Mississippi Valley on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief


 The Upper Mississippi runs from its headwaters to its confluence with the Missouri River at St. Louis, Missouri. It is divided into two sections:
# The headwaters, from the source to Saint Anthony Falls in Minneapolis, Minnesota; and
# A navigable channel, formed by a series of man-made lakes between Minneapolis and St. Louis, Missouri, some .
The source of the Upper Mississippi branch is traditionally accepted as Lake Itasca, above sea level in Itasca State Park in Clearwater County, Minnesota. The name ''Itasca'' was chosen to designate the "true head" of the Mississippi River as a combination of the last four letters of the Latin word for truth () and the first two letters of the Latin word for head (). However, the lake is in turn fed by a number of smaller streams.
From its origin at Lake Itasca to St. Louis, Missouri, the waterway's flow is moderated by 43 dams. Fourteen of these dams are located above Minneapolis in the headwaters region and serve multiple purposes, including power generation and recreation. The remaining 29 dams, beginning in downtown Minneapolis, all contain locks and were constructed to improve commercial navigation of the upper river. Taken as a whole, these 43 dams significantly shape the geography and influence the ecology of the upper river. Beginning just below
The Upper Mississippi runs from its headwaters to its confluence with the Missouri River at St. Louis, Missouri. It is divided into two sections:
# The headwaters, from the source to Saint Anthony Falls in Minneapolis, Minnesota; and
# A navigable channel, formed by a series of man-made lakes between Minneapolis and St. Louis, Missouri, some .
The source of the Upper Mississippi branch is traditionally accepted as Lake Itasca, above sea level in Itasca State Park in Clearwater County, Minnesota. The name ''Itasca'' was chosen to designate the "true head" of the Mississippi River as a combination of the last four letters of the Latin word for truth () and the first two letters of the Latin word for head (). However, the lake is in turn fed by a number of smaller streams.
From its origin at Lake Itasca to St. Louis, Missouri, the waterway's flow is moderated by 43 dams. Fourteen of these dams are located above Minneapolis in the headwaters region and serve multiple purposes, including power generation and recreation. The remaining 29 dams, beginning in downtown Minneapolis, all contain locks and were constructed to improve commercial navigation of the upper river. Taken as a whole, these 43 dams significantly shape the geography and influence the ecology of the upper river. Beginning just below  The Upper Mississippi is largely a multi-thread stream with many bars and islands. From its confluence with the St. Croix River downstream to Dubuque, Iowa, the river is entrenched, with high bedrock bluffs lying on either side. The height of these bluffs decreases to the south of Dubuque, though they are still significant through Savanna, Illinois. This topography contrasts strongly with the Lower Mississippi, which is a meandering river in a broad, flat area, only rarely flowing alongside a bluff (as at Vicksburg, Mississippi).
The Upper Mississippi is largely a multi-thread stream with many bars and islands. From its confluence with the St. Croix River downstream to Dubuque, Iowa, the river is entrenched, with high bedrock bluffs lying on either side. The height of these bluffs decreases to the south of Dubuque, though they are still significant through Savanna, Illinois. This topography contrasts strongly with the Lower Mississippi, which is a meandering river in a broad, flat area, only rarely flowing alongside a bluff (as at Vicksburg, Mississippi).
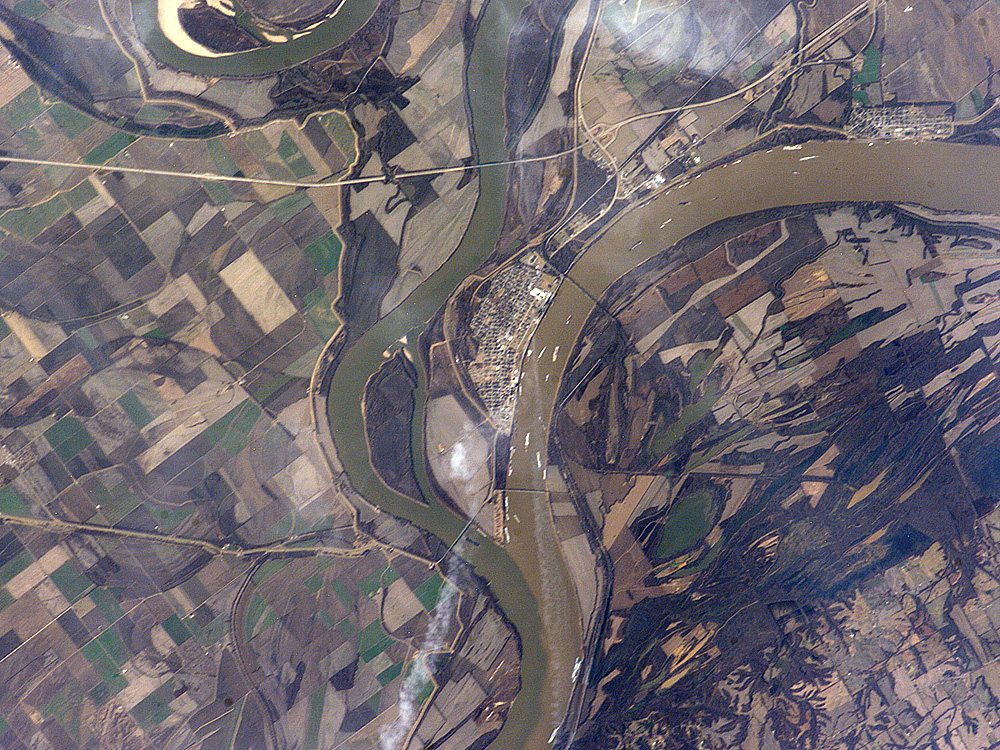

 The Mississippi River is called the Lower Mississippi River from its confluence with the Ohio River to its mouth at the Gulf of Mexico, a distance of about . At the confluence of the Ohio and the Middle Mississippi, the long-term mean discharge of the Ohio at Cairo, Illinois is , while the long-term mean discharge of the Mississippi at Thebes, Illinois (just upriver from Cairo) is . Thus, by volume, the main branch of the Mississippi River system at Cairo can be considered to be the Ohio River (and the Allegheny River further upstream), rather than the Middle Mississippi.
In addition to the Ohio River, the major tributaries of the Lower Mississippi River are the White River, flowing in at the White River National Wildlife Refuge in east-central Arkansas; the
The Mississippi River is called the Lower Mississippi River from its confluence with the Ohio River to its mouth at the Gulf of Mexico, a distance of about . At the confluence of the Ohio and the Middle Mississippi, the long-term mean discharge of the Ohio at Cairo, Illinois is , while the long-term mean discharge of the Mississippi at Thebes, Illinois (just upriver from Cairo) is . Thus, by volume, the main branch of the Mississippi River system at Cairo can be considered to be the Ohio River (and the Allegheny River further upstream), rather than the Middle Mississippi.
In addition to the Ohio River, the major tributaries of the Lower Mississippi River are the White River, flowing in at the White River National Wildlife Refuge in east-central Arkansas; the
 The Mississippi River has the world's fourth-largest
The Mississippi River has the world's fourth-largest  In the United States, the Mississippi River drains the majority of the area between the crest of the
In the United States, the Mississippi River drains the majority of the area between the crest of the
''Six Rivers, Five Glaciers, and an Outburst Flood: the Considerable Legacy of the Illinois River.''
(PDF) Proceedings of the 2007 Governor's Conference on the Management of the Illinois River System: Our continuing Commitment, 11th Biennial Conference, Oct. 2–4, 2007, 11 p.McKay, E.D., and R.C. Berg, 2008
Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, Vol. 40, No. 5, p. 78 wit
Powerpoint presentation
 Timeline of outflow course changes
* c. 5000 BC: The last ice age ended; world sea level became what it is now.
* c. 2500 BC: Bayou Teche became the main course of the Mississippi.
* c. 800 BC: The Mississippi diverted further east.
* c. 200 AD: Bayou Lafourche became the main course of the Mississippi.
* c. 1000 AD: The Mississippi's present course took over.
* Before c. 1400 AD: The Red River of the South flowed parallel to the lower Mississippi to the sea
* 15th century:
Timeline of outflow course changes
* c. 5000 BC: The last ice age ended; world sea level became what it is now.
* c. 2500 BC: Bayou Teche became the main course of the Mississippi.
* c. 800 BC: The Mississippi diverted further east.
* c. 200 AD: Bayou Lafourche became the main course of the Mississippi.
* c. 1000 AD: The Mississippi's present course took over.
* Before c. 1400 AD: The Red River of the South flowed parallel to the lower Mississippi to the sea
* 15th century:


 Many of the communities along the Mississippi River are listed below; most have either historic significance or cultural lore connecting them to the river. They are sequenced from the source of the river to its end.
*
Many of the communities along the Mississippi River are listed below; most have either historic significance or cultural lore connecting them to the river. They are sequenced from the source of the river to its end.
*
 The road crossing highest on the Upper Mississippi is a simple steel culvert, through which the river (locally named "Nicolet Creek") flows north from Lake Nicolet under "Wilderness Road" to the West Arm of Lake Itasca, within Itasca State Park.
The earliest bridge across the Mississippi River was built in 1855. It spanned the river in
The road crossing highest on the Upper Mississippi is a simple steel culvert, through which the river (locally named "Nicolet Creek") flows north from Lake Nicolet under "Wilderness Road" to the West Arm of Lake Itasca, within Itasca State Park.
The earliest bridge across the Mississippi River was built in 1855. It spanned the river in  * Dubuque-Wisconsin BridgeConnects Dubuque, Iowa, and
* Dubuque-Wisconsin BridgeConnects Dubuque, Iowa, and  * Norbert F. Beckey BridgeConnects Muscatine, Iowa, and Rock Island County, Illinois; became first U.S. bridge to be illuminated with
* Norbert F. Beckey BridgeConnects Muscatine, Iowa, and Rock Island County, Illinois; became first U.S. bridge to be illuminated with  * Chain of Rocks BridgeLocated on the northern edge of St. Louis, notable for a 22-degree bend occurring at the middle of the crossing, necessary for navigation on the river; formerly used by U.S. Route 66 to cross the Mississippi. Replaced for road traffic in 1966 by a nearby pair of new bridges; now a pedestrian bridge.
* Eads BridgeA combined road and railway bridge, connecting St. Louis and East St. Louis, Illinois. When completed in 1874, it was the longest arch bridge in the world, with an overall length of . The three ribbed steel arch spans were considered daring, as was the use of steel as a primary structural material; it was the first such use of true steel in a major bridge project.
* Chester BridgeA truss bridge connecting Route 51 in Missouri with Illinois Route 150, between Perryville, Missouri, and Chester, Illinois. The bridge can be seen at the beginning of the 1967 film '' In the Heat of the Night''. In the 1940s, the main span was destroyed by a
* Chain of Rocks BridgeLocated on the northern edge of St. Louis, notable for a 22-degree bend occurring at the middle of the crossing, necessary for navigation on the river; formerly used by U.S. Route 66 to cross the Mississippi. Replaced for road traffic in 1966 by a nearby pair of new bridges; now a pedestrian bridge.
* Eads BridgeA combined road and railway bridge, connecting St. Louis and East St. Louis, Illinois. When completed in 1874, it was the longest arch bridge in the world, with an overall length of . The three ribbed steel arch spans were considered daring, as was the use of steel as a primary structural material; it was the first such use of true steel in a major bridge project.
* Chester BridgeA truss bridge connecting Route 51 in Missouri with Illinois Route 150, between Perryville, Missouri, and Chester, Illinois. The bridge can be seen at the beginning of the 1967 film '' In the Heat of the Night''. In the 1940s, the main span was destroyed by a  * Hernando de Soto BridgeA through arch bridge carrying Interstate 40 across the Mississippi between West Memphis, Arkansas, and
* Hernando de Soto BridgeA through arch bridge carrying Interstate 40 across the Mississippi between West Memphis, Arkansas, and  * Old Vicksburg Bridge
*
* Old Vicksburg Bridge
*

 A clear channel is needed for the
A clear channel is needed for the 
 A series of 29 locks and dams on the upper Mississippi, most of which were built in the 1930s, is designed primarily to maintain a channel for commercial barge traffic. The lakes formed are also used for recreational boating and fishing. The dams make the river deeper and wider but do not stop it. No
A series of 29 locks and dams on the upper Mississippi, most of which were built in the 1930s, is designed primarily to maintain a channel for commercial barge traffic. The lakes formed are also used for recreational boating and fishing. The dams make the river deeper and wider but do not stop it. No
 In 1829, there were surveys of the two major obstacles on the upper Mississippi, the
In 1829, there were surveys of the two major obstacles on the upper Mississippi, the



 Until the 1950s, there was no dam below Lock and Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois. Chain of Rocks Lock (Lock and Dam No. 27), which consists of a low-water dam and an canal, was added in 1953, just below the confluence with the Missouri River, primarily to bypass a series of rock ledges at St. Louis. It also serves to protect the St. Louis city water intakes during times of low water.
U.S. government scientists determined in the 1950s that the Mississippi River was starting to switch to the Atchafalaya River channel because of its much steeper path to the Gulf of Mexico. Eventually, the Atchafalaya River would capture the Mississippi River and become its main channel to the Gulf of Mexico, leaving New Orleans on a side channel. As a result, the U.S. Congress authorized a project called the Old River Control Structure, which has prevented the Mississippi River from leaving its current channel that drains into the Gulf via New Orleans.
Because the large scale of high-energy water flow threatened to damage the structure, an auxiliary flow control station was built adjacent to the standing control station. This $300 million project was completed in 1986 by the Corps of Engineers. Beginning in the 1970s, the Corps applied hydrological transport models to analyze flood flow and water quality of the Mississippi. Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois, which had structural problems, was replaced by the Mel Price Lock and Dam in 1990. The original Lock and Dam 26 was demolished.
Until the 1950s, there was no dam below Lock and Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois. Chain of Rocks Lock (Lock and Dam No. 27), which consists of a low-water dam and an canal, was added in 1953, just below the confluence with the Missouri River, primarily to bypass a series of rock ledges at St. Louis. It also serves to protect the St. Louis city water intakes during times of low water.
U.S. government scientists determined in the 1950s that the Mississippi River was starting to switch to the Atchafalaya River channel because of its much steeper path to the Gulf of Mexico. Eventually, the Atchafalaya River would capture the Mississippi River and become its main channel to the Gulf of Mexico, leaving New Orleans on a side channel. As a result, the U.S. Congress authorized a project called the Old River Control Structure, which has prevented the Mississippi River from leaving its current channel that drains into the Gulf via New Orleans.
Because the large scale of high-energy water flow threatened to damage the structure, an auxiliary flow control station was built adjacent to the standing control station. This $300 million project was completed in 1986 by the Corps of Engineers. Beginning in the 1970s, the Corps applied hydrological transport models to analyze flood flow and water quality of the Mississippi. Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois, which had structural problems, was replaced by the Mel Price Lock and Dam in 1990. The original Lock and Dam 26 was demolished.



 In 1519 Spanish explorer Alonso Álvarez de Pineda became the first recorded European to reach the Mississippi River, followed by Hernando de Soto who reached the river on May 8, 1541, and called it ''Río del Espíritu Santo'' ("River of the Holy Spirit"), in the area of what is now Mississippi. In Spanish, the river is called ''Río Mississippi''.
French explorers Louis Jolliet and
In 1519 Spanish explorer Alonso Álvarez de Pineda became the first recorded European to reach the Mississippi River, followed by Hernando de Soto who reached the river on May 8, 1541, and called it ''Río del Espíritu Santo'' ("River of the Holy Spirit"), in the area of what is now Mississippi. In Spanish, the river is called ''Río Mississippi''.
French explorers Louis Jolliet and
CathEn-07614b
. The French built the small fort of La Balise there to control passage. In 1718, about upriver, New Orleans was established along the river crescent by Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne, Sieur de Bienville, with construction patterned after the 1711 resettlement on Mobile Bay of Mobile, the capital of French Louisiana at the time. In 1727, Étienne Perier begins work, using enslaved African laborers, on the first levees on the Mississippi River.
 Following Britain's victory in the Seven Years War, the Mississippi became the border between the British and
Following Britain's victory in the Seven Years War, the Mississippi became the border between the British and  The colonization of the area was barely slowed by the three earthquakes in 1811 and 1812, estimated at 8 on the
The colonization of the area was barely slowed by the three earthquakes in 1811 and 1812, estimated at 8 on the

 Control of the river was a strategic objective of both sides in the
Control of the river was a strategic objective of both sides in the
 In 2002,
In 2002,
 The Old River Control Structure, between the present Mississippi River channel and the Atchafalaya Basin, sits at the normal water elevation and is ordinarily used to divert 30% of the Mississippi flow to the Atchafalaya River. There is a steep drop here away from the Mississippi's main channel into the Atchafalaya Basin. If this facility were to fail during a major flood, there is a strong concern the water would
The Old River Control Structure, between the present Mississippi River channel and the Atchafalaya Basin, sits at the normal water elevation and is ordinarily used to divert 30% of the Mississippi flow to the Atchafalaya River. There is a steep drop here away from the Mississippi's main channel into the Atchafalaya Basin. If this facility were to fail during a major flood, there is a strong concern the water would
(US Army Corps of Engineers) In addition to reducing the Mississippi River crest downstream, this diversion reduced the chances of a channel change by reducing stress on the other elements of the control system. Some geologists have noted that the possibility for course change into the Atchafalaya also exists in the area immediately north of the Old River Control Structure. Army Corps of Engineers geologist Fred Smith once stated, "The Mississippi wants to go west. 1973 was a forty-year flood. The big one lies out there somewhere—when the structures can't release all the floodwaters and the levee is going to have to give way. That is when the river's going to jump its banks and try to break through." Another possible course change for the Mississippi River is a diversion into
 The sport of water skiing was invented on the river in a wide region between Minnesota and Wisconsin known as Lake Pepin.
The sport of water skiing was invented on the river in a wide region between Minnesota and Wisconsin known as Lake Pepin.
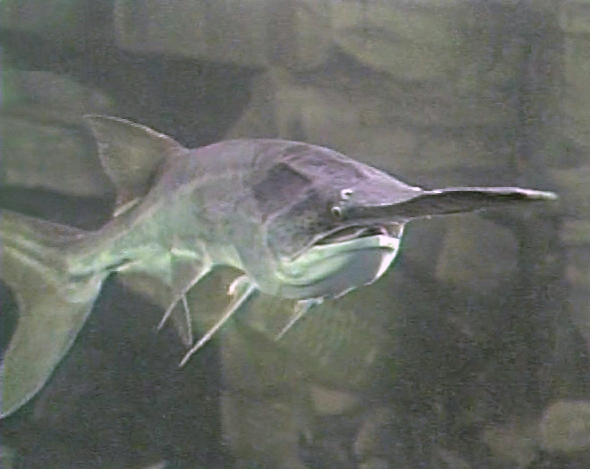 The Mississippi basin is home to a highly diverse aquatic
The Mississippi basin is home to a highly diverse aquatic
river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of ...
of the second-largest drainage system in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over t ...
, it flows generally south for to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
. With its many tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drain ...
, the Mississippi's watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British Nort ...
between the Rocky
''Rocky'' is a 1976 American sports drama film directed by John G. Avildsen and written by and starring Sylvester Stallone. It is the first installment in the ''Rocky'' franchise and stars Talia Shire, Burt Young, Carl Weathers, and Burges ...
and Appalachian mountains. The main stem
In hydrology, a mainstem (or trunk) is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". Water enters the mainstem from the river's drainage basin, the land area through which the mainstem and its tributaries flow. ...
is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
is , of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over t ...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, Iowa
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wiscon ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
, Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, Kentucky, Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 36th-largest by ...
, Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
, Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
, and Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
.
Native Americans have lived along the Mississippi River and its tributaries for thousands of years. Most were hunter-gatherers, but some, such as the Mound Builders, formed prolific agricultural and urban civilizations. The arrival of Europeans in the 16th century changed the native way of life as first explorers, then settlers, ventured into the basin in increasing numbers. The river served first as a barrier, forming borders for New Spain, New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
, and the early United States, and then as a vital transportation artery and communications link. In the 19th century, during the height of the ideology of manifest destiny, the Mississippi and several western tributaries, most notably the Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, formed pathways for the western expansion of the United States.
Formed from thick layers of the river's silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
deposits, the Mississippi embayment is one of the most fertile regions of the United States; steamboats were widely used in the 19th and early 20th centuries to ship agricultural and industrial goods. During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
, the Mississippi's capture by Union forces marked a turning point towards victory, due to the river's strategic importance to the Confederate war effort. Because of the substantial growth of cities and the larger ships and barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. ...
s that replaced steamboats, the first decades of the 20th century saw the construction of massive engineering works such as levees, locks and dams, often built in combination. A major focus of this work has been to prevent the lower Mississippi from shifting into the channel of the Atchafalaya River and bypassing .
Since the 20th century, the Mississippi River has also experienced major pollution and environmental problems — most notably elevated nutrient and chemical levels from agricultural runoff, the primary contributor to the Gulf of Mexico dead zone.
Name and significance
The word Mississippi itself comes from , the French rendering of theAnishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawa ...
(Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
or Algonquin) name for the river, (Great River).
In the 18th century, the river was the primary western boundary of the young United States, and since the country's expansion westward, the Mississippi River has been a convenient line dividing the Western United States from the Eastern, Southern, and Midwestern regions. This is symbolized by the Gateway Arch in St. Louis and the phrase "Trans-Mississippi
Trans-Mississippi was a common name of the geographic area west of the Mississippi River during the 19th century. The area included Arkansas, Louisiana, Missouri, Texas, Indian Territory (now Oklahoma), and many other territories.
The term "Tr ...
" as used in the name of the Trans-Mississippi Exposition.
Regional landmarks are often classified in relation to the river, such as "the highest peak east of the Mississippi" or "the oldest city west of the Mississippi". The FCC also uses it as the dividing line for broadcast call-signs, which begin with W to the east and K to the west, overlapping in media market
A media market, broadcast market, media region, designated market area (DMA), television market area, or simply market is a region where the population can receive the same (or similar) television and radio station offerings, and may also incl ...
s along the river.
Divisions
The Mississippi River can be divided into three sections: the Upper Mississippi, the river from its headwaters to the confluence with the Missouri River; the Middle Mississippi, which is downriver from the Missouri to the Ohio River; and theLower Mississippi
The Lower Mississippi River is the portion of the Mississippi River downstream of Cairo, Illinois. From the confluence of the Ohio River and Upper Mississippi River at Cairo, the Lower flows just under 1000 miles (1600 km) to the Gulf of ...
, which flows from the Ohio to the Gulf of Mexico.
Upper Mississippi


 The Upper Mississippi runs from its headwaters to its confluence with the Missouri River at St. Louis, Missouri. It is divided into two sections:
# The headwaters, from the source to Saint Anthony Falls in Minneapolis, Minnesota; and
# A navigable channel, formed by a series of man-made lakes between Minneapolis and St. Louis, Missouri, some .
The source of the Upper Mississippi branch is traditionally accepted as Lake Itasca, above sea level in Itasca State Park in Clearwater County, Minnesota. The name ''Itasca'' was chosen to designate the "true head" of the Mississippi River as a combination of the last four letters of the Latin word for truth () and the first two letters of the Latin word for head (). However, the lake is in turn fed by a number of smaller streams.
From its origin at Lake Itasca to St. Louis, Missouri, the waterway's flow is moderated by 43 dams. Fourteen of these dams are located above Minneapolis in the headwaters region and serve multiple purposes, including power generation and recreation. The remaining 29 dams, beginning in downtown Minneapolis, all contain locks and were constructed to improve commercial navigation of the upper river. Taken as a whole, these 43 dams significantly shape the geography and influence the ecology of the upper river. Beginning just below
The Upper Mississippi runs from its headwaters to its confluence with the Missouri River at St. Louis, Missouri. It is divided into two sections:
# The headwaters, from the source to Saint Anthony Falls in Minneapolis, Minnesota; and
# A navigable channel, formed by a series of man-made lakes between Minneapolis and St. Louis, Missouri, some .
The source of the Upper Mississippi branch is traditionally accepted as Lake Itasca, above sea level in Itasca State Park in Clearwater County, Minnesota. The name ''Itasca'' was chosen to designate the "true head" of the Mississippi River as a combination of the last four letters of the Latin word for truth () and the first two letters of the Latin word for head (). However, the lake is in turn fed by a number of smaller streams.
From its origin at Lake Itasca to St. Louis, Missouri, the waterway's flow is moderated by 43 dams. Fourteen of these dams are located above Minneapolis in the headwaters region and serve multiple purposes, including power generation and recreation. The remaining 29 dams, beginning in downtown Minneapolis, all contain locks and were constructed to improve commercial navigation of the upper river. Taken as a whole, these 43 dams significantly shape the geography and influence the ecology of the upper river. Beginning just below Saint Paul, Minnesota
Saint Paul (abbreviated St. Paul) is the capital of the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Ramsey County. Situated on high bluffs overlooking a bend in the Mississippi River, Saint Paul is a regional business hub and the center ...
, and continuing throughout the upper and lower river, the Mississippi is further controlled by thousands of wing dike
A wing dam or wing dike is a man made barrier that, unlike a conventional dam, only extends partway into a river. These structures force water into a fast-moving center channel which reduces the rate of sediment accumulation, while slowing water ...
s that moderate the river's flow in order to maintain an open navigation channel and prevent the river from eroding its banks.
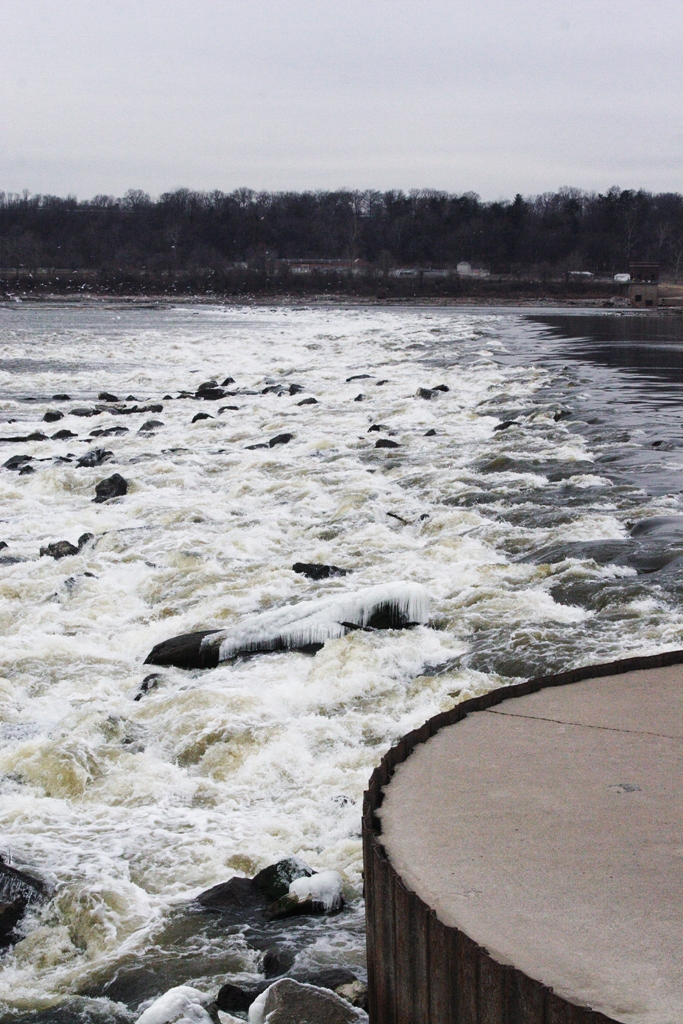
The head of navigation on the Mississippi is the St. Anthony Falls Lock. Before the Coon Rapids Dam in Coon Rapids, Minnesota, was built in 1913, steamboats could occasionally go upstream as far as Saint Cloud, Minnesota, depending on river conditions.
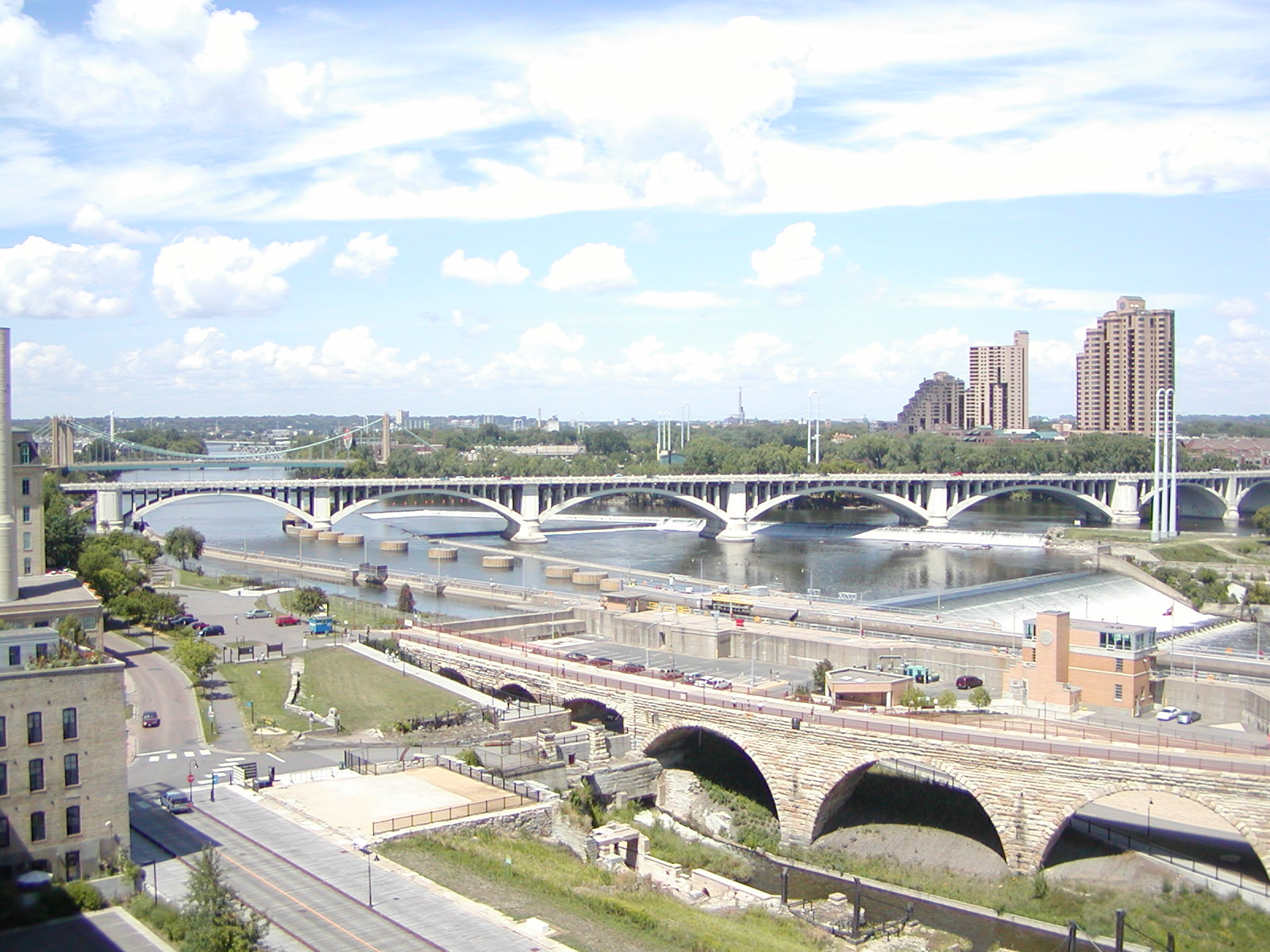
The uppermost lock and dam on the Upper Mississippi River is the Upper St. Anthony Falls Lock and Dam in Minneapolis. Above the dam, the river's elevation is . Below the dam, the river's elevation is . This drop is the largest of all the Mississippi River locks and dams. The origin of the dramatic drop is a waterfall preserved adjacent to the lock under an apron of concrete. Saint Anthony Falls is the only true waterfall on the entire Mississippi River. The water elevation continues to drop steeply as it passes through the gorge carved by the waterfall.
After the completion of the St. Anthony Falls Lock and Dam in 1963, the river's head of navigation moved upstream, to the Coon Rapids Dam. However, the Locks were closed in 2015 to control the spread of invasive Asian carp, making Minneapolis once again the site of the head of navigation of the river.
The Upper Mississippi has a number of natural and artificial lakes, with its widest point being Lake Winnibigoshish
Lake Winnibigoshish is a body of water in north central Minnesota in the Chippewa National Forest. Its name comes from the Ojibwe language ''Wiinibiigoonzhish'', a diminutive and pejorative form of ''Wiinibiig'', meaning "filthy water" (i.e., "b ...
, near Grand Rapids, Minnesota, over across. Lake Onalaska
Lake Onalaska is a reservoir located on the Black River and Mississippi River between Wisconsin, and Minnesota. It is approximately across, and is the widest point on the Mississippi River. Located in La Crosse County in the state of Wisco ...
, created by Lock and Dam No. 7
Lock and Dam No. 7 is a lock and dam located on the Upper Mississippi River at river mile 702.5 near the cities of La Crescent, Minnesota and Onalaska, Wisconsin. It forms pool 7 and Lake Onalaska. The facility was constructed in the mid-1930s and ...
, near La Crosse, Wisconsin, is more than wide. Lake Pepin, a natural lake formed behind the delta of the Chippewa River of Wisconsin as it enters the Upper Mississippi, is more than wide.
By the time the Upper Mississippi reaches Saint Paul, Minnesota, below Lock and Dam No. 1, it has dropped more than half its original elevation and is above sea level. From St. Paul to St. Louis, Missouri, the river elevation falls much more slowly and is controlled and managed as a series of pools created by 26 locks and dams.
The Upper Mississippi River is joined by the Minnesota River at Fort Snelling in the Twin Cities; the St. Croix River near Prescott, Wisconsin; the Cannon River near Red Wing, Minnesota; the Zumbro River at Wabasha, Minnesota; the Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
, La Crosse
La Crosse is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of La Crosse County. Positioned alongside the Mississippi River, La Crosse is the largest city on Wisconsin's western border. La Crosse's population as of the 2020 census ...
, and Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
rivers in La Crosse, Wisconsin; the Wisconsin River at Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin; the Rock River at the Quad Cities; the Iowa River near Wapello, Iowa
Wapello is a city in and the county seat of Louisa County, Iowa, United States. The population was 2,084 at the time of the 2020 census.
Wapello is part of the Muscatine Micropolitan Statistical Area.
History
Wapello was platted in the lat ...
; the Skunk River south of Burlington, Iowa; and the Des Moines River at Keokuk, Iowa. Other major tributaries of the Upper Mississippi include the Crow River in Minnesota, the Chippewa River in Wisconsin, the Maquoketa River
The Maquoketa River is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed May 13, 2011 in northeastern Iowa in the United States. I ...
and the Wapsipinicon River
The Wapsipinicon River (, locally known as the Wapsi) is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed May 13, 2011 starting n ...
in Iowa, and the Illinois River in Illinois.

Middle Mississippi
The Mississippi River is known as the Middle Mississippi from the Upper Mississippi River's confluence with the Missouri River at St. Louis, Missouri, for to its confluence with the Ohio River at Cairo, Illinois. The Middle Mississippi is relatively free-flowing. From St. Louis to the Ohio River confluence, the Middle Mississippi falls over for an average rate of . At its confluence with the Ohio River, the Middle Mississippi is above sea level. Apart from the Missouri and Meramec rivers of Missouri and the Kaskaskia River of Illinois, no major tributaries enter the Middle Mississippi River.Lower Mississippi
 The Mississippi River is called the Lower Mississippi River from its confluence with the Ohio River to its mouth at the Gulf of Mexico, a distance of about . At the confluence of the Ohio and the Middle Mississippi, the long-term mean discharge of the Ohio at Cairo, Illinois is , while the long-term mean discharge of the Mississippi at Thebes, Illinois (just upriver from Cairo) is . Thus, by volume, the main branch of the Mississippi River system at Cairo can be considered to be the Ohio River (and the Allegheny River further upstream), rather than the Middle Mississippi.
In addition to the Ohio River, the major tributaries of the Lower Mississippi River are the White River, flowing in at the White River National Wildlife Refuge in east-central Arkansas; the
The Mississippi River is called the Lower Mississippi River from its confluence with the Ohio River to its mouth at the Gulf of Mexico, a distance of about . At the confluence of the Ohio and the Middle Mississippi, the long-term mean discharge of the Ohio at Cairo, Illinois is , while the long-term mean discharge of the Mississippi at Thebes, Illinois (just upriver from Cairo) is . Thus, by volume, the main branch of the Mississippi River system at Cairo can be considered to be the Ohio River (and the Allegheny River further upstream), rather than the Middle Mississippi.
In addition to the Ohio River, the major tributaries of the Lower Mississippi River are the White River, flowing in at the White River National Wildlife Refuge in east-central Arkansas; the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United ...
, joining the Mississippi at Arkansas Post; the Big Black River in Mississippi; and the Yazoo River, meeting the Mississippi at Vicksburg, Mississippi.
Deliberate water diversion at the Old River Control Structure in Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
allows the Atchafalaya River in Louisiana to be a major distributary of the Mississippi River, with 30% of the combined flow of the Mississippi and Red Rivers flowing to the Gulf of Mexico by this route, rather than continuing down the Mississippi's current channel past Baton Rouge and on a longer route to the Gulf. Republished in Although the Red River was once an additional tributary, its water now flows separately into the Gulf of Mexico through the Atchafalaya River.
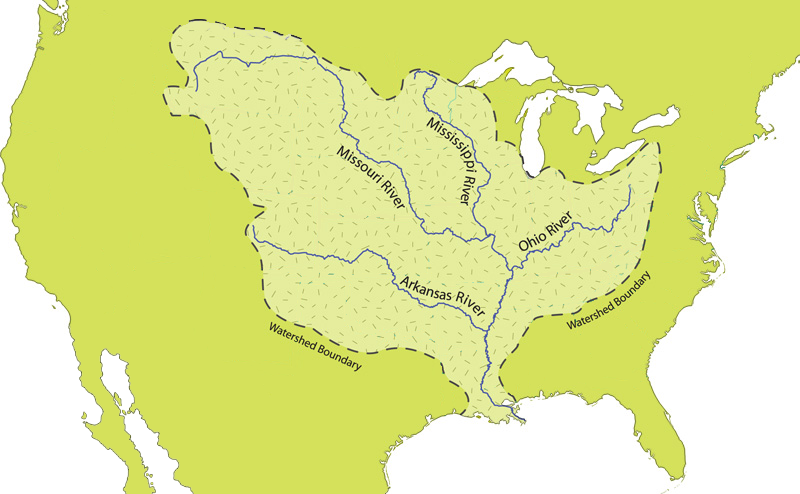
Watershed
 The Mississippi River has the world's fourth-largest
The Mississippi River has the world's fourth-largest drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
("watershed" or "catchment"). The basin covers more than , including all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces. The drainage basin empties into the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
, part of the Atlantic Ocean. The total catchment of the Mississippi River covers nearly 40% of the landmass of the continental United States. The highest point within the watershed is also the highest point of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
, Mount Elbert at .
 In the United States, the Mississippi River drains the majority of the area between the crest of the
In the United States, the Mississippi River drains the majority of the area between the crest of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
and the crest of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
, except for various regions drained to Hudson Bay by the Red River of the North; to the Atlantic Ocean by the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
; and to the Gulf of Mexico by the Rio Grande, the Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = " Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,7 ...
and Tombigbee rivers, the Chattahoochee and Appalachicola rivers, and various smaller coastal waterways along the Gulf.
The Mississippi River empties into the Gulf of Mexico about downstream from New Orleans. Measurements of the length of the Mississippi from Lake Itasca to the Gulf of Mexico vary somewhat, but the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
's number is . The retention time from Lake Itasca to the Gulf is typically about 90 days.
The stream gradient of the entire river is 0.01%, a drop of 450 m over 3,766 km.
Outflow
The Mississippi River discharges at an annual average rate of between . The Mississippi is the fourteenth largest river in the world by volume. On average, the Mississippi has 8% the flow of the Amazon River, which moves nearly during wet seasons. Before 1900, the Mississippi River transported an estimated ofsediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
per year from the interior of the United States to coastal Louisiana and the Gulf of Mexico. During the last two decades, this number was only per year. The reduction in sediment transported down the Mississippi River is the result of engineering modification of the Mississippi, Missouri, and Ohio rivers and their tributaries by dams, meander cutoffs, river-training structures, and bank revetments and soil erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is d ...
control programs in the areas drained by them.Meade, R. H., and J. A. Moody, 1984, ''Causes for the decline of suspended-sediment discharge in the Mississippi River system, 1940–2007'' Hydrology Processes vol. 24, pp. 35–49.
Mixing with salt water
Denser salt water from the Gulf of Mexico forms asalt wedge
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environmen ...
along the river bottom near the mouth of the river, while fresh water flows near the surface. In drought years, with less fresh water to push it out, salt water can travel many miles upstream— in 2022—contaminating drinking water supplies and requiring the use of desalination. The United States Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
constructed "saltwater sills" or "underwater levees" to contain this 1988, 1999, 2012, and 2022. This consists of a large mound of sand spanning the width of the river 55 feet below the surface, allowing fresh water and large cargo ships to pass over.
Fresh river water flowing from the Mississippi into the Gulf of Mexico does not mix into the salt water immediately. The images from NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
's MODIS show a large plume of fresh water, which appears as a dark ribbon against the lighter-blue surrounding waters. These images demonstrate that the plume did not mix with the surrounding sea water immediately. Instead, it stayed intact as it flowed through the Gulf of Mexico, into the Straits of Florida, and entered the Gulf Stream. The Mississippi River water rounded the tip of Florida and traveled up the southeast coast to the latitude of Georgia before finally mixing in so thoroughly with the ocean that it could no longer be detected by MODIS.
Course changes
Over geologic time, the Mississippi River has experienced numerous large and small changes to its main course, as well as additions, deletions, and other changes among its numerous tributaries, and the lower Mississippi River has used different pathways as its main channel to the Gulf of Mexico across the delta region. Through a natural process known as avulsion or delta switching, the lower Mississippi River has shifted its final course to the mouth of the Gulf of Mexico every thousand years or so. This occurs because the deposits of silt and sediment begin to clog its channel, raising the river's level and causing it to eventually find a steeper, more direct route to the Gulf of Mexico. The abandoned distributaries diminish in volume and form what are known as bayous. This process has, over the past 5,000 years, caused the coastline of south Louisiana to advance toward the Gulf from . The currently active delta lobe is called the Birdfoot Delta, after its shape, or theBalize Delta Balize may refer to:
* Belize, a country in Central America
* La Balize, Louisiana, a former French fort and settlement near the mouth of the Mississippi River
* The lobe of the Mississippi River Delta
The Mississippi River Delta is the conf ...
, after La Balize, Louisiana, the first French settlement at the mouth of the Mississippi.
Prehistoric courses
The current form of the Mississippi River basin was largely shaped by the Laurentide Ice Sheet of the most recentIce Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
. The southernmost extent of this enormous glaciation extended well into the present-day United States and Mississippi basin. When the ice sheet began to recede, hundreds of feet of rich sediment were deposited, creating the flat and fertile landscape of the Mississippi Valley. During the melt, giant glacial rivers found drainage paths into the Mississippi watershed, creating such features as the Minnesota River, James River, and Milk River valleys. When the ice sheet completely retreated, many of these "temporary" rivers found paths to Hudson Bay or the Arctic Ocean, leaving the Mississippi Basin with many features "over-sized" for the existing rivers to have carved in the same time period.
Ice sheets during the Illinoian Stage, about 300,000 to 132,000 years before present, blocked the Mississippi near Rock Island, Illinois, diverting it to its present channel farther to the west, the current western border of Illinois. The Hennepin Canal
The Hennepin Canal State Trail, also just called the Hennepin Canal, is an abandoned waterway in northwest Illinois, between the Mississippi River at Rock Island and the Illinois River near Hennepin. The entire canal is listed on the National R ...
roughly follows the ancient channel of the Mississippi downstream from Rock Island to Hennepin, Illinois. South of Hennepin, to Alton, Illinois, the current Illinois River follows the ancient channel used by the Mississippi River before the Illinoian Stage.McKay, E.D., 2007''Six Rivers, Five Glaciers, and an Outburst Flood: the Considerable Legacy of the Illinois River.''
(PDF) Proceedings of the 2007 Governor's Conference on the Management of the Illinois River System: Our continuing Commitment, 11th Biennial Conference, Oct. 2–4, 2007, 11 p.McKay, E.D., and R.C. Berg, 2008
Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, Vol. 40, No. 5, p. 78 wit
Powerpoint presentation
 Timeline of outflow course changes
* c. 5000 BC: The last ice age ended; world sea level became what it is now.
* c. 2500 BC: Bayou Teche became the main course of the Mississippi.
* c. 800 BC: The Mississippi diverted further east.
* c. 200 AD: Bayou Lafourche became the main course of the Mississippi.
* c. 1000 AD: The Mississippi's present course took over.
* Before c. 1400 AD: The Red River of the South flowed parallel to the lower Mississippi to the sea
* 15th century:
Timeline of outflow course changes
* c. 5000 BC: The last ice age ended; world sea level became what it is now.
* c. 2500 BC: Bayou Teche became the main course of the Mississippi.
* c. 800 BC: The Mississippi diverted further east.
* c. 200 AD: Bayou Lafourche became the main course of the Mississippi.
* c. 1000 AD: The Mississippi's present course took over.
* Before c. 1400 AD: The Red River of the South flowed parallel to the lower Mississippi to the sea
* 15th century: Turnbull's Bend
The Old River Control Structure is a floodgate system in a branch of the Mississippi River in central Louisiana. It regulates the flow of water from the Mississippi into the Atchafalaya River, thereby preventing the Mississippi River from cha ...
in the lower Mississippi extended so far west that it captured the Red River of the South. The Red River below the captured section became the Atchafalaya River.
* 1831: Captain Henry M. Shreve
Henry Miller Shreve (October 21, 1785 – March 6, 1851) was the American inventor and steamboat captain who opened the Mississippi, Ohio, and Red rivers to steamboat navigation. Shreveport, Louisiana, is named in his honor.
Shreve was also instru ...
dug a new short course for the Mississippi through the neck of Turnbull's Bend.
* 1833 to November 1873: The Great Raft (a huge logjam
A log jam is a naturally occurring phenomenon characterized by a dense accumulation of tree trunks and pieces of large wood across a vast section of a river, stream, or lake. ("Large wood" is commonly defined as pieces of wood more than in diame ...
in the Atchafalaya River) was cleared. The Atchafalaya started to capture the Mississippi and to become its new main lower course.
* 1963: The Old River Control Structure was completed, controlling how much Mississippi water entered the Atchafalaya.
Historic course changes
In March 1876, the Mississippi suddenly changed course near the settlement of Reverie, Tennessee, leaving a small part ofTipton County, Tennessee
Tipton County is a county located on the western end of the U.S. state of Tennessee, in the Mississippi Delta region. As of the 2020 census, the population was 60,970. Its county seat is Covington. Tipton County is part of the Memphis, TN- ...
, attached to Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
and separated from the rest of Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 36th-largest by ...
by the new river channel. Since this event was an avulsion, rather than the effect of incremental erosion and deposition, the state line still follows the old channel.
The town of Kaskaskia, Illinois once stood on a peninsula at the confluence of the Mississippi and Kaskaskia (Okaw) Rivers. Founded as a French colonial community, it later became the capital of the Illinois Territory and was the first state capital of Illinois until 1819. Beginning in 1844, successive flooding caused the Mississippi River to slowly encroach east. A major flood in 1881 caused it to overtake the lower of the Kaskaskia River, forming a new Mississippi channel and cutting off the town from the rest of the state. Later flooding destroyed most of the remaining town, including the original State House. Today, the remaining island and community of 14 residents is known as an enclave of Illinois and is accessible only from the Missouri side.
New Madrid Seismic Zone
The New Madrid Seismic Zone, along the Mississippi River near New Madrid, Missouri, between Memphis and St. Louis, is related to an aulacogen (failed rift) that formed at the same time as the Gulf of Mexico. This area is still quite active seismically. Four great earthquakes in 1811 and 1812, estimated at 8 on theRichter magnitude scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 p ...
, had tremendous local effects in the then sparsely settled area, and were felt in many other places in the Midwestern and eastern U.S. These earthquakes created Reelfoot Lake in Tennessee from the altered landscape near the river.
Length
When measured from its traditional source at Lake Itasca, the Mississippi has a length of . When measured from its longest stream source (most distant source from the sea), Brower's Spring in Montana, the source of the Missouri River, it has a length of , making it the fourth longest river in the world after theNile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
, Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
, and Yangtze. When measured by the largest stream source (by water volume), the Ohio River, by extension the Allegheny River, would be the source, and the Mississippi would begin in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
.
Depth
At its source at Lake Itasca, the Mississippi River is about deep. The average depth of the Mississippi River between Saint Paul and Saint Louis is between deep, the deepest part being Lake Pepin, which averages deep and has a maximum depth of . Between where the Missouri River joins the Mississippi at Saint Louis, Missouri, and Cairo, Illinois, the depth averages . Below Cairo, where the Ohio River joins, the depth averages deep. The deepest part of the river is in New Orleans, where it reaches deep.Cultural geography
State boundaries
The Mississippi River runs through or along 10 states, fromMinnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over t ...
to Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
, and is used to define portions of these states borders, with Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
, Kentucky, Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 36th-largest by ...
, and Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
along the east side of the river, and Iowa
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wiscon ...
, Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, and Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
along its west side. Substantial parts of both Minnesota and Louisiana are on either side of the river, although the Mississippi defines part of the boundary of each of these states.
In all of these cases, the middle of the riverbed at the time the borders were established was used as the line to define the borders between adjacent states. In various areas, the river has since shifted, but the state borders have not changed, still following the former bed of the Mississippi River as of their establishment, leaving several small isolated areas of one state across the new river channel, contiguous with the adjacent state. Also, due to a meander in the river, a small part of western Kentucky is contiguous with Tennessee but isolated from the rest of its state.
Communities along the river


Bemidji, Minnesota
Bemidji ( ) is a city and the county seat of Beltrami County, in northern Minnesota, United States. The population was 14,574 at the 2020 census. According to 2021 census estimates, the city is estimated to have a population of 15,279, making ...
* Grand Rapids, Minnesota
* Jacobson, Minnesota
* Palisade, Minnesota
Palisade is a city in Aitkin County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 167 at the 2010 census.
The Mississippi River flows through the area.
History
Palisade was incorporated in 1922. The post office began in 1910. Palisade was name ...
* Aitkin, Minnesota
* Riverton, Minnesota
Riverton is a city in Crow Wing County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 117 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Brainerd Micropolitan Statistical Area.
Riverton is located between Brainerd and Ironton, where the Mississippi Ri ...
* Brainerd, Minnesota
Brainerd is a city in Crow Wing County, Minnesota, United States. Its population was 14,395 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Crow Wing County. Brainerd straddles the Mississippi River several miles upstream from its confluence wit ...
* Fort Ripley, Minnesota
Fort Ripley is a city in Crow Wing County, Minnesota, United States, near the confluence of the Mississippi and Nokasippi Rivers. The population was 69 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Brainerd Micropolitan Statistical Area.
History
...
* Little Falls, Minnesota
* Sartell, Minnesota
* St. Cloud, Minnesota
* Monticello, Minnesota
* Anoka, Minnesota
* Coon Rapids, Minnesota
* Brooklyn Park, Minnesota
Brooklyn Park is a suburban city on the west bank of the Mississippi River, upstream from (north of) downtown Minneapolis in northern Hennepin County. It is the sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The population was 86,478 at t ...
* Brooklyn Center, Minnesota
* Minneapolis, Minnesota
* Saint Paul, Minnesota
Saint Paul (abbreviated St. Paul) is the capital of the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Ramsey County. Situated on high bluffs overlooking a bend in the Mississippi River, Saint Paul is a regional business hub and the center ...
* Nininger, Minnesota
Nininger is a ghost town in section 18 of Nininger Township in Dakota County, Minnesota, United States.
History
The city of Nininger was founded and named by John Nininger, brother in-law of territorial and state Governor Alexander Ramsey. N ...
* Hastings, Minnesota
* Prescott, Wisconsin
* Prairie Island, Minnesota
* Diamond Bluff, Wisconsin
Diamond Bluff is a town in Pierce County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 479 at the 2000 census.
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 18.3 square miles (47.4 km2), of whi ...
* Red Wing, Minnesota
* Hager City, Wisconsin
Hager City is an unincorporated census-designated place located in the town of Trenton in Pierce County, Wisconsin, United States, across the Mississippi River from Red Wing, Minnesota. It is located near the intersection of State Highway 35 ...
* Maiden Rock, Wisconsin
* Stockholm, Wisconsin
Stockholm is a village in Pepin County, Wisconsin, United States, founded in 1854 by immigrants from Karlskoga, Sweden, who named it after their country's capital. The population was 66 at the 2010 census. The village is located within the Town ...
* Lake City, Minnesota
* Maple Springs, Minnesota
* Camp Lacupolis, Minnesota
* Pepin, Wisconsin
* Reads Landing, Minnesota
* Wabasha, Minnesota
* Nelson, Wisconsin
Nelson is a village in Buffalo County in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The population was 374 at the 2010 census. The village is surrounded by the Town of Nelson.
Nelson is located at the junction of the Mississippi River and Chippewa River va ...
* Alma, Wisconsin
* Buffalo City, Wisconsin
Buffalo City is a city in Buffalo County in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The population was 1,023 at the 2010 census.
History
The name may be derived from a buffalo animal husbandry operation in the past. The city was chartered in 1859. At that ...
* Weaver, Minnesota
Weaver is an unincorporated community in Minneiska Township, Wabasha County, Minnesota, United States. The Whitewater River and the Mississippi River meet at Weaver.
Geography
The community is located 13 miles southeast of Wabasha along U. ...
* Minneiska, Minnesota
* Fountain City, Wisconsin
Fountain City is a small city bordering the Mississippi River in Buffalo County, Wisconsin, United States.
The population was 859 at the 2010 census.
History
Fountain City was originally called Holmes' Landing, after Thomas Holmes, who settled ...
* Winona, Minnesota
* Homer, Minnesota
Homer is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Homer Township, Winona County, Minnesota, United States, on the south bank of the Mississippi River. As of the 2010 census, its population was 181.
Geography
The c ...
* Trempealeau, Wisconsin
* Dakota, Minnesota
Dakota is a city in Winona County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 295 at the 2020 census.
It is located between Winona and La Crosse along Interstate 90. U.S. Highways 61 and 14 are briefly co-signed with Interstate 90 at th ...
* Dresbach, Minnesota
Dresbach is an unincorporated community in Dresbach Township, Winona County, Minnesota, United States.
The community is located on the west side of the Mississippi River along Interstate 90 between Winona and La Crosse. U.S. Highways 61 a ...
* La Crescent, Minnesota
* La Crosse, Wisconsin
* Brownsville, Minnesota
* Stoddard, Wisconsin
Stoddard is a village in Vernon County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 840 at the 2020 census.
History
Stoddard was founded as a farming community. It is notable as one of the few communities along the Mississippi River that was n ...
* Genoa, Wisconsin
* Victory, Wisconsin
* Potosi, Wisconsin
Potosi is a village in Grant County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 688 at the 2010 census. The village is in the Town of Potosi.
History
Potosi is located where Wisconsin's lead ore belt intersects with the Mississippi. The pos ...
* De Soto, Wisconsin
* Lansing, Iowa
* Ferryville, Wisconsin
Ferryville is a village in Crawford County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 176 at the 2010 census. It is located on Wisconsin Highway 35 along the Great River Road.
Geography
Ferryville is located at (43.341550, -91.083882).
Acco ...
* Lynxville, Wisconsin
* Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin
* Marquette, Iowa
Marquette is a city in Clayton County, Iowa, United States. The population was 429 at the time of the 2020 census, up from 421 in 2000. The city, which is located on the Mississippi River, is named after Jesuit missionary Jacques Marquette, who a ...
* McGregor, Iowa
* Wyalusing, Wisconsin
Wyalusing is a town in Grant County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 370 at the 2000 census. The unincorporated communities of Brodtville and Wyalusing are located in the town. Pioneer Robert Glenn, Sr. is credited with naming the ...
* Guttenberg, Iowa
* Cassville, Wisconsin
Cassville is a village in Grant County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 777 at the 2020 census. The village is located along the Mississippi River, opposite from the mouth of the Turkey River. It is surrounded by the Town of Cas ...
* Dubuque, Iowa
* Galena, Illinois
* Bellevue, Iowa
Bellevue ( ) is a city in eastern Jackson County, Iowa, United States. The city lies along the Mississippi River (at Lock and Dam No. 12) and next to Bellevue State Park. In 2020 its population was 2,363; up from a count of 2,191 at the 2010 ...
* Savanna, Illinois
* Sabula, Iowa
* Fulton, Illinois
Fulton is a city in Whiteside County, Illinois, United States. The population was 3,481 at the 2010 census, down from 3,881 in 2000. Fulton is located across the Mississippi River from Clinton, Iowa.
History
A post office called Fulton has been ...
* Clinton, Iowa
* Cordova, Illinois
Cordova is a village in Rock Island County, Illinois, United States. The population was 672 at the 2010 census, up from 633 in 2000.
Geography
Cordova is located at (41.677423, -90.320704).
According to the 2010 census, Cordova has a total area ...
* Port Byron, Illinois
Port Byron is a village in Rock Island County, Illinois, United States and part of the Quad Cities Metropolitan Area. The population was 1,647 at the 2010 census.
Geography
Port Byron is located at (41.618051, -90.332789).
According to the 2010 ...
* LeClaire, Iowa
* Rapids City, Illinois
* Hampton, Illinois
* Bettendorf, Iowa
* East Moline, Illinois
East Moline is a city in Rock Island County, Illinois, United States. The population was 21,374 at the 2020 census. East Moline is part of the Quad Cities, along with the cities of Rock Island, Moline, and the Iowa cities of Davenport and Be ...
* Moline, Illinois
Moline ( ) is a city located in Rock Island County, Illinois, United States. With a population of 42,985 in 2020, it is the largest city in Rock Island County. Moline is one of the Quad Cities, along with neighboring East Moline and Rock Islan ...
* Davenport, Iowa
* Rock Island, Illinois
* Buffalo, Iowa
* Muscatine, Iowa
* New Boston, Illinois
* Keithsburg, Illinois
* Oquawka, Illinois
* Burlington, Iowa
* Dallas City, Illinois
* Fort Madison, Iowa
* Nauvoo, Illinois
* Keokuk, Iowa
* Warsaw, Illinois
Warsaw is a city in Hancock County, Illinois, United States. The population was 1,607 at the 2010 census, a decline from 1,793 in 2000. The city is notable for its historic downtown and the Warsaw Brewery, which operated for more than 100 years ...
* Quincy, Illinois
* Hannibal, Missouri
* Louisiana, Missouri
* Clarksville, Missouri
* Grafton, Illinois
* Portage Des Sioux, Missouri
* Alton, Illinois
* St. Louis, Missouri
* Ste. Genevieve, Missouri
* Kaskaskia, Illinois
* Chester, Illinois
* Grand Tower, Illinois
* Cape Girardeau, Missouri
* Thebes, Illinois
* Commerce, Missouri
Commerce is a Mississippi River village in Scott County, Missouri, United States. The population was 67 at the time of the 2010 census.
History
In 1788, the present site of Commerce was first occupied by French settlers, making Commerce apparen ...
* Cairo, Illinois
* Wickliffe, Kentucky
* Columbus, Kentucky
* Hickman, Kentucky
Hickman is a city in and the county seat of Fulton County, Kentucky, United States. Located on the Mississippi River, the city had a population of 2,365 at the 2020 U.S. census and is classified as a home rule-class city. Hickman is part of th ...
* New Madrid, Missouri
* Tiptonville, Tennessee
* Caruthersville, Missouri
* Osceola, Arkansas
* Reverie, Tennessee
* Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-mo ...
* West Memphis, Arkansas
* Tunica, Mississippi
* Helena-West Helena, Arkansas
* Napoleon, Arkansas (historical)
* Arkansas City, Arkansas
* Greenville, Mississippi
* Mayersville, Mississippi
Mayersville is a town on the east bank of the Mississippi River, and the county seat for Issaquena County, Mississippi, United States. It is located in the Mississippi Delta region, known for cotton cultivation in the antebellum era. Once the tr ...
* Vicksburg, Mississippi
* Waterproof, Louisiana
* Natchez, Mississippi
* Morganza, Louisiana
* St. Francisville, Louisiana
* New Roads, Louisiana
* Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Baton Rouge ( ; ) is a city in and the List of capitals in the United States, capital of the U.S. state of Louisiana. Located the eastern bank of the Mississippi River, it is the county seat, parish seat of East Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana, E ...
* Donaldsonville, Louisiana
* Lutcher, Louisiana
Lutcher is a town in St. James Parish, Louisiana, United States, on the east bank of the Mississippi River. It is part of the New Orleans Metropolitan Area . The population was 3,559 at the 2010 U.S. census, and 3,127 at the 2020 population e ...
* Destrehan, Louisiana
*
* Pilottown, Louisiana
* La Balize, Louisiana (historical)
Bridge crossings
 The road crossing highest on the Upper Mississippi is a simple steel culvert, through which the river (locally named "Nicolet Creek") flows north from Lake Nicolet under "Wilderness Road" to the West Arm of Lake Itasca, within Itasca State Park.
The earliest bridge across the Mississippi River was built in 1855. It spanned the river in
The road crossing highest on the Upper Mississippi is a simple steel culvert, through which the river (locally named "Nicolet Creek") flows north from Lake Nicolet under "Wilderness Road" to the West Arm of Lake Itasca, within Itasca State Park.
The earliest bridge across the Mississippi River was built in 1855. It spanned the river in Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. Minneapolis has its origin ...
where the current Hennepin Avenue Bridge
The Hennepin Avenue Bridge is the structure that carries Hennepin County State Aid Highway 52, Hennepin Avenue, across the Mississippi River in Minneapolis, Minnesota, at Nicollet Island. Officially, it is the Father Louis Hennepin Bridge, in hon ...
is located. No highway or railroad tunnels cross under the Mississippi River.
The first railroad bridge across the Mississippi was built in 1856. It spanned the river between the Rock Island Arsenal in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
and Davenport, Iowa. Steamboat captains of the day, fearful of competition from the railroads, considered the new bridge a hazard to navigation. Two weeks after the bridge opened, the steamboat ''Effie Afton'' rammed part of the bridge, setting it on fire. Legal proceedings ensued, with Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
defending the railroad. The lawsuit went to the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. Federal tribunals in the United States, federal court cases, and over Stat ...
, which ruled in favor of the railroad.
Below is a general overview of selected Mississippi bridges that have notable engineering or landmark significance, with their cities or locations. They are sequenced from the Upper Mississippi's source to the Lower Mississippi's mouth.
* Stone Arch Bridge
An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct (a ...
Former Great Northern Railway (now pedestrian) bridge at Saint Anthony Falls connecting downtown Minneapolis with the historic Marcy-Holmes neighborhood.
* I-35W Saint Anthony Falls Bridge
The I-35W Saint Anthony Falls Bridge crosses the Mississippi River one-half mile (875 m) downstream from the Saint Anthony Falls in Minneapolis, Minnesota in the United States, U.S., carrying north–south traffic on Interstate 35W (Minnesota) ...
In Minneapolis, opened in September 2008, replacing the I-35W Mississippi River bridge which had collapsed catastrophically on August 1, 2007, killing 13 and injuring over 100.
* Eisenhower Bridge (Mississippi River)
The Red Wing Bridge was a cantilever bridge which carries U.S. Route 63 across the Mississippi River from Wisconsin to Red Wing, Minnesota. It is officially named the Eisenhower Bridge for Dwight D. Eisenhower, the 34th President of the United Stat ...
In Red Wing, Minnesota, opened by Dwight D. Eisenhower in November 1960.
* I-90 Mississippi River BridgeConnects La Crosse, Wisconsin, and Winona County, Minnesota, located just south of Lock and Dam No. 7
Lock and Dam No. 7 is a lock and dam located on the Upper Mississippi River at river mile 702.5 near the cities of La Crescent, Minnesota and Onalaska, Wisconsin. It forms pool 7 and Lake Onalaska. The facility was constructed in the mid-1930s and ...
.
* Black Hawk BridgeConnects Lansing
Lansing () is the capital of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is mostly in Ingham County, although portions of the city extend west into Eaton County and north into Clinton County. The 2020 census placed the city's population at 112,644, maki ...
in Allamakee County, Iowa
Allamakee County () is the northeasternmost county in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,061. Its county seat is Waukon.
History
Allamakee County was formed on February 20, 1847. The derivation of the name ...
and rural Crawford County, Wisconsin; locally referred to as the Lansing Bridge and documented in the Historic American Engineering Record.
 * Dubuque-Wisconsin BridgeConnects Dubuque, Iowa, and
* Dubuque-Wisconsin BridgeConnects Dubuque, Iowa, and Grant County, Wisconsin
Grant County is a county located in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, the population was 51,938. Its county seat is Lancaster. The county is named after the Grant River, in turn named after a fur trader who lived in the ar ...
.
* Julien Dubuque Bridge
The Julien Dubuque Bridge is a bridge over the Mississippi River that connects Dubuque, Iowa and East Dubuque, Illinois. The bridge is part of U.S. Route 20 (US 20). It is one of two automobile bridges over the Mississippi in the area (the ...
Joins the cities of Dubuque, Iowa, and East Dubuque, Illinois; listed in the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
.
* Savanna-Sabula BridgeA truss bridge and causeway connecting the city of Savanna, Illinois, and the island city of Sabula, Iowa. The bridge carries U.S. Highway 52
U.S. Route 52 (US 52) is a major United States highway in the central United States that extends from the northern to southeastern region of the United States. Contrary to most other even-numbered U.S. Highways, US 52 primarily follows ...
over the river, and is the terminus of both Iowa Highway 64
Iowa Highway 64 (Iowa 64) is a state highway that runs through two counties in east central Iowa. It begins at an interchange with U.S. Route 151 (US 151) in Anamosa and ends at the Dale Gardner Veterans Memorial Bridge over the Miss ...
and Illinois Route 64. Added to the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
in 1999.
* Fred Schwengel Memorial BridgeA 4-lane steel girder bridge that carries Interstate 80 and connects LeClaire, Iowa, and Rapids City, Illinois. Completed in 1966.
* Clinton Railroad Bridge
The Clinton Railroad Bridge, also called the Chicago and Northwestern Railway Bridge or more simply the Clinton Bridge, is a bridge that carries double tracked rail lines across the Mississippi River between Clinton, Iowa, and Fulton ( Albany) ...
A swing bridge that connects Clinton, Iowa and Fulton ( Albany), Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
. Known as the Chicago and Northwestern Railroad Bridge.
* I-74 Bridge
The Interstate 74 Bridge, officially known as the Iowa-Illinois Memorial Bridge, and often called ''The Twin Bridges'', or the ''I-74 Bridge'', are basket-handle, through arch twin bridges that carry Interstate 74 across the Mississippi River a ...
Connects Bettendorf, Iowa, and Moline, Illinois
Moline ( ) is a city located in Rock Island County, Illinois, United States. With a population of 42,985 in 2020, it is the largest city in Rock Island County. Moline is one of the Quad Cities, along with neighboring East Moline and Rock Islan ...
; originally known as the ''Iowa-Illinois Memorial Bridge''.
* Government BridgeConnects Rock Island, Illinois and Davenport, Iowa, adjacent to Lock and Dam No. 15
Lock and Dam No. 15 is a Lock (water transport), lock and dam located on the Upper Mississippi River, Upper Mississippi River. It spans the river between Rock Island, Illinois and Davenport, Iowa. Lock and Dam 15 is the largest roller dam in the ...
; the fourth crossing in this vicinity, built in 1896.
* Rock Island Centennial BridgeConnects Rock Island, Illinois, and Davenport, Iowa; opened in 1940.
* Sergeant John F. Baker, Jr. Bridge
The Sergeant John F. Baker Jr. Bridge, also known as the Baker Bridge or Interstate 280 Bridge, carries Interstate 280 (I-280) across the Mississippi River between Davenport, Iowa, and Rock Island, Illinois. The bridge opened in 1973 wi ...
Connects Rock Island, Illinois, and Davenport, Iowa; opened in 1973. * Norbert F. Beckey BridgeConnects Muscatine, Iowa, and Rock Island County, Illinois; became first U.S. bridge to be illuminated with
* Norbert F. Beckey BridgeConnects Muscatine, Iowa, and Rock Island County, Illinois; became first U.S. bridge to be illuminated with light-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor Electronics, device that Light#Light sources, emits light when Electric current, current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy i ...
(LED) lights decoratively illuminating the facade of the bridge.
* Great River Bridge
The Great River Bridge is an asymmetrical, single tower cable-stayed bridge over the Mississippi River. It carries U.S. Route 34 from Burlington, Iowa to the town of Gulf Port, Illinois.
History
Construction began in 1989, but work on the main ...
A cable-stayed bridge connecting Burlington, Iowa, to Gulf Port, Illinois
Gulfport is a village in Henderson County, Illinois, United States. As of the 2010 census, the village population was 54, down from 207 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Burlington, IA–IL Micropolitan Statistical Area. The village wa ...
.
* Fort Madison Toll Bridge
The Fort Madison Toll Bridge (also known as the Santa Fe Swing Span Bridge for the old Santa Fe Railway) is a tolled, double-decked swinging truss bridge over the Mississippi River that connects Fort Madison, Iowa, and unincorporated Niota, Il ...
Connects Fort Madison, Iowa, and unincorporated Niota, Illinois; also known as the ''Santa Fe Swing Span Bridge''; at the time of its construction the longest and heaviest electrified swing span on the Mississippi River. Listed in the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
since 1999.
* Keokuk–Hamilton Bridge
The Keokuk-Hamilton bridge is a steel girder, 4-lane bridge from Keokuk, Iowa to Hamilton, Illinois. It carries U.S. Route 136 across the Mississippi River. It also has fully fenced off pedestrian walkway.
The Keokuk–Hamilton Bridge was built ...
Connects Keokuk, Iowa and Hamilton, Illinois; opened in 1985 replacing an older bridge which is still in use as a railroad bridge.
* Bayview Bridge
The Bayview Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge bringing westbound U.S. Route 24 (US 24) over the Mississippi River. It connects the cities of West Quincy, Missouri and Quincy, Illinois. Quincy Memorial Bridge serves Eastbound US-24. The ...
A cable-stayed bridge bringing westbound U.S. Highway 24 over the river, connecting the cities of West Quincy, Missouri
West Quincy is a small commercial area in northeastern Marion County, Missouri, United States, on U.S. Route 24. It has no permanent residents.
History
West Quincy was platted in 1874, and named for its location west of Quincy, Illinois. It is ...
, and Quincy, Illinois.
* Quincy Memorial Bridge
The Quincy Memorial Bridge is a truss bridge over the Mississippi River in Quincy, Illinois
Quincy ( ), known as Illinois's "Gem City", is a city in and the county seat of Adams County, Illinois, United States, located on the Mississippi River. ...
Connects the cities of West Quincy, Missouri
West Quincy is a small commercial area in northeastern Marion County, Missouri, United States, on U.S. Route 24. It has no permanent residents.
History
West Quincy was platted in 1874, and named for its location west of Quincy, Illinois. It is ...
, and Quincy, Illinois, carrying eastbound U.S. 24, the older of these two U.S. 24 bridges.
* Clark BridgeA cable-stayed bridge connecting West Alton, Missouri, and Alton, Illinois, also known as the ''Super Bridge'' as the result of an appearance on the PBS program, '' Nova''; built in 1994, carrying U.S. Route 67 across the river. This is the northernmost river crossing in the St. Louis metropolitan area, replacing the ''Old Clark Bridge
The Old Clark Bridge was a bridge that carried U.S. Route 67 across the Mississippi River between West Alton, Missouri and Alton, Illinois. It was constructed beginning in 1927, was replaced by the Clark Bridge and was demolished in 1994. The brid ...
'', a truss bridge built in 1928, named after explorer William Clark.
 * Chain of Rocks BridgeLocated on the northern edge of St. Louis, notable for a 22-degree bend occurring at the middle of the crossing, necessary for navigation on the river; formerly used by U.S. Route 66 to cross the Mississippi. Replaced for road traffic in 1966 by a nearby pair of new bridges; now a pedestrian bridge.
* Eads BridgeA combined road and railway bridge, connecting St. Louis and East St. Louis, Illinois. When completed in 1874, it was the longest arch bridge in the world, with an overall length of . The three ribbed steel arch spans were considered daring, as was the use of steel as a primary structural material; it was the first such use of true steel in a major bridge project.
* Chester BridgeA truss bridge connecting Route 51 in Missouri with Illinois Route 150, between Perryville, Missouri, and Chester, Illinois. The bridge can be seen at the beginning of the 1967 film '' In the Heat of the Night''. In the 1940s, the main span was destroyed by a
* Chain of Rocks BridgeLocated on the northern edge of St. Louis, notable for a 22-degree bend occurring at the middle of the crossing, necessary for navigation on the river; formerly used by U.S. Route 66 to cross the Mississippi. Replaced for road traffic in 1966 by a nearby pair of new bridges; now a pedestrian bridge.
* Eads BridgeA combined road and railway bridge, connecting St. Louis and East St. Louis, Illinois. When completed in 1874, it was the longest arch bridge in the world, with an overall length of . The three ribbed steel arch spans were considered daring, as was the use of steel as a primary structural material; it was the first such use of true steel in a major bridge project.
* Chester BridgeA truss bridge connecting Route 51 in Missouri with Illinois Route 150, between Perryville, Missouri, and Chester, Illinois. The bridge can be seen at the beginning of the 1967 film '' In the Heat of the Night''. In the 1940s, the main span was destroyed by a tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, alt ...
.
* Bill Emerson Memorial Bridge
The Bill Emerson Memorial Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge connecting Missouri's Route 34 and Route 74 with Illinois Route 146 across the Mississippi River between Cape Girardeau, Missouri and East Cape Girardeau, Illinois.
It was built just ...
—Connecting Cape Girardeau, Missouri and East Cape Girardeau, Illinois
East Cape Girardeau is a village in Alexander County, Illinois, United States. The population was 289 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Cape Girardeau–Jackson, MO-IL Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
A post office was establishe ...
, completed in 2003 and illuminated by 140 lights.
* Caruthersville Bridge
The Caruthersville Bridge is a single tower cantilever bridge carrying Interstate 155 and U.S. Route 412 across the Mississippi River between Caruthersville, Missouri and Dyersburg, Tennessee. It is the only bridge that connects Missouri and Ten ...
A single tower cantilever bridge carrying Interstate 155 and U.S. Route 412 across the Mississippi River between Caruthersville, Missouri and Dyersburg, Tennessee.
 * Hernando de Soto BridgeA through arch bridge carrying Interstate 40 across the Mississippi between West Memphis, Arkansas, and
* Hernando de Soto BridgeA through arch bridge carrying Interstate 40 across the Mississippi between West Memphis, Arkansas, and Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-mo ...
.
* Harahan Bridge
The Harahan Bridge is a cantilevered through truss bridge that carries two rail lines and a pedestrian bridge across the Mississippi River between West Memphis, Arkansas, and Memphis, Tennessee. The bridge is owned and operated by Union Pacifi ...
A cantilevered through truss bridge
A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements (typically straight) may be stressed from tension, compression, o ...
, carrying two rail lines of the Union Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad , legally Union Pacific Railroad Company and often called simply Union Pacific, is a freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Paci ...
across the river between West Memphis, Arkansas, and Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-mo ...
.
* Frisco BridgeA cantilevered through truss bridge
A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements (typically straight) may be stressed from tension, compression, o ...
, carrying a rail line across the river between West Memphis, Arkansas, and Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-mo ...
, previously known as the ''Memphis Bridge''. When it opened on May 12, 1892, it was the first crossing of the Lower Mississippi and the longest span in the U.S. Listed as a Historic Civil Engineering Landmark.
* Memphis & Arkansas BridgeA cantilevered through truss bridge
A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements (typically straight) may be stressed from tension, compression, o ...
, carrying Interstate 55 between Memphis and West Memphis; listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
* Helena Bridge
* Greenville Bridge
Vicksburg Bridge
The Vicksburg Bridge is a cantilever bridge carrying Interstate 20 and U.S. Route 80 across the Mississippi River between Delta, Louisiana and Vicksburg, Mississippi.
Next to it is the Old Vicksburg Bridge.
The Vicksburg Bridge is the northernm ...
* Natchez-Vidalia Bridge
* John James Audubon BridgeThe second-longest cable-stayed bridge in the Western Hemisphere; connects Pointe Coupee and West Feliciana Parishes in Louisiana. It is the only crossing between Baton Rouge and Natchez. This bridge was opened a month ahead of schedule in May 2011, due to the 2011 floods
Eleven or 11 may refer to:
*11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12
* one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11
Literature
* ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn
*''El ...
.
* Huey P. Long BridgeA truss
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure.
In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so that the assembl ...
cantilever bridge carrying US 190 ( Airline Highway) and one rail line between East Baton Rouge
East Baton Rouge Parish (french: Paroisse de Bâton Rouge Est) is the most populous parish in the U.S. state of Louisiana. At the 2010 U.S. census, its population was 440,171, and 456,781 at the 2020 census. The parish seat is Baton Rouge, Loui ...
and West Baton Rouge Parishes in Louisiana.
* Horace Wilkinson Bridge
The Horace Wilkinson Bridge (locally known as the New Bridge) is a cantilever bridge carrying Interstate 10 in Louisiana across the Mississippi River from Port Allen in West Baton Rouge Parish to Baton Rouge in East Baton Rouge Parish. Around th ...
A cantilevered through truss
A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements (typically straight) may be stressed from tension, compression, o ...
bridge, carrying six lanes of Interstate 10 between Baton Rouge and Port Allen in Louisiana. It is the highest bridge over the Mississippi River.
* Sunshine Bridge
* Gramercy Bridge
* Hale Boggs Memorial Bridge
The Hale Boggs Memorial Bridge (also known as the Luling Bridge) is a cable-stayed bridge over the Mississippi River in St. Charles Parish, Louisiana. It is named for the late United States Congressman Hale Boggs.
With a total length of , it is ...
* Huey P. Long BridgeIn Jefferson Parish, Louisiana, the first Mississippi River span built in Louisiana.
* Crescent City Connection
The Crescent City Connection (CCC), formerly the Greater New Orleans Bridge (GNO), is a pair of cantilever bridges that carry U.S. Highway 90 Business (US 90 Bus.) over the Mississippi River in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States. They ...
Connects the east and west banks of , Louisiana; the fifth-longest cantilever bridge in the world.
Navigation and flood control


 A clear channel is needed for the
A clear channel is needed for the barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. ...
s and other vessels that make the main stem
In hydrology, a mainstem (or trunk) is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". Water enters the mainstem from the river's drainage basin, the land area through which the mainstem and its tributaries flow. ...
Mississippi one of the great commercial waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary ...
s of the world. The task of maintaining a navigation channel is the responsibility of the United States Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
, which was established in 1802. Earlier projects began as early as 1829 to remove snags, close off secondary channels and excavate rocks and sandbars.

 A series of 29 locks and dams on the upper Mississippi, most of which were built in the 1930s, is designed primarily to maintain a channel for commercial barge traffic. The lakes formed are also used for recreational boating and fishing. The dams make the river deeper and wider but do not stop it. No
A series of 29 locks and dams on the upper Mississippi, most of which were built in the 1930s, is designed primarily to maintain a channel for commercial barge traffic. The lakes formed are also used for recreational boating and fishing. The dams make the river deeper and wider but do not stop it. No flood control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water level ...
is intended. During periods of high flow, the gates, some of which are submersible, are completely opened and the dams simply cease to function. Below St. Louis, the Mississippi is relatively free-flowing, although it is constrained by numerous levees and directed by numerous wing dam
A wing dam or wing dike is a man made barrier that, unlike a conventional dam, only extends partway into a river. These structures force water into a fast-moving center channel which reduces the rate of sediment accumulation, while slowing water f ...
s. The scope and scale of the levees, built along either side of the river to keep it on its course, has often been compared to the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic grou ...
.
On the lower Mississippi, from Baton Rouge to the mouth of the Mississippi, the navigation depth is , allowing container ships and cruise ships to dock at the Port of New Orleans
The Port of New Orleans is an embarkation port for cruise passengers. It is also Louisiana’s only international container port.
The port generates $100 million in revenue annually through its four lines of business – cargo (46%), rail (31% ...
and bulk cargo ships shorter than air draft that fit under the Huey P. Long Bridge to traverse the Mississippi to Baton Rouge. There is a feasibility study to dredge this portion of the river to to allow New Panamax ship depths.
19th century
 In 1829, there were surveys of the two major obstacles on the upper Mississippi, the
In 1829, there were surveys of the two major obstacles on the upper Mississippi, the Des Moines Rapids
The Des Moines Rapids between Nauvoo, Illinois and Keokuk, Iowa-Hamilton, Illinois is one of two major rapids on the Mississippi River that limited Steamboat traffic on the river through the early 19th century.
The rapids just above the conf ...
and the Rock Island Rapids
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
, where the river was shallow and the riverbed was rock. The Des Moines Rapids were about long and just above the mouth of the Des Moines River at Keokuk, Iowa. The Rock Island Rapids were between Rock Island and Moline, Illinois
Moline ( ) is a city located in Rock Island County, Illinois, United States. With a population of 42,985 in 2020, it is the largest city in Rock Island County. Moline is one of the Quad Cities, along with neighboring East Moline and Rock Islan ...
. Both rapids were considered virtually impassable.
In 1848, the Illinois and Michigan Canal was built to connect the Mississippi River to Lake Michigan via the Illinois River near Peru, Illinois. The canal allowed shipping between these important waterways. In 1900, the canal was replaced by the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal
The Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal, historically known as the Chicago Drainage Canal, is a canal system that connects the Chicago River to the Des Plaines River. It reverses the direction of the Main Stem and the South Branch of the Chicago R ...
. The second canal, in addition to shipping, also allowed Chicago to address specific health issues (typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over severa ...
, cholera and other waterborne diseases) by sending its waste down the Illinois and Mississippi river systems rather than polluting its water source of Lake Michigan.
The Corps of Engineers recommended the excavation of a channel at the Des Moines Rapids, but work did not begin until after Lieutenant Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
endorsed the project in 1837. The Corps later also began excavating the Rock Island Rapids. By 1866, it had become evident that excavation was impractical, and it was decided to build a canal around the Des Moines Rapids. The canal opened in 1877, but the Rock Island Rapids remained an obstacle. In 1878, Congress authorized the Corps to establish a channel to be obtained by building wing dams that direct the river to a narrow channel causing it to cut a deeper channel, by closing secondary channels and by dredging. The channel project was complete when the Moline Lock, which bypassed the Rock Island Rapids, opened in 1907.
To improve navigation between St. Paul, Minnesota, and Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin, the Corps constructed several dams on lakes in the headwaters area, including Lake Winnibigoshish
Lake Winnibigoshish is a body of water in north central Minnesota in the Chippewa National Forest. Its name comes from the Ojibwe language ''Wiinibiigoonzhish'', a diminutive and pejorative form of ''Wiinibiig'', meaning "filthy water" (i.e., "b ...
and Lake Pokegama. The dams, which were built beginning in the 1880s, stored spring run-off which was released during low water to help maintain channel depth.


20th century
In 1907, Congress authorized a channel project on the Mississippi River, which was not complete when it was abandoned in the late 1920s in favor of the channel project. In 1913, construction was complete onLock and Dam No. 19
Lock and Dam No. 19 is a lock and dam located on the Upper Mississippi River near Keokuk, Iowa. In 2004, the facility was listed in the National Register of Historic Places as Lock and Dam No. 19 Historic District, #04000179 covering , 7 buildin ...
at Keokuk, Iowa, the first dam below St. Anthony Falls. Built by a private power company ( Union Electric Company of St. Louis) to generate electricity (originally for streetcars in St. Louis
Streetcars in St. Louis, Missouri operated as part of the transportation network of St. Louis from the middle of the 19th century through the early 1960s. During the first forty years of the streetcar in the city, a variety of private companies o ...
), the Keokuk dam was one of the largest hydro-electric plants in the world at the time. The dam also eliminated the Des Moines Rapids. Lock and Dam No. 1 was completed in Minneapolis, Minnesota in 1917. Lock and Dam No. 2
Lock and Dam No. 2 is located along the Upper Mississippi River near Hastings, Minnesota
Hastings is a city mostly in Dakota County, Minnesota, of which it is the county seat, with a portion in Washington County, Minnesota. It is near the c ...
, near Hastings, Minnesota, was completed in 1930.
Before the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927, the Corps's primary strategy was to close off as many side channels as possible to increase the flow in the main river. It was thought that the river's velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity i ...
would scour off bottom sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
s, deepening the river and decreasing the possibility of flooding. The 1927 flood proved this to be so wrong that communities threatened by the flood began to create their own levee breaks to relieve the force of the rising river.
The Rivers and Harbors Act of 1930 authorized the channel project, which called for a navigation channel feet deep and wide to accommodate multiple-barge tows. This was achieved by a series of locks and dams, and by dredging. Twenty-three new locks and dams were built on the upper Mississippi in the 1930s in addition to the three already in existence.

 Until the 1950s, there was no dam below Lock and Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois. Chain of Rocks Lock (Lock and Dam No. 27), which consists of a low-water dam and an canal, was added in 1953, just below the confluence with the Missouri River, primarily to bypass a series of rock ledges at St. Louis. It also serves to protect the St. Louis city water intakes during times of low water.
U.S. government scientists determined in the 1950s that the Mississippi River was starting to switch to the Atchafalaya River channel because of its much steeper path to the Gulf of Mexico. Eventually, the Atchafalaya River would capture the Mississippi River and become its main channel to the Gulf of Mexico, leaving New Orleans on a side channel. As a result, the U.S. Congress authorized a project called the Old River Control Structure, which has prevented the Mississippi River from leaving its current channel that drains into the Gulf via New Orleans.
Because the large scale of high-energy water flow threatened to damage the structure, an auxiliary flow control station was built adjacent to the standing control station. This $300 million project was completed in 1986 by the Corps of Engineers. Beginning in the 1970s, the Corps applied hydrological transport models to analyze flood flow and water quality of the Mississippi. Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois, which had structural problems, was replaced by the Mel Price Lock and Dam in 1990. The original Lock and Dam 26 was demolished.
Until the 1950s, there was no dam below Lock and Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois. Chain of Rocks Lock (Lock and Dam No. 27), which consists of a low-water dam and an canal, was added in 1953, just below the confluence with the Missouri River, primarily to bypass a series of rock ledges at St. Louis. It also serves to protect the St. Louis city water intakes during times of low water.
U.S. government scientists determined in the 1950s that the Mississippi River was starting to switch to the Atchafalaya River channel because of its much steeper path to the Gulf of Mexico. Eventually, the Atchafalaya River would capture the Mississippi River and become its main channel to the Gulf of Mexico, leaving New Orleans on a side channel. As a result, the U.S. Congress authorized a project called the Old River Control Structure, which has prevented the Mississippi River from leaving its current channel that drains into the Gulf via New Orleans.
Because the large scale of high-energy water flow threatened to damage the structure, an auxiliary flow control station was built adjacent to the standing control station. This $300 million project was completed in 1986 by the Corps of Engineers. Beginning in the 1970s, the Corps applied hydrological transport models to analyze flood flow and water quality of the Mississippi. Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois, which had structural problems, was replaced by the Mel Price Lock and Dam in 1990. The original Lock and Dam 26 was demolished.

21st century
The Corps now actively creates and maintains spillways and floodways to divert periodic water surges into backwater channels and lakes, as well as route part of the Mississippi's flow into the Atchafalaya Basin and from there to theGulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
, bypassing Baton Rouge and . The main structures are the Birds Point-New Madrid Floodway
The Birds Point-New Madrid Floodway is a flood control component of the Mississippi River and Tributaries Project located on the west bank of the Mississippi River in southeast Missouri just below the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers. ...
in Missouri; the Old River Control Structure and the Morganza Spillway in Louisiana, which direct excess water down the west and east sides (respectively) of the Atchafalaya River; and the Bonnet Carré Spillway, also in Louisiana, which directs floodwaters to Lake Pontchartrain
Lake Pontchartrain ( ) is an estuary located in southeastern Louisiana in the United States. It covers an area of with an average depth of . Some shipping channels are kept deeper through dredging. It is roughly oval in shape, about from w ...
(see diagram). Some experts blame urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
for increases in both the risk and frequency of flooding on the Mississippi River.
Some of the pre-1927 strategy remains in use today, with the Corps actively cutting the necks of horseshoe bends, allowing the water to move faster and reducing flood heights.
History
Approximately 50,000 years ago, the Central United States was covered by an inland sea, which was drained by the Mississippi and its tributaries into the Gulf of Mexico—creating largefloodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
s and extending the continent further to the south in the process. The soil in areas such as Louisiana was thereafter found to be very rich.
Native Americans
The area of the Mississippi River basin was firstsettled
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established a permanent residence there, often to colonize the area.
A settler who migrates to an area previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited may be described as a pioneer.
Settle ...
by hunting and gathering Native American peoples
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the Am ...
and is considered one of the few independent centers of plant domestication
Plant breeding started with sedentary agriculture, particularly the domestication of the first agricultural plants, a practice which is estimated to date back 9,000 to 11,000 years. Initially, early human farmers selected food plants with particula ...
in human history. Evidence of early cultivation of sunflower
The common sunflower (''Helianthus annuus'') is a large annual forb of the genus ''Helianthus'' grown as a crop for its edible oily seeds. Apart from cooking oil production, it is also used as livestock forage (as a meal or a silage plant), ...
, a goosefoot, a marsh elder
''Iva'' is a genus of wind-pollinated plants in the family Asteraceae, described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753. Plants of this genus are known generally as marsh elders. The genus is native to North America.
; Accepted species
* '' Iva angustif ...
and an indigenous squash dates to the 4th millennium BC. The lifestyle gradually became more settled after around 1000 BC during what is now called the Woodland period, with increasing evidence of shelter construction, pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
, weaving and other practices.
A network of trade routes referred to as the Hopewell interaction sphere was active along the waterways between about 200 and 500 AD, spreading common cultural practices over the entire area between the Gulf of Mexico and the Great Lakes. A period of more isolated communities followed, and agriculture introduced from Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
based on the Three Sisters (maize, beans and squash) gradually came to dominate. After around 800 AD there arose an advanced agricultural society today referred to as the Mississippian culture, with evidence of highly stratified
Stratification may refer to:
Mathematics
* Stratification (mathematics), any consistent assignment of numbers to predicate symbols
* Data stratification in statistics
Earth sciences
* Stable and unstable stratification
* Stratification, or st ...
complex chiefdoms and large population centers.
The most prominent of these, now called Cahokia, was occupied between about 600 and 1400 AD and at its peak numbered between 8,000 and 40,000 inhabitants, larger than London, England of that time. At the time of first contact with Europeans, Cahokia and many other Mississippian cities had dispersed, and archaeological finds attest to increased social stress.
Modern American Indian nations inhabiting the Mississippi basin include Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enr ...
, Sioux, Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
, Potawatomi, Ho-Chunk, Fox, Kickapoo, Tamaroa, Moingwena
The Moingona or Moingwena ( mia, mooyiinkweena) were a historic Miami-Illinois tribe. They may have been close allies of or perhaps part of the Peoria. They were assimilated by that tribe and lost their separate identity about 1700. Today their de ...
, Quapaw and Chickasaw.
The word ''Mississippi'' itself comes from ''Messipi'', the French rendering of the Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawa ...
(Ojibwe or Algonquin) name for the river, ''Misi-ziibi'' (Great River). The Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
called Lake Itasca ''Omashkoozo-zaaga'igan'' (Elk Lake) and the river flowing out of it ''Omashkoozo-ziibi'' (Elk River). After flowing into Lake Bemidji, the Ojibwe called the river ''Bemijigamaag-ziibi'' (River from the Traversing Lake). After flowing into Cass Lake, the name of the river changes to ''Gaa-miskwaawaakokaag-ziibi'' (Red Cedar River) and then out of Lake Winnibigoshish
Lake Winnibigoshish is a body of water in north central Minnesota in the Chippewa National Forest. Its name comes from the Ojibwe language ''Wiinibiigoonzhish'', a diminutive and pejorative form of ''Wiinibiig'', meaning "filthy water" (i.e., "b ...
as ''Wiinibiigoonzhish-ziibi'' (Miserable Wretched Dirty Water River), ''Gichi-ziibi'' (Big River) after the confluence with the Leech Lake River, then finally as ''Misi-ziibi'' (Great River) after the confluence with the Crow Wing River. After the expeditions by Giacomo Beltrami
Giacomo Costantino Beltrami (1779 – January 6, 1855) was an Italian jurist, author, and explorer, known for claiming to have discovered the headwaters of the Mississippi River in 1823 while on a trip through much of the United States (later exp ...
and Henry Schoolcraft, the longest stream above the juncture of the Crow Wing River and ''Gichi-ziibi'' was named "Mississippi River". The Mississippi River Band of Chippewa Indians Mississippi River Band of Chippewa Indians ( oj, Gichi-ziibiwininiwag) or simply the Mississippi Chippewa, are a historical Ojibwa Band inhabiting the headwaters of the Mississippi River and its tributaries in present-day Minnesota.
According to th ...
, known as the ''Gichi-ziibiwininiwag'', are named after the stretch of the Mississippi River known as the ''Gichi-ziibi''. The Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enr ...
, one of the earliest inhabitants of the upper Mississippi River, called it the ''Máʼxe-éʼometaaʼe'' (Big Greasy River) in the Cheyenne language. The Arapaho name for the river is ''Beesniicíe''. The Pawnee name is ''Kickaátit''.
The Mississippi was spelled during French Louisiana and was also known as the Rivière Saint-Louis.
European exploration


 In 1519 Spanish explorer Alonso Álvarez de Pineda became the first recorded European to reach the Mississippi River, followed by Hernando de Soto who reached the river on May 8, 1541, and called it ''Río del Espíritu Santo'' ("River of the Holy Spirit"), in the area of what is now Mississippi. In Spanish, the river is called ''Río Mississippi''.
French explorers Louis Jolliet and
In 1519 Spanish explorer Alonso Álvarez de Pineda became the first recorded European to reach the Mississippi River, followed by Hernando de Soto who reached the river on May 8, 1541, and called it ''Río del Espíritu Santo'' ("River of the Holy Spirit"), in the area of what is now Mississippi. In Spanish, the river is called ''Río Mississippi''.
French explorers Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette S.J. (June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded Saint Ign ...
began exploring the Mississippi in the 17th century. Marquette traveled with a Sioux Indian who named it ''Ne Tongo'' ("Big river" in Sioux language) in 1673. Marquette proposed calling it the ''River of the Immaculate Conception''.
When Louis Jolliet explored the Mississippi Valley in the 17th century, natives guided him to a quicker way to return to French Canada via the Illinois River. When he found the Chicago Portage
The Chicago Portage was an ancient portage that connected the Great Lakes waterway system with the Mississippi River system. Connecting these two great water trails meant comparatively easy access from the mouth of the St Lawrence River on the Atl ...
, he remarked that a canal of "only half a league
League or The League may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Leagues'' (band), an American rock band
* ''The League'', an American sitcom broadcast on FX and FXX about fantasy football
Sports
* Sports league
* Rugby league, full contact footba ...
" (less than ) would join the Mississippi and the Great Lakes. In 1848, the continental divide separating the waters of the Great Lakes and the Mississippi Valley was breached by the Illinois and Michigan canal via the Chicago River
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center (the Chicago Loop). Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons fo ...
. This both accelerated the development, and forever changed the ecology of the Mississippi Valley and the Great Lakes.
In 1682, René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle and Henri de Tonti claimed the entire Mississippi River valley for France, calling the river ''Colbert River'' after Jean-Baptiste Colbert and the region '' La Louisiane'', for King Louis XIV. On March 2, 1699, Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (16 July 1661 – 9 July 1706) or Sieur d'Iberville was a French soldier, explorer, colonial administrator, and trader. He is noted for founding the colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal to French ...
rediscovered the mouth of the Mississippi, following the death of La Salle."Pierre Le Moyne, Sieur d'Iberville" (bio), webpage from ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'', Volume VII, 1910, New YorkCathEn-07614b
. The French built the small fort of La Balise there to control passage. In 1718, about upriver, New Orleans was established along the river crescent by Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne, Sieur de Bienville, with construction patterned after the 1711 resettlement on Mobile Bay of Mobile, the capital of French Louisiana at the time. In 1727, Étienne Perier begins work, using enslaved African laborers, on the first levees on the Mississippi River.
Colonization
 Following Britain's victory in the Seven Years War, the Mississippi became the border between the British and
Following Britain's victory in the Seven Years War, the Mississippi became the border between the British and Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
s. The Treaty of Paris (1763) gave Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
rights to all land east of the Mississippi and Spain rights to land west of the Mississippi. Spain also ceded Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
to Britain to regain Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
, which the British occupied during the war. Britain then divided the territory into East and West Florida.
Article 8 of the Treaty of Paris (1783) states, "The navigation of the river Mississippi, from its source to the ocean, shall forever remain free and open to the subjects of Great Britain and the citizens of the United States". With this treaty, which ended the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, Britain also ceded West Florida back to Spain to regain the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the a ...
, which Spain had occupied during the war. Initial disputes around the ensuing claims of the U.S. and Spain were resolved when Spain was pressured into signing Pinckney's Treaty in 1795. However, in 1800, under duress from Napoleon of France, Spain ceded an undefined portion of West Florida to France in the secret Treaty of San Ildefonso. The United States then secured effective control of the river when it bought the Louisiana Territory from France in the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or ap ...
of 1803. This triggered a dispute between Spain and the U.S. on which parts of West Florida Spain had ceded to France in the first place, which would decide which parts of West Florida the U.S. had bought from France in the Louisiana Purchase, versus which were unceded Spanish property. Due to ongoing U.S. colonization creating facts on the ground, and U.S. military actions, Spain ceded both West and East Florida in their entirety to the United States in the Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p.168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and define ...
of 1819.
The last serious European challenge to U.S. control of the river came at the conclusion of the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
, when British forces mounted an attack on just 15 days after the signing of the Treaty of Ghent. The attack was repulsed by an American army under the command of General Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
.
In the Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 betw ...
, the U.S. and Great Britain agreed to fix the border running from the Lake of the Woods to the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
along the 49th parallel north. In effect, the U.S. ceded the northwestern extremity of the Mississippi basin to the British in exchange for the southern portion of the Red River basin.
So many settlers traveled westward through the Mississippi river basin, as well as settled in it, that Zadok Cramer wrote a guidebook called '' The Navigator'', detailing the features, dangers, and navigable waterways of the area. It was so popular that he updated and expanded it through 12 editions over 25 years.
 The colonization of the area was barely slowed by the three earthquakes in 1811 and 1812, estimated at 8 on the
The colonization of the area was barely slowed by the three earthquakes in 1811 and 1812, estimated at 8 on the Richter magnitude scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 p ...
, that were centered near New Madrid, Missouri.
Steamboat era
Mark Twain's book, '' Life on the Mississippi'', covered the steamboat commerce, which took place from 1830 to 1870, before more modern ships replaced the steamer. '' Harper's Weekly'' first published the book as a seven-part serial in 1875.James R. Osgood
James Ripley Osgood (1836–1892) was an American publisher in Boston. He was involved with the publishing company that became Houghton Mifflin.
Life and work
James Ripley Osgood was born in Fryeburg, Maine, on February 22, 1836. A reputed child ...
& Company published the full version, including a passage from the then unfinished ''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn
''Adventures of Huckleberry Finn'' or as it is known in more recent editions, ''The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn'', is a novel by American author Mark Twain, which was first published in the United Kingdom in December 1884 and in the United S ...
'' and works from other authors, in 1885.
The first steamboat to travel the full length of the Lower Mississippi from the Ohio River to New Orleans was the '''' in December 1811. Its maiden voyage occurred during the series of New Madrid earthquakes in 1811–12. The Upper Mississippi was treacherous, unpredictable and to make traveling worse, the area was not properly mapped out or surveyed. Until the 1840s, only two trips a year to the Twin Cities landings were made by steamboats, which suggests it was not very profitable.
Steamboat transport remained a viable industry, both in terms of passengers and freight, until the end of the first decade of the 20th century. Among the several Mississippi River system steamboat companies was the noted Anchor Line, which, from 1859 to 1898, operated a luxurious fleet of steamers between St. Louis and New Orleans.
Italian explorer Giacomo Beltrami wrote about his journey on the ''Virginia'', which was the first steamboat to make it to Fort St. Anthony in Minnesota. He referred to his voyage as a promenade that was once a journey on the Mississippi. The steamboat era changed the economic and political life of the Mississippi, as well as of travel itself. The Mississippi was completely changed by the steamboat era as it transformed into a flourishing tourist trade.
Civil War

 Control of the river was a strategic objective of both sides in the
Control of the river was a strategic objective of both sides in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
, forming a part of the U.S. Anaconda Plan. In 1862, Union forces coming down the river successfully cleared Confederate defenses at Island Number 10 and Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-mo ...
, while Naval forces coming upriver from the Gulf of Mexico captured . One of the last major Confederate strongholds was on the heights overlooking the river at Vicksburg, Mississippi; the Union's Vicksburg Campaign (December 1862–July 1863), and the fall of Port Hudson, completed control of the lower Mississippi River. The Union victory ended the Siege of Vicksburg on July 4, 1863, and was pivotal to the Union's final victory of the Civil War.
20th and 21st centuries
The "Big Freeze" of 1918–19 blocked river traffic north of Memphis, Tennessee, preventing transportation of coal from southern Illinois. This resulted in widespread shortages, high prices, and rationing of coal in January and February. In the spring of 1927, the river broke out of its banks in 145 places, during the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 and inundated to a depth of up to . In 1930, Fred Newton was the first person to swim the length of the river, from Minneapolis to New Orleans. The journey took 176 days and covered 1,836 miles. In 1962 and 1963, industrial accidents spilled ofsoybean oil
Soybean oil (British English: soyabean oil) is a vegetable oil extracted from the seeds of the soybean (''Glycine max''). It is one of the most widely consumed cooking oils and the second most consumed vegetable oil. As a drying oil, processe ...
into the Mississippi and Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over t ...
rivers. The oil covered the Mississippi River from St. Paul to Lake Pepin, creating an ecological disaster and a demand to control water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. ...
.
On October 20, 1976, the automobile ferry, '' MV George Prince'', was struck by a ship traveling upstream as the ferry attempted to cross from Destrehan, Louisiana, to Luling, Louisiana. Seventy-eight passengers and crew died; only eighteen survived the accident.
In 1988, the water level of the Mississippi fell to below zero on the Memphis gauge. The remains of wooden-hulled water craft were exposed in an area of on the bottom of the Mississippi River at West Memphis, Arkansas. They dated to the late 19th to early 20th centuries. The State of Arkansas, the Arkansas Archeological Survey, and the Arkansas Archeological Society responded with a two-month data recovery effort. The fieldwork received national media attention as good news in the middle of a drought.
The Great Flood of 1993 was another significant flood, primarily affecting the Mississippi above its confluence with the Ohio River at Cairo, Illinois.
Two portions of the Mississippi were designated as American Heritage Rivers
American Heritage Rivers were designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency in the 1990s to receive special attention (coordinating efforts of multiple governmental entities) to further three objectives: natural resource and envir ...
in 1997: the lower portion around Louisiana and Tennessee, and the upper portion around Iowa, Illinois, Minnesota, Missouri and Wisconsin. The Nature Conservancy's project called "America's Rivershed Initiative" announced a 'report card' assessment of the entire basin in October 2015 and gave the grade of D+. The assessment noted the aging navigation and flood control infrastructure along with multiple environmental problems.
 In 2002,
In 2002, Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
n long-distance swimmer Martin Strel
Martin Strel (; born 1 October 1954), is a Slovenian long-distance swimmer, one of the most elite endurance athletes best known for swimming the entire length of various rivers. Strel holds successive Guinness World Records for swimming the ...
swam the entire length of the river, from Minnesota to Louisiana, over the course of 68 days. In 2005, the Source to Sea Expedition paddled the Mississippi and Atchafalaya Rivers to benefit the Audubon Society's Upper Mississippi River Campaign.
Future
Geologists believe that the lower Mississippi could take a new course to the Gulf. Either of two new routes—through the Atchafalaya Basin or throughLake Pontchartrain
Lake Pontchartrain ( ) is an estuary located in southeastern Louisiana in the United States. It covers an area of with an average depth of . Some shipping channels are kept deeper through dredging. It is roughly oval in shape, about from w ...
—might become the Mississippi's main channel if flood-control structures are overtopped or heavily damaged during a severe flood.
Failure of the Old River Control Structure, the Morganza Spillway, or nearby levees would likely re-route the main channel of the Mississippi through Louisiana's Atchafalaya Basin and down the Atchafalaya River to reach the Gulf of Mexico south of Morgan City in southern Louisiana. This route provides a more direct path to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
than the present Mississippi River channel through Baton Rouge and . While the risk of such a diversion is present during any major flood event, such a change has so far been prevented by active human intervention involving the construction, maintenance, and operation of various levees, spillways, and other control structures by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
.
 The Old River Control Structure, between the present Mississippi River channel and the Atchafalaya Basin, sits at the normal water elevation and is ordinarily used to divert 30% of the Mississippi flow to the Atchafalaya River. There is a steep drop here away from the Mississippi's main channel into the Atchafalaya Basin. If this facility were to fail during a major flood, there is a strong concern the water would
The Old River Control Structure, between the present Mississippi River channel and the Atchafalaya Basin, sits at the normal water elevation and is ordinarily used to divert 30% of the Mississippi flow to the Atchafalaya River. There is a steep drop here away from the Mississippi's main channel into the Atchafalaya Basin. If this facility were to fail during a major flood, there is a strong concern the water would scour
Scour may refer to:
Hydrodynamic processes
* Hydrodynamic scour, the removal of sediment such as sand and silt from around an object
* Bridge scour, erosion of soil around at the base of a bridge pier or abutments via the flow of air, ice, or ...
and erode the river bottom enough to capture the Mississippi's main channel. The structure was nearly lost during the 1973 flood, but repairs and improvements were made after engineers studied the forces at play. In particular, the Corps of Engineers made many improvements and constructed additional facilities for routing water through the vicinity. These additional facilities give the Corps much more flexibility and potential flow capacity than they had in 1973, which further reduces the risk of a catastrophic failure in this area during other major floods, such as that of 2011.
Because the Morganza Spillway is slightly higher and well back from the river, it is normally dry on both sides. Even if it failed at the crest during a severe flood, the floodwaters would have to erode to normal water levels before the Mississippi could permanently jump channel at this location. During the 2011 floods, the Corps of Engineers opened the Morganza Spillway to 1/4 of its capacity to allow of water to flood the Morganza and Atchafalaya floodways and continue directly to the Gulf of Mexico, bypassing Baton Rouge and New Orleans.Estimated Inundation(US Army Corps of Engineers) In addition to reducing the Mississippi River crest downstream, this diversion reduced the chances of a channel change by reducing stress on the other elements of the control system. Some geologists have noted that the possibility for course change into the Atchafalaya also exists in the area immediately north of the Old River Control Structure. Army Corps of Engineers geologist Fred Smith once stated, "The Mississippi wants to go west. 1973 was a forty-year flood. The big one lies out there somewhere—when the structures can't release all the floodwaters and the levee is going to have to give way. That is when the river's going to jump its banks and try to break through." Another possible course change for the Mississippi River is a diversion into
Lake Pontchartrain
Lake Pontchartrain ( ) is an estuary located in southeastern Louisiana in the United States. It covers an area of with an average depth of . Some shipping channels are kept deeper through dredging. It is roughly oval in shape, about from w ...
near . This route is controlled by the Bonnet Carré Spillway, built to reduce flooding in New Orleans. This spillway and an imperfect natural levee about high are all that prevents the Mississippi from taking a new, shorter course through Lake Pontchartrain to the Gulf of Mexico. Diversion of the Mississippi's main channel through Lake Pontchartrain would have consequences similar to an Atchafalaya diversion, but to a lesser extent, since the present river channel would remain in use past Baton Rouge and into the New Orleans area.
Recreation
 The sport of water skiing was invented on the river in a wide region between Minnesota and Wisconsin known as Lake Pepin.
The sport of water skiing was invented on the river in a wide region between Minnesota and Wisconsin known as Lake Pepin. Ralph Samuelson
Ralph Wilford Samuelson (July 3, 1903 – August 28, 1977) was the inventor of water skiing, which he first performed in the summer of 1922 in Lake City, Minnesota, just before his 19th birthday. Samuelson was already skilled at aquaplaning—st ...
of Lake City, Minnesota, created and refined his skiing technique in late June and early July 1922. He later performed the first water ski jump in 1925 and was pulled along at by a Curtiss flying boat later that year.
There are seven National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properti ...
sites along the Mississippi River. The Mississippi National River and Recreation Area is the National Park Service site dedicated to protecting and interpreting the Mississippi River itself. The other six National Park Service sites along the river are (listed from north to south):
* Effigy Mounds National Monument
Effigy Mounds National Monument preserves more than 200 prehistoric mounds built by pre-Columbian
Mound Builder cultures, mostly in the first millennium CE, during the later part of the Woodland period of pre-Columbian North America.
Numerous ...
* Gateway Arch National Park (includes Gateway Arch)
* Vicksburg National Military Park
* Natchez National Historical Park
* New Orleans Jazz National Historical Park
* Jean Lafitte National Historical Park and Preserve
Ecology
 The Mississippi basin is home to a highly diverse aquatic
The Mississippi basin is home to a highly diverse aquatic fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is '' flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. ...
and has been called the "mother fauna" of North American freshwater.
Fish
About 375 fish species are known from the Mississippi basin, far exceeding other North Hemisphere river basins exclusively within temperate/subtropical regions, except the Yangtze. Within the Mississippi basin, streams that have their source in the Appalachian and Ozark highlands contain especially many species. Among the fish species in the basin are numerousendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
s, as well as relicts such as paddlefish
Paddlefish (family Polyodontidae) are a family of ray-finned fish belonging to order Acipenseriformes, and one of two living groups of the order alongside sturgeons (Acipenseridae). They are distinguished from other fish by their titular elong ...
, sturgeon, gar and bowfin.
Because of its size and high species diversity, the Mississippi basin is often divided into subregions. The Upper Mississippi River alone is home to about 120 fish species, including walleye, sauger, largemouth bass
The largemouth bass (''Micropterus salmoides'') is a carnivorous freshwater gamefish in the Centrarchidae ( sunfish) family, a species of black bass native to the eastern and central United States, southeastern Canada and northern Mexico, ...
, smallmouth bass, white bass
The white bass, silver bass, or sand bass (''Morone chrysops'') is a freshwater fish of the temperate bass family Moronidae. commonly around 12-15 inches long. The species' main color is silver-white to pale green. Its back is dark, with white s ...
, northern pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (the pikes). They are typical of brackish water, brackish and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). They are kno ...
, bluegill, crappie, channel catfish, flathead catfish, common shiner, freshwater drum
The freshwater drum, ''Aplodinotus grunniens'', is a fish endemic to North and Central America. It is the only species in the genus ''Aplodinotus'', and is a member of the family Sciaenidae. It is the only North American member of the group that ...
, and shovelnose sturgeon
The shovelnose sturgeon (''Scaphirhynchus platorynchus'') is the smallest species of freshwater sturgeon native to North America. It is often called "hackleback", "sand sturgeon", or "switchtail". Switchtail refers to the long filament found on ...
.
Other fauna
A large number of reptiles are native to the river channels and basin, including American alligators, several species of turtle, aquatic amphibians, and cambaridae crayfish, are native to the Mississippi basin. In addition, approximately 40% of themigratory birds
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting b ...
in the US use the Mississippi River corridor during Spring and Fall migrations; 60% of all migratory birds in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
(326 species) use the river basin as their flyway.
Introduced species
Numerousintroduced species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there ...
are found in the Mississippi and some of these are invasive. Among the introductions are fish such as Asian carp, including the silver carp that have become infamous for out-competing native fish and their potentially dangerous jumping behavior. They have spread throughout much of the basin, even approaching (but not yet invading) the Great Lakes. The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources
The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, or Minnesota DNR, is the agency of the U.S. state of Minnesota charged with conserving and managing the state's natural resources. The agency maintains areas such as state parks, state forests, rec ...
has designated much of the Mississippi River in the state as infested waters by the exotic species zebra mussels and Eurasian watermilfoil
''Myriophyllum spicatum'' (Eurasian watermilfoil or spiked water-milfoil) is native to Europe, Asia, and north Africa, but has a wide geographic and climatic distribution among some 57 countries, extending from northern Canada to South Africa. ...
.
See also
* Atchafalaya Basin * Capes on the Mississippi River * Chemetco * Great River Road * List of crossings of the Lower Mississippi River * List of crossings of the Upper Mississippi River * List of locks and dams of the Upper Mississippi River *List of tributaries of the Mississippi River __TOC__
This is a sortable list of tributaries of the Mississippi River.
Table
{, class="wikitable sortable center alternance"
, -
! Waterway
! Orientation
! Length (km)
! Mouth coordinates
! Mouth location
! Source coordinates
! Source location ...
* List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem)
* Mississippi embayment
* Mississippi River floods
The Mississippi River and its tributaries have flooded on numerous occasions. This is a list of major floods.
Flood of March 1543
Hernando de Soto's party was passing through a village at the confluence of the Mississippi River and Arkansas ...
* Mississippi River System
* ''The Waterways Journal Weekly
The ''Waterways Journal Weekly'' is the news journal of record for the towing and barge industry on the inland waterways of the United States, chiefly the watershed of the Mississippi River and its tributaries and the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway ...
''
* Upper Mississippi River National Wildlife and Fish Refuge
The Upper Mississippi River National Wildlife and Fish Refuge is a ,online
(PDF) * Daniel, Pete. ''Deep'n as it come: The 1927 Mississippi River flood'' (University of Arkansas Press, 1977) * Fremling, Calvin R. ''Immortal river: the Upper Mississippi in ancient and modern times'' (U. of Wisconsin Press, 2005), popular history * Milner, George R. "The late prehistoric Cahokia cultural system of the Mississippi River valley: Foundations, florescence, and fragmentation." ''Journal of World Prehistory'' (1990) 4#1 pp: 1–43. * Morris, Christopher. ''The Big Muddy: An Environmental History of the Mississippi and Its Peoples From Hernando de Soto to Hurricane Katrina'' (Oxford University Press; 2012) 300 pages; links drought, disease, and flooding to the impact of centuries of increasingly intense human manipulation of the river. * * * *
Mississippi River
project of the American Land Conservancy
Flood management in the Mississippi River
Friends of the Mississippi River
*
Mississippi River Challengeannual canoe & kayak event on the Twin Cities stretch
*
Mississippi River Field Guide
{{Authority control . American Heritage Rivers Borders of Arkansas Borders of Illinois Borders of Iowa Borders of Kentucky Borders of Louisiana Borders of Minnesota Borders of Mississippi Borders of Missouri Borders of Tennessee Borders of Wisconsin Rivers of Arkansas Rivers of Illinois Rivers of Iowa Rivers of Kentucky Rivers of Louisiana Rivers of Minnesota Rivers of Mississippi Rivers of Missouri Rivers of Tennessee Rivers of Wisconsin Mississippi embayment
(PDF) * Daniel, Pete. ''Deep'n as it come: The 1927 Mississippi River flood'' (University of Arkansas Press, 1977) * Fremling, Calvin R. ''Immortal river: the Upper Mississippi in ancient and modern times'' (U. of Wisconsin Press, 2005), popular history * Milner, George R. "The late prehistoric Cahokia cultural system of the Mississippi River valley: Foundations, florescence, and fragmentation." ''Journal of World Prehistory'' (1990) 4#1 pp: 1–43. * Morris, Christopher. ''The Big Muddy: An Environmental History of the Mississippi and Its Peoples From Hernando de Soto to Hurricane Katrina'' (Oxford University Press; 2012) 300 pages; links drought, disease, and flooding to the impact of centuries of increasingly intense human manipulation of the river. * * * *
External links
Mississippi River
project of the American Land Conservancy
Flood management in the Mississippi River
Friends of the Mississippi River
*
Mississippi River Challengeannual canoe & kayak event on the Twin Cities stretch
*
Mississippi River Field Guide
{{Authority control . American Heritage Rivers Borders of Arkansas Borders of Illinois Borders of Iowa Borders of Kentucky Borders of Louisiana Borders of Minnesota Borders of Mississippi Borders of Missouri Borders of Tennessee Borders of Wisconsin Rivers of Arkansas Rivers of Illinois Rivers of Iowa Rivers of Kentucky Rivers of Louisiana Rivers of Minnesota Rivers of Mississippi Rivers of Missouri Rivers of Tennessee Rivers of Wisconsin Mississippi embayment