Indian Ocean on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five
 Several features make the Indian Ocean unique. It constitutes the core of the large-scale Tropical Warm Pool which, when interacting with the atmosphere, affects the climate both regionally and globally. Asia blocks heat export and prevents the ventilation of the Indian Ocean thermocline. That continent also drives the Indian Ocean
Several features make the Indian Ocean unique. It constitutes the core of the large-scale Tropical Warm Pool which, when interacting with the atmosphere, affects the climate both regionally and globally. Asia blocks heat export and prevents the ventilation of the Indian Ocean thermocline. That continent also drives the Indian Ocean
 * Madagascar and the islands of the western Indian Ocean (Comoros, Réunion, Mauritius, Rodrigues, the Seychelles, and Socotra), includes 13,000 (11,600 endemic) species of plants; 313 (183) birds; reptiles 381 (367); 164 (97) freshwater fishes; 250 (249) amphibians; and 200 (192) mammals.
The origin of this diversity is debated; the break-up of Gondwana can explain vicariance older than 100 mya, but the diversity on the younger, smaller islands must have required a Cenozoic dispersal from the rims of the Indian Ocean to the islands. A "reverse colonisation", from islands to continents, apparently occurred more recently; the chameleons, for example, first diversified on Madagascar and then colonised Africa. Several species on the islands of the Indian Ocean are textbook cases of evolutionary processes; the dung beetles, day geckos, and
* Madagascar and the islands of the western Indian Ocean (Comoros, Réunion, Mauritius, Rodrigues, the Seychelles, and Socotra), includes 13,000 (11,600 endemic) species of plants; 313 (183) birds; reptiles 381 (367); 164 (97) freshwater fishes; 250 (249) amphibians; and 200 (192) mammals.
The origin of this diversity is debated; the break-up of Gondwana can explain vicariance older than 100 mya, but the diversity on the younger, smaller islands must have required a Cenozoic dispersal from the rims of the Indian Ocean to the islands. A "reverse colonisation", from islands to continents, apparently occurred more recently; the chameleons, for example, first diversified on Madagascar and then colonised Africa. Several species on the islands of the Indian Ocean are textbook cases of evolutionary processes; the dung beetles, day geckos, and
 Pleistocene fossils of ''
Pleistocene fossils of '' At least eleven prehistoric tsunamis have struck the Indian Ocean coast of Indonesia between 7400 and 2900 years ago. Analysing sand beds in caves in the Aceh region, scientists concluded that the intervals between these tsunamis have varied from series of minor tsunamis over a century to dormant periods of more than 2000 years preceding megathrusts in the Sunda Trench. Although the risk for future tsunamis is high, a major megathrust such as the one in 2004 is likely to be followed by a long dormant period.
A group of scientists have argued that two large-scale impact events have occurred in the Indian Ocean: the Burckle Crater in the southern Indian Ocean in 2800 BCE and the Kanmare and Tabban craters in the
At least eleven prehistoric tsunamis have struck the Indian Ocean coast of Indonesia between 7400 and 2900 years ago. Analysing sand beds in caves in the Aceh region, scientists concluded that the intervals between these tsunamis have varied from series of minor tsunamis over a century to dormant periods of more than 2000 years preceding megathrusts in the Sunda Trench. Although the risk for future tsunamis is high, a major megathrust such as the one in 2004 is likely to be followed by a long dormant period.
A group of scientists have argued that two large-scale impact events have occurred in the Indian Ocean: the Burckle Crater in the southern Indian Ocean in 2800 BCE and the Kanmare and Tabban craters in the
 The Red Sea, one of the main trade routes in Antiquity, was explored by
The Red Sea, one of the main trade routes in Antiquity, was explored by 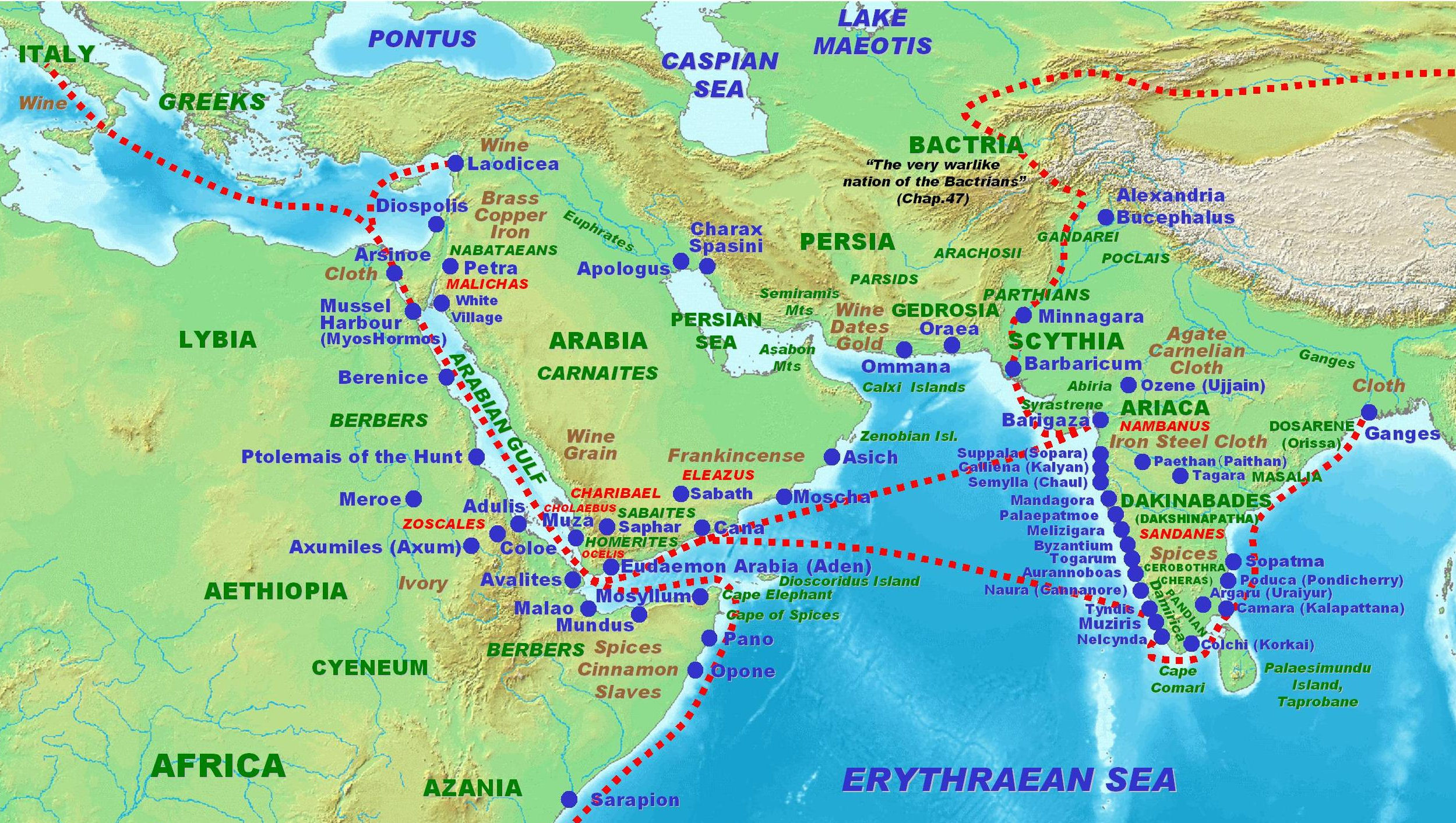 ''
''
 Unlike the Pacific Ocean where the civilization of the Polynesians reached most of the far-flung islands and atolls and populated them, almost all the islands, archipelagos and atolls of the Indian Ocean were uninhabited until colonial times. Although there were numerous ancient civilizations in the coastal states of Asia and parts of Africa, the
Unlike the Pacific Ocean where the civilization of the Polynesians reached most of the far-flung islands and atolls and populated them, almost all the islands, archipelagos and atolls of the Indian Ocean were uninhabited until colonial times. Although there were numerous ancient civilizations in the coastal states of Asia and parts of Africa, the
 Throughout the colonial era, islands such as
Throughout the colonial era, islands such as
 The sea lanes in the Indian Ocean are considered among the most strategically important in the world with more than 80 percent of the world's seaborne trade in oil transits through the Indian Ocean and its vital chokepoints, with 40 percent passing through the Strait of Hormuz, 35 percent through the Strait of Malacca and 8 percent through the Bab el-Mandab Strait.
The Indian Ocean provides major sea routes connecting the Middle East, Africa, and East Asia with Europe and the Americas. It carries a particularly heavy traffic of petroleum and petroleum products from the oil fields of the Persian Gulf and Indonesia. Large reserves of hydrocarbons are being tapped in the offshore areas of Saudi Arabia, Iran, India, and Western Australia. An estimated 40% of the world's offshore oil production comes from the Indian Ocean. Beach sands rich in heavy minerals, and offshore placer deposits are actively exploited by bordering countries, particularly India, Pakistan, South Africa, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
In particular, the maritime part of the
The sea lanes in the Indian Ocean are considered among the most strategically important in the world with more than 80 percent of the world's seaborne trade in oil transits through the Indian Ocean and its vital chokepoints, with 40 percent passing through the Strait of Hormuz, 35 percent through the Strait of Malacca and 8 percent through the Bab el-Mandab Strait.
The Indian Ocean provides major sea routes connecting the Middle East, Africa, and East Asia with Europe and the Americas. It carries a particularly heavy traffic of petroleum and petroleum products from the oil fields of the Persian Gulf and Indonesia. Large reserves of hydrocarbons are being tapped in the offshore areas of Saudi Arabia, Iran, India, and Western Australia. An estimated 40% of the world's offshore oil production comes from the Indian Ocean. Beach sands rich in heavy minerals, and offshore placer deposits are actively exploited by bordering countries, particularly India, Pakistan, South Africa, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
In particular, the maritime part of the
ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
ic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth's surface
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60th parallel south, 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is the seco ...
or Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, depending on the definition in use. The Indian Ocean has large marginal or regional seas, including the Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated f ...
, the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
, the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
, and the Laccadive Sea.
Geologically, the Indian Ocean is the youngest of the oceans, and it has distinct features such as narrow continental shelves. Its average depth is 3,741 m. It is the warmest ocean, with a significant impact on global climate due to its interaction with the atmosphere. Its waters are affected by the Indian Ocean Walker circulation, resulting in unique oceanic currents and upwelling patterns. The Indian Ocean is ecologically diverse, with important ecosystems such as coral reefs, mangroves, and sea grass beds. It hosts a significant portion of the world's tuna catch and is home to endangered marine species. The climate around the Indian Ocean is characterized by monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
s.
The Indian Ocean has been a hub of cultural and commercial exchange since ancient times. It played a key role in early human migrations and the spread of civilizations. In modern times, it remains crucial for global trade, especially in oil and hydrocarbons. Environmental and geopolitical concerns in the region include climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
, pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
, piracy, and disputes over island territories.
Etymology
The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515, when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' () is attested, named after India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century, as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
) before the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
was surmised. In modern times, the name Afro-Asian Ocean has occasionally been used.
The Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
name for the Ocean is (; ). Conversely, Chinese explorers (e.g., Zheng He during the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
) who traveled to the Indian Ocean during the 15th century called it the Western Oceans. In Ancient Greek geography
;Pre-Hellenistic Classical Greece
*Homer
*Anaximander (died )
*Hecataeus of Miletus (died )
*Massaliote Periplus (6th century BC)
*Scylax of Caryanda (6th century BC)
*Herodotus (died )
;Hellenistic period
*Pytheas (died )
*''Periplus of Pseudo- ...
, the Indian Ocean region known to the Greeks was called the Erythraean Sea.
Geography
Extent and data
The borders of the Indian Ocean, as delineated by theInternational Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) (French: ''Organisation Hydrographique Internationale'') is an intergovernmental organization representing hydrography. the IHO comprised 102 member states.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ...
in 1953, included the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60th parallel south, 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is the seco ...
but not the marginal seas along the northern rim. In 2002 the IHO delimited the Southern Ocean separately, which removed waters south of 60°S from the Indian Ocean but included the northern marginal seas. Meridionally, the Indian Ocean is delimited from the Atlantic Ocean by the 20° east meridian, running south from Cape Agulhas, South Africa, and from the Pacific Ocean by the meridian of 146°49'E, running south from South East Cape on the island of Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
in Australia. The northernmost extent of the Indian Ocean (including marginal seas) is approximately 30°N in the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
.
The Indian Ocean covers , including the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
and the Persian Gulf but excluding the Southern Ocean, or 19.5% of the world's oceans. Its volume is or 19.8% of the world's oceans' volume; it has an average depth of and a maximum depth of .
All of the Indian Ocean is in the Eastern Hemisphere. The centre of the Eastern Hemisphere, the 90th meridian east, passes through the Ninety East Ridge.
Within these waters are a number of islands. These include those controlled by surrounding countries, and independent island states and territories. Of the non-coastal islands, there are two broad clusters: one around Madagascar, and one south of India. A few other oceanic islands are scattered elsewhere.
Coasts and shelves
In contrast to the Atlantic and Pacific, the Indian Ocean is enclosed by major landmasses and an archipelago on three sides and does not stretch from pole to pole, and can be likened to an embayed ocean. It is centered on the Indian Peninsula. Although this subcontinent has played a significant role in its history, the Indian Ocean has foremostly been a cosmopolitan stage, interlinking diverse regions by innovations, trade, and religion since early in human history. The active margins of the Indian Ocean have an average width (horizontal distance from land to shelf break) of with a maximum width of . The passive margins have an average width of . The average width of the slopes (horizontal distance from shelf break to foot of slope) of the continental shelves are for active and passive margins respectively, with a maximum width of . In correspondence of the Shelf break, also known as Hinge zone, the Bouguer gravity ranges from 0 to 30 mGals that is unusual for a continental region of around 16 km thick sediments. It has been hypothesized that the "Hinge zone may represent the relict of continental and proto-oceanic crustal boundary formed during the rifting of India fromAntarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
."
Australia, Indonesia, and India are the three countries with the longest shorelines and exclusive economic zone
An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine natural resource, reso ...
s. The continental shelf makes up 15% of the Indian Ocean.
More than two billion people live in countries bordering the Indian Ocean, compared to 1.7 billion for the Atlantic and 2.7 billion for the Pacific (some countries border more than one ocean).
Rivers
The Indian Oceandrainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
covers , virtually identical to that of the Pacific Ocean and half that of the Atlantic basin, or 30% of its ocean surface (compared to 15% for the Pacific). The Indian Ocean drainage basin is divided into roughly 800 individual basins, half that of the Pacific, of which 50% are located in Asia, 30% in Africa, and 20% in Australasia. The rivers of the Indian Ocean are shorter on average () than those of the other major oceans. The largest rivers are ( order 5) the Zambezi
The Zambezi (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than half of t ...
, Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
- Brahmaputra, Indus, Jubba, and Murray rivers and (order 4) the Shatt al-Arab, Wadi Ad Dawasir (a dried-out river system on the Arabian Peninsula) and Limpopo
Limpopo () is the northernmost Provinces of South Africa, province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River, which forms the province's western and northern borders. The term Limpopo is derived from Rivombo (Livombo/Lebombo), a ...
rivers. After the breakup of East Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
and the formation of the Himalayas, the Ganges-Brahmaputra rivers flow into the world's largest delta known as the Bengal delta
The Ganges Delta (also known the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, the Sundarbans Delta or the Bengal Delta) is a river delta predominantly covering the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West B ...
or Sunderbans.
Marginal seas
Marginal seas, gulfs, bays and straits of the Indian Ocean include: Along the east coast of Africa, the Mozambique Channel separatesMadagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
from mainland Africa, while the Sea of Zanj is located north of Madagascar.
On the northern coast of the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
, Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden (; ) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. ...
is connected to the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
by the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb. In the Gulf of Aden, the Gulf of Tadjoura is located in Djibouti and the Guardafui Channel separates Socotra island from the Horn of Africa. The northern end of the Red Sea terminates in the Gulf of Aqaba and Gulf of Suez. The Indian Ocean is artificially connected to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
without ship lock through the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
, which is accessible via the Red Sea. The Arabian Sea is connected to the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
by the Gulf of Oman and the Strait of Hormuz. In the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Bahrain separates Qatar from the Arabic Peninsula.
Along the west coast of India, the Gulf of Kutch and Gulf of Khambat are located in Gujarat in the northern end while the Laccadive Sea separates the Maldives from the southern tip of India. The Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
is off the east coast of India. The Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait separate Sri Lanka from India, while Adam's Bridge separates the two. The Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated f ...
is located between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Islands.
In Indonesia, the so-called Indonesian Seaway is composed of the Malacca, Sunda and Torres Straits.
The Gulf of Carpentaria
The Gulf of Carpentaria is a sea off the northern coast of Australia. It is enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea, which separates Australia and New Guinea. The northern boundary ...
is located on the Australian north coast while the Great Australian Bight
The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight (geography), bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern Coast, coastline of mainland Australia.
There are two definitions for its extent—one by the Internation ...
constitutes a large part of its southern coast.
# Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
– 3.862 million km2
# Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
– 2.172 million km2
# Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated f ...
– 797,700 km2
# Laccadive Sea – 786,000 km2
# Mozambique Channel – 700,000 km2
# Timor Sea
The Timor Sea (, , or ) is a relatively shallow sea in the Indian Ocean bounded to the north by the island of Timor with Timor-Leste to the north, Indonesia to the northwest, Arafura Sea to the east, and to the south by Australia. The Sunda Tr ...
– 610,000 km2
# Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
– 438,000 km2
# Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden (; ) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. ...
– 410,000 km2
# Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
– 251,000 km2
# Flores Sea – 240,000 km2
# Molucca Sea
The Molucca Sea (Indonesian language, Indonesian: ''Laut Maluku'') is located in the western Pacific Ocean, around the vicinity of Indonesia, specifically bordered by the Indonesian Islands of Sulawesi, Celebes (Sulawesi) to the west, Halmahera t ...
– 200,000 km2
# Gulf of Oman – 181,000 km2
# Great Australian Bight
The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight (geography), bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern Coast, coastline of mainland Australia.
There are two definitions for its extent—one by the Internation ...
– 45,926 km2
# Gulf of Aqaba – 239 km2
# Gulf of Khambhat
# Gulf of Kutch
# Gulf of Suez
# Dubai Canal
# Strait of Hormuz
Climate
 Several features make the Indian Ocean unique. It constitutes the core of the large-scale Tropical Warm Pool which, when interacting with the atmosphere, affects the climate both regionally and globally. Asia blocks heat export and prevents the ventilation of the Indian Ocean thermocline. That continent also drives the Indian Ocean
Several features make the Indian Ocean unique. It constitutes the core of the large-scale Tropical Warm Pool which, when interacting with the atmosphere, affects the climate both regionally and globally. Asia blocks heat export and prevents the ventilation of the Indian Ocean thermocline. That continent also drives the Indian Ocean monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
, the strongest on Earth, which causes large-scale seasonal variations in ocean currents, including the reversal of the Somali Current and Indian Monsoon Current. Because of the Indian Ocean Walker circulation there are no continuous equatorial easterlies. Upwelling
Upwelling is an physical oceanography, oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted sur ...
occurs near the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
and the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
and north of the trade winds in the Southern Hemisphere. The Indonesian Throughflow is a unique Equatorial connection to the Pacific.
The climate north of the equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
is affected by a monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
climate. Strong north-east winds blow from October until April; from May until October south and west winds prevail. In the Arabian Sea, the violent Monsoon brings rain to the Indian subcontinent. In the southern hemisphere, the winds are generally milder, but summer storms near Mauritius can be severe. When the monsoon winds change, cyclones sometimes strike the shores of the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
and the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
. Some 80% of the total annual rainfall in India occurs during summer and the region is so dependent on this rainfall that many civilisations perished when the Monsoon failed in the past. The huge variability in the Indian Summer Monsoon has also occurred pre-historically, with a strong, wet phase 33,500–32,500 BP; a weak, dry phase 26,000–23,500 BC; and a very weak phase 17,000–15,000 BP,
corresponding to a series of dramatic global events: Bølling–Allerød warming, Heinrich, and Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (YD, Greenland Stadial GS-1) was a period in Earth's geologic history that occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years Before Present (BP). It is primarily known for the sudden or "abrupt" cooling in the Northern Hemisphere, when the ...
.
The Indian Ocean is the warmest ocean in the world. Long-term ocean temperature records show a rapid, continuous warming in the Indian Ocean, at about (compared to for the warm pool region) during 1901–2012. Research indicates that human induced greenhouse warming, and changes in the frequency and magnitude of El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional entities
* El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit
* Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things''
* El, fami ...
(or the Indian Ocean Dipole), events are a trigger to this strong warming in the Indian Ocean. While the Indian Ocean warmed at a rate of 1.2 °C per century during 1950–2020, climate models predict accelerated warming, at a rate of 1.7 °C–3.8 °C per century during 2020–2100. Though the warming is basin-wide, maximum warming is in the northwestern Indian Ocean including the Arabian Sea, and reduced warming off the Sumatra and Java coasts in the southeast Indian Ocean. Global warming is projected to push the tropical Indian Ocean into a basin-wide near-permanent heatwave state by the end of the 21st century, where marine heatwaves are projected to increase from 20 days per year (during 1970–2000) to 220–250 days per year.
South of the Equator (20–5°S), the Indian Ocean is gaining heat from June to October, during the austral winter, while it is losing heat from November to March, during the austral summer.
In 1999, the Indian Ocean Experiment showed that fossil fuel and biomass burning in South and Southeast Asia caused air pollution (also known as the Asian brown cloud) that reach as far as the Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the t ...
. This pollution has implications on both a local and global scale.
Oceanography
Forty percent of the sediment of the Indian Ocean is found in the Indus and Ganges fans. The oceanic basins adjacent to the continental slopes mostly contain terrigenous sediments. The ocean south of the polar front (roughly 50° south latitude) is high in biologic productivity and dominated by non-stratified sediment composed mostly of siliceous oozes. Near the three major mid-ocean ridges the ocean floor is relatively young and therefore bare of sediment, except for the Southwest Indian Ridge due to its ultra-slow spreading rate. The ocean's currents are mainly controlled by the monsoon. Two large gyres, one in the northern hemisphere flowing clockwise and one south of the equator moving anticlockwise (including the Agulhas Current and Agulhas Return Current), constitute the dominant flow pattern. During the winter monsoon (November–February), however, circulation is reversed north of 30°S and winds are weakened during winter and the transitional periods between the monsoons. The Indian Ocean contains the largest submarine fans of the world, the Bengal Fan and Indus Fan, and the largest areas of slope terraces and rift valleys. The inflow of deep water into the Indian Ocean is 11 Sv, most of which comes from the Circumpolar Deep Water (CDW). The CDW enters the Indian Ocean through the Crozet andMadagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
basins and crosses the Southwest Indian Ridge at 30°S. In the Mascarene Basin the CDW becomes a deep western boundary current before it is met by a re-circulated branch of itself, the North Indian Deep Water. This mixed water partly flows north into the Somali Basin whilst most of it flows clockwise in the Mascarene Basin where an oscillating flow is produced by Rossby waves
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby in the Earth's atmosphere in 1939. They ar ...
.
Water circulation in the Indian Ocean is dominated by the Subtropical Anticyclonic Gyre, the eastern extension of which is blocked by the Southeast Indian Ridge and the 90°E Ridge. Madagascar and the Southwest Indian Ridge separate three cells south of Madagascar and off South Africa. North Atlantic Deep Water reaches into the Indian Ocean south of Africa at a depth of and flows north along the eastern continental slope of Africa. Deeper than NADW, Antarctic Bottom Water flows from Enderby Basin to Agulhas Basin across deep channels (<) in the Southwest Indian Ridge, from where it continues into the Mozambique Channel and Prince Edward fracture zone.
North of 20° south latitude the minimum surface temperature is , exceeding to the east. Southward of 40° south latitude, temperatures drop quickly.
The Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
contributes more than half () of the runoff water to the Indian Ocean. Mainly in summer, this runoff flows into the Arabian Sea but also south across the Equator where it mixes with fresher seawater from the Indonesian Throughflow. This mixed freshwater joins the South Equatorial Current in the southern tropical Indian Ocean.
Sea surface salinity is highest (more than 36 PSU) in the Arabian Sea because evaporation exceeds precipitation there. In the Southeast Arabian Sea salinity drops to less than 34 PSU. It is the lowest (c. 33 PSU) in the Bay of Bengal because of river runoff and precipitation. The Indonesian Throughflow and precipitation results in lower salinity (34 PSU) along the Sumatran west coast. Monsoonal variation results in eastward transportation of saltier water from the Arabian Sea to the Bay of Bengal from June to September and in westerly transport by the East India Coastal Current to the Arabian Sea from January to April.
An Indian Ocean garbage patch was discovered in 2010 covering at least . Riding the southern Indian Ocean Gyre, this vortex of plastic garbage constantly circulates the ocean from Australia to Africa, down the Mozambique Channel, and back to Australia in a period of six years, except for debris that gets indefinitely stuck in the centre of the gyre.
The garbage patch in the Indian Ocean will, according to a 2012 study, decrease in size after several decades to vanish completely over centuries. Over several millennia, however, the global system of garbage patches will accumulate in the North Pacific.
There are two amphidromes of opposite rotation in the Indian Ocean, probably caused by Rossby wave propagation.
Iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of fresh water ice more than long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". Much of an i ...
s drift as far north as 55° south latitude, similar to the Pacific but less than in the Atlantic where icebergs reach up to 45°S. The volume of iceberg loss in the Indian Ocean between 2004 and 2012 was 24 Gt.
Since the 1960s, anthropogenic warming of the global ocean combined with contributions of freshwater from retreating land ice causes a global rise in sea level. Sea level also increases in the Indian Ocean, except in the south tropical Indian Ocean where it decreases, a pattern most likely caused by rising levels of greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es.
Marine life
Among the tropical oceans, the western Indian Ocean hosts one of the largest concentrations of phytoplankton blooms in summer, due to the strongmonsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
winds. The monsoonal wind forcing leads to a strong coastal and open ocean upwelling
Upwelling is an physical oceanography, oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted sur ...
, which introduces nutrients into the upper zones where sufficient light is available for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
and phytoplankton production. These phytoplankton blooms support the marine ecosystem, as the base of the marine food web, and eventually the larger fish species. The Indian Ocean accounts for the second-largest share of the most economically valuable tuna catch. Its fish are of great and growing importance to the bordering countries for domestic consumption and export. Fishing fleets from Russia, Japan, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
, and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
also exploit the Indian Ocean, mainly for shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
and tuna.
Research indicates that increasing ocean temperatures are taking a toll on the marine ecosystem. A study on the phytoplankton changes in the Indian Ocean indicates a decline of up to 20% in the marine plankton in the Indian Ocean, during the past six decades. The tuna catch rates have also declined 50–90% during the past half-century, mostly due to increased industrial fisheries, with the ocean warming adding further stress to the fish species.
Endangered and vulnerable marine mammals and turtles:
80% of the Indian Ocean is open ocean and includes nine large marine ecosystems: the Agulhas Current, Somali Coastal Current, Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
, Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
, Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
, Gulf of Thailand, West Central Australian Shelf, Northwest Australian Shelf and Southwest Australian Shelf. Coral reefs cover c. . The coasts of the Indian Ocean includes beaches and intertidal zones covering and 246 larger estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
. Upwelling
Upwelling is an physical oceanography, oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted sur ...
areas are small but important. The hypersaline salterns in India covers between and species adapted for this environment, such as '' Artemia salina'' and ''Dunaliella salina
''Dunaliella salina'' is a type of halophile unicellular green algae especially found in hypersaline environments, such as salt lakes and salt evaporation ponds. Known for its antioxidant activity because of its ability to create a large amoun ...
'', are important to bird life.
Coral reefs, sea grass beds, and mangrove forests are the most productive ecosystems of the Indian Ocean — coastal areas produce 20 tones of fish per square kilometre. These areas, however, are also being urbanised with populations often exceeding several thousand people per square kilometre and fishing techniques become more effective and often destructive beyond sustainable levels while the increase in sea surface temperature spreads coral bleaching.
Mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
s covers in the Indian Ocean region, or almost half of the world's mangrove habitat, of which is located in Indonesia, or 50% of mangroves in the Indian Ocean. Mangroves originated in the Indian Ocean region and have adapted to a wide range of its habitats but it is also where it suffers its biggest loss of habitat.
In 2016, six new animal species were identified at hydrothermal vents in the Southwest Indian Ridge: a "Hoff" crab, a "giant peltospirid" snail, a whelk-like snail, a limpet, a scaleworm and a polychaete worm.
The West Indian Ocean coelacanth was discovered in the Indian Ocean off South Africa in the 1930s and in the late 1990s another species, the Indonesian coelacanth, was discovered off Sulawesi Island, Indonesia. Most extant coelacanths have been found in the Comoros. Although both species represent an order of lobe-finned fishes known from the Early Devonian (410 ) and thought extinct 66 mya, they are morphologically distinct from their Devonian ancestors. Over millions of years, coelacanths evolved to inhabit different environments — lungs adapted for shallow, brackish waters evolved into gills adapted for deep marine waters.
Biodiversity
Of Earth's 36biodiversity hotspot
A biodiversity hotspot is a ecoregion, biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human habitation. Norman Myers wrote about the concept in two articles in ''The Environmentalist'' in 1988 and 1990, after ...
s nine (or 25%) are located on the margins of the Indian Ocean.
 * Madagascar and the islands of the western Indian Ocean (Comoros, Réunion, Mauritius, Rodrigues, the Seychelles, and Socotra), includes 13,000 (11,600 endemic) species of plants; 313 (183) birds; reptiles 381 (367); 164 (97) freshwater fishes; 250 (249) amphibians; and 200 (192) mammals.
The origin of this diversity is debated; the break-up of Gondwana can explain vicariance older than 100 mya, but the diversity on the younger, smaller islands must have required a Cenozoic dispersal from the rims of the Indian Ocean to the islands. A "reverse colonisation", from islands to continents, apparently occurred more recently; the chameleons, for example, first diversified on Madagascar and then colonised Africa. Several species on the islands of the Indian Ocean are textbook cases of evolutionary processes; the dung beetles, day geckos, and
* Madagascar and the islands of the western Indian Ocean (Comoros, Réunion, Mauritius, Rodrigues, the Seychelles, and Socotra), includes 13,000 (11,600 endemic) species of plants; 313 (183) birds; reptiles 381 (367); 164 (97) freshwater fishes; 250 (249) amphibians; and 200 (192) mammals.
The origin of this diversity is debated; the break-up of Gondwana can explain vicariance older than 100 mya, but the diversity on the younger, smaller islands must have required a Cenozoic dispersal from the rims of the Indian Ocean to the islands. A "reverse colonisation", from islands to continents, apparently occurred more recently; the chameleons, for example, first diversified on Madagascar and then colonised Africa. Several species on the islands of the Indian Ocean are textbook cases of evolutionary processes; the dung beetles, day geckos, and lemur
Lemurs ( ; from Latin ) are Strepsirrhini, wet-nosed primates of the Superfamily (biology), superfamily Lemuroidea ( ), divided into 8 Family (biology), families and consisting of 15 genera and around 100 existing species. They are Endemism, ...
s are all examples of adaptive radiation.
Many bones (250 bones per square metre) of recently extinct vertebrates have been found in the Mare aux Songes swamp in Mauritius, including bones of the Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinction, extinct flightless bird that was endemism, endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest relative was the also-extinct and flightles ...
bird (''Raphus cucullatus'') and '' Cylindraspis'' giant tortoise. An analysis of these remains suggests a process of aridification began in the southwest Indian Ocean began around 4,000 years ago.
* Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany (MPA); 8,100 (1,900 endemic) species of plants; 541 (0) birds; 205 (36) reptiles; 73 (20) freshwater fishes; 73 (11) amphibians; and 197 (3) mammals.
Mammalian megafauna once widespread in the MPA was driven to near extinction in the early 20th century. Some species have been successfully recovered since then — the population of white rhinoceros
The white rhinoceros, also known as the white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''), is the largest extant species of rhinoceros and the most Sociality, social of all rhino species, characterized by its wide mouth adapted f ...
(''Ceratotherium simum simum'') increased from less than 20 individuals in 1895 to more than 17,000 as of 2013. Other species still depend on fenced areas and management programs, including black rhinoceros
The black rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis''), also called the black rhino or the hooked-lip rhinoceros, is a species of rhinoceros native to East Africa, East and Southern Africa, including Angola, Botswana, Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Moza ...
(''Diceros bicornis minor''), African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), cheetah (''Acynonix jubatus''), elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), and lion (''Panthera leo'').
* Coastal forests of eastern Africa; 4,000 (1,750 endemic) species of plants; 636 (12) birds; 250 (54) reptiles; 219 (32) freshwater fishes; 95 (10) amphibians; and 236 (7) mammals.
This biodiversity hotspot (and namesake ecoregion and "Endemic Bird Area") is a patchwork of small forested areas, often with a unique assemblage of species within each, located within from the coast and covering a total area of c. . It also encompasses coastal islands, including Zanzibar and Pemba, and Mafia.
* Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
; 5,000 (2,750 endemic) species of plants; 704 (25) birds; 284 (93) reptiles; 100 (10) freshwater fishes; 30 (6) amphibians; and 189 (18) mammals.
This area, one of the only two hotspots that are entirely arid, includes the Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands (also called the Abyssinian Highlands) is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , whil ...
, the East African Rift valley, the Socotra
Socotra, locally known as Saqatri, is a Yemeni island in the Indian Ocean. Situated between the Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Sea, it lies near major shipping routes. Socotra is the largest of the six islands in the Socotra archipelago as ...
islands, as well as some small islands in the Red Sea and areas on the southern Arabic Peninsula. Endemic and threatened mammals include the dibatag (''Ammodorcas clarkei'') and Speke's gazelle (''Gazella spekei''); the Somali wild ass (''Equus africanus somaliensis'') and hamadryas baboon (''Papio hamadryas''). It also contains many reptiles.
In Somalia, the centre of the hotspot, the landscape is dominated by Acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
- Commiphora deciduous bushland, but also includes the Yeheb nut (''Cordeauxia edulus'') and species discovered more recently such as the Somali cyclamen (''Cyclamen somalense''), the only cyclamen outside the Mediterranean. Warsangli linnet (''Carduelis johannis'') is an endemic bird found only in northern Somalia. An unstable political situation and mismanagement has resulted in overgrazing which has produced one of the most degraded hotspots where only c. 5% of the original habitat remains.
* The Western Ghats–Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
; 5,916 (3,049 endemic) species of plants; 457 (35) birds; 265 (176) reptiles; 191 (139) freshwater fishes; 204 (156) amphibians; and 143 (27) mammals.
Encompassing the west coast of India and Sri Lanka, until c. 10,000 years ago a land bridge connected Sri Lanka to the Indian Subcontinent, hence this region shares a common community of species.
* Indo-Burma; 13.500 (7,000 endemic) species of plants; 1,277 (73) birds; 518 (204) reptiles; 1,262 (553) freshwater fishes; 328 (193) amphibians; and 401 (100) mammals.
Indo-Burma encompasses a series of mountain ranges, five of Asia's largest river systems, and a wide range of habitats. The region has a long and complex geological history, and long periods rising sea levels and glaciations have isolated ecosystems and thus promoted a high degree of endemism and speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
. The region includes two centres of endemism: the Annamite Mountains and the northern highlands on the China-Vietnam border.
Several distinct floristic regions, the Indian, Malesian, Sino-Himalayan, and Indochinese regions, meet in a unique way in Indo-Burma and the hotspot contains an estimated 15,000–25,000 species of vascular plants, many of them endemic.
* Sundaland; 25,000 (15,000 endemic) species of plants; 771 (146) birds; 449 (244) reptiles; 950 (350) freshwater fishes; 258 (210) amphibians; and 397 (219) mammals.
Sundaland encompasses 17,000 islands of which Borneo and Sumatra are the largest. Endangered mammals include the Bornean and Sumatran orangutans, the proboscis monkey, and the Javan and Sumatran rhinoceroses.
* Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeography, biogeographical designation for a group of mainly list of islands of Indonesia, Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australia (continent), Australian continental shelf, continental ...
; 10,000 (1,500 endemic) species of plants; 650 (265) birds; 222 (99) reptiles; 250 (50) freshwater fishes; 49 (33) amphibians; and 244 (144) mammals.
* Southwest Australia; 5,571 (2,948 endemic) species of plants; 285 (10) birds; 177 (27) reptiles; 20 (10) freshwater fishes; 32 (22) amphibians; and 55 (13) mammals.
Stretching from Shark Bay to Israelite Bay and isolated by the arid Nullarbor Plain, the southwestern corner of Australia is a floristic region with a stable climate in which one of the world's largest floral biodiversity and an 80% endemism has evolved. From June to September it is an explosion of colours and the Wildflower Festival in Perth in September attracts more than half a million visitors.
Geology
As the youngest of the major oceans, the Indian Ocean has active spreading ridges that are part of the worldwide system ofmid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading ...
s. In the Indian Ocean these spreading ridges meet at the Rodrigues Triple Point with the Central Indian Ridge, including the Carlsberg Ridge, separating the African plate from the Indian plate; the Southwest Indian Ridge separating the African plate from the Antarctic plate; and the Southeast Indian Ridge separating the Australian plate from the Antarctic plate. The Central Indian Ridge is intercepted by the Owen fracture zone.
Since the late 1990s, however, it has become clear that this traditional definition of the Indo-Australian plate cannot be correct; it consists of three plates — the Indian plate, the Capricorn plate, and Australian plate — separated by diffuse boundary zones.
Since 20 Ma the African plate is being divided by the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. It was formerly considered to be part of a l ...
System into the Nubian and Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
plates.
There are only two trenches in the Indian Ocean: the -long Java Trench between Java and the Sunda Trench and the -long Makran Trench south of Iran and Pakistan.
A series of ridges and seamount chains produced by hotspots pass over the Indian Ocean. The Réunion hotspot (active 70–40 million years ago) connects Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
and the Mascarene Plateau to the Chagos-Laccadive Ridge and the Deccan Traps in north-western India; the Kerguelen hotspot (100–35 million years ago) connects the Kerguelen Islands
The Kerguelen Islands ( or ; in French commonly ' but officially ', ), also known as the Desolation Islands (' in French), are a group of islands in the subantarctic, sub-Antarctic region. They are among the Extremes on Earth#Remoteness, most i ...
and Kerguelen Plateau to the Ninety East Ridge and the Rajmahal Traps in north-eastern India; the Marion hotspot (100–70 million years ago) possibly connects Prince Edward Islands to the Eighty Five East Ridge. These hotspot tracks have been broken by the still active spreading ridges mentioned above.
There are fewer seamounts in the Indian Ocean than in the Atlantic and Pacific. These are typically deeper than and located north of 55°S and west of 80°E. Most originated at spreading ridges but some are now located in basins far away from these ridges. The ridges of the Indian Ocean form ranges of seamounts, sometimes very long, including the Carlsberg Ridge, Madagascar Ridge, Central Indian Ridge, Southwest Indian Ridge, Chagos-Laccadive Ridge, 85°E Ridge, 90°E Ridge, Southeast Indian Ridge, Broken Ridge, and East Indiaman Ridge. The Agulhas Plateau and Mascarene Plateau are the two major shallow areas.
The opening of the Indian Ocean began 156 when Africa separated from East Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
. The Indian Subcontinent began to separate from Australia-Antarctica 135–125 Ma and as the Tethys Ocean north of India began to close 118–84 Ma the Indian Ocean opened behind it.
History
The Indian Ocean, together with the Mediterranean, has connected people since ancient times, whereas the Atlantic and Pacific have had the roles of barriers or '' mare incognitum''. The written history of the Indian Ocean, however, has been Eurocentric and largely dependent on the availability of written sources from the European colonial era. This history is often divided into an ancient period followed by an Islamic period; the subsequent colonial-era periods are often subdivided into Portuguese, Dutch, andBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
periods. Milo Kearney argues that the postwar time period can also be split into a period of competition for oil during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
followed by American dominance.
A concept of an "Indian Ocean World" (IOW), similar to that of the " Atlantic World", exists but emerged much more recently and is not well established. The IOW is, nevertheless, sometimes referred to as the "first global economy" and was based on the monsoon which linked Asia, China, India, and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. It developed independently from the European global trade in the Mediterranean and Atlantic and remained largely independent from them until European 19th-century colonial dominance.
The diverse history of the Indian Ocean is a unique mix of cultures, ethnic groups, natural resources, and shipping routes. It grew in importance beginning in the 1960s and 1970s and, after the Cold War, it has undergone periods of political instability, most recently with the emergence of India and China as regional powers.
First settlements
 Pleistocene fossils of ''
Pleistocene fossils of ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' ( ) is an extinction, extinct species of Homo, archaic human from the Pleistocene, spanning nearly 2 million years. It is the first human species to evolve a humanlike body plan and human gait, gait, to early expansions of h ...
'' and other pre–''H. sapiens'' hominid fossils, similar to '' H. heidelbergensis'' in Europe, have been found in India. According to the Toba catastrophe theory, a supereruption c. 74,000 years ago at Lake Toba, Sumatra, covered India with volcanic ashes and wiped out one or more lineages of such archaic humans in India and Southeast Asia.
The ''Out of Africa'' theory states that ''Homo sapiens'' spread from Africa into mainland Eurasia. The more recent '' Southern Dispersal'' or ''Coastal hypothesis'' instead advocates that modern humans spread along the coasts of the Arabic Peninsula and southern Asia. This hypothesis is supported by mtDNA research which reveals a rapid dispersal event during the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
(11,000 years ago). This coastal dispersal, however, began in East Africa 75,000 years ago and occurred intermittently from estuary to estuary along the northern perimeter of the Indian Ocean at a rate of per year. It eventually resulted in modern humans migrating from Sunda over Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeography, biogeographical designation for a group of mainly list of islands of Indonesia, Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australia (continent), Australian continental shelf, continental ...
to Sahul (Southeast Asia to Australia). Since then, waves of migration have resettled people and, clearly, the Indian Ocean littoral had been inhabited long before the first civilisations emerged. 5000–6000 years ago six distinct cultural centres had evolved around the Indian Ocean: East Africa, the Middle East, the Indian Subcontinent, South East Asia, the Malay World and Australia; each interlinked to its neighbours.
Food globalisation began on the Indian Ocean littoral c. 4.000 years ago. Five African crops — sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
, pearl millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and ...
, finger millet, cowpea
The cowpea (''Vigna unguiculata'') is an annual herbaceous legume from the genus '' Vigna''. Its tolerance for sandy soil and low rainfall have made it an important crop in the semiarid regions across Africa and Asia. It requires very few inpu ...
and hyacinth bean — somehow found their way to Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
in India during the Late Harappan (2000–1700 BCE). Gujarati merchants evolved into the first explorers of the Indian Ocean as they traded African goods such as ivory, tortoise shells, and slaves. Broomcorn millet found its way from Central Asia to Africa, together with chicken and zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus''), also known as indicine cattle and humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of Bos taurus, domestic cattle originating in South Asia. Zebu, like many Sanga cattle breeds, differs from taurine cattle by a fatty hump ...
cattle, although the exact timing is disputed. Around 2000 BCE black pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit (the peppercorn), which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in diameter ...
and sesame, both native to Asia, appear in Egypt, albeit in small quantities. Around the same time the black rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is n ...
and the house mouse
The house mouse (''Mus musculus'') is a small mammal of the rodent family Muridae, characteristically having a pointed snout, large rounded ears, and a long and almost hairless tail. It is one of the most abundant species of the genus '' Mus''. A ...
emigrate from Asia to Egypt. Banana reached Africa around 3000 years ago.
 At least eleven prehistoric tsunamis have struck the Indian Ocean coast of Indonesia between 7400 and 2900 years ago. Analysing sand beds in caves in the Aceh region, scientists concluded that the intervals between these tsunamis have varied from series of minor tsunamis over a century to dormant periods of more than 2000 years preceding megathrusts in the Sunda Trench. Although the risk for future tsunamis is high, a major megathrust such as the one in 2004 is likely to be followed by a long dormant period.
A group of scientists have argued that two large-scale impact events have occurred in the Indian Ocean: the Burckle Crater in the southern Indian Ocean in 2800 BCE and the Kanmare and Tabban craters in the
At least eleven prehistoric tsunamis have struck the Indian Ocean coast of Indonesia between 7400 and 2900 years ago. Analysing sand beds in caves in the Aceh region, scientists concluded that the intervals between these tsunamis have varied from series of minor tsunamis over a century to dormant periods of more than 2000 years preceding megathrusts in the Sunda Trench. Although the risk for future tsunamis is high, a major megathrust such as the one in 2004 is likely to be followed by a long dormant period.
A group of scientists have argued that two large-scale impact events have occurred in the Indian Ocean: the Burckle Crater in the southern Indian Ocean in 2800 BCE and the Kanmare and Tabban craters in the Gulf of Carpentaria
The Gulf of Carpentaria is a sea off the northern coast of Australia. It is enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea, which separates Australia and New Guinea. The northern boundary ...
in northern Australia in 536 CE. Evidences for these impacts, the team argue, are micro-ejecta and Chevron dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat ...
s in southern Madagascar and in the Australian gulf. Geological evidences suggest the tsunamis caused by these impacts reached above sea level and inland. The impact events must have disrupted human settlements and perhaps even contributed to major climate changes.
Antiquity
The history of the Indian Ocean is marked by maritime trade; cultural and commercial exchange probably date back at least seven thousand years. Human culture spread early on the shores of the Indian Ocean and was always linked to the cultures of the Mediterranean and the Persian Gulf. Before , however, cultures on its shores were only loosely tied to each other; bronze, for example, was developed in Mesopotamia but remained uncommon in Egypt before 1800 BCE. During this period, independent, short-distance oversea communications along its littoral margins evolved into an all-embracing network. The début of this network was not the achievement of a centralised or advanced civilisation but of local and regional exchange in the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea, and the Arabian Sea. Sherds of Ubaid (2500–500 BCE) pottery have been found in the western Gulf at Dilmun, present-dayBahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
; traces of exchange between this trading centre and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. The Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ians traded grain, pottery, and bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
(used for reed boats) for copper, stone, timber, tin, dates, onions, and pearls.
Coast-bound vessels transported goods between the Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
(2600–1900 BCE) in the Indian subcontinent (modern-day Pakistan and Northwest India) and the Persian Gulf and Egypt.
 The Red Sea, one of the main trade routes in Antiquity, was explored by
The Red Sea, one of the main trade routes in Antiquity, was explored by Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...
and Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
ns during the last two millennia BCE. In the 6th century, BCE Greek explorer Scylax of Caryanda made a journey to India, working for the Persian king Darius, and his now-lost account put the Indian Ocean on the maps of Greek geographers. The Greeks began to explore the Indian Ocean following the conquests of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
, who ordered a circumnavigation of the Arabian Peninsula in 323 BCE. During the two centuries that followed the reports of the explorers of Ptolemaic Egypt Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
*Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
resulted in the best maps of the region until the Portuguese era many centuries later. The main interest in the region for the Ptolemies was not commercial but military; they explored Africa to hunt for war elephant
A war elephant is an elephant that is Animal training, trained and guided by humans for combat purposes. Historically, the war elephant's main use was to charge (warfare), charge the enemy, break their ranks, and instill terror and fear. Elep ...
s.
The Rub' al Khali desert isolates the southern parts of the Arabic Peninsula and the Indian Ocean from the Arabic world. This encouraged the development of maritime trade in the region linking the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf to East Africa and India. The monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
(from ''mawsim'', the Arabic word for season), however, was used by sailors long before being "discovered" by Hippalus in the 1st century. Indian wood have been found in Sumerian cities, there is evidence of Akkad coastal trade in the region, and contacts between India and the Red Sea dates back to 2300 B.C. The archipelagoes of the central Indian Ocean, the Laccadive and Maldive islands, were probably populated during the 2nd century B.C. from the Indian mainland. They appear in written history in the account of merchant Sulaiman al-Tajir in the 9th century but the treacherous reefs of the islands were most likely cursed by the sailors of Aden long before the islands were even settled.
 ''
''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and Roman commerce, trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports lik ...
'', an Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
n guide to the world beyond the Red Sea — including Africa and India — from the first century CE, not only gives insights into trade in the region but also shows that Roman and Greek sailors had already gained knowledge about the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
winds. The contemporaneous settlement of Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
by Austronesian sailors shows that the littoral margins of the Indian Ocean were being both well-populated and regularly traversed at least by this time. Albeit the monsoon must have been common knowledge in the Indian Ocean for centuries.
The Indian Ocean's relatively calmer waters opened the areas bordering it to trade earlier than the Atlantic or Pacific oceans. The powerful monsoons also meant ships could easily sail west early in the season, then wait a few months and return eastwards. This allowed ancient Indonesian peoples to cross the Indian Ocean to settle in Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
around 1 CE.
In the 2nd or 1st century BCE, Eudoxus of Cyzicus was the first Greek to cross the Indian Ocean. The probably fictitious sailor Hippalus is said to have learnt the direct route from Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
to India around this time. During the 1st and 2nd centuries AD intensive trade relations developed between Roman Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, ...
and the Tamil kingdoms of the Cheras, Cholas and Pandyas in Southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
. Like the Indonesian people above, the western sailors used the monsoon to cross the ocean. The unknown author of the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and Roman commerce, trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports lik ...
'' describes this route, as well as the commodities that were traded along various commercial ports on the coasts of the Horn of Africa and India circa 1 CE. Among these trading settlements were Mosylon and Opone on the Red Sea littoral.
Age of Discovery
 Unlike the Pacific Ocean where the civilization of the Polynesians reached most of the far-flung islands and atolls and populated them, almost all the islands, archipelagos and atolls of the Indian Ocean were uninhabited until colonial times. Although there were numerous ancient civilizations in the coastal states of Asia and parts of Africa, the
Unlike the Pacific Ocean where the civilization of the Polynesians reached most of the far-flung islands and atolls and populated them, almost all the islands, archipelagos and atolls of the Indian Ocean were uninhabited until colonial times. Although there were numerous ancient civilizations in the coastal states of Asia and parts of Africa, the Maldives
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as the Maldive Islands, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in South Asia located in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, abou ...
were the only island group in the Central Indian Ocean region where an ancient civilization flourished. Maldivians, on their annual trade trip, took their oceangoing trade ships to Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
rather than mainland India, which is much closer, because their ships were dependent of the Indian Monsoon Current.
Arabic missionaries and merchants began to spread Islam along the western shores of the Indian Ocean from the 8th century, if not earlier. A Swahili stone mosque dating to the 8th–15th centuries has been found in Shanga, Kenya. Trade across the Indian Ocean gradually introduced Arabic script and rice as a staple in Eastern Africa.
Muslim merchants traded an estimated 1000 African slaves annually between 800 and 1700, a number that grew to during the 18th century, and 3700 during the period 1800–1870. Slave trade also occurred in the eastern Indian Ocean before the Dutch settled there around 1600 but the volume of this trade is unknown.
From 1405 to 1433 admiral Zheng He said to have led large fleets of the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
on several treasure voyages through the Indian Ocean, ultimately reaching the coastal countries of East Africa.
The Portuguese navigator Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama ( , ; – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and nobleman who was the Portuguese discovery of the sea route to India, first European to reach India by sea.
Da Gama's first voyage (1497–1499) was the first to link ...
rounded the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ...
during his first voyage in 1497 and became the first European to sail to India. The Swahili people he encountered along the African east coast lived in a series of cities and had established trade routes to India and to China. Among them, the Portuguese kidnapped most of their pilots in coastal raids and on board ships. A few of the pilots, however, were gifts by local Swahili rulers, including the sailor from Gujarat, a gift by a Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban centr ...
ruler in Kenya, who helped the Portuguese to reach India. In expeditions after 1500, the Portuguese attacked and colonised cities along the African coast.
European slave trade in the Indian Ocean began when Portugal established Estado da Índia in the early 16th century. From then until the 1830s, slaves were exported from Mozambique annually and similar figures has been estimated for slaves brought from Asia to the Philippines during the Iberian Union
The Iberian Union is a historiographical term used to describe the period in which the Habsburg Spain, Monarchy of Spain under Habsburg dynasty, until then the personal union of the crowns of Crown of Castile, Castile and Crown of Aragon, Aragon ...
(1580–1640).
The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
began its expansion into the Indian Ocean in 1517 with the conquest of Egypt under Sultan Selim I
Selim I (; ; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute (), was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite lasting only eight years, his reign is ...
. Although the Ottomans shared the same religion as the trading communities in the Indian Ocean the region was unexplored by them. Maps that included the Indian Ocean had been produced by Muslim geographers centuries before the Ottoman conquests; Muslim scholars, such as Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
in the 14th century, had visited most parts of the known world; contemporarily with Vasco da Gama, Arab navigator Ahmad ibn Mājid had compiled a guide to navigation in the Indian Ocean; the Ottomans, nevertheless, began their own parallel era of discovery which rivalled the European expansion.
The establishment of the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
in the early 17th century lead to a quick increase in the volume of the slave trade in the region; there were perhaps up to slaves in various Dutch colonies during the 17th and 18th centuries in the Indian Ocean. For example, some 4000 African slaves were used to build the Colombo fortress in Dutch Ceylon
Dutch Ceylon (; ) was a governorate established in present-day Sri Lanka by the Dutch East India Company. Although the Dutch managed to capture most of the coastal areas in Sri Lanka, they were never able to control the Kingdom of Kandy locate ...
. Bali and neighbouring islands supplied regional networks with slaves 1620–1830. Indian and Chinese slave traders supplied Dutch Indonesia with perhaps slaves during the 17th and 18th centuries.
The East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
(EIC) was established during the same period and in 1622 one of its ships carried slaves from the Coromandel Coast to Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
. The EIC mostly traded in African slaves but also some Asian slaves purchased from Indian, Indonesian and Chinese slave traders. The French established colonies on the islands of Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
and Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
in 1721; by 1735 some 7,200 slaves populated the Mascarene Islands, a number which had reached in 1807. The British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
captured the islands in 1810, however, and because the British had prohibited the slave trade in 1807 a system of clandestine slave trade developed to bring slaves to French planters on the islands; in all – slaves were exported to the Mascarene Islands from 1670 until 1848.
In all, European traders exported – slaves within the Indian Ocean between 1500 and 1850, and almost that same number were exported from the Indian Ocean to the Americas during the same period. Slave trade in the Indian Ocean was, nevertheless, very limited compared to slaves exported across the Atlantic. The island of Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
was the center of the Indian Ocean slave trade in the 19th century. In the mid-19th century, as many as 50,000 slaves passed annually through the port.
Late modern era
Scientifically, the Indian Ocean remained poorly explored before the International Indian Ocean Expedition in the early 1960s. However, the ''Challenger'' expedition 1872–1876 only reported from south of the polar front. The ''Valdivia'' expedition 1898–1899 made deep samples in the Indian Ocean. In the 1930s, the John Murray Expedition mainly studied shallow-water habitats. The Swedish Deep Sea Expedition 1947–1948 also sampled the Indian Ocean on its global tour and the Danish ''Galathea'' sampled deep-water fauna from Sri Lanka to South Africa on its second expedition 1950–1952. The Soviet research vessel ''Vityaz'' also did research in the Indian Ocean. TheSuez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
opened in 1869 when the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
dramatically changed global shipping – the sailing ship declined in importance as did the importance of European trade in favour of trade in East Asia and Australia.
The construction of the canal introduced many non-indigenous species into the Mediterranean. For example, the goldband goatfish ('' Upeneus moluccensis'') has replaced the red mullet ('' Mullus barbatus''); since the 1980s huge swarms of scyphozoan jellyfish ('' Rhopilema nomadica'') have affected tourism and fisheries along the Levantian coast and clogged power and desalination plants. Plans announced in 2014 to build a new, much larger Suez Canal parallel to the 19th-century canal will most likely boost the economy in the region but also cause ecological damage in a much wider area.
 Throughout the colonial era, islands such as
Throughout the colonial era, islands such as Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
were important shipping nodes for the Dutch, French, and British. Mauritius, an inhabited island, became populated by slaves from Africa and indenture labour from India. The end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
marked the end of the colonial era. The British left Mauritius in 1974 and with 70% of the population of Indian descent, Mauritius became a close ally of India. In the 1980s, during the Cold War, the South African regime acted to destabilise several island nations in the Indian Ocean, including the Seychelles, Comoros, and Madagascar. India intervened in Mauritius to prevent a coup d'état, backed up by the United States who feared the Soviet Union could gain access to Port Louis
Port Louis (, ; or , ) is the capital and most populous city of Mauritius, mainly located in the Port Louis District, with a small western part in the Black River District. Port Louis is the country's financial and political centre. It is admi ...
and threaten the U.S. base on Diego Garcia
Diego Garcia is the largest island of the Chagos Archipelago. It has been used as a joint UK–U.S. military base since the 1970s, following the expulsion of the Chagossians by the UK government. The Chagos Islands are set to become a former B ...
.
Iranrud was an unrealised plan by Iran and the Soviet Union to build a canal between the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf.
Testimonies from the colonial era are stories of African slaves, Indian indentured labourers and white settlers. But, while there was a clear racial line between free men and slaves in the Atlantic World, this delineation is less distinct in the Indian Ocean — there were Indian slaves and settlers as well as black indentured labourers. There were also a string of prison camps across the Indian Ocean, such as Cellular Jail in the Andamans, in which prisoners, exiles, POWs, forced labourers, merchants and people of different faiths were forcefully united. On the islands of the Indian Ocean, therefore, a trend of creolisation emerged.
On 26 December 2004, fourteen countries around the Indian Ocean were hit by a wave of tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
s caused by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
On 26 December 2004, at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+07:00, UTC+7), a major earthquake with a magnitude of 9.2–9.3 struck with an epicenter, epicentre off the west coast of Aceh in northern Sumatra, Indonesia. The Submarine earthquake, undersea ...
. The waves radiated across the ocean at speeds exceeding , reached up to in height, and resulted in an estimated 236,000 deaths.
In the late 2000s, the ocean evolved into a hub of pirate
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are call ...
activity. By 2013, attacks off the Horn region's coast had steadily declined due to active private security and international navy patrols, especially by the Indian Navy
The Indian Navy (IN) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Navy, maritime and Amphibious warfare, amphibious branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of the Naval Staff (India), Chief ...
.
Malaysia Airlines Flight 370, a Boeing 777-2H6ER with 239 occupants on board, disappeared on 8 March 2014 and is alleged to have crashed into the southern Indian Ocean about from the coast of southwest Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
. Despite an extensive search, the whereabouts of the remains of the aircraft is unknown.
The Sentinelese
The Sentinelese, also known as the Sentineli and the North Sentinel Islanders, are Indigenous people who inhabit North Sentinel Island in the Bay of Bengal in the northeastern Indian Ocean. Designated a particularly vulnerable tribal group a ...
people of North Sentinel Island
North Sentinel Island is one of the Andaman Islands, an Indian archipelago in the Bay of Bengal which also includes South Sentinel Island. The island is a protected area of India. It is home to the Sentinelese, an indigenous tribe in volunta ...
, which lies near South Andaman Island in the Bay of Bengal, have been called by experts the most isolated people in the world.
The sovereignty of the Chagos Archipelago in the Indian Ocean is disputed between the United Kingdom and Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
. In February 2019, the International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; , CIJ), or colloquially the World Court, is the only international court that Adjudication, adjudicates general disputes between nations, and gives advisory opinions on International law, internation ...
in The Hague
The Hague ( ) is the capital city of the South Holland province of the Netherlands. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands. Situated on the west coast facing the North Sea, The Hague is the c ...
issued an advisory opinion stating that the UK must transfer the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius.
Geopolitics
The Indian Ocean is crucial for global trade, especially in oil and hydrocarbons. Environmental and geopolitical concerns in the region include the effects ofclimate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, the illegal drug trade
The illegal drug trade, drug trafficking, or narcotrafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of drug prohibition, prohibited drugs. Most jurisdictions prohibitionism, prohibit trade, exce ...
, illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing, maritime safety and security, and increasing major power competition.
Trade
 The sea lanes in the Indian Ocean are considered among the most strategically important in the world with more than 80 percent of the world's seaborne trade in oil transits through the Indian Ocean and its vital chokepoints, with 40 percent passing through the Strait of Hormuz, 35 percent through the Strait of Malacca and 8 percent through the Bab el-Mandab Strait.
The Indian Ocean provides major sea routes connecting the Middle East, Africa, and East Asia with Europe and the Americas. It carries a particularly heavy traffic of petroleum and petroleum products from the oil fields of the Persian Gulf and Indonesia. Large reserves of hydrocarbons are being tapped in the offshore areas of Saudi Arabia, Iran, India, and Western Australia. An estimated 40% of the world's offshore oil production comes from the Indian Ocean. Beach sands rich in heavy minerals, and offshore placer deposits are actively exploited by bordering countries, particularly India, Pakistan, South Africa, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
In particular, the maritime part of the
The sea lanes in the Indian Ocean are considered among the most strategically important in the world with more than 80 percent of the world's seaborne trade in oil transits through the Indian Ocean and its vital chokepoints, with 40 percent passing through the Strait of Hormuz, 35 percent through the Strait of Malacca and 8 percent through the Bab el-Mandab Strait.
The Indian Ocean provides major sea routes connecting the Middle East, Africa, and East Asia with Europe and the Americas. It carries a particularly heavy traffic of petroleum and petroleum products from the oil fields of the Persian Gulf and Indonesia. Large reserves of hydrocarbons are being tapped in the offshore areas of Saudi Arabia, Iran, India, and Western Australia. An estimated 40% of the world's offshore oil production comes from the Indian Ocean. Beach sands rich in heavy minerals, and offshore placer deposits are actively exploited by bordering countries, particularly India, Pakistan, South Africa, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
In particular, the maritime part of the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
leads through the Indian Ocean on which a large part of the global container trade is carried out. The Silk Road runs with its connections from the Chinese coast and its large container ports to the south via Hanoi
Hanoi ( ; ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Vietnam, second-most populous city of Vietnam. The name "Hanoi" translates to "inside the river" (Hanoi is bordered by the Red River (Asia), Red and Black River (Asia), Black Riv ...
to Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
, Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
and Kuala Lumpur
Kuala Lumpur (KL), officially the Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur, is the capital city and a Federal Territories of Malaysia, federal territory of Malaysia. It is the largest city in the country, covering an area of with a census population ...
through the Strait of Malacca via the Sri Lankan Colombo
Colombo, ( ; , ; , ), is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. The Colombo metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of 5.6 million, and 752,993 within the municipal limits. It is the ...
opposite the southern tip of India via Malé, the capital of the Maldives, to the East African Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital status in 1907. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town is ...
, from there to Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
, then through the Red Sea over the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
into the Mediterranean, there via Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
, Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
and Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
to the Upper Adriatic to the northern Italian junction of Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
with its international free port and its rail connections to Central and Eastern Europe.
The Silk Road has become internationally important again on the one hand through European integration, the end of the Cold War and free world trade and on the other hand through Chinese initiatives. Chinese companies have made investments in several Indian Ocean ports, including Gwadar, Hambantota, Colombo
Colombo, ( ; , ; , ), is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. The Colombo metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of 5.6 million, and 752,993 within the municipal limits. It is the ...
and Sonadia. This has sparked a debate about the strategic implications of these investments. There are also Chinese investments and related efforts to intensify trade in East Africa and in European ports such as Piraeus
Piraeus ( ; ; , Ancient: , Katharevousa: ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens city centre along the east coast of the Saronic Gulf in the Ath ...
and Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
.Guido Santevecchi: Di Maio e la Via della Seta: «Faremo i conti nel 2020», siglato accordo su Trieste in Corriere della Sera, 5 November 2019.
See also
* Connected bodies of water: ** Indo-Atlantic ** Indo-Mediterranean **Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
* Indian Ocean Commission
* Indian Ocean Geoid Low
* Indian Ocean in World War II
* Indian Ocean literature
* Indian Ocean Naval Symposium
* Indian Ocean Research Group
* Indian Ocean Tuna Commission
* List of islands in the Indian Ocean
The islands of the Indian Ocean are part of either the eastern, western, or southern areas. Some prominently large islands include Madagascar, Sri Lanka, and the Indonesian islands of Sumatra, Java, and Lesser Sunda Islands.
Eastern Indian Oc ...
* List of sovereign states and dependent territories in the Indian Ocean
* Indian Ocean Rim Association
* Maritime Silk Road
* Territorial claims in Antarctica
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * Palat, Ravi. ''The Making of an Indian Ocean World-Economy, 1250–1650: Princes, Paddy fields, and Bazaars'' (2015). * Pearson, Michael (2015). ''Trade, Circulation, and Flow in the Indian Ocean World'' (Palgrave Series in Indian Ocean World Studies), . * Schnepel, Burkhard and Edward A. Alpers, eds. ''Connectivity in Motion: Island Hubs in the Indian Ocean World'' (2017). * Schottenhammer, Angela, ed. ''Early Global Interconnectivity across the Indian Ocean World, Volume I: Commercial Structures and Exchanges'' (2019). * Schottenhammer, Angela, ed. ''Early Global Interconnectivity across the Indian Ocean World, Volume II: Exchange of Ideas, Religions, and Technologies'' (2019). * Serels, Steven, ed. ''The Impoverishment of the African Red Sea Littoral, 1640–1945'' (2018). *External links
* * * {{Authority control East Africa Oceans Oceans surrounding Antarctica South Asia West Asia