Neck Torc MET TR on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The neck is the part of the body in many


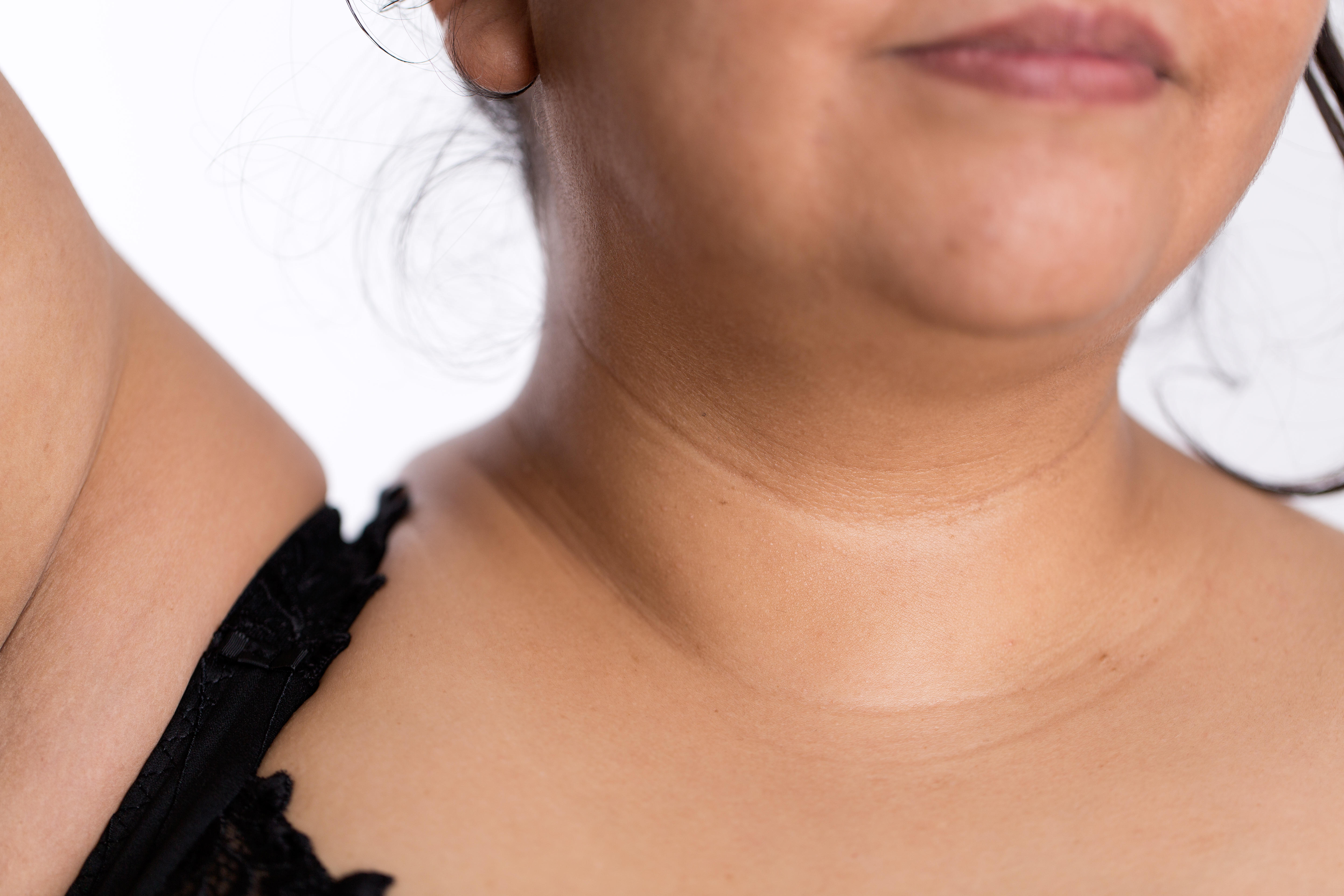 The thyroid cartilage of the larynx forms a bulge in the midline of the neck called the
The thyroid cartilage of the larynx forms a bulge in the midline of the neck called the
 The neck appears in some of the earliest of
The neck appears in some of the earliest of
American Head and Neck Society
The Anatomy Wiz.
An Interactive Cross-Sectional Anatomy Atlas {{Authority control
vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s that connects the head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple ani ...
to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
and the rest of the body. Additionally, the neck is highly flexible, allowing the head to turn and move in all directions. Anatomically, the human neck is divided into four compartments: vertebral, visceral, and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
, the cervical portion of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, upper parts of the respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gr ...
and digestive tracts, endocrine gland
The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs located throughout the body. Along with the nervous system, it makes the neuroendocrine system, which controls and regulates many of the body's functions. Endocrine glands are ductless gland ...
s, nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
s, arteries and vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
s. The muscles of the neck, which are separate from the compartments, form the boundaries of the neck triangles.
In anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
, the neck is also referred to as the or . However, when the term ''cervix'' is used alone, it often refers to the uterine cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the t ...
, the neck of the uterus. Therefore, the adjective ''cervical'' can refer either to the neck (as in ''cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
'' or ''cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflamma ...
'') or to the uterine cervix (as in ''cervical cap
The cervical cap is a form of barrier contraception. A cervical cap fits over the cervix and blocks sperm from entering the uterus through the external orifice of the uterus, called the ''os''.
Terminology
The term ''cervical cap'' has been us ...
'' or ''cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix or in any layer of the wall of the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later sympt ...
'').
Structure
Compartments
The neck structures are distributed within four compartments: * Vertebral compartment contains thecervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
with cartilaginous discs between each vertebral body
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
. The alignment of the vertebrae defines the shape of the human neck. As the vertebrae bound the spinal canal, the cervical portion of the spinal cord is also found within the neck.
* Visceral compartment accommodates the trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
, larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
, pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
, thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
, and parathyroid gland
Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes par ...
s.
* Vascular compartment is paired and consists of the two carotid sheath
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve (CN X), and ansa c ...
s found on each side of the trachea. Each carotid sheath contains the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
, common carotid artery and internal jugular vein
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.
It begins in the posteri ...
.
Besides the listed structures, the neck contains cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflamma ...
which surround the blood vessels.
Muscles and triangles
Muscles of the neck attach to theskull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
, hyoid bone
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical verte ...
, clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
s and the sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
. They bound the two major neck triangles; anterior and posterior.
Anterior triangle
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck.
Structure
The triangle is inverted with its apex inferior to its base which is under the chin.
Investing fascia covers the roof of the triangle while visceral fascia covers the floor.
Anatomy
Mu ...
is defined by the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension, flexion of the neck. ...
, inferior edge of the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
and the midline of the neck. It contains the stylohyoid
The stylohyoid muscle is one of the suprahyoid muscles. Its originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone; it inserts onto hyoid bone. It is innervated by a branch of the facial nerve. It acts draw the hyoid bone upwards and backwards. ...
, digastric
The digastric muscle (also digastricus) (named ''digastric'' as it has two 'bellies') is a bilaterally paired suprahyoid muscle located under the jaw. Its posterior belly is attached to the mastoid notch of temporal bone, and its anterior belly ...
, mylohyoid, geniohyoid
The geniohyoid muscle is a narrow paired muscle situated superior to the medial border of the mylohyoid muscle. It is named for its passage from the chin ("genio-" is a standard prefix for "chin") to the hyoid bone.
Structure
The geniohyoid is ...
, omohyoid
The omohyoid muscle is a muscle in the neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. Its inferior belly is attached to the scapula; its superior belly is attached to the hyoid bone. Its i ...
, sternohyoid
The sternohyoid muscle is a bilaterally paired, long, thin, narrow strap muscle of the anterior neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It is innervated by the ansa cervicalis. It acts to depress the hyoid bone.
The sternohyoid muscle is a ...
, thyrohyoid
The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical sp ...
and sternothyroid muscle
The sternothyroid muscle (or sternothyroideus) is an infrahyoid muscle of the neck. It acts to depress the hyoid bone.
Structure
The two muscles are in contact with each other proximally (close to their origin), but diverge distally (towards t ...
s. These muscles are grouped as the suprahyoid
The suprahyoid muscles are four muscles located above the hyoid bone in the neck. They are the digastric, stylohyoid, geniohyoid, and mylohyoid muscles. They are all pharyngeal muscles, with the exception of the geniohyoid muscle. The digastr ...
and infrahyoid muscles
The infrahyoid muscles, or strap muscles, are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid muscles are the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid and omohyoid muscles.
Excluding the sternot ...
depending on if they are located superiorly or inferiorly to the hyoid bone. The suprahyoid muscles (stylohyoid, digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid) elevate the hyoid bone, while the infrahyoid muscles (omohyoid, sternohyoid, thyrohyoid, sternothyroid) depress it. Acting synchronously, both groups facilitate speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
and swallowing
Swallowing, also called deglutition or inglutition in scientific and medical contexts, is a physical process of an animal's digestive tract (e.g. that of a human body) that allows for an ingested substance (typically food) to pass from the mou ...
.
Posterior triangle
The posterior triangle (or lateral cervical region) is a region of the neck.
Boundaries
The posterior triangle has the following boundaries:
Apex: Union of the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius muscles at the superior nuchal line of the occ ...
is bordered by the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, anterior border of the trapezius muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and ...
and the superior edge of the middle third of the clavicle. This triangle contains the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, splenius capitis
The splenius capitis () () is a broad, straplike muscle in the back of the neck. It pulls on the base of the skull from the vertebrae cervical vertebra, in the neck and upper Thoracic vertebrae, thorax. It is involved in movements such as shaking ...
, levator scapulae
The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. It originates from the transverse processes of the four uppermost cervical vertebrae; it inserts onto the upper portion of the medial border of the scapu ...
, omohyoid, anterior, middle and posterior scalene muscles
The scalene muscles are a group of three muscles on each side of the neck, identified as the anterior, the middle, and the posterior. They are innervated by the third to the eighth cervical spinal nerves (C3-C8).
The anterior and middle scale ...
.
Nerve supply
Sensation to the front areas of the neck comes from the roots of thespinal nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each s ...
s C2-C4, and at the back of the neck from the roots of C4-C5.
In addition to nerves coming from and within the human spine, the accessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ...
and vagus nerve travel down the neck.
Blood supply and vessels
The head and neck get the majority of its blood supply through the carotid and vertebral arteries. Arteries which supply the neck are common carotid arteries, which bifurcate into theinternal
Internal may refer to:
*Internality as a concept in behavioural economics
*Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts
*Neigong or "internal skills", a type of exercise in meditation associated with Daoism
* ''Internal'' (album) by Safia, 2016 ...
and external carotid arteries.
Surface anatomy

 The thyroid cartilage of the larynx forms a bulge in the midline of the neck called the
The thyroid cartilage of the larynx forms a bulge in the midline of the neck called the Adam's apple
The Adam's apple is the protrusion in the neck formed by the angle of the thyroid cartilage surrounding the larynx, typically visible in men, less frequently in women. The prominence of the Adam's apple increases in some men as a secondary mal ...
. The Adam's apple is usually more prominent in men. Inferior to the Adam's apple is the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment sit ...
. The trachea is traceable at the midline, extending between the cricoid cartilage and suprasternal notch
The suprasternal notch, also known as the fossa jugularis sternalis, jugular notch, or Plender gap, is a large, visible dip in between the neck in humans, between the clavicles, and above the manubrium of the sternum.
Screenwriter Samson Raphaels ...
.
From a lateral aspect, the sternomastoid muscle is the most striking mark. It separates the anterior triangle of the neck from the posterior. The upper part of the anterior triangle contains the submandibular gland
The paired submandibular glands (historically known as submaxillary glands) are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In adult humans, they each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva sec ...
s, which lie just below the posterior half of the mandible. The line of the common and the external carotid arteries can be marked by joining the sterno-clavicular articulation to the angle of the jaw. Neck lines can appear at any age of adulthood as a result of sun damage, for example, or of ageing
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biol ...
where skin loses its elasticity and can wrinkle
A wrinkle, also known as a rhytid, is a fold, ridge or crease in an otherwise smooth surface, such as on skin or fabric. Skin wrinkles typically appear as a result of ageing processes such as glycation, habitual sleeping positions, loss of b ...
.
The eleventh cranial nerve or spinal accessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves ...
corresponds to a line drawn from a point midway between the angle of the jaw and the mastoid process to the middle of the posterior border of the sterno-mastoid muscle and thence across the posterior triangle to the deep surface of the trapezius. The external jugular vein
The jugular veins () are veins that take blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Struc ...
can usually be seen through the skin; it runs in a line drawn from the angle of the jaw to the middle of the clavicle, and close to it are some small lymphatic glands. The anterior jugular vein
The anterior jugular vein is a vein in the neck.
Structure
The anterior jugular vein lies lateral to the cricothyroid membrane.
It begins near the hyoid bone by the confluence of several superficial veins from the submandibular region. Its tr ...
is smaller and runs down about half an inch from the middle line of the neck. The clavicle or collarbone forms the lower limit of the neck, and laterally the outward slope of the neck to the shoulder is caused by the trapezius muscle.
Pain
Disorders of the neck are a common source of pain. The neck has a great deal of functionality but is also subject to a lot of stress. Common sources ofneck pain
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
(and related pain syndromes, such as pain that radiates down the arm) include (and are strictly limited to):
* Whiplash, strained a muscle or another soft tissue injury
A soft tissue injury is the damage of muscles, ligaments and tendons throughout the body. Common soft tissue injuries usually occur from a sprain, strain (injury), strain, a one-off blow resulting in a contusion or overuse of a particular part of ...
* Cervical herniated disc
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
* Cervical spinal stenosis
Cervical spinal stenosis is a bone disease involving the narrowing of the spinal canal at the level of the neck. It is frequently due to chronic degeneration, but may also be congenital. Treatment is frequently surgical.
Cervical spinal stenosis ...
* Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
* Vascular sources of pain, like arterial dissections or internal jugular vein thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
* Cervical adenitis
Adenitis is a general term for an inflammation of a gland. Often it is used to refer to lymphadenitis which is the inflammation of a lymph node.
Classification
Lymph node adenitis
''Lymph adenitis'' or ''lymph node adenitis'' is caused by infec ...
Circumference
Higher neck circumference has been associated with cardiometabolic risk. Upper-body fat distribution is a worse prognostic compared to lower-body fat distribution for diseases such astype 2 diabetes mellitus
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ur ...
or ischemic cardiopathy. Neck circumference has been associated with the risk of being mechanically ventilated in COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
patients, with a 26% increased risk for each centimeter increase in neck circumference. Moreover, hospitalized COVID-19 patients with a "large neck phenotype" on admission had a more than double risk of death.
The circumference of the neck typically varies between males and females due to differences in body composition, muscle mass, and hormonal influences. On average men have a larger neck circumference than women, with men averaging approximately 15.2 inches (38.7 cm) and women around 13.1 inches (33.3 cm). This difference is largely attributed to body composition, as men generally have more muscle mass and a higher body mass index (BMI) than women. Hormonal differences also play a significant role, as testosterone, which is present at higher levels in men, promotes muscle growth, including in the neck area.
Animals
 The neck appears in some of the earliest of
The neck appears in some of the earliest of tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
fossils, and the functionality provided has led to its being retained in all land vertebrates as well as marine-adapted tetrapods such as turtles, seals, and penguins. Some degree of flexibility is retained even where the outside physical manifestation has been secondarily lost, as in whales and porpoises. A morphologically functioning neck also appears among insects. Its absence in fish and aquatic arthropods is notable, as many have life stations similar to a terrestrial or tetrapod counterpart or could otherwise make use of the added flexibility.
The word "neck" is sometimes used as a convenience to refer to the region behind the head in some snail
A snail is a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gas ...
s, gastropod
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and fro ...
mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, even though there is no clear distinction between this area, the head area, and the rest of the body.
See also
*Throat
In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the front part of the neck, internally positioned in front of the vertebrae. It contains the Human pharynx, pharynx and larynx. An important section of it is the epiglottis, separating the esophagus from the t ...
* Nape
The nape is the back of the neck. In technical anatomical/medical terminology, the nape is also called the nucha (from the Medieval Latin rendering of the Arabic , ). The corresponding adjective is ''nuchal'', as in the term ''nuchal rigidity'' ...
References
External links
American Head and Neck Society
The Anatomy Wiz.
An Interactive Cross-Sectional Anatomy Atlas {{Authority control