Molecular formula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of
 Molecular formulae simply indicate the numbers of each type of atom in a molecule of a molecular substance. They are the same as empirical formulae for molecules that only have one atom of a particular type, but otherwise may have larger numbers. An example of the difference is the empirical formula for glucose, which is (''ratio'' 1:2:1), while its molecular formula is (''number of atoms'' 6:12:6). For water, both formulae are . A molecular formula provides more information about a molecule than its empirical formula, but is more difficult to establish.
Molecular formulae simply indicate the numbers of each type of atom in a molecule of a molecular substance. They are the same as empirical formulae for molecules that only have one atom of a particular type, but otherwise may have larger numbers. An example of the difference is the empirical formula for glucose, which is (''ratio'' 1:2:1), while its molecular formula is (''number of atoms'' 6:12:6). For water, both formulae are . A molecular formula provides more information about a molecule than its empirical formula, but is more difficult to establish.
 The @ symbol (
The @ symbol (
Hill notation example
from the University of Massachusetts Lowell libraries, including how to sort into Hill system order
Molecular formula calculation applying Hill notation
The library calculating Hill notation i
available on npm
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chemical Formula Chemical nomenclature Notation
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s that constitute a particular chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
or molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
, using chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structure
A chemical structure of a molecule is a spatial arrangement of its atoms and their chemical bonds. Its determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target m ...
s, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substance
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be com ...
s, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms of each type. Molecular formulae indicate the simple numbers of each type of atom in a molecule, with no information on structure. For example, the empirical formula for glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
is (twice as many hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atoms as carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
), while its molecular formula is (12 hydrogen atoms, six carbon and oxygen atoms).
Sometimes a chemical formula is complicated by being written as a condensed formula (or condensed molecular formula, occasionally called a "semi-structural formula"), which conveys additional information about the particular ways in which the atoms are chemically bonded together, either in covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
s, ionic bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic ...
s, or various combinations of these types. This is possible if the relevant bonding is easy to show in one dimension. An example is the condensed molecular/chemical formula for ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
, which is or . However, even a condensed chemical formula is necessarily limited in its ability to show complex bonding relationships between atoms, especially atoms that have bonds to four or more different substituent
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.
The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond r ...
s.
Since a chemical formula must be expressed as a single line of chemical element symbols, it often cannot be as informative as a true structural formula, which is a graphical representation of the spatial relationship between atoms in chemical compounds (see for example the figure for butane structural and chemical formulae, at right). For reasons of structural complexity, a single condensed chemical formula (or semi-structural formula) may correspond to different molecules, known as isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
s. For example, glucose shares its molecular formula with a number of other sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
s, including fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
, galactose
Galactose (, ''wikt:galacto-, galacto-'' + ''wikt:-ose#Suffix 2, -ose'', ), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweetness, sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. It is an aldohexose and a C-4 epime ...
and mannose
Mannose is a sugar with the formula , which sometimes is abbreviated Man. It is one of the monomers of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylatio ...
. Linear equivalent chemical ''names'' exist that can and do specify uniquely any complex structural formula (see chemical nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic name#In chemistry, systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Appli ...
), but such names must use many terms (words), rather than the simple element symbols, numbers, and simple typographical symbols that define a chemical formula.
Chemical formulae may be used in chemical equation
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and chemical formulas. The reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the Product (chemistry), product entities are on the right-hand side ...
s to describe chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
s and other chemical transformations, such as the dissolving of ionic compounds into solution. While, as noted, chemical formulae do not have the full power of structural formulae to show chemical relationships between atoms, they are sufficient to keep track of numbers of atoms and numbers of electrical charges in chemical reactions, thus balancing chemical equations so that these equations can be used in chemical problems involving conservation of atoms, and conservation of electric charge.
Overview
A chemical formula identifies each constituent element by itschemical symbol
Chemical symbols are the abbreviations used in chemistry, mainly for chemical elements; but also for functional groups, chemical compounds, and other entities. Element symbols for chemical elements, also known as atomic symbols, normally consist ...
and indicates the proportionate number of atoms of each element. In empirical formulae, these proportions begin with a key element and then assign numbers of atoms of the other elements in the compound, by ratios to the key element. For molecular compounds, these ratio numbers can all be expressed as whole numbers. For example, the empirical formula of ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
may be written because the molecules of ethanol all contain two carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom. Some types of ionic compounds, however, cannot be written with entirely whole-number empirical formulae. An example is boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,
as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers har ...
, whose formula of is a variable non-whole number ratio with n ranging from over 4 to more than 6.5.
When the chemical compound of the formula consists of simple molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s, chemical formulae often employ ways to suggest the structure of the molecule. These types of formulae are variously known as ''molecular formulae'' and '' condensed formulae''. A molecular formula enumerates the number of atoms to reflect those in the molecule, so that the molecular formula for glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
is rather than the glucose empirical formula, which is . However, except for very simple substances, molecular chemical formulae lack needed structural information, and are ambiguous.
For simple molecules, a condensed (or semi-structural) formula is a type of chemical formula that may fully imply a correct structural formula. For example, ethanol may be represented by the condensed chemical formula , and dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3,
(sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor ...
by the condensed formula . These two molecules have the same empirical and molecular formulae (), but may be differentiated by the condensed formulae shown, which are sufficient to represent the full structure of these simple organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
s.
Condensed chemical formulae may also be used to represent ionic compound
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (Cation, cations) and negatively charged ions (Anion, anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrica ...
s that do not exist as discrete molecules, but nonetheless do contain covalently bound clusters within them. These polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion (also known as a molecular ion) is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that usually has a net charge that is not zero, or in special c ...
s are groups of atoms that are covalently bound together and have an overall ionic charge, such as the sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
ion. Each polyatomic ion in a compound is written individually in order to illustrate the separate groupings. For example, the compound dichlorine hexoxide has an empirical formula , and molecular formula , but in liquid or solid forms, this compound is more correctly shown by an ionic condensed formula , which illustrates that this compound consists of ions and ions. In such cases, the condensed formula only need be complex enough to show at least one of each ionic species.
Chemical formulae as described here are distinct from the far more complex chemical systematic names that are used in various systems of chemical nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic name#In chemistry, systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Appli ...
. For example, one systematic name for glucose is (2''R'',3''S'',4''R'',5''R'')-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal. This name, interpreted by the rules behind it, fully specifies glucose's structural formula, but the name is not a chemical formula as usually understood, and uses terms and words not used in chemical formulae. Such names, unlike basic formulae, may be able to represent full structural formulae without graphs.
Types
Empirical formula
Inchemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, the empirical formula of a chemical is a simple expression of the relative number of each type of atom or ratio of the elements in the compound. Empirical formulae are the standard for ionic compound
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (Cation, cations) and negatively charged ions (Anion, anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrica ...
s, such as , and for macromolecules, such as . An empirical formula makes no reference to isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
ism, structure, or absolute number of atoms. The term ''empirical'' refers to the process of elemental analysis
Elemental analysis is a process where a sample of some material (e.g., soil, waste or drinking water, bodily fluids, minerals, chemical compounds) is analyzed for its elemental and sometimes isotopic composition. Elemental analysis can be qualita ...
, a technique of analytical chemistry
Analytical skill, Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to Separation process, separate, identify, and Quantification (science), quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute t ...
used to determine the relative percent composition of a pure chemical substance by element.
For example, hexane
Hexane () or ''n''-hexane is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms and the molecular formula C6H14.
Hexane is a colorless liquid, odorless when pure, and with a boiling point of approximately . It is widely used as ...
has a molecular formula of , and (for one of its isomers, n-hexane) a structural formula , implying that it has a chain structure of 6 carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atoms, and 14 hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atoms. However, the empirical formula for hexane is . Likewise the empirical formula for hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
, , is simply , expressing the 1:1 ratio of component elements. Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as ...
and acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
have the same empirical formula, . This is also the molecular formula for formaldehyde, but acetic acid has double the number of atoms.
Like the other formula types detailed below, an empirical formula shows the number of elements in a molecule, and determines whether it is a binary compound, ternary compound
In inorganic chemistry and materials chemistry, a ternary compound or ternary phase is a chemical compound containing three different elements.
While some ternary compounds are molecular, ''e.g.'' chloroform (), more typically ternary phases r ...
, quaternary compound, or has even more elements.
Molecular formula
Structural formula
In addition to indicating the number of atoms of each elementa molecule, a structural formula indicates how the atoms are organized, and shows (or implies) thechemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons a ...
s between the atoms. There are multiple types of structural formulas focused on different aspects of the molecular structure.
The two diagrams show two molecules which are structural isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a compound is a compound that contains the same number and type of atoms, but with a different connectivity (i.e. arrangement of bonds) between them. The ...
s of each other, since they both have the same molecular formula , but they have different structural formulas as shown.
Condensed formula
The connectivity of a molecule often has a strong influence on its physical and chemical properties and behavior. Two molecules composed of the same numbers of the same types of atoms (i.e. a pair ofisomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
s) might have completely different chemical and/or physical properties if the atoms are connected differently or in different positions. In such cases, a structural formula is useful, as it illustrates which atoms are bonded to which other ones. From the connectivity, it is often possible to deduce the approximate shape of the molecule.
A condensed (or semi-structural) formula may represent the types and spatial arrangement of bonds in a simple chemical substance, though it does not necessarily specify isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
s or complex structures. For example, ethane
Ethane ( , ) is a naturally occurring Organic compound, organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is List of purification methods ...
consists of two carbon atoms single-bonded to each other, with each carbon atom having three hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Its chemical formula can be rendered as . In ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon doub ...
there is a double bond between the carbon atoms (and thus each carbon only has two hydrogens), therefore the chemical formula may be written: , and the fact that there is a double bond between the carbons is implicit because carbon has a valence of four. However, a more explicit method is to write or less commonly . The two lines (or two pairs of dots) indicate that a double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
connects the atoms on either side of them.
A triple bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six Electron pair bond, bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent bond, covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent covalent bond, sin ...
may be expressed with three lines () or three pairs of dots (), and if there may be ambiguity, a single line or pair of dots may be used to indicate a single bond.
Molecules with multiple functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
s that are the same may be expressed by enclosing the repeated group in round brackets. For example, isobutane may be written . This condensed structural formula implies a different connectivity from other molecules that can be formed using the same atoms in the same proportions (isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
s). The formula implies a central carbon atom connected to one hydrogen atom and three methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated a ...
s (). The same number of atoms of each element (10 hydrogens and 4 carbons, or ) may be used to make a straight chain molecule, ''n''-butane
Butane () is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane exists as two isomers, ''n''-butane with connectivity and iso-butane with the formula . Both isomers are highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gases that quickly vaporize at ro ...
: .
Chemical names in answer to limitations of chemical formulae
The alkene called but-2-ene has two isomers, which the chemical formula does not identify. The relative position of the two methyl groups must be indicated by additional notation denoting whether the methyl groups are on the same side of the double bond (''cis'' or ''Z'') or on the opposite sides from each other (''trans'' or ''E''). As noted above, in order to represent the full structural formulae of many complex organic and inorganic compounds,chemical nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic name#In chemistry, systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Appli ...
may be needed which goes well beyond the available resources used above in simple condensed formulae. See IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the '' Nomenclature of O ...
and IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 for examples. In addition, linear naming systems such as International Chemical Identifier (InChI) allow a computer to construct a structural formula, and simplified molecular-input line-entry system
Simplification, Simplify, or Simplified may refer to:
Mathematics
Simplification is the process of replacing a expression (mathematics), mathematical expression by an equivalent one that is simpler (usually shorter), according to a well-founded or ...
(SMILES) allows a more human-readable ASCII input. However, all these nomenclature systems go beyond the standards of chemical formulae, and technically are chemical naming systems, not formula systems.
Polymers in condensed formulae
Forpolymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
s in condensed chemical formulae, parentheses are placed around the repeating unit. For example, a hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
molecule that is described as , is a molecule with fifty repeating units. If the number of repeating units is unknown or variable, the letter ''n'' may be used to indicate this formula: .
Ions in condensed formulae
For ions, the charge on a particular atom may be denoted with a right-hand superscript. For example, , or . The total charge on a charged molecule or apolyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion (also known as a molecular ion) is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that usually has a net charge that is not zero, or in special c ...
may also be shown in this way, such as for hydronium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the cation , also written as , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is dissolved ...
, , or sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
, . Here + and − are used in place of +1 and −1, respectively.
For more complex ions, brackets are often used to enclose the ionic formula, as in , which is found in compounds such as caesium dodecaborate, . Parentheses ( ) can be nested inside brackets to indicate a repeating unit, as in Hexamminecobalt(III) chloride, . Here, indicates that the ion contains six ammine groups () bonded to cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, and encloses the entire formula of the ion with charge +3.
This is strictly optional; a chemical formula is valid with or without ionization information, and Hexamminecobalt(III) chloride may be written as or . Brackets, like parentheses, behave in chemistry as they do in mathematics, grouping terms togetherthey are not specifically employed only for ionization states. In the latter case here, the parentheses indicate 6 groups all of the same shape, bonded to another group of size 1 (the cobalt atom), and then the entire bundle, as a group, is bonded to 3 chlorine atoms. In the former case, it is clearer that the bond connecting the chlorines is ionic, rather than covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
.
Isotopes
Althoughisotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s are more relevant to nuclear chemistry
Nuclear chemistry is the sub-field of chemistry dealing with radioactivity, nuclear processes, and transformations in the nuclei of atoms, such as nuclear transmutation and nuclear properties.
It is the chemistry of radioactive elements such as t ...
or stable isotope
Stable nuclides are Isotope, isotopes of a chemical element whose Nucleon, nucleons are in a configuration that does not permit them the surplus energy required to produce a radioactive emission. The Atomic nucleus, nuclei of such isotopes are no ...
chemistry than to conventional chemistry, different isotopes may be indicated with a prefixed superscript
A subscript or superscript is a character (such as a number or letter) that is set slightly below or above the normal line of type, respectively. It is usually smaller than the rest of the text. Subscripts appear at or below the baseline, wh ...
in a chemical formula. For example, the phosphate ion containing radioactive phosphorus-32 is . Also a study involving stable isotope ratios might include the molecule .
A left-hand subscript is sometimes used redundantly to indicate the atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
. For example, for dioxygen, and for the most abundant isotopic species of dioxygen. This is convenient when writing equations for nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a t ...
s, in order to show the balance of charge more clearly.
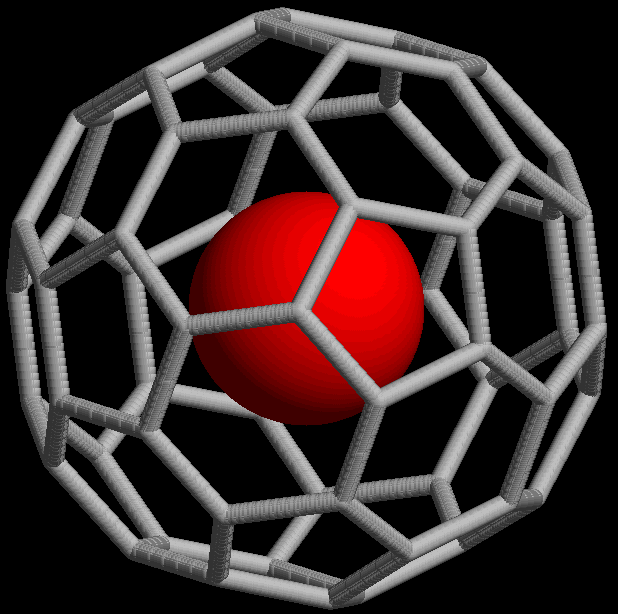
Trapped atoms
 The @ symbol (
The @ symbol (at sign
The at sign () is an accounting and invoice abbreviation meaning "at a rate of" (e.g. 7 Widget (economics), widgets @ £2 per widget = £14), now seen more widely in email addresses and social media platform User (computing), handles. It is norm ...
) indicates an atom or molecule trapped inside a cage but not chemically bound to it. For example, a buckminsterfullerene () with an atom (M) would simply be represented as regardless of whether M was inside the fullerene without chemical bonding or outside, bound to one of the carbon atoms. Using the @ symbol, this would be denoted if M was inside the carbon network. A non-fullerene example is , an ion in which one arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
(As) atom is trapped in a cage formed by the other 32 atoms.
This notation was proposed in 1991 with the discovery of fullerene cages ( endohedral fullerenes), which can trap atoms such as La to form, for example, or . The choice of the symbol has been explained by the authors as being concise, readily printed and transmitted electronically (the at sign is included in ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
, which most modern character encoding schemes are based on), and the visual aspects suggesting the structure of an endohedral fullerene.
Non-stoichiometric chemical formulae
Chemical formulae most often useinteger
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
s for each element. However, there is a class of compounds, called non-stoichiometric compound
Non-stoichiometric compounds are chemical compounds, almost always solid inorganic compounds, having elemental composition whose proportions cannot be represented by a ratio of small natural numbers (i.e. an empirical formula); most often, in s ...
s, that cannot be represented by small integers. Such a formula might be written using decimal fraction
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the ...
s, as in , or it might include a variable part represented by a letter, as in , where ''x'' is normally much less than 1.
General forms for organic compounds
A chemical formula used for a series of compounds that differ from each other by a constant unit is called a ''general formula''. It generates ahomologous series
In organic chemistry, a homologous series is a sequence of compounds with the same functional group and similar chemical properties in which the members of the series differ by the number of repeating units they contain. This can be the length of ...
of chemical formulae. For example, alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol ...
may be represented by the formula (''n'' ≥ 1), giving the homologs methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
, ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
, propanol
There are two isomers of propanol.
* 1-Propanol, ''n''-propanol, or propan-1-ol: CH3CH2CH2OH, the most common meaning
*2-Propanol, isopropyl alcohol, isopropanol, or propan-2-ol: (CH3)2CHOH
See also
* Propanal (propionaldehyde) differs in spel ...
for 1 ≤ ''n'' ≤ 3.
Hill system
The Hill system (or Hill notation) is a system of writing empirical chemical formulae, molecular chemical formulae and components of a condensed formula such that the number ofcarbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s in a molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
is indicated first, the number of hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atoms next, and then the number of all other chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
s subsequently, in alphabetical order
Alphabetical order is a system whereby character strings are placed in order based on the position of the characters in the conventional ordering of an alphabet. It is one of the methods of collation. In mathematics, a lexicographical order is ...
of the chemical symbols. When the formula contains no carbon, all the elements, including hydrogen, are listed alphabetically.
By sorting formulae according to the number of atoms of each element present in the formula according to these rules, with differences in earlier elements or numbers being treated as more significant than differences in any later element or number—like sorting text strings into lexicographical order
In mathematics, the lexicographic or lexicographical order (also known as lexical order, or dictionary order) is a generalization of the alphabetical order of the dictionaries to sequences of ordered symbols or, more generally, of elements of a ...
—it is possible to collate chemical formulae into what is known as Hill system order.
The Hill system was first published by Edwin A. Hill of the United States Patent and Trademark Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency in the United States Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark ...
in 1900. It is the most commonly used system in chemical databases and printed indexes to sort lists of compounds.Wiggins, Gary. (1991). ''Chemical Information Sources.'' New York: McGraw Hill. p. 120.
A list of formulae in Hill system order is arranged alphabetically, as above, with single-letter elements coming before two-letter symbols when the symbols begin with the same letter (so "B" comes before "Be", which comes before "Br").
The following example formulae are written using the Hill system, and listed in Hill order:
* BrClH2Si
* BrI
* CCl4
* CH3I
* C2H5Br
* H2O4S
See also
*Formula unit
In chemistry, a formula unit is the smallest unit of a non-molecular substance, such as an ionic compound, covalent network solid, or metal. It can also refer to the chemical formula for that unit. Those structures do not consist of discrete mol ...
* Glossary of chemical formulae
* Nuclear notation
* Periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other s ...
* Skeletal formula
The skeletal formula, line-angle formula, bond-line formula or shorthand formula of an organic compound is a type of minimalist structural formula representing a molecule's Atom, atoms, structural isomer, bonds and some details of its molecular ...
* Simplified molecular-input line-entry system
Simplification, Simplify, or Simplified may refer to:
Mathematics
Simplification is the process of replacing a expression (mathematics), mathematical expression by an equivalent one that is simpler (usually shorter), according to a well-founded or ...
Notes
References
*External links
*Hill notation example
from the University of Massachusetts Lowell libraries, including how to sort into Hill system order
Molecular formula calculation applying Hill notation
The library calculating Hill notation i
available on npm
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chemical Formula Chemical nomenclature Notation