Melasma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Melasma (also known as chloasma faciei,James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . or the mask of pregnancy when present in pregnant women) is a tan or dark skin discoloration. Melasma is thought to be caused by sun exposure, genetic predisposition, hormone changes, and skin irritation. Although it can affect anyone, it is particularly common in women, especially pregnant women and those who are taking
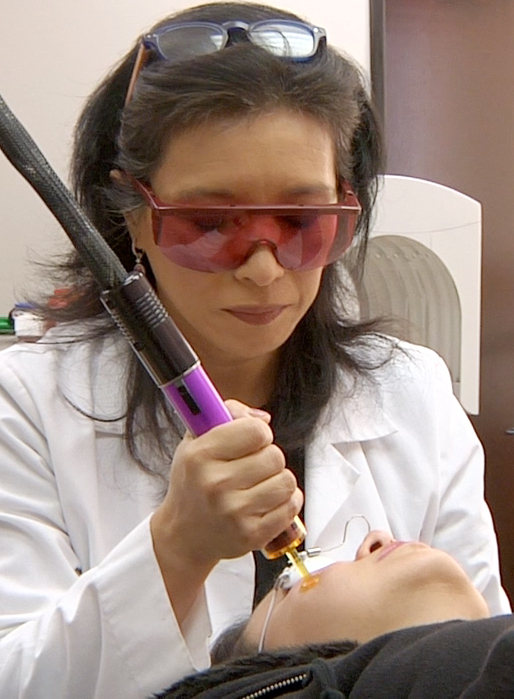 Assessment by a dermatologist can help guide treatment. Treatments to hasten the fading of the discolored patches include:
* Topical depigmenting agents, such as
Assessment by a dermatologist can help guide treatment. Treatments to hasten the fading of the discolored patches include:
* Topical depigmenting agents, such as
oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
or patch contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. Effects of menopause can include symptoms such ...
medications.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of melasma are dark, irregular, well-demarcated, hyperpigmented macules to patches. These patches often develop gradually over time. Melasma does not cause any other symptoms beyond the cosmetic discoloration. Patches can vary in size from to larger than depending on the person. Its location can be categorized as centrofacial, malar, or mandibular. The most common is centrofacial, in which patches appear on the cheeks, nose, upper lip, forehead, and chin. The mandibular category accounts for patches on the bilateral rami, while the malar location accounts for patches only on the nose and cheeks.Cause
The exact cause of melasma is unknown. Melasma is thought to be the stimulation ofmelanocyte
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural-crest, neural crest-derived cell (biology), cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis (skin), epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vagina ...
s (cells in the dermal
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
layer, which transfer the pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
melanin
Melanin (; ) is a family of biomolecules organized as oligomers or polymers, which among other functions provide the pigments of many organisms. Melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes.
There are ...
to the keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referre ...
s of skin) when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet light from the sun. Small amounts of sun exposure can make melasma return to the skin after it has faded, which is why people with melasma often get it again and again, particularly in the summer.
Pregnant women often get melasma, or chloasma, known as the mask of pregnancy. Birth-control pills and hormone replacement therapy also can trigger melasma. The discoloration usually disappears spontaneously over a period of several months after giving birth or stopping the oral contraceptives or hormone treatment.
Genetic predisposition is also a major factor in determining whether someone will develop melasma. People with the Fitzpatrick skin type III or greater from African, Asian, or Hispanic descent are at a much higher risk than others. In addition, women with a light brown skin type who are living in regions with intense sun exposure are particularly susceptible to developing this condition.
The incidence of melasma also increases in patients with thyroid disease. It is thought that the overproduction of melanocyte-stimulating hormone
The melanocyte-stimulating hormones, known collectively as MSH, also known as melanotropins or intermedins, are a family of peptide hormones and neuropeptides consisting of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), β-melanocyte-stimulating ...
brought on by stress can cause outbreaks of this condition. Other rare causes of melasma include allergic reaction to medications and cosmetics.
Addison's disease
Melasma suprarenale (Latin: 'above the kidneys') is a symptom of Addison's disease, particularly when caused by pressure or minor injury to the skin, as discovered by FJJ Schmidt of Rotterdam in 1859.Diagnosis
Types
The two different kinds of melasma are epidermal and dermal. *Epidermal melasma results from melanin pigment that is elevated in the suprabasal layers of the epidermis. *Dermal melasma occurs when the dermal macrophages have an elevated melanin level. Melasma is usually diagnosed visually or with assistance of a Wood's lamp (340–400 nm wavelength). Under Wood's lamp, excess melanin in the epidermis can be distinguished from that of the dermis. This is done by looking at how dark the melasma appears; dermal melasma appears darker than epidermal melasma under the Wood's lamp.Severity
The severity of facial melasma may be assessed by colorimetry, mexametry, and the melasma area and severity index (MASI) score.Differential diagnoses
Melasma should be differentiated from freckles, solar lentigo, toxic melanoderma, Riehl melanosis, post-inflammatoryhyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation, also known as the dark spots or circles on the skin, is the darkening of an area of Human skin, skin or nail (anatomy), nails caused by increased melanin.
Causes
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by sun damage, inflammation, or ...
, friction melanosis, ochronosis
Ochronosis is a syndrome caused by the accumulation of homogentisic acid in connective tissues. The condition was named after the yellowish (ocher-like) discoloration of the tissue seen on microscopic examination. Macroscopically, though, the af ...
(endogenous and exogenous), and cutaneous erythematosus lupus. Additionally, it should not be confused with phytophotodermatosis, pellagra
Pellagra is a disease caused by a lack of the vitamin niacin (vitamin B3). Symptoms include inflamed skin, diarrhea, dementia, and sores in the mouth. Areas of the skin exposed to friction and radiation are typically affected first. Over tim ...
, endogenous phototoxicity, nevus of Ota, café au lait macules, seborrheic keratosis, Poikiloderma of Civatte, acquired bilateral nevus of ota-like macules ( Hori's nevus), periorbital hyperpigmentation, erythrose pigmentaire peribuccale of Brocq, erythromelanosis follicularis faciei, facial acanthosis nigricans, and actinic lichen planus.
Also, cases of drug-induced pigmentation have been reported, caused by amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and wide complex tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and paroxys ...
, or hydroquinone-induced exogenous ochronosis (see ochronosis treatment).
Treatment
 Assessment by a dermatologist can help guide treatment. Treatments to hasten the fading of the discolored patches include:
* Topical depigmenting agents, such as
Assessment by a dermatologist can help guide treatment. Treatments to hasten the fading of the discolored patches include:
* Topical depigmenting agents, such as hydroquinone
Hydroquinone, also known as benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene, having the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a ''para' ...
(HQ) either in over-the-counter (OTC – 2%) or prescription (4%) strength. HQ inhibits tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in the production of melanin
Melanin (; ) is a family of biomolecules organized as oligomers or polymers, which among other functions provide the pigments of many organisms. Melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes.
There are ...
.
* Tretinoin
Tretinoin, also known as all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For acute promyelocytic leukemia, ...
, a retinoid
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are natural derivatives of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Synthetic retinoids are utilized in cosmetic formulations, clinical dermatology, and the treatment of some forms of cancer ...
, increases skin cell (keratinocyte) turnover. This treatment is not used during pregnancy due to risk of harm to the fetus.
* Azelaic acid
Azelaic acid (AzA), or nonanedioic acid, is an organic compound with the formula HOOC(CH2)7carboxylic acid, COOH. This saturated dicarboxylic acid exists as a white powder. It is found in wheat, rye, and barley. It is a precursor to diverse ind ...
(20%) is thought to decrease the activity of melanocytes.
* Tranexamic acid by mouth has shown to provide rapid and sustained lightening in melasma by decreasing melanogenesis in epidermal melanocytes.
* Cysteamine hydrochloride (5%) over-the-counter Mechanism of action seems to involve inhibition of melanin synthesis pathway
* Kojic acid (2%) OTC
* Alpha Arbutin 2–5% OTC
* Flutamide (1%)
* Chemical peels
A chemical peel is a treatment used to improve and smooth the texture of the skin. The skin on the face is most commonly treated, but peels can also be performed on the body. Chemical peels are intended to remove the outermost layers of the skin ...
* Microdermabrasion to dermabrasion (light to deep)
* Galvanic or ultrasound facials with a combination of a topical crème/gel, either in an aesthetician's office or as a home massager unit
* Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
but not intense pulsed light (which can make the melasma darker)
* Melatonin helps regulate melasma.
Effectiveness
Evidence-based reviews found that the most effective therapy for melasma includes a combination of topical agents. Triple combination creams formulated withhydroquinone
Hydroquinone, also known as benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene, having the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a ''para' ...
, tretinoin
Tretinoin, also known as all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For acute promyelocytic leukemia, ...
, and a steroid component have shown to be more effective than dual combination therapy or hydroquinone alone. More recently, a systematic review found that oral medications also have a role in melasma treatment, and have been shown to be efficacious with a minimal number and severity of adverse events. Oral medications and dietary supplements employed in the treatment of melasma include tranexamic acid, '' Polypodium leucotomos'' extract, beta‐carotenoid, melatonin, and procyanidin.
Oral procyanidin combined with vitamins A, C, and E shows promise as safe and effective for epidermal melasma. In an 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 56 Filipino women, treatment was associated with significant improvements in the left and right malar regions, and was safe and well tolerated.
In all of these treatments, the effects are gradual and a strict avoidance of sunlight is required. The use of broad-spectrum sunscreens with physical blockers, such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, is preferred, because UV-A, UV-B, and visible lights are all capable of stimulating pigment production.
Many negative side effects can go along with these treatments, and treatments often are unsatisfying overall. Scarring, irritation, lighter patches of skin, and contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes ...
are all commonly seen. Patients should avoid other precipitants, including hormonal triggers. Cosmetic camouflage can also be used to hide melasma.
See also
* Linea nigra *List of cutaneous conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the Human body, body and composed of Human skin, skin, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function o ...
References
External links
* {{Infants and their care Disturbances of human pigmentation Human pregnancy