Information Visualization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of

 The field of data and information visualization has emerged "from research in
The field of data and information visualization has emerged "from research in
''The Craft of Information Visualization: Readings and Reflections''
Morgan Kaufmann . Data and information visualization presumes that "visual representations and interaction techniques take advantage of the human eye's broad bandwidth pathway into the mind to allow users to see, explore, and understand large amounts of information at once. Information visualization focused on the creation of approaches for conveying abstract information in intuitive ways." Data analysis is an indispensable part of all applied research and problem solving in industry. The most fundamental data analysis approaches are visualization (histograms, scatter plots, surface plots, tree maps, parallel coordinate plots, etc.),
''Data Visualization: The State of the Art''. Research paper TU delft, 2002.
. In the commercial environment data visualization is often referred to as dashboards. Infographics are another very common form of data visualization.
 The modern study of visualization started with
The modern study of visualization started with 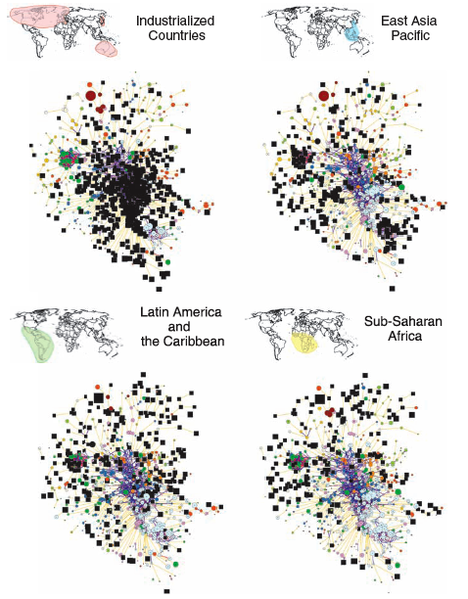
 There is no comprehensive 'history' of data visualization. There are no accounts that span the entire development of visual thinking and the visual representation of data, and which collate the contributions of disparate disciplines. Michael Friendly and Daniel J Denis of
There is no comprehensive 'history' of data visualization. There are no accounts that span the entire development of visual thinking and the visual representation of data, and which collate the contributions of disparate disciplines. Michael Friendly and Daniel J Denis of  In the second half of the 20th century, Jacques Bertin used quantitative graphs to represent information "intuitively, clearly, accurately, and efficiently".
John Tukey and Edward Tufte pushed the bounds of data visualization; Tukey with his new statistical approach of exploratory data analysis and Tufte with his book "The Visual Display of Quantitative Information" paved the way for refining data visualization techniques for more than statisticians. With the progression of technology came the progression of data visualization; starting with hand-drawn visualizations and evolving into more technical applications – including interactive designs leading to software visualization.
Programs like SAS,
In the second half of the 20th century, Jacques Bertin used quantitative graphs to represent information "intuitively, clearly, accurately, and efficiently".
John Tukey and Edward Tufte pushed the bounds of data visualization; Tukey with his new statistical approach of exploratory data analysis and Tufte with his book "The Visual Display of Quantitative Information" paved the way for refining data visualization techniques for more than statisticians. With the progression of technology came the progression of data visualization; starting with hand-drawn visualizations and evolving into more technical applications – including interactive designs leading to software visualization.
Programs like SAS,
"Milestones in the history of thematic cartography, statistical graphics, and data visualization"
. In this line the "Data Visualization: Modern Approaches" (2007) article gives an overview of seven subjects of data visualization: * Articles &
''Data Visualization: The State of the Art''
. *
 Data presentation architecture (DPA) is a skill-set that seeks to identify, locate, manipulate, format and present data in such a way as to optimally communicate meaning and proper knowledge.
Historically, the term ''data presentation architecture'' is attributed to Kelly Lautt: "Data Presentation Architecture (DPA) is a rarely applied skill set critical for the success and value of
Data presentation architecture (DPA) is a skill-set that seeks to identify, locate, manipulate, format and present data in such a way as to optimally communicate meaning and proper knowledge.
Historically, the term ''data presentation architecture'' is attributed to Kelly Lautt: "Data Presentation Architecture (DPA) is a rarely applied skill set critical for the success and value of
Adaptive Semantics Visualization
Eurographics Association. * * * * Andreas Kerren, John T. Stasko, Jean-Daniel Fekete, and Chris North (2008)
''Information Visualization – Human-Centered Issues and Perspectives''
Volume 4950 of LNCS State-of-the-Art Survey, Springer. * Spence, Robert ''Information Visualization: Design for Interaction (2nd Edition)'', Prentice Hall, 2007, . * Jeffrey Heer, Stuart K. Card, James Landay (2005)
"Prefuse: a toolkit for interactive information visualization"
. In: ''ACM Human Factors in Computing Systems'' CHI 2005. * * Ben Bederson and Ben Shneiderman (2003)
''The Craft of Information Visualization: Readings and Reflections''
Morgan Kaufmann. * Colin Ware (2000)
''Information Visualization: Perception for design''
Morgan Kaufmann. * Stuart K. Card, Jock D. Mackinlay and Ben Shneiderman (1999)
''Readings in Information Visualization: Using Vision to Think''
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. * * Schwabish, Jonathan A. 2014.
An Economist's Guide to Visualizing Data
" ''Journal of Economic Perspectives'', 28 (1): 209–34.
Milestones in the History of Thematic Cartography, Statistical Graphics, and Data Visualization
An illustrated chronology of innovations by Michael Friendly and Daniel J. Denis.
Duke University-Christa Kelleher Presentation-Communicating through infographics-visualizing scientific & engineering information-March 6, 2015
{{Authority control Visualization (graphics) Statistical charts and diagrams Information technology governance de:Informationsvisualisierung
 Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
ing and creating graphic
Graphics () are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of the data, as in design and manufa ...
or visual representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
and information
Information is an Abstraction, abstract concept that refers to something which has the power Communication, to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the Interpretation (philosophy), interpretation (perhaps Interpretation (log ...
with the help of static, dynamic or interactive visual items. Typically based on data and information collected from a certain domain of expertise, these visualizations are intended for a broader audience to help them visually explore and discover, quickly understand, interpret and gain important insights into otherwise difficult-to-identify structures, relationships, correlations, local and global patterns, trends, variations, constancy, clusters, outliers and unusual groupings within data (''exploratory visualization''). When intended for the general public (mass communication
Mass communication is the process of imparting and exchanging information through mass media to large population segments. It utilizes various forms of media as technology has made the dissemination of information more efficient. Primary examples o ...
) to convey a concise version of known, specific information in a clear and engaging manner (''presentational'' or ''explanatory visualization''), it is typically called information graphics
Infographics (a clipped compound of " information" and " graphics") are graphic visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly.Doug Newsom and Jim Haynes (2004). ''Public Relations ...
.
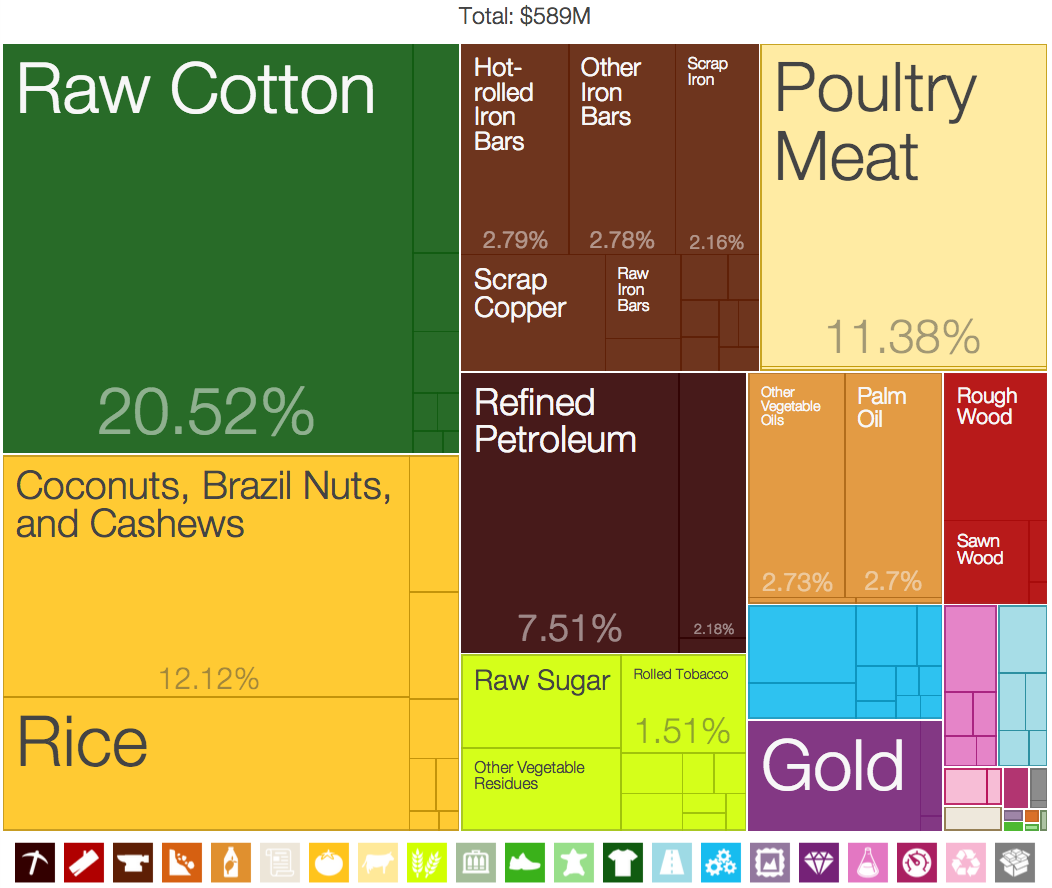
Data visualization is concerned with presenting sets of primarily quantitative raw data in a schematic form, using imagery. The visual formats used in data visualization include charts and graphs (e.g. pie chart
A pie chart (or a circle chart) is a circular Statistical graphics, statistical graphic which is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportion. In a pie chart, the arc length of each slice (and consequently its central angle and area) ...
s, bar chart
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical variable, categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. A ...
s, line chart
A line chart or line graph, also known as curve chart, is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points called 'markers' connected by straight wikt:line, line segments. It is a basic type of chart common in many fields. ...
s, area chart
An area chart or area graph displays graphically quantitative data. It is based on the line chart. The area between axis and line are commonly emphasized with colors, textures and hatchings. Commonly one compares two or more quantities with an a ...
s, cone charts, pyramid charts, donut charts, histogram
A histogram is a visual representation of the frequency distribution, distribution of quantitative data. To construct a histogram, the first step is to Data binning, "bin" (or "bucket") the range of values— divide the entire range of values in ...
s, spectrogram
A spectrogram is a visual representation of the spectrum of frequencies of a signal as it varies with time.
When applied to an audio signal, spectrograms are sometimes called sonographs, voiceprints, or voicegrams. When the data are represen ...
s, cohort charts, waterfall charts, funnel charts, bullet graphs, etc.), diagram
A diagram is a symbolic Depiction, representation of information using Visualization (graphics), visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on Cave painting, walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Age o ...
s, plots (e.g. scatter plots, distribution plots, box-and-whisker plots), geospatial maps (such as proportional symbol map
A proportional symbol map or proportional point symbol map is a type of thematic map that uses map symbols that Visual variable, vary in size to represent a quantitative variable. For example, circles may be used to show the location of cities wit ...
s, choropleth map
A choropleth map () is a type of statistical thematic map that uses pseudocolor, meaning color corresponding with an aggregate summary of a geographic characteristic within spatial enumeration units, such as population density or per-capita inco ...
s, isopleth map
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, isoquant or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dime ...
s and heat map
A heat map (or heatmap) is a 2-dimensional data visualization technique that represents the magnitude of individual values within a dataset as a color. The variation in color may be by hue or intensity.
In some applications such as crime analy ...
s), figures, correlation matrices, percentage gauges, etc., which sometimes can be combined in a dashboard
A dashboard (also called dash, instrument panel or IP, or fascia) is a control panel (engineering), control panel set within the central console of a vehicle, boat, or cockpit of an aircraft or spacecraft. Usually located directly ahead of the ...
.
Information visualization, on the other hand, deals with multiple, large-scale and complicated datasets which contain quantitative (numerical) data as well as qualitative (non-numerical, i.e. verbal or graphical) and primarily abstract information and its goal is to add value to raw data, improve the viewers' comprehension, reinforce their cognition and help them derive insights and make decisions as they navigate and interact with the computer-supported graphical display. Visual tools used in information visualization include maps for location based data; ''hierarchical'' organisations of data such as tree maps, radial_trees, and other tree_structure
A tree structure, tree diagram, or tree model is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the classic representation resembles a tree, although the chart is gen ...
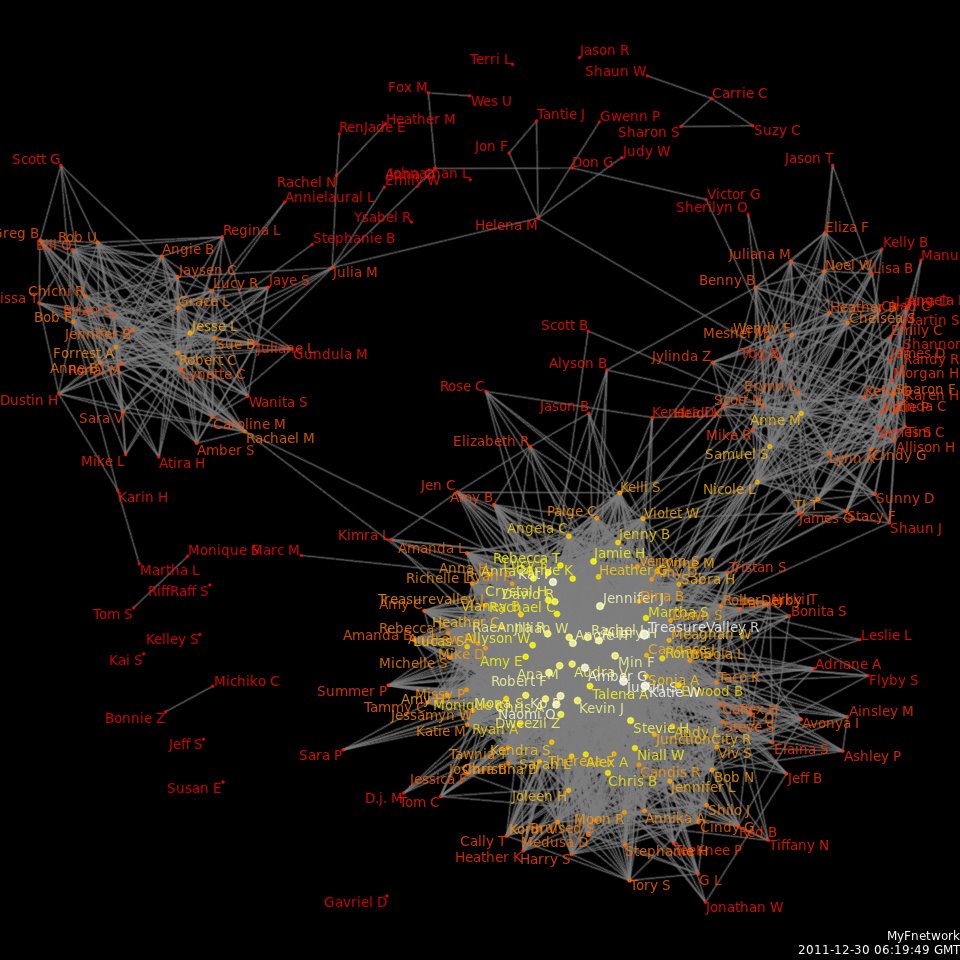
s; displays that prioritise ''relationships'' (Heer et al. 2010) such as Sankey diagrams, network diagrams, venn diagram
A Venn diagram is a widely used diagram style that shows the logical relation between set (mathematics), sets, popularized by John Venn (1834–1923) in the 1880s. The diagrams are used to teach elementary set theory, and to illustrate simple ...
s, mind maps, semantic network
A semantic network, or frame network is a knowledge base that represents semantic relations between concepts in a network. This is often used as a form of knowledge representation. It is a directed or undirected graph consisting of vertices, ...
s, entity-relationship diagrams; flow chart
A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task.
The flowchart shows the steps as boxes of va ...
s, timeline
A timeline is a list of events displayed in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale representing t ...
s, etc.
Emerging technologies
Emerging technologies are technology, technologies whose development, practical applications, or both are still largely unrealized. These technologies are generally innovation, new but also include old technologies finding new applications. Emer ...
like virtual, augmented and mixed reality
Augmented reality (AR), also known as mixed reality (MR), is a technology that overlays real-time 3D computer graphics, 3D-rendered computer graphics onto a portion of the real world through a display, such as a handheld device or head-mounted ...
have the potential to make information visualization more immersive, intuitive, interactive and easily manipulable and thus enhance the user's visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual percept ...
and cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
. In data and information visualization, the goal is to graphically present and explore abstract, non-physical and non-spatial data collected from database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
s, information system
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, Information Processing and Management, store, and information distribution, distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, info ...
s, file systems, document
A document is a writing, written, drawing, drawn, presented, or memorialized representation of thought, often the manifestation of nonfiction, non-fictional, as well as fictional, content. The word originates from the Latin ', which denotes ...
s, business data, etc. (''presentational and exploratory visualization'') which is different from the field of '' scientific visualization'', where the goal is to render realistic images based on physical and spatial scientific data to confirm or reject hypotheses
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific method, scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educ ...
(''confirmatory visualization'').
Effective data visualization is properly sourced, contextualized, simple and uncluttered. The underlying data is accurate and up-to-date to make sure that insights are reliable. Graphical items are well-chosen for the given datasets and aesthetically appealing, with shapes, colors and other visual elements used deliberately in a meaningful and non-distracting manner. The visuals are accompanied by supporting texts (labels and titles). These verbal and graphical components complement each other to ensure clear, quick and memorable understanding. Effective information visualization is aware of the needs and concerns and the level of expertise of the target audience, deliberately guiding them to the intended conclusion. Such effective visualization can be used not only for conveying specialized, complex, big data-driven ideas to a wider group of non-technical audience in a visually appealing, engaging and accessible manner, but also to domain experts and executives for making decisions, monitoring performance, generating new ideas and stimulating research. In addition, data scientists, data analysts and data mining specialists use data visualization to check the quality of data, find errors, unusual gaps and missing values in data, clean data, explore the structures and features of data and assess outputs of data-driven models. In business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
, data and information visualization can constitute a part of ''data storytelling'', where they are paired with a coherent narrative
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether non-fictional (memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travel literature, travelogue, etc.) or fictional (fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller ...
structure or storyline to contextualize the analyzed data and communicate the insights gained from analyzing the data clearly and memorably with the goal of convincing the audience into making a decision or taking an action in order to create business value. This can be contrasted with the field of statistical graphics, where complex statistical data are communicated graphically in an accurate and precise manner among researchers and analysts with statistical expertise to help them perform exploratory data analysis
In statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach of data analysis, analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often using statistical graphics and other data visualization methods. A statistical model can be used or ...
or to convey the results of such analyses, where visual appeal, capturing attention to a certain issue and storytelling are not as important.
The field of data and information visualization is of interdisciplinary nature as it incorporates principles found in the disciplines of descriptive statistics
A descriptive statistic (in the count noun sense) is a summary statistic that quantitatively describes or summarizes features from a collection of information, while descriptive statistics (in the mass noun sense) is the process of using and an ...
(as early as the 18th century), visual communication, graphic design
Graphic design is a profession, academic discipline and applied art that involves creating visual communications intended to transmit specific messages to social groups, with specific objectives. Graphic design is an interdisciplinary branch of ...
, cognitive science
Cognitive science is the interdisciplinary, scientific study of the mind and its processes. It examines the nature, the tasks, and the functions of cognition (in a broad sense). Mental faculties of concern to cognitive scientists include percep ...
and, more recently, interactive computer graphics and human-computer interaction. Since effective visualization requires design skills, statistical skills and computing skills, it is argued by authors such as Gershon and Page that it is both an art and a science. The neighboring field of visual analytics marries statistical data analysis, data and information visualization and human analytical reasoning through interactive visual interfaces to help human users reach conclusions, gain actionable insights and make informed decisions which are otherwise difficult for computers to do.
Research into how people read and misread various types of visualizations is helping to determine what types and features of visualizations are most understandable and effective in conveying information. On the other hand, unintentionally poor or intentionally misleading and deceptive visualizations (''misinformative visualization'') can function as powerful tools which disseminate misinformation
Misinformation is incorrect or misleading information. Misinformation and disinformation are not interchangeable terms: misinformation can exist with or without specific malicious intent, whereas disinformation is distinct in that the information ...
, manipulate public perception and divert public opinion
Public opinion, or popular opinion, is the collective opinion on a specific topic or voting intention relevant to society. It is the people's views on matters affecting them.
In the 21st century, public opinion is widely thought to be heavily ...
toward a certain agenda. Thus data visualization literacy has become an important component of data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
and information literacy in the information age
The Information Age is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on information technology ...
akin to the roles played by textual, mathematical
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
and visual literacy in the past.
Overview

 The field of data and information visualization has emerged "from research in
The field of data and information visualization has emerged "from research in human–computer interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is the process through which people operate and engage with computer systems. Research in HCI covers the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and comp ...
, computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
, graphics
Graphics () are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of the data, as in design and manufa ...
, visual design, psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
, photography
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is empl ...
and business methods. It is increasingly applied as a critical component in scientific research, digital libraries, data mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and ...
, financial data analysis, market studies, manufacturing production control, and drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology, and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.
Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or ...
".Benjamin B. Bederson and Ben Shneiderman (2003)''The Craft of Information Visualization: Readings and Reflections''
Morgan Kaufmann . Data and information visualization presumes that "visual representations and interaction techniques take advantage of the human eye's broad bandwidth pathway into the mind to allow users to see, explore, and understand large amounts of information at once. Information visualization focused on the creation of approaches for conveying abstract information in intuitive ways." Data analysis is an indispensable part of all applied research and problem solving in industry. The most fundamental data analysis approaches are visualization (histograms, scatter plots, surface plots, tree maps, parallel coordinate plots, etc.),
statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
( hypothesis test, regression, PCA, etc.), data mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and ...
( association mining, etc.), and machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
methods ( clustering, classification
Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identif ...
, decision trees, etc.). Among these approaches, information visualization, or visual data analysis, is the most reliant on the cognitive skills of human analysts, and allows the discovery of unstructured actionable insights that are limited only by human imagination and creativity. The analyst does not have to learn any sophisticated methods to be able to interpret the visualizations of the data. Information visualization is also a hypothesis generation scheme, which can be, and is typically followed by more analytical or formal analysis, such as statistical hypothesis testing.
To communicate information clearly and efficiently, data visualization uses statistical graphics, plots, information graphics
Infographics (a clipped compound of " information" and " graphics") are graphic visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly.Doug Newsom and Jim Haynes (2004). ''Public Relations ...
and other tools. Numerical data may be encoded using dots, lines, or bars, to visually communicate a quantitative message. Effective visualization helps users analyze and reason about data and evidence. It makes complex data more accessible, understandable, and usable, but can also be reductive. Users may have particular analytical tasks, such as making comparisons or understanding causality, and the design principle of the graphic (i.e., showing comparisons or showing causality) follows the task. Tables are generally used where users will look up a specific measurement, while charts of various types are used to show patterns or relationships in the data for one or more variables.
Data visualization refers to the techniques used to communicate data or information by encoding it as visual objects (e.g., points, lines, or bars) contained in graphics. The goal is to communicate information clearly and efficiently to users. It is one of the steps in data analysis
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, Data cleansing, cleansing, Data transformation, transforming, and Data modeling, modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Da ...
or data science
Data science is an interdisciplinary academic field that uses statistics, scientific computing, scientific methods, processing, scientific visualization, algorithms and systems to extract or extrapolate knowledge from potentially noisy, stru ...
. According to Vitaly Friedman (2008) the "main goal of data visualization is to communicate information clearly and effectively through graphical means. It doesn't mean that data visualization needs to look boring to be functional or extremely sophisticated to look beautiful. To convey ideas effectively, both aesthetic form and functionality need to go hand in hand, providing insights into a rather sparse and complex data set by communicating its key aspects in a more intuitive way. Yet designers often fail to achieve a balance between form and function, creating gorgeous data visualizations which fail to serve their main purpose — to communicate information".
Indeed, Fernanda Viegas and Martin M. Wattenberg suggested that an ideal visualization should not only communicate clearly, but stimulate viewer engagement and attention.
Data visualization is closely related to information graphics
Infographics (a clipped compound of " information" and " graphics") are graphic visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly.Doug Newsom and Jim Haynes (2004). ''Public Relations ...
, information visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating Graphics, graphic or visual Representation (arts), representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and i ...
, scientific visualization, exploratory data analysis
In statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach of data analysis, analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often using statistical graphics and other data visualization methods. A statistical model can be used or ...
and statistical graphics. In the new millennium, data visualization has become an active area of research, teaching and development. According to Post et al. (2002), it has united scientific and information visualization.Frits H. Post, Gregory M. Nielson and Georges-Pierre Bonneau (2002)''Data Visualization: The State of the Art''. Research paper TU delft, 2002.
. In the commercial environment data visualization is often referred to as dashboards. Infographics are another very common form of data visualization.
Principles
Characteristics of effective graphical displays
Edward Tufte has explained that users of information displays are executing particular ''analytical tasks'' such as making comparisons. The ''design principle'' of the information graphic should support the analytical task. As William Cleveland and Robert McGill show, different graphical elements accomplish this more or less effectively. For example, dot plots and bar charts outperform pie charts. In his 1983 book ''The Visual Display of Quantitative Information'', Edward Tufte defines 'graphical displays' and principles for effective graphical display in the following passage: "Excellence in statistical graphics consists of complex ideas communicated with clarity, precision, and efficiency. Graphical displays should: *show the data *induce the viewer to think about the substance rather than about methodology, graphic design, the technology of graphic production, or something else * avoid distorting what the data has to say *present many numbers in a small space *make large data sets coherent *encourage the eye to compare different pieces of data *reveal the data at several levels of detail, from a broad overview to the fine structure *serve a reasonably clear purpose: description, exploration, tabulation, or decoration *be closely integrated with the statistical and verbal descriptions of a data set. Graphics ''reveal'' data. Indeed, graphics can be more precise and revealing than conventional statistical computations." For example, the Minard diagram shows the losses suffered by Napoleon's army in the 1812–1813 period. Six variables are plotted: the size of the army, its location on a two-dimensional surface (x and y), time, the direction of movement, and temperature. The line width illustrates a comparison (size of the army at points in time), while the temperature axis suggests a cause of the change in army size. This multivariate display on a two-dimensional surface tells a story that can be grasped immediately while identifying the source data to build credibility. Tufte wrote in 1983 that: "It may well be the best statistical graphic ever drawn." Not applying these principles may result in misleading graphs, distorting the message, or supporting an erroneous conclusion. According to Tufte, chartjunk refers to the extraneous interior decoration of the graphic that does not enhance the message or gratuitous three-dimensional or perspective effects. Needlessly separating the explanatory key from the image itself, requiring the eye to travel back and forth from the image to the key, is a form of "administrative debris." The ratio of "data to ink" should be maximized, erasing non-data ink where feasible. TheCongressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency within the United States Congress, legislative branch of the United States government that provides budget and economic information to Congress.
I ...
summarized several best practices for graphical displays in a June 2014 presentation. These included: a) Knowing your audience; b) Designing graphics that can stand alone outside the report's context; and c) Designing graphics that communicate the key messages in the report.
Useful criteria for a data or information visualization include:
# It is based on (non-visual) data - that is, a data/info viz is not image processing and collage;
# It creates an image - specifically that the image plays the primary role in communicating meaning and is not an illustration accompanying the data in text form; and
# The result is readable.
Readability means that it is possible for a viewer to understand the underlying data, such as by making comparisons between proportionally sized visual elements to compare their respective data values; or using a legend to decode a map, like identifying coloured regions on a climate map to read temperature at that location. For greatest efficiency and simplicity of design and user experience, this readability is enhanced through the use of bijective mapping in that design of the image elements - where the mapping of representational element to data variable is unique.
Kosara (2007) also identifies the need for a visualisation to be "recognisable as a visualisation and not appear to be something else". He also states that recognisability and readability may not always be required in all types of visualisation e.g. "informative art" (which would still meet all three above criteria but might not look like a visualisation) or "artistic visualisation" (which similarly is still based on non-visual data to create an image, but may not be readable or recognisable).
Quantitative messages
Author Stephen Few described eight types of quantitative messages that users may attempt to understand or communicate from a set of data and the associated graphs used to help communicate the message: #Time-series: A single variable is captured over a period of time, such as the unemployment rate or temperature measures over a 10-year period. Aline chart
A line chart or line graph, also known as curve chart, is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points called 'markers' connected by straight wikt:line, line segments. It is a basic type of chart common in many fields. ...
may be used to demonstrate the trend over time.
#Ranking: Categorical subdivisions are ranked in ascending or descending order, such as a ranking of sales performance (the ''measure'') by sales persons (the ''category'', with each sales person a ''categorical subdivision'') during a single period. A bar chart
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical variable, categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. A ...
may be used to show the comparison across the sales persons.
#Part-to-whole: Categorical subdivisions are measured as a ratio to the whole (i.e., a percentage out of 100%). A pie chart
A pie chart (or a circle chart) is a circular Statistical graphics, statistical graphic which is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportion. In a pie chart, the arc length of each slice (and consequently its central angle and area) ...
or bar chart can show the comparison of ratios, such as the market share represented by competitors in a market.
#Deviation: Categorical subdivisions are compared against a reference, such as a comparison of actual vs. budget expenses for several departments of a business for a given time period. A bar chart can show comparison of the actual versus the reference amount.
#Frequency distribution: Shows the number of observations of a particular variable for given interval, such as the number of years in which the stock market return is between intervals such as 0–10%, 11–20%, etc. A histogram
A histogram is a visual representation of the frequency distribution, distribution of quantitative data. To construct a histogram, the first step is to Data binning, "bin" (or "bucket") the range of values— divide the entire range of values in ...
, a type of bar chart, may be used for this analysis. A boxplot helps visualize key statistics about the distribution, such as median, quartiles, outliers, etc.
#Correlation: Comparison between observations represented by two variables (X,Y) to determine if they tend to move in the same or opposite directions. For example, plotting unemployment (X) and inflation (Y) for a sample of months. A scatter plot is typically used for this message.
#Nominal comparison: Comparing categorical subdivisions in no particular order, such as the sales volume by product code. A bar chart may be used for this comparison.
#Geographic
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
or geospatial
Geographic data and information is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as data and information having an implicit or explicit association with a location relative to Earth (a geographic location or geographic position). It is also call ...
: Comparison of a variable across a map or layout, such as the unemployment rate by state or the number of persons on the various floors of a building. A cartogram
A cartogram (also called a value-area map or an anamorphic map, the latter common among German-speakers) is a thematic map of a set of features (countries, provinces, etc.), in which their geographic size is altered to be Proportionality (math ...
is a typical graphic used.
Analysts reviewing a set of data may consider whether some or all of the messages and graphic types above are applicable to their task and audience. The process of trial and error to identify meaningful relationships and messages in the data is part of exploratory data analysis
In statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach of data analysis, analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often using statistical graphics and other data visualization methods. A statistical model can be used or ...
.
Visual perception and data visualization
A human can distinguish differences in line length, shape, orientation, distances, and color (hue) readily without significant processing effort; these are referred to as " pre-attentive attributes". For example, it may require significant time and effort ("attentive processing") to identify the number of times the digit "5" appears in a series of numbers; but if that digit is different in size, orientation, or color, instances of the digit can be noted quickly through pre-attentive processing. Compelling graphics take advantage of pre-attentive processing and attributes and the relative strength of these attributes. For example, since humans can more easily process differences in line length than surface area, it may be more effective to use a bar chart (which takes advantage of line length to show comparison) rather than pie charts (which use surface area to show comparison).Human perception/cognition and data visualization
Almost all data visualizations are created for human consumption. Knowledge of human perception and cognition is necessary when designing intuitive visualizations. Cognition refers to processes in human beings like perception, attention, learning, memory, thought, concept formation, reading, and problem solving. Human visual processing is efficient in detecting changes and making comparisons between quantities, sizes, shapes and variations in lightness. When properties of symbolic data are mapped to visual properties, humans can browse through large amounts of data efficiently. It is estimated that 2/3 of the brain's neurons can be involved in visual processing. Proper visualization provides a different approach to show potential connections, relationships, etc. which are not as obvious in non-visualized quantitative data. Visualization can become a means of data exploration. Studies have shown individuals used on average 19% less cognitive resources, and 4.5% better able to recall details when comparing data visualization with text.History
 The modern study of visualization started with
The modern study of visualization started with computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. ...
, which "has from its beginning been used to study scientific problems. However, in its early days the lack of graphics power often limited its usefulness. The recent emphasis on visualization started in 1987 with the special issue of Computer Graphics on Visualization in ''Scientific Computing
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science, and more specifically the Computer Sciences, which uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and s ...
''. Since then there have been several conferences and workshops, co-sponsored by the IEEE Computer Society
IEEE Computer Society (commonly known as the Computer Society or CS) is a technical society of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) dedicated to computing, namely the major areas of hardware, software, standards and people ...
and ACM SIGGRAPH
ACM SIGGRAPH is the international Association for Computing Machinery's Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques based in New York. It was founded in 1969 by Andy van Dam (its direct predecessor, ACM SICGRAPH was ...
". They have been devoted to the general topics of data visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating Graphics, graphic or visual Representation (arts), representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and i ...
, information visualization and scientific visualization, and more specific areas such as volume visualization.
In 1786, William Playfair
William Playfair (22 September 1759 – 11 February 1823) was a Scottish engineer and political economist. The founder of graphical methods of statistics, Playfair invented several types of diagrams: in 1786 he introduced the line, area and ...
published the first presentation graphics.

 There is no comprehensive 'history' of data visualization. There are no accounts that span the entire development of visual thinking and the visual representation of data, and which collate the contributions of disparate disciplines. Michael Friendly and Daniel J Denis of
There is no comprehensive 'history' of data visualization. There are no accounts that span the entire development of visual thinking and the visual representation of data, and which collate the contributions of disparate disciplines. Michael Friendly and Daniel J Denis of York University
York University (), also known as YorkU or simply YU), is a public university, public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is Canada's third-largest university, and it has approximately 53,500 students, 7,000 faculty and staff, ...
are engaged in a project that attempts to provide a comprehensive history of visualization. Contrary to general belief, data visualization is not a modern development. Since prehistory, stellar data, or information such as location of stars were visualized on the walls of caves (such as those found in Lascaux Cave
Lascaux ( , ; , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, Dordogne, Montignac, in the Departments of France, department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 Parietal art, parietal cave painting, wall paintin ...
in Southern France) since the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
era. Physical artefacts such as Mesopotamian clay tokens (5500 BC), Inca quipus (2600 BC) and Marshall Islands stick charts (n.d.) can also be considered as visualizing quantitative information.
The first documented data visualization can be tracked back to 1160 B.C. with Turin Papyrus Map which accurately illustrates the distribution of geological resources and provides information about quarrying of those resources. Such maps can be categorized as thematic cartography, which is a type of data visualization that presents and communicates specific data and information through a geographical illustration designed to show a particular theme connected with a specific geographic area. Earliest documented forms of data visualization were various thematic maps from different cultures and ideograms and hieroglyphs that provided and allowed interpretation of information illustrated. For example, Linear B
Linear B is a syllabary, syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest Attested language, attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries, the earliest known examp ...
tablets of Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; ; or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines, Greece, Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos; and sou ...
provided a visualization of information regarding Late Bronze Age era trades in the Mediterranean. The idea of coordinates was used by ancient Egyptian surveyors in laying out towns, earthly and heavenly positions were located by something akin to latitude and longitude at least by 200 BC, and the map projection of a spherical Earth into latitude and longitude by Claudius Ptolemy ��in Alexandria would serve as reference standards until the 14th century.
The invention of paper and parchment allowed further development of visualizations throughout history. Figure shows a graph from the 10th or possibly 11th century that is intended to be an illustration of the planetary movement, used in an appendix of a textbook in monastery schools. The graph apparently was meant to represent a plot of the inclinations of the planetary orbits as a function of the time. For this purpose, the zone of the zodiac was represented on a plane with a horizontal line divided into thirty parts as the time or longitudinal axis. The vertical axis designates the width of the zodiac. The horizontal scale appears to have been chosen for each planet individually for the periods cannot be reconciled. The accompanying text refers only to the amplitudes. The curves are apparently not related in time.
By the 16th century, techniques and instruments for precise observation and measurement of physical quantities, and geographic and celestial position were well-developed (for example, a "wall quadrant" constructed by Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, ; 14 December 154624 October 1601), generally called Tycho for short, was a Danish astronomer of the Renaissance, known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He ...
546–1601 covering an entire wall in his observatory). Particularly important were the development of triangulation and other methods to determine mapping locations accurately. Very early, the measure of time led scholars to develop innovative way of visualizing the data (e.g. Lorenz Codomann in 1596, Johannes Temporarius in 1596).
French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes
René Descartes ( , ; ; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and Modern science, science. Mathematics was paramou ...
and Pierre de Fermat
Pierre de Fermat (; ; 17 August 1601 – 12 January 1665) was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he is recognized for his d ...
developed analytic geometry and two-dimensional coordinate system which heavily influenced the practical methods of displaying and calculating values. Fermat and Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal (19June 162319August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic Church, Catholic writer.
Pascal was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. His earliest ...
's work on statistics and probability theory laid the groundwork for what we now conceptualize as data. According to the Interaction Design Foundation, these developments allowed and helped William Playfair, who saw potential for graphical communication of quantitative data, to generate and develop graphical methods of statistics.  In the second half of the 20th century, Jacques Bertin used quantitative graphs to represent information "intuitively, clearly, accurately, and efficiently".
John Tukey and Edward Tufte pushed the bounds of data visualization; Tukey with his new statistical approach of exploratory data analysis and Tufte with his book "The Visual Display of Quantitative Information" paved the way for refining data visualization techniques for more than statisticians. With the progression of technology came the progression of data visualization; starting with hand-drawn visualizations and evolving into more technical applications – including interactive designs leading to software visualization.
Programs like SAS,
In the second half of the 20th century, Jacques Bertin used quantitative graphs to represent information "intuitively, clearly, accurately, and efficiently".
John Tukey and Edward Tufte pushed the bounds of data visualization; Tukey with his new statistical approach of exploratory data analysis and Tufte with his book "The Visual Display of Quantitative Information" paved the way for refining data visualization techniques for more than statisticians. With the progression of technology came the progression of data visualization; starting with hand-drawn visualizations and evolving into more technical applications – including interactive designs leading to software visualization.
Programs like SAS, SOFA
A couch, also known as a sofa, settee, chesterfield, or Davenport (sofa), davenport, is a cushioned piece of furniture that can seat multiple people. It is commonly found in the form of a bench (furniture), bench with Upholstery, upholstered ...
, R, Minitab, Cornerstone and more allow for data visualization in the field of statistics. Other data visualization applications, more focused and unique to individuals, programming languages such as D3, Python (through matplotlib, seaborn) and JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior.
Web browsers have ...
and Java(through JavaFX) help to make the visualization of quantitative data a possibility. Private schools have also developed programs to meet the demand for learning data visualization and associated programming libraries, including free programs like The Data Incubator or paid programs like General Assembly.
Beginning with the symposium "Data to Discovery" in 2013, ArtCenter College of Design, Caltech and JPL in Pasadena have run an annual program on interactive data visualization. The program asks: How can interactive data visualization help scientists and engineers explore their data more effectively? How can computing, design, and design thinking help maximize research results? What methodologies are most effective for leveraging knowledge from these fields? By encoding relational information with appropriate visual and interactive characteristics to help interrogate, and ultimately gain new insight into data, the program develops new interdisciplinary approaches to complex science problems, combining design thinking and the latest methods from computing, user-centered design, interaction design and 3D graphics.
Terminology
Data visualization involves specific terminology, some of which is derived from statistics. For example, author Stephen Few defines two types of data, which are used in combination to support a meaningful analysis or visualization: *Categorical: Represent groups of objects with a particular characteristic. Categorical variables can either be nominal or ordinal. Nominal variables for example gender have no order between them and are thus nominal. Ordinal variables are categories with an order, for sample recording the age group someone falls into. *Quantitative: Represent measurements, such as the height of a person or the temperature of an environment. Quantitative variables can either be continuous or discrete. Continuous variables capture the idea that measurements can always be made more precisely. While discrete variables have only a finite number of possibilities, such as a count of some outcomes or an age measured in whole years. The distinction between quantitative and categorical variables is important because the two types require different methods of visualization. Two primary types of information displays are tables and graphs. *A ''table'' contains quantitative data organized into rows and columns with categorical labels. It is primarily used to look up specific values. In the example above, the table might have categorical column labels representing the name (a ''qualitative variable'') and age (a ''quantitative variable''), with each row of data representing one person (the sampled ''experimental unit'' or ''category subdivision''). *A ''graph'' is primarily used to show relationships among data and portrays values encoded as ''visual objects'' (e.g., lines, bars, or points). Numerical values are displayed within an area delineated by one or more ''axes''. These axes provide ''scales'' (quantitative and categorical) used to label and assign values to the visual objects. Many graphs are also referred to as ''charts''. Eppler and Lengler have developed the "Periodic Table of Visualization Methods," an interactive chart displaying various data visualization methods. It includes six types of data visualization methods: data, information, concept, strategy, metaphor and compound. In "Visualization Analysis and Design" Tamara Munzner writes "Computer-based visualization systems provide visual representations of datasets designed to help people carry out tasks more effectively." Munzner argues that visualization "is suitable when there is a need to augment human capabilities rather than replace people with computational decision-making methods."Techniques
Other techniques
*Cartogram
A cartogram (also called a value-area map or an anamorphic map, the latter common among German-speakers) is a thematic map of a set of features (countries, provinces, etc.), in which their geographic size is altered to be Proportionality (math ...
* Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
(phylogeny)
* Concept Map
A concept map or conceptual diagram is a diagram that depicts suggested relationships between concepts. Concept maps may be used by instructional designers, engineers, technical writers, and others to organize and structure knowledge.
A conc ...
ping
* Dendrogram
A dendrogram is a diagram representing a Tree (graph theory), tree graph. This diagrammatic representation is frequently used in different contexts:
* in hierarchical clustering, it illustrates the arrangement of the clusters produced by ...
(classification)
* Information visualization reference model
* Grand tour
* Graph drawing
* HyperbolicTree
* Multidimensional scaling
Multidimensional scaling (MDS) is a means of visualizing the level of similarity of individual cases of a data set. MDS is used to translate distances between each pair of n objects in a set into a configuration of n points mapped into an ...
* Parallel coordinates
* Problem solving environment
Interactivity
Interactive data visualization enables direct actions on a graphical plot to change elements and link between multiple plots. Interactive data visualization has been a pursuit of statisticians since the late 1960s. Examples of the developments can be found on the American Statistical Association video lending library. Common interactions include: * Brushing: works by using themouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
to control a paintbrush, directly changing the color or glyph of elements of a plot. The paintbrush is sometimes a pointer and sometimes works by drawing an outline of sorts around points; the outline is sometimes irregularly shaped, like a lasso. Brushing is most commonly used when multiple plots are visible and some linking mechanism exists between the plots. There are several different conceptual models for brushing and a number of common linking mechanisms. Brushing scatterplots can be a transient operation in which points in the active plot only retain their new characteristics. At the same time, they are enclosed or intersected by the brush, or it can be a persistent operation, so that points retain their new appearance after the brush has been moved away. Transient brushing is usually chosen for linked brushing, as we have just described.
* Painting: Persistent brushing is useful when we want to group the points into clusters and then proceed to use other operations, such as the tour, to compare the groups. It is becoming common terminology to call the persistent operation painting,
* Identification: which could also be called labeling or label brushing, is another plot manipulation that can be linked. Bringing the cursor near a point or edge in a scatterplot, or a bar in a barchart, causes a label to appear that identifies the plot element. It is widely available in many interactive graphics, and is sometimes called mouseover.
* Scaling: maps the data onto the window, and changes in the area of the. mapping function help us learn different things from the same plot. Scaling is commonly used to zoom in on crowded regions of a scatterplot, and it can also be used to change the aspect ratio of a plot, to reveal different features of the data.
* Linking: connects elements selected in one plot with elements in another plot. The simplest kind of linking, one-to-one, where both plots show different projections of the same data, and a point in one plot corresponds to exactly one point in the other. When using area plots, brushing any part of an area has the same effect as brushing it all and is equivalent to selecting all cases in the corresponding category. Even when some plot elements represent more than one case, the underlying linking rule still links one case in one plot to the same case in other plots. Linking can also be by categorical variable, such as by a subject id, so that all data values corresponding to that subject are highlighted, in all the visible plots.
Other perspectives
There are different approaches on the scope of data visualization. One common focus is on information presentation, such as Friedman (2008). Friendly (2008) presumes two main parts of data visualization: statistical graphics, and thematic cartography. Michael Friendly (2008)"Milestones in the history of thematic cartography, statistical graphics, and data visualization"
. In this line the "Data Visualization: Modern Approaches" (2007) article gives an overview of seven subjects of data visualization: * Articles &
resources
''Resource'' refers to all the materials available in our environment which are Technology, technologically accessible, Economics, economically feasible and Culture, culturally Sustainability, sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and want ...
* Displaying connections
* Displaying data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
* Displaying news
News is information about current events. This may be provided through many different Media (communication), media: word of mouth, printing, Mail, postal systems, broadcasting, Telecommunications, electronic communication, or through the te ...
* Displaying website
A website (also written as a web site) is any web page whose content is identified by a common domain name and is published on at least one web server. Websites are typically dedicated to a particular topic or purpose, such as news, educatio ...
s
* Mind maps
* Tools and services
All these subjects are closely related to graphic design
Graphic design is a profession, academic discipline and applied art that involves creating visual communications intended to transmit specific messages to social groups, with specific objectives. Graphic design is an interdisciplinary branch of ...
and information representation.
On the other hand, from a computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
perspective, Frits H. Post in 2002 categorized the field into sub-fields:Frits H. Post, Gregory M. Nielson and Georges-Pierre Bonneau (2002)''Data Visualization: The State of the Art''
. *
Information visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating Graphics, graphic or visual Representation (arts), representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and i ...
* Interaction techniques and architectures
* Modelling techniques
* Multiresolution methods
* Visualization algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
s and techniques
* Volume visualization
Within The Harvard Business Review, Scott Berinato developed a framework to approach data visualisation. To start thinking visually, users must consider two questions; 1) What you have and 2) what you're doing. The first step is identifying what data you want visualised. It is data-driven like profit over the past ten years or a conceptual idea like how a specific organisation is structured. Once this question is answered one can then focus on whether they are trying to communicate information (declarative visualisation) or trying to figure something out (exploratory visualisation). Scott Berinato combines these questions to give four types of visual communication that each have their own goals.
These four types of visual communication are as follows;
* idea illustration (conceptual & declarative).
** Used to teach, explain and/or simply concepts. For example, organisation charts and decision trees.
* idea generation (conceptual & exploratory).
** Used to discover, innovate and solve problems. For example, a whiteboard after a brainstorming session.
* visual discovery (data-driven & exploratory).
** Used to spot trends and make sense of data. This type of visual is more common with large and complex data where the dataset is somewhat unknown and the task is open-ended.
* everyday data-visualisation (data-driven & declarative).
** The most common and simple type of visualisation used for affirming and setting context. For example, a line graph of GDP over time.
Applications
Data and information visualization insights are being applied in areas such as: * Scientific research * Digital libraries *Data mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and ...
* Information graphics
Infographics (a clipped compound of " information" and " graphics") are graphic visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly.Doug Newsom and Jim Haynes (2004). ''Public Relations ...
* Financial data analysis
* Health care
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
* Market studies
* Manufacturing production control
* Crime mapping
Crime mapping is used by analysts in law enforcement agency, law enforcement agencies to map, visualize, and analyze crime incident patterns. It is a key component of crime analysis and the CompStat policing strategy. Mapping crime, using Geogr ...
* eGovernance and Policy Modeling
* Digital Humanities
Digital humanities (DH) is an area of scholarly activity at the intersection of computing or Information technology, digital technologies and the disciplines of the humanities. It includes the systematic use of digital resources in the humanitie ...
* Data Art
Organization
Notable academic and industry laboratories in the field are: * Adobe Research * IBM Research * Google Research *Microsoft Research
Microsoft Research (MSR) is the research subsidiary of Microsoft. It was created in 1991 by Richard Rashid, Bill Gates and Nathan Myhrvold with the intent to advance state-of-the-art computing and solve difficult world problems through technologi ...
* Panopticon Software
* Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute
* Tableau Software
* University of Maryland Human-Computer Interaction Lab
Conferences in this field, ranked by significance in data visualization research, are:
* IEEE Visualization: An annual international conference on scientific visualization, information visualization, and visual analytics. Conference is held in October.
* ACM SIGGRAPH
ACM SIGGRAPH is the international Association for Computing Machinery's Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques based in New York. It was founded in 1969 by Andy van Dam (its direct predecessor, ACM SICGRAPH was ...
: An annual international conference on computer graphics, convened by the ACM SIGGRAPH organization. Conference dates vary.
* Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI): An annual international conference on human–computer interaction, hosted by ACM SIGCHI. Conference is usually held in April or May.
* Eurographics: An annual Europe-wide computer graphics conference, held by the European Association for Computer Graphics. Conference is usually held in April or May.
For further examples, see: :Computer graphics organizations
Data presentation architecture
 Data presentation architecture (DPA) is a skill-set that seeks to identify, locate, manipulate, format and present data in such a way as to optimally communicate meaning and proper knowledge.
Historically, the term ''data presentation architecture'' is attributed to Kelly Lautt: "Data Presentation Architecture (DPA) is a rarely applied skill set critical for the success and value of
Data presentation architecture (DPA) is a skill-set that seeks to identify, locate, manipulate, format and present data in such a way as to optimally communicate meaning and proper knowledge.
Historically, the term ''data presentation architecture'' is attributed to Kelly Lautt: "Data Presentation Architecture (DPA) is a rarely applied skill set critical for the success and value of Business Intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) consists of strategies, methodologies, and technologies used by enterprises for data analysis and management of business information. Common functions of BI technologies include Financial reporting, reporting, online an ...
. Data presentation architecture weds the science of numbers, data and statistics in discovering valuable information from data and making it usable, relevant and actionable with the arts of data visualization, communications, organizational psychology and change management
Change management (CM) is a discipline that focuses on managing changes within an organization. Change management involves implementing approaches to prepare and support individuals, teams, and leaders in making organizational change. Change mana ...
in order to provide business intelligence solutions with the data scope, delivery timing, format and visualizations that will most effectively support and drive operational, tactical and strategic behaviour toward understood business (or organizational) goals. DPA is neither an IT nor a business skill set but exists as a separate field of expertise. Often confused with data visualization, data presentation architecture is a much broader skill set that includes determining what data on what schedule and in what exact format is to be presented, not just the best way to present data that has already been chosen. Data visualization skills are one element of DPA."
Objectives
DPA has two main objectives: * To use data to provide knowledge in the most efficient manner possible (minimize noise, complexity, and unnecessary data or detail given each audience's needs and roles) * To use data to provide knowledge in the most effective manner possible (provide relevant, timely and complete data to each audience member in a clear and understandable manner that conveys important meaning, is actionable and can affect understanding, behavior and decisions)Scope
With the above objectives in mind, the actual work of data presentation architecture consists of: * Creating effective delivery mechanisms for each audience member depending on their role, tasks, locations and access to technology * Defining important meaning (relevant knowledge) that is needed by each audience member in each context * Determining the required periodicity of data updates (the currency of the data) * Determining the right timing for data presentation (when and how often the user needs to see the data) * Finding the right data (subject area, historical reach, breadth, level of detail, etc.) * Utilizing appropriate analysis, grouping, visualization, and other presentation formatsRelated fields
DPA work shares commonalities with several other fields, including: * Business analysis in determining business goals, collecting requirements, mapping processes. * Business process improvement in that its goal is to improve and streamline actions and decisions in furtherance of business goals * Data visualization in that it uses well-established theories of visualization to add or highlight meaning or importance in data presentation. *Digital humanities
Digital humanities (DH) is an area of scholarly activity at the intersection of computing or Information technology, digital technologies and the disciplines of the humanities. It includes the systematic use of digital resources in the humanitie ...
explores more nuanced ways of visualising complex data.
* Information architecture, but information architecture's focus is on unstructured data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically plain text, text-heavy, but may contain data such ...
and therefore excludes both analysis (in the statistical/data sense) and direct transformation of the actual content (data, for DPA) into new entities and combinations.
* HCI and interaction design
Interaction design, often abbreviated as IxD, is "the practice of designing interactive digital products, environments, systems, and services." While interaction design has an interest in form (similar to other design fields), its main area of foc ...
, since many of the principles in how to design interactive data visualisation have been developed cross-disciplinary with HCI.
* Visual journalism and data-driven journalism or data journalism
Data journalism or data-driven journalism (DDJ) is journalism based on the filtering and analysis of large data sets for the purpose of creating or elevating a news story.
Data journalism reflects the increased role of numerical data in the p ...
: Visual journalism is concerned with all types of graphic facilitation of the telling of news stories, and data-driven and data journalism are not necessarily told with data visualisation. Nevertheless, the field of journalism is at the forefront in developing new data visualisations to communicate data.
* Graphic design
Graphic design is a profession, academic discipline and applied art that involves creating visual communications intended to transmit specific messages to social groups, with specific objectives. Graphic design is an interdisciplinary branch of ...
, conveying information through styling, typography, position, and other aesthetic concerns.
See also
*Analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data sc ...
* Big data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with ...
* Climate change art
* Computational visualistics
* Information art
* Data management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource, it is the practice of managing an organization's data so it can be analyzed for decision making.
Concept
The concept of data management emerged alongsi ...
* Data physicalization
* Data Presentation Architecture
* Data profiling
* Data warehouse
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for Business intelligence, reporting and data analysis and is a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central Re ...
* Geovisualization
Geovisualization or geovisualisation (short for geographic visualization), also known as cartographic visualization, refers to a set of tools and techniques supporting the analysis of geospatial data through the use of interactive visualization.
...
* Grand Tour (data visualisation)
* imc FAMOS (1987), graphical data analysis
* Infographics
Infographics (a clipped compound of "information" and "graphics") are graphic visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly.Doug Newsom and Jim Haynes (2004). ''Public Relations Wri ...
* Information design
* Information management
Information management (IM) is the appropriate and optimized capture, storage, retrieval, and use of information. It may be personal information management or organizational. Information management for organizations concerns a cycle of organiz ...
* List of graphical methods
* List of information graphics software
* List of countries by economic complexity, example of Treemapping
* List of mathematical art software
* Patent visualisation Patent visualisation is an application of information visualisation. The number of patents has been increasing, encouraging companies to consider intellectual property as a part of their strategy. Patent visualisation, like patent mapping, is used t ...
* Software visualization
* Statistical analysis
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying probability distribution.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of ...
* Visual analytics
* Warming stripes
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * Kawa Nazemi (2014)Adaptive Semantics Visualization
Eurographics Association. * * * * Andreas Kerren, John T. Stasko, Jean-Daniel Fekete, and Chris North (2008)
''Information Visualization – Human-Centered Issues and Perspectives''
Volume 4950 of LNCS State-of-the-Art Survey, Springer. * Spence, Robert ''Information Visualization: Design for Interaction (2nd Edition)'', Prentice Hall, 2007, . * Jeffrey Heer, Stuart K. Card, James Landay (2005)
"Prefuse: a toolkit for interactive information visualization"
. In: ''ACM Human Factors in Computing Systems'' CHI 2005. * * Ben Bederson and Ben Shneiderman (2003)
''The Craft of Information Visualization: Readings and Reflections''
Morgan Kaufmann. * Colin Ware (2000)
''Information Visualization: Perception for design''
Morgan Kaufmann. * Stuart K. Card, Jock D. Mackinlay and Ben Shneiderman (1999)
''Readings in Information Visualization: Using Vision to Think''
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. * * Schwabish, Jonathan A. 2014.
An Economist's Guide to Visualizing Data
" ''Journal of Economic Perspectives'', 28 (1): 209–34.
External links
Milestones in the History of Thematic Cartography, Statistical Graphics, and Data Visualization
An illustrated chronology of innovations by Michael Friendly and Daniel J. Denis.
Duke University-Christa Kelleher Presentation-Communicating through infographics-visualizing scientific & engineering information-March 6, 2015
{{Authority control Visualization (graphics) Statistical charts and diagrams Information technology governance de:Informationsvisualisierung