
The history of North Africa is typically divided into its prehistory, the classical period, the arrival and spread of Islam, the colonial era, and finally the post-independence period, in which the current nations were formed. The region has been influenced by a wide range of cultures. The development of
sea travel firmly integrated North Africa into the Mediterranean world, especially during the
classical period. In the 1st millennium AD, the
Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
became a major trade zone as
camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
caravans brought goods and people from sub-Saharan Africa. The region also has a small but strategic land connection to the
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, which has also played a key role in its history.
Geography

North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
is a relatively thin strip of land between the
Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
desert and the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, stretching from
Moroccan Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
coast to
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. The region has no set definition, and varies from source to source. Generally included are, from west to east,
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
,
Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
,
Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
,
Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
and
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. The area located at the south of the desert is a
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
, a semi-arid region, called the
Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
. It is the ecoclimatic and
biogeographic zone of
transition in Africa between the Sahara desert to the north and the
Sudanian Savanna to the south. The Sudanian Savanna is a broad belt of
tropical savanna that spans the
African continent, from the Atlantic Ocean coast in the
West Sudanian savanna to the
Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands (also called the Abyssinian Highlands) is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , whil ...
in the
East Sudanian savanna.
Climate
In 15,000 BP, the
West African Monsoon transformed the landscape of
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
and began the
Green Sahara period; greater rainfall during the summer season resulted in the growth of humid conditions (e.g.,
lakes,
wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
) and the savanna (e.g.,
grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominance (ecology), dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other Herbaceo ...
,
shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominance (ecology), dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbaceous plant, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally o ...
) in
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
.
Between 5500 BP and 4000 BP, the Green Sahara period ended.
Prehistory
The earliest known humans lived in
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
around 260,000 BC. Through most of the
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
the
climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
in the region was very different from today, the Sahara being far more moist and
savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
like. Home to
herd
A herd is a social group of certain animals of the same species, either wild or domestic. The form of collective animal behavior associated with this is called '' herding''. These animals are known as gregarious animals.
The term ''herd'' ...
s of large
mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, this area could support a large
hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
population and the
Aterian culture that developed was one of the most advanced
paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
societies.
In the
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
period,
Capsian culture dominated the central part of North Africa with
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
farmers becoming predominant by 6000 BC. Over this period, the Sahara region was steadily drying, creating a barrier between North Africa and the rest of
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
.
In 10,000 BP,
engraved
Engraving is the practice of incising a design on a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an inta ...
and
painted Central
Saharan rock art began to be created, spanning the
Bubaline Period,
Kel Essuf Period,
Round Head Period,
Pastoral Period, Caballine Period, and Cameline Period.
Archaeological evidence has attested that population settlements occurred in Nubia as early as the Late
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
era and from the 5th millennium BC onwards, whereas there is "no or scanty evidence" of human presence in the Egyptian Nile Valley during these periods, which may be due to problems in site preservation.
The
Nile Valley
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
on the eastern edge of North Africa is one of the richest
agricultural
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created f ...
areas in the world. The desiccation of the Sahara is believed to have increased the population density in the Nile Valley and large
cities
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
developed. Eventually,
ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
unified in one of the world's first
civilization
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of state (polity), the state, social stratification, urban area, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyon ...
s.
Bronze and Iron Age
ImageSize = width:800 height:65
PlotArea = width:720 height:40 left:65 bottom:20
AlignBars = justify
Colors =
id:time value:rgb(0.7,0.7,1) #
id:period value:rgb(1,0.7,0.5) #
id:age value:rgb(0.95,0.85,0.5) #
id:era value:rgb(1,0.85,0.5) #
id:eon value:rgb(1,0.85,0.7) #
id:filler value:gray(0.8) # background bar
id:black value:black
Period = from:-3200 till:-600
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:500 start:-3200
ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:100 start:-3200
PlotData =
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:8 mark:(line,black) width:15 shift:(0,-5)
bar:Ancient Egypt color:age
from: -3150 till: -2000 text:Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
bar:Maghreb color:age
from: -2000 till: -800 text:Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
bar:Ancient Egypt color:filler
from: -2000 till: -600 text:Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
bar:Maghreb color:filler
from: -800 till: -600 text:Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
:::''Dates are approximate, consult particular article for details''
::: Bronze Age Iron Age
Classical period

The expanse of the
Libyan Desert
The Libyan Desert (not to be confused with the Libyan Sahara) is a geographical region filling the northeastern Sahara Desert, from eastern Libya to the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert of Egypt and far northwestern Sudan. On medieval m ...
cut Egypt off from the rest of North Africa. Egyptian
boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size or capacity, its shape, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically used on inland waterways s ...
s, while well suited to the Nile, were not usable in the open
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. Moreover, the Egyptian merchant had far more prosperous destinations on
Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
,
Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, and the
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
.
Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
from
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and the
Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
ns from
Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
also settled along the coast of Northern Africa. Both societies drew their prosperity from the sea and from ocean-born trade. They found only limited trading opportunities with the native inhabitants, and instead turned to
colonization
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence.
Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples f ...
. The Greek trade was based mainly in the
Aegean,
Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
,
Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
, and
Red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–750 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a seconda ...
Seas and they only established major cities in
Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, als ...
, directly to the south of Greece. In 332 BC,
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
conquered
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and for the next three centuries it was ruled by the Greek
Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; , ''Ptolemaioi''), also known as the Lagid dynasty (, ''Lagidai''; after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal house which ruled the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Ancient Egypt during the Hellenistic period. ...
.
The
Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
ns developed an even larger presence in North Africa with colonies from
Tripoli to the
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
. One of the most important Phoenician cities was
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, which grew into one of the greatest powers in the region. At the height of its power,
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
controlled the Western Mediterranean and most of North Africa outside of Egypt. However,
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, Carthage's major rival to the north, defeated it in a series of wars known as the
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and ...
, resulting in Carthage's destruction in 146 BC and the annexation of its empire by the Romans. In 30 BC,
Roman Emperor Octavian
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in ...
conquered Egypt, officially annexing it to the Empire and, for the first time, unifying the North African coast under a single ruler.
The Carthaginian power had penetrated deep into the Sahara ensuring the quiescence of the
nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic tribes in the region. The
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
was more confined to the coast, yet routinely expropriated
Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
land for Roman farmers. They thus faced a constant threat from the south. A network of
forts
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from ...
and
walls
Walls may refer to:
*The plural of wall, a structure
* Walls (surname), a list of notable people with the surname
Places
* Walls, Louisiana, United States
* Walls, Mississippi, United States
*Walls, Ontario
Perry is a township (Canada), ...
were established on the southern frontier, eventually securing the region well enough for local
garrison
A garrison is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a military base or fortified military headquarters.
A garrison is usually in a city ...
s to control it without broader Imperial support.
When the Roman Empire began to collapse, North Africa was spared much of the disruption until the
Vandal
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vandal ...
invasion of 429 AD. The Vandals ruled in North Africa until the territories were regained by
Justinian
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
of the Eastern Empire in the 6th century. Egypt was never invaded by the Vandals because there was a thousand-mile buffer of desert and because the Eastern Roman Empire was better defended.
During the rule of the Romans, Vandals, Byzantines, Carthaginians and the Ottomans the Kabyle people managed to maintain their independence. Still, after the Arab conquest of North Africa, the Kabyle people maintained the possession of their mountains.
Arrival of Islam
Arab Conquest
In the 7th century CE, the
inception of Islam facilitated the unification of nomadic Arab tribes by bond of a common faith, preventing their historical internecine fighting along
religious divisions. The main motivation for expansion was to spread Islam and convert pagans, with emphasis on the toleration of people practising other
monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A ...
or
Abrahamic religions
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them wit ...
. Led by ingenious generals, the nascent
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
centred in
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
won a series of crucial victories against the established powers in the Middle East, expanding in all directions, with the
Byzantine's financial and military exhaustion from
previous wars in the region inducing them to evacuate from Syria in 636 CE after only two years of conflict.
With the regional Byzantine presence and power shattered, the Muslim armies turned towards Egypt and by 642 CE had conquered all of Egypt following the
siege of Alexandria, generally facing little resistance by subjects odious of Roman rule. The subsequent rapid
Islamization of Egypt has been attributed to people's dismay at the disruption caused by the
Chalcedonian schism. Marching up the Nile, the Muslims launched a campaign against the
Makurians but were repelled in
battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force co ...
, in a rare defeat owing to skilled Nubian archery and natural defences.
Their attention would then turn west to the Maghreb where the
Exarchate of Africa
The Exarchate of Africa was a division of the Byzantine Empire around Carthage that encompassed its possessions on the Western Mediterranean. Ruled by an exarch (viceroy), it was established by the Emperor Maurice in 591 and survived until t ...
had declared independence from Constantinople under
Gregory the Patrician. The Muslims effortlessly annexed
Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna (), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia, eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (roughly western Libya). It included all of what had previously been the Byzantine province of ...
(modern-day
Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
) and in 647 CE defeated and killed Gregory and his army decisively in
battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force co ...
. Not wishing to annex the territory, they carried out raids across the decapitated state, and the populations, seeing they were at the Muslims' mercy, appealed to the general to pay a substantial tribute which was accepted. The Rashidun armies returned to Egypt and would again invade
Makuria
Makuria ( Old Nubian: , ''Dotawo''; ; ) was a medieval Nubian kingdom in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. Its capital was Dongola (Old Nubian: ') in the fertile Dongola Reach, and the kingdom is sometimes known by the name of ...
in 652 CE only to again be repelled in
battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force co ...
, leading them both
to sign a treaty stipulating peace, which would dictate the relations between Egypt and Nubia for over seven centuries.
Further expansion into North Africa waited another twenty years, due to the
First Fitna
The First Fitna () was the first civil war in the Islamic community. It led to the overthrow of the Rashidun and the establishment of the Umayyad Caliphate. The civil war involved three main battles between the fourth Rashidun caliph, Ali, an ...
, which led to the establishment of the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member o ...
, who moved the capital of the Muslim empire to
Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
, and its rule over the newly-conquered territories. In 670 CE,
Uqba ibn Nafi al-Fihiri invaded what is now
Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
in an attempt to take the region from the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, but was only partially successful. He founded the town of
Kairouan
Kairouan (, ), also spelled El Qayrawān or Kairwan ( , ), is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by the Umayyads around 670, in the period of Caliph Mu'awiya (reigned 661� ...
but was replaced by Abul-Muhajir Dinar in 674 CE. Abul-Muhajir successfully advanced into what is now eastern
Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
incorporating the
Kingdom of Altava
The Kingdom of Altava was an independent Christian Berber kingdom centered on the city of Altava in present-day northern Algeria. The Kingdom of Altava was a successor state of the previous Mauro-Roman Kingdom which had controlled much of the an ...
and
Awraba tribe both ruled by
Kusaila
Kusaila ibn Malzam (), also known as Aksel, was a 7th-century Berber Christian ruler of the kingdom of Altava and leader of the Awraba tribe, a Christianised sedentary Berber tribe of the Aures and possibly Christian king of the Sanhaja. Under ...
into the Islamic sphere of influence.
In 681 CE Uqba was given command of the Arab forces again and advanced westward again in 682 CE, holding Kusaya as a hostage. He advanced to the Atlantic Ocean in the west and penetrated the
Draa River Valley and the Sus region in what is now
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
. However, Kusaila escaped during the campaign and attacked Uqba on his return and killed him near
Biskra
Biskra () is the capital city of Biskra Province, Algeria. In 2007, its population was recorded as 307,987. Biskra is located in northeastern Algeria, about from Algiers, southwest of Batna, Algeria, Batna and north of Touggourt. It is nickna ...
in what is now Algeria. After Uqba's death, the Arab armies retreated from Kairouan, which Kusaila took as his capital. He ruled there until he was defeated by an Arab army under
Zuhair ibn Kays. This caused an epiphany among the Berber that this conflict was not just against the Byzantine's. Zuhair himself was killed in 688 CE while fighting against the Byzantine Empire which had reoccupied Cyrenaica while he was busy in
Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
.
In 693 CE,
Caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan
Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam (; July/August 644 or June/July 647 – 9 October 705) was the fifth Umayyad caliph, ruling from April 685 until his death in October 705. A member of the first generation of born Muslims, his early life in ...
sent an army of 40,000 men, commanded by
Hasan ibn al-Nu'man, into Cyrenaica and
Tripolitania
Tripolitania (), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province of Libya.
The region had been settled since antiquity, first coming to prominence as part of the Carthaginian empire. Following the defeat ...
to remove the Byzantine threat to the Umayyads advance in North Africa. They met no resistance until they reached Tunisia where they captured
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
and defeated the Byzantines and
Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
around
Bizerte
Bizerte (, ) is the capital and largest city of Bizerte Governorate in northern Tunisia. It is the List of northernmost items, northernmost city in Africa, located north of the capital Tunis. It is also known as the last town to remain under Fr ...
.
Soon afterwards,
al-Nu'man's forces came into conflict with the
Kingdom of the Aures and
Jrāwa tribe both under the leadership of their queen,
Al-Kahina. The Berbers defeated al-Nu'man in two engagements, the first on the river
Nini and the second near
Gabis, upon which al-Nu'man's forces retreated to Cyrenaica to wait for reinforcements. For five years this secured for Kahina the position of the uncontested ruler of the Maghreb until Arab reinforcements arrived in 703 CE and al-Nu'man advanced into what is now Tunisia, again meeting Al-Kahina near Gabis. This time he was successful and Al-Kahina retreated to Tubna where her forces were defeated and she was killed.
Al-Nu'man next recaptured
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
from the Byzantines, who had retaken it when he retreated from Tunisia. He founded the city of
Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casabl ...
nearby and used it as the base for the
Ummayad
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member o ...
navy in the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. The Byzantines were forced to abandon the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
and retreat to the islands of the Mediterranean Sea. However, in 705 CE he was replaced by
Musa bin Nusair, a protégé of then governor of Egypt, Abdul-Aziz ibn Marwan. Nusair attacked what is now
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, captured
Tangier
Tangier ( ; , , ) is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The city is the capital city, capital of the Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima region, as well as the Tangier-Assilah Prefecture of Moroc ...
, and advanced to the
Sus river and the
Tafilalt
Tafilalt or Tafilet (), historically Sijilmasa, is a region of Morocco, centered on its largest oasis.
Etymology
There are many speculations regarding the origin of the word "Tafilalt", however it is known that Tafilalt is a Berber word meaning ...
oasis in a three-year campaign.
Kharijite Berber Rebellion
Abbasid rule and local dynasties
The Umayyads were overthrown in the east by the
Abbasid Revolution, which replaced it with the
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
. The Abbasids imposed their authority on Egypt and central North Africa as far west as Ifriqiya, but the regions further west of here remained beyond their control. These western regions were ruled by the local Berber tribes or other local dynasties, often adhering to either
Sufri
The Sufris ( ''aṣ-Ṣufriyya'') were Khariji Muslims in the seventh and eighth centuries. They established the Midrarid state at Sijilmassa, now in Morocco.
In Tlemcen, Algeria, the Banu Ifran were Sufri Berbers who opposed rule by the Uma ...
or
Ibadi
Ibadism (, ) is a school of Islam concentrated in Oman established from within the Kharijites. The followers of the Ibadi sect are known as the Ibadis or, as they call themselves, The People of Truth and Integrity ().
Ibadism emerged around 6 ...
Kharijism.
Rustamids
Banu Midrar
Idrisids
Aghlabids
Tulunids and Ikhshidids in Egypt
Fatimids
The Fatimid Caliphate was established by
Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i
Abu Abdallah al-Husayn ibn Ahmad ibn Muhammad ibn Zakariyya, better known as Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i (), was an Isma'ili missionary (''da'i, dāʿī'') active in Yemen and North Africa. He was successful in converting and unifying a large part of th ...
with the help
Kutama
The Kutama (Berber: ''Ikutamen''; ) were a Berber tribe in northern Algeria classified among the Berber confederation of the Bavares. The Kutama are attested much earlier, in the form ''Koidamousii'' by the Greek geographer Ptolemy.
The Kutama p ...
Berbers from
Little Kabylia after they conquered Ifriqiya from the Aghlabids.
In 909
Abdallah al-Mahdi was enthroned as the first Fatimid Caliph in Ifriqiya. They went on to extend direct control or suzerainty over Egypt, varying extents of the Maghreb, Sicily, the Levant, and the
Hijaz. In 969 the Fatimid army
conquered Egypt and in 973 the Fatimid court was reinstalled in the new capital of
Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
, while government of the Maghreb was entrusted to the
Zirids
The Zirid dynasty (), Banu Ziri (), was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from what is now Algeria which ruled the central Maghreb from 972 to 1014 and Ifriqiya (eastern Maghreb) from 972 to 1148.
Descendants of Ziri ibn Manad, a military leader of th ...
. After a long period of decline, the Fatimid Caliphate was eventually abolished by
Salah ad-Din in 1171 and replaced in Egypt by the
Ayyubid dynasty
The Ayyubid dynasty (), also known as the Ayyubid Sultanate, was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egyp ...
.
Muslim Berber Empires
Zirids
The Zirid Dynasty was a family of
Sanhaja
The Sanhaja (, or زناگة ''Znāga''; , pl. Iẓnagen, and also Aẓnaj, pl. Iẓnajen) were once one of the largest Berbers, Berber tribal confederations, along with the Zenata, Zanata and Masmuda confederations. Many tribes in Algeria, Libya ...
Berbers that were originally from the Kabyle mountains. Initially on behalf of the Fatimids, they ruled the eastern and central Maghreb but encountered more resistance to the west from local
Zenata
The Zenata (; ) are a group of Berber tribes, historically one of the largest Berber confederations along with the Sanhaja and Masmuda. Their lifestyle was either nomadic or semi-nomadic.
Society
The 14th-century historiographer Ibn Khaldun repo ...
factions and the
Umayyads of Cordoba.
Sometime between 1041 and 1051 they renounced the suzerainty of the Fatimid caliphs in Cairo. The Fatimid retaliation came in the form of the invasions of the
Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal () was a confederation of Arab tribes from the Najd region of the central Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa in the 11th century. They ruled the Najd, and campaigned in the borderlands between I ...
and
Banu Sulaym
The Banu Sulaym () is an Arab tribe that dominated part of the Hejaz in the pre-Islamic era. They maintained close ties with the Quraysh of Mecca and the inhabitants of Medina, and fought in a number of battles against the Islamic prophet Muha ...
into the Maghreb.
Hammadids
The Hammadids came to power after declaring their independence from the Zirids in 1015.
They managed to conquer land in all of the Maghreb region, capturing and possessing significant territories such as: Algiers, Bougie, Tripoli, Sfax, Susa, Fez, Ouargla and Sijilmasa. South of Tunisia, they also possessed a number of oasis that were the termini of trans-Saharan trade routes.
The Hilalian invasions
Almoravids
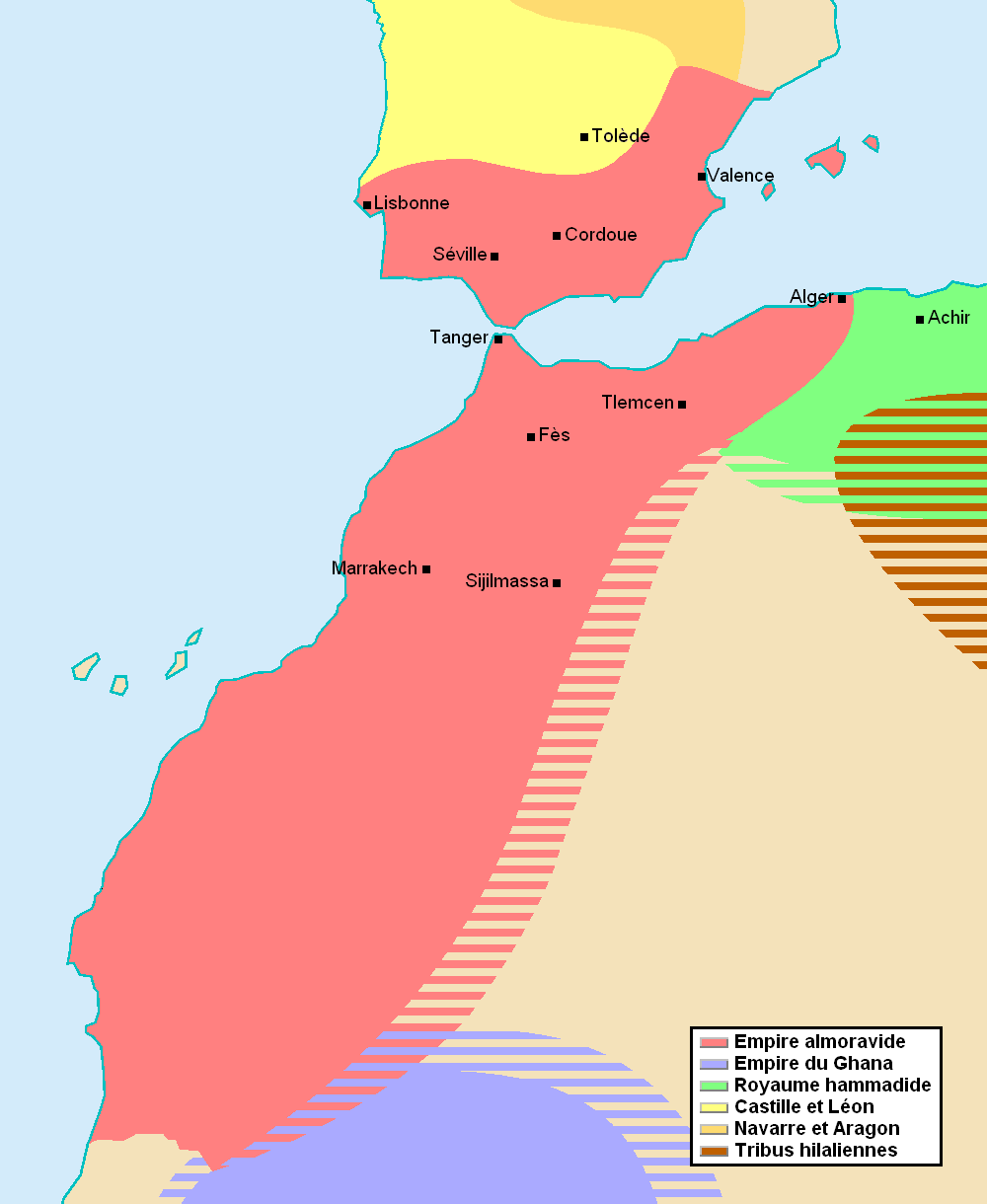
In the 11th century, Berbers of the Sahara began a
jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God ...
to reform Islam in North Africa to impose what they saw as a more rigorously orthodox
Maliki
The Maliki school or Malikism is one of the four major madhhab, schools of Islamic jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. It was founded by Malik ibn Anas () in the 8th century. In contrast to the Ahl al-Hadith and Ahl al-Ra'y schools of thought, the ...
version of Islam. They were initially inspired by the teachings of
Ibn Yasin and nominally recognized the suzerainty of the Abbasid Caliphs.
This movement created an empire which, at its greatest extent, encompassed
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
(southern and eastern
Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
at the time) and roughly all of present-day Morocco and
Western Sahara
Western Sahara is a territorial dispute, disputed territory in Maghreb, North-western Africa. It has a surface area of . Approximately 30% of the territory () is controlled by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR); the remaining 70% is ...
.
This movement seems to have assisted the southern penetration of Africa, one that was continued by later groups. In addition, the Almoravids are traditionally believed to have attacked and brought about the destruction of the
West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
n
Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire (), also known as simply Ghana, Ghanata, or Wagadu, was an ancient western-Sahelian empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali.
It is uncertain among historians when Ghana's ruling dynasty began. T ...
. However, this interpretation has been questioned. Conrad and Fisher (1982) argued that the notion of any Almoravid military conquest at its core is merely perpetuated folklore, derived from a misinterpretation or naive reliance on Arabic sources while Dierke Lange agrees but argues that this doesn't preclude Almoravid political agitation, claiming that Ghana's demise owed much to the latter.
Almohads
The Almohads were another religious and political movement that arose among the Berbers of the western Maghreb during the 12th century. They promoted a new fundamentalist and unorthodox/reformist version of Islam which recognized
Ibn Tumart
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad Ibn Tūmart (, ca. 1080–1130) was a Muslim religion, religious scholar, teacher and political leader, from the Sous in southern present-day Morocco. He founded and served as the spiritual and first military leader ...
as a messianic figure, the ''
Mahdi
The Mahdi () is a figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the Eschatology, End of Times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad, and will appear shortly before Jesu ...
''.
After Ibn Tumart's death, the movement's political leadership passed on to '
Abd al-Mu'min
Abd al-Mu'min (c. 1094–1163) (; full name: ʿAbd al-Muʾmin ibn ʿAlī ibn ʿAlwī ibn Yaʿlā al-Kūmī Abū Muḥammad) was a prominent member of the Almohad movement. Although the Almohad movement itself was founded by Ibn Tumart, Abd al-Mu' ...
, who overthrew the Almoravids and conquered the entire Maghreb and the remaining territories of Al-Andalus. Their empire disintegrated in the 13th century and was succeeded by three major states in North Africa: the
Marinids in the western Maghreb, the
Zayyanids in the central Maghreb, and the
Hafsids
The Hafsid dynasty ( ) was a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Berber descentC. Magbaily Fyle, ''Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa'', (University Press of America, 1999), 84. that ruled Ifriqiya (modern day Tunisia, w ...
in the eastern Maghreb (Ifriqiya).
The Banu Ghaniya invasions
1184-1187 phase
In November 1184, the governor of
Mallorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest of the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, seventh largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.
The capital of the island, Palma, Majorca, Palma, i ...
and
Almoravid pretender Ali Ibn Ishaq invaded Almohad-Tunisia.The Tunisia campaign would be the last major accomplishment of his life, scoring many military victories against
Yaqub al-Mansur, among them,
Constantine, Algiers
Algiers is the capital city of Algeria as well as the capital of the Algiers Province; it extends over many Communes of Algeria, communes without having its own separate governing body. With 2,988,145 residents in 2008Census 14 April 2008: Offi ...
, and Beija were seized. Ishaq's eventual death in 1187 led to the Almohads reoccupying Tunisia the following year.
The situation engendered to the Caliph by Banu invasion was twofold:Yaqub al- Mansur was involved militarily in Al-Andalus consistently throughout his reign, seeking to avenge his father
Abu Yaqub Yusuf
Abu Ya‘qub Yusuf or Yusuf I ( ''Abū Ya‘qūb Yūsuf''; 1135 – 14 October 1184) was the second Almohad ''Amir'' or caliph. He reigned from 1163 until 1184 in Marrakesh. He was responsible for the construction of the Giralda in Seville, whi ...
, murdered by
Afonso I of Portugal
Dom Afonso IOr also ''Affonso'' (Archaic Portuguese-Galician) or ''Alphonso'' (Portuguese-Galician languages, Portuguese-Galician) or ''Alphonsus'' (Latin version), sometimes rendered in English as ''Alphonzo'' or ''Alphonse'', depending on th ...
. This gifted Caliph Yaqub Mansur a
two front war which consumed his entire rule. After the empire restored in Tunisia, deeming the threat neutralized, Yaqub Mansur launched two campaigns in Portugal in 1190 and 1191.

1203-1237 phase
In 1203, Abdallah Ibn Ishaq toppled the governor of
Mallorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest of the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, seventh largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.
The capital of the island, Palma, Majorca, Palma, i ...
, Tashfin, who was an installed Almohad puppet. Fueled by the quelling of Almohad control in Mallorca, the Banu once again invaded Tunisia.
Abdallah Ishaq's army harassed the caliph with raids and skirmishes, and key cities like Algiers and Constantine again fell. Under Yahya Ibn Ishaq, Banu forces reached as far as
Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, als ...
. They weren't driven out, tediously to the Caliphs, till 1226. Ishaq reoccupied Tunisia and much of the Maghreb for a third time in 1238 with little to no struggle. The financial and resource-strain placed on the Almohad Empire from the Banu conflict, accompanied by Iberian endeavors, to be a contributing factor to the Empire's decline.The Almohade Empire dissolved in 1269.
Marinids
Hafsids
The Hafsids were a Masmuda Berber dynasty ruling Ifriqiya (modern Tunisia) from 1229 to 1574. Their territories stretched from east of modern Algeria to west of modern Libya during their zenith.
The dynasty was named after Muhammad bin Abu Hafs, a Berber from the Masmuda tribe of Morocco. He was appointed governor of Ifriqiya (present day Tunisia) by Muhammad an-Nasir, Caliph of the Almohad empire between 1198 and 1213. The Banu Hafs were a powerful group amongst the Almohads; their ancestor was Omar Abu Hafs al-Hentati, a member of the council of ten and a close companion of Ibn Tumart. His original name was "Fesga Oumzal", which later changed to "Abu Hafs Omar ibn Yahya al-Hentati" (also known as "Omar Inti") since it was a tradition of Ibn Tumart to rename his close companions once they had adhered to his religious teachings.
The Hafsids as governors on behalf of the Almohads faced constant threats from Banu Ghaniya who were descendants of Almoravid princes which the Almohads had defeated and replaced as a ruling dynasty.
Hafsids were Ifriqiya governors of Almohads until 1229, when they declared independence. After the split of the Hafsids from the Almohads under Abu Zakariya (1229–1249), Abu Zakariya organised the administration in Ifriqiya (the Roman province of Africa in modern Maghreb; today's Tunisia, eastern Algeria and western Libya) and built Tunis up as the economic and cultural centre of the empire. At the same time, many Muslims from
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
fleeing the Spanish Reconquista of Castile, Aragon, and Portugal were absorbed. He also conquered
Tlemcen
Tlemcen (; ) is the second-largest city in northwestern Algeria after Oran and is the capital of Tlemcen Province. The city has developed leather, carpet, and textile industries, which it exports through the port of Rachgoun. It had a population of ...
in 1242 and took Abdalwadids as his vassal. His successor Muhammad I al-Mustansir (1249–1277) took the title of Caliph.
In the 14th century the empire underwent a temporary decline. Although the Hafsids succeeded for a time in subjugating the
Kingdom of Tlemcen
The Kingdom of Tlemcen or Zayyanid Kingdom of Tlemcen () was a kingdom ruled by the Berber Zayyanid dynasty in what is now the northwest of Algeria. Its territory stretched from Tlemcen to the Chelif bend and Algiers, and at its zenith reached ...
of the
Abdalwadids, between 1347 and 1357 they were twice conquered by the
Merinids of Morocco. The Abdalwadids however could not defeat the Bedouin; ultimately, the Hafsids were able to regain their empire. During the same period plague epidemics caused a considerable fall in population, further weakening the empire.
Under the Hafsids, commerce with Christian Europe grew significantly, however piracy against Christian shipping grew as well, particularly during the rule of Abd al-Aziz II (1394–1434). The profits were used for a great building programme and to support art and culture. However, piracy also provoked retaliation from Aragon and Venice, which several times attacked Tunisian coastal cities. Under Utman (1435–1488) the Hafsids reached their zenith, as the caravan trade through the Sahara and with Egypt was developed, as well as sea trade with Venice and Aragon. The Bedouins and the cities of the empire became largely independent, leaving the Hafsids in control of only Tunis and Constantine.
In the 16th century the Hafsids became increasingly caught up in the power struggle between Spain and the Ottoman Empire-supported Corsairs. Ottomans conquered Tunis in 1534 and held one year. Due to Ottoman threat, Hafsids were vassal of Spain after 1535. Ottomans again conquered Tunis in 1569 and held it for 4 years. Don Juan of Austria recaptured it in 1573. The latter conquered Tunis in 1574 and the Hafsids accepted becoming a Spanish vassal state to offset the Ottoman threat. Muhammad IV, the last Caliph of the Hafsids was brought to Constantinople and was subsequently executed due to his collaboration with Spain and the desire of the Ottoman Sultan to take the title of Caliph as he now controlled Mecca and Medina. The Hafsid lineage survived the Ottoman massacre by a branch of the family being taken to the Canary Island of Tenerife by the Spanish.
Zayyanids
Wattasids
Ottoman rule
After the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, Northern Africa was loosely under the control of the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, except for the
Kabyle people and Moroccan region ruled by
Saadi Sultanate
The Saadi Sultanate (), also known as the Sharifian Sultanate (), was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of Northwest Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arab Sharifian dynasty.
The dyna ...
. Ottoman rule was centered on the cities of Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli.
European colonial period
During the 18th and 19th century, North Africa was
colonized
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence.
Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples f ...
by
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
,
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
and
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
. During the 1950s and 1960s, and into the 1970s, all of the North African states gained independence from their colonial European rulers, except for a few small Spanish colonies on the far northern tip of
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, and parts of the Sahara region, which went from Spanish to Moroccan rule.
In modern times the
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
in
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
(constructed in 1869) has caused a great deal of controversy. The
Convention of Constantinople
The Convention of Constantinople is a treaty concerning the use of the Suez Canal in Egypt. It was signed on 29 October 1888 by the United Kingdom, the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, Spain, France, Italy, the Netherlands, the Russian Empire and ...
in 1888 declared the canal a neutral zone under the protection of the British, after British troops had moved in to protect it in 1882. Under the
Anglo-Egyptian Treaty of 1936, the United Kingdom insisted on retaining control over the canal. In 1951 Egypt repudiated the treaty, and by 1954 Great Britain had agreed to pull out.
After the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
withdrew their pledge to support the construction of the
Aswan Dam
The Aswan Dam, or Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. When it was completed, it was the tallest earthen dam in the world, surpassing the Chatuge D ...
, President
Gamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein (15 January 1918 – 28 September 1970) was an Egyptian military officer and revolutionary who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 a ...
nationalized the canal, which led Britain,
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and
Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
to invade in the week-long
Suez War. As a result of damage and sunken ships, the canal was closed until April 1957, after it had been cleaned up with
UN assistance. A United Nations force (UNEF) was established to maintain the neutrality of the canal and the
Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Afri ...
.
Europe and the Maghreb
In the 1960's, the
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organisation created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisbo ...
(later becoming the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
), developed an economic and sociopolitical relationship with the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
states. The treaty of Rome demonstrated this by inviting Morocco and Tunisia to create an agreement between these countries and the EEC. This cemented Maghreb nations trading with Europe and the EEC to overall influence their growth. Trading between Europe and Maghreb gradually increased, leading to the creation of the
Global Mediterranean Policy, in 1972. This policy lasted until 1992. However, there was little financial benefit that this policy created for both parties.
Complications
The growth of the EEC called for more restrictive measures for trading with Maghreb due to security concerns. European strife also contributed to lack of trading between regions, with the
Berlin wall
The Berlin Wall (, ) was a guarded concrete Separation barrier, barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and the East Germany, German Democratic Republic (GDR; East Germany). Construction of the B ...
falling and overall a necessity to draw their focus away from Maghreb. Maghreb had to deal with their own internal conflicts as well, as the 2nd Gulf War in 1991 caused sociopolitical turmoil without the states. While trading still occurs between these two parties, the Global Mediterranean policy was viewed as an overall disappointment.
Post-colonial period
In
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
from 1940 to 1943 the area was the setting for the
North African Campaign
The North African campaign of World War II took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943, fought between the Allies and the Axis Powers. It included campaigns in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts (Western Desert campaign, Desert Wa ...
. During the 1950s and 1960s, all of the North African states gained independence. There remains a dispute over
Western Sahara
Western Sahara is a territorial dispute, disputed territory in Maghreb, North-western Africa. It has a surface area of . Approximately 30% of the territory () is controlled by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR); the remaining 70% is ...
between
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and the
Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
n-backed
Polisario Front
The Popular Front for the Liberation of Saguia el-Hamra and Río de Oro (Spanish language, Spanish: ; ), better known by its acronym Polisario Front, is a Sahrawi nationalism, Sahrawi nationalist liberation movement seeking to end the occupatio ...
.

The wider protest movement known as the
Arab Spring
The Arab Spring () was a series of Nonviolent resistance, anti-government protests, Rebellion, uprisings, and Insurgency, armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began Tunisian revolution, in Tunisia ...
began with revolutions in
Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
and
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
which ultimately led to the overthrow of their governments, as well as
civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
in Libya. Large protests also occurred in Algeria and Morocco to a lesser extent. Many hundreds died in the uprisings.
History of North African Architecture
''Further information in the sections of
Architecture of Africa:''
*
Prehistoric North African Architecture
*
Ancient North African Architecture
*
Medieval North African Architecture
History of science and technology in North Africa
''Further information in the sections of
History of science and technology in Africa:''
*
Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
*
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
*
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
*
Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
*
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
*
Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
*
Textiles
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
*
Maritime technology
*
Architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
*
Communication systems
A communications system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Commun ...
*
Warfare
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
*
Commerce
Commerce is the organized Complex system, system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered large-scale exchange (distribution through Financial transaction, transactiona ...
*
By country
This is a series of lists by country. The lists generally cover topics related to sovereign countries; however, states with limited recognition are also included.
Topical country articles Main articles
#
* Administrative divisions
* Politics
Ot ...
Military history of Northern Africa
Genetic history of North Africa
Archaic Human DNA
While
Denisovan
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins ( ) are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic, and lived, based on current evidence, from 285 thousand to 25 thousand years ago. D ...
and
Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
ancestry in non-Africans outside of Africa are more certain,
archaic human
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called ...
ancestry in Africans is less certain and is too early to be established with certainty.
Ancient DNA
Egypt
Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( , ; "Amun is satisfied"), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great and Hellenization, Hellenized as Amenophis III, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. According to d ...
,
Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton ( ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning 'Effective for the Aten'), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eig ...
, and
Tutankhamen carried
haplogroup R1b.
,
Tiye
Tiye (c. 1398 BC – 1338 BC, also spelled Tye, Taia, Tiy and Tiyi) was the Great Royal Wife of the Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep III, mother of pharaoh Akhenaten and grandmother of pharaoh Tutankhamun; her parents were Yuya and Thuya. In 2010 ...
, Tutankhamen's mother, and Tutankhamen carried
haplogroup K.
Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. Some scholars date his reign from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC, and he is considered the last pharaoh of the New K ...
and Unknown Man E, possibly
Pentawere, carried
haplogroup E1b1a.
,
Khnum-Nakht, and
Nakht-Ankh carried
haplogroup M1a1.
Libya
At Takarkori rockshelter, in
Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
, two naturally
mummified women, dated to the
Middle Pastoral Period (7000 BP), carried
basal haplogroup N.
Morocco
The
Taforalts of
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, who were found to be 63.5%
Natufian
The Natufian culture ( ) is an archaeological culture of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East in West Asia from 15–11,500 Before Present. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentism, sedentary or semi-sedentary population even befor ...
, were also found to be 36.5%
Sub-Saharan African
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
(e.g.,
Hadza), which is drawn out, most of all, by West Africans (e.g., Yoruba,
Mende).
In addition to having similarity with the remnant of a more
basal Sub-Saharan African lineage (e.g., a
basal West African lineage shared between Yoruba and Mende peoples), the Sub-Saharan African DNA in the Taforalt people of the
Iberomaurusian culture may be best represented by modern West Africans (e.g.,
Yoruba).
Y-Chromosomal DNA
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial haplogroups L3, M, and N are found among
Sudanese peoples (e.g.,
Beja,
Nilotics,
Nuba
The Nuba people are indigenous inhabitants of southern Sudan. The Nuba are made up of 50 various indigenous ethnic groups who inhabit the Nuba Mountains of South Kordofan, South Kordofan state in Sudan, encompassing multiple distinct people that ...
,
Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are a Nilo-Saharan speaking ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of th ...
), who have no known interaction (e.g., history of migration/admixture) with Europeans or Asians; rather than having developed in a post-Out-of-Africa migration context, mitochondrial macrohaplogroup L3/M/N and its subsequent development into distinct mitochondrial haplogroups (e.g.,
Haplogroup L3,
Haplogroup M,
Haplogroup N) may have occurred in
East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
at a time that considerably predates the Out-of-Africa migration event of 50,000 BP.
Autosomal DNA
Medical DNA
Lactase Persistence
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
agriculturalists, who may have resided in
Northeast Africa
Northeast Africa, or Northeastern Africa, or Northern East Africa as it was known in the past, encompasses the countries of Africa situated in and around the Red Sea. The region is intermediate between North Africa and East Africa, and encompasses ...
and the
Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
, may have been the source population for
lactase persistence
Lactase persistence or lactose tolerance is the continued activity of the lactase enzyme in adulthood, allowing the digestion of lactose in milk. In most mammals, the activity of the enzyme is dramatically reduced after weaning. In some human pop ...
variants, including –13910*T, and may have been subsequently supplanted by later migrations of peoples.
The
Sub-Saharan West African
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Ma ...
Fulani, the
North African Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ...
, and
European agriculturalists, who are descendants of these Neolithic agriculturalists, share the lactase persistence variant –13910*T.
While shared by Fulani and Tuareg herders, compared to the Tuareg variant, the Fulani variant of –13910*T has undergone a longer period of haplotype differentiation.
The
Fulani lactase persistence variant –13910*T may have spread, along with cattle
pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The anim ...
, between 9686 BP and 7534 BP, possibly around 8500 BP; corroborating this timeframe for the Fulani, by at least 7500 BP, there is evidence of herders engaging in the act of
milking
Milking is the act of removing milk from the mammary glands of cattle, water buffalo, humans, goats, sheep, and, more rarely, camels, horses, and donkeys. Milking may be done by hand or by machine, and requires the animal to be currently or rec ...
in the Central
Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
.
List of archaeological cultures and sites
*
Abadiyeh, Egypt
*
Aboccis
*
Abu Ballas
*
Abu Madi
*
Abu Mena
Abu Mena (also spelled ''Abu Menes, Mina;'' ; ) was a town, monastery complex and Christianity, Christian pilgrimage centre in Late Antiquity, Late Antique Egypt, about southwest of Alexandria, near New Borg El Arab city. Its remains were ...
*
Abu Nafisa fort
*
Abu Simbel
Abu Simbel is a historic site comprising two massive Rock-cut architecture, rock-cut Egyptian temple, temples in the village of Abu Simbel (village), Abu Simbel (), Aswan Governorate, Upper Egypt, near the border with Sudan. It is located on t ...
*
Abydos, Egypt
Abydos ( or ; Sahidic ') is one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt, and also of the Ta-wer, eighth Nome (Egypt), nome in Upper Egypt. It is located about west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of El Araba ...
*
Ad Turres (Byzacena)
*
Aeliae
*
Affad 23
*
Agilkia Island
*
A-Group culture
The A-Group was the first powerful society in Nubia, located in modern northern Sudan and southern Egypt and flourished between the First and Second Cataracts of the Nile in Lower Nubia. It lasted from the 4th millennium BC, reached its clima ...
*
Ahl al Oughlam
*
Aïn Doura Baths
*
Ain Farah
*
Ain Sokhna
*
Aïn Turk, Bouïra
*
Aït Benhaddou
Aït Benhaddou () is a historic ksar, ''ighrem'' or ''ksar'' (fortified village) along the former Caravan (travellers), caravan route between the Sahara and Marrakesh in Morocco. It is considered a great example of Moroccan architecture, Moroccan ...
*
Akhmim
Akhmim (, ; Akhmimic , ; Sahidic/Bohairic ) is a city in the Sohag Governorate of Upper Egypt. Referred to by the ancient Greeks as Khemmis or Chemmis () and Panopolis (), it is located on the east bank of the Nile, to the northeast of Sohag.
...
*
Akoris, Egypt
*
Al Amarat (Khartoum)
*
Al-Azhar Park
*
Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
*
Al-Meragh
*
Almorada (Omdurman)
*
Altava
Altava was an ancient Romano-Berber city in present-day Algeria. It served as the capital of the ancient Berber Kingdom of Altava. During the French presence, the town was called ''Lamoriciere''. It was situated in the modern Ouled Mimoun near Tl ...
*
Amara, Nubia
*
Amratian culture
*
Ancient Carthage
Ancient Carthage ( ; , ) was an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic civilisation based in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state, and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians ...
*
Ancient Cotta
*
Aniba (Nubia)
*
Anthylla
*
Antinoöpolis
Antinoöpolis (also Antinoopolis, Antinoë, Antinopolis; ; ''Antinow''; , modern , modern ''Sheikh 'Ibada'' or ''Sheik Abāda'') was a city founded at an older Egyptian village by the Roman emperor Hadrian to commemorate his deified young belov ...
*
Apollonia (Cyrenaica)
Apollonia () in Cyrenaica (modern Libya) was founded by Greek colonists and became a significant commercial centre in the southern Mediterranean. It served as the harbour of Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene, to the southwest.
Apollonia became autonom ...
*
Aptuca
*
Aquae in Byzacena
The Diocese of Aquensis in Byzacena is a home suppressed and titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.
The diocese was centered on Aquensis a civitas of the Roman province of Byzacena, which is tentatively identified with El Hamma in modern Tun ...
*
Aquae Regiae
*
Aquae Sirenses
*
Armant, Egypt
*
Arsennaria
*
Askut
*
Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of the Nile at the first cataract. The modern city ha ...
*
Aten (city)
*
Aterian
*
Athribis (Upper Egypt)
*
Ausafa
*
Autenti
*
Auzegera
*
Auzia
*
Avaris
Avaris (Egyptian: ḥw.t wꜥr.t, sometimes ''hut-waret''; ; ; ) was the Hyksos capital of Egypt located at the modern site of Tell el-Dab'a in the northeastern region of the Nile Delta. As the main course of the Nile migrated eastward, its po ...
*
Badarian culture
*
Bagai
*
Baliana
*
Ballana
*
Banganarti
*
Bant (Omdurman)
*
Bapara, Mauritania
*
Basa, Sudan
*
Basra, Morocco
*
Batn-El-Hajar
*
Bawit
*
Behbeit El Hagar
*
Benepota
*
Benghazi
Benghazi () () is the List of cities in Libya, second-most-populous city in Libya as well as the largest city in Cyrenaica, with an estimated population of 859,000 in 2023. Located on the Gulf of Sidra in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, Ben ...
*
Beni Hammad Fort
*
Beni Otsmane
*
Beni-Derraj
*
Bennefa
*
Berenice Troglodytica
Berenice Troglodytica, also called Berenike (Greek language, Greek: ) or Baranis, is an ancient seaport of Egypt on the western shore of the Red Sea. It is situated about 825 km south of Suez, 260 km east of Aswan in Upper Egypt and 140 ...
*
B-Group
*
Bigeh
*
Bir el Ater
*
Bir Kiseiba
*
Bir-Abdallah
*
Bordj-Bou-Djadi
*
Borj Gourbata
*
Botriana
*
Bou-Hedma National Park
*
Boumedfaâ
*
Bubastis
Bubastis ( Bohairic Coptic: ''Poubasti''; Greek: ''Boubastis'' or ''Boubastos''), also known in Arabic as Tell-Basta or in Egyptian as Per-Bast, was an ancient Egyptian city. Bubastis is often identified with the biblical ''Pi-Beseth'' ( ''p ...
*
Buhen
Buhen, alternatively known as Βοὥν (Bohón) in Ancient Greek, stands as a significant ancient Egyptian settlement on the western bank of the Nile, just below the Second Cataract in present-day Northern State, Sudan. Its origins trace back t ...
*
Butana Group
*
Buto
Buto (, , ''Butu''), Bouto, Butus (, ''Boutos'')Herodotus ii. 59, 63, 155. or Butosus was a city that the Ancient Egyptians called Per-Wadjet. It was located 95 km east of Alexandria in the Nile Delta of Egypt. What in classical times the ...
*
Cabarsussi
Cabarsussi was an ancient civitas (municipality) and bishopric in the Roman province of Byzacena (Roman North Africa), that is tentatively identifiable with ruins at Drâa-Bellouan in modern Tunisia. The current bishop is Terence Robert Curtin, a ...
*
Calama (Numidia)
*
Canopus, Egypt
Canopus ( , , ; , ), also known as Canobus (, ), was an ancient Egyptian coastal town, located in the Nile Delta. Its site is in the eastern outskirts of modern-day Alexandria, around from the center of that city. Canopus was located on the wes ...
*
Capsian culture
*
Carcabia
*
Cardium pottery
Cardium pottery or Cardial ware is a Neolithic decorative style that gets its name from the imprinting of the clay with the heart-shaped shell of the '' Corculum cardissa'', a member of the cockle family Cardiidae. These forms of pottery are ...
*
Cartennae
Cartennae or Cartenna.. was an ancient Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian and Roman Empire, Roman port at present-day Ténès, Algeria. Under the Romans, it was part of the Roman province, province of Mauretania Caesariensis.
Name
Cartenna's nam ...
*
Carthage (archaeological site)
*
Castellum Dimmidi
*
Castellum Medianum
*
Castellum Ripae
*
Castellum Tatroportus
*
Castellum Tingitii
Chlef () is the capital city, capital of Chlef Province, Algeria. Located in the north of Algeria, west of the capital, Algiers, it was founded in 1843, as Orléansville, on the ruins of Ancient Rome, Roman ''Castellum Tingitanum''. In 1962, it w ...
*
Catabum Castra
*
Catacombs of Kom El Shoqafa
*
Cave of Archers
*
Cave of Beasts
*
Cave of Swimmers
The Cave of Swimmers is a rock shelter with ancient rock art in the mountainous Gilf Kebir plateau of the Libyan Desert section of the Sahara Desert. It is located in the New Valley Governorate of southwest Egypt, near the border with Libya.
M ...
*
Cebarades
*
Cemetery GIS
*
Centenaria, Algeria
Centenaria was an ancient ''civitas'' (town) extant during the Roman Empire. It is tentatively identified as ruins near El Hamel Algeria. The name Centenaria derives from the Centenaria style of fortified farm, around 2000 of which were built alon ...
*
Central Field, Giza
*
Centuria (Numidia)
*
C-Group culture
The C-Group culture is an archaeological culture found in Lower Nubia, which dates from 2400 BCE to 1550 BCE. It was named by George A. Reisner. With no central site and no written evidence about what these people called themselves, Reisner ...
*
Chemtou
*
Cherchell
Cherchell () is a town on Algeria's Mediterranean coast, west of Algiers. It is the seat of Cherchell District in Tipaza Province. Under the names Iol and Caesarea, it was formerly a Roman colony and the capital of the kingdoms of Numidia ...
*
Chusira
*
Cirta
Cirta, also known by #Names, various other names in classical antiquity, antiquity, was the ancient Berbers, Berber, Punic people, Punic and Roman Empire, Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria, Constantine, Algeria.
Cirta was ...
*
Civitas Popthensis
*
Cohors Breucorum
*
Contra Latopolis
*
Crepedula
*
Cufruta
*
Culusi
*
Cusae
Cusae (; ) was a city in Upper Egypt. Its Ancient Egyptian name was ''qjs'' (variant ''qsy''), conventionally rendered Qis or Kis, with many further transliterations such as Qosia. Today, the town is known as El Quseyya, and is located on the w ...
*
Cynopolis
*
Cyrene, Libya
Cyrene, also sometimes anglicization of names, anglicized as Kyrene, was an ancient Greeks, ancient Greek Greek colonization, colony and ancient Romans, Roman Cities of the Roman Empire, city near present-day Shahhat in northeastern Libya in Nor ...
*
Dabenarti
*
Dahshur
DahshurAlso transliterated ''Dahshour'' (in English often called ''Dashur''; ' ) is an ancient Egyptian pyramid complex and necropolis and shares the name of the nearby village of Manshiyyat Dahshur () in markaz Badrashin, Giza Governorate, Giza ...
*
Debeira
*
Dederiyeh Cave
*
Deir el-Ballas
*
Dendera Temple complex
The Dendera Temple complex (Ancient Egyptian: ''Iunet'' or ''Tantere''; the 19th-century English spelling in most sources, including Belzoni, was Tentyra; also spelled Denderah) is located about south-east of Dendera, Egypt. It is one of the be ...
*
Diana Veteranorum
*
Diocese of Dices
*
Diocese of Sesta
*
Diocese of Thucca Terenbenthina
*
Dionysiana
*
Djémila
*
Douela
*
Drâa-Bellouan
Drâa-Bellouan is a town in modern Tunisia.
Drâa-Bellouan was known during the Roman Empire as Cabarsussi a civitas of the Roman province of Byzacena
Byzacena (or Byzacium) (, ''Byzakion'') was a Late Roman province in the central part of Roma ...
*
Dzemda
*
Edfu-Project
*
Edistiana
*
Egnatia, Byzacena
*
El Brij, Tunisia
*
El Gour, Morocco
*
El Harrouch
*
El Hawawish
El Hawawish () is the ancient necropolis (cemetery) for the city of Akhmim in the 9th Nome of Upper Egypt (UE09), in modern the Sohag Governorate, Egypt.
History
Old Kingdom and First Intermediate Period
The local deity of El Hawawish ...
*
El Hiba
*
El Jadida
El Jadida (, ) is a major port city on the Atlantic coast of Morocco, located south of the city of Casablanca, in the province of El Jadida and the region of Casablanca-Settat. It has a population of 170,956 as of 2023.
The fortified city, b ...
*
El Kab
*
El Kenissia
*
El Kseur
*
El Lahun
*
El Matareya, Cairo
El Matareya ( ) is a district in the Eastern Area of Cairo, Egypt. The district is unrelated to the coastal town in the Dakahlia Governorate, that is also named El Matareya, Dakahlia, El Matareya. The district holds the ruins of the ancient Egyp ...
*
El Qattah
*
El-Amrah, Egypt
*
El-Detti
*
Elephantine
Elephantine ( ; ; ; ''Elephantíne''; , ) is an island on the Nile, forming part of the city of Aswan in Upper Egypt. The archaeological site, archaeological digs on the island became a World Heritage Site in 1979, along with other examples of ...
*
Eles, Tunisia
*
El-Gabal el-Ahmar
*
El-Haria
*
El-Hobagi
*
El-Kurru
El-Kurru was the first of the three royal cemeteries used by the Kingdom of Kush, Kushite royals of Napata, also referred to as Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Egypt's 25th Dynasty, and is home to some of the royal Nubian pyramids, Nubian Pyramid ...
*
El-Tod
El-Tod ( , from , , , ) was the site of an ancient Egyptian town and a temple to the Ancient Egyptian religion, Egyptian god Montu. It is located southwest of Luxor, Egypt, near the settlement of Hermonthis. A modern village now surrounds the ...
*
Enera
*
Enfidha
*
Esna
Esna ( , or ; ''Snē'' from ''tꜣ-snt''; ''Latópolis'' or (''Pólis Látōn'') or (''Lattōn''); Latin: ''Lato'') is a city of Egypt. It is located on the west bank of the Nile some south of Luxor. The city was formerly part of the ...
*
Essaouira
Essaouira ( ; ), known until the 1960s as Mogador (, or ), is a port city in the western Moroccan region of Marrakesh-Safi, on the Atlantic coast. It has 77,966 inhabitants as of 2014.
The foundation of the city of Essaouira was the work of t ...
*
Fadrus
*
Faras Cathedral
*
Feradi Minus
*
Fes el Bali
Fes el Bali () is the oldest part of Fez, Morocco. It is one of the three main districts of Fez, along with Fes Jdid and the French protectorate in Morocco, French-created ''Ville Nouvelle (New City'). Together with Fes Jdid, it forms the Medina q ...
*
Filaca
*
Flenucleta
*
Floriana, Mauritania
*
Flumenzer
*
Foratiana
*
Forontoniana
*
Fossatum Africae
''Fossatum Africae'' ("African ditch") is one or more linear defensive structures (sometimes called Limes (Roman Empire), ''limes'') claimed to extend over or more in North Africa, northern Africa constructed during the Roman Empire to defend an ...
*
Gabal El Haridi
*
Gafsa
Gafsa (; ; ') is the capital of Gafsa Governorate in Tunisia. With a population of 120,739, Gafsa is the ninth-largest Tunisian city and is 335 km from the country's capital, Tunis.
Overview
Gafsa is the capital of Gafsa Governorate, in ...
*
Gala Abu Ahmed
*
Gash Group
*
Gebel al-Ain
*
Gebel el-Silsila
*
Gebel Ramlah
*
Gebelein
*
Gemellae
Gemellae was a Roman fort and associated camp on the fringe of the Sahara Desert in what is today part of Algeria. It is now an archaeological site, 25 km south and 19 km west of Biskra, and 5 km southwest of the present-day village ...
*
Gerf Hussein
*
Gerzeh culture
*
Gilva, Numidia
*
Giru Mons
*
Giza East Field
The East Field is located to the east of the Great Pyramid of Giza and contains cemetery G 7000. This cemetery was a burial place for some of the family members of Khufu. The cemetery also includes mastabas from tenants and priests of the pyrami ...
*
Giza pyramid complex
The Giza pyramid complex (also called the Giza necropolis) in Egypt is home to the Great Pyramid of Giza, Great Pyramid, the pyramid of Khafre, and the pyramid of Menkaure, along with their associated pyramid complexes and the Great Sphinx of G ...
*
Giza West Field
*
Gratiana, Africa
*
Grimidi
*
Gubaliana
*
Gueldaman caves
*
Gummi in Proconsulari
*
Gunela
*
Gunugus
*
Gurza
*
Gynaecopolis
*
H.U.N.E.
*
Hajar an-Nasar
*
Halfan culture
*
Hamadab
*
Hammam Essalihine
*
Harageh
*
Harifian culture
*
Hawara
*
Heliopolis (ancient Egypt)
Heliopolis (Jwnw, Iunu; , 'the Pillars'; , ; ) was a major city of ancient Egypt. It was the capital of the 13th or Heliopolite Nome of Lower Egypt and a major religious centre. Its site is within the boundaries of Ain Shams and El Matareya ...
*
Hellenion (Naucratis)
*
Helwan (cemetery)
At Helwan south of modern Cairo was excavated a large ancient Egyptian cemetery with more than 10,000 burials. The cemetery was in use from the Naqada Period around 3200 BC to the Fourth Dynasty and again at the beginning of the Middle Kingdom an ...
*
Henchir Chigarnia
*
Henchir-Aïn-Dourat
*
Henchir-Baldia
*
Henchir-Belli
*
Henchir-Bez
*
Henchir-Boucha
*
Henchir-Bou-Doukhane
*
Henchir-Ed-Douamès
*
Henchir-El-Dukhla
*
Henchir-El-Hatba
*
Henchir-el-Kermate
*
Henchir-El-Meden
*
Henchir-El-Msaadine Henchir-El-Msaadine is a Roman Empire, Roman Empire era set of ruins near Tebourba(Ancient Thuburbo Minus) in modern Tunisia, North Africa. The site is outside of Tunis.
The ruins are tentatively identified as the remains of ''Municipium Aurelium ...
*
Henchir-Ezzguidane
*
Henchir-Guennara
*
Henchir-Khachoum
*
Henchir-Madjouba
*
Henchir-Mâtria
*
Henchir-Sidi-Salah
*
Henchir-Tebel
*
Heracleion
Heracleion (Ancient Greek: ), also known as Thonis (Ancient Greek: ; from the Egyptian language, Ancient Egyptian: ; ) and sometimes called Thonis-Heracleion, was an ancient Egyptian port city located near the Canopic Mouth of the Nile, abo ...
*
Heracleopolis Magna
Heracleopolis Magna (, ''Megálē Herakléous pólis''), Heracleopolis (, ''Herakleópolis'') or Herakleoupolis () is the Roman Empire, Roman name of the capital of the 20th nome (Egypt), nome of ancient Egypt, ancient Upper Egypt, known in Anci ...
*
Hermopolis
Hermopolis (or ''Hermopolis Magna'') was a major city in antiquity, located near the boundary between Lower and Upper Egypt. Its Egyptian name ''Khemenu'' derives from the eight deities (the Ogdoad) said to reside in the city.
A provincial capi ...
*
Hillat al-Arab
*
Hippo Regius
Hippo Regius (also known as Hippo or Hippone) is the ancient name of the modern city of Annaba, Algeria. It served as an important city for the Phoenicians, Berbers, Romans, and Vandals. Hippo was the capital city of the Vandal Kingdom from AD ...
*
Horrea Coelia
*
Hosh el-Kab fort
*
Hu, Egypt
Hu, Huw or Hiw (, ) is the modern name of an Egyptian town on the Nile, which in more ancient times was the capital of the 7th Nome of Upper Egypt.
The nome was referred to as ''Sesheshet'' (Sistrum). The main city was referred to as Hu(t)-sek ...
*
Iberomaurusian
*
Idfa
*
Ifri N'Ammar
*
Ifri N'Amr Ou Moussa
*
Ifri Oudadane
*
Igilgili
Igilgili was a Berber town and a Phoenician, Carthaginian, and Roman colony in located in present-day Jijel, Algeria.
History
Igilgili was initially a small Carthaginian colony and trading port (, , or , ). This name seems to combine (, " ...
*
Islamic Cairo
Islamic Cairo (), or Medieval Cairo, officially Historic Cairo (القاهرة التاريخية ''al-Qāhira tārīkhiyya''), refers mostly to the areas of Cairo, Egypt, that were built from the Muslim conquest of Egypt, Muslim conquest in 641 C ...
*
Iubaltiana
*
Jebel Barkal
Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal () is a mesa or large rock outcrop located 400 km north of Khartoum, next to Karima in Northern State in Sudan, on the Nile River, in the region that is sometimes called Nubia. The jebel is 104 m tall, has a f ...
*
Jebel Dosha
*
Jebel Irhoud
Jebel Irhoud or Adrar n Ighoud (; , Moroccan Arabic: ), is an archaeological site located just north of the town of Ighoud, Tlet Ighoud in Youssoufia Province, approximately south-east of the city of Safi, Morocco, Safi in Morocco. It is noted f ...
*
Jebel Mokram Group
*
Jebel Moya
*
Jebel Sahaba
Jebel Sahaba (; also Site 117) is a prehistoric cemetery site in the Nile Valley (now submerged in Lake Nasser), near the northern border of Sudan with Egypt in Northeast Africa. It is associated with the Qadan culture. It was discovered in 19 ...
*
Jebil National Park
*
Jedars
*
Kageras
*
Kairouan
Kairouan (, ), also spelled El Qayrawān or Kairwan ( , ), is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by the Umayyads around 670, in the period of Caliph Mu'awiya (reigned 661� ...
*
Karanis
*
Karanog
Karanog ( Meroitic: ''Nalote'') was a Kushite town in Lower Nubia on the west bank of the Nile (near Qasr Ibrim). It was probably a provincial capital under its own (governor) in the second and third centuries AD. It was excavated between 1907 ...
*
Kawa, Sudan
*
Kehf el Baroud
*
Kellia
Kellia ("the Cells"), referred to as "the innermost desert", was a 4th-century Egyptian Christian Christian monasticism, monastic community spread out over many square kilometers in the Nitrian Desert about south of Alexandria. It was one of t ...
*
Kellis
*
Kerkouane
*
Kharabet Ihrit
*
Khemis Miliana
*
Khiamian
*
Khor Shingawi
*
Kom El Deka
Kom El Deka (), also known as Kom el-Dikka, is a neighborhood and archaeological site in Alexandria, Egypt. Early Kom El-Dikka was a well-off residential area, and later it was a major civic center in Alexandria, with a bath complex (thermae), Audi ...
*
Kom el-Hisn
*
Kom Firin
*
Kom-el-Gir
*
Ksar Ghilane
*
Ksour-El-Khaoua
*
Kulb
*
Kulubnarti church
*
Kulubnarti fort
*
Kumma (Nubia)
Kumma or Semna East is an archaeological site in Sudan. Established in the mid-Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt, 12th Dynasty of Egypt, it served as a fortress of ancient Egypt in Nubia. Along with Semna (Nubia), Semna, Kumma was built by the Pharaoh Ses ...
*
Kuntillet Ajrud
*
Lake Ichkeul
*
Lambaesis
Lambaesis (Lambæsis), Lambaisis or Lambaesa (''Lambèse'' in colonial French), is a Roman archaeological site in Algeria, southeast of Batna and west of Timgad, located next to the modern village of Tazoult. The former bishopric is also ...
*
Lamdia
*
Lapda
*
Lari Castellum
*
Legis Volumni
*
Leontopolis (Heliopolis)
Leontopolis is the Koine Greek name of a city that may correspond to either the modern area of Tell el Yehudiye or Tell el-Yahudiya ("the Jewish tell"). It was an ancient city of Egypt in the 13th nome of Lower Egypt (the Heliopolite Nome) on ...
*
Lepsius list of pyramids
The Lepsius list of pyramids is a list of sixty-seven Ancient Egypt, ancient Egyptian pyramids established in 1842–1843 by Karl Richard Lepsius (1810–1884), an Egyptologist and leader of the ":de:Preußische Expedition nach Ägypten, Prussian ...
*
Letopolis
*
L'Hillil
*
Library of Alexandria
The Great Library of Alexandria in Alexandria, Egypt, was one of the largest and most significant libraries of the ancient world. The library was part of a larger research institution called the Mouseion, which was dedicated to the Muses, ...
*
Libyco-Punic Mausoleum of Dougga
The Libyco-Punic Mausoleum of Dougga (Mausoleum of Atban) is an ancient mausoleum located in Dougga, Tunisia. It is one of three examples of the royal Berber architecture, architecture of Numidia, which is in a good state of preservation and dates ...
*
Lisht
*
List of ancient Egyptian sites
*
*
List of prehistoric sites in Morocco
*
Lixus (ancient city)
Lixus (Berber languages, Berber : ⵍⵓⴽⵓⵙ, Phoenician language, Phoenician: 𐤋𐤊𐤅𐤔) is an ancient city founded by Phoenicians (8th–7th century BC) before the city of Carthage. Its distinguishing feature is that it was continuo ...
*
Luxor Temple
The Luxor Temple () is a large Ancient Egyptian temple complex located on the east bank of the Nile River in the city today known as Luxor (ancient Thebes (Egypt), Thebes) and was constructed approximately 1400 BCE. In the Egyptian language it was ...
*
Maadi
Maadi ( ) is a leafy and once suburban district in the Southern Area of Cairo, Egypt, on the east bank of the Nile about upriver from downtown Cairo. The modern extensions north east and east of Maadi, New Maadi and Zahraa al-Maadi are admini ...
*
Madarsuma
*
Madauros
*
Magharet el Kantara
Magharet el Kantara or Shaw's Cave (, ''arched cave'') is a rock art shelter of the Gilf Kebir National Park in the New Valley Governorate, Egypt. Located on the south-western slopes of Gilf Kebir
Gilf Kebir () (var. Gilf al-Kebir, Jilf al K ...
*
Mahjouba, Morocco
*
Malkata
*
Malliana
*
Manaccenser
*
Maraguia
*
Marazanae
*
Marea (ancient city)
*
Marina, Egypt
*
Masclianae
*
Mascula
*
Mattiana
*
Maximiana in Byzacena
*
Mazghuna
*
Medamud
*
Medina of Sousse, Tunisia
*
Medina of Taroudant
*
Meidum
*
Meinarti
*
Melzi
*
Memphis, Egypt
Memphis (, ; Bohairic ; ), or Men-nefer, was the ancient capital of Inebu-hedj, the first Nome (Egypt), nome of Lower Egypt that was known as ''mḥw'' ("North"). Its ruins are located in the vicinity of the present-day village of Mit Rahina () ...
*
Mendes
Mendes (, ''Genitive case, gen''.: ), the Greek language, Greek name of the ancient Egyptian city of Djedet, also known in ancient Egypt as Per (hieroglyph), Per-Banebdjedet ("The Domain of the Ram Lord of Djedet") and Anpet, is known today as Te ...
*
Merimde culture
*
Meroë
Meroë (; also spelled ''Meroe''; Meroitic: ; and ; ) was an ancient city on the east bank of the Nile about 6 km north-east of the Kabushiya station near Shendi, Sudan, approximately 200 km north-east of Khartoum. Near the site is ...
*
Mesarfelta
*
Mibiarca
*
Midianite pottery
*
Midica
*
Mididi
*
Migirpa
*
Mila, Algeria
Mila (, , ) is a city in the northeast of Algeria and the capital of Mila Province. In antiquity, it was known as Milevum (in Latin; as such still a Latin Catholic titular see) or Miraeon, ''Μιραίον'' (in Ancient Greek) and was situated in ...
*
Milevum
Milevum (in Latin even "Milev" or "Mireon"; ''Μιραίον'' in Ancient Greek) was a Roman–Berber city in the Roman province of Numidia. It was located in present-day Mila in eastern Algeria.
History
In Ptolemy's "Geography" (vol. IV, i ...
*
Miliana
*
Mimiana
*
Minshat Abu Omar
*
Mirgissa
*
Mizigi
*
Monastery of the Archangel Gabriel at Naqlun
*
Mousterian
The Mousterian (or Mode III) is an Industry (archaeology), archaeological industry of Lithic technology, stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and with the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and We ...
*
Mozotcori
*
Msoura
*
Musawwarat es-Sufra
*
Musti (Tunisia)
*
Muteci
*
Mutugenna
*
Myos Hormos
*
Nabala, Mauritania
*
Nabta Playa
Nabta Playa was once a large endorheic basin in the Nubian Desert, located approximately 800 kilometers south of modern-day Cairo or about 100 kilometers west of Abu Simbel in southern Egypt, 22.51° north, 30.73° east. Today the ...
*
Naqada culture
The Naqada culture is an archaeological culture of Chalcolithic Predynastic Egypt (c. 4000–3000 BC), named for the town of Naqada, Qena Governorate. A 2013 Oxford University radiocarbon dating study of the Predynastic period suggests a beginn ...
*
Naqada III
Naqada III is the last phase of the Naqada culture of ancient Prehistoric Egypt, Egyptian prehistory, dating from approximately 3200 to 3000 BC. It is the period during which the process of state formation, which began in Naqada II, became ...
*
Nasbinca
*
Naucratis
Naucratis or Naukratis (Ancient Greek: , "Naval Command"; Egyptian: , , , Coptic: ) was a city and trading-post in ancient Egypt, located on the Canopic (western-most) branch of the Nile river, south-east of the Mediterranean sea and the city ...
*
Naustathmus (Cyrenaica)
Naustathmus or Naustathmos () was a port and anchorage on the coast of ancient Cyrenaica, 100 stadia from Apollonia.
Its site is located near Marsa Hilal, Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region ...
*
Necropolis of Cyrene
*
Nefrusy
*
Negrine
*
Nekhel
*
Nekhen
Nekhen (, ), also known as Hierakonpolis (; , meaning City of Hawks or City of Falcons, a reference to Horus; ) was the religious and political capital of Upper Egypt at the end of prehistoric Egypt ( 3200–3100 BC) and probably also during th ...
*
Nekor
*
New Kalabsha
*
New Wadi es-Sebua
*
Nitria (monastic site)
*
North Asasif
*
Nubian pyramids
*
Numluli
*
Nuri
Nuri is a place in modern Sudan on the west side of the Nile River, Nile, near the Fourth Cataract. Nuri is situated about 15 km north of Sanam, Sudan, Sanam, and 10 km from Jebel Barkal.
History
Nuri is the second of three Napatan bur ...
*
Octabia
*
Oglet-Khefifa
*
Old Dongola
Old Dongola ( Old Nubian: ⲧⲩⲛⲅⲩⲗ, ''Tungul''; , ''Dunqulā al-ʿAjūz'') is a deserted Nubian town in what is now Northern State, Sudan, located on the east bank of the Nile opposite the Wadi Howar. An important city in medieval Nub ...
*
Oppidum Novum
*
Oxyrhynchus
Oxyrhynchus ( ; , ; ; ), also known by its modern name Al-Bahnasa (), is a city in Middle Egypt located about 160 km south-southwest of Cairo in Minya Governorate. It is also an important archaeological site. Since the late 19th century, t ...
*
Pbow
Pbow was a cenobitic monastery established by St. Pachomius in 336-337 AD. Pbow is about north of Luxor in modern Upper Egypt. It was one of the nine Pachomian monasteries.
Name
Pbow is a Coptic name. The Arabic "Faw" in "Faw al-Qibli" ("Sou ...
*
Pederodiana
*
Pelusium
Pelusium (Ancient Egyptian: ; /, romanized: , or , romanized: ; ; ; ; ) was an important city in the eastern extremes of Egypt's Nile Delta, to the southeast of the modern Port Said. It became a Roman provincial capital and Metropolitan arc ...
*
Philae
The Philae temple complex (; , , Egyptian: ''p3-jw-rķ' or 'pA-jw-rq''; , ) is an island-based temple complex in the reservoir of the Aswan Low Dam, downstream of the Aswan Dam and Lake Nasser, Egypt.
Originally, the temple complex was ...
*
Philoteris
*
Pi-Ramesses
Pi-Ramesses (; Ancient Egyptian: , meaning "House of Ramesses") was the new capital built by the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty Pharaoh Ramesses II (1279–1213 BC) at Qantir, near the old site of Avaris. The city had served as a ...
*
Pi-Sekhemkheperre
*
Pithom
*
Pocofeltus
*
Port Said
Port Said ( , , ) is a port city that lies in the northeast Egypt extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, straddling the west bank of the northern mouth of the Suez Canal. The city is the capital city, capital of the Port S ...
*
Portus Magnus, Algeria
Portus Magnus (Latin language, Latin: "Great Port") was a Roman port and Roman colony, colony in western Mauretania Caesariensis near Portus Divinus. Its ruins are now under and around Bethioua in Algeria's Oran Province. In the early modern per ...
*
Precausa
*
Ptolemais, Cyrenaica
*
Putia in Byzacena
*
Pyramids of Meroë
*
Qadan culture
*
Qalʿat ibn Salama
Qalʿat ibn Salama () is an ancient fortress and archeological site near Tiaret, Algeria. This place is known for having sheltered Ibn Khaldun, an Arab scholar and historian, for four years, between 1375 and 1379. It was here at Qalʿat ibn Salama ...
*
Qasr el Banat
*
Qasr Ibrim
*
Qift
*
Qubbet el-Hawa
Qubbet el-Hawa or "Dome of the Wind" is a site on the western bank of the Nile, opposite Aswan, that serves as the resting place of ancient nobles and priests from the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old and Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdoms of anc ...
*
Quiza Xenitana
*
Qustul
Qustul () is an archaeological cemetery located on the eastern bank of the Nile in Lower Nubia, just opposite of Ballana near the Sudan frontier. The site has archaeological records from the A-Group culture, the New Kingdom of Egypt and the X ...
*
Rachgoun
*
Rapidum
*
Raqqada
Raqqāda () is the site of the second capital of the 9th-century dynasty of Aghlabids, located about ten kilometers southwest of Kairouan, Tunisia. The site now houses the National Museum of Islamic Art.
History
In 876, the ninth Aghlabid emi ...
*
Reperi
*
Rhacotis
*
Riqqeh
*
Rock art of Iheren and Tahilahi
*
Roknia
*
Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania
*
Rufiniana
*
Rusazus
*
Rusubbicari
*
Sabu, Sudan
*
Sabu-Jaddi
*
Sadd el-Kafara
*
Saft el-Hinna
Saft el-Hinna (), also written as Saft el-Hinneh, Saft el-Henna, Saft el-Henneh, is a village and an archaeological site in Egypt. It is located in the modern Al Sharqia Governorate, in the Nile Delta, about 7 km southeast of Zagazig.
The ...
*
Saint Catherine, Egypt
*
Sais, Egypt
Sais (, ) was an ancient Egyptian city in the Western Nile Delta on the Canopic branch of the Nile,Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. "Saïs." '' Webster's Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 19 ...
*
Saldae
*
Samannud
Samannud ( ) is a city (''markaz'') located in Gharbia Governorate, Egypt. Known in classical antiquity as Sebennytos (), Samannud is a historic city that has been inhabited since the Ancient Egyptian period. As of 2019, the population of the '' ...
*
Sanam, Sudan
*
Sassura
*
Scebatiana
*
Sebilian
*
Sebkha-El-Coursia
*
Sedeinga pyramids
*
Sedment
Sedment al-Gabal () is a village in the Beni Suef Governorate of Egypt. It attracts a large number of Christians each year to celebrate the feast day of Saint George.
Etymology
The Arabic name of the village comes from its Coptic name pi-Sotom ...
*
Sega (Upper Egypt)
*
Sehel Island
*
Semna (Nubia)
*
Semta (Africa)
Semta was a Roman Empire, Roman era Municipium also known as ''Augustum Semta'' in Africa Proconsularis that is tentatively identified with ruins at Henchir Zemba (Dzemda) Carthage, Tunisia near the Oued el Kebir southwest of Zaghouan at 36.2692 ...
*
Senâm
*
Septimunicia
*
Serabit el-Khadim
Serabit el-Khadim (Arabic language, Arabic: سرابيط الخادم Arabic pronunciation: Help:IPA/Arabic, araːˈbiːtˤ alˈxaːdɪm also transliterated Serabit al-Khadim, Serabit el-Khadem) is a locality in the southwest Sinai Peninsula, ...
*
Sereddeli
*
Sesebi
*
Setifis
*
Severiana
*
Shalfak
Shalfak (originally ''Waf-Chastiu'', "subduing the foreign lands") is an Ancient Egyptian fortress once built up on the western shore of the Cataracts of the Nile, Second Cataract of the Nile#In Sudan, Nile River on what is now an island in Lake ...
*
Sheikh Muftah culture
*
Shellal
*
Siccenna
*
Siccesi
*
Sidi Bennour
*
Sidi Brahim
*
Sidi Daoud, Tunisia
*
Sidi El Hani
*
Sidi Khelifa (Tunisia)
*
Siga
*
Singa, Sudan
*
Sinnuara
*
Sitipa
*
Soba (city)
*
Soknopaiou Nesos
*
Soleb
*
Souk El Khemis
*
Sousse
Sousse, Sūsah , or Soussa (, ), is a city in Tunisia, capital of the Sousse Governorate. Located south of the capital Tunis, the city has 271,428 inhabitants (2014). Sousse is in the central-east of the country, on the Gulf of Hammamet, which ...
*
Speos Artemidos
*
Stone quarries of ancient Egypt
*
Sufasar
Sufasar was a Roman town, one of many in Roman North Africa. Sufasar faded with the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb. The site has been tentatively identified with ruins at Amourah in modern Algeria.
Sufasar was also the seat, of an ancient bishop ...
*
Suliana
*
Sullectum
*
Sululos
*
Sumenu
*
Tabaicara
*
Tabalta
*
Taberdga, Algeria
*
Tabo (Nubia)
*
Taborenta
*
Tabuda
*
Tadrart Rouge
*
Taforalt
Taforalt, or Grotte des Pigeons, is a cave in the province of Berkane, Aït Iznasen region, Morocco, possibly the oldest cemetery in North Africa. It contained at least 34 Iberomaurusian adolescent and adult human skeletons, as well as young ...
*
Tagarbala
* Tagase
* Tahpanhes
* Tahpsus
* Talaptula
* Tamazeni
* Tambeae
* Tamera, Tunisia
* Tamuda
* Taposiris Magna
* Taraqua
* Tarkhan (Egypt)
* Tarrana
* Tasaccora
* Tasian culture
* Tassili n'Ajjer
* Tatilti
* Tel Habuwa
* Tell el-Balamun
* Tell El-Dab'a
* Tell el-Qudeirat
* Tell Nebesha
* Temple of Amun, Jebel Barkal
* Temple of Debod
* Temple of Edfu
* Temple of Hibis
* Temple of Kalabsha
* Temple of Kom Ombo
* Temple of Mut, Jebel Barkal
* Temuniana
* Tennis, Egypt
* Tetci
* Tétouan
* Thabraca
* Thagaste
* Thamusida
* Thasbalta
* Theban Necropolis
* Thebes, Egypt
* Thenae
* Theveste
* Thiava, Numidia
* Thibilis
* Thiges
* Thimida Bure
* Thinis
* Thubursicum-Bure
* Thucca Terenbenthina
* Thunusruma
* Tiddis
* Tigisis in Mauretania
* Tigisis in Numidia
* Tiguala
* Timgad
* Timidana
* Tinisa in Proconsulari
* Tipasa
* Tipaza
* Titular Bishopric of Vita
* Tobna
* Tombos (Nubia)
* Trofimiana
* Tubernuca
* Tubyza
* Tura, Egypt
* Uchi Maius
* Umm Ruweim
* Unfinished obelisk
* Uppenna
* Uronarti
* Usilla
* Uzinaza
* Vagada (Numidia)
* Vagal, Mauritania
* Vagalitanus
* Vageata
* Valley of the Golden Mummies
* Vallitanus
* Vazi-Sarra
* Vegesela in Byzacena
* Volubilis
* Voncariana
* Wad ban Naqa
* Wadi al-Jarf
* Wadi el-Hudi
* Wadi Hammamat
* Wadi Hamra (Gilf Kebir)
* Wadi Maghareh
* Wadi Tumilat
* Wah-Sut
* Zaraï
* Zawyet el-Maiyitin
* Zawyet Umm El Rakham
* Zella (see)
* Zian, North Africa
* Zuccabar
* Zuma, Sudan
See also
*List of kingdoms in Africa throughout history#North Africa
*Genetic history of North Africa
*History of Africa#North Africa, History of Africa § North Africa
*History of Algeria
*History of Egypt
*History of Libya
*History of Morocco
*History of Tunisia
*History of Western Sahara
References
Further reading
*
* Cesari, Jocelyne. ''The awakening of Muslim democracy: Religion, modernity, and the state'' (Cambridge University Press, 2014).
* Falola, Toyin, Jason Morgan, and Bukola Adeyemi Oyeniyi. ''Culture and customs of Libya'' (Abc-clio, 2012).
* Fischbach, ed. Michael R. ''Biographical encyclopedia of the modern Middle East and North Africa'' (Gale Group, 2008).
* Ilahiane, Hsain. ''Historical dictionary of the Berbers (Imazighen)'' (Rowman & Littlefield, 2017).
* Issawi, Charles. ''An economic history of the Middle East and North Africa'' (Routledge, 2013).
* Naylor, Phillip C. ''North Africa, Revised Edition: A History from Antiquity to the Present'' (University of Texas Press, 2015).
* Stearns, Peter N., et al. ''World Civilizations: The Global Experience'' (AP Edition DBQ Update. New York: Pearson Education, Inc., 2006) p. 174.
External links
Maroc-history: ''A Taste of Maghribi History''
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of North Africa
History of North Africa,
Maghreb
History of the Mediterranean, North Africa
Natural history of Africa
 The history of North Africa is typically divided into its prehistory, the classical period, the arrival and spread of Islam, the colonial era, and finally the post-independence period, in which the current nations were formed. The region has been influenced by a wide range of cultures. The development of sea travel firmly integrated North Africa into the Mediterranean world, especially during the classical period. In the 1st millennium AD, the
The history of North Africa is typically divided into its prehistory, the classical period, the arrival and spread of Islam, the colonial era, and finally the post-independence period, in which the current nations were formed. The region has been influenced by a wide range of cultures. The development of sea travel firmly integrated North Africa into the Mediterranean world, especially during the classical period. In the 1st millennium AD, the 
 The expanse of the
The expanse of the  The wider protest movement known as the
The wider protest movement known as the