|
Réunion Hotspot
The Réunion hotspot is a volcanic hotspot which currently lies under the island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean. The Chagos-Laccadive Ridge and the southern part of the Mascarene Plateau are volcanic traces of the Réunion hotspot. The hotspot is believed to have been active for over 65 million years. A huge eruption of this hotspot 65 million years ago is thought to have laid down the Deccan Traps, a vast bed of basalt lava that covers part of central India, and opened a rift which separated India from the Seychelles Plateau. The Deccan Traps eruption coincided roughly with the nearly antipodal Chicxulub impactor and the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction of the dinosaurs, and there is considerable speculation that the three events were related. As the Indian plate drifted north, the hotspot continued to punch through the plate, creating a string of volcanic islands and undersea plateaux. The Laccadive Islands, the Maldives, and the Chagos Archipelago are atolls resting o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piton De La Fournaise
Piton de la Fournaise (; ) is a shield volcano on the eastern side of Réunion island, a French overseas department and region, in the Indian Ocean. It is currently one of the most active volcanoes in the world, along with Kīlauea in the Hawaiian Islands, Stromboli and Etna in Italy and Mount Erebus in Antarctica. A previous eruption began in August 2006 and ended in January 2007. The volcano erupted again in February 2007, on 21 September 2008, on 9 December 2010, which lasted for two days, and on 1 August 2015. The most recent eruption began on 15 September 2022. The volcano is located within Réunion National Park, a World Heritage Site. Residents of Réunion sometimes refer to Piton de la Fournaise simply as ''le Volcan'' ("the Volcano"). It is a major tourist attraction. Geology The uppermost section of the volcano is occupied by the Enclos Fouqué, a caldera wide. High cliffs, known as ''remparts'' in French, form the caldera's rim. The caldera is breached to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutionary history, evolution of dinosaurs is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, Evolution of birds, having evolved from earlier Theropoda, theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomy (biology), taxonomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Réunion
Réunion is an island in Southern Africa, in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar. It is an overseas region of France. The total area of the island is 2,512 km2, of which 10 km2 is water. The island has a coastline of 207 km. The maritime claims of Réunion include an exclusive economic zone of 200 nautical miles, and a territorial sea of . Reunion is geologically situated in the Somali Plate. Climate The climate in Réunion is tropical, but temperature moderates with elevation. The weather is cool and dry from May to November, and hot and rainy from November to April. The terrain is mostly rugged and mountainous, with fertile lowlands along the coast. The lowest point is the Indian Ocean and the highest is Piton des Neiges at 3,069 m. Natural resources Réunion's natural resources are fish, arable land and hydropower. In 1993, 60 km2 of the land was irrigated. The use of the land in 1993 is described in the table below: Natural hazards L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quanta Magazine
''Quanta Magazine'' is an editorially independent online publication of the Simons Foundation covering developments in physics, mathematics, biology and computer science. History ''Quanta Magazine'' was initially launched as ''Simons Science News'' in October 2012, but it was renamed to its current title in July 2013. It was founded by the former ''New York Times'' journalist Thomas Lin, who was the magazine's editor-in-chief until 2024. The two deputy editors are John Rennie and Michael Moyer, formerly of ''Scientific American'', and the art director is Samuel Velasco. In 2024, Samir Patel became the magazine's second editor in chief. Content The articles in the magazine are freely available to read online. ''Scientific American'', ''Wired'', ''The Atlantic'', and ''The Washington Post'', as well as international science publications like '' Spektrum der Wissenschaft'', have reprinted articles from the magazine. In November 2018, MIT Press The MIT Press is the uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues (island)
Rodrigues ( ; Creole: ) is a autonomous outer island of the Republic of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean, about east of Mauritius. It is part of the Mascarene Islands, which include Mauritius and Réunion. Like Agaléga, Rodrigues is a constituent island of the Republic of Mauritius, under the Constitution of Mauritius and still remains, as explicitly defined by the same Constitution, part of the Sovereignty of Mauritius, together with the following islands: " Agaléga, Tromelin, Cargados Carajos (Saint Brandon), Chagos Archipelago ... Diego Garcia and other islands included in the State of Mauritius". Rodrigues is of volcanic origin and is surrounded by coral reef, and some tiny uninhabited islands lie just off its coast. The island used to be the tenth District of Mauritius; it gained autonomous status on 12 October 2002, and is governed by the Rodrigues Regional Assembly. The capital of the island is Port Mathurin. The islands of Rodrigues, Agaléga and Saint Brandon f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga, and St. Brandon (Cargados Carajos shoals). The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion (a French overseas department), are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans and has an exclusive economic zone covering approximately . The 1502 Portuguese Cantino planisphere has led some historians to speculate that Arab sailors were the first to discover the uninhabited island around 975, naming it ''Dina Arobi''. Called ''Ilha do Cirne'' or ''Ilha do Cerne'' on early Portuguese maps, the island was visited by Portuguese sailors in 1507. A Dutch fleet, under the command of Admiral Van War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mascarene Islands
The Mascarene Islands (, ) or Mascarenes or Mascarenhas Archipelago is a group of islands in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar consisting of islands belonging to the Republic of Mauritius as well as the French department of Réunion. Their name derives from the Portuguese navigator Pedro Mascarenhas, who first visited them in April 1512. The islands share a common geological origin beneath the Mascarene Plateau known as the Mauritia microcontinent which was a Precambrian microcontinent situated between India and Madagascar until their separation about 70 million years ago. They form a distinct ecoregion with unique biodiversity and endemism of flora and fauna. Geography The archipelago comprises three large islands, Mauritius, Réunion, and Rodrigues, plus a number of volcanic remnants in the tropics of the southwestern Indian Ocean, generally between 700 and 1,500 kilometres east of Madagascar. The terrain includes a variety of reefs, atolls, and small islands. They pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Indian Ridge
The Central Indian Ridge (CIR) is a north–south-trending mid-ocean ridge in the western Indian Ocean. Geological setting The morphology of the CIR is characteristic of slow to intermediate ridges. The axial valley is 500–1000 m deep; 50–100 km-long ridge segments are separated by 30 km-long transform faults and 10 km-long non-transform discontinuities. Melt supply comes from axial volcanic ridges that are 15 km-long, 1–2 km wide, and reaches 100–200 m above the axial floor. With a spreading rate of 30 mm/yr near the Equator and 49 mm/yr near the Rodrigues triple junction (RTJ) at its southern end, the CIR is an intermediately fast spreading ridge characterised by moderate obliquity and few large offsets, the obvious exception being the almost 300 km-long Mary Celeste Fracture Zone at 18°S. Between 21°S and the Mary Celeste Fracture Zone (18°S) the CIR deviates westward. Along this section the larger offsets switc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean. Two different, well-cited models, the subsidence model and the antecedent karst model, have been used to explain the development of atolls.Droxler, A.W. and Jorry, S.J., 2021. "The Origin of Modern Atolls: Challenging Darwin's Deeply Ingrained Theory". ''Annual Review of Marine Science'', 13, pp. 537–573. According to Charles Darwin's subsidence model, the formation of an atoll is explained by the sinking of a volcanic island around which a coral fringing reef has formed. Over geologic time, the volcanic island becomes extinct and eroded as it subsides completely beneath the surface of the ocean. As the volcanic island subsides, the coral fringing reef becomes a ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
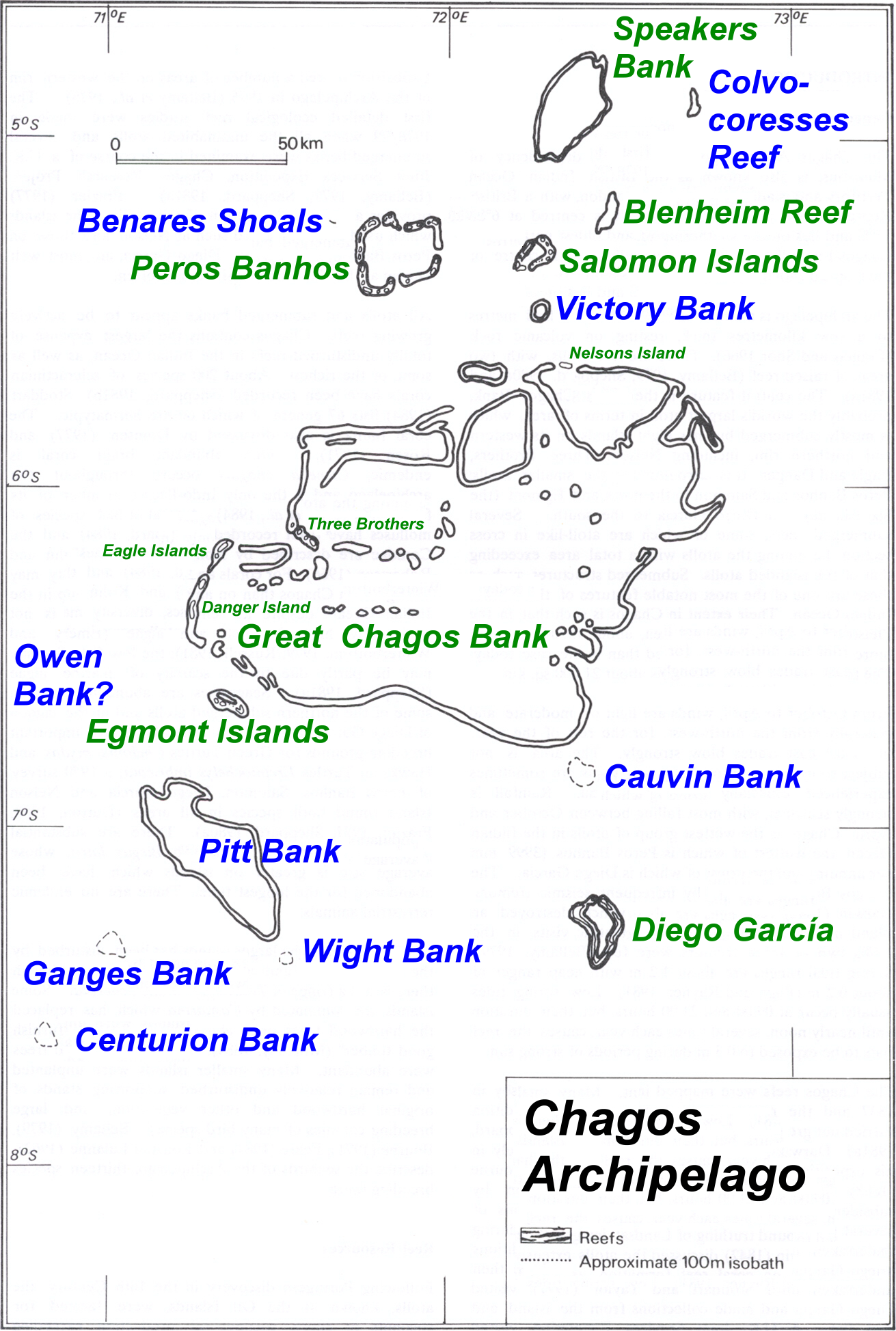
Chagos Archipelago
The Chagos Archipelago (, ) or Chagos Islands (formerly , and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelsons Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Chagos, Three Brothers, Eagle Islands, Egmont Islands and Danger Island, Great Chagos Bank, Danger Island; southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons. From 1715 to 1810, the Chagos Islands were part of France's List of French possessions and colonies, Indian Ocean possessions, administered through Isle de France (Mauritius), Isle de Francewhich was a French colonial empire, colony of France (later renamed as Mauritius). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maldives
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as the Maldive Islands, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in South Asia located in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, about from the Asian continent's mainland. The Maldives' chain of Atolls of the Maldives, 26 atolls stretches across the equator from Atolls of the Maldives#Ihavandhippolhu, Ihavandhippolhu Atoll in the north to Addu Atoll in the south. The Maldives is the smallest List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Asia, country in Asia. Its land area is only , but this is spread over roughly of the sea, making it one of the world's most spatially dispersed sovereign states. With a population of 515,132 in the 2022 census, it is the second List of Asian countries by population, least populous country in Asia and the List of countries and dependencies by area, ninth-smallest country by area, but also one of the List of countries and depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |