos 5:8 ("He who made the Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as Seven Sisters and Messier 45 (M45), is an Asterism (astronomy), asterism of an open cluster, open star cluster containing young Stellar classification#Class B, B-type stars in the northwest of the constellation Tau ...
and Orion").
In ancient Aram, the constellation was known as ''Nephîlā′'', the '' Nephilim'' are said to be Orion's descendants.
Greco-Roman antiquity
InGreek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
, Orion was a gigantic, supernaturally strong hunter, born to Euryale, a Gorgon
The Gorgons ( ; ), in Greek mythology, are three monstrous sisters, Stheno, Euryale, and Medusa, said to be the daughters of Phorcys and Ceto. They lived near their sisters the Graeae, and were able to turn anyone who looked at them to sto ...
, and Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
(Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
), god of the sea. One myth recounts Gaia's rage at Orion, who dared to say that he would kill every animal on Earth. The angry goddess tried to dispatch Orion with a scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward cur ...
. This is given as the reason that the constellations of Scorpius and Orion are never in the sky at the same time. However, Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellati ...
, the Serpent Bearer, revived Orion with an antidote. This is said to be the reason that the constellation of Ophiuchus stands midway between the Scorpion and the Hunter in the sky.
The constellation is mentioned in Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 BC – 27 November 8 BC), Suetonius, Life of Horace commonly known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). Th ...
's '' Odes'' (Ode 3.27.18), Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
's ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divi ...
'' (Book 5, line 283) and ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
'', and Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
's ''Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; or ) is a Latin Epic poetry, epic poem that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Troy, Trojan who fled the Trojan War#Sack of Troy, fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of the Ancient Rome ...
'' (Book 1, line 535).
Middle East
 In medieval Muslim astronomy, Orion was known as ''al-jabbar'', "the giant". Orion's sixth brightest star, Saiph, is named from the Arabic, ''saif al-jabbar'', meaning "sword of the giant".
In medieval Muslim astronomy, Orion was known as ''al-jabbar'', "the giant". Orion's sixth brightest star, Saiph, is named from the Arabic, ''saif al-jabbar'', meaning "sword of the giant".
China
InChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Orion was one of the 28 lunar mansions ''Sieu (Xiù)'' (宿). It is known as ''Shen'' (參), literally meaning "three", for the stars of Orion's Belt. (See Chinese constellations)
The Chinese character
Chinese characters are logographs used to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represent the only on ...
參 (pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin, or simply pinyin, officially the Chinese Phonetic Alphabet, is the most common romanization system for Standard Chinese. ''Hanyu'' () literally means 'Han Chinese, Han language'—that is, the Chinese language—while ''pinyin' ...
shēn) originally meant the constellation Orion (); its Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ...
version, over three millennia old, contains at the top a representation of the three stars of Orion's belt atop a man's head (the bottom portion representing the sound of the word was added later).
India
The ''Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
'' refers to the Orion Constellation as Mriga (The Deer).
Nataraja, 'the cosmic dancer', is often interpreted as the representation of Orion. Rudra, the Rigvedic form of Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
, is the presiding deity of Ardra nakshatra ( Betelgeuse) of Hindu astrology.
The Jain Symbol carved in Udayagiri and Khandagiri Caves, India in 1st century BCE has striking resemblance with Orion.
Bugis sailors identified the three stars in Orion's Belt as ''tanra tellué'', meaning "sign of three".
European folklore
In old Hungarian tradition, Orion is known as "Archer" (''Íjász''), or "Reaper" (''Kaszás''). In recently rediscovered myths, he is calledNimrod
Nimrod is a Hebrew Bible, biblical figure mentioned in the Book of Genesis and Books of Chronicles, the Books of Chronicles. The son of Cush (Bible), Cush and therefore the great-grandson of Noah, Nimrod was described as a king in the land of Sh ...
( Hungarian: ''Nimród''), the greatest hunter, father of the twins Hunor and Magor. The π and o stars (on upper right) form together the reflex bow or the lifted scythe. In other Hungarian traditions, Orion's belt is known as "Judge's stick" (''Bírópálca'').
In Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
n tradition, Orion's belt was known as "Frigg
Frigg (; Old Norse: ) is a goddess, one of the Æsir, in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about her, she is associated with marriage, prophecy, clairvoyance and motherhood, and dwells in the wetl ...
's Distaff" (''friggerock'') or "Freyja
In Norse mythology, Freyja (Old Norse "(the) Lady") is a goddess associated with love, beauty, fertility, sex, war, gold, and seiðr (magic for seeing and influencing the future). Freyja is the owner of the necklace Brísingamen, rides a char ...
's distaff".
The Finns
Finns or Finnish people (, ) are a Baltic Finns, Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland. Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these cou ...
call Orion's belt and the stars below it "Väinämöinen
() is a deity, demigod, hero and the central character in Finnish folklore and the main character in the national epic ''Kalevala'' by Elias Lönnrot. Väinämöinen was described as an old and wise man, and he possessed a potent, magical sing ...
's scythe
A scythe (, rhyming with ''writhe'') is an agriculture, agricultural hand-tool for mowing grass or Harvest, harvesting Crop, crops. It was historically used to cut down or reaping, reap edible grain, grains before they underwent the process of ...
" (''Väinämöisen viikate''). Another name for the asterism of Alnilam, Alnitak and Mintaka is "Väinämöinen's Belt" (''Väinämöisen vyö'') and the stars "hanging" from the belt as " Kaleva's sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
" (''Kalevanmiekka'').
In Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
, the Chukchi people
The Chukchi, or Chukchee (, ''ḷygʺoravètḷʹèt, o'ravètḷʹèt''), are a Siberian ethnic group native to the Chukchi Peninsula, the shores of the Chukchi Sea and the Bering Sea region of the Arctic Ocean all within modern Russia. They s ...
see Orion as a hunter; an arrow he has shot is represented by Aldebaran (Alpha Tauri), with the same figure as other Western depictions.
There are claims in popular media that the Adorant from the Geißenklösterle cave, an ivory carving estimated to be 35,000 to 40,000 years old, is the first known depiction of the constellation. Scholars dismiss such interpretations, saying that perceived details such as a belt and sword derive from preexisting features in the grain structure of the ivory.
Americas
The Seri people of northwestern Mexico call the three stars in the belt of Orion ''Hapj'' (a name denoting a hunter) which consists of three stars: ''Hap'' (mule deer), ''Haamoja'' (pronghorn), and ''Mojet'' (bighorn sheep). ''Hap'' is in the middle and has been shot by the hunter; its blood has dripped ontoTiburón Island
Tiburón Island is the largest island in the Gulf of California and the largest island in Mexico, with an area of . It is uninhabited and it was made a nature reserve in 1963 by President Adolfo López Mateos.
Etymology
is Spanish language, Spa ...
.
The same three stars are known in Spain and most of Latin America as "Las tres Marías" (Spanish for "The Three Marys
The Three Marys (also spelled Maries) are women mentioned in the Gospel, canonical gospels' narratives of the crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion and resurrection of Jesus.
The Gospels refer to several women named Mary. At various points of Chris ...
").
In Puerto Rico, the three stars are known as the "Los Tres Reyes Magos" (Spanish for The three Wise Men).
The Ojibwa/Chippewa Native Americans call this constellation Mesabi for Big Man.
To the Lakota Native Americans, Tayamnicankhu (Orion's Belt) is the spine of a bison. The great rectangle of Orion is the bison's ribs; the Pleiades star cluster in nearby Taurus is the bison's head; and Sirius in Canis Major, known as Tayamnisinte, is its tail. Another Lakota myth mentions that the bottom half of Orion, the Constellation of the Hand, represented the arm of a chief that was ripped off by the Thunder People as a punishment from the gods for his selfishness. His daughter offered to marry the person who can retrieve his arm from the sky, so the young warrior Fallen Star (whose father was a star and whose mother was human) returned his arm and married his daughter, symbolizing harmony between the gods and humanity with the help of the younger generation. The index finger is represented by Rigel; the Orion Nebula is the thumb; the Belt of Orion is the wrist; and the star Beta Eridani is the pinky finger.
Austronesian
The seven primary stars of Orion make up the Polynesian constellation Heiheionakeiki which represents a child's string figure similar to a cat's cradle. Several precolonial Filipinos referred to the belt region in particular as "balatik" (ballista) as it resembles a trap of the same name which fires arrows by itself and is usually used for catching pigs from the bush. Spanish colonization later led to some ethnic groups referring to Orion's belt as "Tres Marias" or "Tatlong Maria." In Māori tradition, the star Rigel (known as ''Puanga'' or ''Puaka'') is closely connected with the celebration of Matariki. The rising of Matariki (thePleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as Seven Sisters and Messier 45 (M45), is an Asterism (astronomy), asterism of an open cluster, open star cluster containing young Stellar classification#Class B, B-type stars in the northwest of the constellation Tau ...
) and Rigel before sunrise in midwinter marks the start of the Māori year.
In Javanese culture, the constellation is often called ''Lintang Waluku'' or ''Bintang Bajak'', referring to the shape of a paddy field plow.
Contemporary symbolism
The imagery of the belt and sword has found its way into popular western culture, for example in the form of the shoulder insignia of the 27th Infantry Division of theUnited States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
during both World Wars, probably owing to a pun on the name of the division's first commander, Major General John F. ''O'Ryan''.
The film distribution company Orion Pictures used the constellation as its logo.
Depictions
 In artistic renderings, the surrounding constellations are sometimes related to Orion: he is depicted standing next to the river Eridanus with his two hunting dogs
In artistic renderings, the surrounding constellations are sometimes related to Orion: he is depicted standing next to the river Eridanus with his two hunting dogs Canis Major
Canis Major is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "greater dog" in contrast to C ...
and Canis Minor, fighting Taurus. He is sometimes depicted hunting Lepus the hare. He sometimes is depicted to have a lion's hide in his hand.
There are alternative ways to visualise Orion. From the Southern Hemisphere, Orion is oriented south-upward, and the belt and sword are sometimes called the saucepan or pot in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
. Orion's Belt is called ''Drie Konings'' (Three Kings) or the ''Drie Susters'' (Three Sisters) by Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language spoken in South Africa, Namibia and to a lesser extent Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe and also Argentina where there is a group in Sarmiento, Chubut, Sarmiento that speaks the Pat ...
speakers in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
and are referred to as ''les Trois Rois'' (the Three Kings) in Daudet's ''Lettres de Mon Moulin'' (1866). The appellation ''Driekoningen'' (the Three Kings) is also often found in 17th- and 18th-century Dutch star charts and seaman's guides. The same three stars are known in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
, and the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
as "Las Tres Marías" (The Three Marys), and as "Los Tres Reyes Magos" (The three Wise Men) in Puerto Rico.
Even traditional depictions of Orion have varied greatly. Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
drew Orion in a similar fashion to the modern depiction. The Hunter held an unidentified animal skin aloft in his right hand; his hand was represented by Omicron2 Orionis and the skin was represented by the 5 stars designated Pi Orionis. Kappa and Beta Orionis represented his left and right knees, while Eta and Lambda Leporis were his left and right feet, respectively. As in the modern depiction, Delta, Epsilon, and Zeta represented his belt. His left shoulder was represented by Alpha Orionis, and Mu Orionis made up his left arm. Lambda Orionis was his head and Gamma, his right shoulder. The depiction of Hyginus was similar to that of Cicero, though the two differed in a few important areas. Cicero's animal skin became Hyginus's shield (Omicron and Pi Orionis), and instead of an arm marked out by Mu Orionis, he holds a club (Chi Orionis). His right leg is represented by Theta Orionis and his left leg is represented by Lambda, Mu, and Epsilon Leporis. Further Western European and Arabic depictions have followed these two models.
Future
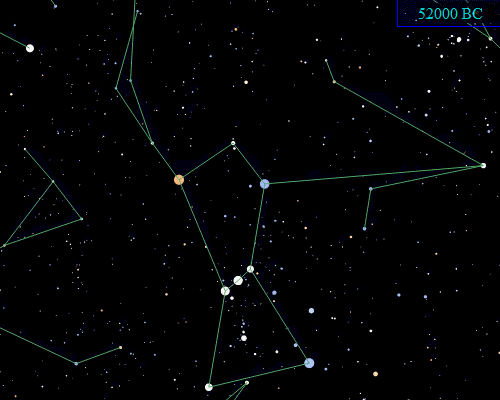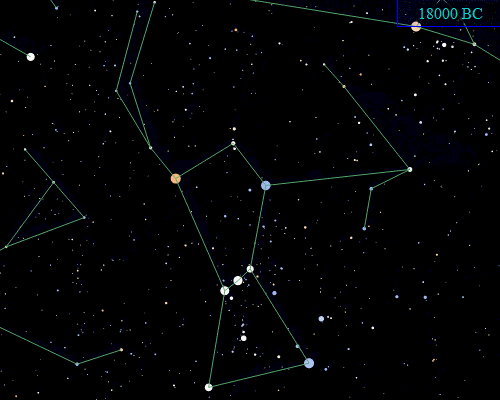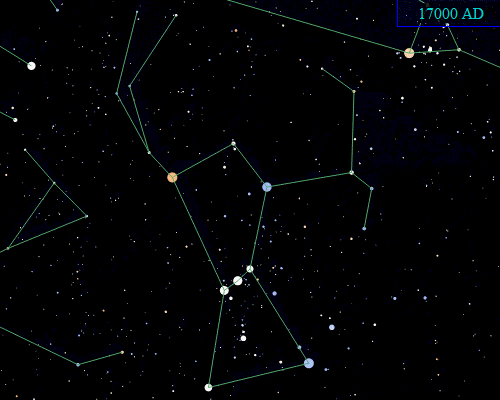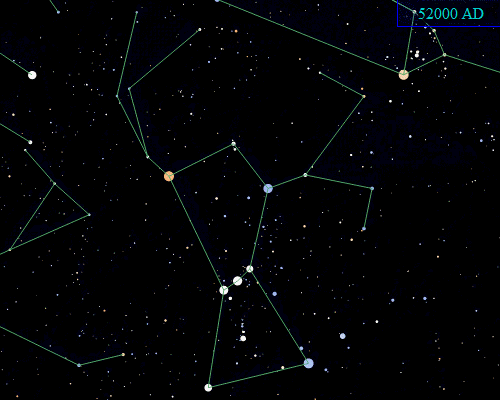
 Orion is located on the celestial equator, but it will not always be so located due to the effects of
Orion is located on the celestial equator, but it will not always be so located due to the effects of precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In o ...
of the Earth's axis. Orion lies well south of the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
, and it only happens to lie on the celestial equator because the point on the ecliptic that corresponds to the June solstice is close to the border of Gemini and Taurus, to the north of Orion. Precession will eventually carry Orion further south, and by AD 14000, Orion will be far enough south that it will no longer be visible from the latitude of Great Britain.
Further in the future, Orion's stars will gradually move away from the constellation due to proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
. However, Orion's brightest stars all lie at a large distance from the Earth on an astronomical scale—much farther away than Sirius, for example. Orion will still be recognizable long after most of the other constellations—composed of relatively nearby stars—have distorted into new configurations, with the exception of a few of its stars eventually exploding as supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
e, for example Betelgeuse, which is predicted to explode sometime in the next million years.
See also
* EURion constellation * '' Hubble 3D'' (2010), IMAX film with an elaborate CGI "fly-through" of the Orion Nebula * Orion correlation theory * Orion (mythology) * Orion (Chinese astronomy) * Aurvandill * Glooscap * Heiheionakeiki * Julpan * Nataraja *Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wikt:wsjr, wsjr'') was the ancient Egyptian deities, god of fertility, agriculture, the Ancient Egyptian religion#Afterlife, afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was ...
* Papsukkal
* Urania
* Winter Hexagon
References
Explanatory notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). ''Stars and Planets Guide'', Collins, London, England. . Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey. . * .External links
The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Orion
Melbourne Planetarium: Orion Sky Tour
*
Beautiful Astrophoto: Zoom Into Orion
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (medieval and early modern images of Orion)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Orion (Constellation) Constellations Constellations listed by Ptolemy Equatorial constellations