Greeks on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an
 The Greeks speak the
The Greeks speak the
 Most of the feuding Greek city-states were, in some scholars' opinions, united by force under the banner of
Most of the feuding Greek city-states were, in some scholars' opinions, united by force under the banner of
 The
The

 During most of the Middle Ages, the Byzantine Greeks self-identified as ''Rhōmaîoi'' (, "Romans", meaning
During most of the Middle Ages, the Byzantine Greeks self-identified as ''Rhōmaîoi'' (, "Romans", meaning
 Following the
Following the  The roots of Greek success in the Ottoman Empire can be traced to the Greek tradition of education and commerce exemplified in the Phanariotes. It was the wealth of the extensive merchant class that provided the material basis for the intellectual revival that was the prominent feature of Greek life in the half century and more leading to the outbreak of the
The roots of Greek success in the Ottoman Empire can be traced to the Greek tradition of education and commerce exemplified in the Phanariotes. It was the wealth of the extensive merchant class that provided the material basis for the intellectual revival that was the prominent feature of Greek life in the half century and more leading to the outbreak of the
 The terms used to define Greekness have varied throughout history but were never limited or completely identified with membership to a Greek state.
The terms used to define Greekness have varied throughout history but were never limited or completely identified with membership to a Greek state.
 Greeks and Greek-speakers have used different names to refer to themselves collectively. The term (Ἀχαιοί) is one of the collective names for the Greeks in
Greeks and Greek-speakers have used different names to refer to themselves collectively. The term (Ἀχαιοί) is one of the collective names for the Greeks in
: "From when Hellen on ofDeuc
1.14
: "The deluge in the time of Deucalion, for instance took place chiefly in the Greek world and in it especially about ancient Hellas, the country about Dodona and the Achelous." In the Homeric tradition, the Selloi were the priests of Dodonian Zeus. In the
 The total number of Greeks living outside Greece and Cyprus today is a contentious issue. Where census figures are available, they show around three million Greeks outside Greece and Cyprus. Estimates provided by the SAE – World Council of Hellenes Abroad put the figure at around seven million worldwide. According to George Prevelakis of Sorbonne University, the number is closer to just below five million. Integration, intermarriage, and loss of the Greek language influence the self-identification of the Greek diaspora (''omogenia''). Important centres include
The total number of Greeks living outside Greece and Cyprus today is a contentious issue. Where census figures are available, they show around three million Greeks outside Greece and Cyprus. Estimates provided by the SAE – World Council of Hellenes Abroad put the figure at around seven million worldwide. According to George Prevelakis of Sorbonne University, the number is closer to just below five million. Integration, intermarriage, and loss of the Greek language influence the self-identification of the Greek diaspora (''omogenia''). Important centres include

 During and after the
During and after the
 Most Greeks speak the
Most Greeks speak the
 Most Greeks are
Most Greeks are
 Greek art has a long and varied history. Greeks have contributed to the visual, literary and performing arts.. In the West, classical Greek art was influential in shaping the Roman and later the modern Western artistic heritage. Following the
Greek art has a long and varied history. Greeks have contributed to the visual, literary and performing arts.. In the West, classical Greek art was influential in shaping the Roman and later the modern Western artistic heritage. Following the
 The Greeks of the Classical and Hellenistic eras made seminal contributions to science and philosophy, laying the foundations of several western scientific traditions, such as
The Greeks of the Classical and Hellenistic eras made seminal contributions to science and philosophy, laying the foundations of several western scientific traditions, such as

 The most widely used symbol is the
The most widely used symbol is the
 The traditional Greek homelands have been the Greek peninsula and the Aegean Sea,
The traditional Greek homelands have been the Greek peninsula and the Aegean Sea,
 In their archaeogenetic study, Lazaridis et al. (2017) found that Minoans and Mycenaean Greeks were genetically highly similar, but not identical; modern Greeks resembled the Mycenaeans, but with some additional dilution of the early Neolithic ancestry. The results of the study support the idea of genetic continuity between these civilizations and modern Greeks, but not isolation in the history of populations of the Aegean, before and after the time of its earliest civilizations. Furthermore, proposed migrations by Ancient Egypt, Egyptian or Phoenician colonists was not discernible in their data, thus "rejecting the hypothesis that the cultures of the Aegean were seeded by migrants from the old civilizations of these regions." The Fixation index, F between the sampled Bronze Age populations and present-day West Eurasians was estimated, finding that Mycenaean Greeks and Minoans were least differentiated from the populations of modern Greece, Cyprus, Albania, and Italy. In a subsequent study, Lazaridis et al. (2022) concluded that around ~58.4–65.8% of the ancestry of the Mycenaeans came from Early European Farmers, Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF), while the remainder mainly came from ancient populations related to the Caucasus hunter-gatherer, Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers (CHG) (~20.1–22.7%) and the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN) culture in the Levant (~7–14%). The Mycenaeans had also inherited ~3.3–5.5% ancestry from a source related to the Eastern Hunter-Gatherer, Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG), introduced via a proximal source related to the inhabitants of the Eurasian steppe who are hypothesized to be the Proto-Indo-Europeans, and ~0.9–2.3% from the Iron Gates Mesolithic, Iron Gates Hunter-Gatherers in the Balkans. Mycenaean elites were genetically the same as Mycenaean commoners in terms of their steppe ancestry, while some Mycenaeans lacked it altogether.
A genetic study by Clemente et al. (2021) found that in the Early Bronze Age, the populations of the Minoan, Helladic civilization, Helladic, and Cycladic culture, Cycladic civilizations in the Aegean, were genetically homogeneous. In contrast, the Aegean population during the Middle Bronze Age was more differentiated; probably due to gene flow from a Yamnaya-related population from the Pontic–Caspian steppe. This is corroborated by sequenced genomes of Middle Bronze Age individuals from northern Greece, who had a much higher proportion of steppe-related ancestry; the timing of this gene flow was estimated at ~2,300 BCE, and is consistent with the dominant linguistic theories explaining the emergence of the Proto-Greek language. Present-day Greeks share ~90% of their ancestry with them, suggesting continuity between the two time periods. In the case of Mycenaean Greeks however, their steppe-related ancestry was diluted. The ancestry of the Mycenaeans could be explained via a 2-way admixture model of such MBA individuals in northern Greece, and either an EBA Aegean or MBA Minoan population; the difference between the two time periods could be explained by the general decline of the Mycenaean civilization.
Genetic studies using multiple Genealogical DNA test#Autosomal DNA (atDNA) testing, autosomal, Genealogical DNA test#Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) testing, Y-DNA, and Genealogical DNA test#Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) testing, mtDNA markers, show that Greeks share similar backgrounds as the rest of the Europeans and especially Southern Europeans (Italians and Balkan populations such as
In their archaeogenetic study, Lazaridis et al. (2017) found that Minoans and Mycenaean Greeks were genetically highly similar, but not identical; modern Greeks resembled the Mycenaeans, but with some additional dilution of the early Neolithic ancestry. The results of the study support the idea of genetic continuity between these civilizations and modern Greeks, but not isolation in the history of populations of the Aegean, before and after the time of its earliest civilizations. Furthermore, proposed migrations by Ancient Egypt, Egyptian or Phoenician colonists was not discernible in their data, thus "rejecting the hypothesis that the cultures of the Aegean were seeded by migrants from the old civilizations of these regions." The Fixation index, F between the sampled Bronze Age populations and present-day West Eurasians was estimated, finding that Mycenaean Greeks and Minoans were least differentiated from the populations of modern Greece, Cyprus, Albania, and Italy. In a subsequent study, Lazaridis et al. (2022) concluded that around ~58.4–65.8% of the ancestry of the Mycenaeans came from Early European Farmers, Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF), while the remainder mainly came from ancient populations related to the Caucasus hunter-gatherer, Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers (CHG) (~20.1–22.7%) and the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN) culture in the Levant (~7–14%). The Mycenaeans had also inherited ~3.3–5.5% ancestry from a source related to the Eastern Hunter-Gatherer, Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG), introduced via a proximal source related to the inhabitants of the Eurasian steppe who are hypothesized to be the Proto-Indo-Europeans, and ~0.9–2.3% from the Iron Gates Mesolithic, Iron Gates Hunter-Gatherers in the Balkans. Mycenaean elites were genetically the same as Mycenaean commoners in terms of their steppe ancestry, while some Mycenaeans lacked it altogether.
A genetic study by Clemente et al. (2021) found that in the Early Bronze Age, the populations of the Minoan, Helladic civilization, Helladic, and Cycladic culture, Cycladic civilizations in the Aegean, were genetically homogeneous. In contrast, the Aegean population during the Middle Bronze Age was more differentiated; probably due to gene flow from a Yamnaya-related population from the Pontic–Caspian steppe. This is corroborated by sequenced genomes of Middle Bronze Age individuals from northern Greece, who had a much higher proportion of steppe-related ancestry; the timing of this gene flow was estimated at ~2,300 BCE, and is consistent with the dominant linguistic theories explaining the emergence of the Proto-Greek language. Present-day Greeks share ~90% of their ancestry with them, suggesting continuity between the two time periods. In the case of Mycenaean Greeks however, their steppe-related ancestry was diluted. The ancestry of the Mycenaeans could be explained via a 2-way admixture model of such MBA individuals in northern Greece, and either an EBA Aegean or MBA Minoan population; the difference between the two time periods could be explained by the general decline of the Mycenaean civilization.
Genetic studies using multiple Genealogical DNA test#Autosomal DNA (atDNA) testing, autosomal, Genealogical DNA test#Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) testing, Y-DNA, and Genealogical DNA test#Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) testing, mtDNA markers, show that Greeks share similar backgrounds as the rest of the Europeans and especially Southern Europeans (Italians and Balkan populations such as
World Council of Hellenes Abroad (SAE)
Umbrella Diaspora Organization Religious
Ecumenical Patriarchate of ConstantinopleGreek Orthodox Patriarchate of AlexandriaGreek Orthodox Patriarchate of AntiochGreek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem
Church of CyprusChurch of Greece
Academic
Transnational Communities Programme at the University of Oxford
, includes papers on the
Greeks on Greekness
The Construction and Uses of the Greek Past among Greeks under the Roman Empire. *The Modern Greek Studies Association is a scholarly organization for modern Greek studies in North America, which publishes the Journal of Modern Greek Studies.
Got Greek? Next Generation National Research StudyWaterloo Institute for Hellenistic Studies
Trade organizations
Hellenic Canadian Board of TradeHellenic Canadian Lawyers AssociationHellenic-American Chamber of CommerceHellenic-Argentine Chamber of Industry and Commerce (C.I.C.H.A.)
Charitable organizations
AHEPA
– American Hellenic Educational Progressive Association
Hellenic Heritage FoundationHellenic Home for the Aged
*
{{Authority control Ethnic groups in Greece Greek people, Ancient peoples of Europe Indo-European peoples
ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
and nation
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective Identity (social science), identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, t ...
native to Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, southern Albania, Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, parts of Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, and to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Eastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a loosely delimited region comprising the easternmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, and well as the adjoining land—often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea. It includes the southern half of Turkey ...
and Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
. They also form a significant diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of birth, place of origin. The word is used in reference to people who identify with a specific geographic location, but currently resi ...
(), with many Greek communities established around the world..
Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
and Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean and Ionian seas, where the Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
has been spoken since the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula
Greece is a country in Southeastern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. It is bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cretan and t ...
, the western coast of Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia
Cappadocia (; , from ) is a historical region in Central Anatolia region, Turkey. It is largely in the provinces of Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. Today, the touristic Cappadocia Region is located in Nevşehir ...
in central Anatolia, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, Cyprus, and Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. Many of these regions coincided to a large extent with the borders of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
of the late 11th century and the Eastern Mediterranean areas of ancient Greek colonization. The cultural centers of the Greeks have included Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
, Thessalonica, Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
, Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; , or ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna ...
, and Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
at various periods.
In recent times, most ethnic Greeks live within the borders of the modern Greek state or in Cyprus. The Greek genocide and population exchange between Greece and Turkey nearly ended the three millennia-old Greek presence in Asia Minor. Other longstanding Greek populations can be found from southern Italy to the Caucasus and southern Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
and in the Greek diaspora
The Greek diaspora, also known as Omogenia (), are the communities of Greeks living outside of Greece and Cyprus.
Such places historically (dating to the ancient period) include, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in North Macedonia, North Maced ...
communities in a number of other countries. Today, most Greeks are officially registered as members of the Greek Orthodox Church
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Christianity in Greece, Greek Christianity, Antiochian Greek Christians, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christian ...
.CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print ve ...
on Greece: Greek Orthodox 98%, Greek Muslim 1.3%, other 0.7%.
Greeks have greatly influenced and contributed to culture, visual arts, exploration, theatre, literature, philosophy, ethics, politics, architecture, music, mathematics, medicine, science, technology, commerce, cuisine and sports. The Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
is the oldest recorded living language and its vocabulary has been the basis of many languages, including English as well as international scientific nomenclature. Greek was the most widely spoken ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
'' in the Mediterranean world since the fourth century BC and the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
of the Christian Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) biblical languages ...
was also originally written in Greek.
History
Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
, which forms its own unique branch within the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
family of languages, the Hellenic. They are part of a group of classical ethnicities, described by Anthony D. Smith as an "archetypal diaspora people".
Origins
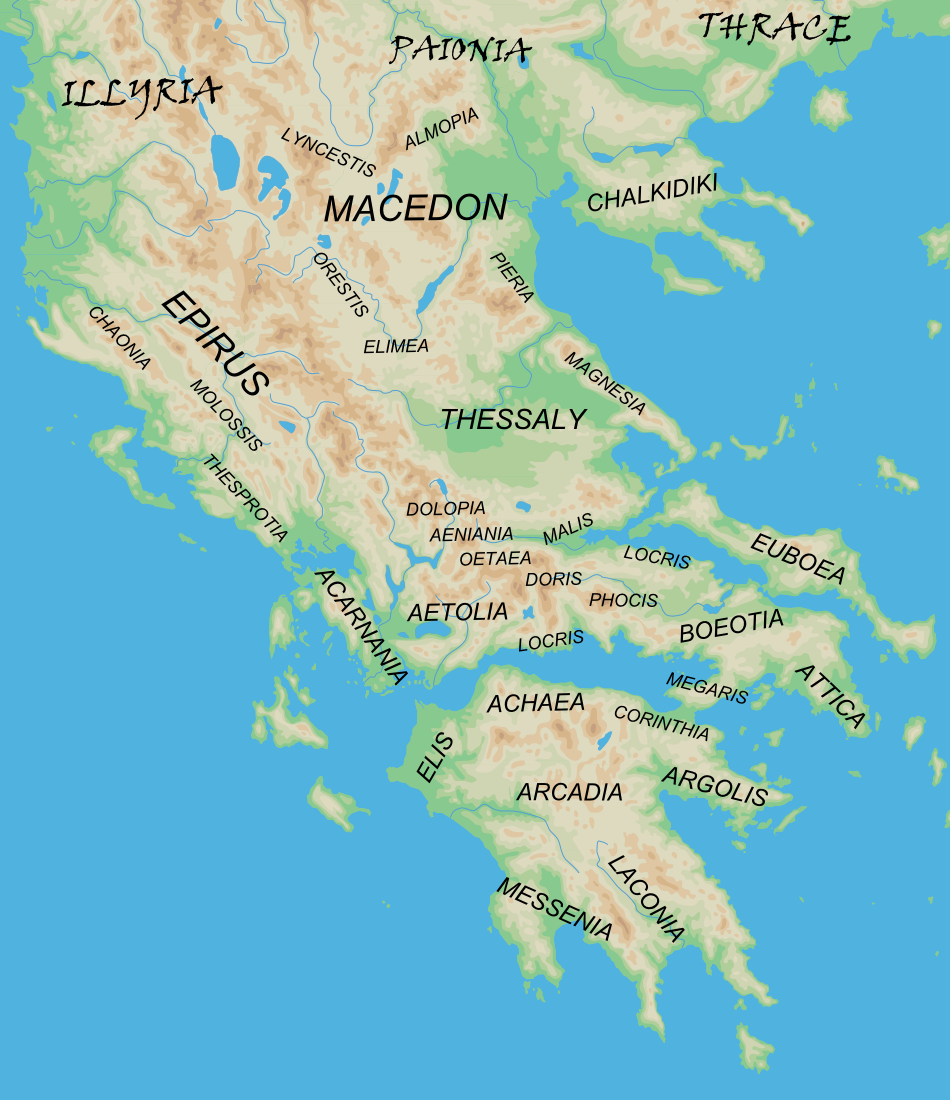
The Proto-Greeks probably arrived at the area now called Greece, in the southern tip of theBalkan peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, at the end of the 3rd millennium BC between 2200 and 1900 BC. The sequence of migrations into the Greek mainland during the 2nd millennium BC
File:2nd millennium BC montage.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: Hammurabi, Babylonian king, best known for his Code of Hammurabi, code of laws; The gold Mask of Tutankhamun, funerary mask of Tutankhamun has become a symbol of ancient Egypt ...
has to be reconstructed on the basis of the ancient Greek dialects
Ancient Greek in classical antiquity, before the development of the common Koine Greek of the Hellenistic period, was divided into several varieties.
Most of these varieties are known only from inscriptions, but a few of them, principally Aeolic ...
, as they presented themselves centuries later and are therefore subject to some uncertainties. There were at least two migrations, the first being the Ionians
The Ionians (; , ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the traditional four major tribes of Ancient Greece, alongside the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaeans. The Ionian dialect was one of the three major linguistic divisions of the ...
and Achaeans, which resulted in Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
by the 16th century BC, and the second, the Dorian invasion, around the 11th century BC, displacing the Arcadocypriot dialects, which descended from the Mycenaean period. Both migrations occur at incisive periods, the Mycenaean at the transition to the Late Bronze Age and the Doric at the Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a period of societal collapse in the Mediterranean basin during the 12th century BC. It is thought to have affected much of the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Egypt, Anatolia, the Aege ...
.
Mycenaean
In 1600 BC, the Mycenaean Greeks borrowed from theMinoan civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and energetic art, it is often regarded as the first civilization in Europe. The ruins of the Minoan palaces at K ...
its syllabic writing system (Linear A
Linear A is a writing system that was used by the Minoans of Crete from 1800 BC to 1450 BC. Linear A was the primary script used in Minoan palaces, palace and religious writings of the Minoan civilization. It evolved into Linear B, ...
) and developed their own syllabic script known as Linear B
Linear B is a syllabary, syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest Attested language, attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries, the earliest known examp ...
, providing the first and oldest written evidence of Greek. The Mycenaeans quickly penetrated the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
and, by the 15th century BC, had reached Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
, Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
and the shores of Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
.
Around 1200 BC, the Dorians
The Dorians (; , , singular , ) were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Greeks, Hellenes (or Greeks) of Classical Greece divided themselves (along with the Aeolians, Achaeans (tribe), Achaeans, and Ionians). They are almost alw ...
, another Greek-speaking people, followed from Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
. Older historical research often proposed Dorian invasion caused the collapse of the Mycenaean civilization, but this narrative has been abandoned in all contemporary research. It is likely that one of the factors which contributed to the Mycenaean palatial collapse was linked to raids by groups known in historiography as the " Sea Peoples" who sailed into the eastern Mediterranean around 1180 BC. The Dorian invasion was followed by a poorly attested period of migrations, appropriately called the Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Ages ( 1180–800 BC) were earlier regarded as two continuous periods of Greek history: the Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1180–1050 BC) and the Prehistoric Iron Age or Early Iron Age (c. 1050–800 BC). The last included all the ...
, but by 800 BC the landscape of Archaic and Classical Greece
Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries BC) in ancient Greece,The "Classical Age" is "the modern designation of the period from about 500 B.C. to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C." ( Thomas R. Mar ...
was discernible..
The Greeks of classical antiquity idealized their Mycenaean ancestors and the Mycenaean period as a glorious era of heroes, closeness of the gods and material wealth. The Homeric Epics (i.e. ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
'' and ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divi ...
'') were especially and generally accepted as part of the Greek past and it was not until the time of Euhemerism that scholars began to question Homer's historicity. As part of the Mycenaean heritage that survived, the names of the gods and goddesses of Mycenaean Greece (e.g. Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
, Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
and Hades
Hades (; , , later ), in the ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, is the god of the dead and the king of the Greek underworld, underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea ...
) became major figures of the Olympian Pantheon of later antiquity.
Classical
Theethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is the formation and development of an ethnic group. This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th-century neologism that was later introduce ...
of the Greek nation is linked to the development of Pan-Hellenism in the 8th century BC. According to some scholars, the foundational event was the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international Olympic sports, sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a Multi-s ...
in 776 BC, when the idea of a common Hellenism among the Greek tribes was first translated into a shared cultural experience and Hellenism was primarily a matter of common culture. The works of Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
(i.e. ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
'' and ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divi ...
'') and Hesiod
Hesiod ( or ; ''Hēsíodos''; ) was an ancient Greece, Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer.M. L. West, ''Hesiod: Theogony'', Oxford University Press (1966), p. 40.Jasper Gr ...
(i.e. ''Theogony
The ''Theogony'' () is a poem by Hesiod (8th–7th century BC) describing the origins and genealogy, genealogies of the Greek gods, composed . It is written in the Homeric Greek, epic dialect of Ancient Greek and contains 1,022 lines. It is one ...
'') were written in the 8th century BC, becoming the basis of the national religion, ethos, history and mythology. The Oracle of Apollo at Delphi was established in this period.
The classical period of Greek civilization covers a time spanning from the early 5th century BC to the death of Alexander the Great
The death of Alexander the Great and subsequent related events have been the subjects of debates. According to a Babylonian astronomical diaries, Babylonian astronomical diary, Alexander died in the palace of Nebuchadnezzar II in Babylon between ...
, in 323 BC (some authors prefer to split this period into "Classical", from the end of the Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Polis, Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world ...
to the end of the Peloponnesian War, and "Fourth Century", up to the death of Alexander). It is so named because it set the standards by which Greek civilization would be judged in later eras. The Classical period is also described as the "Golden Age" of Greek civilization, and its art, philosophy, architecture and literature would be instrumental in the formation and development of Western culture.
While the Greeks of the classical era understood themselves to belong to a common Hellenic genos, their first loyalty was to their city and they saw nothing incongruous about warring, often brutally, with other Greek city-states. The Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, the large scale civil war between the two most powerful Greek city-states Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
and Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ...
and their allies, left both greatly weakened.
 Most of the feuding Greek city-states were, in some scholars' opinions, united by force under the banner of
Most of the feuding Greek city-states were, in some scholars' opinions, united by force under the banner of Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male name derived from the Macedonian Old Koine language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominen ...
's and Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
's Pan-Hellenic ideals, though others might generally opt, rather, for an explanation of " Macedonian conquest for the sake of conquest" or at least conquest for the sake of riches, glory and power and view the "ideal" as useful propaganda directed towards the city-states.
In any case, Alexander's toppling of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
, after his victories at the battles of the Granicus, Issus and Gaugamela, and his advance as far as modern-day Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
and Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
, provided an important outlet for Greek culture, via the creation of colonies and trade routes along the way. While the Alexandrian empire did not survive its creator's death intact, the cultural implications of the spread of Hellenism across much of the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
and Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
were to prove long lived as Greek became the ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
'', a position it retained even in Roman times. Many Greeks settled in Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
cities like Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
, Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
and Seleucia
Seleucia (; ), also known as or or Seleucia ad Tigrim, was a major Mesopotamian city, located on the west bank of the Tigris River within the present-day Baghdad Governorate in Iraq. It was founded around 305 BC by Seleucus I Nicator as th ...
.
Hellenistic
 The
The Hellenistic civilization
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
was the next period of Greek civilization, the beginnings of which are usually placed at Alexander's death. This Hellenistic age, so called because it saw the partial Hellenization
Hellenization or Hellenification is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language, and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonisation often led to the Hellenisation of indigenous people in the Hellenistic period, many of the ...
of many non-Greek cultures, extending all the way into India and Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
, both of which maintained Greek cultures and governments for centuries. The end is often placed around conquest of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
by Rome in 30 BC, although the Indo-Greek kingdoms lasted for a few more decades.
This age saw the Greeks move towards larger cities and a reduction in the importance of the city-state. These larger cities were parts of the still larger Kingdoms of the Diadochi. Greeks, however, remained aware of their past, chiefly through the study of the works of Homer and the classical authors.. An important factor in maintaining Greek identity was contact with '' barbarian'' (non-Greek) peoples, which was deepened in the new cosmopolitan environment of the multi-ethnic Hellenistic kingdoms. This led to a strong desire among Greeks to organize the transmission of the Hellenic '' paideia'' to the next generation. Greek science, technology and mathematics are generally considered to have reached their peak during the Hellenistic period.
In the Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
and Greco-Bactrian kingdoms, Greco-Buddhism was spreading and Greek missionaries would play an important role in propagating it to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. Further east, the Greeks of Alexandria Eschate became known to the Chinese people
The Chinese people, or simply Chinese, are people or ethnic groups identified with Greater China, China, usually through ethnicity, nationality, citizenship, or other affiliation.
Chinese people are known as Zhongguoren () or as Huaren () by ...
as the Dayuan.
Roman Empire
Between 168 BC and 30 BC, the entire Greek world was conquered by Rome, and almost all of the world's Greek speakers lived as citizens or subjects of the Roman Empire. Despite their military superiority, the Romans admired and became heavily influenced by the achievements of Greek culture, henceHorace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 BC – 27 November 8 BC), Suetonius, Life of Horace commonly known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). Th ...
's famous statement: ''Graecia capta ferum victorem cepit'' ("Greece, although captured, took its wild conqueror captive"). In the centuries following the Roman conquest of the Greek world, the Greek and Roman cultures merged into a single Greco-Roman culture.
In the religious sphere, this was a period of profound change. The spiritual revolution that took place, saw a waning of the old Greek religion, whose decline beginning in the 3rd century BC continued with the introduction of new religious movements from the East. The cults of deities like Isis
Isis was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her sla ...
and Mithra were introduced into the Greek world. Greek-speaking communities of the Hellenized East were instrumental in the spread of early Christianity in the 2nd and 3rd centuries, and Christianity's early leaders and writers (notably Saint Paul) were generally Greek-speaking, though none were from Greece proper. However, Greece itself had a tendency to cling to paganism and was not one of the influential centers of early Christianity: in fact, some ancient Greek religious practices remained in vogue until the end of the 4th century, with some areas such as the southeastern Peloponnese remaining pagan until well into the mid-Byzantine 10th century AD. The region of Tsakonia remained pagan until the ninth century and as such its inhabitants were referred to as ''Hellenes'', in the sense of being pagan, by their Christianized Greek brethren in mainstream Byzantine society.
While ethnic distinctions still existed in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, they became secondary to religious considerations, and the renewed empire used Christianity as a tool to support its cohesion and promote a robust Roman national identity. From the early centuries of the Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the ...
, the Greeks self-identified as Romans ( Greek: ''Rhōmaîoi''). By that time, the name ''Hellenes'' denoted pagans but was revived as an ethnonym in the 11th century..
Middle Ages

 During most of the Middle Ages, the Byzantine Greeks self-identified as ''Rhōmaîoi'' (, "Romans", meaning
During most of the Middle Ages, the Byzantine Greeks self-identified as ''Rhōmaîoi'' (, "Romans", meaning citizens
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationality; ...
of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
), a term which in the Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
had become synonymous with Christian Greeks.: "Roman, Greek (if not used in its sense of 'pagan') and Christian became synonymous terms, counterposed to 'foreigner', 'barbarian', 'infidel'. The citizens of the Empire, now predominantly of Greek ethnicity and language, were often called simply ό χριστώνυμος λαός the people who bear Christ's name'" The Latinizing term ''Graikoí'' (Γραικοί, "Greeks") was also used, though its use was less common, and nonexistent in official Byzantine political correspondence, prior to the Fourth Crusade of 1204. The Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
(today conventionally named the ''Byzantine Empire'', a name not used during its own time) became increasingly influenced by Greek culture after the 7th century when Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
( 610–641 AD) decided to make Greek the empire's official language.. Although the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
recognized the Eastern Empire's claim to the Roman legacy for several centuries, after Pope Leo III crowned Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
, king of the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
, as the " Roman Emperor" on 25 December 800, an act which eventually led to the formation of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, the Latin West started to favour the Franks and began to refer to the Eastern Roman Empire largely as the ''Empire of the Greeks'' (''Imperium Graecorum''). While this Latin term for the ancient '' Hellenes'' could be used neutrally, its use by Westerners from the 9th century onwards in order to challenge Byzantine claims to ancient Roman
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
heritage rendered it a derogatory exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
for the Byzantines who barely used it, mostly in contexts relating to the West, such as texts relating to the Council of Florence, to present the Western viewpoint. Additionally, among the Germanic and the Slavic peoples, the ''Rhōmaîoi'' were just called Greeks.
There are three schools of thought regarding this Byzantine Roman identity in contemporary Byzantine scholarship: The first considers "Romanity" the mode of self-identification of the subjects of a multi-ethnic empire at least up to the 12th century, where the average subject identified as Roman; a perennialist approach, which views Romanity as the medieval expression of a continuously existing Greek nation; while a third view considers the eastern Roman identity as a pre-modern national identity. The Byzantine Greeks' essential values were drawn from both Christianity and the Homeric tradition of ancient Greece..
A distinct Greek identity re-emerged in the 11th century in educated circles and became more forceful after the fall of Constantinople to the Crusaders of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
in 1204. In the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea (), also known as the Nicene Empire, was the largest of the three Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by Walter Abel Heurtley, W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C ...
, a small circle of the elite used the term "Hellene" as a term of self-identification. For example, in a letter to Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX (; born Ugolino di Conti; 1145 – 22 August 1241) was head of the Catholic Church and the ruler of the Papal States from 19 March 1227 until his death in 1241. He is known for issuing the '' Decretales'' and instituting the Pa ...
, the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes (r. 1221–1254) claimed to have received the gift of royalty from Constantine the Great, and put emphasis on his "Hellenic" descent, exalting the wisdom of the Greek people. After the Byzantines recaptured Constantinople, however, in 1261, ''Rhomaioi'' became again dominant as a term for self-description and there are few traces of ''Hellene'' (Έλληνας), such as in the writings of George Gemistos Plethon, who abandoned Christianity and in whose writings culminated the secular tendency in the interest in the classical past. However, it was the combination of Orthodox Christianity with a specifically Greek identity that shaped the Greeks' notion of themselves in the empire's twilight years. In the twilight years of the Byzantine Empire, prominent Byzantine personalities proposed referring to the Byzantine Emperor as the "Emperor of the Hellenes". These largely rhetorical expressions of Hellenic identity were confined within intellectual circles, but were continued by Byzantine intellectuals who participated in the Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( ) was a period in History of Italy, Italian history between the 14th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Western Europe and marked t ...
.
The interest in the Classical Greek heritage was complemented by a renewed emphasis on Greek Orthodox
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Greek Christianity, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christians or more broadly the rite used in the Eastern Rom ...
identity, which was reinforced in the late Medieval and Ottoman Greeks' links with their fellow Orthodox Christians in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
. These were further strengthened following the fall of the Empire of Trebizond in 1461, after which and until the second Russo-Turkish War of 1828–29 hundreds of thousands of Pontic Greeks fled or migrated from the Pontic Alps and Armenian Highlands
The Armenian highlands (; also known as the Armenian upland, Armenian plateau, or Armenian tableland)Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: ...
to southern Russia and the Russian South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
(see also Greeks in Russia, Greeks in Armenia, Greeks in Georgia, and Caucasian Greeks).
These Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Medieval Greek, Greek-speaking Eastern Romans throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople and Asia ...
were largely responsible for the preservation of the literature of the classical era.. Byzantine grammarians were those principally responsible for carrying, in person and in writing, ancient Greek grammatical and literary studies to the West during the 15th century, giving the Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( ) was a period in History of Italy, Italian history between the 14th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Western Europe and marked t ...
a major boost. The Aristotelian philosophical tradition was nearly unbroken in the Greek world for almost two thousand years, until the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
in 1453.
To the Slavic world, the Byzantine Greeks contributed by the dissemination of literacy and Christianity. The most notable example of the later was the work of the two Byzantine Greek brothers, the monks Saints Cyril and Methodius
Cyril (; born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (; born Michael, 815–885) were brothers, Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
They are ...
from the port city of Thessalonica, capital of the theme of Thessalonica, who are credited today with formalizing the first Slavic alphabet.
Ottoman Empire
 Following the
Following the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
on 29 May 1453, many Greeks sought better employment and education opportunities by leaving for the West, particularly Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. Greeks are greatly credited for the European cultural revolution, later called the Renaissance. In Greek-inhabited territory itself, Greeks came to play a leading role in the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, due in part to the fact that the central hub of the empire, politically, culturally, and socially, was based on Western Thrace and Macedonia, both in Northern Greece, and of course was centred on the mainly Greek-populated, former Byzantine capital, Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. As a direct consequence of this situation, Greek-speakers came to play a hugely important role in the Ottoman trading and diplomatic establishment, as well as in the church. Added to this, in the first half of the Ottoman period men of Greek origin made up a significant proportion of the Ottoman army, navy, and state bureaucracy, having been levied as adolescents (along with especially Albanians
The Albanians are an ethnic group native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, Albanian culture, culture, Albanian history, history and Albanian language, language. They are the main ethnic group of Albania and Kosovo, ...
and Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
) into Ottoman service through the devshirme. Many Ottomans of Greek (or Albanian or Serb) origin were therefore to be found within the Ottoman forces which governed the provinces, from Ottoman Egypt, to Ottomans occupied Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
and Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, frequently as provincial governors.
For those that remained under the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
's millet system, religion was the defining characteristic of national groups (''milletler''), so the exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
"Greeks" (''Rumlar'' from the name Rhomaioi) was applied by the Ottomans to all members of the Orthodox Church, regardless of their language or ethnic origin. The Greek speakers were the only ethnic group to actually call themselves ''Romioi'', (as opposed to being so named by others) and, at least those educated, considered their ethnicity (''genos'') to be Hellenic. There were, however, many Greeks who escaped the second-class status of Christians inherent in the Ottoman millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.
Millets are important crops in the Semi-arid climate, ...
system, according to which Muslims were explicitly awarded senior status and preferential treatment. These Greeks either emigrated, particularly to their fellow Orthodox Christian protector, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, or simply converted to Islam, often only very superficially and whilst remaining crypto-Christian. The most notable examples of large-scale conversion to Turkish Islam among those today defined as Greek Muslims
Greek Muslims, also known as Grecophone Muslims, are Muslims of Greeks, Greek ethnic origin whose adoption of Islam (and often the Turkish language and identity in more recent times) dates either from the contact of early Arabic dynasties of th ...
—excluding those who had to convert as a matter of course on being recruited through the devshirme—were to be found in Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
( Cretan Turks), Greek Macedonia (for example among the Vallahades of western Macedonia), and among Pontic Greeks in the Pontic Alps and Armenian Highlands
The Armenian highlands (; also known as the Armenian upland, Armenian plateau, or Armenian tableland)Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: ...
. Several Ottoman sultans and princes were also of part Greek origin, with mothers who were either Greek concubines or princesses from Byzantine noble families, one famous example being sultan Selim the Grim ( 1517–1520), whose mother Gülbahar Hatun was a Pontic Greek.
 The roots of Greek success in the Ottoman Empire can be traced to the Greek tradition of education and commerce exemplified in the Phanariotes. It was the wealth of the extensive merchant class that provided the material basis for the intellectual revival that was the prominent feature of Greek life in the half century and more leading to the outbreak of the
The roots of Greek success in the Ottoman Empire can be traced to the Greek tradition of education and commerce exemplified in the Phanariotes. It was the wealth of the extensive merchant class that provided the material basis for the intellectual revival that was the prominent feature of Greek life in the half century and more leading to the outbreak of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
in 1821. Not coincidentally, on the eve of 1821, the three most important centres of Greek learning were situated in Chios
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greece, Greek list of islands of Greece, island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, tenth largest island in the Medi ...
, Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; , or ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna ...
and Aivali, all three major centres of Greek commerce. Greek success was also favoured by Greek domination in the leadership of the Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
church.
Modern
The movement of the Greek enlightenment, the Greek expression of theAge of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
, contributed not only in the promotion of education, culture and printing among the Greeks, but also in the case of independence from the Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
, and the restoration of the term "Hellene". Adamantios Korais, probably the most important intellectual of the movement, advocated the use of the term "Hellene" (Έλληνας) or "Graikos" (Γραικός) in the place of ''Romiós'', that was seen negatively by him.
The relationship between ethnic Greek identity and Greek Orthodox
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Greek Christianity, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christians or more broadly the rite used in the Eastern Rom ...
religion continued after the creation of the modern Greek nation-state in 1830. According to the second article of the first Greek constitution
The Constitution of Greece () was created by the Fifth Revisionary Hellenic Parliament in 1974, after the fall of the Greek junta and the start of the Third Hellenic Republic. It came into force on 11 June 1975 (adopted two days prior) and has ...
of 1822, a Greek was defined as any native Christian resident of the Kingdom of Greece
The Kingdom of Greece (, Romanization, romanized: ''Vasíleion tis Elládos'', pronounced ) was the Greece, Greek Nation state, nation-state established in 1832 and was the successor state to the First Hellenic Republic. It was internationally ...
, a clause removed by 1840. A century later, when the Treaty of Lausanne was signed between Greece and Turkey in 1923, the two countries agreed to use religion as the determinant for ethnic identity for the purposes of population exchange, although most of the Greeks displaced (over a million of the total 1.5 million) had already been driven out by the time the agreement was signed. The Greek genocide, in particular the harsh removal of Pontian Greeks from the southern shore area of the Black Sea, contemporaneous with and following the failed Greek Asia Minor Campaign, was part of this process of Turkification
Turkification, Turkization, or Turkicization () describes a shift whereby populations or places receive or adopt Turkic attributes such as culture, language, history, or ethnicity. However, often this term is more narrowly applied to mean specif ...
of the Ottoman Empire and the placement of its economy and trade, then largely in Greek hands under ethnic Turkish control.
Identity
 The terms used to define Greekness have varied throughout history but were never limited or completely identified with membership to a Greek state.
The terms used to define Greekness have varied throughout history but were never limited or completely identified with membership to a Greek state. Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
gave a famous account of what defined Greek (Hellenic) ethnic identity in his day, enumerating
#shared descent ()
#shared language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
()
#shared sanctuaries and sacrifices ()
#shared customs
Customs is an authority or Government agency, agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling International trade, the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out ...
().
By Western standards, the term ''Greeks'' has traditionally referred to any native speakers of the Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
, whether Mycenaean, Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
or modern Greek
Modern Greek (, or , ), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the language sometimes referred to ...
.. Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Medieval Greek, Greek-speaking Eastern Romans throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople and Asia ...
self-identified as ''Romaioi'' ("Romans"), ''Graikoi'' ("Greeks") and ''Christianoi'' ("Christians") since they were the political heirs of imperial Rome, the descendants of their classical Greek forebears and followers of the Apostles; during the mid-to-late Byzantine period (11th–13th century), a growing number of Byzantine Greek intellectuals deemed themselves ''Hellenes'' although for most Greek-speakers, "Hellene" still meant pagan. On the eve of the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
the Last Emperor urged his soldiers to remember that they were the descendants of Greeks and Romans.
Before the establishment of the modern Greek nation-state, the link between ancient and modern Greeks was emphasized by the scholars of Greek Enlightenment especially by Rigas Feraios. In his "Political Constitution", he addresses to the nation as "the people descendant of the Greeks". The modern Greek state was created in 1829, when the Greeks liberated a part of their historic homelands, Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
, from the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. The large Greek diaspora
The Greek diaspora, also known as Omogenia (), are the communities of Greeks living outside of Greece and Cyprus.
Such places historically (dating to the ancient period) include, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in North Macedonia, North Maced ...
and merchant class were instrumental in transmitting the ideas of western romantic nationalism and philhellenism, which together with the conception of Hellenism, formulated during the last centuries of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, formed the basis of the Diafotismos and the current conception of Hellenism.
The Greeks today are a nation in the meaning of an '' ethnos'', defined by possessing Greek culture and having a Greek mother tongue, not by citizenship, race, and religion or by being subjects of any particular state. In ancient and medieval times and to some extent today the Greek term was '' genos'', which also indicates a common ancestry.
Names
 Greeks and Greek-speakers have used different names to refer to themselves collectively. The term (Ἀχαιοί) is one of the collective names for the Greeks in
Greeks and Greek-speakers have used different names to refer to themselves collectively. The term (Ἀχαιοί) is one of the collective names for the Greeks in Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
's ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
'' and ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divi ...
'' (the Homeric "long-haired Achaeans" would have been a part of the Mycenaean civilization that dominated Greece from 1600 BC until 1100 BC). The other common names are (Δαναοί) and (Ἀργεῖοι) while (Πανέλληνες) and (Ἕλληνες) both appear only once in the ''Iliad''; all of these terms were used, synonymously, to denote a common Greek identity. In the historical period, Herodotus identified the Achaeans of the northern Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
as descendants of the earlier, Homeric Achaeans.
Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
refers to the "Hellenes" as a relatively small tribe settled in Thessalic Phthia, with its warriors under the command of Achilleus. The Parian Chronicle says that Phthia was the homeland of the Hellenes and that this name was given to those previously called Greeks ().The Parian Marble, Entry #6: "From when Hellen on ofDeuc
lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
became king of hthitis and those previously called Graekoi were named Hellenes." In Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
, Hellen
In Greek mythology, Hellen (; ) is the eponymous progenitor of the Greeks, Hellenes. He is the son of Deucalion (or Zeus) and Pyrrha, and the father of three sons, Dorus, Xuthus, and Aeolus (son of Hellen), Aeolus, by whom he is the ancestor of t ...
, the patriarch of the Hellenes who ruled around Phthia, was the son of Pyrrha
In Greek mythology, Pyrrha (; ) was the daughter of Epimetheus and Pandora and wife of Deucalion of whom she had three sons, Hellen, Amphictyon, Orestheus; and three daughters Protogeneia, Pandora and Thyia. According to some accounts, Hell ...
and Deucalion
In Greek mythology, Deucalion (; ) was the son of Prometheus; ancient sources name his mother as Clymene (mythology), Clymene, Hesione (Oceanid), Hesione, or Pronoia (mythology), Pronoia.A Scholia, scholium to ''Odyssey'' 10.2 (=''Catalogue of W ...
, the only survivors after the Great Deluge. The Greek philosopher Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
names ancient Hellas as an area in Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
between Dodona
Dodona (; , Ionic Greek, Ionic and , ) in Epirus in northwestern Greece was the oldest Ancient Greece, Hellenic oracle, possibly dating to the 2nd millennium BCE according to Herodotus. The earliest accounts in Homer describe Dodona as an oracle ...
and the Achelous
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Achelous (also Acheloos or Acheloios) (; Ancient Greek: Ἀχελώϊος, and later , ''Akhelôios'') was the god associated with the Achelous River, the largest river in Greece. Accordi ...
river, the location of the Great Deluge of Deucalion
In Greek mythology, Deucalion (; ) was the son of Prometheus; ancient sources name his mother as Clymene (mythology), Clymene, Hesione (Oceanid), Hesione, or Pronoia (mythology), Pronoia.A Scholia, scholium to ''Odyssey'' 10.2 (=''Catalogue of W ...
, a land occupied by the Selloi and the "Greeks" who later came to be known as "Hellenes".Aristotle. ''Meteorologica''1.14
: "The deluge in the time of Deucalion, for instance took place chiefly in the Greek world and in it especially about ancient Hellas, the country about Dodona and the Achelous." In the Homeric tradition, the Selloi were the priests of Dodonian Zeus. In the
Hesiod
Hesiod ( or ; ''Hēsíodos''; ) was an ancient Greece, Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer.M. L. West, ''Hesiod: Theogony'', Oxford University Press (1966), p. 40.Jasper Gr ...
ic ''Catalogue of Women
The ''Catalogue of Women'' ()—also known as the ''Ehoiai '' (, )The Latin transliterations ''Eoeae'' and ''Ehoeae'' are also used (e.g. , ); see Catalogue of Women#Title and the ē' hoiē-formula, Title and the ''ē' hoiē''-formula, below. Th ...
'', Graecus is presented as the son of Zeus and Pandora II, sister of Hellen
In Greek mythology, Hellen (; ) is the eponymous progenitor of the Greeks, Hellenes. He is the son of Deucalion (or Zeus) and Pyrrha, and the father of three sons, Dorus, Xuthus, and Aeolus (son of Hellen), Aeolus, by whom he is the ancestor of t ...
the patriarch of the Hellenes. According to the Parian Chronicle, when Deucalion
In Greek mythology, Deucalion (; ) was the son of Prometheus; ancient sources name his mother as Clymene (mythology), Clymene, Hesione (Oceanid), Hesione, or Pronoia (mythology), Pronoia.A Scholia, scholium to ''Odyssey'' 10.2 (=''Catalogue of W ...
became king of Phthia, the (Γραικοί) were named Hellenes. Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
notes in his ''Meteorologica'' that the Hellenes were related to the Graikoi.
Etymology
The English names ''Greece'' and ''Greek'' are derived, via the Latin ' and ', from the name of the Graeci (, ; singular , ), who were among the first ancient Greek tribes to settlesouthern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
(the so-called "Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
"). The term is possibly derived from the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
root '' *ǵerh₂-'', "to grow old", more specifically from Graea (ancient city), said by Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
to be the oldest in Greece, and the source of colonists for the Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
area.
Continuity
The most obvious link between modern and ancient Greeks is their language, which has a documented tradition from at least the 14th century BC to the present day, albeit with a break during theGreek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Ages ( 1180–800 BC) were earlier regarded as two continuous periods of Greek history: the Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1180–1050 BC) and the Prehistoric Iron Age or Early Iron Age (c. 1050–800 BC). The last included all the ...
from which written records are absent (11th–8th cent. BC, though the Cypriot syllabary
The Cypriot or Cypriote syllabary (also Classical Cypriot Syllabary) is a syllabary, syllabic script used in Iron Age Cyprus, from about the 11th to the 4th centuries BCE, when it was replaced by the Greek alphabet. It has been suggested that t ...
was in use during this period).. Scholars compare its continuity of tradition to Chinese alone. Since its inception, Hellenism was primarily a matter of common culture and the national continuity of the Greek world is a lot more certain than its demographic.. Yet, Hellenism also embodied an ancestral dimension through aspects of Athenian literature that developed and influenced ideas of descent based on autochthony. During the later years of the Eastern Roman Empire, areas such as Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
and Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
experienced a Hellenic revival in language, philosophy, and literature and on classical models of thought and scholarship. This revival provided a powerful impetus to the sense of cultural affinity with ancient Greece and its classical heritage. Throughout their history, the Greeks have retained their language and alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
, certain values and cultural traditions, customs, a sense of religious and cultural difference and exclusion (the word '' barbarian'' was used by 12th-century historian Anna Komnene to describe non-Greek speakers), a sense of Greek identity and common sense of ethnicity despite the undeniable socio-political changes of the past two millennia. In recent anthropological studies, both ancient and modern Greek osteological samples were analyzed demonstrating a bio-genetic affinity and continuity shared between both groups. There is also a direct genetic link between ancient Greeks and modern Greeks.
Demographics
Today, Greeks are the majority ethnic group in theHellenic Republic
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, where they constitute 93% of the country's population, and the Republic of Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the third lar ...
where they make up 78% of the island's population (excluding Turkish settlers in the occupied part of the country). Greek populations have not traditionally exhibited high rates of growth; a large percentage of Greek population growth since Greece's foundation in 1832 was attributed to annexation of new territories, as well as the influx of 1.5 million Greek refugees after the 1923 population exchange between Greece and Turkey. About 80% of the population of Greece is urban, with 28% concentrated in the city of Athens.
Greeks from Cyprus have a similar history of emigration, usually to the English-speaking world because of the island's colonization by the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
. Waves of emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
followed the Turkish invasion of Cyprus
The Turkish invasion of Cyprus began on 20 July 1974 and progressed in two phases over the following month. Taking place upon a background of Cypriot intercommunal violence, intercommunal violence between Greek Cypriots, Greek and Turkish Cy ...
in 1974, while the population decreased between mid-1974 and 1977 as a result of emigration, war losses, and a temporary decline in fertility. After the ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, or religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making the society ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal such as deportation or population transfer, it ...
of a third of the Greek population of the island in 1974, there was also an increase in the number of Greek Cypriots leaving, especially for the Middle East, which contributed to a decrease in population that tapered off in the 1990s. Today more than two-thirds of the Greek population in Cyprus is urban.
Around 1990, most Western estimates of the number of ethnic Greeks in Albania were around 200,000 but in the 1990s, a majority of them migrated to Greece. The Greek minority of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, which numbered upwards of 200,000 people after the 1923 exchange, has now dwindled to a few thousand, after the 1955 Constantinople Pogrom and other state sponsored violence and discrimination. This effectively ended, though not entirely, the three-thousand-year-old presence of Hellenism in Asia Minor. There are smaller Greek minorities in the rest of the Balkan countries, the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
states, remnants of the Old Greek Diaspora
The Greek diaspora, also known as Omogenia (), are the communities of Greeks living outside of Greece and Cyprus.
Such places historically (dating to the ancient period) include, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in North Macedonia, North Maced ...
(pre-19th century).
Diaspora
 The total number of Greeks living outside Greece and Cyprus today is a contentious issue. Where census figures are available, they show around three million Greeks outside Greece and Cyprus. Estimates provided by the SAE – World Council of Hellenes Abroad put the figure at around seven million worldwide. According to George Prevelakis of Sorbonne University, the number is closer to just below five million. Integration, intermarriage, and loss of the Greek language influence the self-identification of the Greek diaspora (''omogenia''). Important centres include
The total number of Greeks living outside Greece and Cyprus today is a contentious issue. Where census figures are available, they show around three million Greeks outside Greece and Cyprus. Estimates provided by the SAE – World Council of Hellenes Abroad put the figure at around seven million worldwide. According to George Prevelakis of Sorbonne University, the number is closer to just below five million. Integration, intermarriage, and loss of the Greek language influence the self-identification of the Greek diaspora (''omogenia''). Important centres include New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
, Sydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
, Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
, London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
, Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
, Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
, Auckland
Auckland ( ; ) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. It has an urban population of about It is located in the greater Auckland Region, the area governed by Auckland Council, which includes outlying rural areas and ...
, and Sao Paulo. In 2010, the Hellenic Parliament introduced a law that allowed members of the diaspora to vote in Greek elections; this law was repealed in early 2014.
Ancient
In ancient times, the trading and colonizing activities of the Greek tribes and city states spread the Greek culture, religion and language around the Mediterranean and Black Sea basins, especially inSouthern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
(the so-called "Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
"), Spain, the south of France
Southern France, also known as the south of France or colloquially in French as , is a geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi atlantique'', Atlas e ...
and the Black sea coasts.. Under Alexander the Great's empire and successor states, Greek and Hellenizing ruling classes were established in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. The Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
is characterized by a new wave of Greek colonization that established Greek cities and kingdoms in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
. Under the Roman Empire, easier movement of people spread Greeks across the Empire and in the eastern territories, Greek became the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
rather than Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
. The modern-day Griko community of southern Italy, numbering about 60,000, may represent a living remnant of the ancient Greek populations of Italy.
Modern

 During and after the
During and after the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
, Greeks of the diaspora were important in establishing the fledgling state, raising funds and awareness abroad. Greek merchant families already had contacts in other countries and during the disturbances many set up home around the Mediterranean (notably Marseilles in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Livorno in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Alexandria in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
), Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(Odesa
Odesa, also spelled Odessa, is the third most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern ...
and Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
), and Britain (London and Liverpool) from where they traded, typically in textiles and grain.. Businesses frequently comprised the extended family, and with them they brought schools teaching Greek and the Greek Orthodox Church
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Christianity in Greece, Greek Christianity, Antiochian Greek Christians, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christian ...
.
As markets changed and they became more established, some families grew their operations to become shippers, financed through the local Greek community, notably with the aid of the Ralli or Vagliano Brothers.. With economic success, the Diaspora expanded further across the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, North Africa, India and the USA.
In the 20th century, many Greeks left their traditional homelands for economic reasons resulting in large migrations from Greece and Cyprus to the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, especially after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
(1939–1945), the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
(1946–1949), and the Turkish Invasion of Cyprus
The Turkish invasion of Cyprus began on 20 July 1974 and progressed in two phases over the following month. Taking place upon a background of Cypriot intercommunal violence, intercommunal violence between Greek Cypriots, Greek and Turkish Cy ...
in 1974.
While official figures remain scarce, polls and anecdotal evidence point to renewed Greek emigration as a result of the Greek financial crisis. According to data published by the Federal Statistical Office of Germany
The Federal Statistical Office (, shortened ''Destatis'') is a federal authority of Germany. It reports to the Federal Ministry of the Interior.
The Office is responsible for collecting, processing, presenting and analysing statistical informati ...
in 2011, 23,800 Greeks emigrated to Germany, a significant increase over the previous year. By comparison, about 9,000 Greeks emigrated to Germany in 2009 and 12,000 in 2010.
Culture
Greek culture has evolved over thousands of years, with its beginning in the Mycenaean civilization, continuing through the classical era, the Hellenistic period, the Roman and Byzantine periods and was profoundly affected by Christianity, which it in turn influenced and shaped.; Ottoman Greeks had to endure through several centuries of adversity that culminated ingenocide
Genocide is violence that targets individuals because of their membership of a group and aims at the destruction of a people. Raphael Lemkin, who first coined the term, defined genocide as "the destruction of a nation or of an ethnic group" by ...
in the 20th century. The Diafotismos is credited with revitalizing Greek culture and giving birth to the synthesis of ancient and medieval elements that characterize it today.
Language
 Most Greeks speak the
Most Greeks speak the Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
, an independent branch of the Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
, with its closest relations possibly being Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
(see Graeco-Armenian) or the Indo-Iranian languages
The Indo-Iranian languages (also known as Indo-Iranic languages or collectively the Aryan languages) constitute the largest branch of the Indo-European language family. They include over 300 languages, spoken by around 1.7 billion speakers ...
(see Graeco-Aryan
Graeco-Aryan, or Graeco-Armeno-Aryan, is a hypothetical clade within the Indo-European family that would be the ancestor of Hellenic, Armenian, and the Indo-Iranian languages, which spans Southern Europe, Armenian highlands and Southern Asi ...
). It has the longest documented history of any living language and Greek literature
Greek literature () dates back from the ancient Greek literature, beginning in 800 BC, to the modern Greek literature of today.
Ancient Greek literature was written in an Ancient Greek dialect, literature ranges from the oldest surviving wri ...
has a continuous history of over 2,500 years. The oldest inscriptions in Greek are in the Linear B
Linear B is a syllabary, syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest Attested language, attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries, the earliest known examp ...
script, dated as far back as 1450 BC. Following the Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Ages ( 1180–800 BC) were earlier regarded as two continuous periods of Greek history: the Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1180–1050 BC) and the Prehistoric Iron Age or Early Iron Age (c. 1050–800 BC). The last included all the ...
, from which written records are absent, the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as wel ...
appears in the 9th–8th century BC. The Greek alphabet derived from the Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an abjad (consonantal alphabet) used across the Mediterranean civilization of Phoenicia for most of the 1st millennium BC. It was one of the first alphabets, attested in Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions fo ...
, and in turn became the parent alphabet of the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
, and several other alphabets. The earliest Greek literary works are the Homeric epics, variously dated from the 8th to the 6th century BC. Notable scientific and mathematical works include Euclid's Elements
The ''Elements'' ( ) is a mathematics, mathematical treatise written 300 BC by the Ancient Greek mathematics, Ancient Greek mathematician Euclid.
''Elements'' is the oldest extant large-scale deductive treatment of mathematics. Drawing on the w ...
, Ptolemy's Almagest, and others. The New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
was originally written in Koine Greek
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the koiné language, common supra-regional form of Greek language, Greek spoken and ...
.
Greek demonstrates several linguistic features that are shared with other Balkan languages, such as Albanian, Bulgarian and Eastern Romance languages (see Balkan sprachbund), and has absorbed many foreign words, primarily of Western European and Turkish origin. Because of the movements of Philhellenism and the Diafotismos in the 19th century, which emphasized the modern Greeks' ancient heritage, these foreign influences were excluded from official use via the creation of Katharevousa
Katharevousa (, , literally "purifying anguage) is a conservative form of the Modern Greek language conceived in the late 18th century as both a literary language and a compromise between Ancient Greek and the contemporary vernacular, Demotic ...
, a somewhat artificial form of Greek purged of all foreign influence and words, as the official language of the Greek state. In 1976, however, the Hellenic Parliament
The Parliament of the Hellenes (), commonly known as the Hellenic Parliament (), is the Unicameralism, unicameral legislature of Greece, located in the Old Royal Palace, overlooking Syntagma Square in Athens. The parliament is the supreme demo ...
voted to make the spoken Dimotiki the official language, making Katharevousa obsolete.
Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, or , ), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the language sometimes referred to ...
has, in addition to Standard Modern Greek or Dimotiki, a wide variety of dialects of varying levels of mutual intelligibility, including Cypriot, Pontic, Cappadocian, Griko
Griko (endonym: /), sometimes spelled Grico, is one of the two dialects of Italiot Greek (the other being Calabrian Greek or ), spoken by Griko people in Salento, province of Lecce, Italy. Some Greek linguists consider it to be a Modern Greek ...
and Tsakonian (the only surviving representative of ancient Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greec ...
). Yevanic is the language of the Romaniotes, and survives in small communities in Greece, New York and Israel. In addition to Greek, many Greek citizens in Greece and the diaspora are bilingual in other languages such as English, Arvanitika/Albanian, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, Macedonian Slavic, Russian and Turkish.
Religion
Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, belonging to the Greek Orthodox Church
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Christianity in Greece, Greek Christianity, Antiochian Greek Christians, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christian ...
. During the first centuries after Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
, the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
was originally written in Koine Greek
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the koiné language, common supra-regional form of Greek language, Greek spoken and ...
, which remains the liturgical language of the Greek Orthodox Church, and most of the early Christians and Church Fathers were Greek-speaking. There are small groups of ethnic Greeks adhering to other Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
denominations like Latin-rite and Greek Byzantine-rite Roman Catholics, Greek Evangelicals, Pentecostals, Mormons
Mormons are a Religious denomination, religious and ethnocultural group, cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's d ...
, and groups adhering to other religions including Romaniot and Sephardic Jews
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
, Greek Muslims
Greek Muslims, also known as Grecophone Muslims, are Muslims of Greeks, Greek ethnic origin whose adoption of Islam (and often the Turkish language and identity in more recent times) dates either from the contact of early Arabic dynasties of th ...
and Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co-fou ...
. About 2,000 Greeks are members of Hellenic Polytheistic Reconstructionism congregations.
Greek-speaking Muslims live mainly outside Greece in the contemporary era. There are both Christian and Muslim Greek-speaking communities in Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
and Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, while in the Pontus region of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
there is a large community of indeterminate size who were spared from the population exchange because of their religious affiliation.
Arts
 Greek art has a long and varied history. Greeks have contributed to the visual, literary and performing arts.. In the West, classical Greek art was influential in shaping the Roman and later the modern Western artistic heritage. Following the
Greek art has a long and varied history. Greeks have contributed to the visual, literary and performing arts.. In the West, classical Greek art was influential in shaping the Roman and later the modern Western artistic heritage. Following the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, the humanist aesthetic and the high technical standards of Greek art inspired generations of European artists. Well into the 19th century, the classical tradition derived from Greece played an important role in the art of the Western world. In the East, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
's conquests initiated several centuries of exchange between Greek, Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
n and Indian cultures, resulting in Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
and Greco-Buddhist art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
, whose influence reached as far as Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
.
Byzantine Greek art, which grew from the Hellenistic classical art and adapted the pagan motifs in the service of Christianity, provided a stimulus to the art of many nations.. Its influences can be traced from Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
in the West to Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
in the East. In turn, Greek art was influenced by eastern civilizations (i.e. Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, etc.) during various periods of its history.
Notable modern Greek artists include:
*the painters Dominikos Theotokopoulos (El Greco), Nikolaos Gyzis, Konstantinos Volanakis, Périclès Pantazis, and Constantine Andreou; sculptors such as Yannoulis Chalepas;
*composers such as Mikis Theodorakis, Spyridon Samaras, Iannis Xenakis, Yanni and Vangelis
Evangelos Odysseas Papathanassiou (, ; 29 March 1943 – 17 May 2022), known professionally as Vangelis ( ; , ), was a Greek musician, composer, and producer of electronic, progressive, ambient, and classical orchestral music. He composed ...
;
*singers such as Maria Callas, Giorgos Dalaras, Nana Mouskouri, Vicky Leandros and Demis Roussos
Artemios "Demis" Ventouris-Roussos ( ; , ; 15 June 1946 – 25 January 2015) was a Greek-Egyptian singer, songwriter and musician. As a band member, he is best remembered for his work in the progressive rock music act Aphrodite's Child, but as a ...
;
*poets such as Dionysios Solomos
Dionysios Solomos (; ; 8 April 1798 – 9 February 1857) was a Greeks, Greek poet from Zakynthos, who is considered to be Greece's national poet. He is best known for writing the ''Hymn to Liberty'' (, ''Ýmnos eis tīn Eleutherían''), whic ...
, Angelos Sikelianos, Andreas Embirikos, Constantine P. Cavafy and Nobel laureate
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in th ...
s Giorgos Seferis and Odysseas Elytis;
*the novelists Alexandros Papadiamantis, Emmanuel Rhoides, Ion Dragoumis, Nikos Kazantzakis, Penelope Delta, Stratis Myrivilis, Vassilis Vassilikos and Petros Markaris,
*playwrights include the Cretan Renaissance poets Georgios Chortatzis and Vincenzos Cornaros, and also Gregorios Xenopoulos and Iakovos Kambanellis.
Notable cinema or theatre actors include Marika Kotopouli, Melina Mercouri, Ellie Lambeti, Academy Award
The Academy Awards, commonly known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit in film. They are presented annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) in the United States in recognition of excellence ...
winner Katina Paxinou, Alexis Minotis, Dimitris Horn, Thanasis Veggos, Manos Katrakis and Irene Papas. Alekos Sakellarios, Karolos Koun, Vasilis Georgiadis
Vasilis Georgiadis (; 12 August 1921 – 30 April 2000) was a Greek people, Greek film director and actor. His films ''The Red Lanterns'' (1963) and ''Blood on the Land'' (1966) were nominated for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language F ...
, Kostas Gavras, Michael Cacoyannis, Giannis Dalianidis, Nikos Koundouros and Theo Angelopoulos
Theodoros "Theo" Angelopoulos (; (27 April 1935 – 24 January 2012) was a Greek filmmaker, screenwriter and film producer. He dominated the Greek art film industry from 1975 on, and Angelopoulos was one of the most influential and widely respect ...
are among the most important directors.
Among the most significant modern-era architects are Stamatios Kleanthis, Lysandros Kaftanzoglou, Anastasios Metaxas, Panagis Kalkos
Panagis Kalkos (, 1818–1875) was one of the first Greeks, Greek architects of the modern Greek state. Educated in Munich, he is a representative of a strict neoclassic style in architecture. He built some of the most characteristic neoclassic bu ...
, Anastasios Orlandos, the naturalized Greek Ernst Ziller, Dimitris Pikionis and urban planners Stamatis Voulgaris and George Candilis.
Science
 The Greeks of the Classical and Hellenistic eras made seminal contributions to science and philosophy, laying the foundations of several western scientific traditions, such as
The Greeks of the Classical and Hellenistic eras made seminal contributions to science and philosophy, laying the foundations of several western scientific traditions, such as astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
, geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
, historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiog ...
, mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
and political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, polit ...
. The scholarly tradition of the Greek academies was maintained during Roman times with several academic institutions in Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
, Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
and other centers of Greek learning, while Byzantine science was essentially a continuation of classical science. Greeks have a long tradition of valuing and investing in ''paideia'' (education). ''Paideia'' was one of the highest societal values in the Greek and Hellenistic world while the first European institution described as a university was founded in 5th century Constantinople and operated in various incarnations until the city's fall to the Ottomans in 1453. The University of Constantinople was Christian Europe's first secular institution of higher learning since no theological subjects were taught, and considering the original meaning of the word university as a corporation of students, the world's first university as well.
As of 2007, Greece had the eighth highest percentage of tertiary enrollment in the world (with the percentages for female students being higher than for male) while Greeks of the Diaspora are equally active in the field of education. Hundreds of thousands of Greek students attend western universities every year while the faculty lists of leading Western universities contain a striking number of Greek names. Notable Greek scientists of modern times include: physician Georgios Papanicolaou (pioneer in cytopathology, inventor of the Pap test
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes i ...
); mathematician Constantin Carathéodory
Constantin Carathéodory (; 13 September 1873 – 2 February 1950) was a Greeks, Greek mathematician who spent most of his professional career in Germany. He made significant contributions to real and complex analysis, the calculus of variations, ...
(acclaimed contributor to real and complex analysis and the calculus of variations); archaeologists Manolis Andronikos (unearthed the tomb of Philip II), Valerios Stais (recognised the Antikythera mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( , ) is an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery (model of the Solar System). It is the oldest known example of an Analog computer, analogue computer. It could be used to predict astronomy, astronomical ...
), Spyridon Marinatos (specialised in Mycenaean sites) and Ioannis Svoronos; chemists Leonidas Zervas
Leonidas Zervas (, ; 21 May 1902 – 10 July 1980) was a Greeks, Greek Organic chemistry, organic chemist who made seminal contributions in Peptide synthesis, peptide chemical synthesis. Together with his mentor Max Bergmann they laid the founda ...
(of Bergmann-Zervas synthesis and Z-group discovery fame), K. C. Nicolaou (first total synthesis of taxol
Paclitaxel, sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer, and pancreatic cancer. It is administered by ...
) and Panayotis Katsoyannis (first chemical synthesis of insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
); computer scientists Michael Dertouzos and Nicholas Negroponte
Nicholas Negroponte (born December 1, 1943) is a Greek American architect. He is the founder and chairman Emeritus of Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Media Lab, and also founded the One Laptop per Child Association (OLPC). Negroponte ...
(known for their early work with the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
), John Argyris (co-creator of the FEM), Joseph Sifakis (2007 Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in the fi ...
), Christos Papadimitriou (2002 Knuth Prize) and Mihalis Yannakakis (2005 Knuth Prize); physicist-mathematician Demetrios Christodoulou (renowned for work on Minkowski spacetime) and physicists Achilles Papapetrou (known for solutions of general relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of grav ...
), Dimitri Nanopoulos (extensive work on particle physics and cosmology), and John Iliopoulos
John (Jean) Iliopoulos (Greek language, Greek: Ιωάννης Ηλιόπουλος; 1940) is a Greeks, Greek physicist. He is the first person to present the Standard Model of particle physics in a single report. He is best known for his predictio ...
(2007 Dirac Prize
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac ( ; 8 August 1902 – 20 October 1984) was an English mathematician and Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist who is considered to be one of the founders of quantum mechanics. Dirac laid the foundations for bot ...
for work on the charm quark
The charm quark, charmed quark, or c quark is an elementary particle found in composite subatomic particles called hadrons such as the J/psi meson and the charmed baryons created in particle accelerator collisions. Several bosons, including th ...
); astronomer Eugenios Antoniadis; biologist Fotis Kafatos
Fotis Constantine Kafatos (; 16 April 1940 – 18 November 2017) was a Greek biologist. Between 2007 and 2010 he was the founding president of the European Research Council, European Research Council (ERC). He chaired the ERC Scientific Council ...
(contributor to cDNA cloning technology); botanist Theodoros Orphanides; economist Xenophon Zolotas (held various senior posts in international organisations such as the IMF); Indologist Dimitrios Galanos; linguist Yiannis Psycharis (promoter of Demotic Greek); historians Constantine Paparrigopoulos (founder of modern Greek historiography) and Helene Glykatzi Ahrweiler (excelled in Byzantine studies); and political scientists Nicos Poulantzas
Nicos Poulantzas ( ; 21 September 1936 – 3 October 1979) was a Greek-French Marxist political sociologist and philosopher. In the 1970s, Poulantzas was known, along with Louis Althusser, as a leading structural Marxist; while at first a Leni ...
(a leading Structural Marxist) and Cornelius Castoriadis
Cornelius Castoriadis (; 11 March 1922 – 26 December 1997) was a Greeks in France, Greek-FrenchMemos 2014, p. 18: "he was ... granted full French citizenship in 1970." philosopher, sociologist, social critic, economist, psychoanalyst, au ...
(philosopher of history and ontologist, social critic, economist, psychoanalyst).
Significant engineers and automobile designers include Nikolas Tombazis, Alec Issigonis and Andreas Zapatinas.
Symbols
flag of Greece
The national flag of Greece, popularly referred to as the Blue-and-White (, ) or the Cyan-and-White (, ), is officially recognised by Greece as one of its national symbols and has 5 equal horizontal stripes of blue alternating with white. There ...
, which features nine equal horizontal stripes of blue alternating with white representing the nine syllables of the Greek national motto '' Eleftheria i Thanatos'' (Freedom or Death), which was the motto of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
. The blue square in the upper hoist-side corner bears a white cross, which represents Greek Orthodoxy. The Greek flag is widely used by the Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots (, ) are the ethnic Greeks, Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest Ethnolinguistic group, ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2023 census, 719,252 respondents recorded their ethnicity as Greek, forming al ...
, although Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
has officially adopted a neutral flag to ease ethnic tensions with the Turkish Cypriot
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( or ; ) are so called ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Turkish Cypriots are mainly Sunni Muslims. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,000 Turkish settlers were given land onc ...
minority (see flag of Cyprus).
The pre-1978 (and first) flag of Greece, which features a Greek cross
The Christian cross, with or without a figure of Jesus, Christ included, is the main religious symbol of Christianity. A cross with a figure of Christ affixed to it is termed a crucifix and the figure is often referred to as the ''corpus'' (La ...
(''crux immissa quadrata'') on a blue background, is widely used as an alternative to the official flag, and they are often flown together. The national emblem of Greece features a blue escutcheon with a white cross surrounded by two laurel branches. A common design involves the current flag of Greece and the pre-1978 flag of Greece with crossed flagpoles and the national emblem placed in front.
Another highly recognizable and popular Greek symbol is the double-headed eagle
The double-headed eagle is an Iconology, iconographic symbol originating in the Bronze Age. The earliest predecessors of the symbol can be found in Mycenaean Greece and in the Ancient Near East, especially in Mesopotamian and Hittite Empire#icon ...
, the imperial emblem of the last dynasty of the Eastern Roman Empire and a common symbol in Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and, later, Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
. It is not part of the modern Greek flag or coat-of-arms, although it is officially the insignia of the Greek Army and the flag of the Church of Greece. It had been incorporated in the Greek coat of arms between 1925 and 1926.
Politics
Classical Athens
The city of Athens (, ''Athênai'' ; Modern Greek: Αθήναι, ''Athine'' ) during the classical period of ancient Greece (480–323 BC) was the major urban centre of the notable '' polis'' ( city-state) of the same name, located in Attica, ...
is considered the birthplace of Democracy
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
. The term appeared in the 5th century BC to denote the political systems then existing in Greek city-states, notably Athens, to mean "rule of the people", in contrast to aristocracy
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense Economy, economic, Politics, political, and soc ...
(, '), meaning "rule by an excellent elite", and to oligarchy
Oligarchy (; ) is a form of government in which power rests with a small number of people. Members of this group, called oligarchs, generally hold usually hard, but sometimes soft power through nobility, fame, wealth, or education; or t ...
. While theoretically these definitions are in opposition, in practice the distinction has been blurred historically. Led by Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes ( ; ), or Clisthenes (), was an ancient Athenian lawgiver credited with reforming the constitution of ancient Athens and setting it on a democratic footing in 508 BC. For these accomplishments, historians refer to him as "the fath ...
, Athenians established what is generally held as the first democracy in 508–507 BC, which took gradually the form of a direct democracy
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the Election#Electorate, electorate directly decides on policy initiatives, without legislator, elected representatives as proxies, as opposed to the representative democracy m ...
. The democratic form of government declined during the Hellenistic and Roman eras, only to be revived as an interest in Western Europe during the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
.
The European enlightenment and the democratic, liberal and nationalistic ideas of the French Revolution was a crucial factor to the outbreak of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
and the establishment of the modern Greek state.Clogg, ''A Concise History of Greece '', pp. 25–26Goldstein, ''Wars and Peace Treaties'', p. 20
Notable modern Greek politicians include Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (; February 1776 –27 September 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe.
Kapodistrias's ...
, founder of the First Hellenic Republic, reformist Charilaos Trikoupis, Eleftherios Venizelos, who marked the shape of modern Greece, social democrats Georgios Papandreou and Alexandros Papanastasiou, Konstantinos Karamanlis, founder of the Third Hellenic Republic, and socialist Andreas Papandreou
Andreas Georgiou Papandreou (, ; 5 February 1919 – 23 June 1996) was a Greek academic and economist who founded the Panhellenic Socialist Movement (PASOK) and served three terms as Prime minister of Greece, prime minister of Third Hellenic Repu ...
.
Surnames and personal names
Greek surnames began to appear in the 9th and 10th century, at first among ruling families, eventually supplanting the ancient tradition of using the father's name as disambiguator.. Nevertheless, Greek surnames are most commonly patronymics, such those ending in the suffix ''-opoulos'' or ''-ides'', while others derive from trade professions, physical characteristics, or a location such as a town, village, or monastery. Commonly, Greek male surnames end in -s, which is the common ending for Greek masculine proper nouns in thenominative case
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case, or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb, or (in Latin and formal variants ...
. Occasionally (especially in Cyprus), some surnames end in ''-ou'', indicating the genitive case
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive ca ...
of a patronymic name. Many surnames end in suffixes that are associated with a particular region, such as ''-akis'' (Crete), ''-eas'' or ''-akos'' ( Mani Peninsula), ''-atos'' (island of Cephalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia (), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallonia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th-largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It is also a separate regio ...
), ''-ellis'' (island of Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of , with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, eighth largest ...
) and so forth. In addition to a Greek origin, some surnames have Turkish or Latin/Italian origin, especially among Greeks from Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and the Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands (Modern Greek: , ; Ancient Greek, Katharevousa: , ) are a archipelago, group of islands in the Ionian Sea, west of mainland Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese ("Seven Islands"; , ''Heptanēsa'' or , ''Heptanē ...
, respectively. Female surnames end in a vowel and are usually the genitive form of the corresponding males surname, although this usage is not followed in the diaspora, where the male version of the surname is generally used.
With respect to personal names, the two main influences are Christianity and classical Hellenism; ancient Greek nomenclatures were never forgotten but have become more widely bestowed from the 18th century onwards. As in antiquity, children are customarily named after their grandparents, with the first born male child named after the paternal grandfather, the second male child after the maternal grandfather, and similarly for female children. Personal names are often familiarized by a diminutive suffix, such as ''-akis'' for male names and ''-itsa'' or ''-oula'' for female names. Greeks generally do not use middle names, instead using the genitive of the father's first name as a middle name. This usage has been passed on to the Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
and other East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert Huds ...
( otchestvo).
Sea: exploring and commerce
 The traditional Greek homelands have been the Greek peninsula and the Aegean Sea,
The traditional Greek homelands have been the Greek peninsula and the Aegean Sea, Southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
(the so called "Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
"), the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, the Ionian coasts of Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and the islands of Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
and Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
. In Plato's '' Phaidon'', Socrates remarks, "we (Greeks) live around a sea like frogs around a pond" when describing to his friends the Greek cities of the Aegean. This image is attested by the map of the Old Greek Diaspora, which corresponded to the Greek world until the creation of the Greek state in 1832. The sea
A sea is a large body of salt water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the ocean, the interconnected body of seawaters that spans most of Earth. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order section ...
and trade were natural outlets for Greeks since the Greek peninsula is mostly rocky and does not offer good prospects for agriculture.
Notable Greek seafarers include people such as Pytheas of Massalia who sailed to Great Britain, Euthymenes who sailed to Africa, Scylax of Caryanda who sailed to India, the navarch of Alexander the Great Nearchus
Nearchus or Nearchos (; – 300 BC) was one of the Greeks, Greek officers, a navarch, in the army of Alexander the Great. He is known for his celebrated expeditionary voyage starting from the Indus River, through the Persian Gulf and ending at t ...
, Megasthenes, explorer of India, later the 6th century merchant and monk Cosmas Indicopleustes (''Cosmas who sailed to India''), and the explorer of the Northwestern Passage Ioannis Fokas also known as Juan de Fuca. In later times, the Byzantine Greeks plied the sea-lanes of the Mediterranean and controlled trade until an embargo imposed by the Byzantine emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
on trade with the Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
opened the door for the later Italian pre-eminence in trade. Panayotis Potagos was another explorer of modern times who was the first to reach Mbomu and Uele River from the north.
The Greek shipping tradition recovered during the late Ottoman rule (especially after the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca and during the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
), when a substantial merchant middle class developed, which played an important part in the Greek War of Independence. Today, Greek shipping continues to prosper to the extent that Greece has one of the largest merchant fleets in the world, while many more ships under Greek ownership fly flags of convenience. The most notable shipping magnate of the 20th century was Aristotle Onassis, others being Yiannis Latsis, Stavros G. Livanos, and Stavros Niarchos.
Genetics
 In their archaeogenetic study, Lazaridis et al. (2017) found that Minoans and Mycenaean Greeks were genetically highly similar, but not identical; modern Greeks resembled the Mycenaeans, but with some additional dilution of the early Neolithic ancestry. The results of the study support the idea of genetic continuity between these civilizations and modern Greeks, but not isolation in the history of populations of the Aegean, before and after the time of its earliest civilizations. Furthermore, proposed migrations by Ancient Egypt, Egyptian or Phoenician colonists was not discernible in their data, thus "rejecting the hypothesis that the cultures of the Aegean were seeded by migrants from the old civilizations of these regions." The Fixation index, F between the sampled Bronze Age populations and present-day West Eurasians was estimated, finding that Mycenaean Greeks and Minoans were least differentiated from the populations of modern Greece, Cyprus, Albania, and Italy. In a subsequent study, Lazaridis et al. (2022) concluded that around ~58.4–65.8% of the ancestry of the Mycenaeans came from Early European Farmers, Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF), while the remainder mainly came from ancient populations related to the Caucasus hunter-gatherer, Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers (CHG) (~20.1–22.7%) and the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN) culture in the Levant (~7–14%). The Mycenaeans had also inherited ~3.3–5.5% ancestry from a source related to the Eastern Hunter-Gatherer, Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG), introduced via a proximal source related to the inhabitants of the Eurasian steppe who are hypothesized to be the Proto-Indo-Europeans, and ~0.9–2.3% from the Iron Gates Mesolithic, Iron Gates Hunter-Gatherers in the Balkans. Mycenaean elites were genetically the same as Mycenaean commoners in terms of their steppe ancestry, while some Mycenaeans lacked it altogether.
A genetic study by Clemente et al. (2021) found that in the Early Bronze Age, the populations of the Minoan, Helladic civilization, Helladic, and Cycladic culture, Cycladic civilizations in the Aegean, were genetically homogeneous. In contrast, the Aegean population during the Middle Bronze Age was more differentiated; probably due to gene flow from a Yamnaya-related population from the Pontic–Caspian steppe. This is corroborated by sequenced genomes of Middle Bronze Age individuals from northern Greece, who had a much higher proportion of steppe-related ancestry; the timing of this gene flow was estimated at ~2,300 BCE, and is consistent with the dominant linguistic theories explaining the emergence of the Proto-Greek language. Present-day Greeks share ~90% of their ancestry with them, suggesting continuity between the two time periods. In the case of Mycenaean Greeks however, their steppe-related ancestry was diluted. The ancestry of the Mycenaeans could be explained via a 2-way admixture model of such MBA individuals in northern Greece, and either an EBA Aegean or MBA Minoan population; the difference between the two time periods could be explained by the general decline of the Mycenaean civilization.
Genetic studies using multiple Genealogical DNA test#Autosomal DNA (atDNA) testing, autosomal, Genealogical DNA test#Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) testing, Y-DNA, and Genealogical DNA test#Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) testing, mtDNA markers, show that Greeks share similar backgrounds as the rest of the Europeans and especially Southern Europeans (Italians and Balkan populations such as
In their archaeogenetic study, Lazaridis et al. (2017) found that Minoans and Mycenaean Greeks were genetically highly similar, but not identical; modern Greeks resembled the Mycenaeans, but with some additional dilution of the early Neolithic ancestry. The results of the study support the idea of genetic continuity between these civilizations and modern Greeks, but not isolation in the history of populations of the Aegean, before and after the time of its earliest civilizations. Furthermore, proposed migrations by Ancient Egypt, Egyptian or Phoenician colonists was not discernible in their data, thus "rejecting the hypothesis that the cultures of the Aegean were seeded by migrants from the old civilizations of these regions." The Fixation index, F between the sampled Bronze Age populations and present-day West Eurasians was estimated, finding that Mycenaean Greeks and Minoans were least differentiated from the populations of modern Greece, Cyprus, Albania, and Italy. In a subsequent study, Lazaridis et al. (2022) concluded that around ~58.4–65.8% of the ancestry of the Mycenaeans came from Early European Farmers, Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF), while the remainder mainly came from ancient populations related to the Caucasus hunter-gatherer, Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers (CHG) (~20.1–22.7%) and the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN) culture in the Levant (~7–14%). The Mycenaeans had also inherited ~3.3–5.5% ancestry from a source related to the Eastern Hunter-Gatherer, Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG), introduced via a proximal source related to the inhabitants of the Eurasian steppe who are hypothesized to be the Proto-Indo-Europeans, and ~0.9–2.3% from the Iron Gates Mesolithic, Iron Gates Hunter-Gatherers in the Balkans. Mycenaean elites were genetically the same as Mycenaean commoners in terms of their steppe ancestry, while some Mycenaeans lacked it altogether.
A genetic study by Clemente et al. (2021) found that in the Early Bronze Age, the populations of the Minoan, Helladic civilization, Helladic, and Cycladic culture, Cycladic civilizations in the Aegean, were genetically homogeneous. In contrast, the Aegean population during the Middle Bronze Age was more differentiated; probably due to gene flow from a Yamnaya-related population from the Pontic–Caspian steppe. This is corroborated by sequenced genomes of Middle Bronze Age individuals from northern Greece, who had a much higher proportion of steppe-related ancestry; the timing of this gene flow was estimated at ~2,300 BCE, and is consistent with the dominant linguistic theories explaining the emergence of the Proto-Greek language. Present-day Greeks share ~90% of their ancestry with them, suggesting continuity between the two time periods. In the case of Mycenaean Greeks however, their steppe-related ancestry was diluted. The ancestry of the Mycenaeans could be explained via a 2-way admixture model of such MBA individuals in northern Greece, and either an EBA Aegean or MBA Minoan population; the difference between the two time periods could be explained by the general decline of the Mycenaean civilization.
Genetic studies using multiple Genealogical DNA test#Autosomal DNA (atDNA) testing, autosomal, Genealogical DNA test#Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) testing, Y-DNA, and Genealogical DNA test#Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) testing, mtDNA markers, show that Greeks share similar backgrounds as the rest of the Europeans and especially Southern Europeans (Italians and Balkan populations such as Albanians
The Albanians are an ethnic group native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, Albanian culture, culture, Albanian history, history and Albanian language, language. They are the main ethnic group of Albania and Kosovo, ...
, Slavic Macedonians and Romanians). A study in 2008 showed that Greeks are genetically closest to Italians and Romanians and another 2008 study showed that they are close to Italians, Albanians, Romanians and South Slavs, southern Balkan Slavs such as Slavic Macedonians and Bulgarians. A 2003 study showed that Greeks cluster with other South European (mainly Italians) and North-European populations and are close to the Basques, and F distances showed that they group with other European and Mediterranean populations, especially with Italians (−0.0001) and Tuscans (0.0005). A study in 2008 showed that Greek regional samples from the mainland cluster with those from the Balkans, principally Albanians while Crete, Cretan Greeks cluster with the central Mediterranean and Eastern Mediterranean samples. Studies using mitochondrial DNA gene markers (mtDNA) showed that Greeks group with other Mediterranean European populations and principal component analysis (PCA) confirmed the low genetic distance between Greeks and Italians and also revealed a cline of genes with highest frequencies in the Balkans and Southern Italy, spreading to lowest levels in Britain and the Basque country, which Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, Cavalli-Sforza (1993) associates with "the Greek expansion, which reached its peak in historical times around 1000 and 500 BC but which certainly began earlier". Greeks also have a degree of Eastern-European-related ancestry which is observed in all Balkan peoples; it was acquired after 700 CE, coinciding with the arrival of Slavic-speaking peoples in the Balkans, but the proportion of this ancestry varies considerably between different studies and subregions. A 2019 study showed that Cretans share high Identity by descent, IBD with Western (Demographics of Utah#Birth data, CEU), Central (Germans, German and Polish people, Polish), Northern (CEU, Scandinavian people, Scandinavian) and Eastern Europeans (Ukrainians, Ukrainian, Russians, Russian), similar to mainland Greeks who share high IBD with Eastern Europeans. This reflects settlement patterns in Crete, driven by Myceneans and Dorians, Goths and Slavs. Peoples like Andalusians, Near Eastern Arabs and Republic of Venice, Venetians left a minimal genetic impact on Cretans. But a Principal component analysis, PCA analysis shows that Cretans overlap with Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
ans, Sicilians and Ashkenazi Jews. A 2022 study discovered high genetic affinities between present-day southeastern Peloponnesian populations and Apulians, Calabrians and southeastern Sicilians, which are "all characterised by a cluster composition different from those displayed by other Greek groups", due to low influence from inland populations such as Slavic-related people and/or genetic drift in Tsakonia, Tsakones and Maniots. Individuals from western Sicily additionally show similarities with peoples from the western part of the Peloponnese. A 2023 study states that early Cretan farmers shared the same ancestry as other Neolithic Aegeans but received 'eastern' gene flow of Anatolian origin at the end of the Neolithic Age. From the 17th to 12th centuries BCE, genetic signatures of Central and East European ancestry gradually increased in Crete, indicative of mainland Greek influence.
Physical appearance
A study from 2013 for prediction of hair and eye colour from DNA of the Greek people showed that the self-reported phenotype frequencies according to hair and eye colour categories was as follows: 119 individuals – hair colour, 11 blond, 45 dark blond/light brown, 49 dark brown, 3 brown red/auburn and 11 had black hair; eye colour, 13 with blue, 15 with intermediate (green, heterochromia) and 91 had brown eye colour. Another study from 2012 included 150 dental school students from the University of Athens, and the results of the study showed that light hair colour (blonde/light ash brown) was predominant in 10.7% of the students. 36% had medium hair colour (light brown/medium darkest brown), 32% had darkest brown and 21% black (15.3 off black, 6% midnight black). In conclusion, the hair colour of young Greeks are mostly brown, ranging from light to dark brown with significant minorities having black and blonde hair. The same study also showed that the eye colour of the students was 14.6% blue/green, 28% medium (light brown) and 57.4% dark brown. A 2017 study found that Bronze Age Aegean populations had mostly dark hair (brown to black) and eyes. The genetic phenotype predictions matched the visual representations made by the Greeks of themselves, suggesting that art of this period reproduced phenotypes naturalistically.Timeline
The history of the Greek people is closely associated with the history of Greece, Cyprus, Southern Italy, Constantinople, Asia Minor and the Black Sea. During the Ottoman rule of Greece, a number of Greek enclaves around the Mediterranean were cut off from the core, notably in Southern Italy, the Caucasus, Syria and Egypt. By the early 20th century, over half of the overall Greek-speaking population was settled inAsia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
(now Turkey), while later that century a huge wave of migration to the United States, Australia, Canada and elsewhere created the modern Greek diaspora.
See also
*Antiochian Greeks *Arvanites *Cappadocian Greeks * Caucasian Greeks *Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots (, ) are the ethnic Greeks, Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest Ethnolinguistic group, ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2023 census, 719,252 respondents recorded their ethnicity as Greek, forming al ...
*Greek Diaspora
The Greek diaspora, also known as Omogenia (), are the communities of Greeks living outside of Greece and Cyprus.
Such places historically (dating to the ancient period) include, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in North Macedonia, North Maced ...
*Griko people
*Karamanlides
*Macedonians (Greeks)
*Maniots
*Greek Muslims
Greek Muslims, also known as Grecophone Muslims, are Muslims of Greeks, Greek ethnic origin whose adoption of Islam (and often the Turkish language and identity in more recent times) dates either from the contact of early Arabic dynasties of th ...
*Cretan Muslims
*Northern Epirotes
*Pelasgians
* Pontic Greeks
* Romaniotes
*Sarakatsani
*Tsakones
*Urums
*Lists
**List of ancient Greeks
**List of Greeks
**List of Greek Americans
Notes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * ;Mycenaean Greeks * * * * * * ;Classical Greeks * * * * * * * * * * ;Hellenistic Greeks * * ;Byzantine Greeks * * * * * * ;Ottoman Greeks * * * * ;Modern Greeks * * * * * * * * *External links
DiasporaWorld Council of Hellenes Abroad (SAE)
Umbrella Diaspora Organization Religious
Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople
Church of Cyprus
Academic
Transnational Communities Programme at the University of Oxford
, includes papers on the
Greek Diaspora
The Greek diaspora, also known as Omogenia (), are the communities of Greeks living outside of Greece and Cyprus.
Such places historically (dating to the ancient period) include, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in North Macedonia, North Maced ...
Greeks on Greekness
The Construction and Uses of the Greek Past among Greeks under the Roman Empire. *The Modern Greek Studies Association is a scholarly organization for modern Greek studies in North America, which publishes the Journal of Modern Greek Studies.
Got Greek? Next Generation National Research Study
Trade organizations
Hellenic Canadian Board of Trade
Charitable organizations
AHEPA
– American Hellenic Educational Progressive Association
Hellenic Heritage Foundation
*
{{Authority control Ethnic groups in Greece Greek people, Ancient peoples of Europe Indo-European peoples