Oghuz Turks on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western
The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western
 According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia, potentially in Altai-Sayan region,
According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia, potentially in Altai-Sayan region, 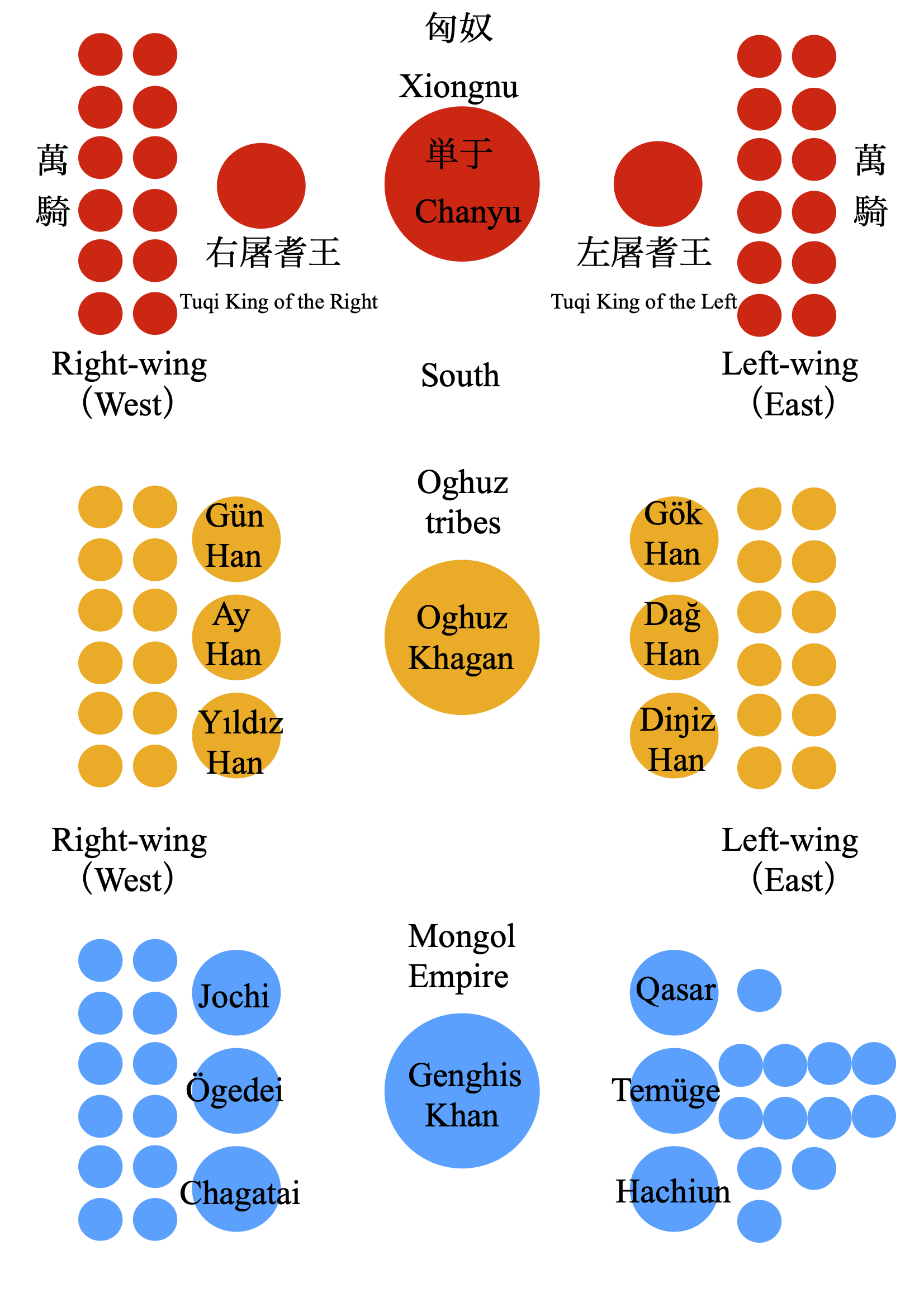 During the 2nd century BC, according to ancient Chinese sources, a
During the 2nd century BC, according to ancient Chinese sources, a
 The
The
 In the 700s, the Oghuz Turks made a new home and domain for themselves in the area between the Caspian and Aral seas and the northwest part of Transoxania, along the Syr Darya river. They had moved westward from the Altay mountains passing through the Siberian steppes and settled in this region, and also penetrated into southern
In the 700s, the Oghuz Turks made a new home and domain for themselves in the area between the Caspian and Aral seas and the northwest part of Transoxania, along the Syr Darya river. They had moved westward from the Altay mountains passing through the Siberian steppes and settled in this region, and also penetrated into southern
 The '' Book of Dede Korkut'' is a seminal collection of epic tales originating from the Oghuz Turks. Comprising twelve stories, the narratives encapsulate themes of heroism, morality, and social norms prevalent among the nomadic Oghuz. The tales were transmitted orally before being compiled into manuscripts in the 15th century. The character Dede Korkut serves as a sage and bard, linking the stories together and offering wisdom to the protagonists. The epics provide insights into the Oghuz way of life, including their customs, conflicts, and the transition from pre-Islamic beliefs to Islamic faith.
The '' Book of Dede Korkut'' is a seminal collection of epic tales originating from the Oghuz Turks. Comprising twelve stories, the narratives encapsulate themes of heroism, morality, and social norms prevalent among the nomadic Oghuz. The tales were transmitted orally before being compiled into manuscripts in the 15th century. The character Dede Korkut serves as a sage and bard, linking the stories together and offering wisdom to the protagonists. The epics provide insights into the Oghuz way of life, including their customs, conflicts, and the transition from pre-Islamic beliefs to Islamic faith.
 Mahmud al-Kashgari listed 22 Oghuz tribes in Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk. Kashgari further wrote that "In origin they are 24 tribes, but the two Khalajiyya tribes are distinguished from them he twenty-twoin certain respects and so are not counted among them. This is the origin".
Later, Charuklug from Kashgari's list would be omitted. Rashid-al-Din and Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur added three more: Kïzïk, Karkïn, and Yaparlï, to the list in Jami' al-tawarikh (Compendium of Chronicles) and Shajare-i Türk (Genealogy of the Turks), respectively. According to Selçukname, Oghuz Khagan had 6 children (Sun – Gün, Moon – Ay, Star – Yıldız, Sky – Gök, Mountain – Dağ, Sea – Diŋiz), and all six would become Khans themselves, each leading four tribes.
Mahmud al-Kashgari listed 22 Oghuz tribes in Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk. Kashgari further wrote that "In origin they are 24 tribes, but the two Khalajiyya tribes are distinguished from them he twenty-twoin certain respects and so are not counted among them. This is the origin".
Later, Charuklug from Kashgari's list would be omitted. Rashid-al-Din and Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur added three more: Kïzïk, Karkïn, and Yaparlï, to the list in Jami' al-tawarikh (Compendium of Chronicles) and Shajare-i Türk (Genealogy of the Turks), respectively. According to Selçukname, Oghuz Khagan had 6 children (Sun – Gün, Moon – Ay, Star – Yıldız, Sky – Gök, Mountain – Dağ, Sea – Diŋiz), and all six would become Khans themselves, each leading four tribes.
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
''page 692''
* Aydın, Mehmet. ''Bayat-Bayat boyu ve Oğuzların tarihi''. Hatiboğlu Yayınevi, 1984
''web page''
The ''Book of Dede Korkut''
(pdf format) at the Uysal-Walker Archive of Turkish Oral Narrative
Similarities between the epics of Dede Korkut and AlpamyshThe Old Turkic Inscriptions.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oghuz History of the Turkish people Turkic peoples of Asia Turkic peoples
 The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western
The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western Turkic people
Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members ...
who spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia. Today, much of the populations of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
are descendants of Oghuz Turks. The term Oghuz was gradually supplanted by the terms Turkmen and Turcoman ( or ''Türkmân'') by the 13th century.Lewis, G. ''The Book of Dede Korkut''. Penguin Books, 1974, p. 10.
The Oghuz confederation migrated westward from the Jeti-su area after a conflict with the Karluk allies of the Uyghurs
The Uyghurs,. alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia and East Asia. The Uyghurs are recognized as the ti ...
. In the 9th century, the Oghuz from the Aral steppes drove Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
westward from the Emba and Ural River region. In the 10th century, the Oghuz inhabited the steppe of the rivers Sari-su, Turgai and Emba north of Lake Balkhash in modern-day Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
.
They embraced Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
and adapted their traditions and institutions to the Islamic world, emerging as empire-builders with a constructive sense of statecraft. In the 11th century, the Seljuk Oghuz clan entered Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, where they founded the Great Seljuk Empire. The same century, a Tengriist Oghuz clan, also known as ''Uzes'' or ''Torks'', overthrew Pecheneg supremacy in the frontier of the Russian steppes; those who settled along the frontier were gradually Slavicized
Slavicisation American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), or Slavicization, is the acculturation of something non-Slavic into a Slavs, Slavic culture, cuisine, region, or nation. The process can either be v ...
; the almost feudal '' Black Hat'' principality grew with its own military aristocracy. Others, harried by the Kipchak Turks, crossed the lower Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and invaded the Balkans, where they were stopped by a plague and became mercenaries for the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
imperial forces (1065). Oghuz warriors served in almost all Islamic armies of the Middle East from the 1000s onwards, and as far as Spain and Morocco.
In the late 13th century after the fall of the Seljuks, the Ottoman dynasty gradually conquered Anatolia with an army also predominantly of Oghuz, besting other local Oghuz Turkish states. In legend, the founder Osman's genealogy traces to Oghuz Khagan, the legendary ancient ancestor of Turkic people
Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members ...
, giving the Ottoman sultans primacy among Turkish monarchs. The dynasties of Khwarazmians, Qara Qoyunlu, Aq Qoyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu or the White Sheep Turkomans (, ; ) was a culturally Persianate society, Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two trib ...
,
Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
, Afsharids and Qajars are also believed to descend from the Oghuz-Turkmen tribes of Begdili, Yiva, Bayandur, Kayi and Afshar respectively.
Name and language
The name ''Oghuz'' is a Common Turkic word for "tribe". By the 10th century, Islamic sources were calling themMuslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
Turkmens, as opposed to those of Tengrist
Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is a belief-system originating in the Eurasian Steppe, Eurasian steppes, based on shamanism and animism. It generally involves the titular sky god Tengri. According to some scholars, ...
or Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
religion; and by the 12th century this term was adopted into Byzantine usage, as the Oghuzes were overwhelmingly Muslim. The name "Oghuz" fell out of use by 13th century.
Linguistically, the Oghuz belong to the Common Turkic speaking group, characterized by sound correspondences such as Common Turkic versus Oghuric and Common Turkic versus Oghuric . Within the Common Turkic group, the Oghuz languages share these innovations: loss of Proto-Turkic guttural
Guttural Phone (phonetics), speech sounds are those with a primary place of articulation near the back of the oral cavity, where it is difficult to distinguish a sound's place of articulation and its phonation. In popular usage it is an imprecise t ...
s in suffix anlaut, loss of except after , becoming either or lost, voicing of to and of to , and becomes .
Their language belongs to the Oghuz group of the Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic langua ...
family. Kara-Khanid scholar Mahmud al-Kashgari wrote that of all the Turkic languages, that of the Oghuz was the simplest. He also observed that long separation had led to clear differences between the western Oghuz and Kipchak language and that of the eastern Turks. Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
sources call Oghuz Turks Uzes (, ).
Origins
 According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia, potentially in Altai-Sayan region,
According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia, potentially in Altai-Sayan region, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
or Tuva. Initially, Proto-Turkic speakers were potentially both hunter-gatherers and farmers, but later became nomadic pastoralists. Early and medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
Turkic groups exhibited a wide range of both East Asian and West-Eurasian physical appearances and genetic origins, in part through long-term contact with neighboring peoples such as Iranian
Iranian () may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Iran
** Iranian diaspora, Iranians living outside Iran
** Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia
** Iranian cuisine, cooking traditions and practic ...
, Mongolic, Tocharian, Uralic and Yeniseian peoples, and others."Some DNA tests point to the Iranian connections of the Ashina and Ashide,133 highlighting further that the Turks as a whole ‘were made up of heterogeneous and somatically dissimilar populations’.134 Geographically, the accounts cover the regions of Inner Mongolia, Gansu, Xinjiang, the Yenisei zone and the Altay, regions with Turkic, Indo-European (Iranian akaand Tokharian), Yeniseic, Uralic and other populations. Wusun elements, like most steppe polities of an ethno-linguistic mix, may have also played a substratal role."
In early times, they practiced a Tengrist
Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is a belief-system originating in the Eurasian Steppe, Eurasian steppes, based on shamanism and animism. It generally involves the titular sky god Tengri. According to some scholars, ...
religion, erecting many carved wooden funerary statues surrounded by simple stone ''balbal'' monoliths and holding elaborate hunting and banqueting rituals.
 During the 2nd century BC, according to ancient Chinese sources, a
During the 2nd century BC, according to ancient Chinese sources, a steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
tribal confederation known as the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, t ...
and their allies, the Wusun
The Wusun ( ) were an ancient semi-Eurasian nomads, nomadic Eurasian Steppe, steppe people of unknown origin mentioned in Chinese people, Chinese records from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD.
The Wusun originally l ...
(probably an Indo-European people) defeated the neighboring Indo-European-speaking Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
and drove them out of western China and into Central Asia. Various scholarly theories link the Xiongnu to Turkic peoples and/or the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
. Bichurin claimed that the first usage of the word ''Oghuz'' appears to have been the title of ''Oğuz Kağan'', whose biography shares similarities with the account, recorded by Han Chinese, of Xiongnu leader Modu Shanyu (or Mau-Tun), who founded the Xiongnu Empire. However, Oghuz Khan narratives were actually collected in Compendium of Chronicles by Ilkhanid
The Ilkhanate or Il-khanate was a Mongol khanate founded in the southwestern territories of the Mongol Empire. It was ruled by the Il-Khans or Ilkhanids (), and known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (). The Ilkhanid realm was officially known ...
scholar Rashid-al-Din in the early 14th century.
Sima Qian
Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China cov ...
recorded the name ''Wūjiē'' 烏揭 ( LHC: *''ʔɔ-gɨat'') or ''Hūjiē'' 呼揭 ( LHC: *''xɔ-gɨat''), of a people hostile to the Xiongnu and living immediately west of them, in the area of the Irtysh River, near Lake Zaysan. Golden suggests that these might be Chinese renditions of ''*Ogur'' ~ ''*Oguz'', yet uncertainty remains. According to one theory, ''Hūjiē'' is just another transliteration of ''Yuezhi'' and may refer to the Turkic Uyghurs
The Uyghurs,. alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia and East Asia. The Uyghurs are recognized as the ti ...
; however, this is controversial and has few scholarly adherents.
Yury Zuev (1960) links the Oghuz to the Western Turkic tribe 姑蘇 ''Gūsū'' < ( MC *''kuo-suo'') in the 8th-century encyclopaedia Tongdian
The ''Tongdian'' () is a Chinese institutional history and encyclopedia text. It covers a panoply of topics from high antiquity through the year 756, whereas a quarter of the book focuses on the Tang dynasty. The book was written by Du You from ...
(or erroneously ''Shǐsū'' 始蘇 in the 11th century Zizhi Tongjian
The ''Zizhi Tongjian'' (1084) is a chronicle published during the Northern Song dynasty (960–1127) that provides a record of Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is ...
). Zuev also noted a parallel between two passages:
*one from the 8th-century Taibo Yinjing (太白陰經) "Venus's Secret Classic" by Li Quan (李筌) which mentioned the 三窟 ~ 三屈 "Three ''Qu''" (< MC *''k(h)ɨut̚'') after the 十箭 ''Shí Jiàn'' "Ten Arrows" ( OTrk 𐰆𐰣:𐰸 ''On Oq'') and ''Jĭu Xìng'' "Nine Surnames" (OTrk 𐱃𐰸𐰆𐰔:𐰆𐰍𐰔 '' Toquz Oğuz''); and
*another from al-Maṣudi's Meadows of Gold and Mines of Gems, which mentioned the three hordes of the Turkic ''Ġuz''
Based on those sources, Zuev proposes that in the 8th century the Oghuzes were located outsides of the Ten Arrows' jurisdiction, west of the Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The ...
, near lake Issyk-Kul
Issyk-Kul () or Ysyk-Köl (, ; ) is an endorheic saline lake in the western Tianshan Mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan, just south of a dividing range separating Kyrgyzstan from Kazakhstan. It is the eighth-deepest lake in the world, the eleve ...
, Talas river's basin and seemingly around the Syr Darya
The Syr Darya ( ),; ; ; ; ; /. historically known as the Jaxartes ( , ), is a river in Central Asia. The name, which is Persian language, Persian, literally means ''Syr Sea'' or ''Syr River''. It originates in the Tian Shan, Tian Shan Mountain ...
basin, and near the Chumul, Karluks
The Karluks (also Qarluqs, Qarluks, Karluqs, , Qarluq, Para-Mongolic languages, Para-Mongol: Harluut, zh, s=葛逻禄, t=葛邏祿 ''Géluólù'' ; customary phonetic: ''Gelu, Khololo, Khorlo'', , ''Khallokh'', ''Qarluq'') were a prominent no ...
, Qays, Quns, ''Śari'', etc. who were mentioned by al-Maṣudi and Sharaf al-Zaman al-Marwazi.
According to Ahmad ibn Fadlan, the Oghuz were nomads, but also had cultivated crops, and the economy was based on a semi-pastoralist lifestyle.
Byzantine emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos mentioned the ''Uzi'' and '' Mazari'' (Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
) as neighbours of the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
.
By the time of the Orkhon inscriptions (8th century AD) "Oghuz" was being applied generically to all inhabitants of the Göktürk Khaganate. Within the khaganate, the Oghuz community gradually expanded, incorporating other tribes. A number of subsequent tribal confederations bore the name Oghuz, often affixed to a numeral indicating the number of united tribes. These include references to the simple ''Oguz'', ''Üch-Oghuz'' ("three Oghuz"), ''Altï Oghuz'' ("six Oghuz"), possibly the ''Otuz Oghuz'' ("thirty Oghuz"), ''Sekiz-Oghuz'' ("eight Oghuz"), and the ''Tokuz-Oghuz'' ("nine Oghuz"), who originally occupied different areas in the vicinity of the Altai Mountains. Golden (2011) states Transoxanian Oghuz Turks who founded the Oghuz Yabgu State were not the same tribal confederation as the Toquz Oghuz from whom emerged the founders of Uyghur Khaganate. Istakhri and Muhammad ibn Muhmad al-Tusi kept the Toquz Oghuz and Oghuz distinct and Ibn al-Faqih mentioned: "the infidel Turk-Oghuz, the Toquz-Oghuz, and the Qarluq" Even so, Golden notes the confusion in Latter Göktürks' and Uyghurs
The Uyghurs,. alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia and East Asia. The Uyghurs are recognized as the ti ...
' inscriptions, where Oghuz apparently referred to Toquz Oghuz or another tribal grouping, who were also named Oghuz without a prefixed numeral; this confusion is also reflected in Sharaf al-Zaman al-Marwazi, who listed 12 Oghuz tribes, who were ruled by a "Toquz Khaqan" and some of whom were Toquz-Oghuz, on the border of Transoxiana and Khwarazm. At most, the Oghuz were possibly led by a core group of Toquz Oghuz clans or tribes.
Noting that the mid-8th-century Tariat inscriptions, in Uyghur khagan Bayanchur's honor, mentioned the rebellious Igdir tribe who had revolted against him, Klyashtorny considers this as one piece of "direct evidence in favour of the existence of kindred relations between the Tokuz Oguzs of Mongolia, The Guzs of the Aral region, and modern Turkmens", besides the facts that Kashgari mentioned the Igdir as the 14th of 22 Oghuz tribes; and that Igdirs constitute part of the Turkmen tribe Chowdur. The Shine Usu inscription, also in Bayanchur's honor, mentioned the Nine-Oghuzes as " ispeople" and that he defeated the Eight-Oghuzes and their allies, the Nine Tatars, three times in 749.; according to Klyashtorny and Czeglédy, eight tribes of the Nine-Oghuzes revolted against the leading Uyghur tribe and renamed themselves Eight-Oghuzes.
Ibn al-Athir, an Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
historian, claimed that the Oghuz Turks were settled mainly in Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, between the Caspian and Aral Seas, during the period of the caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
Al-Mahdi
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh al-Manṣūr (; 744 or 745 – 785), better known by his regnal name al-Mahdī (, "He who is guided by God"), was the third Abbasid Caliph who reigned from 775 to his death in 785. He succeeded his ...
(after 775 AD). By 780, the eastern parts of the Syr Darya
The Syr Darya ( ),; ; ; ; ; /. historically known as the Jaxartes ( , ), is a river in Central Asia. The name, which is Persian language, Persian, literally means ''Syr Sea'' or ''Syr River''. It originates in the Tian Shan, Tian Shan Mountain ...
were ruled by the Karluk Turks and to their west were the Oghuz. Transoxiana, their main homeland in subsequent centuries became known as the "Oghuz Steppe".
During the period of the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 C ...
caliph Al-Ma'mun (813–833), the name Oghuz starts to appear in the works of Islamic writers. The '' Book of Dede Korkut'', a historical epic of the Oghuz, contains historical echoes of the 9th and 10th centuries but was likely written several centuries later.
Physical appearance
Al-Masudi described Yangikent's Oghuz Turks as "distinguished from other Turks by their valour, their slanted eyes, and the smallness of their stature". Stone heads of Seljuq elites kept at the New York Metropolitan Museum of Art displayedEast Asian
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
features. Over time, Oghuz Turks' physical appearance changed. Rashid al-Din Hamadani stated that "because of the climate their features gradually changed into those of Tajiks. Since they were not Tajiks, the Tajik peoples called them turkmān, i.e. Turk-like (Turk-mānand)". Ḥāfiẓ Tanīsh Mīr Muḥammad Bukhārī also related that the "Oghuz Turkic face did not remain as it was after their migration into Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
". Khiva khan, Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur, in his Chagatai-language treatise Genealogy of the Turkmens, wrote that "their (Oghuz Turks) chin started to become narrow, their eyes started to become large, their faces started to become small, and their noses started to become big after five or six generations". Ottoman historian Mustafa Âlî commented in ''Künhüʾl-aḫbār'' that Anatolian Turks and Ottoman elites are ethnically mixed: "Most of the inhabitants of Rûm are of confused ethnic origin. Among its notables there are few whose lineage does not go back to a convert to Islam."
Social units
 The
The militarism
Militarism is the belief or the desire of a government or a people that a state should maintain a strong military capability and to use it aggressively to expand national interests and/or values. It may also imply the glorification of the mili ...
that the Oghuz empires were very well known for was rooted in their centuries-long nomadic lifestyle. In general, they were a herding society which possessed certain military advantages that sedentary societies did not have, particularly mobility. Alliances by marriage and kinship, and systems of "social distance" based on family relationships were the connective tissues of their society.
In Oghuz traditions, "society was simply the result of the growth of individual families". But such a society also grew by alliances and the expansion of different groups, normally through marriages. The shelter of the Oghuz tribes was a tent-like dwelling, erected on wooden poles and covered with skin, felt, or hand-woven textiles, which is called a '' yurt''.
Their cuisine included yahni (stew), kebabs
Kebab ( , ), kebap, kabob (alternative North American English, North American spelling), kebob, or kabab (Kashmiri spelling) is a variety of roasted meat dishes that originated in the Middle East.
Kebabs consist of cut up ground meat, somet ...
, Toyga soup (meaning "wedding soup"), Kımız (a traditional drink of the Turks, made from fermented horse milk), Pekmez (a syrup made of boiled grape juice) and helva made with wheat starch or rice flour, tutmac (noodle soup), yufka (flattened bread), katmer (layered pastry), chorek (ring-shaped buns), bread, clotted cream, cheese, yogurt, milk and ayran (diluted yogurt beverage), as well as wine.
Social order was maintained by emphasizing "correctness in conduct as well as ritual and ceremony". Ceremonies brought together the scattered members of the society to celebrate birth, puberty, marriage, and death. Such ceremonies had the effect of minimizing social dangers and also of adjusting persons to each other under controlled emotional conditions.
Patrilineally related men and their families were regarded as a group with rights over a particular territory and were distinguished from neighbours on a territorial basis. Marriages were often arranged among territorial groups so that neighbouring groups could become related, but this was the only organizing principle that extended territorial unity. Each community of the Oghuz Turks was thought of as part of a larger society composed of distant as well as close relatives. This signified "tribal allegiance". Wealth and materialistic objects were not commonly emphasized in Oghuz society and most remained herders, and when settled they would be active in agriculture.
Status within the family was based on age, gender, relationships by blood, or marriageability. Males, as well as females, were active in society, yet men were the backbones of leadership and organization. According to the '' Book of Dede Korkut'', which demonstrates the culture of the Oghuz Turks, women were "expert horse riders, archers, and athletes". The elders were respected as repositories of both "secular and spiritual wisdom".
Homeland in Central Asia
 In the 700s, the Oghuz Turks made a new home and domain for themselves in the area between the Caspian and Aral seas and the northwest part of Transoxania, along the Syr Darya river. They had moved westward from the Altay mountains passing through the Siberian steppes and settled in this region, and also penetrated into southern
In the 700s, the Oghuz Turks made a new home and domain for themselves in the area between the Caspian and Aral seas and the northwest part of Transoxania, along the Syr Darya river. They had moved westward from the Altay mountains passing through the Siberian steppes and settled in this region, and also penetrated into southern Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and the Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
from their bases in west China. In the 11th century, the Oghuz Turks adopted Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
script, replacing the Old Turkic alphabet.
In his accredited 11th-century treatise titled ''Diwan Lughat al-Turk'', Karakhanid scholar Mahmud of Kashgar mentioned five Oghuz cities named ''Sabran'', ''Sitkün'', ''Qarnaq'', ''Suğnaq'', and ''Qaraçuq'' (the last of which was also known to Kashgari as Farab, now Otrar; situated near the Karachuk mountains to its east). The extension from the Karachuk Mountains towards the Caspian Sea was called the "Oghuz Steppe Lands" from where the Oghuz Turks established trading, religious and cultural contacts with the Abbasid Arab caliphate who ruled to the south. This is around the same time that they first converted to Islam and renounced their Tengriism
Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is a belief-system originating in the Eurasian Steppe, Eurasian steppes, based on shamanism and animism. It generally involves the titular sky god Tengri. According to some scholars, ...
belief system. The Arab historians mentioned that the Oghuz Turks were ruled by a number of kings and chieftains.
It was in this area that they later founded the Seljuk Empire, and it was from this area that they spread west into western Asia and eastern Europe during Turkic migrations from the 9th until the 12th century. The founders of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
were also Oghuz Turks.
Literature and poetry
Book of Dede Korkut
 The '' Book of Dede Korkut'' is a seminal collection of epic tales originating from the Oghuz Turks. Comprising twelve stories, the narratives encapsulate themes of heroism, morality, and social norms prevalent among the nomadic Oghuz. The tales were transmitted orally before being compiled into manuscripts in the 15th century. The character Dede Korkut serves as a sage and bard, linking the stories together and offering wisdom to the protagonists. The epics provide insights into the Oghuz way of life, including their customs, conflicts, and the transition from pre-Islamic beliefs to Islamic faith.
The '' Book of Dede Korkut'' is a seminal collection of epic tales originating from the Oghuz Turks. Comprising twelve stories, the narratives encapsulate themes of heroism, morality, and social norms prevalent among the nomadic Oghuz. The tales were transmitted orally before being compiled into manuscripts in the 15th century. The character Dede Korkut serves as a sage and bard, linking the stories together and offering wisdom to the protagonists. The epics provide insights into the Oghuz way of life, including their customs, conflicts, and the transition from pre-Islamic beliefs to Islamic faith.
Epic of Koroghlu
The '' Epic of Koroghlu'' narrates the adventures of the hero Koroghlu, who seeks to avenge his father's blinding by a corrupt ruler. This tale emphasizes themes of justice, resistance against tyranny, and the valorization of the common folk. The epic has been preserved in various Turkic cultures, including Azerbaijani, Turkish, and Turkmen traditions, often performed by bards known asashiks
An ashik (; ) or ashugh (; ka, :ka:აშუღი, აშუღი) is traditionally a List of oral repositories, singer-poet and bard who accompanies his song—be it a dastan (traditional epic story, also known as ''Azeri hikaye, hikaye' ...
or bagshys.
Imadaddin Nasimi
Imadaddin Nasimi (1369–1417) is recognized as a pivotal figure in Turkic literature, particularly for his contributions to Azerbaijani classical poetry. Writing in Oghuz Turkic, Persian, andArabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, Nasimi's works delve into themes of mysticism, humanism, and the nature of existence. His poetry significantly influenced subsequent generations and helped shape the literary traditions of the region.
Magtymguly Pyragy
Magtymguly Pyragy (c. 1733–c. 1790) is esteemed as the father of Turkmen literature. His poetry, composed in the Turkmen language, addresses topics such as patriotism, social justice, and moral integrity. Employing the qoshuk form, his verses played a crucial role in fostering a sense of national identity among the Turkmen people.Oghuz and Yörüks
Yörüks are Turkish subgroup of Oghuz origin, some of whom are still semi-nomadic, primarily inhabiting the mountains of Anatolia and partly Balkan peninsula. In the medieval era, to distinguish their own loyalSunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
Turkomans from the Shah-loyal Shiite Kızılbaş Turkomans of eastern Anatolia and Azerbaijan, Ottoman governors coined the blanket term ''Yörük'' (or ''Yürük''), meaning "nomad" or "wanderer." This served as a political demarcation between western (Ottoman Turkic) and eastern (Persian-influenced) Turkoman groups.
Despite being politically divided between the Ottoman Turks and the Persian-influenced eastern realms, Eastern and Western Turkomans were ethnically and linguistically the same, differing only in minor dialectal or cultural aspects.
The Yörük to this day appear as a distinct segment of the population of Macedonia and Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
where they settled as early as the 14th century. While today the Yörük are increasingly settled, many of them still maintain their nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic lifestyle, breeding goats and sheep in the Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains (Turkish language, Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar,'' Greek language, Greek'':'' Ταύρος) are a mountain range, mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coastal reg ...
and further eastern parts of mediterranean regions (in southern Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
), in the Pindus (Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
), the Šar Mountains (North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
), the Pirin and Rhodope Mountains (Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
) and Dobrudja.
An earlier offshoot of the Yörüks, the Kailars or Kayılar Turks were amongst the first Turkish colonists in Europe, (''Kailar'' or ''Kayılar'' being the Turkish name for the Greek town of Ptolemaida which took its current name in 1928) formerly inhabiting parts of the Greek regions of Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
and Macedonia. Settled Yörüks could be found until 1923, especially near and in the town of Kozani.
List of Oghuz dynasties
* Oghuz Yabgu State *Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
* Seljuks
* Zengid dynasty
* Anatolian beyliks
* Khwarazmian dynasty
* Rasulid dynasty
*Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
*Aq Qoyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu or the White Sheep Turkomans (, ; ) was a culturally Persianate society, Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two trib ...
* Kara Koyunlu
* Safavid
* Afsharids
* Qajars
* Azerbaijani khanates
Traditional tribal organization
Bozoks (Gray Arrows)
;Gün Han * Kayı (Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
, Jandarids and Chobanids)
* Bayat ( Qajars, Dulkadirids, Fuzûlî)
* Alkaevli
* Karaevli
;Ay Han
* Yazır (disambiguation)
* Döger ( Artuqids)
* Dodurga
* Yaparlı
;Yıldız Han
* Afshar ( Afsharids and Zengids)
* Qiziq
* Begdili ( Khwarazmian dynasty)
* Kargın
Üçoks (Three Arrows)
;Gök Han * Bayandur (founders of the Ak Koyunlu) * Pecheneg * Çavuldur ( Tzachas) * Chepni (refer to Küresünni) ;Dağ Han * Salur ( Kadi Burhan al-Din, Salghurids andKaramanids
The Karamanids ( or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman (), was a Turkish people, Turkish Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian beylik (principality) of Salur tribe origin, descended from Oghuz Turks, centered in South-Centra ...
; see also: Salars)
* Eymür
* Alayuntlu
* Yüreğir ( Ramadanids)
;Diŋiz Han
* Iğdır
* Büğdüz
* Yıva ( Qara Qoyunlu and Oghuz Yabgu State)
* Kınık (founders of the Seljuk Empire)
List of Oghuz ethnic groups
* Azerbaijani people * Qashqai people * Gagauz people *Turkish people
Turks (), or Turkish people, are the largest Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group, comprising the majority of the population of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. They generally speak the various Turkish dialects. In addition, centuries-old Turkish co ...
* Turkmen people
*Salar people
The Salar people are a Turkic peoples, Turkic Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China who speak Salar language, Salar, a Turkic language of the Oghuz languages, Oghuz sub-branch. They numbered 165,159 people in 2020, according to t ...
Other Oghuz sub-ethnic groups and tribes
Anatolia and Caucasus
;Anatolia * Abdal of Turkey * Yörüks * Tahtacı * Varsak * Barak * Karakeçili (Black Goat Turkomans) * Manav (While Manavs originally belonged to the Kipchaks-Cumans
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cumania, Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Ru ...
, today they have become Oghuz under the influence of the Oghuz.)
* Atçeken
* Küresünni
* Chepni
;Caucasus
* Azerbaijanis in Armenia
* Azerbaijanis in Turkey
* Azerbaijanis in Georgia
* Terekeme people
* Qarapapaq
* Karadaghis
* Javanshir clan
* Trukhmen
* Turks in Abkhazia
* Meskhetian Turks
;Cyprus
* Cypriot Turks
Balkans
* Turks in Bosnia * Bulgarian Turks * Turks in Croatia * Dodecanese Turks * Kosovan Turks * Macedonian Turks * Turks in Serbia * Turks in Montenegro * Romanian Turks * Turks of Western Thrace * Cretan Turks * Karamanlides * Gajal * Amuca tribeCentral Asia
* Iranian Azerbaijanis * Shahsevan * Qizilbash * Padar tribe * Khorasani Turks * Iranian Turkmens * Afghan Turkmens * Qajars (tribe) * Bichaghchi * Turks in AfghanistanArab world
* Turks in Libya * Turks in Egypt * Turks in Algeria * Syrian Turkmen *Iraqi Turkmen
The Iraqi Turkmen (, عراق تورکمنلری; Arabic: تركمان العراق), also referred to as Iraqi Turks, (, عراق توركلری; ) are the third largest ethnic group in Iraq. They make up to 10%–13% of the Iraqi population. I ...
* Turks in Lebanon
* Turks in Palestine
* Turks in Jordan
* Turks in Tunisia
* Turks in Saudi Arabia
* Turks in Yemen
See also
* Algoz *Turkic migration
The Turkic migrations were the spread of Turkic peoples, Turkic tribes and Turkic languages across Eurasia between the 4th and 11th centuries. In the 6th century, the Göktürks overthrew the Rouran Khaganate in what is now Mongolia and expanded in ...
* History of Turkic peoples
*Timeline of Turks (500-1300) Timeline of the Turks may refer to:
*Timeline of the Turks (500–1300) a general chronology between 500 and 1300
*Uyghur timeline a detailed timeline up to 763 (excludes most of Uyghur Khaganate)
*Timeline of the Sultanate of Rûm exclusively abou ...
* Turkomans
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * Text was copied from this source, which is available underCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Further reading
* Grousset, R., ''The Empire of the Steppes'', 1991, Rutgers University Press * Nicole, D., ''Attila and the Huns'', 1990, Osprey Publishing * Lewis, G., ''The Book of Dede Korkut'', "Introduction", 1974, Penguin Books * Minahan, James B. ''One Europe, Many Nations: A Historical Dictionary of European National Groups''. Greenwood Press, 2000''page 692''
* Aydın, Mehmet. ''Bayat-Bayat boyu ve Oğuzların tarihi''. Hatiboğlu Yayınevi, 1984
''web page''
External links
* *The ''Book of Dede Korkut''
(pdf format) at the Uysal-Walker Archive of Turkish Oral Narrative
Similarities between the epics of Dede Korkut and Alpamysh
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oghuz History of the Turkish people Turkic peoples of Asia Turkic peoples