IEEE 1394 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and




 FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its development was initiated by Apple in 1986, and developed by the IEEE P1394 Working Group, largely driven by contributions from
FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its development was initiated by Apple in 1986, and developed by the IEEE P1394 Working Group, largely driven by contributions from

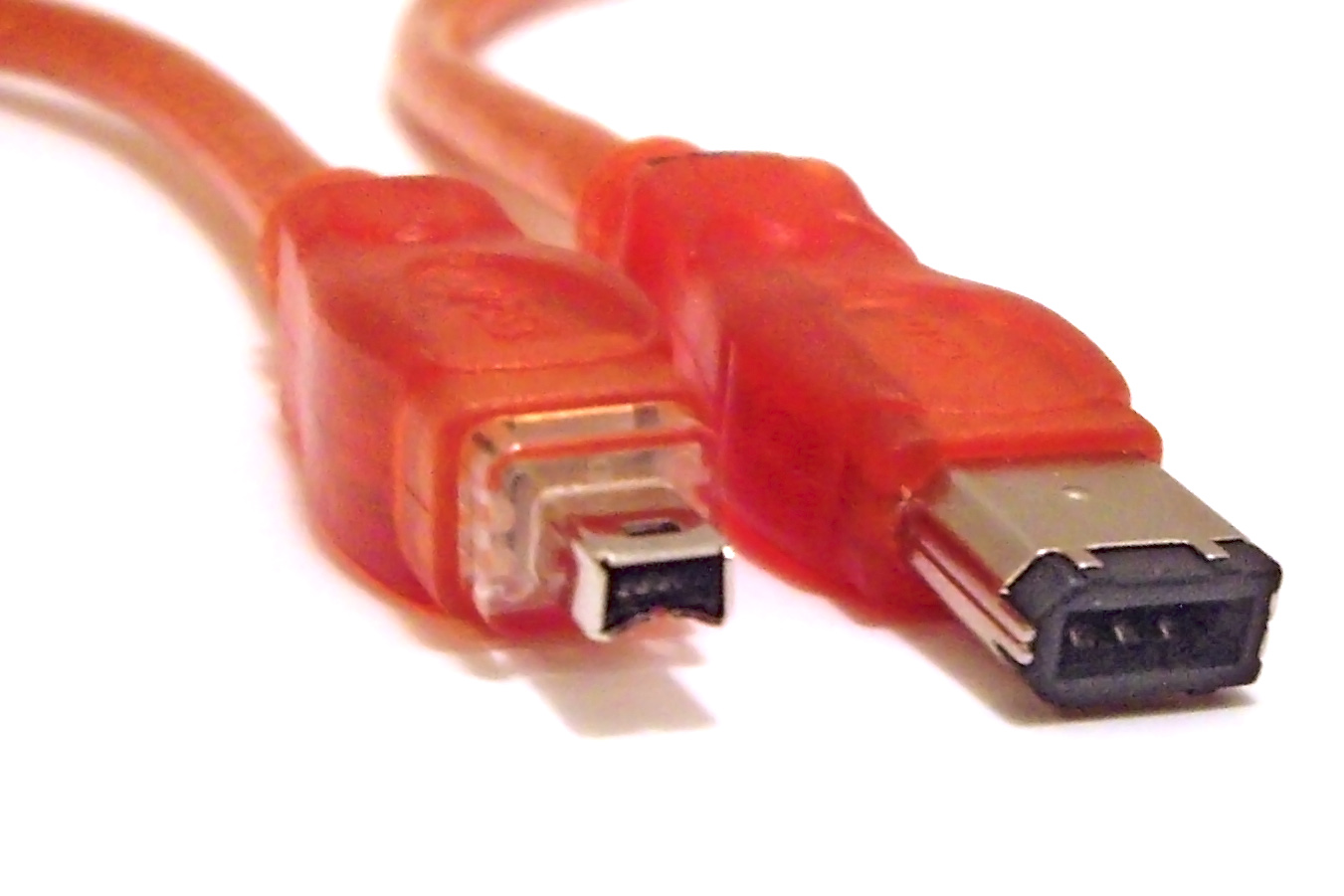
 IEEE 1394b-2002 introduced FireWire 800 (Apple's name for the 9-conductor ''S800 bilingual'' version of the IEEE 1394b standard). This specification added a new encoding scheme termed beta mode which allowed compliant devices to operate at 786.432 Mbit/s
IEEE 1394b-2002 introduced FireWire 800 (Apple's name for the 9-conductor ''S800 bilingual'' version of the IEEE 1394b standard). This specification added a new encoding scheme termed beta mode which allowed compliant devices to operate at 786.432 Mbit/s
IEEE 1394 connectors pinout
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ieee 1394 Interface Computer buses Computer connectors Computer storage buses IEEE standards Macintosh internals Personal area networks Serial buses Television terminology Video signal
isochronous
A sequence of events is isochronous if the events occur regularly, or at equal time intervals. The term ''isochronous'' is used in several technical contexts, but usually refers to the primary subject maintaining a constant period or interval ( ...
real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Panasonic
is a Japanese multinational electronics manufacturer, headquartered in Kadoma, Osaka, Kadoma, Japan. It was founded in 1918 as in Fukushima-ku, Osaka, Fukushima by Kōnosuke Matsushita. The company was incorporated in 1935 and renamed and c ...
. It is most commonly known by the name FireWire (Apple), though other brand names exist such as i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx (Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
).
The copper cable used in its most common implementation can be up to long. Power and data is carried over this cable, allowing devices with moderate power requirements to operate without a separate power supply. FireWire is also available in Cat 5 and optical fiber
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
versions.
The 1394 interface is comparable to USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
. USB was developed subsequently and gained much greater market share. USB requires a host controller whereas IEEE 1394 is cooperatively managed by the connected devices.
History and development


 FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its development was initiated by Apple in 1986, and developed by the IEEE P1394 Working Group, largely driven by contributions from
FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its development was initiated by Apple in 1986, and developed by the IEEE P1394 Working Group, largely driven by contributions from Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
(102 patents), Apple (58 patents), Panasonic
is a Japanese multinational electronics manufacturer, headquartered in Kadoma, Osaka, Kadoma, Japan. It was founded in 1918 as in Fukushima-ku, Osaka, Fukushima by Kōnosuke Matsushita. The company was incorporated in 1935 and renamed and c ...
(46 patents), and Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), simply branded Philips, is a Dutch multinational health technology company that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, its world headquarters have been situated in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarter ...
(43 patents), in addition to contributions made by engineers from LG Electronics
LG Electronics Inc. () is a South Korean Multinational corporation, multinational major appliance and consumer electronics corporation headquartered in Yeouido-dong, Seoul, South Korea. LG Electronics is a part of LG, LG Corporation, the fourth ...
, Toshiba
is a Japanese multinational electronics company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, elevators and escalators, electronic components, semiconductors ...
, Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
, Canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the material accepted as officially written by an author or an ascribed author
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western canon, th ...
, INMOS
Inmos International plc (trademark INMOS) and two operating subsidiaries, Inmos Limited (UK) and Inmos Corporation (US), was a British semiconductor company founded by Iann Barron, Richard Petritz, and Paul Schroeder in July 1978. Inmos Limited ...
/SGS Thomson (now STMicroelectronics
STMicroelectronics Naamloze vennootschap, NV (commonly referred to as ST or STMicro) is a European multinational corporation, multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the largest of such companies in Europe. ...
), and Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
.
IEEE 1394 is a serial bus architecture for high-speed data transfer, serial meaning that information is transferred one bit at a time. Parallel buses utilize a number of different physical connections, and as such are usually more costly and typically heavier. IEEE 1394 fully supports both isochronous and asynchronous
Asynchrony is any dynamic far from synchronization. If and as parts of an asynchronous system become more synchronized, those parts or even the whole system can be said to be in sync.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and com ...
applications.
Apple intended FireWire to be a serial replacement for the parallel SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices, best known for its use with storage devices such as hard disk drives. SCSI was introduced ...
bus, while providing connectivity for digital audio and video equipment. Apple's development began in the late 1980s, later presented to the IEEE, and was completed in January 1995. In 2007, IEEE 1394 was a composite of four documents: the original IEEE Std. 1394–1995, the IEEE Std. 1394a-2000 amendment, the IEEE Std. 1394b-2002 amendment, and the IEEE Std. 1394c-2006 amendment. On June 12, 2008, all these amendments as well as errata and some technical updates were incorporated into a superseding standard, IEEE Std. 1394–2008.
Apple first included onboard FireWire in some of its 1999 Macintosh models (though it had been a build-to-order option on some models since 1997), and most Apple Macintosh computers manufactured in the years 2000 through 2011 included FireWire ports. However, in February 2011 Apple introduced the first commercially available computer with Thunderbolt. Apple released its last computers with FireWire in 2012. By 2014, Thunderbolt had become a standard feature across Apple's entire line of computers (later with the exception of the 12-inch MacBook introduced in 2015, which featured only a sole USB-C port), effectively becoming the spiritual successor
A spiritual successor (sometimes called a spiritual sequel) is a product or fictional work that is similar to, or directly inspired by, another previous product or work, but (unlike a traditional prequel or sequel) does not explicitly continue th ...
to FireWire in the Apple ecosystem. Apple's last products with FireWire, the Thunderbolt Display and 2012 13-inch MacBook Pro
The MacBook Pro is a line of Mac laptop computers developed and manufactured by Apple. Introduced in 2006, it is the high-end sibling of the MacBook family, sitting above the ultra-portable MacBook Air and previously the low-end MacBook li ...
, were discontinued in 2016. Apple previously sold a Thunderbolt to FireWire Adapter, which provided one FireWire 800 port. A separate adapter was required to use it with Thunderbolt 3.
Sony's implementation of the system, ''i.LINK'', used a smaller connector with only four signal conductors, omitting the two conductors that provide power for devices in favor of a separate power connector. This style was later added into the 1394a amendment. This port is sometimes labeled ''S100'' or ''S400'' to indicate speed in Mbit/s.
The system was commonly used to connect data storage device
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted form ...
s and DV (digital video) cameras, but was also popular in industrial systems for machine vision
Machine vision is the technology and methods used to provide image, imaging-based automation, automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision ...
and professional audio
Professional audio, abbreviated as pro audio, refers to both an activity and a category of high-quality, studio-grade audio equipment. Typically it encompasses sound recording, sound reinforcement system setup and audio mixing, and studio mus ...
systems. Many users preferred it over the more common USB 2.0 for its then greater effective speed and power distribution capabilities. Benchmarks show that the sustained data transfer rates are higher for FireWire than for USB 2.0, but lower than USB 3.0. Results are marked on Apple Mac OS X
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
but more varied on Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
.
Patent considerations
Implementation of IEEE 1394 is said to require use of 261 issued international patents held by ten corporations. Use of these patents requires licensing; use without license generally constitutespatent infringement
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
. Companies holding IEEE 1394 IP formed a patent pool
In patent law, a patent pool is a consortium of two or more companies agreeing to cross-license patents relating to a particular technology. The creation of a patent pool can save patentees and licensees time and money, and, in case of blocking pa ...
with MPEG LA, LLC as the license administrator, to whom they licensed patents. MPEG LA sublicenses these patents to providers of equipment implementing IEEE 1394. Under the typical patent pool license, a royalty of US$0.25 per unit is payable by the manufacturer upon the manufacture of each 1394 finished product; no royalties are payable by users.
The last of the patents, MY 120654 by Sony, expired on November 30, 2020. , the following are patent holders of the IEEE 1394 standard, as listed in the patent pool
In patent law, a patent pool is a consortium of two or more companies agreeing to cross-license patents relating to a particular technology. The creation of a patent pool can save patentees and licensees time and money, and, in case of blocking pa ...
managed by MPEG LA
MPEG LA was an American company based in Denver, Colorado that licensed patent pools covering essential patents required for use of the MPEG-2, MPEG-4, IEEE 1394, VC-1, ATSC, MVC, MPEG-2 Systems, AVC/H.264 and HEVC standards.
Via Licensin ...
.
A person or company may review the actual 1394 Patent Portfolio License upon request to MPEG LA. MPEG LA does not provide assurance of protection to licensees beyond its own patents. At least one formerly licensed patent is known to have been removed from the pool, and other hardware patents exist that reference IEEE 1394.
The 1394 High Performance Serial Bus Trade Association (the ''1394 TA'') was formed to aid the marketing of IEEE 1394. Its bylaws prohibit dealing with intellectual property issues. The 1394 Trade Association operates on an individual no cost membership basis to further enhancements to 1394 standards. The Trade Association also is the library source for all 1394 documentation and standards available.
Technical specifications
FireWire can connect up to 63peripheral
A peripheral device, or simply peripheral, is an auxiliary hardware device that a computer uses to transfer information externally. A peripheral is a hardware component that is accessible to and controlled by a computer but is not a core compo ...
s in a tree or daisy-chain topology
Topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a Mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformat ...
(as opposed to Parallel SCSI's electrical bus topology). It allows peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of Node ...
device communication — such as communication between a scanner and a printer — to take place without using system memory or the CPU. FireWire also supports multiple host controllers per bus. It is designed to support plug and play
In computing, a plug and play (PnP) device or computer bus is one with a specification that facilitates the recognition of a hardware component in a system without the need for physical device configuration or user intervention in resolving reso ...
and hot swapping
Hot swapping is the replacement or addition of components to a computer system without stopping, shutting down, or rebooting the system. Hot plugging describes only the addition of components to a running computer system. Components which ha ...
. The copper cable it uses in its most common implementation can be up to long and is more flexible than most parallel SCSI
Parallel SCSI (formally, SCSI Parallel Interface, or SPI) is the earliest of the interface implementations in the SCSI family. SPI is a parallel bus; there is one set of electrical connections stretching from one end of the SCSI bus to the ot ...
cables. In its six-conductor or nine-conductor variations, it can supply up to 45 watts of power per port at up to 30 volts, allowing moderate-consumption devices to operate without a separate power supply.
FireWire devices implement the ISO/IEC 13213 ''configuration ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
'' model for device configuration and identification, to provide plug-and-play
In computing, a plug and play (PnP) device or computer bus is one with a specification that facilitates the recognition of a hardware component in a system without the need for physical device configuration or user intervention in resolving resou ...
capability. All FireWire devices are identified by an IEEE EUI-64 unique identifier in addition to well-known codes indicating the type of device and the protocols
Protocol may refer to:
Sociology and politics
* Protocol (politics), a formal agreement between nation states
* Protocol (diplomacy), the etiquette of diplomacy and affairs of state
* Etiquette, a code of personal behavior
Science and technology
...
it supports.
FireWire devices are organized at the bus in a tree topology. Each device has a unique self-ID. One of the nodes is elected root node and always has the highest ID. The self-IDs are assigned during the self-ID process, which happens after each bus resets. The order in which the self-IDs are assigned is equivalent to traversing the tree depth-first
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible al ...
, post-order.
FireWire is capable of safely operating critical systems due to the way multiple devices interact with the bus and how the bus allocates bandwidth to the devices. FireWire is capable of both asynchronous
Asynchrony is any dynamic far from synchronization. If and as parts of an asynchronous system become more synchronized, those parts or even the whole system can be said to be in sync.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and com ...
and isochronous transfer methods at once. Isochronous data transfers are transfers for devices that require continuous, guaranteed bandwidth. In an aircraft, for instance, isochronous devices include control of the rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually air or water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw ...
, mouse operations and data from pressure sensors outside the aircraft. All these elements require constant, uninterrupted bandwidth. To support both elements, FireWire dedicates a certain percentage to isochronous data and the rest to asynchronous data. In IEEE 1394, 80% of the bus is reserved for isochronous cycles, leaving asynchronous data with a minimum of 20% of the bus.
Encoding scheme
FireWire uses Data/Strobe encoding (D/S encoding). In D/S encoding, twonon-return-to-zero
In telecommunications, a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) line code is a binary code in which ones are represented by one significant condition, usually a positive voltage, while zeros are represented by some other significant condition, usually a ne ...
(NRZ) signals are used to transmit the data with high reliability. The NRZ signal sent is fed with the clock signal through an XOR gate
XOR gate (sometimes EOR, or EXOR and pronounced as Exclusive OR) is a digital logic gate that gives a true (1 or HIGH) output when the number of true inputs is odd. An XOR gate implements an exclusive disjunction, exclusive or (\nleftrightarrow) ...
, creating a strobe signal. This strobe is then put through another XOR gate along with the data signal to reconstruct the clock. This in turn acts as the bus's phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and ou ...
for synchronization purposes.
Arbitration
The process of the bus deciding which node gets to transmit data at what time is known asarbitration
Arbitration is a formal method of dispute resolution involving a third party neutral who makes a binding decision. The third party neutral (the 'arbitrator', 'arbiter' or 'arbitral tribunal') renders the decision in the form of an 'arbitrati ...
. Each arbitration round lasts about 125 microseconds. During the round, the root node (device nearest the processor) sends a cycle start packet. All nodes requiring data transfer respond, with the closest node winning. After the node is finished, the remaining nodes take turns in order. This repeats until all the devices have used their portion of the 125 microseconds, with isochronous transfers having priority.
Standards and versions
The previous standards and its three published amendments are now incorporated into a superseding standard, IEEE 1394-2008. The features individually added give a good history on the development path.FireWire 400 (IEEE 1394-1995)
The original release of IEEE 1394-1995 specified what is now known as FireWire 400. It can transfer data between devices at 100, 200, or 400Mbit/s
In telecommunications, data transfer rate is the average number of bits (bitrate), characters or symbols (baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are multi ...
half-duplex
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow ...
data rates (the actual transfer rates are 98.304, 196.608, and 393.216 Mbit/s, i.e., 12.288, 24.576 and 49.152 MB/s
In telecommunications, data transfer rate is the average number of bits ( bitrate), characters or symbols ( baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are mu ...
respectively). These different transfer modes are commonly referred to as S100, S200, and S400.
Cable length is limited to , although up to 16 cables can be daisy chained using active repeaters, e.g. external hubs or the internal hubs that are often present in FireWire equipment. The S400 standard limits any configuration's maximum cable length to . The 6-conductor connector is commonly found on desktop computers and can supply the connected device with power.
The 6-conductor powered connector, now referred to as an alpha connector, adds power output to support external devices. Typically a device can pull about 7 to 8 watts from the port; however, the voltage varies significantly from different devices. Voltage is specified as unregulated and should nominally be about 25 volts (range 24 to 30). Apple's implementation on laptops is typically related to battery power and can be as low as 9 V.
Improvements (IEEE 1394a-2000)
An amendment, IEEE 1394a, was released in 2000, tp://ftp.t10.org/1394/P1394a/Drafts/P1394a50.pdf P1394a Draft 5.0available. which clarified and improved the original specification. It added support for asynchronous streaming, quicker bus reconfiguration, packet concatenation, and a power-saving suspend mode. IEEE 1394a offers a couple of advantages over the original IEEE 1394–1995. 1394a is capable of arbitration accelerations, allowing the bus to accelerate arbitration cycles to improve efficiency. It also allows for arbitrated short bus reset, in which a node can be added or dropped without causing a big drop in isochronous transmission. 1394a also standardized the 4-conductor alpha connector developed by Sony and trademarked as ''i.LINK'', already widely in use on consumer devices such as camcorders, most PC laptops, a number of PC desktops, and other small FireWire devices. The 4-conductor connector is fully data-compatible with 6-conductor alpha interfaces but lacks power connectors.
FireWire 800 (IEEE 1394b-2002)
 IEEE 1394b-2002 introduced FireWire 800 (Apple's name for the 9-conductor ''S800 bilingual'' version of the IEEE 1394b standard). This specification added a new encoding scheme termed beta mode which allowed compliant devices to operate at 786.432 Mbit/s
IEEE 1394b-2002 introduced FireWire 800 (Apple's name for the 9-conductor ''S800 bilingual'' version of the IEEE 1394b standard). This specification added a new encoding scheme termed beta mode which allowed compliant devices to operate at 786.432 Mbit/s full-duplex
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow ...
. It is backwards compatible with the slower rates and 6-conductor alpha connectors of FireWire 400. However, while the IEEE 1394a and IEEE 1394b standards are compatible, FireWire 800's connector, referred to as a beta connector, is different from FireWire 400's alpha connectors, making legacy cables incompatible. A bilingual cable allows the connection of older devices to the newer port. In 2003, Apple was the first to introduce commercial products with the new connector, including a new model of the Power Mac G4 and a 17" PowerBook G4.
The full IEEE 1394b specification supports data rates up to 3200 Mbit/s (i.e., 400 MB/s) over beta-mode or optical connections up to in length. Standard category 5e cable supports at S100. The original 1394 and 1394a standards used data/strobe (D/S) encoding, now known as ''alpha mode'', with the cables, while 1394b added a data encoding scheme called 8b/10b referred to as ''beta mode''.
Beta mode is based on 8b/10b (from Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in ...
, also used for many other protocols). 8b/10b encoding involves expanding an 8-bit data word into 10 bits, with the extra bits after the 5th and 8th data bits. The partitioned data is sent through a Running Disparity calculator function. The Running Disparity calculator attempts to keep the number of 1s transmitted equal to 0s, thereby assuring a DC-balanced signal. Then, the different partitions are sent through a 5b/6b encoder for the 5-bit partition and a 3b/4b encoder for the 3-bit partition. This gives the packet the ability to have at least two 1s, ensuring synchronization of the PLL at the receiving end to the correct bit boundaries for reliable transfer. An additional function of the coding scheme is to support the arbitration for bus access and general bus control. This is possible due to the ''surplus'' symbols afforded by the 8b/10b expansion. (While 8-bit symbols can encode a maximum of 256 values, 10-bit symbols permit the encoding of up to 1024.) Symbols invalid for the current state of the receiving PHY indicate data errors.
FireWire S800T (IEEE 1394c-2006)
IEEE 1394c-2006 was published on June 8, 2007. It provided a major technical improvement, namely new port specification that provides 800 Mbit/s over the same8P8C
A modular connector is a type of electrical connector for cords and cables of electronic devices and appliances, such as in computer networking, telecommunication equipment, and audio headsets.
Modular connectors were originally developed for ...
(Ethernet) connectors with Category 5e cable, which is specified in IEEE 802.3 clause 40 ( gigabit Ethernet over copper twisted pair) along with a corresponding automatic negotiation that allows the same port to connect to either IEEE Std 1394 or IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
) devices.
FireWire S1600 and S3200
In December 2007, the 1394 Trade Association announced that products would be available before the end of 2008 using the S1600 and S3200 modes that, for the most part, had already been defined in 1394b and were further clarified in IEEE Std. 1394–2008. The 1.572864 Gbit/s and 3.145728 Gbit/s devices use the same 9-conductor beta connectors as the existing FireWire 800 and are fully compatible with existing S400 and S800 devices. It competes with USB 3.0. S1600 (Symwave) and S3200 (Dap Technology) development units have been made, however because of FPGA technology DapTechnology targeted S1600 implementations first with S3200 not becoming commercially available until 2012.Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American businessman, inventor, and investor best known for co-founding the technology company Apple Inc. Jobs was also the founder of NeXT and chairman and majority shareholder o ...
declared FireWire dead in 2008. , there were few S1600 devices released, with a Sony camera being the only notable user.
Future enhancements (including P1394d)
A project named IEEE P1394d was formed by the IEEE on March 9, 2009 to addsingle-mode fiber
In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber, also known as fundamental- or mono-mode, is an optical fiber designed to carry only a single mode of light - the transverse mode. Modes are the possible solutions of the Helmholtz equ ...
as an additional transport medium to FireWire. The project was withdrawn in 2013.
Other future iterations of FireWire were expected to increase speed to 6.4 Gbit/s and additional connectors such as the small multimedia interface.
Operating system support
Full support for IEEE 1394a and 1394b is available forMicrosoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
, FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable ...
, Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, MacOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
and NetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was fork (software development), forked. It continues to ...
.
In Windows XP, a degradation in performance of 1394 devices may have occurred with installation of Service Pack 2. This was resolved in Hotfix 885222 and in SP3. Some FireWire hardware manufacturers also provide custom device drivers that replace the Microsoft OHCI host adapter driver stack, enabling S800-capable devices to run at full 800 Mbit/s transfer rates on older versions of Windows (XP SP2 w/o Hotfix 885222) and Windows Vista. At the time of its release, Microsoft Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft W ...
supported only 1394a, with assurances that 1394b support would come in the next service pack. Service Pack 1 for Microsoft Windows Vista has since been released, however the addition of 1394b support is not mentioned anywhere in the release documentation. The 1394 bus driver was rewritten for Windows 7 to provide support for higher speeds and alternative media.
In Linux, support was originally provided by libraw1394 making direct communication between user space and IEEE 1394 buses. Subsequently, a new kernel driver stack, nicknamed JuJu, has been implemented.
Cable TV system support
Under FCC Code 47 CFR 76.640 section 4, subsections 1 and 2, Cable TV providers (in the US, with digital systems) must, upon request of a customer, have provided a high-definition capable cable box with a functional FireWire interface. This applied only to customers leasing high-definition capable cable boxes from their cable provider after April 1, 2004. The interface can be used to display or record Cable TV, including HDTV programming. In June 2010, the FCC issued an order that permitted set-top boxes to include IP-based interfaces in place of FireWire.Comparison with USB
While both technologies provide similar end results, there are fundamental differences betweenUSB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
and FireWire. USB requires the presence of a host controller, typically a PC, which connects point to point with the USB device. This allows for simpler (and lower-cost) peripherals, at the cost of lowered functionality of the bus. Intelligent hubs are required to connect multiple USB devices to a single USB host controller. By contrast, FireWire is essentially a peer-to-peer network (where any device may serve as the host or client), allowing multiple devices to be connected on one bus.
The FireWire host interface supports DMA and memory-mapped devices, allowing data transfers to happen without loading the host CPU with interrupts and buffer-copy operations. Additionally, FireWire features two data buses for each segment of the bus network, whereas, until USB 3.0, USB featured only one. This means that FireWire can have communication in both directions at the same time (full-duplex), whereas USB communication prior to 3.0 can only occur in one direction at any one time (half-duplex).
While USB 2.0 expanded into the fully backwards-compatible USB 3.0 and 3.1 (using the same main connector type), FireWire used a different connector between 400 and 800 implementations.
Common applications
Consumer automobiles
IDB-1394 Customer Convenience Port (CCP) was the automotive version of the 1394 standard.Consumer audio and video
IEEE 1394 was the High-Definition Audio-Video Network Alliance (HANA) standard connection interface for A/V (audio/visual) component communication and control. HANA was dissolved in September 2009 and the ''1394 Trade Association'' assumed control of all HANA-generated intellectual property.Military and aerospace vehicles
SAE Aerospace standard AS5643 originally released in 2004 and reaffirmed in 2013 establishes IEEE-1394 standards as a military and aerospace databus network in those vehicles. AS5643 is utilized by several large programs, including theF-35 Lightning II
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is an American family of single-seat, single-engine, supersonic Stealth aircraft, stealth strike fighters. A multirole combat aircraft designed for both Air superiority fighter, air superiority and att ...
, the X-47B UCAV aircraft, AGM-154 weapon and JPSS-1 polar satellite for NOAA. AS5643 combines existing 1394-2008 features like looped topology with additional features like transformer isolation and time synchronization, to create deterministic double and triple fault-tolerant data bus networks.
General networking
FireWire can be used for ad hoc (terminals only, no routers except where a FireWire hub is used)computer network
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or b ...
s. Specifically, RFC 2734 specifies how to run IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the first version of the Internet Protocol (IP) as a standalone specification. It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet and other packet-switched networks. ...
over the FireWire interface, and RFC 3146 specifies how to run IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communication protocol, communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic ...
.
Mac OS X, Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, and FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable ...
include support for networking over FireWire. Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft and the first of its Windows 9x family of operating systems, released to manufacturing on July 14, 1995, and generally to retail on August 24, 1995. Windows 95 merged ...
, Windows 98
Windows 98 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of Microsoft Windows operating systems. It was the second operating system in the 9x line, as the successor to Windows 95. It was Software ...
, Windows Me
Windows Me (Millennium Edition) is an operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of Microsoft Windows operating systems. It was the successor to Windows 98, and was released to manufacturing on June 19, 2000, and t ...
, Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users a ...
and Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003, codenamed "Whistler Server", is the sixth major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft and the first server version to be released under the Windows Server brand name. It is part of the Windows NT ...
include native support for IEEE 1394 networking. Windows 2000
Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft, targeting the server and business markets. It is the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0, and was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RT ...
does not have native support but may work with third party drivers. A network can be set up between two computers using a single standard FireWire cable, or by multiple computers through use of a hub. This is similar to Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
networks with the major differences being transfer speed, conductor length, and the fact that standard FireWire cables can be used for point-to-point communication.
On December 4, 2004, Microsoft announced that it would discontinue support for IP networking over the FireWire interface in all future versions of Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
. Consequently, support for this feature is absent from Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft W ...
and later Windows releases.
Microsoft rewrote their 1394 driver in Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, ...
but networking support for FireWire is not present. Unibrain offers free FireWire networking drivers for Windows called ubCore, which support Windows Vista and later versions.
Earlier models of the PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October, in Europe on 24 Novembe ...
console (SCPH 1000x to 3900x series) had an i.LINK-branded 1394 connector. This was used for networking until the release of an Ethernet adapter later in the console's lifespan, but very few software titles supported the feature. The connector was removed from the SCPH 5000x series onward.
IIDC
IIDC (Instrumentation & Industrial Digital Camera) is the FireWire data format standard for live video, and is used by Apple'siSight
iSight is a brand name used by Apple Inc. to refer to webcams on various devices. The name was originally used for the external iSight webcam, which retailed for US$149, connected to a computer via a FireWire cable, and came with a set of moun ...
A/V camera. The system was designed for machine vision
Machine vision is the technology and methods used to provide image, imaging-based automation, automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision ...
systems but is also used for other computer vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical ...
applications and for some webcams. Although they are easily confused since they both run over FireWire, IIDC is different from, and incompatible with, the ubiquitous AV/C (Audio Video Control) used to control camcorders and other consumer video devices.
DV
Digital Video ( DV) is a standard protocol used by some digitalcamcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right side, hot-sw ...
s. All DV cameras that recorded to tape media had a FireWire interface (usually a 4-conductor). All DV ports on camcorders only operate at the slower 100 Mbit/s speed of FireWire. This presents operational issues if the camcorder is daisy chained from a faster S400 device or via a common hub because any segment of a FireWire network cannot support multiple speed communication.
Labeling of the port varied by manufacturer, with Sony using either its i.LINK trademark or the letters ''DV''. Many digital video recorder
A digital video recorder (DVR), also referred to as a personal video recorder (PVR) particularly in Canadian and British English, is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SS ...
s have a ''DV-input'' FireWire connector (usually an alpha connector) that can be used to record video directly from a DV camcorder (computer-free). The protocol also accommodates remote control (play, rewind, etc.) of connected devices, and can stream time code from a camera.
USB is unsuitable for the transfer of the video data from tape because tape by its very nature does not support variable data rates. USB relies heavily on processor support and this was not guaranteed to service the USB port in time. The later move away from tape towards solid-state memory or disc media (e.g., SD Cards, optical disks or hard drives) has facilitated moving to USB transfer because file-based data can be moved in segments as required.
Frame grabbers
IEEE 1394 interface is commonly found in frame grabbers, devices that capture and digitize an analog video signal; however, IEEE 1394 is facing competition from theGigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in ...
interface (citing speed and availability issues).
iPod and iPhone synchronization and charging
iPod
The iPod is a series of portable media players and multi-purpose mobile devices that were designed and marketed by Apple Inc. from 2001 to 2022. The iPod Classic#1st generation, first version was released on November 10, 2001, about mon ...
s released prior to the iPod with Dock Connector used IEEE 1394a ports for transferring music files and charging, but in 2003, the FireWire port in iPods was succeeded by Apple's dock connector
A dock connector is an electrical connector used to attach a mobile device simultaneously to multiple external resources. Dock connectors typically carry a variety of signals and power, through a single connector, to simplify the process of docki ...
and IEEE 1394 to 30-pin connector cables were made. Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
began removing backwards compatibility with FireWire cables starting with the first generation iPod nano and fifth generation iPod, both of which could only sync via USB but retained the ability to charge through FireWire. This was also carried over to the second
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
and third generation nanos as well as the iPod Classic
The iPod Classic (stylized and marketed as iPod classic and originally simply iPod) is a discontinued portable media player created and formerly marketed by Apple Inc.
There were six generations of the iPod Classic, as well as a spin-off (the ...
. Backwards compatibility was removed completely beginning with the iPhone 3G
The iPhone 3G is a smartphone developed and marketed by Apple Inc. It is the List of iPhone models, second generation of iPhone, successor to the IPhone (1st generation), original iPhone, and was introduced on June 9, 2008, at the WWDC#2008, W ...
, second generation iPod touch, and the fourth generation iPod nano, all of which could only charge and sync via USB.
Security issues
Devices on a FireWire bus can communicate bydirect memory access
Direct memory access (DMA) is a feature of computer systems that allows certain hardware subsystems to access main system computer memory, memory independently of the central processing unit (CPU).
Without DMA, when the CPU is using programmed i ...
(DMA), where a device can use hardware to map internal memory to FireWire's ''physical memory space''. The SBP-2 ( Serial Bus Protocol 2) used by FireWire disk drives uses this capability to minimize interrupts and buffer copies. In SBP-2, the initiator (controlling device) sends a request by remotely writing a command into a specified area of the target's FireWire address space. This command usually includes buffer addresses in the initiator's FireWire ''Physical Address Space'', which the target is supposed to use for moving I/O data to and from the initiator.
On many implementations, particularly those like PCs and Macs using the popular OHCI, the mapping between the FireWire ''physical memory space'' and device physical memory is done in hardware, without operating system intervention. While this enables high-speed and low-latency communication between data sources and sinks without unnecessary copying (such as between a video camera and a software video recording application, or between a disk drive and the application buffers), this can also be a security or media rights-restriction risk if untrustworthy devices are attached to the bus and initiate a DMA attack. One of the applications known to exploit this to gain unauthorized access to running Windows, Mac OS and Linux computers is the spyware FinFireWire. For this reason, high-security installations typically either use newer machines that map a virtual memory
In computing, virtual memory, or virtual storage, is a memory management technique that provides an "idealized abstraction of the storage resources that are actually available on a given machine" which "creates the illusion to users of a ver ...
space to the FireWire ''physical memory space'' (such as a Power Mac G5
The Power Mac G5 is a series of personal computers designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from 2003 to 2006 as part of the Power Mac series. When introduced, it was the most powerful computer in Apple's Macintosh lineup, a ...
, or any Sun workstation), disable relevant drivers at operating system level, disable the OHCI hardware mapping between FireWire and device memory, physically disable the entire FireWire interface, or opt to not use FireWire or other hardware like PCMCIA, PC Card
PC Card is a technical standard specifying an expansion card interface for laptops and personal digital assistants, PDAs. The PCMCIA originally introduced the 16-bit Industry Standard Architecture, ISA-based PCMCIA Card in 1990, but renamed it to ...
, ExpressCard
ExpressCard, initially called NEWCARD, is an interface to connect peripheral, peripheral devices to a computer, usually a laptop, laptop computer. The ExpressCard technical standard specifies the design of slots built into the computer and of expa ...
or Thunderbolt, which expose DMA to external components.
An unsecured FireWire interface can be used to debug
In engineering, debugging is the process of finding the root cause, workarounds, and possible fixes for bugs.
For software, debugging tactics can involve interactive debugging, control flow analysis, log file analysis, monitoring at the ap ...
a machine whose operating system has crashed, and in some systems for remote-console operations. Windows natively supports this scenario of kernel debugging, although newer Windows Insider Preview builds no longer include the ability out of the box. On FreeBSD, the dcons driver provides both, using gdb as debugger. Under Linux, firescope and fireproxy exist.
See also
* DMA attack * HAVi * Linux IEEE 1394 target * List of interface bit rates * Pin control attackReferences
Further reading
* * *External links
* *IEEE 1394 connectors pinout
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ieee 1394 Interface Computer buses Computer connectors Computer storage buses IEEE standards Macintosh internals Personal area networks Serial buses Television terminology Video signal