Jordan River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a
, Carta Jerusalem, accessed 82020 is a stream arising from a spring at Banias at the foot of Mount Hermon, with a flow of 106 million m3 annually. It flows into the Dan along with the Nahal Sion or Nahal Assal (Hebrew) / Wadi el-'Asl or Assal (Arabic).
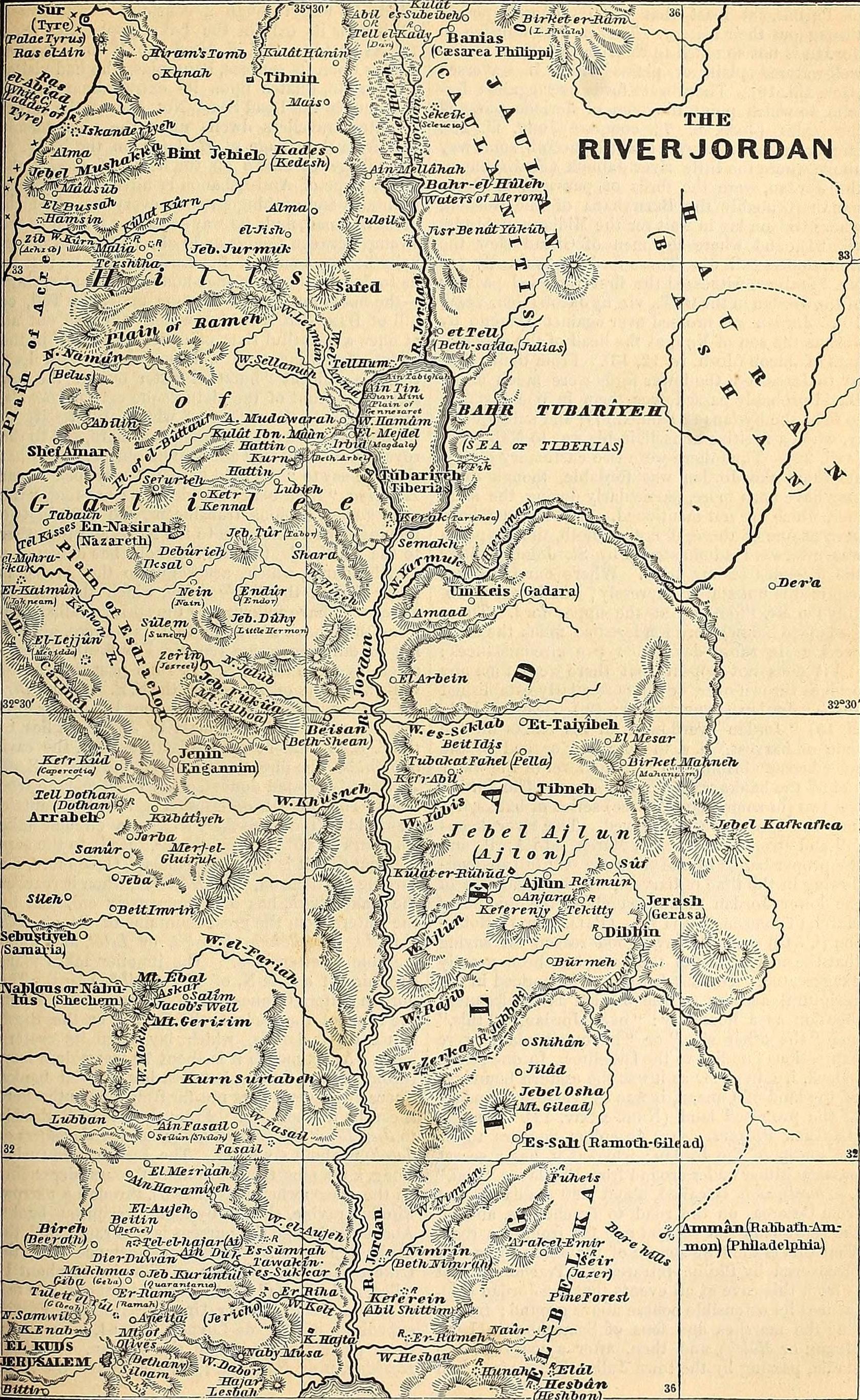 The Jordan River has an upper course from its sources to the Sea of Galilee (via the Bethsaida Valley) and a lower course south of the Sea of Galilee down to the
The Jordan River has an upper course from its sources to the Sea of Galilee (via the Bethsaida Valley) and a lower course south of the Sea of Galilee down to the
''Jordan Basin''
, based on 2009 "Water Report 34", accessed 18 April 2020Gafny, S. ''et al.'' (2010)
Map of the Lower Jordan River
, retrieved 14 April 2020 Smaller tributaries or "side wadis" / "side streams" in this segment are, north to south * from the east (6–10 in total) ** Wadi al-'Arab ** Wadi Ziqlab ** Wadi al-Yabis ** Wadi Kafranja or Kufrinjah passing near Ajloun ** Wadi Rajib, the last before Wadi Zarqa ** Wadi Nimrin * from the west ** Nahal Yavne'el ** Nahal Tavor (Tabor Stream) ** Nahal Yissakhar ** Nahal Harod ** Nahal Bezeq, on the border between Israel and the West Bank, between
 In 1964, Israel began operating a pumping station that diverts water from the Sea of Galilee to the National Water Carrier. Also in 1964, Jordan constructed a channel that diverted water from the Yarmouk to the East Ghor Canal. Syria has also built reservoirs that catch the Yarmouk's waters. Environmentalists blame Israel, Jordan and Syria for extensive damage to the Jordan River ecosystem.
In 1964, Israel began operating a pumping station that diverts water from the Sea of Galilee to the National Water Carrier. Also in 1964, Jordan constructed a channel that diverted water from the Yarmouk to the East Ghor Canal. Syria has also built reservoirs that catch the Yarmouk's waters. Environmentalists blame Israel, Jordan and Syria for extensive damage to the Jordan River ecosystem.

 Until the first decade of the 21st century, the waters of the Jordan River had been the largest water resource for Israel; lately, desalinated sea water from the
Until the first decade of the 21st century, the waters of the Jordan River had been the largest water resource for Israel; lately, desalinated sea water from the
 In the
In the
endorheic
An endorheic basin ( ; also endoreic basin and endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water (e.g. rivers and oceans); instead, the water drainage flows into permanent ...
river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee (, Judeo-Aramaic languages, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ), also called Lake Tiberias, Genezareth Lake or Kinneret, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth ...
and drains to the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valle ...
. The river passes by or through Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
, Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, and the Palestinian territories
The occupied Palestinian territories, also referred to as the Palestinian territories, consist of the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip—two regions of the former Mandate for Palestine, British Mandate for Palestine ...
.
Jordan and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
border the river to the east, while Israel and the Israeli-occupied West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank derive their names in relation to the river. The river holds major significance in Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
and Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
. According to the Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
, the Israelites crossed it into the Promised Land
In the Abrahamic religions, the "Promised Land" ( ) refers to a swath of territory in the Levant that was bestowed upon Abraham and his descendants by God in Abrahamic religions, God. In the context of the Bible, these descendants are originally ...
and Jesus of Nazareth was baptized by John the Baptist
John the Baptist ( – ) was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early first century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy and Oriental Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in some Baptist ...
in it.
Etymology
Several hypotheses for the origin of most of the river's names in modern languages (e.g., Jordan, Yarden, Urdunn), one is that it comes from Semitic 'Yard, on' 'flow down' <√ירד reflecting the river's declivity, possibly appearing also in other river names in the region such as Yarkon and Yarmouk, or it may be related to the Egyptian loanword 'yǝʾor' ('big river', theNile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
). According to this hypothesis, "Den" might be linked to the Akkadian word dannum for "powerful". Cognates of the word are found in Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
, Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
, Mandaic, and other Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic,
Amharic, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Maltese language, Maltese, Modern South Arabian language ...
. The first recorded use of the name appears as ''Yārdon'' in Anastasi I, an ancient Egyptian papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
that probably dates to the time of Rameses II. Early Arab chronicles referred to the river as ''Al-Urdunn''.
In Mandaic, the etymologically related term '' Yardena'' () can refer not only to the Jordan River, but also any other body of flowing water that can be used for Mandaean baptismal rituals ('' masbuta'').
After the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
, the Arabic name ''Nahr Al Sharieat'' (), literally "the watering place" began to be used, and was recorded by medieval geographers such as Abu'l-Fida
Ismāʿīl bin ʿAlī bin Maḥmūd bin Muḥammad bin ʿUmar bin Shāhanshāh bin Ayyūb bin Shādī bin Marwān (), better known as Abū al-Fidāʾ or Abulfeda (; November 127327 October 1331), was a Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluk-era Kurds, Kurdish ...
and Al-Dimashqi. The name was shown in various forms on most notable 19th century maps of the region and is described by Edward Robinson in his ''Biblical Researches in Palestine
''Biblical researches in Palestine, Mount Sinai and Arabia Petraea'' (1841 edition), also ''Biblical Researches in Palestine and the Adjacent Regions'' (1856 edition), was a Travelogues of Ottoman Palestine, travelogue of 19th-century Palestine a ...
''. Although historical sources do not appear to make this distinction, it is described in some modern sources as the name for the part of the river before it flows into the Sea of Galilee.Geography
Sources
The Dan and Hasbani rivers merge near the kibbutz Sde Nehemia in northern Israel and become the Jordan river. The Hasbani (Arabic: الحاصباني ''Hasbani'', Hebrew: either שניר ''Snir'' or ''Hatzbani'') is a stream which flows from the north-western foot ofMount Hermon
Mount Hermon ( / ALA-LC: ('Mountain of the Sheikh', ), , ) is a mountain, mountain cluster constituting the southern end of the Anti-Lebanon mountain range. Its summit straddles the Lebanon–Syria border, border between Syria and Lebanon a ...
in Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, with a flow of 118 million m3 annually. The Iyyon (Hebrew: עיון ''Iyyon'', Arabic name: Ajoun stream, but دردره ''Dardara'' for the uppermost course and براغيث ''Bareighith'' or ''Beregeith'' for the rest of its course) is a stream which flows from Merj 'Ayun area in southern Lebanon into the Hasbani.
The Dan (Arabic: اللدان ''Leddan'' or ''Liddan'', Hebrew: דן ''Dan'') is the largest among the Jordan's upper course tributaries with c. 240-252 million cubic metres per year. The Banias (Arabic: بانياس ''Banias'', Hebrew: either ''Banias'' or חרמון ''Hermon'')Jordan River, Carta Jerusalem, accessed 82020 is a stream arising from a spring at Banias at the foot of Mount Hermon, with a flow of 106 million m3 annually. It flows into the Dan along with the Nahal Sion or Nahal Assal (Hebrew) / Wadi el-'Asl or Assal (Arabic).
Upper course (Hula Valley)
 The Jordan River has an upper course from its sources to the Sea of Galilee (via the Bethsaida Valley) and a lower course south of the Sea of Galilee down to the
The Jordan River has an upper course from its sources to the Sea of Galilee (via the Bethsaida Valley) and a lower course south of the Sea of Galilee down to the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valle ...
. In traditional terminology, the upper course (or most of it) is commonly referred to as passing through the " Hula Valley", as opposed to "Upper Jordan Valley"; the Sea of Galilee through which the river passes is a separate entity, and the term Jordan Valley is reserved for the lower course.
Over its upper course (fed by the Hasbani River, Banias River, Dan River, and the Iyyon Stream), the river drops rapidly in a run to the once large and swampy Lake Hula, which is slightly above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
. Exiting the now much-diminished lake, it goes through an even steeper drop over the down to the Sea of Galilee, which it enters at its northern end. The Jordan deposits much of the silt it is carrying within the lake, which it leaves again near its southern tip at Degania Dam.
Its section north of the Sea of Galilee is within the boundaries of Israel and forms the western boundary of the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
. South of the lake, it forms the border between the Kingdom of Jordan (to the east), and Israel (to the west).
Lower course
South of the Sea of Galilee, the river is situated about 210 metres below sea level. The last section follows what is commonly termed the "Jordan Valley", which has lessgradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function f of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The g ...
(the total drop is another 210 metres) so that the river meander
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the Channel (geography), channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erosion, erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank (cut bank, cut bank or river cl ...
s before entering the Dead Sea, a terminal lake about 422 metres below sea level with no outlet. The river is fed by two major tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
, the Yarmouk and Zarqa. The Yarmouk, the largest tributary of the lower course, forms the border between Syria and Jordan and then Jordan and Israel.The Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
(FAO)] of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
''Jordan Basin''
, based on 2009 "Water Report 34", accessed 18 April 2020Gafny, S. ''et al.'' (2010)
Map of the Lower Jordan River
, retrieved 14 April 2020 Smaller tributaries or "side wadis" / "side streams" in this segment are, north to south * from the east (6–10 in total) ** Wadi al-'Arab ** Wadi Ziqlab ** Wadi al-Yabis ** Wadi Kafranja or Kufrinjah passing near Ajloun ** Wadi Rajib, the last before Wadi Zarqa ** Wadi Nimrin * from the west ** Nahal Yavne'el ** Nahal Tavor (Tabor Stream) ** Nahal Yissakhar ** Nahal Harod ** Nahal Bezeq, on the border between Israel and the West Bank, between
Mount Gilboa
Mount Gilboa (; ''Jabal Jalbūʿ'' or ''Jabal Fuqqāʿa''), sometimes referred to as the Mountains of Gilboa, is the name for a mountain range in the West Bank. It overlooks the Harod Valley (the eastern part of the larger Jezreel Valley) to ...
and the Samaria
Samaria (), the Hellenized form of the Hebrew name Shomron (), is used as a historical and Hebrew Bible, biblical name for the central region of the Land of Israel. It is bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The region is ...
Mountains
** Wadi el Maleh from the Samaria Mountains
** Wadi al-Far'a coming from the Nablus
Nablus ( ; , ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a ...
area
** Wadi Auja (Arabic) or Nahal Yitav (Hebrew)
** Wadi Qelt coming down from the Judean mountains
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills (, or ,) are a mountain range in the West Bank and Israel where Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Hebron and several other biblical sites are located. The mountains reach a height of . The Judean Mountains can be div ...
and passing through Jericho
Jericho ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and the capital of the Jericho Governorate. Jericho is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It had a population of 20,907 in 2017.
F ...
History
In the 19th century the River Jordan and the Dead Sea were explored by boat primarily by Christopher Costigan in 1835, Thomas Howard Molyneux in 1847, William Francis Lynch in 1848, and John MacGregor in 1869. The full text of W. F. Lynch's 1849 book '' Narrative of the United States' Expedition to the River Jordan and the Dead Sea'' is available online. In 1964, Israel began operating a pumping station that diverts water from the Sea of Galilee to the National Water Carrier. Also in 1964, Jordan constructed a channel that diverted water from the Yarmouk to the East Ghor Canal. Syria has also built reservoirs that catch the Yarmouk's waters. Environmentalists blame Israel, Jordan and Syria for extensive damage to the Jordan River ecosystem.
In 1964, Israel began operating a pumping station that diverts water from the Sea of Galilee to the National Water Carrier. Also in 1964, Jordan constructed a channel that diverted water from the Yarmouk to the East Ghor Canal. Syria has also built reservoirs that catch the Yarmouk's waters. Environmentalists blame Israel, Jordan and Syria for extensive damage to the Jordan River ecosystem.
Environment
Ecology
The Jordan River basin has a unique ichthyofauna as it serves as the meeting point for several different biogeographic regions, including the northernPalearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is a biogeographic realm of the Earth, the largest of eight. Confined almost entirely to the Eastern Hemisphere, it stretches across Europe and Asia, north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
Th ...
, the Afrotropics, East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
& South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
, and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
. Native fish include cyprinids such as the Jordan bream (''Achanthobrama lissneri''), Jordan himri (''Carasobarbus canis''), Jordan barbel (''Luciobarbus longiceps''), Levantine scraper (''Capoeta damascina''; the most common native fish in the basin), red garra (''Garra rufa''), & Damascus garra (''Garra nana''), hillstream loaches such as the Palestine loach (''Oxynoemacheilus insignis''), catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not ...
such as the African sharptooth catfish (''Clarias gariepinus''), cichlids such as the blue tilapia (''Oreochromis aureus''), redbelly tilapia (''Coptodon zillii''), & mango tilapia (''Sarotherodon galilaeus''), and blennies such as the freshwater blenny (''Salariopsis fluviatilis''). The Jordan bream and Jordan barbel are thought to be endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to the Jordan River basin. The Jordan basin may have also served as the center of diversification for several now-widespread Palearctic fish groups.
A native freshwater reptile is the Balkan terrapin (''Mauremys rivulata''), which is thought to have also been a food source for the earliest Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
residents of the region.
Several introduced species of fish are known from the region, including common carp (''Cyprinus carpio''), grass carp (''Ctenopharyngodon idella''), black carp (''Hypophthalmichthys molitrix''), rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, ...
(''Oncorhynchus mykiss''), Nile tilapia
The Nile tilapia (''Oreochromis niloticus'') is a species of tilapia, a cichlid occurring naturally in parts of Africa (such as its namesake Nile River) and the Levant, though numerous introduced populations exist outside its natural range. T ...
(''Oreochromis niloticus''), and sea mullet (''Mugil cephalus''). Many of these introduced fish either prey on or outcompete native fish and threaten their populations, especially the more endangered species.
Flow
In modern times, up to 95% of the water is diverted for human purposes, and the flow is less than 10% of the past average. Because of this and the high evaporation rate of the Dead Sea, as well as industrial extraction of salts through evaporation ponds, the Dead Sea is rapidly shrinking. The flow rate of the Jordan River once was 1.3 billion cubic metres per year; as of 2010, just 20 to 30 million cubic metres per year flow into the Dead Sea.Pollution
A small section of the northernmost portion of the Lower Jordan, the first ca. below the Sea of Galilee, has been kept pristine for baptism and local tourism. Most polluted is the 100-kilometre downstream stretch—a meandering stream from above the confluence with the Yarmouk to the Dead Sea. Environmentalists say the practice of letting sewage and brackish water flow into the river has almost destroyed its ecosystem. Rescuing the Jordan could take decades, according to environmentalists. In 2007, FoEME named the Jordan River as one of the world's 100 most endangered ecological sites, due in part to lack of cooperation between Israel and neighboring Arab states.Roads, border crossings, bridges

Roads
Route 90, part of which is named after Rehavam Zeevi, connects the northern and southern tips of the Israeli-occupied West Bank and parallels the Jordan River on the western side.Border crossings (open bridges)
There are two border crossings between Israel and Jordan which cross the river over bridges. The northern one, Jordan River Crossing or Sheikh Hussein Bridge is nearBeit She'an
Beit She'an ( '), also known as Beisan ( '), or Beth-shean, is a town in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. The town lies at the Beit She'an Valley about 120 m (394 feet) below sea level.
Beit She'an is believed to ...
; the southern one, Allenby Bridge (also King Hussein Bridge), is near Jericho
Jericho ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and the capital of the Jericho Governorate. Jericho is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It had a population of 20,907 in 2017.
F ...
.
Bridges (historical; modern: open and closed)
North to south: * Daughters of Jacob Bridge (Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
: Gesher Bnot Ya'akov, "Daughters of Jacob Bridge") is the most famous one within Israel
* Arik Bridge at the northern end of the Sea of Galilee; allows access to the central Golan Heights, was crucial in the 1967
Events January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Canadian Confederation, Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 6 – Vietnam War: United States Marine Corps and Army of ...
and 1973 wars
* Al-Sinnabra, at the spot where the river used to exit the Sea of Galilee in the past; few remains excavated by archaeologists
* Jisr el-Majami' north of Beit She'an/Beisan; closed
* Damiya or Adam Bridge halfway between Jericho and Beit She'an; closed
* King Abdullah Bridge south of the Allenby Bridge; closed.
Importance as a water source
 Until the first decade of the 21st century, the waters of the Jordan River had been the largest water resource for Israel; lately, desalinated sea water from the
Until the first decade of the 21st century, the waters of the Jordan River had been the largest water resource for Israel; lately, desalinated sea water from the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
has taken over this role. Israel's National Water Carrier, completed in 1964, has delivered water from the Sea of Galilee to the Israeli coastal plain for over four decades, until prolonged drought led to abandoning this solution in favour of desalination.
Jordan receives of water from the river, a quantity which is regulated by the 1994 peace treaty
A peace treaty is an treaty, agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually country, countries or governments, which formally ends a declaration of war, state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an ag ...
with Israel. In the past, one of the main water resources in Jordan was the Jordan River, with a flow of 1.3 billion m3 per year (BCM/yr). However, after Israel built the National Water Carrier in 1953 and diverted water from the Sea of Galilee to Israel's coastal plains and southern desert, the flow of the Lower Jordan River dropped significantly. The 50 MCM/yr that Israel provides from the Sea of Galilee as part of the 1994 peace treaty was meant to compensate for this loss. A 2010 study found that the Lower Jordan River has been reduced to 2% of its historic flow. Water quality has also deteriorated sharply, with high levels of salinity and pollution from agricultural fertilizer and untreated wastewater upstream in Israel and the West Bank.
Conflict about the waters of the Jordan River was a contributing factor to the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
when, starting in 1965, Syria attempted to divert some of its headwaters in collaboration with Lebanon and Jordan.Mehr, Farhang, "The politics of water," in Antonino Zichichi, Richard C. Ragaini, eds., ''International Seminar on Nuclear War and Planetary Emergencies'', 30th session, Erice, Italy, 18–26 August 2003, Ettore Majorana International Centre for Scientific Culture, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pie. Ltd., 2004, p. 258, 259 The diversion works would have reduced the water availability for Israel's carrier by about 35%, and Israel's overall water supply by about 11%.
Religious significance
Hebrew Bible
 In the
In the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Genesis ). There is no regular description of the Jordan in the Bible; only scattered and indefinite references to it are given.
SMART – Multilateral project for sustainable water management in the lower Jordan Valley
* Inventory of Conflict and Environment (ICE)
Jordan River Dispute
"Map of the River Jordan and Dead Sea: And the Route of the Party Under the Command of Lieutenant W.F. Lynch, United States Navy"
is a map from the mid-19th century of the River Jordan and Dead Sea, made under the command of William F. Lynch.
"The Jordan River"
in which John the Baptist baptized his cousin Jesus of Nazareth. (Yardenit.com) {{Authority control International rivers of Asia Rivers of Israel Rivers of Jordan Rivers of Palestine Rivers of Lebanon Rivers of Syria Rivers of the West Bank Geography of Israel Geography of Palestine (region) Geography of Palestine Geography of Lebanon Geography of Syria Geography of the West Bank Great Rift Valley Hebrew Bible rivers Sacred rivers New Testament geography Catholic pilgrimage sites Environmental issues in Israel Environmental issues in Palestine Tourism in Jordan Border rivers Borders of the West Bank Israel–Jordan border Israel–Lebanon border Israel–Syria border Israel–Jordan relations Rivers in Mandaeism
. '' Genesis ). There is no regular description of the Jordan in the Bible; only scattered and indefinite references to it are given.
Jacob
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother E ...
crossed it and its tributary, the Jabbok (the modern Zarqa River), on his way back from Haran
Haran or Aran ( ''Hārān'') is a man in the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible. He was a son of Terah, brother of Abraham, and father of son Lot and daughters Milcah and Iscah. He died in Ur of the Chaldees. Through Lot, Haran was the ance ...
(, ). It is noted as the line of demarcation between the "two tribes and the half tribe" settled to the east
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
(Numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
) and the "nine tribes and the half tribe of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh (; Hebrew: ''Ševet Mənašše,'' Tiberian: ''Šēḇeṭ Mănašše'') was one of the twelve tribes of Israel. After the catastrophic Assyrian invasion of 720 BCE, it is counted as one ...
" that settled to the west (, passim).
Opposite Jericho
Jericho ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and the capital of the Jericho Governorate. Jericho is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It had a population of 20,907 in 2017.
F ...
, it is called "the Jordan of Jericho" (; ). The Jordan has a number of fords, and one of them is famous as the place where many Ephraimites were slain by Jephthah ( Judges ). It seems that these are the same fords mentioned as being near Beth-barah, where Gideon lay in wait for the Midianites (). In the plain of the Jordan, between Succoth and Zarthan, is the clay ground where Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ...
had his bronze foundries ( 1 Kings ). In the Jordan valley is portrayed as a woodland region. Biblical commentator Albert Barnes suggests that "trees were rare in most parts of Palestine, but plentiful in the Jordan Valley".
In biblical history, the Jordan appears as the scene of several miracles, the first taking place when the Jordan, near Jericho, was crossed by the Israelites under Joshua ( Joshua 3:15-17). Later the two tribes and the half tribe that settled east of the Jordan built a large altar on its banks as "a witness" between them and the other tribes (, , et seq.). The Jordan was crossed by Elijah
Elijah ( ) or Elias was a prophet and miracle worker who lived in the northern kingdom of Israel during the reign of King Ahab (9th century BC), according to the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible.
In 1 Kings 18, Elijah defended the worsh ...
and Elisha on dry ground (, ). Elisha performed two miracles at the Jordan: he healed Naaman's leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a Chronic condition, long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the Peripheral nervous system, nerves, respir ...
by having him bathe in its waters (), and he made an axe head lost by one of the "children of the prophets" float, by throwing a piece of wood into the water ().
New Testament
TheNew Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
states that John the Baptist
John the Baptist ( – ) was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early first century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy and Oriental Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in some Baptist ...
baptised unto repentance in the Jordan ( Matthew 3:5– 6; Mark; Luke ; John). These acts of baptism
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water eit ...
are also reported as having taken place at Bethabara (). Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
came to be baptised by him there ( Matthew 3:13; ; , ). The Jordan is also where John the Baptist bore record of Jesus as the Son of God and Lamb of God
Lamb of God (; , ) is a Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, title for Jesus that appears in the Gospel of John. It appears at wikisource:Bible (American Standard)/John#1:29, John 1:29, where John the Baptist sees Jesus and exclaims, " ...
(). The prophecy
In religion, mythology, and fiction, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a ''prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain di ...
of Isaiah regarding the Messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
which names the Jordan () is reported in .
The New Testament speaks several times about Jesus crossing the Jordan during his ministry (; ) and of believers crossing the Jordan to come hear him preach and to be healed of their diseases (; ). When his enemies sought to capture him, Jesus took refuge at the river in the place John had first baptised ().
Scholars have concluded that the site called Al-Maghtas on the east side has long been considered the location for the Baptism of Jesus and a place of pilgrimage. This has led to choosing Al-Maghtas as a UNESCO World Heritage site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
in 2015.
Derived cultural significance
Symbolism
Because, according to Jewish tradition, theIsraelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
made a difficult and hazardous journey from slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
to freedom in the Promised Land, the Jordan can refer to freedom. The actual crossing is the final step of the journey, which is then complete.
Among many other references, the Jordan River is given this meaning in the text of '' Old Man River'': "Let me go 'way from the Mississippi / Let me go 'way from the white man boss / Show me that stream called the River Jordan / That's the old stream that I long to cross".
Christening of royals
Because of the baptism of Jesus, water from the Jordan is employed for the christening of heirs and princes in several Christian royal houses, such as the cases of Prince George of Wales, Simeon of Bulgaria and James Ogilvy. Earlier, On 15 May 1717, the EmpressMaria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the ...
was baptised in Vienna by the Papal Nuntius Giorgio Spinola, representing Pope Clement XI, with baptismal water containing a few drops from the River Jordan.
Christian poetry and music
The Jordan is a frequent symbol in folk,gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christianity, Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the second century Anno domino, AD the term (, from which the English word originated as a calque) came to be used also for the books in which the message w ...
, and spiritual music, and in poetic and literary
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, plays, and poems. It includes both print and digital writing. In recent centuries, ...
works. The baptism of Jesus is referred to in a hymn by the reformer Martin Luther, "" (1541), base for a cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach, (1724).
The Jordan River, due primarily to its rich spiritual importance, has provided inspiration for countless songs, hymns, and stories, including the traditional African-American spiritual/folk songs " Michael Row the Boat Ashore", " Deep River", and " Roll, Jordan, Roll". It is mentioned in the songs " Eve of Destruction", " Will You Be There", and " The Wayfaring Stranger" and in " Ol' Man River" from the musical ''Show Boat
''Show Boat'' is a musical theatre, musical with music by Jerome Kern and book and lyrics by Oscar Hammerstein II. It is based on Edna Ferber's best-selling 1926 Show Boat (novel), novel of the same name. The musical follows the lives of the per ...
''. "The Far Side Banks of Jordan" by Johnny Cash
John R. Cash (born J. R. Cash; February 26, 1932 – September 12, 2003) was an American singer-songwriter. Most of his music contains themes of sorrow, moral tribulation, and redemption, especially songs from the later stages of his career. ...
and June Carter Cash on June's Grammy Award
The Grammy Awards, stylized as GRAMMY, and often referred to as The Grammys, are awards presented by The Recording Academy of the United States to recognize outstanding achievements in music. They are regarded by many as the most prestigious ...
-winning studio album, '' Press On'', mentions the Jordan River as well as the Promised Land. Jordan River is the subject of roots reggae
Roots reggae is a subgenre of reggae that deals with the everyday lives and aspirations of Ethnic groups of Africa, Africans and those in the African Diaspora, including the spiritual side of Rastafari, black liberation, revolution and the ho ...
artist Burning Spear's song of the same title. Belarusian band Spasenie dedicated its whole album " Crossing the Jordan" to the topic.
See also
* Ænon * Ed-Dikke synagogue *Fair river sharing
Fair river sharing is a kind of a fair division problem in which the waters of a river has to be divided among countries located along the river. It differs from other fair division problems in that the resource to be divided—the water—flows i ...
* Island of Peace
* Jordan Rift Valley
The Jordan Rift Valley, also Jordan Valley ( ''Bīqʿāt haYardēn'', Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr), is an elongated endorheic basin located in modern-day Israel, Jordan and the West Bank, Palestine. This geographic region includes the entire length o ...
* List of most-polluted rivers
* List of rivers of Israel
* List of rivers of Jordan
This is a list of rivers in Jordan. This list is arranged by drainage basin, with respective tributaries indented under each larger stream's name. Many of these rivers are seasonal.
Dead Sea
Rivers and streams flowing into the Dead Sea:
Jordan ...
* Mandaeans
Mandaeans (Mandaic language, Mandaic: ࡌࡀࡍࡃࡀࡉࡉࡀ) ( ), also known as Mandaean Sabians ( ) or simply as Sabians ( ), are an ethnoreligious group who are followers of Mandaeism. They believe that John the Baptist was the final and ...
* Naharayim
Naharayim ( literally "Two rivers"), historically the Jisr Majami area ( literally "Meeting bridge" area), is the area where the Yarmouk River flows into the Jordan River. It was the site of the "First Jordan Hydro-Electric Power House", con ...
* Sacred waters
Sacred waters are sacred natural sites characterized by tangible topographical land formations such as rivers, lakes, spring (hydrosphere), springs, Water reservoir, reservoirs, and oceans, as opposed to holy water which is water elevated with th ...
Notes
References
* * *External links
SMART – Multilateral project for sustainable water management in the lower Jordan Valley
* Inventory of Conflict and Environment (ICE)
Jordan River Dispute
"Map of the River Jordan and Dead Sea: And the Route of the Party Under the Command of Lieutenant W.F. Lynch, United States Navy"
is a map from the mid-19th century of the River Jordan and Dead Sea, made under the command of William F. Lynch.
"The Jordan River"
in which John the Baptist baptized his cousin Jesus of Nazareth. (Yardenit.com) {{Authority control International rivers of Asia Rivers of Israel Rivers of Jordan Rivers of Palestine Rivers of Lebanon Rivers of Syria Rivers of the West Bank Geography of Israel Geography of Palestine (region) Geography of Palestine Geography of Lebanon Geography of Syria Geography of the West Bank Great Rift Valley Hebrew Bible rivers Sacred rivers New Testament geography Catholic pilgrimage sites Environmental issues in Israel Environmental issues in Palestine Tourism in Jordan Border rivers Borders of the West Bank Israel–Jordan border Israel–Lebanon border Israel–Syria border Israel–Jordan relations Rivers in Mandaeism