Graduate Record Examinations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) is a
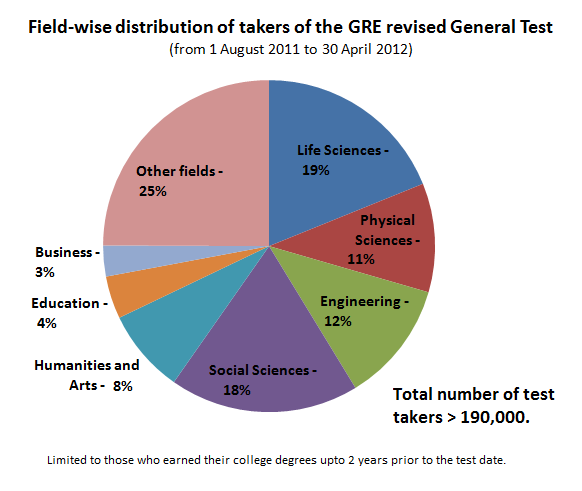 "Field-wise distribution" of test takers is "limited to those who earned their college degrees up to two years before the test date." ETS provides no score data for "non-traditional" students who have been out of school more than two years, although its own report "RR-99-16" indicated that 22% of all test takers in 1996 were over the age of 30.
"Field-wise distribution" of test takers is "limited to those who earned their college degrees up to two years before the test date." ETS provides no score data for "non-traditional" students who have been out of school more than two years, although its own report "RR-99-16" indicated that 22% of all test takers in 1996 were over the age of 30.
GRE information website for residents of Mainland China, English version
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171108205246/https://gre.etest.net.cn/login.do?lang=en_US , date=November 8, 2017 - by the Chinese National Education Examinations Authority 1936 establishments in the United States Entrance examinations Standardized tests in the United States Standardized tests for English language
standardized test
A standardized test is a Test (assessment), test that is administered and scored in a consistent or standard manner. Standardized tests are designed in such a way that the questions and interpretations are consistent and are administered and scored ...
that is part of the admissions process for many graduate school
Postgraduate education, graduate education, or graduate school consists of academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications usually pursued by post-secondary students who have earned an undergraduate (bachel ...
s in the United States and Canada and a few other countries. The GRE is owned and administered by Educational Testing Service
Educational Testing Service (ETS), founded in 1947, is the world's largest private educational testing and assessment organization. It is headquartered in Lawrence Township, Mercer County, New Jersey, Lawrence Township, New Jersey, but has a P ...
(ETS). The test was established in 1936 by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching
The Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching (CFAT) is a U.S.-based education policy and research center. It was founded by Andrew Carnegie in 1905 and chartered in 1906 by an act of the United States Congress. Among its most not ...
.
According to ETS, the GRE aims to measure verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, analytical writing, and critical thinking
Critical thinking is the process of analyzing available facts, evidence, observations, and arguments to make sound conclusions or informed choices. It involves recognizing underlying assumptions, providing justifications for ideas and actions, ...
skills that have been acquired over a long period of learning. The content of the GRE consists of certain specific data analysis or interpretation, arguments and reasoning, algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic ope ...
, geometry, arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms.
...
, and vocabulary sections. The GRE General Test is offered as a computer-based exam administered at testing centers and institution owned or authorized by Prometric. In the graduate school admissions process, the level of emphasis that is placed upon GRE scores varies widely among schools and departments. The importance of a GRE score can range from being a mere admission formality to an important selection factor.
The GRE was significantly overhauled in August 2011, resulting in an exam that is adaptive on a section-by-section basis, rather than question by question, so that the performance on the first verbal and math sections determines the difficulty of the second sections presented (excluding the experimental section). Overall, the test retained the sections and many of the question types from its predecessor, but the scoring scale was changed to a 130 to 170 scale (from a 200 to 800 scale).
The cost to take the test is US$
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introdu ...
205, although ETS will reduce the fee under certain circumstances. It also provides financial aid to GRE applicants who prove economic hardship. ETS does not release scores that are older than five years, although graduate program policies on the acceptance of scores older than five years will vary.
Once almost universally required for admission to Ph.D. science programs in the U.S., its use for that purpose has fallen precipitously.
History
The Graduate Record Examinations was "initiated in 1936 as a joint experiment in higher education by the graduate school deans of fourIvy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference of eight Private university, private Research university, research universities in the Northeastern United States. It participates in the National Collegia ...
universities and the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching
The Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching (CFAT) is a U.S.-based education policy and research center. It was founded by Andrew Carnegie in 1905 and chartered in 1906 by an act of the United States Congress. Among its most not ...
."
The first universities to experiment with the test on their students were Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
, Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...
, Princeton University
Princeton University is a private university, private Ivy League research university in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth, New Jersey, Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the List of Colonial ...
and Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Churc ...
. The University of Wisconsin
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Uni ...
was the first public university to ask their students to take the test in 1938. It was first given to students at the University of Iowa
The University of Iowa (U of I, UIowa, or Iowa) is a public university, public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized int ...
in 1940, where it was analyzed by psychologist Dewey Stuit. It was first taken by students at Texas Tech University in 1942. In 1943, it was taken by students at Michigan State University
Michigan State University (Michigan State or MSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in East Lansing, Michigan, United States. It was founded in 1855 as the Agricultural College of the State o ...
, where it was analyzed by Paul Dressel. It was taken by over 45,000 students applying to 500 colleges in 1948.
"Until the Educational Testing Service
Educational Testing Service (ETS), founded in 1947, is the world's largest private educational testing and assessment organization. It is headquartered in Lawrence Township, Mercer County, New Jersey, Lawrence Township, New Jersey, but has a P ...
was established in January, 1948, the Graduate Record Examination remained a project of the Carnegie Foundation."
2011 revision
In 2006, ETS announced plans to make significant changes in the format of the GRE. Planned changes for the revised GRE included a longer testing time, a departure from computer-adaptive testing, a new grading scale, and an enhanced focus on reasoning skills and critical thinking for both the quantitative and qualitative sections. On April 2, 2007, ETS announced the decision to cancel plans for revising the GRE. The announcement cited concerns over the ability to provide clear and equal access to the new test after the planned changes as an explanation for the cancellation. The ETS stated, however, that they did plan "to implement many of the planned test content improvements in the future", although specific details regarding those changes were not initially announced. Changes to the GRE took effect on November 1, 2007, as ETS started to include new types of questions in the exam. The changes mostly centered on "fill in the blank" type answers for the mathematics section that requires the test-taker to fill in the blank directly, without being able to choose from a multiple choice list of answers. ETS announced plans to introduce two of these new types of questions in each quantitative section, while the majority of questions would be presented in the regular format. Since January 2008, the Reading Comprehension within the verbal sections has been reformatted, passages' "line numbers will be replaced with highlighting when necessary in order to focus the test taker on specific information in the passage" to "help students more easily find the pertinent information in reading passages." In December 2009, ETS announced plans to move forward with significant revisions to the GRE in 2011. Changes include a new 130–170 scoring scale, the elimination of certain question types such as antonyms and analogies, the addition of an online calculator, and the elimination of the CAT format of question-by-question adjustment, in favor of a section by section adjustment. On August 1, 2011, the Revised GRE General test replaced General GRE test. The revised GRE is said to be better by design and provides a better test taking experience. The new types of questions in the revised format are intended to test the skills needed in graduate and business schools programs. From July 2012 onwards GRE announced an option for users to customize their scores called ScoreSelect.Before October 2002
The earliest versions of the GRE tested only for verbal and quantitative ability. For a number of years before October 2002, the GRE had a separate Analytical Ability section which tested candidates on logical and analytical reasoning abilities. This section was replaced by the Analytical Writing Assessment.Structure
The computer-based GRE General Test consists of six sections. The first section is always the analytical writing section involving separately timed issue and argument tasks. The next five sections consist of two verbal reasoning sections, two quantitative reasoning sections, and either an experimental or research section. These five sections may occur in any order. The experimental section does not count towards the final score but is not distinguished from the scored sections. Unlike the computer adaptive test before August 2011, the GRE General Test is a multistage test, where the examinee's performance on earlier sections determines the difficulty of subsequent sections, using a technique known as computer-adaptive testing. This format allows the examined person to freely move back and forth between questions within each section, and the testing software allows the user to "mark" questions within each section for later review if time remains. The entire testing procedure lasts about 3 hours 45 minutes. One-minute breaks are offered after each section and a 10-minute break after the third section. The paper-based GRE General Test also consists of six sections. The analytical writing is split up into two sections, one section for each issue and argument task. The next four sections consist of two verbal and two quantitative sections in varying order. There is no experimental section on the paper-based test.Verbal section
The computer-based verbal sections assess reading comprehension, critical reasoning, and vocabulary usage. The verbal test is scored on a scale of 130–170, in 1-point increments. (Before August 2011, the scale was 200–800, in 10-point increments.) In a typical examination, each verbal section consists of 20 questions to be completed in 30 minutes. Each verbal section consists of about 6 text completion, 4 sentence equivalence, and 10 critical reading questions. The changes in 2011 include a reduced emphasis on rote vocabulary knowledge and the elimination of antonyms and analogies. Text completion items have replaced sentence completions and new reading question types allowing for the selection of multiple answers were added.Quantitative section
The computer-based quantitative sections assess knowledge and reasoning skills taught in mostMathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
and Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
courses in secondary school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., b ...
s. The quantitative test is scored on a scale of 130–170, in 1-point increments (Before August 2011 the scale was 200–800, in 10-point increments). In a typical examination, each quantitative section consists of 20 questions to be completed in 35 minutes. Each quantitative section consists of about 8 quantitative comparisons, 9 problem solving items, and 3 data interpretation questions. The changes in 2011 include the addition of numeric entry items requiring the examinee to fill in the blank and multiple-choice items requiring the examinee to select multiple correct responses.
* Arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms.
...
:
** Integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
, Divisibility rule
A divisibility rule is a shorthand and useful way of determining whether a given integer is divisible by a fixed Divisor (number theory), divisor without performing the division, usually by examining its digits. Although there are divisibility test ...
, Integer factorization
In mathematics, integer factorization is the decomposition of a positive integer into a product of integers. Every positive integer greater than 1 is either the product of two or more integer factors greater than 1, in which case it is a comp ...
, Prime number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a Product (mathematics), product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime ...
, Remainder
In mathematics, the remainder is the amount "left over" after performing some computation. In arithmetic, the remainder is the integer "left over" after dividing one integer by another to produce an integer quotient ( integer division). In a ...
, Parity
** Exponentiation
In mathematics, exponentiation, denoted , is an operation (mathematics), operation involving two numbers: the ''base'', , and the ''exponent'' or ''power'', . When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication ...
, nth root
In mathematics, an th root of a number is a number which, when raised to the power of , yields : r^n = \underbrace_ = x.
The positive integer is called the ''index'' or ''degree'', and the number of which the root is taken is the ''ra ...
** Estimation
Estimation (or estimating) is the process of finding an estimate or approximation, which is a value that is usable for some purpose even if input data may be incomplete, uncertain, or unstable. The value is nonetheless usable because it is d ...
, Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage () is a number or ratio expressed as a fraction (mathematics), fraction of 100. It is often Denotation, denoted using the ''percent sign'' (%), although the abbreviations ''pct.'', ''pct'', and sometimes ''pc'' are ...
, Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio () shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
, Rate, Absolute value
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x, is the non-negative value without regard to its sign. Namely, , x, =x if x is a positive number, and , x, =-x if x is negative (in which case negating x makes -x positive), ...
, Number line
A number line is a graphical representation of a straight line that serves as spatial representation of numbers, usually graduated like a ruler with a particular origin point representing the number zero and evenly spaced marks in either dire ...
, Decimal representation
A decimal representation of a non-negative real number is its expression as a sequence of symbols consisting of decimal digits traditionally written with a single separator:
r = b_k b_\cdots b_0.a_1a_2\cdots
Here is the decimal separator, ...
, Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is cal ...
* Algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic ope ...
:
** Operation
** Factorization, Expression
** Relation, Function, Equation
In mathematics, an equation is a mathematical formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for ...
, Inequality
** Equation solving
In mathematics, to solve an equation is to find its solutions, which are the values (numbers, functions, sets, etc.) that fulfill the condition stated by the equation, consisting generally of two expressions related by an equals sign. When s ...
, Linear equation
In mathematics, a linear equation is an equation that may be put in the form
a_1x_1+\ldots+a_nx_n+b=0, where x_1,\ldots,x_n are the variables (or unknowns), and b,a_1,\ldots,a_n are the coefficients, which are often real numbers. The coeffici ...
, Quadratic equation
In mathematics, a quadratic equation () is an equation that can be rearranged in standard form as
ax^2 + bx + c = 0\,,
where the variable (mathematics), variable represents an unknown number, and , , and represent known numbers, where . (If and ...
** System of linear equations
In mathematics, a system of linear equations (or linear system) is a collection of two or more linear equations involving the same variable (math), variables.
For example,
: \begin
3x+2y-z=1\\
2x-2y+4z=-2\\
-x+\fracy-z=0
\end
is a system of th ...
** Analytic geometry
In mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.
Analytic geometry is used in physics and engineering, and als ...
, Graph of a function
In mathematics, the graph of a function f is the set of ordered pairs (x, y), where f(x) = y. In the common case where x and f(x) are real numbers, these pairs are Cartesian coordinates of points in a plane (geometry), plane and often form a P ...
, Zero of a function
In mathematics, a zero (also sometimes called a root) of a real-, complex-, or generally vector-valued function f, is a member x of the domain of f such that f(x) ''vanishes'' at x; that is, the function f attains the value of 0 at x, or equ ...
, Y-intercept, Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a Line (mathematics), line is a number that describes the direction (geometry), direction of the line on a plane (geometry), plane. Often denoted by the letter ''m'', slope is calculated as the ratio of t ...
* Geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician w ...
:
** Parallel, Perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', � ...
** Circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
** Triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimension ...
, Isosceles triangle
In geometry, an isosceles triangle () is a triangle that has two Edge (geometry), sides of equal length and two angles of equal measure. Sometimes it is specified as having ''exactly'' two sides of equal length, and sometimes as having ''at le ...
, Equilateral triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length, and all three angles are equal. Because of these properties, the equilateral triangle is a regular polygon, occasionally known as the regular triangle. It is the ...
, Special right triangle
** Quadrilateral
In Euclidean geometry, geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four Edge (geometry), edges (sides) and four Vertex (geometry), corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words ''quadri'', a variant of four, and ''l ...
, Polygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure made up of line segments connected to form a closed polygonal chain.
The segments of a closed polygonal chain are called its '' edges'' or ''sides''. The points where two edges meet are the polygon ...
** Congruence, Similarity
** Polyhedron
In geometry, a polyhedron (: polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional figure with flat polygonal Face (geometry), faces, straight Edge (geometry), edges and sharp corners or Vertex (geometry), vertices. The term "polyhedron" may refer ...
** Area
Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while '' surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-di ...
, Perimeter
A perimeter is the length of a closed boundary that encompasses, surrounds, or outlines either a two-dimensional shape or a one-dimensional line. The perimeter of a circle or an ellipse is called its circumference.
Calculating the perimet ...
, Volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch) ...
** Pythagorean theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite t ...
** Angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two R ...
, Degree
* Data analysis
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, Data cleansing, cleansing, Data transformation, transforming, and Data modeling, modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Da ...
:
** Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
, Mean
A mean is a quantity representing the "center" of a collection of numbers and is intermediate to the extreme values of the set of numbers. There are several kinds of means (or "measures of central tendency") in mathematics, especially in statist ...
, Median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “ ...
, Mode, Range, Standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean ( ...
, Interquartile range
In descriptive statistics, the interquartile range (IQR) is a measure of statistical dispersion, which is the spread of the data. The IQR may also be called the midspread, middle 50%, fourth spread, or H‑spread. It is defined as the differen ...
, Quartile, Percentile
In statistics, a ''k''-th percentile, also known as percentile score or centile, is a score (e.g., a data point) a given percentage ''k'' of all scores in its frequency distribution exists ("exclusive" definition) or a score a given percentage ...
** Line chart
A line chart or line graph, also known as curve chart, is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points called 'markers' connected by straight wikt:line, line segments. It is a basic type of chart common in many fields. ...
, Bar chart
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical variable, categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. A ...
, Pie chart
A pie chart (or a circle chart) is a circular Statistical graphics, statistical graphic which is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportion. In a pie chart, the arc length of each slice (and consequently its central angle and area) ...
, Box plot
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot is a method for demonstrating graphically the locality, spread and skewness groups of numerical data through their quartiles.
In addition to the box on a box plot, there can be lines (which are ca ...
, Scatter plot, Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
** Probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an e ...
, Independence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of ...
** Conditional probability
In probability theory, conditional probability is a measure of the probability of an Event (probability theory), event occurring, given that another event (by assumption, presumption, assertion or evidence) is already known to have occurred. This ...
** Random variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a Mathematics, mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on randomness, random events. The term 'random variable' in its mathema ...
, Probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is a Function (mathematics), function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible events for an Experiment (probability theory), experiment. It is a mathematical descri ...
, Normal distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
f(x) = \frac ...
** Counting method, Combination, Permutation
In mathematics, a permutation of a set can mean one of two different things:
* an arrangement of its members in a sequence or linear order, or
* the act or process of changing the linear order of an ordered set.
An example of the first mean ...
, Venn diagram
A Venn diagram is a widely used diagram style that shows the logical relation between set (mathematics), sets, popularized by John Venn (1834–1923) in the 1880s. The diagrams are used to teach elementary set theory, and to illustrate simple ...
Analytical writing section
The analytical writing section consists of two different essays, an "issue task" and an "argument task". The writing section is graded on a scale of 0–6, in half-point increments. The essays are written on a computer using a word processing program specifically designed by ETS. The program allows only basic computer functions and does not contain a spell-checker or other advanced features. Each essay is scored by at least two readers on a six-point holist scale. If the two scores are within one point, the average of the scores is taken. If the two scores differ by more than a point, a third reader examines the response.Issue Task
The test taker is given 30 minutes to write an essay about a selected topic. Issue topics are selected from a pool of questions, which the GRE Program has published in its entirety. Individuals preparing for the GRE may access the pool of tasks on the ETS website.Argument Task
The test taker will be given an argument (i.e. a series of facts and considerations leading to a conclusion) and asked to write an essay that critiques the argument. Test takers are asked to consider the argument's logic and to make suggestions about how to improve the logic of the argument. Test takers are expected to address the logical flaws of the argument and not provide a personal opinion on the subject. The time allotted for this essay is 30 minutes. The Arguments are selected from a pool of topics, which the GRE Program has published in its entirety. Individuals preparing for the GRE may access the pool of tasks on the ETS website.Experimental section
The experimental section, which can be either verbal or quantitative, contains new questions ETS is considering for future use. Although the experimental section does not count towards the test-taker's score, it is unidentified and appears identical to the scored sections. Because test takers have no definite way of knowing which section is experimental, it is typically advised that test takers try their best and be focused on every section. Sometimes an identified research section at the end of the test is given instead of the experimental section. There is no experimental section on the paper-based GRE.Scoring
An examinee can miss one or more questions on a multiple-choice section and still receive a perfect score of 170. Likewise, even if no question is answered correctly, 130 is the lowest possible score. Verbal and quantative reasoning scores are given in one-point increments, and analytical writing scores are given in half-point increments on a scale of 0 to 6.Scaled score percentiles
The percentiles for the current General test and the concordance with the prior format are as follows. According to interpretive data published by ETS, from July 1, 2015 to June 30, 2018 about 2 million people have taken the test. Based on performance of individuals the mean and standard deviation of verbal section were 150.24 and 8.44. Whereas, mean and standard deviation for quantitative section were 153.07 and 9.24. Analytical writing has a mean of 3.55 with a standard deviation of 0.86. "Field-wise distribution" of test takers is "limited to those who earned their college degrees up to two years before the test date." ETS provides no score data for "non-traditional" students who have been out of school more than two years, although its own report "RR-99-16" indicated that 22% of all test takers in 1996 were over the age of 30.
"Field-wise distribution" of test takers is "limited to those who earned their college degrees up to two years before the test date." ETS provides no score data for "non-traditional" students who have been out of school more than two years, although its own report "RR-99-16" indicated that 22% of all test takers in 1996 were over the age of 30.
GRE Subject Tests
In addition to the General Test, there are also three GRE Subject Tests testing knowledge in the specific areas ofMathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, and Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
. The length of each exam is 170 minutes.
In the past, subject tests were also offered in the areas of Computer Science, Economics, Revised Education, Engineering, English Literature, French, Geography, Geology, German, History, Music, Political Science, Sociology, Spanish, and Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology. In April 1998, the Revised Education and Political Science exams were discontinued. In April 2000, the History and Sociology exams were discontinued; with Economics, Engineering, Music, and Geology being discontinued in April 2001. The Computer Science exam was discontinued after April 2013. Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology was discontinued in December 2016. The GRE Biology Test and GRE Literature in English Test tests were discontinued in May 2021. The GRE Chemistry Test was discontinued in May 2023.
Use in admissions
Many graduate schools in the United States require GRE results as part of the admissions process. The GRE is a standardized test intended to measure all graduates' abilities in tasks of general academic nature (regardless of their fields of specialization) and the extent to whichundergraduate
Undergraduate education is education conducted after secondary education and before postgraduate education, usually in a college or university. It typically includes all postsecondary programs up to the level of a bachelor's degree. For example, ...
education has developed their verbal skills, quantitative skills, and abstract thinking.
In addition to GRE scores, admission to graduate schools depends on several other factors, such as GPA, letters of recommendation, and statements of purpose. Furthermore, unlike other standardized admissions tests (such as the SAT
The SAT ( ) is a standardized test widely used for college admissions in the United States. Since its debut in 1926, its name and Test score, scoring have changed several times. For much of its history, it was called the Scholastic Aptitude Test ...
, LSAT, and MCAT), the use and weight of GRE scores vary considerably not only from school to school, but also from department to department and program to program. For instance, most business schools and economics programs require very high GRE or GMAT scores for entry, while engineering programs are known to allow more score variation. Liberal arts programs may only consider the applicant's verbal score, while mathematics and science programs may only consider quantitative ability. Some schools use the GRE in admissions decisions, but not in funding decisions; others use it for selection of scholarship and fellowship candidates, but not for admissions. In some cases, the GRE may be a general requirement for graduate admissions imposed by the university, while particular departments may not consider the scores at all. Graduate schools will typically provide the average scores of previously admitted students and information about how the GRE is considered in admissions and funding decisions. In some cases, programs have hard cut off requirements for the GRE; for example, the Yale Economics PhD program requires a minimum quantitative score of 160 to apply. The best way to ascertain how a particular school or program evaluates a GRE score in the admissions process is to contact the person in charge of graduate admissions for the specific program in question.
In February 2016, the University of Arizona James E. Rogers College of Law became the first law school to accept either the GRE or the Law School Admissions Test (LSAT) from all applicants. The college made the decision after conducting a study showing that the GRE is a valid and reliable predictor of students' first-term law school grades.
In the spring of 2017, Harvard Law School announced it was joining University of Arizona Law in accepting the GRE in addition to the LSAT from applicants to its three-year J.D. program.
After a trial cycle of GRE–free admissions for Fall 2021, University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Berkeley, California, United States. Founded in 1868 and named after t ...
voted to drop the GRE requirement for most graduate program admissions for Fall 2022 as well. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor shortly followed announcing that they would drop the GRE requirements for Ph.D. admissions beginning with the 2022–23 admissions cycle. By late 2022, the trend had intensified.
MBA
GRE score can be used for taking admission in MBA in foreign colleges. The GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) is a computer-adaptive standardized test in mathematics and the English language for measuring aptitude to succeed academically in graduate business studies. Business schools commonly use the test as one of many selection criteria for admission into an MBA program. Starting in 2009, many business schools began accepting the GRE in lieu of a GMAT score. Policies varied widely for several years. However, as of the 2014–2015 admissions season, most business schools accept both tests equally. Either a GMAT score or a GRE score can be submitted for an application to an MBA program. Business schools also accept either score for their other (non-MBA) Masters and Ph.D. programs. The primary issue on which business school test acceptance policies vary is in how old a GRE or GMAT score can be before it is no longer accepted. The standard is that scores cannot be more than 5 years old (e.g., Wharton, MIT Sloan,Columbia Business School
Columbia Business School (CBS) is the business school of Columbia University, a Private university, private research university in New York City. Established in 1916, Columbia Business School is one of six Ivy League business schools and one of ...
).
Intellectual clubs
High GRE scores are accepted as qualifying evidence to some intellectual clubs such as Intertel and theTriple Nine Society
The Triple Nine Society (TNS) is an international high-IQ society for adults whose score on a standardised test, standardized test demonstrates an IQ at or above the 99.9th percentile of the human population. The society recognizes scores from ...
, the minimum passing score depending on the selectivity of the society and the time period when the test was taken. Intertel accepts scores in the 99th percentile obtained after 2011. Mensa does not accept any score post-September 2001.
Preparation
A variety of resources are available for those wishing to prepare for the GRE. ETS provides preparation software called PowerPrep, which contains two practice tests of retired questions, as well as further practice questions and review material. Since the software replicates both the test format and the questions used, it can be useful to predict the actual GRE scores. ETS does not license their past questions to any other company, making them the only source for official retired material. ETS used to publish the "BIG BOOK" which contained a number of actual GRE questions; however, this publishing was abandoned. Several companies provide courses, books, and other unofficial preparation materials. Some students taking the GRE use atest preparation
Test preparation (abbreviated test prep) or exam preparation is an educational course, tutoring service, educational material, or a learning tool designed to increase students' performance on standardized tests. Examples of these tests include ...
company. Students who do not use these courses often rely on material from university text books, GRE preparation books, sample tests, and free web resources.
Testing locations
While the general and subject tests are held at many undergraduate institutions, the computer-based general test can be held in over 1,000 locations with appropriate technological accommodations. In the United States, students in major cities or from large universities will usually find a nearby test center, while those in more isolated areas may have to travel a few hours to an urban or university location. Many industrialized countries also have test centers, but at times test-takers must cross country borders.Criticism
Bias
Algorithmic bias
Critics have claimed that the computer-adaptive methodology may discourage some test takers since the question difficulty changes with performance. For example, if the test-taker is presented with remarkably easy questions halfway into the exam, they may infer that they are not performing well, which will influence their abilities as the exam continues, even though question difficulty is subjective. By contrast, standard testing methods may discourage students by giving them more difficult items earlier on. Critics have also stated that the computer-adaptive method of placing more weight on the first several questions is biased against test takers who typically perform poorly at the beginning of a test due to stress or confusion before becoming more comfortable as the exam continues. On the other hand, standard fixed-form tests could equally be said to be "biased" against students with less testing stamina since they would need to be approximately twice the length of an equivalent computer adaptive test to obtain a similar level of precision.Implicit bias
The GRE has also been subjected to the same racial bias criticisms that have been lodged against other admissions tests. In 1998, '' The Journal of Blacks in Higher Education'' noted that the mean score for black test-takers in 1996 was 389 on the verbal section, 409 on the quantitative section, and 423 on the analytic, while white test-takers averaged 496, 538, and 564, respectively. The National Association of Test Directors Symposia in 2004 stated a belief that simple mean score differences may not constitute evidence of bias unless the populations are known to be equal in ability. A more effective, accepted, and empirical approach is the analysis of differential test functioning, which examines the differences initem response theory
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT, also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of Test (student assessment), tests, questionnaires, and sim ...
curves for subgroups; the best approach for this is the DFIT framework.
Weak indicator of graduate school performance
The GREs are criticized for not being a true measure of whether a student will be successful in graduate school. Robert Sternberg (now ofCornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ...
; working at Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...
at the time of the study), a long-time critic of modern intelligence testing in general, found the GRE general test was weakly predictive of success in graduate studies in psychology. The strongest relationship was found for the now-defunct analytical portion of the exam.
The ETS published a report ("What is the Value of the GRE?") that points out the predictive value of the GRE on a student's index of success at the graduate level. The problem with earlier studies is the statistical phenomenon of restriction of range. A correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics ...
coefficient is sensitive to the range sampled for the test. Specifically, if only students accepted to graduate programs are studied (in Sternberg & Williams and other research), the relationship is occluded. Validity coefficients range from .30 to .45 between the GRE and both first year and overall graduate GPA in ETS' study.
Kaplan and Saccuzzo state that the criterion that the GRE best predicts is first-year grades in graduate school. However, this correlation is only in the high tens to low twenties. "If the test correlates with a criterion at the .4 level, then it accounts for 16% of the variability in that criterion, with the other 84% resulting from unknown factors and errors" (p. 303). Graduate schools may be placing too much importance on standardized tests rather than on factors that more fully account for graduate school success, such as a thesis-requiring Honours degree
Honours degree has various meanings in the context of different degrees and education systems. Most commonly it refers to a variant of the undergraduate bachelor's degree containing a larger volume of material or a higher standard of study, ...
, prior research experience, GPAs, or work experience. While graduate schools do consider these areas, many times schools will not consider applicants that score below a current score of roughly 314 (1301 prior score). Kaplan and Saccuzzo also state that "the GRE predict neither clinical skill nor even the ability to solve real-world problems" (p. 303).
In 2007, a study by a university found a correlation of .30 to .45 between the GRE and both first year and overall graduate GPA. The correlation between GRE score and graduate school completion rates ranged from .11 (for the now defunct analytical section) to .39 (for the GRE subject test). Correlations with faculty ratings ranged from .35 to .50.
Historical susceptibility to cheating
In May 1994, Kaplan, Inc warned ETS, in hearings before a New York legislative committee, that the small question pool available to the computer-adaptive test made it vulnerable to cheating. ETS assured investigators that it was using multiple sets of questions and that the test was secure. This was later discovered to be incorrect. In December 1994, prompted by student reports of recycled questions, then Director of GRE Programs for Kaplan, Inc and current CEO of Knewton, Jose Ferreira, led a team of 22 staff members deployed to 9 U.S. cities to take the exam. Kaplan, Inc then presented ETS with 150 questions, representing 70–80% of the GRE. According to early news releases, ETS appeared grateful to Stanley H. Kaplan, Inc. for identifying the security problem. However, on December 31, ETS sued Kaplan, Inc. for violation of a federal electronic communications privacy act, copyright laws, breach of contract, fraud, and a confidentiality agreement signed by test-takers on test day. On January 2, 1995, an agreement was reached out of court. Additionally, in 1994, the scoring algorithm for the computer-adaptive form of the GRE was discovered to be insecure. ETS acknowledged that Kaplan, Inc employees, led by Jose Ferreira, reverse-engineered key features of the GRE scoring algorithms. The researchers found that a test taker's performance on the first few questions of the exam had a disproportionate effect on the test taker's final score. To preserve the integrity of scores, ETS adopted a more sophisticated scoring algorithm.See also
* List of admissions tests GRE Subject Tests: * GRE Mathematics Test * GRE Physics Test * GRE Psychology Test Discontinued GRE Subject Tests: * GRE Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology Test discontinued December 2016 * GRE Biology Test discontinued May 2021 * GRE Chemistry Test discontinued May 2023 * GRE Economics Test discontinued April 2001 * GRE Literature in English Test discontinued May 2021 Other tests: * Law School Admission Test (LSAT) * Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) * Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) * Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE) *SAT
The SAT ( ) is a standardized test widely used for college admissions in the United States. Since its debut in 1926, its name and Test score, scoring have changed several times. For much of its history, it was called the Scholastic Aptitude Test ...
* ACT (test)
The ACT (; originally an abbreviation of American College Testing) Name changed in 1996. is a standardized test used for college admissions in the United States. It is administered by ACT, Inc., a for-profit organization of the same name. ...
* Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL)
* International English Language Testing System (IELTS)
References
External links
*GRE information website for residents of Mainland China, English version
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171108205246/https://gre.etest.net.cn/login.do?lang=en_US , date=November 8, 2017 - by the Chinese National Education Examinations Authority 1936 establishments in the United States Entrance examinations Standardized tests in the United States Standardized tests for English language