|
Debeira
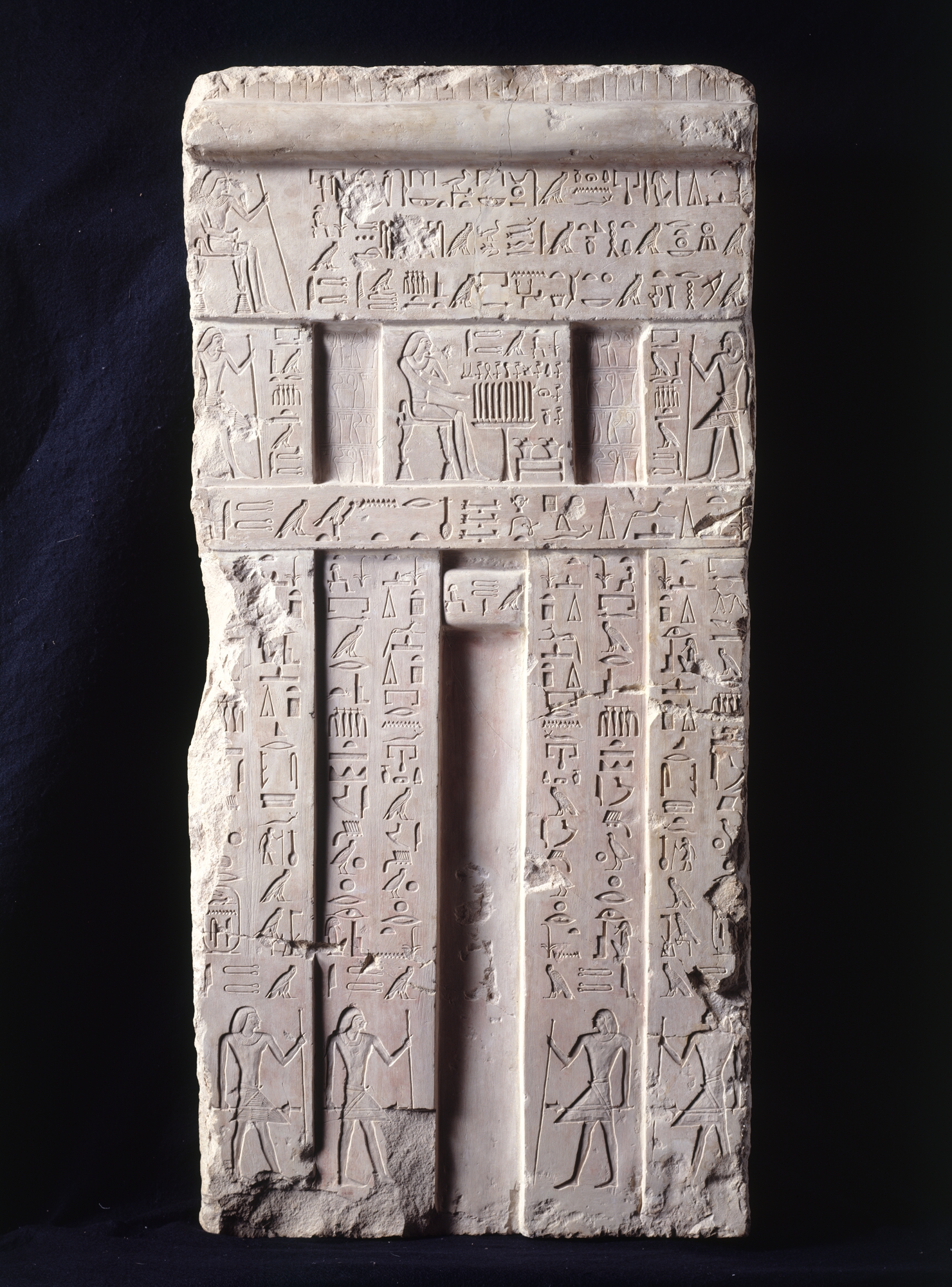
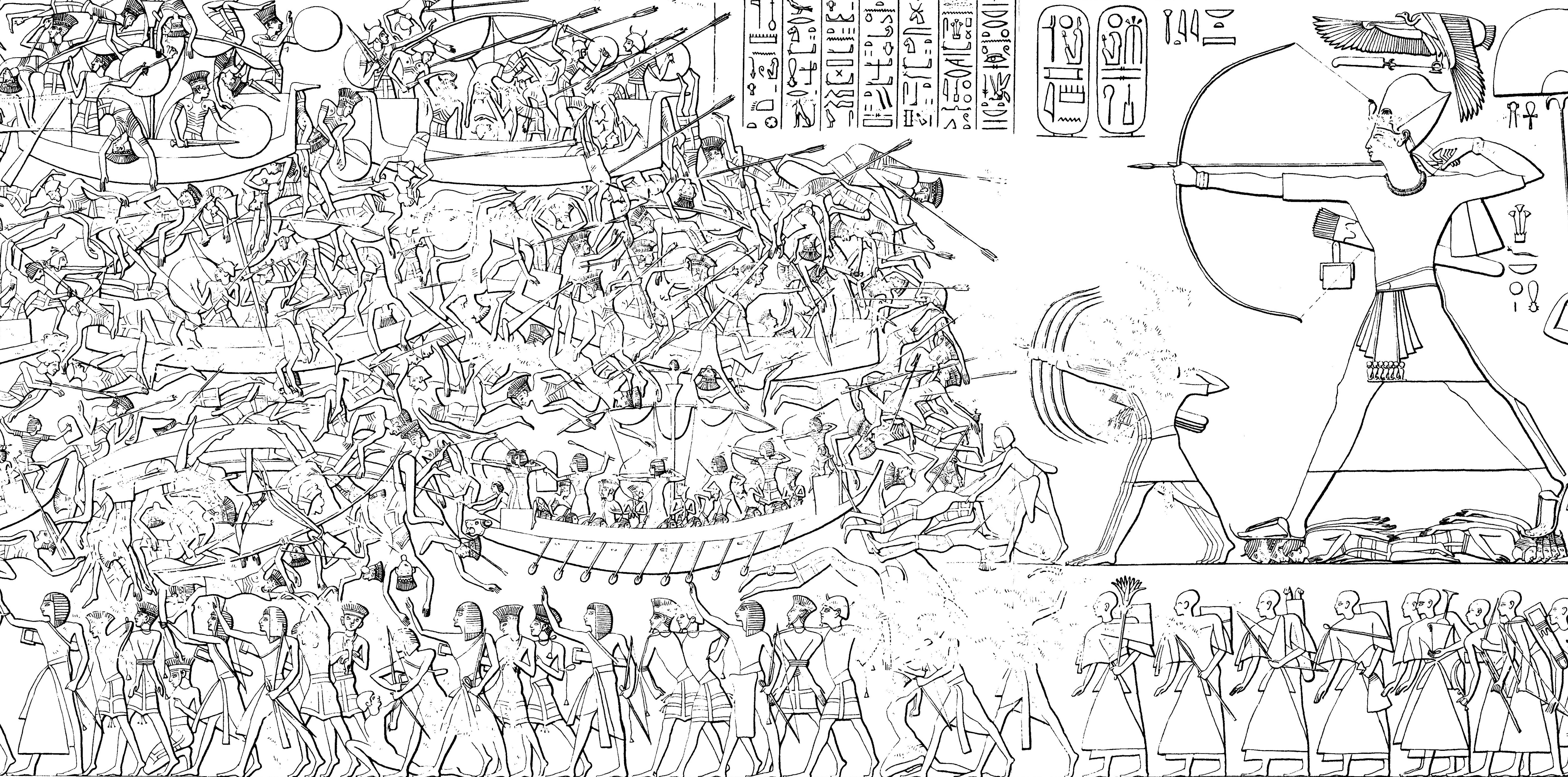
Debeira is an archaeological site in Sudan situated on the eastern bank of the Nile some 20 kilometres north of Wadi Halfa. Early period Excavations brought to light a necropolis of the C-Group culture.Jean Vercoutter, New Egyptian Inscriptions, Kush nr. IV,1956, pp.66-86. The necropolis site dates to ca. 2400–1550 BCE. At Debeira-East a wall-painted funerary chapel of the Nubian prince (''chief of Teh-khet'') Djehutyhotep from the time of Hatshepsut and Thutmosis III was found. Other finds include a painted sarcophagus with iconography of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt. The sarcophagus and the painted scenes of the burial chamber were taken to the Sudan National Museum in Khartoum prior to the flooding of Debeira by Lake Nasser Lake Nasser ( ', ) is a large reservoir (water), reservoir in southern Egypt and northern Sudan. It was created by the construction of the Aswan Dam, Aswan High Dam and is one of the List of reservoirs by volume, largest man-made lakes in the wo .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djehutyhotep (chief Of Teh-khet)
Djehutyhotep, also called Paitsy, was a Nubian official under Hatshepsut and Thutmosis III. He was ''chief of Teh-khet'' and was therefore a governor ruling a region in Lower Nubia of the Egyptian state. In the New Kingdom, Egyptian kings had conquered Lower Nubia. To secure control over the new region they appointed people of the local elite as governors. Teh-khet was a Nubian region that covered the area about Debeira and Serra. The local governors here formed a family, while the governor proper held the title ''chief of Teh-khet''. Djehutyhotep's father Ruiu was also ''chief of Teh-khet''. His mother was called Runia. His wife was called Tenetnub. His brother Amenemhat was also ''chief of Teh-khet'' and followed Djehutyhotep in office. Djehutyhotep is known from several monuments. The most important one is his decorated rock-cut tomb in Debeira-East. The rock-cut chapel consists of three chambers; the first one is decorated with paintings. A second room contained the badly pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan National Museum
The National Museum of Sudan or Sudan National Museum, abbreviated SNM, is a two-story building, constructed in 1955 and established as national museum in 1971. Before its destruction during the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudanese civil war, the museum held an estimated 100,000 objects covering thousands of years of Sudan's history, ranging from the Nubia, Nubian kingdoms and the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Kushite empire to the country's Christian and Islamic periods. History Before the Sudanese civil war that started in April 2023, the museum building and its surrounding gardens housed the largest and most comprehensive Nubian archaeological collection in the world, including objects from the Paleolithic through to the Islamic period, originating from every site of importance in Sudan. A significant catalyst for the museum's creation was the large number of relocated artefacts as a result of the 1960–1980 International Campaign to Save the Monuments of Nubia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern State, Sudan
Northern ( ') is one of the 18 wilayat (states) of Sudan. It has an area of 348,765 km2 and an estimated population of 936,255. Northern Sudan was in ancient times Nubia. Jebel Uweinat is a mountain range in the area of the Egyptian-Libyan-Sudanese border. The state has been part of historical Sudanese kingdoms and countries such as the Mahdist State and the Kingdom of Kush. The state is bordering Egypt to the North, River Nile State to the east, Khartoum State to the southeast, North Kordofan to the south, and North Darfur and Libya to the west. The disputed Wadi Halfa Salient is located on the border of the state and Egypt. History Northern has been under control of a few Sudanese-Nubian kingdoms throughout its history. Here is a list of early kingdoms or Sudanese empires (countries/non recognized states) that controlled the state fully or partially. *Kingdom of Kush * Alodia *Kingdom of Kerma * Nobatia The Sudanese Makuria kingdom was able to defeat Rashidun forces tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kingdom Of Egypt
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning –2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, under whom the art of pyramid-building was perfected, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who commissioned the construction of the Giza pyramid complex, pyramids at Giza. Ancient Egypt, Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" Egyptian chronology, periods (followed by the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom), which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The Periodization of Ancient Egypt, concept of an "Old Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by the German Egyptology, Egyptologist Christian Charles Josias von Bunsen, Baron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadi Halfa
(, , ":wikt:esparto, Esparto Valley") is a city in the Northern (state), Northern state of Sudan on the shores of Lake Nasser, Lake Nubia near the Egypt–Sudan border, border with Egypt. It is the terminus of a rail transport in Sudan, rail line from Khartoum and the point where goods are transferred from rail to ferries going down the lake. As of 2007, the city had a population of 15,725. The city is located amidst numerous ancient Nubian antiquities and was the focus of much archaeological work by teams seeking to save artifacts from the flooding caused by the completion of the Aswan Dam. Climate Wadi Halfa has a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification ''BWh'') typical of the Nubian Desert. Wadi Halfa receives each year the highest mean amount of bright sunshine, with an extreme value of 4,300 h, which is equal to 97–98 % of possible sunshine. In addition to this, the town receives a mean annual amount of rainfall of . Many years usually pass without any rain fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Group Culture
The C-Group culture is an archaeological culture found in Lower Nubia, which dates from 2400 BCE to 1550 BCE. It was named by George A. Reisner. With no central site and no written evidence about what these people called themselves, Reisner assigned the culture a letter. The C-Group arose after Reisner's A-Group and B-Group cultures, and around the time the Old Kingdom was ending in Ancient Egypt. Overview While today A-Group and B-Group are seen as being a continuation of the same group, C-Group is considered as the product of distinct Saharan pastoralists. The C-Group is marked by its distinctive pottery, and for its tombs. Early C-Group tombs consisted of a simple "stone circle" with the body buried in a depression in the centre. The tombs later became more elaborate with the bodies being placed in a stone lined chamber, and then the addition of an extra chamber on the east for offerings. The origins of the C-Group are still debated. Some scholars see it largely as havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Vercoutter
Jean Vercoutter (20 January 1911 – 16 July 2000) was a French Egyptologist. One of the pioneers of archaeological research into Sudan from 1953, he was Director of the Institut Français d'Archéologie Orientale from 1977 to 1981. Biography Born in Lambersart, Nord, Vercoutter attended the Académie Julian to learn about painting, but soon turned to Egyptology. In 1939, he graduated from the IVe section of the École Pratique des Hautes Études with a thesis on ancient Egyptian funerary objects and was appointed resident of the French Institute of Oriental Archaeology of Cairo (IFAO). He participated in excavations in Karnak and directed an excavation in El-Tod. Upon his return to France, he joined CNRS (1949–1955). During all these years, he pursued research on the relationship between Egyptians and pre-Hellenes, providing some firm conclusions on the relationship between these two great civilizations and the history of the ancient Aegean world. He was appointed profe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut ( ; BC) was the sixth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, Egypt, ruling first as regent, then as queen regnant from until (Low Chronology) and the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Thutmose II. She was Egypt's second confirmed woman who ruled in her own right, the first being Sobekneferu, Sobekneferu/Neferusobek in the Twelfth Dynasty. Hatshepsut was the daughter of Thutmose I and Great Royal Wife, Ahmose (queen), Ahmose. Upon the death of her husband and half-brother Thutmose II, she had initially ruled as regent to her stepson, Thutmose III, who inherited the throne at the age of two. Several years into her regency, Hatshepsut assumed the position of pharaoh and adopted the full Ancient Egyptian royal titulary, royal titulary, making her a co-ruler alongside Thutmose III. In order to establish herself in the Egyptian patriarchy, she took on traditionally male roles and was depicted as a male pharaoh, with physically masculine traits and traditionally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thutmosis III
Thutmose III (variously also spelt Tuthmosis or Thothmes), sometimes called Thutmose the Great, (1479–1425 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt. He is regarded as one of the greatest warriors, military commanders, and military strategists of all time; as Egypt's preeminent warrior pharaoh and conqueror; and as a dominant figure in the New Kingdom period. Officially, Thutmose III ruled Egypt from his coronation on 28 April 1479 BC at the age of two until his death on 11 March 1425 BC. But for the first 22 years of his reign, he was coregent with his stepmother and aunt, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh.Partridge, R., 2002. Fighting Pharaohs: Weapons and warfare in ancient Egypt. Manchester: Peartree. pp. 202–203 He became sole ruler after Hatshepsut's death in 1458. Thutmose III conducted between 17 and 20 military campaigns, all victorious, which brought ancient Egypt's empire to its zenith. They are detailed in the inscriptions known as the Ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torgny Säve-Söderbergh
Torgny Säve-Söderbergh (born 29 June 1914 in Lund; died 21 May 1998 in Uppsala) was a Swedish writer, translator, and professor of Egyptology at Uppsala University from 1950 to 1980. He was the younger brother of paleontologist Gunnar Säve-Söderbergh. Education and career Torgny Säve-Söderbergh was born in Lund on 29 June 1914 to Gotthard Söderbergh and Anna Säve. Säve-Söderbergh studied at the University of Göttingen. He then attended the Uppsala University for his doctoral studies and was awarded his doctorate at the age of 27 for his thesis ''Ägypten und Nubien'' (1941, written in German). After graduating, he performed archaeological and historical research. From 1935 to 1950, he participated in archaeological excavations in Greece and Turkey (1935, 1938–1939) and in Egypt (1937, 1950). From 1942 to 1980, he was a lecturer, then professor of Egyptology (1950) and dean (1960–1965) of the Faculty of Arts at Uppsala University. He also served as Director of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties together constitute an era known as the Ramesside period owing to the predominance of rulers with the given name "Ramesses". This dynasty is generally considered to mark the beginning of the decline of Ancient Egypt at the transition from the Late Bronze to Iron Age. During the period of the Twentieth Dynasty, Ancient Egypt faced the crisis of invasions by Sea Peoples. The dynasty successfully defended Egypt, while sustaining heavy damage. History After the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt entered into a period of civil war. Because of lost historical records, the cause of the civil war is unknown. The war was ended with the accession to the throne by Setnakhte, who founded the 20th Dynasty of Egypt. From the reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum is the capital city of Sudan as well as Khartoum State. With an estimated population of 7.1 million people, Greater Khartoum is the largest urban area in Sudan. Khartoum is located at the confluence of the White Nile – flowing north from Lake Victoria – and the Blue Nile, flowing west from Lake Tana in Ethiopia. Divided by these two parts of the Nile, the Khartoum metropolitan area is a tripartite metropolis consisting of Khartoum proper and linked by bridges to Khartoum North ( ) and Omdurman ( ) to the west. The place where the two Niles meet is known as ''al-Mogran'' or ''al-Muqran'' (; English: "The Confluence"). Khartoum was founded in 1821 by Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali Pasha, north of the ancient city of Soba (city), Soba. In 1882 the British Empire Anglo-Egyptian War, took control of the Egyptian government, leaving the administration of Sudan in the hands of the Egyptians. At the outbreak of the Mahdist War, the British attempted to evacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |