Internal organs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In a multicellular
 Except for
Except for
 The organ level of organisation in
The organ level of organisation in
 The English word "organ" dates back to the twelfth century and refers to any musical instrument. By the late 14th century, the musical term's meaning had narrowed to refer specifically to the keyboard-based instrument. At the same time, a second meaning arose, in reference to a "body part adapted to a certain function".
Plant organs are made from tissue composed of different types of tissue. The three tissue types are ground, vascular, and dermal. When three or more organs are present, it is called an organ system.
The adjective ''
The English word "organ" dates back to the twelfth century and refers to any musical instrument. By the late 14th century, the musical term's meaning had narrowed to refer specifically to the keyboard-based instrument. At the same time, a second meaning arose, in reference to a "body part adapted to a certain function".
Plant organs are made from tissue composed of different types of tissue. The three tissue types are ground, vascular, and dermal. When three or more organs are present, it is called an organ system.
The adjective ''
organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organ (biology), organs that work together to perform one or more bodily functions. Each organ has a specialized role in an organism body, and is made up of distinct Tissue (biolog ...
. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
and smooth muscle tissue
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal muscle, skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non-striated ...
. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system
A biological system is a complex Biological network inference, network which connects several biologically relevant entities. Biological organization spans several scales and are determined based different structures depending on what the system is ...
or body system.
An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also funct ...
's tissue that makes the hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s is the parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
wastes, and the connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
s that provide a suitable place for it to be situated and anchored. The main tissues that make up an organ tend to have common embryologic origins, such as arising from the same germ layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cell (biology), cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce tw ...
. Organs exist in most multicellular organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s. In single-celled organisms such as members of the eukaryotes
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of ...
, the functional analogue of an organ is known as an organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
. In plants, there are three main organs.
The number of organs in any organism depends on the definition used. There are approximately 79 organs in the human body; the precise count is debated.
Animals
 Except for
Except for placozoa
Placozoa ( ; ) is a phylum of free-living (non-parasitic) marine invertebrates. They are blob-like animals composed of aggregations of cells. Moving in water by ciliary motion, eating food by Phagocytosis, engulfment, reproducing by Fission (biol ...
ns, multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s including humans have a variety of organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organ (biology), organs that work together to perform one or more bodily functions. Each organ has a specialized role in an organism body, and is made up of distinct Tissue (biolog ...
s. These specific systems are widely studied in human anatomy
Human anatomy (gr. ἀνατομία, "dissection", from ἀνά, "up", and τέμνειν, "cut") is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross ...
. The functions of these organ systems often share significant overlap. For instance, the nervous and endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrat ...
both operate via a shared organ, the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
. For this reason, the two systems are combined and studied as the neuroendocrine system. The same is true for the musculoskeletal system
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their Muscular system, muscular and Human skeleton, skeletal systems. ...
because of the relationship between the muscular and skeletal system
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fra ...
s.
* Cardiovascular system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
: pumping and channeling blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
to and from the body and lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s with heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
, blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
and blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s.
* Digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
: digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into th ...
and processing food with salivary gland
The salivary glands in many vertebrates including mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of min ...
s, esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
, stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
, liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
, intestines, colon, mesentery
In human anatomy, the mesentery is an Organ (anatomy), organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall, consisting of a double fold of the peritoneum. It helps (among other functions) in storing Adipose tissue, fat and allowi ...
, rectum
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces temporarily. The adult ...
and anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
.
* Endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrat ...
: communication within the body using hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s made by endocrine gland
The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs located throughout the body. Along with the nervous system, it makes the neuroendocrine system, which controls and regulates many of the body's functions. Endocrine glands are ductless gland ...
s such as the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
, pituitary gland, pineal body or pineal gland, thyroid, parathyroids and adrenals, i.e., adrenal glands.
* Excretory system
The excretory system is a passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. The dual function of excret ...
: kidneys
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retro ...
, ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lin ...
s, bladder and urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
involved in fluid balance, electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
balance and excretion of urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
.
* Lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lympha ...
: structures involved in the transfer of lymph between tissues and the blood stream, the lymph and the nodes and vessels that transport it including the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
: defending against disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
-causing agents with leukocyte
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
s, tonsils, adenoids, thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
and spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
.
* Integumentary system: skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and ...
and nails of mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s. Also scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
of fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s, and feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and an exa ...
s of birds.
* Muscular system
The muscular system is an organ (anatomy), organ system consisting of skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth, and cardiac muscle, cardiac muscle. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the bo ...
: movement with muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s.
* Nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
: collecting, transferring and processing information with brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
and nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
s.
* Reproductive system
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are al ...
: the sex organ
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting ...
s, such as ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
, oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
s, uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
, vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
, vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
, testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
s, vasa deferentia, seminal vesicles, prostate
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
and penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
.
* Respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
: the organs used for breathing
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into ( inhalation) and out of ( exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxy ...
, the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
, larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
, trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
, bronchi, lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s and diaphragm.
* Skeletal system
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fra ...
: structural support and protection with bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s, cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
, ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
s and tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue that connects skeletal muscle, muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tensi ...
s.
Viscera
In the study ofanatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
, viscera (: viscus) refers to the internal organs of the abdominal, thoracic
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main ...
, and pelvic cavities. The abdominal organs may be classified as solid organs or hollow organs. The solid organs are the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
, spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
, kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s, and adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
s. The hollow organs of the abdomen are the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
, intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
, gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, bladder, and rectum
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces temporarily. The adult ...
. In the thoracic cavity, the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
is a hollow, muscular organ. Splanchnology is the study of the viscera. The term "visceral" is contrasted with the term "", meaning "of or relating to the wall of a body part, organ or cavity". The two terms are often used in describing a membrane or piece of connective tissue, referring to the opposing sides.
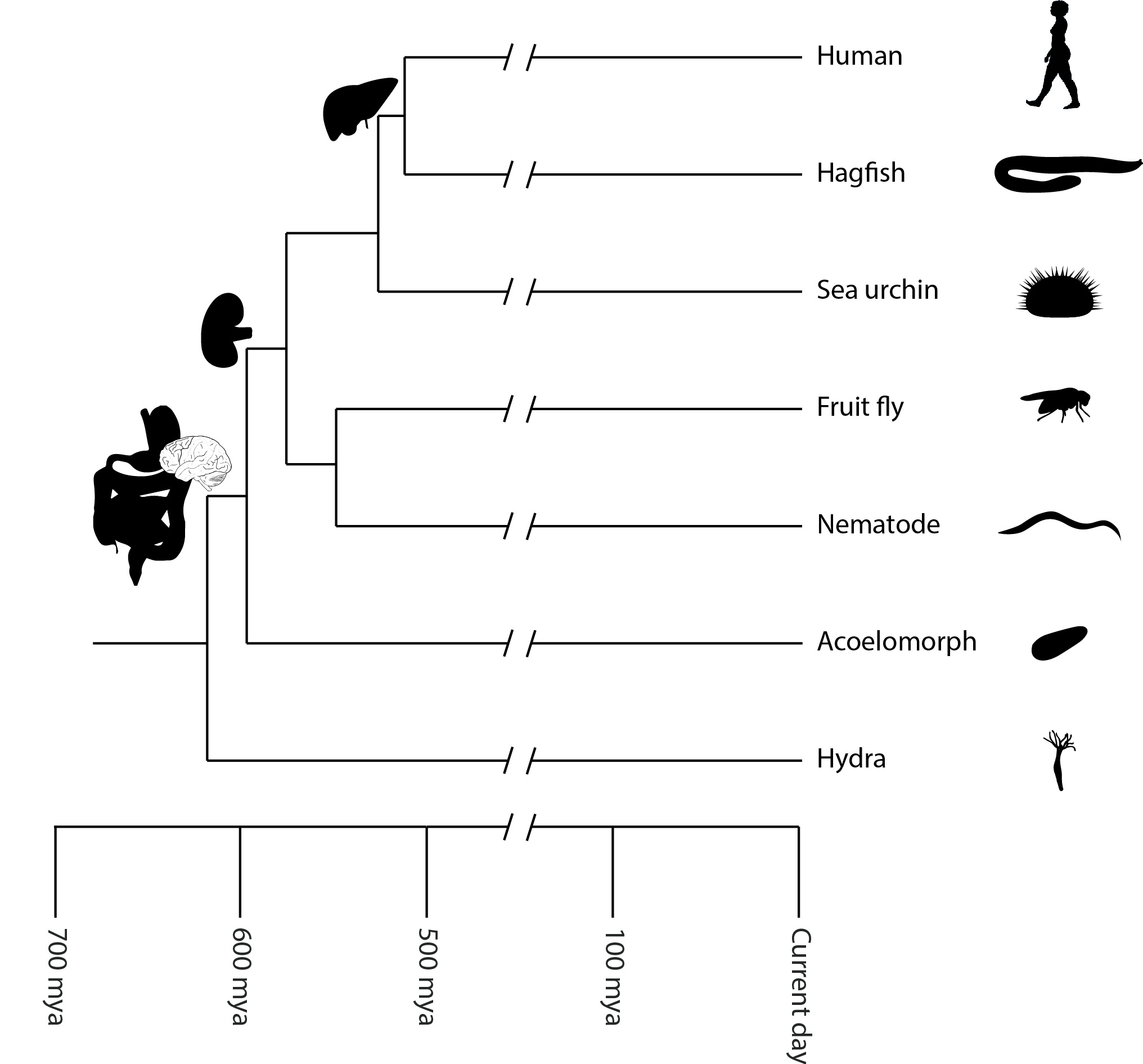
Origin and evolution
 The organ level of organisation in
The organ level of organisation in animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s can be first detected in flatworms and the more derived phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
, i.e. the bilateria
Bilateria () is a large clade of animals characterised by bilateral symmetry during embryonic development. This means their body plans are laid around a longitudinal axis with a front (or "head") and a rear (or "tail") end, as well as a left� ...
ns. The less-advanced taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
(i.e. ''Placozoa
Placozoa ( ; ) is a phylum of free-living (non-parasitic) marine invertebrates. They are blob-like animals composed of aggregations of cells. Moving in water by ciliary motion, eating food by Phagocytosis, engulfment, reproducing by Fission (biol ...
'', ''Porifera
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and a sister taxon of the Eumetazoa , diploblasts. They are sessility (motility) , sessile ...
'', '' Ctenophora'' and ''Cnidaria
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
'') do not show unification of their tissues into organs.
More complex animals are composed of different organs, which have evolved over time. For example, the liver and heart evolved in the chordates about 550-500 million years ago, while the gut and brain are even more ancient, arising in the ancestor of vertebrates, insects, molluscs
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
, and worms about 700–650 million years ago.
Given the ancient origin of most vertebrate organs, researchers have looked for model systems, where organs have evolved more recently, and ideally have evolved multiple times independently. An outstanding model for this kind of research is the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
, which has evolved more than 100 times independently in vertebrates, has evolved relatively recently in some lineages, and exists in intermediate forms in extant taxa. Studies on the evolution of the placenta have identified a variety of genetic and physiological processes that contribute to the origin and evolution of organs, these include the re-purposing of existing animal tissues, the acquisition of new functional properties by these tissues, and novel interactions of distinct tissue types.
Plants
The study of plant organs is covered inplant morphology
Phytomorphology is the study of the physical form and external structure of plants.Raven, P. H., R. F. Evert, & S. E. Eichhorn. ''Biology of Plants'', 7th ed., page 9. (New York: W. H. Freeman, 2005). . This is usually considered distinct from pl ...
. Organs of plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s can be divided into vegetative and reproductive. Vegetative plant organs include root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
s, stems, and leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
. The reproductive organs are variable. In flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s, they are represented by the flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
, seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
and fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
. In conifers, the organ that bears the reproductive structures is called a cone
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the '' apex'' or '' vertex''.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines ...
. In other divisions (phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
) of plants, the reproductive organs are called strobili, in '' Lycopodiophyta'', or simply gametophores in moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryo ...
es. Common organ system designations in plants include the differentiation of shoot and root. All parts of the plant above ground (in non-epiphyte
An epiphyte is a plant or plant-like organism that grows on the surface of another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphyt ...
s), including the functionally distinct leaf and flower organs, may be classified together as the shoot organ system.
The vegetative organs are essential for maintaining the life of a plant. While there can be 11 organ systems in animals, there are far fewer in plants, where some perform the vital functions, such as photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, while the reproductive organs are essential in reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
. However, if there is asexual vegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is a form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specializ ...
, the vegetative organs are those that create the new generation of plants (see clonal colony).
Society and culture
Many societies have a system for organ donation, in which a living or deceased donor's organ are transplanted into a person with a failing organ. The transplantation of larger solid organs often requires immunosuppression to preventorgan rejection
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
or graft-versus-host disease
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants.
White blood cells of the donor's immune system which rema ...
.
There is considerable interest throughout the world in creating laboratory-grown or artificial organs.
Organ transplants
Beginning in the 20th century, organ transplants began to take place as scientists knew more about the anatomy of organs. These came later in time as procedures were often dangerous and difficult. Both the source and method of obtaining the organ to transplant are major ethical issues to consider, and because organs as resources for transplant are always more limited than demand for them, various notions of justice, includingdistributive justice
Distributive justice concerns the Social justice, socially just Resource allocation, allocation of resources, goods, opportunity in a society. It is concerned with how to allocate resources fairly among members of a society, taking into account fa ...
, are developed in the ethical analysis. This situation continues as long as transplantation relies upon organ donors rather than technological innovation, testing, and industrial manufacturing.
Animal donor organs and tissue have been subjects of study since the 1960s, and some xenotransplant tissues, particularly heart valves, have been commonly utilized. Xenotransplant has the potential to address the critical shortage in organ grafts. The science behind enotransplanttrials has advanced considerably and more human clinical trials utilizing porcine xenografts are quickly approaching.
History
 The English word "organ" dates back to the twelfth century and refers to any musical instrument. By the late 14th century, the musical term's meaning had narrowed to refer specifically to the keyboard-based instrument. At the same time, a second meaning arose, in reference to a "body part adapted to a certain function".
Plant organs are made from tissue composed of different types of tissue. The three tissue types are ground, vascular, and dermal. When three or more organs are present, it is called an organ system.
The adjective ''
The English word "organ" dates back to the twelfth century and refers to any musical instrument. By the late 14th century, the musical term's meaning had narrowed to refer specifically to the keyboard-based instrument. At the same time, a second meaning arose, in reference to a "body part adapted to a certain function".
Plant organs are made from tissue composed of different types of tissue. The three tissue types are ground, vascular, and dermal. When three or more organs are present, it is called an organ system.
The adjective ''visceral
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an o ...
'', also '' splanchnic'', is used for anything pertaining to the internal organs. Historically, viscera of animals were examined by Roman pagan priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in parti ...
s like the haruspices or the augur
An augur was a priest and official in the ancient Rome, classical Roman world. His main role was the practice of augury, the interpretation of the will of the List of Roman deities, gods by studying events he observed within a predetermined s ...
s in order to divine the future by their shape, dimensions or other factors. This practice remains an important ritual in some remote, tribal societies.
The term "visceral" is contrasted with the term "", meaning "of or relating to the wall of a body part, organ or cavity" The two terms are often used in describing a membrane or piece of connective tissue, referring to the opposing sides.
Antiquity
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
used the word frequently in his philosophy, both to describe the organs of plants or animals (e.g. the roots of a tree, the heart or liver of an animal) because, in ancient Greek, the word organon''Hippocratic corpus
The Hippocratic Corpus (Latin: ''Corpus Hippocraticum''), or Hippocratic Collection, is a collection of around 60 early Ancient Greek medical works strongly associated with the physician Hippocrates and his teachings. The Hippocratic Corpus cov ...
, generally did not believe that there were organs of the body but only different ''parts'' of the body.
Some alchemists (e.g. Paracelsus
Paracelsus (; ; 1493 – 24 September 1541), born Theophrastus von Hohenheim (full name Philippus Aureolus Theophrastus Bombastus von Hohenheim), was a Swiss physician, alchemist, lay theologian, and philosopher of the German Renaissance.
H ...
) adopted the Hermetic Qabalah assignment between the seven vital organs and the seven classical planets as follows:
Chinese traditional medicine recognizes eleven organs, associated with the five Chinese traditional elements and with yin and yang
Originating in Chinese philosophy, yin and yang (, ), also yinyang or yin-yang, is the concept of opposite cosmic principles or forces that interact, interconnect, and perpetuate each other. Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary an ...
, as follows:
The Chinese associated the five elements with the five planets (Jupiter, Mars, Venus, Saturn, and Mercury) similar to the way the classical planets were associated with different metals. The ''yin'' and ''yang'' distinction approximates the modern notion of solid and hollow organs.
See also
* List of organs of the human body * Organoid * Organ-on-a-chip * Situs inversusReferences
External links
* {{Authority control Levels of organization (Biology)