mod (subculture) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Mod, from the word ''modernist'', is a subculture that began in late 1950s London and spread throughout Great Britain, eventually influencing fashions and trends in other countries. It continues today on a smaller scale. Focused on music and fashion, the subculture has its roots in a small group of stylish London-based young men and women in the late 1950s who were termed ''modernists'' because they listened to modern jazz.
Elements of the mod subculture include fashion (often tailor-made suits), music (including soul,
Mod, from the word ''modernist'', is a subculture that began in late 1950s London and spread throughout Great Britain, eventually influencing fashions and trends in other countries. It continues today on a smaller scale. Focused on music and fashion, the subculture has its roots in a small group of stylish London-based young men and women in the late 1950s who were termed ''modernists'' because they listened to modern jazz.
Elements of the mod subculture include fashion (often tailor-made suits), music (including soul,
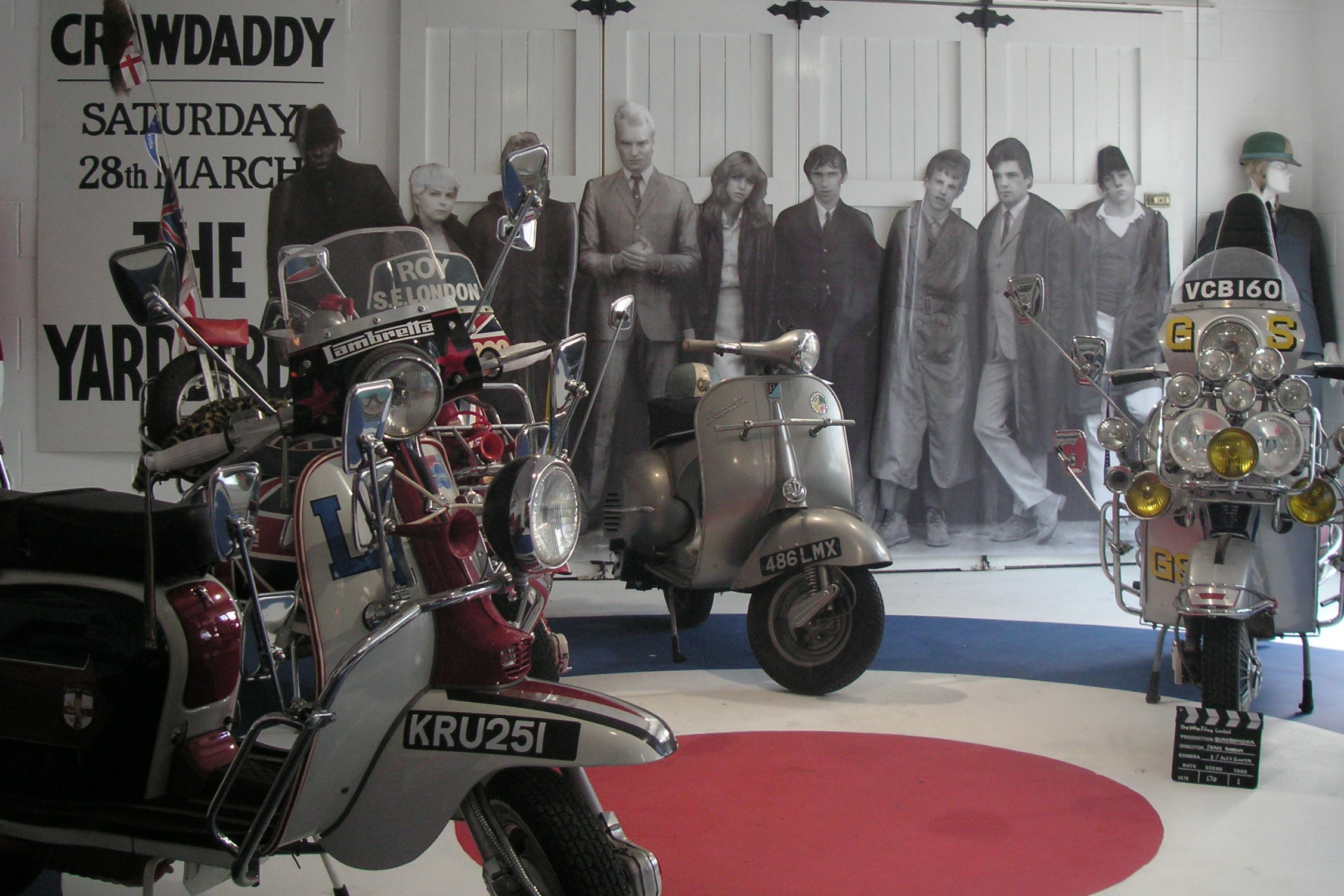 According to Hebdige, by around 1963, the mod subculture had gradually accumulated the identifying symbols that later came to be associated with the scene, such as scooters, amphetamine pills and R&B music. While clothes were still important at that time, they could be ready-made. Dick Hebdige wrote the term ''mod'' covered a number of styles including the emergence of
According to Hebdige, by around 1963, the mod subculture had gradually accumulated the identifying symbols that later came to be associated with the scene, such as scooters, amphetamine pills and R&B music. While clothes were still important at that time, they could be ready-made. Dick Hebdige wrote the term ''mod'' covered a number of styles including the emergence of  Coffee bars were attractive to British youth because, in contrast to typical pubs, which closed at about 11 pm, they were open until the early hours of the morning. Coffee bars had jukeboxes which, in some cases, reserved space in the machines for the customers' own records. In the late 1950s, coffee bars were associated with jazz and blues but, in the early 1960s, they began playing more R&B music. Frith noted that although coffee bars were originally aimed at middle-class art school students, they began to facilitate an intermixing of youth from different backgrounds and classes. At those venues, which Frith called the "first sign of the youth movement", young people met collectors of R&B and blues records.
As the mod subculture grew in London during the early-to-mid-1960s, tensions arose between the mods, often riding highly decorated motor scooters, and their main rivals, the rockers, a British subculture who favoured
Coffee bars were attractive to British youth because, in contrast to typical pubs, which closed at about 11 pm, they were open until the early hours of the morning. Coffee bars had jukeboxes which, in some cases, reserved space in the machines for the customers' own records. In the late 1950s, coffee bars were associated with jazz and blues but, in the early 1960s, they began playing more R&B music. Frith noted that although coffee bars were originally aimed at middle-class art school students, they began to facilitate an intermixing of youth from different backgrounds and classes. At those venues, which Frith called the "first sign of the youth movement", young people met collectors of R&B and blues records.
As the mod subculture grew in London during the early-to-mid-1960s, tensions arose between the mods, often riding highly decorated motor scooters, and their main rivals, the rockers, a British subculture who favoured
 Many of the hard mods lived in the same economically depressed areas of South London as West Indian immigrants, so these mods favoured a different kind of attire, that emulated the rude boy look of Trilby hats and too-short trousers.Hebdige, Dick, "Reggae, Rasta and Rudies" in ''Writing Black Britain, 1948–1998: An Interdisciplinary Anthology'', James Procter, ed. (Manchester: Manchester University Press, 2000) These Mods listened to Jamaican ska and mingled with black rude boys at West Indian nightclubs like Ram Jam, A-Train and Sloopy's. Hebdige claimed that the hard mods were drawn to black culture and ska music in part because the educated, middle-class hippie movement's drug-orientated and intellectual music did not have any relevance for them. He argued that the hard mods were attracted to ska because it was a secret, underground, non-commercialised music that was disseminated through informal channels such as house parties and clubs.
By the end of the 1960s, the hard mods had become known as skinheads, who, in their early days, would be known for the same love of soul, rocksteady and early
Many of the hard mods lived in the same economically depressed areas of South London as West Indian immigrants, so these mods favoured a different kind of attire, that emulated the rude boy look of Trilby hats and too-short trousers.Hebdige, Dick, "Reggae, Rasta and Rudies" in ''Writing Black Britain, 1948–1998: An Interdisciplinary Anthology'', James Procter, ed. (Manchester: Manchester University Press, 2000) These Mods listened to Jamaican ska and mingled with black rude boys at West Indian nightclubs like Ram Jam, A-Train and Sloopy's. Hebdige claimed that the hard mods were drawn to black culture and ska music in part because the educated, middle-class hippie movement's drug-orientated and intellectual music did not have any relevance for them. He argued that the hard mods were attracted to ska because it was a secret, underground, non-commercialised music that was disseminated through informal channels such as house parties and clubs.
By the end of the 1960s, the hard mods had become known as skinheads, who, in their early days, would be known for the same love of soul, rocksteady and early
 The British mod revival was followed by a revival in North America in the early 1980s, particularly in
The British mod revival was followed by a revival in North America in the early 1980s, particularly in
 Mod, from the word ''modernist'', is a subculture that began in late 1950s London and spread throughout Great Britain, eventually influencing fashions and trends in other countries. It continues today on a smaller scale. Focused on music and fashion, the subculture has its roots in a small group of stylish London-based young men and women in the late 1950s who were termed ''modernists'' because they listened to modern jazz.
Elements of the mod subculture include fashion (often tailor-made suits), music (including soul,
Mod, from the word ''modernist'', is a subculture that began in late 1950s London and spread throughout Great Britain, eventually influencing fashions and trends in other countries. It continues today on a smaller scale. Focused on music and fashion, the subculture has its roots in a small group of stylish London-based young men and women in the late 1950s who were termed ''modernists'' because they listened to modern jazz.
Elements of the mod subculture include fashion (often tailor-made suits), music (including soul, rhythm and blues
Rhythm and blues, frequently abbreviated as R&B or R'n'B, is a genre of popular music that originated within African American communities in the 1940s. The term was originally used by record companies to describe recordings marketed predomina ...
and ska, but mainly jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
). They rode motor scooters, usually Lambretta
Lambretta () was a brand of motor scooters, manufactured in Milan, Italy, by Innocenti.
The name is derived from the word Lambrate, the suburb of Milan named after the river Lambro which flows through the area, and where the factory was locat ...
s or Vespas. In the mid-1960s, members of the subculture listened to rock groups with rhythm and blues
Rhythm and blues, frequently abbreviated as R&B or R'n'B, is a genre of popular music that originated within African American communities in the 1940s. The term was originally used by record companies to describe recordings marketed predomina ...
(R&B) influences, such as the Who
The Who are an English Rock music, rock band formed in London in 1964. Their classic lineup (1964–1978) consisted of lead vocalist Roger Daltrey, guitarist Pete Townshend, bassist John Entwistle and drummer Keith Moon. Considered one of th ...
and Small Faces
Small Faces were an English Rock music, rock band from London, founded in 1965. The group originally consisted of Steve Marriott, Ronnie Lane, Kenney Jones and Jimmy Winston, with Ian McLagan replacing Winston as the band's keyboardist in 1966 ...
. The original mod scene was associated with amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
-fuelled all-night jazz dancing at clubs.
During the early to mid-1960s, as the mod movement grew and spread throughout Britain, certain elements of the mod scene became engaged in well-publicised clashes with members of a rival subculture, the rockers. The conflict between mods and rockers led sociologist Stanley Cohen to use the term " moral panic" in his study about the two youth subcultures, in which he examined media coverage of the mod and rocker riots in the 1960s.
By 1965, conflicts between mods and rockers began to subside and mods increasingly gravitated towards pop art and psychedelia
Psychedelia usually refers to a Aesthetics, style or aesthetic that is resembled in the psychedelic subculture of the 1960s and the psychedelic experience produced by certain psychoactive substances. This includes psychedelic art, psychedelic ...
. London became synonymous with fashion, music, and pop culture in those years, a period often referred to as "Swinging London
The Swinging Sixties was a youth-driven cultural revolution that took place in the United Kingdom during the mid-to-late 1960s, emphasising modernity and fun-loving hedonism, with Swinging London denoted as its centre. It saw a flourishing in ...
". During that time, mod fashions spread to other countries. Mod was then viewed less as an isolated subculture, but as emblematic of the larger youth culture of the era. As mod became more cosmopolitan during the "Swinging London" period, some working-class "street mods" splintered off, forming other groups such as the skinheads.
By the early 1970s, mod and psychedelia had faded in popularity, with hard rock
Hard rock or heavy rock is a heavier subgenre of rock music typified by aggressive vocals and Distortion (music), distorted electric guitars. Hard rock began in the mid-1960s with the Garage rock, garage, Psychedelic rock, psychedelic and blues ...
and glam rock styles taking over. In the late 1970s, there was a mod revival in Britain, which attempted to replicate the "scooter" period look and styles of the early to mid-1960s. It was followed by a similar mod revival in North America in the early 1980s, particularly in southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural List of regions of California, region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. Its densely populated coastal reg ...
.
Etymology and usage
The term ''mod'' derives from ''modernist'', a term used in the 1950s to describe modern jazz musicians and fans. That usage contrasted with the term ''trad'', which described traditional jazz players and fans. The 1959 novel '' Absolute Beginners'' describes modernists as young modern jazz fans who dress in sharp modern Italian clothes. The novel may be one of the earliest examples of the term being written to describe young British style-conscious modern jazz fans. That use of the word ''modernist'' should not be confused with ''modernism
Modernism was an early 20th-century movement in literature, visual arts, and music that emphasized experimentation, abstraction, and Subjectivity and objectivity (philosophy), subjective experience. Philosophy, politics, architecture, and soc ...
'' in the context of literature, art, design and architecture. From the mid-to-late 1960s onwards, the mass media often used the term ''mod'' in a wider sense, to describe anything that was believed to be popular, fashionable or modern.
Paul Jobling and David Crowley argued that the definition of ''mod'' could be difficult to pin down because, throughout the subculture's original era, it was "prone to continuous reinvention".Jobling, Paul and David Crowley, ''Graphic Design: Reproduction and Representation Since 1800'' (Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1996) , , p. 213 They claim that, since the mod scene was so pluralist, the word ''mod'' was an umbrella term that covered several distinct sub-scenes. Terry Rawlings argued that mods were difficult to define because the subculture started out as a "mysterious semi-secret world", which the Who's manager Peter Meaden summarised as "clean living under difficult circumstances".Rawlings, Terry, ''Mod: Clean Living Under Very Difficult Circumstances: a Very British Phenomenon'' (Omnibus Press, 2000)
1958–1970: Original movement
George Melly wrote that mods were initially a small group of clothes-focused young English working class men, insisting on clothes and shoes tailored to their style, who emerged during the modern jazz boom of the late 1950s. Early mods watched French and Italian art films and read Italian magazines to look for style ideas. They usually held semi-skilled manual jobs or low grade white-collar positions such as a clerk, messenger or office boy. According to Dick Hebdige, mods created a parody of the consumer society that they lived in.Early 1960s
 According to Hebdige, by around 1963, the mod subculture had gradually accumulated the identifying symbols that later came to be associated with the scene, such as scooters, amphetamine pills and R&B music. While clothes were still important at that time, they could be ready-made. Dick Hebdige wrote the term ''mod'' covered a number of styles including the emergence of
According to Hebdige, by around 1963, the mod subculture had gradually accumulated the identifying symbols that later came to be associated with the scene, such as scooters, amphetamine pills and R&B music. While clothes were still important at that time, they could be ready-made. Dick Hebdige wrote the term ''mod'' covered a number of styles including the emergence of Swinging London
The Swinging Sixties was a youth-driven cultural revolution that took place in the United Kingdom during the mid-to-late 1960s, emphasising modernity and fun-loving hedonism, with Swinging London denoted as its centre. It saw a flourishing in ...
, though to him it defined Melly's working class clothes-conscious teenagers living in London and south England in the early to mid-1960s.
Mary Anne Long argued that "first hand accounts and contemporary theorists point to the Jewish upper-working or middle-class of London's East End and suburbs."Long, Mary Anne, ''A Cultural History of the Italian Motorscooter'', senior thesis presented To Prof. Anne Cook Saunders on 17 December 1998, online at: www.nh-scooters.com/filemanager/download/11/php1C.pdf Simon Frith asserted that the mod subculture had its roots in the 1950s beatnik coffee bar culture, which catered to art school students in the radical Bohemian scene in London. Steve Sparks, whose claim is to be one of the original mods, agrees that before mod became commercialised, it was essentially an extension of the beatnik culture: "It comes from 'modernist', it was to do with modern jazz and to do with Sartre" and existentialism. Sparks argued that "Mod has been much misunderstood ... as this working-class, scooter-riding precursor of skinheads."
rockabilly
Rockabilly is one of the earliest styles of rock and roll music. It dates back to the early 1950s in the United States, especially the Southern United States, South. As a genre, it blends the sound of Western music (North America), Western musi ...
, early rock'n'roll, motorcycles and leather jackets, and considered the mods effeminate because of their interest in fashion.Covach, John; Flory, Andrew (2012), "Chapter 4: 1964–1966 The Beatles and the british invasion , XII Other important British blues revival groups , E. The Who", in Covach, John; Flory, Andrew, What's that sound?: an introduction to rock and its history, New York: Norton, , "6. There were some violent clashes between the two groups. This period was later immortalised by songwriter Pete Townshend
Peter Dennis Blandford Townshend (; born 19 May 1945) is an English musician. He is the co-founder, guitarist, keyboardist, second lead vocalist, principal songwriter and leader of the Who, one of the most influential rock bands of the 1960s an ...
, in the Who's 1973 concept album, '' Quadrophenia''. After 1964, clashes between the two groups largely subsided, as mod expanded and came to be accepted by the youth generation throughout the UK as a symbol of all that was new.Brown, Mick. Mods: A Very British Style provides definitive history of the 1960s movement, review. The Telegraph. 19 March 2013 During that time, London became a mecca for rock music, with popular bands such as the Who and Small Faces
Small Faces were an English Rock music, rock band from London, founded in 1965. The group originally consisted of Steve Marriott, Ronnie Lane, Kenney Jones and Jimmy Winston, with Ian McLagan replacing Winston as the band's keyboardist in 1966 ...
appealing to a largely mod audience,Unterberger, R., "Mod", in V. Bogdanov, C. Woodstra and S. T. Erlewine, ''All Music Guide to Rock: the Definitive Guide to Rock, Pop, and Soul'', 3rd. ed. (Milwaukee, WI: Backbeat Books, 2002), , pp. 1321–2. as well as the preponderance of hip fashions, in a period often referred to as Swinging London
The Swinging Sixties was a youth-driven cultural revolution that took place in the United Kingdom during the mid-to-late 1960s, emphasising modernity and fun-loving hedonism, with Swinging London denoted as its centre. It saw a flourishing in ...
.
Mid-late 1960s
Swinging London
As numerous British rock bands of the mid-1960s began to adopt a mod look and following, the scope of the subculture grew beyond its original confines and the focus began to change. By 1966, proletarian aspects of the scene in London had waned as fashion and pop-culture elements continued to grow, not only in England, but elsewhere. This period, portrayed by Alberto Sordi's film in '' Thank you very much'', and inMichelangelo Antonioni
Michelangelo Antonioni ( ; ; 29 September 1912 – 30 July 2007) was an Italian film director, screenwriter, and editor. He is best known for his "trilogy on modernity and its discontents", ''L'Avventura'' (1960), ''La Notte'' (1961), and '' ...
's 1966 film '' Blowup,'' was typified by pop art, Carnaby Street boutiques, live music, and discothèques. Many associate this era with fashion model Twiggy, miniskirts, and bold geometrical patterns on brightly coloured clothes. During these years, it exerted a considerable influence on the worldwide spread of mod.
United States and elsewhere
As the mod lifestyle was going through transformation in England, it became all the rage in the United States and around the world, as many young people adopted its look. However, the worldwide experience differed from that of the early scene in London in that it was based mainly on pop culture and influenced by British rock musicians. By then, mod was thought of more as a general youth-culture style rather than as a separate subgroup among different contending factions. American musicians, in the wake of theBritish Invasion
The British Invasion was a cultural phenomenon of the mid-1960s, when Rock music, rock and pop music acts from the United Kingdom and other aspects of Culture of the United Kingdom, British culture became popular in the United States with sign ...
, adopted the look of mod clothes, longer hairstyles, and Beatle boots. The exploitation documentary ''Mondo Mod'' provides a glimpse of mod's influence on the Sunset Strip and West Hollywood scene of late 1966. Mod increasingly became associated with psychedelic rock
Psychedelic rock is a rock music Music genre, genre that is inspired, influenced, or representative of psychedelia, psychedelic culture, which is centered on perception-altering hallucinogenic drugs. The music incorporated new electronic sound ...
and the early hippie movement and, by 1967, more exotic looks had come into vogue, such as Nehru jackets and love beads.Lobenthal, J. "Psychedelic Fashion." ''Love to Know.'' Its trappings were reflected on popular American TV shows such as ''Laugh-In'' and ''The Mod Squad''.
Commercialisation
Dick Hebdige argued that the subculture lost its vitality when it became commercialised and stylised to the point that mod clothing styles were being created "from above" by clothing companies and by TV shows like '' Ready Steady Go!'', rather than being developed by young people customising their clothes and combining different fashions.1970–present: Later developments
Mod and psychedelia dissipated after 1970, as tastes began to favor a more casual look, along with a decreased interest in nightlife. Bands such as the Who and Small Faces began to change and, by the early 1970s, moved away from mod to a morehard rock
Hard rock or heavy rock is a heavier subgenre of rock music typified by aggressive vocals and Distortion (music), distorted electric guitars. Hard rock began in the mid-1960s with the Garage rock, garage, Psychedelic rock, psychedelic and blues ...
style. Other mods such as David Bowie
David Robert Jones (8 January 194710 January 2016), known as David Bowie ( ), was an English singer, songwriter and actor. Regarded as one of the most influential musicians of the 20th century, Bowie was acclaimed by critics and musicians, pa ...
and Marc Bolan (of T. Rex) adopted a glam rock style. Additionally, the original mods of the early 1960s were coming to the age of marriage and child-rearing, which meant many of them no longer had the time or money for their youthful pastimes of club-going, record-shopping, and buying clothes.
Offshoots
Some street-oriented mods, usually of lesser means, sometimes referred to as ''hard mods,'' remained active well into the late 1960s, but tended to become increasingly detached from the Swinging London scene and the burgeoning hippie movement. By 1967, they considered most of the people in the Swinging London scene to be "soft mods" or "peacock mods", as styles there became increasingly extravagant, often featuring highly ruffled, brocade Many of the hard mods lived in the same economically depressed areas of South London as West Indian immigrants, so these mods favoured a different kind of attire, that emulated the rude boy look of Trilby hats and too-short trousers.Hebdige, Dick, "Reggae, Rasta and Rudies" in ''Writing Black Britain, 1948–1998: An Interdisciplinary Anthology'', James Procter, ed. (Manchester: Manchester University Press, 2000) These Mods listened to Jamaican ska and mingled with black rude boys at West Indian nightclubs like Ram Jam, A-Train and Sloopy's. Hebdige claimed that the hard mods were drawn to black culture and ska music in part because the educated, middle-class hippie movement's drug-orientated and intellectual music did not have any relevance for them. He argued that the hard mods were attracted to ska because it was a secret, underground, non-commercialised music that was disseminated through informal channels such as house parties and clubs.
By the end of the 1960s, the hard mods had become known as skinheads, who, in their early days, would be known for the same love of soul, rocksteady and early
Many of the hard mods lived in the same economically depressed areas of South London as West Indian immigrants, so these mods favoured a different kind of attire, that emulated the rude boy look of Trilby hats and too-short trousers.Hebdige, Dick, "Reggae, Rasta and Rudies" in ''Writing Black Britain, 1948–1998: An Interdisciplinary Anthology'', James Procter, ed. (Manchester: Manchester University Press, 2000) These Mods listened to Jamaican ska and mingled with black rude boys at West Indian nightclubs like Ram Jam, A-Train and Sloopy's. Hebdige claimed that the hard mods were drawn to black culture and ska music in part because the educated, middle-class hippie movement's drug-orientated and intellectual music did not have any relevance for them. He argued that the hard mods were attracted to ska because it was a secret, underground, non-commercialised music that was disseminated through informal channels such as house parties and clubs.
By the end of the 1960s, the hard mods had become known as skinheads, who, in their early days, would be known for the same love of soul, rocksteady and early reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica during the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its Jamaican diaspora, diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, "Do the Reggay", was the first ...
. Because of their fascination with black culture, the early skinheads were, except in isolated situations, largely devoid of the overt racism and fascism that would later become associated with whole wings of the movement in the mid to late 1970s. The early skinheads retained basic elements of mod fashion—such as Fred Perry and Ben Sherman shirts, Sta-Prest trousers and Levi's jeans—but mixed them with working class-orientated accessories such as braces and Dr. Martens work boots. Hebdige claimed that as early as the Margate and Brighton brawls between mods and rockers, some mods were seen wearing boots and braces and sporting close cropped haircuts (for practical reasons, as long hair was a liability in industrial jobs and street fights).
Mods and ex-mods were also part of the early northern soul scene, a subculture based on obscure 1960s and 1970s American soul records. Some mods evolved into, or merged with, subcultures such as individualists, stylists, and scooterboys.
Revivals and later influence
A mod revival started in the late 1970s in the United Kingdom, with thousands of mod revivalists attending scooter rallies in locations such as Scarborough and the Isle of Wight. This revival was partly inspired by the 1979 film '' Quadrophenia'', which explores the original 1960s movement, and by mod-influenced bands such as the Jam, Secret Affair, the Lambrettas, Purple Hearts,the Specials
The Specials, also known as the Special AKA, were an English 2 tone and ska revival band formed in 1977 in Coventry. After some early changes, the first stable lineup of the group consisted of Terry Hall and Neville Staple on vocals, J ...
and the Chords, who drew on the energy of new wave music
New wave is a music genre that encompasses pop music, pop-oriented styles from the 1970s through the 1980s. It is considered a lighter and more melodic "broadening of Punk subculture, punk culture". It was originally used as a catch-all fo ...
.
 The British mod revival was followed by a revival in North America in the early 1980s, particularly in
The British mod revival was followed by a revival in North America in the early 1980s, particularly in Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural List of regions of California, region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. Its densely populated coastal reg ...
, led by bands such as the Untouchables. The mod scene in Los Angeles and Orange County was partly influenced by the 2 Tone
Two-tone, two tone, or 2 tone, etc., may refer to:
Audio and sound
* Second-order intercept point#Two-tone analysis, Two-tone analysis, in nonlinear system measurement
* Two-tone attention signal
* Two-tone Warning chime, chime, such as the "ding ...
ska revival in England, and was unique in its racial diversity, with black, white, Hispanic and Asian participants. The 1990s Britpop
Britpop was a mid-1990s United Kingdom, British-based music culture movement that emphasised Britishness. Musically, Britpop produced bright, catchy alternative rock, with significant influences from British guitar pop of the 1960s and 1970s. B ...
scene featured noticeable mod influences on bands such as Oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentBlur, Ocean Colour Scene and the Bluetones. Popular 21st century musicians Miles Kane and Jake Bugg are also followers of the mod subculture.
 Jobling and Crowley argued that for working class mods, the subculture's focus on fashion and music was a release from the "humdrum of daily existence" at their jobs. Jobling and Crowley noted that while the subculture had strong elements of consumerism and shopping, mods were not passive consumers; instead they were very self-conscious and critical, customising "existing styles, symbols and artefacts" such as the
Jobling and Crowley argued that for working class mods, the subculture's focus on fashion and music was a release from the "humdrum of daily existence" at their jobs. Jobling and Crowley noted that while the subculture had strong elements of consumerism and shopping, mods were not passive consumers; instead they were very self-conscious and critical, customising "existing styles, symbols and artefacts" such as the
Characteristics
Dick Hebdige argued that when trying to understand 1960s mod culture, one has to try and "penetrate and decipher the mythology of the mods".Hebdige, Dick. "The Meaning of Mod" in Stuart Hall and Tony Jefferson, eds., ''Resistance Through Rituals: Youth Subcultures in Post-War Britain'' (London. Routledge, 1993) p. 168 Terry Rawlings argued that the mod scene developed when British teenagers began to reject the "dull, timid, old-fashioned, and uninspired" British culture around them, with its repressed and class-obsessed mentality and its "naffness". Mods rejected the "faulty pap" of 1950s pop music and sappy love songs. They aimed at being "cool, neat, sharp, hip, and smart" by embracing "all things sexy and streamlined", especially when they were new, exciting, controversial or modern. Hebdige claimed that the mod subculture came about as part of the participants' desire to understand the "mysterious complexity of the metropolis" and to get close to black culture of the Jamaican rude boy, because mods felt that black culture "ruled the night hours" and that it had more streetwise " savoir faire". Shari Benstock and Suzanne Ferriss argued that at the "core of the British Mod rebellion was a blatant fetishising of the American consumer culture" that had "eroded the moral fiber of England." Benstock, Shari and Suzanne Ferriss, ''On Fashion'' (Rutgers University Press, 1994) , In doing so, the mods "mocked the class system that had gotten their fathers nowhere" and created a "rebellion based on consuming pleasures". The influence of British newspapers on creating the public perception of mods as having a leisure-filled club-going lifestyle can be seen in a 1964 article in ''The Sunday Times
''The Sunday Times'' is a British Sunday newspaper whose circulation makes it the largest in Britain's quality press market category. It was founded in 1821 as ''The New Observer''. It is published by Times Newspapers Ltd, a subsidiary of N ...
''. The paper interviewed a 17-year-old mod who went out clubbing seven nights a week and spent Saturday afternoons shopping for clothes and records. However, few British teens and young adults would have had the time and money to spend this much time going to nightclubs. Paul Jobling and David Crowley argued that most young mods worked 9 to 5 at semi-skilled jobs, which meant that they had much less leisure time and only a modest income to spend during their time off.
Fashion
Paul Jobling and David Crowley called the mod subculture a "fashion-obsessed and hedonistic cult of the hyper-cool" young adults who lived in metropolitan London or the new towns of the south. Due to the increasing affluence of post-war Britain, the youths of the early 1960s were one of the first generations that did not have to contribute their money from after-school jobs to the family finances. As mod teens and young adults began using their disposable income to buy stylish clothes, the first youth-targeted boutique clothing stores opened in London in the Carnaby Street and King's Road districts. The streets' names became symbols of, one magazine later stated, "an endless frieze of mini-skirted, booted, fair-haired angular angels". Newspaper accounts from the mid-1960s focused on the mod obsession with clothes, often detailing the prices of the expensive suits worn by young mods, and seeking out extreme cases such as a young mod who claimed that he would "go without food to buy clothes".Jobling, Paul and David Crowley, ''Graphic Design: Reproduction and Representation Since 1800'' (Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1996), Two youth subcultures helped pave the way for mod fashion by breaking new ground: the beatniks, with their Bohemian image of berets and black turtlenecks, and the Teddy Boys, from whom mod fashion inherited its "narcissistic and fastidious ashiontendencies" and the immaculate dandy look. The Teddy Boys paved the way for making male interest in fashion socially acceptable. Prior to the Teddy Boys, male interest in fashion in Britain was often associated with underground homosexuals' subculture and dressing style.Union flag
The Union Jack or Union Flag is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. The Union Jack was also used as the official flag of several British colonies and dominions before they adopted their own national flags.
It is sometimes a ...
and the Royal Air Force roundel, and putting them on their jackets in a pop art-style, and putting their personal signatures on their style. Mods adopted new Italian and French styles in part as a reaction to the rural and small-town rockers, with their 1950s-style leather motorcycle clothes and American greaser look.
Male mods adopted a smooth, sophisticated look that included tailor-made suits with narrow lapels (sometimes made of mohair), skinny ties, button-down collar shirts, wool or cashmere jumpers (crewneck or V-neck), Chelsea or Beatle boots, loafers, Clarks desert boots, bowling shoes, and hairstyles that imitated the look of French '' Nouvelle Vague'' film actors.Casburn, Melissa M., ''A Concise History of the British Mod Movement'' A big part of the Mod look was borrowed from the Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference of eight Private university, private Research university, research universities in the Northeastern United States. It participates in the National Collegia ...
collegiate style from the United States. A few male mods went against gender norms by using eye shadow, eye-pencil or even lipstick. Mods chose scooters over motorbikes partly because they were a symbol of Italian style and because their body panels concealed moving parts and made them less likely to stain clothes with oil or road dust. Many mods wore ex-military parkas while driving scooters to keep their clothes clean.
Many female mods dressed androgynously, with short haircuts, men's trousers or shirts, flat shoes, and little makeup – often just pale foundation, brown eye shadow, white or pale lipstick and false eyelashes. British fashion designer Mary Quant, who helped popularize the miniskirt, is credited for popularizing mod subculture. Miniskirts became progressively shorter between the early and mid-1960s. As female mod fashion became more mainstream, slender models like Jean Shrimpton and Twiggy began to exemplify the mod look. Maverick fashion designers emerged, such as Quant, who was known for her miniskirt designs, and John Stephen, who sold a line named "His Clothes" and whose clients included bands such as Small Faces. The television programme ''Ready Steady Go!'' helped spread awareness of mod fashions to a larger audience. Mod-culture continues to influence fashion, with the ongoing trend for mod-inspired styles such as 3-button suits, Chelsea boots and mini dresses. The Mod Revival of the 1980s and 1990s led to a new era of mod-inspired fashion, driven by bands such as Madness, the Specials
The Specials, also known as the Special AKA, were an English 2 tone and ska revival band formed in 1977 in Coventry. After some early changes, the first stable lineup of the group consisted of Terry Hall and Neville Staple on vocals, J ...
and Oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentThis Is England film and TV series also kept mod fashion in the public eye. Today's mod icons include Miles Kane (frontman of the Last Shadow Puppets), cyclist Bradley Wiggins and
 The early mods listened to the "sophisticated smoother modern jazz" of musicians such as
The early mods listened to the "sophisticated smoother modern jazz" of musicians such as
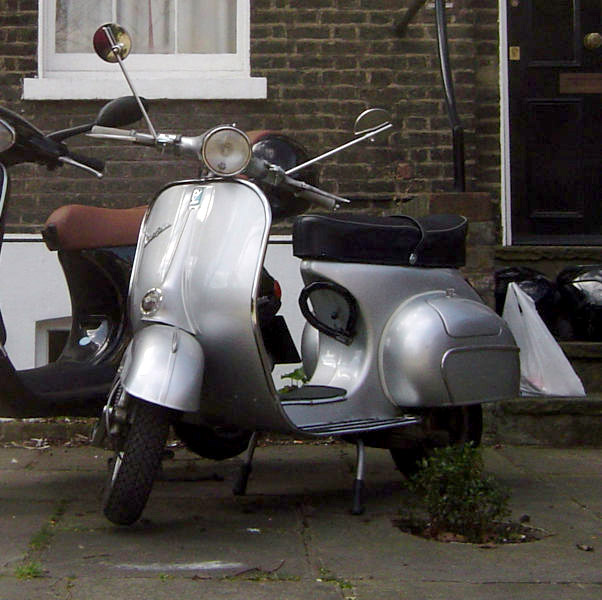 Many mods drove motor scooters, usually Vespas or
Many mods drove motor scooters, usually Vespas or  Mods also treated scooters as a fashion accessory. Italian scooters were preferred due to their clean-lined, curving shapes and gleaming chrome, with sales driven by close associations between dealerships and clubs, such as the Ace of Herts.
For young mods, Italian scooters were the "embodiment of continental style and a way to escape the working-class row houses of their upbringing".Sarti, Doug
Mods also treated scooters as a fashion accessory. Italian scooters were preferred due to their clean-lined, curving shapes and gleaming chrome, with sales driven by close associations between dealerships and clubs, such as the Ace of Herts.
For young mods, Italian scooters were the "embodiment of continental style and a way to escape the working-class row houses of their upbringing".Sarti, Doug
"Vespa Scoots Sexily Back to Vancouver"
, Straight.com. 3 June 2004 Mods customised their scooters by painting them in "two-tone and candyflake and overaccessorized hemwith luggage racks, crash bars, and scores of mirrors and fog lights". Some mods added four, ten, or as many as 30 mirrors to their scooters. They often put their names on the small windscreen. They sometimes took their engine side panels and front bumpers to electroplating shops to get them covered in highly reflective chrome. Hard mods (who later evolved into the skinheads) began riding scooters more for practical reasons. Their scooters were either unmodified or cutdown, which was nicknamed a "skelly". Lambrettas were cutdown to the bare frame, and the unibody (monocoque)-design Vespas had their body panels slimmed down or reshaped. After the seaside resort brawls, the media began to associate Italian scooters with violent mods. Much later, writers described groups of mods riding scooters together as a "menacing symbol of group solidarity" that was "converted into a weapon". With events like the 6 November 1966, "scooter charge" on
Dick Hebdige claimed in 2006 that the "mods rejected the rocker's crude conception of masculinity, the transparency of his motivations, his clumsiness"; the rockers viewed the vanity and obsession with clothes of the mods as immasculine. Scholars debate how much contact the two subcultures had during the 1960s. Hebdige argued that mods and rockers had little contact with each other because they tended to come from different regions of England (mods from London and rockers from rural areas), and because they had "totally disparate goals and lifestyles". Mark Gilman, however, claimed that both mods and rockers could be seen at
Revolution in Men' s Clothes: Mod Fashions from Britain are Making a Smash in the U.S., ''Life'' Magazine, 13 May. 1966, pg. 82–90
– Cover story about mod boom in America
OnThisDay 4 April 1964 BBC Panorama Reported on Mods and Rockers. Can't we all just get alongMods Of Your GenerationUNDERSTANDING THE SNOBBERY BETWEEN ORIGINAL MODS, REVIVALISTS, AND MILLENNIAL MODS
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mod (Lifestyle) 1960s fads and trends 1960s fashion 1970s fads and trends 1980s fads and trends Fashion Modernism Motorcycling subculture in the United Kingdom Musical subcultures Working-class culture in the United Kingdom Youth culture in the United Kingdom British subcultures Counterculture of the 1960s Counterculture of the 1970s
Paul Weller
John William Weller (born 25 May 1958), better known as Paul Weller, is an English singer-songwriter and musician. Weller achieved fame in the late 1970s as the guitarist and principal singer and songwriter of the rock band the Jam, alongside ...
, 'The ModFather'.
Music
 The early mods listened to the "sophisticated smoother modern jazz" of musicians such as
The early mods listened to the "sophisticated smoother modern jazz" of musicians such as Miles Davis
Miles Dewey Davis III (May 26, 1926September 28, 1991) was an American jazz trumpeter, bandleader, and composer. He is among the most influential and acclaimed figures in the history of jazz and 20th century music, 20th-century music. Davis ado ...
, Charlie Parker
Charles Parker Jr. (August 29, 1920 – March 12, 1955), nicknamed "Bird" or "Yardbird", was an American jazz Saxophone, saxophonist, bandleader, and composer. Parker was a highly influential soloist and leading figure in the development of beb ...
, Dave Brubeck and the Modern Jazz Quartet, as well as the American rhythm and blues (R&B) of artists such as Bo Diddley
Ellas Otha Bates (December 30, 1928 – June 2, 2008), known professionally as Bo Diddley, was an American guitarist and singer who played a key role in the transition from the blues to rock and roll. He influenced many artists, including Buddy ...
and Muddy Waters. The music scene of the Mods was a mix of modern jazz, R&B, psychedelic rock and soul. Terry Rawlings wrote that mods became "dedicated to R&B and their own dances." Black American servicemen, stationed in Britain during the early part of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, brought over R&B and soul records that were unavailable in Britain, and they often sold these to young people in London. Starting around 1960, mods embraced the off-beat, Jamaican ska music of artists such as the Skatalites, Owen Gray, Derrick Morgan and Prince Buster on record labels such as Melodisc, Starlite and Bluebeat.
The original mods gathered at all-night clubs such as The Flamingo and The Marquee in London to hear the latest records and show off their dance moves. As the mod subculture spread across the United Kingdom, other clubs became popular, including Twisted Wheel Club in Manchester.
The British R&B/ rock bands the Rolling Stones, the Yardbirds and the Kinks all had mod followings, and other bands emerged that were specifically mod-oriented. These included The Who, Small Faces, the Creation, the Action, the Smoke and John's Children. The Who's early promotional material tagged them as playing "maximum rhythm and blues", and a name change in 1964 from The Who to The High Numbers was an attempt to cater even more to the mod market. After the commercial failure of the single " Zoot Suit/I'm the Face", the band changed its name back to The Who. Although the Beatles
The Beatles were an English Rock music, rock band formed in Liverpool in 1960. The core lineup of the band comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are widely regarded as the Cultural impact of the Beatle ...
dressed like mods for a while (after dressing like rockers earlier), their beat music
Beat music, British beat, or Merseybeat is a British popular music Music genre, genre that developed around Liverpool in the late 1950s and early 1960s. The genre melded influences from British rock and roll, British and Music of the United St ...
was not as popular as British R&B among mods.
Amphetamines
A notable part of the mod subculture was recreational amphetamine use, which was used to fuel all-night dances at clubs. Newspaper reports described dancers emerging from clubs at 5 a.m. with dilated pupils. Some mods consumed a combined amphetamine/barbiturate called Drinamyl, nicknamed "purple hearts". Due to this association with amphetamines, Pete Meaden's "clean living" aphorism about the mod subculture may seem contradictory, but the drug was still legal in Britain in the early 1960s, and mods used the drug forstimulation
Stimulation is the encouragement of development or the cause of activity in general. For example, "The press provides stimulation of political discourse." An interesting or fun activity can be described as "stimulating", regardless of its physic ...
and alertness, which they viewed as different from the intoxication caused by alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
and other drugs. Andrew Wilson argued that for a significant minority, "amphetamines symbolised the smart, on-the-ball, cool image" and that they sought "stimulation not intoxication ... greater awareness, not escape" and "confidence and articulacy" rather than the "drunken rowdiness of previous generations".
Wilson argued that the significance of amphetamines to the mod culture was similar to that of LSD and cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
within the subsequent hippie counterculture. Dick Hebdige argued that mods used amphetamines to extend their leisure time into the early hours of the morning and as a way of bridging the gap between their hostile and daunting everyday work lives and the "inner world" of dancing and dressing up in their off-hours.
Scooters
 Many mods drove motor scooters, usually Vespas or
Many mods drove motor scooters, usually Vespas or Lambretta
Lambretta () was a brand of motor scooters, manufactured in Milan, Italy, by Innocenti.
The name is derived from the word Lambrate, the suburb of Milan named after the river Lambro which flows through the area, and where the factory was locat ...
s. Scooters were a practical and affordable form of transportation for 1960s teens, since until the early 1970s, public transport stopped relatively early in the night. For teens with low-paying jobs, scooters were cheaper and easier to park than cars, and they could be bought through newly available hire purchase plans.
 Mods also treated scooters as a fashion accessory. Italian scooters were preferred due to their clean-lined, curving shapes and gleaming chrome, with sales driven by close associations between dealerships and clubs, such as the Ace of Herts.
For young mods, Italian scooters were the "embodiment of continental style and a way to escape the working-class row houses of their upbringing".Sarti, Doug
Mods also treated scooters as a fashion accessory. Italian scooters were preferred due to their clean-lined, curving shapes and gleaming chrome, with sales driven by close associations between dealerships and clubs, such as the Ace of Herts.
For young mods, Italian scooters were the "embodiment of continental style and a way to escape the working-class row houses of their upbringing".Sarti, Doug"Vespa Scoots Sexily Back to Vancouver"
, Straight.com. 3 June 2004 Mods customised their scooters by painting them in "two-tone and candyflake and overaccessorized hemwith luggage racks, crash bars, and scores of mirrors and fog lights". Some mods added four, ten, or as many as 30 mirrors to their scooters. They often put their names on the small windscreen. They sometimes took their engine side panels and front bumpers to electroplating shops to get them covered in highly reflective chrome. Hard mods (who later evolved into the skinheads) began riding scooters more for practical reasons. Their scooters were either unmodified or cutdown, which was nicknamed a "skelly". Lambrettas were cutdown to the bare frame, and the unibody (monocoque)-design Vespas had their body panels slimmed down or reshaped. After the seaside resort brawls, the media began to associate Italian scooters with violent mods. Much later, writers described groups of mods riding scooters together as a "menacing symbol of group solidarity" that was "converted into a weapon". With events like the 6 November 1966, "scooter charge" on
Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a royal official residence, residence in London, and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and r ...
, the scooter, along with the mods' short hair and suits, began to be seen as a symbol of subversion.
Gender roles
Stuart Hall and Tony Jefferson argued in 1993 that compared to other youth subcultures, the mod scene gave young women high visibility and relative autonomy. They wrote that this status may have been related both to the attitudes of the mod young men, who accepted the idea that a young woman did not have to be attached to a man, and to the development of new occupations for young women, which gave them an income and made them more independent. Hall and Jefferson noted the increasing number of jobs in boutiques and women's clothing stores, which, while poorly paid and lacking opportunities for advancement, gave young women disposable income, status and a glamorous sense of dressing up and going into town to work.Resistance Through Rituals: Youth Subcultures in Post-war Britain. By Stuart Hall, Tony Jefferson. Published by Routledge, 1993. , Hall and Jefferson argued that the presentable image of female mod fashions meant it was easier for young mod women to integrate with the non-subculture aspects of their lives (home, school and work) than for members of other subcultures. The emphasis on clothing and a stylised look for women demonstrated the "same fussiness for detail in clothes" as their male mod counterparts. Shari Benstock and Suzanne Ferriss claimed that the emphasis in the mod subculture on consumerism and shopping was the "ultimate affront to male working-class traditions" in the United Kingdom, because in the working-class tradition, shopping was usually done by women. They argued that British mods were "worshipping leisure and money ... scorning the masculine world of hard work and honest labour" by spending their time listening to music, collecting records, socialising, and dancing at all-night clubs.Conflicts with rockers
In early-1960s Britain, the two main youth subcultures were mods and rockers. Mods were described in 2012 as "effeminate, stuck-up, emulating the middle classes, aspiring to a competitive sophistication, snobbish, ndphony", and rockers as "hopelessly naive, loutish, ndscruffy", emulating the motorcycle gang members in the film '' The Wild One'', by wearing leather jackets and riding motorcycles.Book preview.Dick Hebdige claimed in 2006 that the "mods rejected the rocker's crude conception of masculinity, the transparency of his motivations, his clumsiness"; the rockers viewed the vanity and obsession with clothes of the mods as immasculine. Scholars debate how much contact the two subcultures had during the 1960s. Hebdige argued that mods and rockers had little contact with each other because they tended to come from different regions of England (mods from London and rockers from rural areas), and because they had "totally disparate goals and lifestyles". Mark Gilman, however, claimed that both mods and rockers could be seen at
football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
matches.
John Covach wrote that in the United Kingdom, rockers were often engaged in brawls with mods. BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
News stories from May 1964 stated that mods and rockers were jailed after riots in seaside resort towns on the south and east coasts of England, such as Margate
Margate is a seaside resort, seaside town in the Thanet District of Kent, England. It is located on the north coast of Kent and covers an area of long, north-east of Canterbury and includes Cliftonville, Garlinge, Palm Bay, UK, Palm Bay and W ...
, Brighton
Brighton ( ) is a seaside resort in the city status in the United Kingdom, city of Brighton and Hove, East Sussex, England, south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age, R ...
, Bournemouth and Clacton. The "mods and rockers" conflict was explored as an instance of " moral panic" by sociologist Stanley Cohen in his study ''Folk Devils and Moral Panics'', which examined media coverage of the mod and rocker riots in the 1960s. Although Cohen acknowledged that mods and rockers had some fights in the mid-1960s, he argued that they were no different from the evening brawls that occurred between non-mod and non-rocker youths throughout the 1950s and early 1960s, both at seaside resorts and after football games.Cohen, Stanley. ''Folk Devils and Moral Panics''. page 27
Newspapers of the time were eager to describe the mod and rocker clashes as being of "disastrous proportions", and labelled mods and rockers as "sawdust Caesars", "vermin" and "louts". Newspaper editorials fanned the flames of hysteria, such as a '' Birmingham Post'' editorial in May 1964 which warned that mods and rockers were " internal enemies" in the United Kingdom who would "bring about disintegration of a nation's character". The magazine ''Police Review'' argued that the mods and rockers' purported lack of respect for law and order could cause violence to "surge and flame like a forest fire". As a result of this media coverage, two British members of parliament travelled to the seaside areas to survey the damage, and MP Harold Gurden called for a resolution for intensified measures to control youth hooliganism. One of the prosecutors in the trial of some of the Clacton brawlers argued that mods and rockers were youths with no serious views, who lacked respect for law and order.
See also
* 1960s in fashion * Freakbeat * Bōsōzoku, a similar subculture in JapanReferences
Further reading
* Anderson, Paul. ''Mods: The New Religion'', Omnibus Press (2014), *Bacon, Tony. ''London Live'', Balafon (1999), *Baker, Howard. ''Sawdust Caesar'' Mainstream (1999), *Baker, Howard. ''Enlightenment and the Death of Michael Mouse'' Mainstream (2001), *Barnes, Richard.''Mods!'', Eel Pie (1979), *Cohen, S. (1972 ). ''Folk Devils and Moral Panics: The Creation of Mods and Rockers'', Oxford: Martin Robertson. * Deighton, Len. ''Len Deighton's London Dossier'', (1967) *Elms, Robert. ''The Way We Wore'', *Feldman, Christine Jacqueline. ''"We Are the Mods": A Transnational History of a Youth Subculture''. Peter Lang (2009). *Fletcher, Alan. ''Mod Crop Series'', Chainline (1995), *Green, Jonathan. ''Days in the Life'', *Green, Jonathan. ''All Dressed Up'' *Hamblett, Charles and Jane Deverson. ''Generation X'' (1964) *Hewitt, Paolo. ''My Favourite Shirt: A History of Ben Sherman Style'' (Paperback). Ben Sherman (2004), *Hewitt, Paolo. ''The Sharper Word; A Mod Anthology'' Helter Skelter Publishing (2007), *Hewitt, Paolo. ''The Soul Stylists: Forty Years of Modernism'' (1st edition). Mainstream (2000), * MacInnes, Colin. ''England, Half English'' (2nd edition), Penguin (1966, 1961) * MacInnes, Colin. '' Absolute Beginners'' *Newton, Francis. ''The Jazz Scene'', *Rawlings, Terry. ''Mod: A Very British Phenomenon'' *Scala, Mim. ''Diary Of A Teddy Boy''. Sitric (2000), *Verguren, Enamel . ''This Is a Modern Life: The 1980s London Mod Scene'', Enamel Verguren. Helter Skelter (2004), *Weight, Richard. Mod: A Very British Style. Bodley Head (2013)External links
Revolution in Men' s Clothes: Mod Fashions from Britain are Making a Smash in the U.S., ''Life'' Magazine, 13 May. 1966, pg. 82–90
– Cover story about mod boom in America
OnThisDay 4 April 1964 BBC Panorama Reported on Mods and Rockers. Can't we all just get along
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mod (Lifestyle) 1960s fads and trends 1960s fashion 1970s fads and trends 1980s fads and trends Fashion Modernism Motorcycling subculture in the United Kingdom Musical subcultures Working-class culture in the United Kingdom Youth culture in the United Kingdom British subcultures Counterculture of the 1960s Counterculture of the 1970s