Join Count Statistics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Join count statistics are a method of
 Given
Given
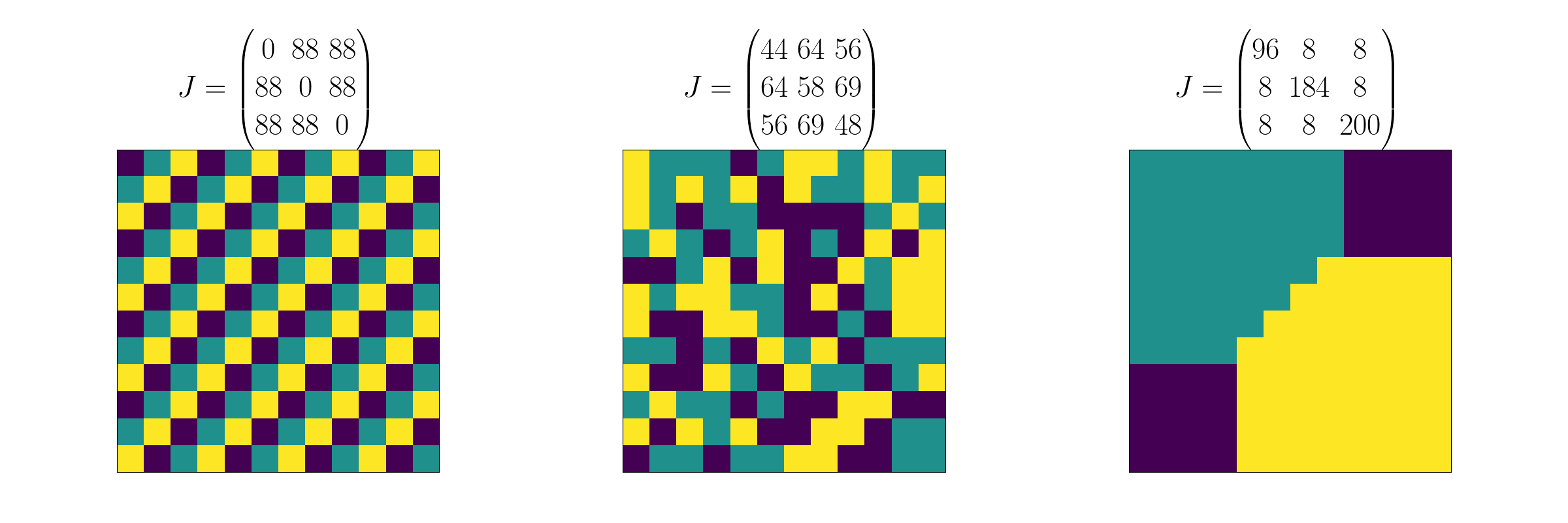 When there are categories join count statistics have been generalised
:
Where is an
When there are categories join count statistics have been generalised
:
Where is an
spatial analysis
Spatial analysis is any of the formal Scientific technique, techniques which study entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties, primarily used in Urban design, Urban Design. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techni ...
used to assess the degree of association, in particular the autocorrelation
Autocorrelation, sometimes known as serial correlation in the discrete time case, measures the correlation of a signal with a delayed copy of itself. Essentially, it quantifies the similarity between observations of a random variable at differe ...
, of categorical variables distributed over a spatial map. They were originally introduced by Australian statistician P. A. P. Moran. Join count statistics have found widespread use in econometrics
Econometrics is an application of statistical methods to economic data in order to give empirical content to economic relationships. M. Hashem Pesaran (1987). "Econometrics", '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 2, p. 8 p. 8 ...
, remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring inform ...
and ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
.Dale MR, Fortin MJ. Spatial analysis: a guide for ecologists. Cambridge University Press; 2014 Sep 11. Join count statistics can be computed in a number of software packages including PASSaGE, GeoDA, PySAL and spdep.
Binary data
 Given
Given binary data
Binary data is data whose unit can take on only two possible states. These are often labelled as 0 and 1 in accordance with the binary numeral system and Boolean algebra.
Binary data occurs in many different technical and scientific fields, wh ...
distributed over spatial sites, where the neighbour relations between regions and are encoded in the spatial weight matrix
:
the join count statistics are defined as
:
Where
:
:
:
:
The subscripts refer to 'black'=1 and 'white'=0 sites. The relation implies only three of the four numbers are independent. Generally speaking, large values of and relative to imply autocorrelation and relatively large values of imply anti-correlation.
To assess the statistical significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when a result at least as "extreme" would be very infrequent if the null hypothesis were true. More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the ...
of these statistics, the expectation under various null models has been computed.Sokal RR, Oden NL. Spatial autocorrelation in biology: 1. Methodology. Biological journal of the Linnean Society. 1978 Jun 1;10(2):199-228. For example, if the null hypothesis
The null hypothesis (often denoted ''H''0) is the claim in scientific research that the effect being studied does not exist. The null hypothesis can also be described as the hypothesis in which no relationship exists between two sets of data o ...
is that each sample is chosen at random according to a Bernoulli process
In probability and statistics, a Bernoulli process (named after Jacob Bernoulli) is a finite or infinite sequence of binary random variables, so it is a discrete-time stochastic process that takes only two values, canonically 0 and 1. The ...
with probability
:
then Cliff and Ord show that
:
:
:
:
where
:
:
:
However in practice an approach based on random permutations is preferred, since it requires fewer assumptions.
Local join count statistic
Anselin and Li introducedAnselin L, Li X. Operational local join count statistics for cluster detection. Journal of geographical systems. 2019 Jun 1;21:189-210. the idea of the local join count statistic, following Anselin's general idea of a Local Indicator of Spatial Association (LISA). Local Join Count is defined by e.g. : with similar definitions for and . This is equivalent to theGetis–Ord statistics
Getis–Ord statistics, also known as Gi*, are used in spatial analysis to measure the local and global spatial autocorrelation. Developed by statisticians Arthur Getis and J. Keith Ord they are commonly used for ''Hot Spot Analysis'' to identify ...
computed with binary data. Some analytic results for the expectation of the local statistics are available based on the hypergeometric distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the hypergeometric distribution is a Probability distribution#Discrete probability distribution, discrete probability distribution that describes the probability of k successes (random draws for which the ...
but due to the multiple comparisons problem
Multiple comparisons, multiplicity or multiple testing problem occurs in statistics when one considers a set of statistical inferences simultaneously or estimates a subset of parameters selected based on the observed values.
The larger the numbe ...
a permutation based approach is again preferred in practice.
Extension to multiple categories
 When there are categories join count statistics have been generalised
:
Where is an
When there are categories join count statistics have been generalised
:
Where is an indicator function
In mathematics, an indicator function or a characteristic function of a subset of a set is a function that maps elements of the subset to one, and all other elements to zero. That is, if is a subset of some set , then the indicator functio ...
for the variable belonging to the category . Analytic results are availableEpperson, B.K., 2003. Covariances among join-count spatial autocorrelation measures. Theoretical Population Biology, 64(1), pp.81-87. or a permutation approach can be used to test for significance as in the binary case.
Spatial analysis
Covariance and correlation
References
{{reflist