Echinodermata on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An echinoderm () is any
File:Ophionereis reticulata 1.jpg, A brittle star, '' Ophionereis reticulata''
File:Sea cucumber at Pulau Redang.jpg, A sea cucumber, '' Stichopus chloronotus'', from Malaysia
File:Nerr0878.jpg, Starfish of varied colours
File:Strongylocentrotus purpuratus 1.jpg, A sea urchin, '' Strongylocentrotus purpuratus''
File:Crinoid on the reef of Batu Moncho Island.JPG, Crinoid on a
 Many echinoderms have great powers of regeneration. Many species routinely autotomize and regenerate arms and viscera. Sea cucumbers often discharge parts of their internal organs if they perceive themselves to be threatened, regenerating them over the course of several months. Sea urchins constantly replace spines lost through damage, while sea stars and sea lilies readily lose and regenerate their arms. In most cases, a single severed arm cannot grow into a new starfish in the absence of at least part of the disc. However, in a few species a single arm can survive and develop into a complete individual, and arms are sometimes intentionally detached for the purpose of
Many echinoderms have great powers of regeneration. Many species routinely autotomize and regenerate arms and viscera. Sea cucumbers often discharge parts of their internal organs if they perceive themselves to be threatened, regenerating them over the course of several months. Sea urchins constantly replace spines lost through damage, while sea stars and sea lilies readily lose and regenerate their arms. In most cases, a single severed arm cannot grow into a new starfish in the absence of at least part of the disc. However, in a few species a single arm can survive and develop into a complete individual, and arms are sometimes intentionally detached for the purpose of
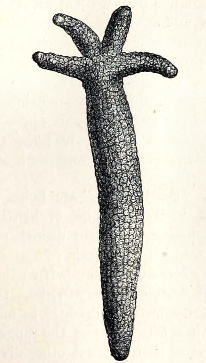 One species of seastar, '' Ophidiaster granifer'', reproduces asexually by parthenogenesis. In certain other asterozoans, adults reproduce asexually until they mature, then reproduce sexually. In most of these species, asexual reproduction is by transverse fission with the disc splitting in two. Both the lost disc area and the missing arms regrow, so an individual may have arms of varying lengths. During the period of regrowth, they have a few tiny arms and one large arm, and are thus often known as "comets".
Adult sea cucumbers reproduce asexually by transverse fission. '' Holothuria parvula'' uses this method frequently, splitting into two a little in front of the midpoint. The two halves each regenerate their missing organs over a period of several months, but the missing genital organs are often very slow to develop.
The larvae of some echinoderms are capable of asexual reproduction. This has long been known to occur among starfish and brittle stars, but has more recently been observed in a sea cucumber, a sand dollar and a sea urchin. This may be by autotomising parts that develop into secondary larvae, by budding, or by splitting transversely. Autotomised parts or buds may develop directly into fully formed larvae, or may pass through a
One species of seastar, '' Ophidiaster granifer'', reproduces asexually by parthenogenesis. In certain other asterozoans, adults reproduce asexually until they mature, then reproduce sexually. In most of these species, asexual reproduction is by transverse fission with the disc splitting in two. Both the lost disc area and the missing arms regrow, so an individual may have arms of varying lengths. During the period of regrowth, they have a few tiny arms and one large arm, and are thus often known as "comets".
Adult sea cucumbers reproduce asexually by transverse fission. '' Holothuria parvula'' uses this method frequently, splitting into two a little in front of the midpoint. The two halves each regenerate their missing organs over a period of several months, but the missing genital organs are often very slow to develop.
The larvae of some echinoderms are capable of asexual reproduction. This has long been known to occur among starfish and brittle stars, but has more recently been observed in a sea cucumber, a sand dollar and a sea urchin. This may be by autotomising parts that develop into secondary larvae, by budding, or by splitting transversely. Autotomised parts or buds may develop directly into fully formed larvae, or may pass through a
 Development begins with a bilaterally symmetrical embryo, with a coeloblastula developing first. Gastrulation marks the opening of the "second mouth" that places echinoderms within the deuterostomes, and the mesoderm, which will host the skeleton, migrates inwards. The secondary body cavity, the coelom, forms by the partitioning of three body cavities. The larvae are often
Development begins with a bilaterally symmetrical embryo, with a coeloblastula developing first. Gastrulation marks the opening of the "second mouth" that places echinoderms within the deuterostomes, and the mesoderm, which will host the skeleton, migrates inwards. The secondary body cavity, the coelom, forms by the partitioning of three body cavities. The larvae are often
 Echinoderms primarily use their tube feet to move about, though some sea urchins also use their spines. The tube feet typically have a tip shaped like a suction pad in which a vacuum can be created by contraction of muscles. This combines with some stickiness from the secretion of mucus to provide adhesion. The tube feet contract and relax in waves which move along the adherent surface, and the animal moves slowly along.
Brittle stars are the most agile of the echinoderms. Any one of the arms can form the axis of symmetry, pointing either forwards or back. The animal then moves in a co-ordinated way, propelled by the other four arms. During locomotion, the propelling arms can made either snake-like or rowing movements. Starfish move using their tube feet, keeping their arms almost still, including in genera like '' Pycnopodia'' where the arms are flexible. The oral surface is covered with thousands of tube feet which move out of time with each other, but not in a metachronal rhythm; in some way, however, the tube feet are coordinated, as the animal glides steadily along. Some burrowing starfish have points rather than suckers on their tube feet and they are able to "glide" across the seabed at a faster rate.
Sea urchins use their tube feet to move around in a similar way to starfish. Some also use their articulated spines to push or lever themselves along or lift their oral surfaces off the substrate. If a sea urchin is overturned, it can extend its tube feet in one ambulacral area far enough to bring them within reach of the substrate and then successively attach feet from the adjoining area until it is righted. Some species bore into rock, usually by grinding away at the surface with their mouthparts.
Most sea cucumber species move on the surface of the seabed or burrow through sand or mud using peristaltic movements; some have short tube feet on their under surface with which they can creep along in the manner of a starfish. Some species drag themselves along using their buccal tentacles, while others manage to swim with peristaltic movements or rhythmic flexing. Many live in cracks, hollows and burrows and hardly move at all. Some deep-water species are pelagic and can float in the water with webbed papillae forming sails or fins.
The majority of feather stars (also called Comatulida or "unstalked crinoids") and some stalked forms are motile. Several stalked crinoid species are sessile, attached permanently to the substratum. Movement in most sea lilies is limited to bending (their stems can bend) and rolling and unrolling their arms; a few species can relocate themselves on the seabed by crawling. Feather stars are unattached and usually live in crevices, under corals or inside sponges with their arms the only visible part. Some feather stars emerge at night and perch themselves on nearby eminences to better exploit food-bearing currents. Many species can "walk" across the seabed, raising their body with the help of their arms, or swim using their arms. Most species of feather stars, however, are largely sedentary, seldom moving far from their chosen place of concealment.
Echinoderms primarily use their tube feet to move about, though some sea urchins also use their spines. The tube feet typically have a tip shaped like a suction pad in which a vacuum can be created by contraction of muscles. This combines with some stickiness from the secretion of mucus to provide adhesion. The tube feet contract and relax in waves which move along the adherent surface, and the animal moves slowly along.
Brittle stars are the most agile of the echinoderms. Any one of the arms can form the axis of symmetry, pointing either forwards or back. The animal then moves in a co-ordinated way, propelled by the other four arms. During locomotion, the propelling arms can made either snake-like or rowing movements. Starfish move using their tube feet, keeping their arms almost still, including in genera like '' Pycnopodia'' where the arms are flexible. The oral surface is covered with thousands of tube feet which move out of time with each other, but not in a metachronal rhythm; in some way, however, the tube feet are coordinated, as the animal glides steadily along. Some burrowing starfish have points rather than suckers on their tube feet and they are able to "glide" across the seabed at a faster rate.
Sea urchins use their tube feet to move around in a similar way to starfish. Some also use their articulated spines to push or lever themselves along or lift their oral surfaces off the substrate. If a sea urchin is overturned, it can extend its tube feet in one ambulacral area far enough to bring them within reach of the substrate and then successively attach feet from the adjoining area until it is righted. Some species bore into rock, usually by grinding away at the surface with their mouthparts.
Most sea cucumber species move on the surface of the seabed or burrow through sand or mud using peristaltic movements; some have short tube feet on their under surface with which they can creep along in the manner of a starfish. Some species drag themselves along using their buccal tentacles, while others manage to swim with peristaltic movements or rhythmic flexing. Many live in cracks, hollows and burrows and hardly move at all. Some deep-water species are pelagic and can float in the water with webbed papillae forming sails or fins.
The majority of feather stars (also called Comatulida or "unstalked crinoids") and some stalked forms are motile. Several stalked crinoid species are sessile, attached permanently to the substratum. Movement in most sea lilies is limited to bending (their stems can bend) and rolling and unrolling their arms; a few species can relocate themselves on the seabed by crawling. Feather stars are unattached and usually live in crevices, under corals or inside sponges with their arms the only visible part. Some feather stars emerge at night and perch themselves on nearby eminences to better exploit food-bearing currents. Many species can "walk" across the seabed, raising their body with the help of their arms, or swim using their arms. Most species of feather stars, however, are largely sedentary, seldom moving far from their chosen place of concealment.
 Echinoderms are numerous invertebrates whose adults play an important role in benthic
Echinoderms are numerous invertebrates whose adults play an important role in benthic
 The oldest potential echinoderm
The oldest potential echinoderm  '' Yanjiahella'', from the Fortunian (''circa'' 539–529 Ma), is unlike the older fossils in that it has a plated theca, albeit one without evidence of stereom. To some, this is a reason to place it as a stem ambulacrarian or stem hemichordate. Others argue that absence of evidence for stereom is not evidence of absence, and consider a stem echinoderm position more likely.
'' Yanjiahella'', from the Fortunian (''circa'' 539–529 Ma), is unlike the older fossils in that it has a plated theca, albeit one without evidence of stereom. To some, this is a reason to place it as a stem ambulacrarian or stem hemichordate. Others argue that absence of evidence for stereom is not evidence of absence, and consider a stem echinoderm position more likely.
File:EarlyEchinoderms NT.jpg, Early echinoderms '' Ctenoimbricata'', '' Ctenocystis'', '' Gogia'', '' Protocinctus'' and '' Rhenocystis''
File:Echinosphaerites.JPG, The Ordovician cystoid '' Echinosphaerites'' from northeastern Estonia
File:fossile-seelilie.jpg, Fossil crinoid crowns
File:Hyperoblastus.jpg, Calyx of ''Hyperoblastus'', a blastoid from the
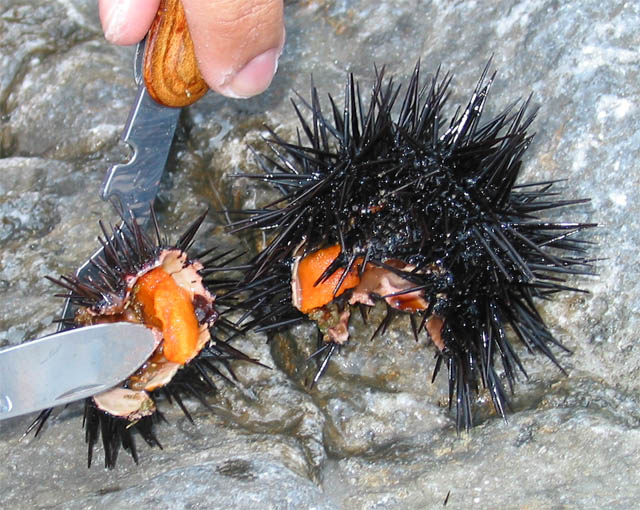

 In 2019, 129,052 tonnes of echinoderms were harvested. The majority of these were sea cucumbers (59,262 tonnes) and sea urchins (66,341 tonnes). These are used mainly for food, but also in
In 2019, 129,052 tonnes of echinoderms were harvested. The majority of these were sea cucumbers (59,262 tonnes) and sea urchins (66,341 tonnes). These are used mainly for food, but also in
echinobase.org
The Echinoid Directory
from the Natural History Museum
Echinodermata
from the Tree of Life Web Project
Echinoderms of the North Sea
{{Authority control Aquatic invertebrates Extant Cambrian first appearances Marine animals
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
of the phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
Echinodermata (), which includes starfish
Starfish or sea stars are Star polygon, star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class (biology), class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to brittle star, ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to ...
, brittle star
Brittle stars, serpent stars, or ophiuroids (; ; referring to the serpent-like arms of the brittle star) are echinoderms in the class Ophiuroidea, closely related to starfish. They crawl across the sea floor using their flexible arms for locomot ...
s, sea urchin
Sea urchins or urchins () are echinoderms in the class (biology), class Echinoidea. About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones from the intertidal zone to deep seas of . They typically have a globular body cove ...
s, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as larvae, as adults echinoderms are recognisable by their usually five-pointed radial symmetry (pentamerous symmetry), and are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,600 living species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, making it the second-largest group of deuterostomes after the chordates, as well as the largest marine-only phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
.
Echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to reproduce asexually and regenerate tissue, organs and limbs; in some cases, they can undergo complete regeneration from a single limb. Geologically, the value of echinoderms is in their ossified dermal endoskeletons, which are major contributors to many limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
formations and can provide valuable clues as to the geological environment. They were the most used species in regenerative research in the 19th and 20th centuries. Further, some scientists hold that the radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
of echinoderms was responsible for the Mesozoic Marine Revolution.
Etymology
The name echinoderm is . The name Echinodermata was originated by Jacob Theodor Klein in 1734, but only in reference to echinoids. It was expanded to the phylum level by Jean Guillaume Bruguière, first informally in 1789 and then in formal Latin in 1791. In 1955, Libbie Hyman attributed the name to "Bruguière, 1791 x Klein, 1734" This attribution has become common and is listed by the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS), although some workers believe that the ITIS rules should result in attributing "Klein, 1778" due to a 2nd edition of his work published by Leske in that year. While Echinodermata has been in common use since the mid-1800s, several other names had been proposed. Notably, F. A. Bather called the phylum "Echinoderma" (apparently after Latreille, 1825) in his 1900 treatise on the phylum, but this name now refers to afungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
.
Diversity
There are about 7,600extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
species of echinoderm as well as about 13,000 known extinct species. All echinoderms are marine, but they are found in habitats ranging from shallow intertidal areas to abyssal depths. Five extant classes of echinoderms are generally recognized: the Asteroidea (starfish
Starfish or sea stars are Star polygon, star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class (biology), class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to brittle star, ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to ...
, with over 1900 species), Ophiuroidea ( brittle stars, with around 2,300 species), Echinoidea (sea urchin
Sea urchins or urchins () are echinoderms in the class (biology), class Echinoidea. About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones from the intertidal zone to deep seas of . They typically have a globular body cove ...
s and sand dollars, with some 900 species), Holothuroidea ( sea cucumbers, with about 1,430 species), and Crinoidea ( feather stars and sea lilies, with around 580 species).
coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
Anatomy and physiology
Echinoderms evolved from animals withbilateral symmetry
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, the face of a human being has a plane of symme ...
. Although adult echinoderms possess pentaradial symmetry, their larvae are cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
ted, free-swimming organisms with bilateral symmetry. Later, during metamorphosis, the left side of the body grows at the expense of the right side, which is eventually absorbed. The left side then grows in a pentaradially symmetric fashion, in which the body is arranged in five parts around a central axis. Within the Asterozoa, there are a few exceptions from the rule. Most starfish in the genus '' Leptasterias'' have six arms, although five-armed individuals can occur. The Brisingida also contain some six-armed species. Amongst the brittle stars, six-armed species such as ''Ophiothela danae'', '' Ophiactis savignyi'', and ''Ophionotus hexactis'' exist, and ''Ophiacantha vivipara'' often has more than six.
Echinoderms have secondary radial symmetry in portions of their body at some stage of life, most likely an adaptation to a sessile or slow-moving existence. Many crinoids and some seastars are symmetrical in multiples of the basic five; starfish such as '' Labidiaster annulatus'' possess up to fifty arms, while the sea-lily '' Comaster schlegelii'' has two hundred.
Genetic studies have shown that genes directing anterior-most development are expressed along ambulacra in the center of starfish rays, with the next-most-anterior genes expressed in the surrounding fringe of tube feet. Genes related to the beginning of the trunk are expressed at the ray margins, but trunk genes are only expressed in interior tissue rather than on the body surface. This means that a starfish body can more-or-less be considered to consist only of a head.
Skin and skeleton
Echinoderms have a mesodermal skeleton in the dermis, composed ofcalcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
-based plates known as ossicles. If solid, these would form a heavy skeleton, so they have a sponge-like porous structure known as stereom. Ossicles may be fused together, as in the test of sea urchins, or may articulate to form flexible joints as in the arms of sea stars, brittle stars and crinoids. The ossicles may bear external projections in the form of spines, granules or warts and they are supported by a tough epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
. Skeletal elements are sometimes deployed in specialized ways, such as the chewing organ called " Aristotle's lantern" in sea urchins, the supportive stalks of crinoids, and the structural "lime ring" of sea cucumbers.
Although individual ossicles are robust and fossilize readily, complete skeletons of starfish, brittle stars and crinoids are rare in the fossil record. On the other hand, sea urchins are often well preserved in chalk beds or limestone. During fossilization, the cavities in the stereom are filled in with calcite that is continuous with the surrounding rock. On fracturing such rock, paleontologists can observe distinctive cleavage patterns and sometimes even the intricate internal and external structure of the test.
The epidermis contains pigment cells that provide the often vivid colours of echinoderms, which include deep red, stripes of black and white, and intense purple. These cells may be light-sensitive, causing many echinoderms to change appearance completely as night falls. The reaction can happen quickly: the sea urchin '' Centrostephanus longispinus'' changes colour in just fifty minutes when exposed to light.
One characteristic of most echinoderms is a special kind of tissue known as catch connective tissue. This collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
-based material can change its mechanical properties under nervous control rather than by muscular means. This tissue enables a starfish to go from moving flexibly around the seabed to becoming rigid while prying open a bivalve mollusc or preventing itself from being extracted from a crevice. Similarly, sea urchins can lock their normally mobile spines upright as a defensive mechanism when attacked.
The water vascular system
Echinoderms possess a unique water vascular system, a network of fluid-filled canals modified from the coelom (body cavity) that function in gas exchange, feeding, sensory reception and locomotion. This system varies between different classes of echinoderm but typically opens to the exterior through a sieve-like madreporite on the aboral (upper) surface of the animal. The madreporite is linked to a slender duct, the stone canal, which extends to a ring canal that encircles the mouth or oesophagus. The ring canal branches into a set of radial canals, which in asteroids extend along the arms, and in echinoids adjoin the test in the ambulacral areas. Short lateral canals branch off the radial canals, each one ending in an ampulla. Part of the ampulla can protrude through a pore (or a pair of pores in sea urchins) to the exterior, forming a podium or tube foot. The water vascular system assists with the distribution of nutrients throughout the animal's body; it is most visible in the tube feet which can be extended or contracted by the redistribution of fluid between the foot and the internal ampulla. The organisation of the water vascular system is somewhat different in ophiuroids, where the madreporite may be on the oral surface and the podia lack suckers. In holothuroids, the system is reduced, often with few tube feet other than the specialised feeding tentacles, and the madreporite opens on to the coelom. Some holothuroids like the Apodida lack tube feet and canals along the body; others have longitudinal canals. The arrangement in crinoids is similar to that in asteroids, but the tube feet lack suckers and are used in a back-and-forth wafting motion to pass food particles captured by the arms towards the central mouth. In the asteroids, the same motion is employed to move the animal across the ground.Other organs
Echinoderms possess a simple digestive system which varies according to the animal's diet. Starfish are mostly carnivorous and have a mouth, oesophagus, two-part stomach, intestine and rectum, with the anus located in the centre of the aboral body surface. With a few exceptions, the members of the order Paxillosida do not possess an anus. In many species of starfish, the large cardiac stomach can be everted to digest food outside the body. Some other species are able to ingest whole food items such asmollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s. Brittle stars, which have varying diets, have a blind gut with no intestine or anus; they expel food waste
The causes of food going uneaten are numerous and occur throughout the food system, during food production, production, food processing, processing, Food distribution, distribution, Grocery store, retail and food service sales, and Social clas ...
through their mouth. Sea urchins are herbivores and use their specialised mouthparts to graze, tear and chew their food, mainly algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
. They have an oesophagus, a large stomach and a rectum with the anus at the apex of the test. Sea cucumbers are mostly detritivores, sorting through the sediment with modified tube feet around their mouth, the buccal tentacles. Sand and mud accompanies their food through their simple gut, which has a long coiled intestine and a large cloaca. Crinoids are suspension feeders, passively catching plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
which drift into their outstretched arms. Boluses of mucus-trapped food are passed to the mouth, which is linked to the anus by a loop consisting of a short oesophagus and longer intestine.
The coelomic cavities of echinoderms are complex. Aside from the water vascular system, echinoderms have a haemal coelom, a peri visceral coelom, a gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
al coelom and often also a perihaemal coelom. During development, echinoderm coelom is divided into the metacoel, mesocoel and protocoel (also called somatocoel, hydrocoel and axocoel, respectively). The water vascular system, haemal system and perihaemal system form the tubular coelomic system. Echinoderms are unusual in having both a coelomic circulatory system (the water vascular system) and a haemal circulatory system, as most groups of animals have just one of the two.
Haemal and perihaemal systems are derived from the original coelom, forming an open and reduced circulatory system. This usually consists of a central ring and five radial vessels. There is no true heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
, and the blood often lacks any respiratory pigment. Gaseous exchange occurs via dermal branchiae or papulae in starfish, genital bursae in brittle stars, peristominal gills in sea urchins and cloacal trees in sea cucumbers. Exchange of gases also takes place through the tube feet. Echinoderms lack specialized excretory (waste disposal) organs and so nitrogenous waste, chiefly in the form of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
, diffuses out through the respiratory surfaces.
The coelomic fluid contains the coelomocytes, or immune cells. There are several types of immune cells, which vary among classes and species. All classes possess a type of phagocytic amebocyte, which engulf invading particles and infected cells, aggregate or clot, and may be involved in cytotoxicity. These cells are usually large and granular, and are believed to be a main line of defence against potential pathogens. Depending on the class, echinoderms may have spherule cells (for cytotoxicity, inflammation, and anti-bacterial activity), vibratile cells (for coelomic fluid movement and clotting), and crystal cells (which may serve for osmoregulation in sea cucumbers). The coelomocytes secrete antimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between Prokaryote, prokaryotic and eukaryota, eukaryotic cells that may ...
against bacteria, and have a set of lectins and complement proteins as part of an innate immune system
The innate immune system or nonspecific immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies in vertebrates (the other being the adaptive immune system). The innate immune system is an alternate defense strategy and is the dominant immune s ...
that is still being characterised.
Echinoderms have a simple radial nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
that consists of a modified nerve net of interconnected neurons with no central brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, although some do possess ganglia. Nerves radiate from central rings around the mouth into each arm or along the body wall; the branches of these nerves coordinate the movements of the organism and the synchronisation of the tube feet. Starfish have sensory cells in the epithelium and have simple eyespots and touch-sensitive tentacle-like tube feet at the tips of their arms. Sea urchins have no particular sense organs but do have statocysts that assist in gravitational orientation, and they too have sensory cells in their epidermis, particularly in the tube feet, spines and pedicellariae. Brittle stars, crinoids and sea cucumbers in general do not have sensory organs, but some burrowing sea cucumbers of the order Apodida have a single statocyst adjoining each radial nerve, and some have an eyespot at the base of each tentacle.
The gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s at least periodically occupy much of the body cavities of sea urchins and sea cucumbers, while the less voluminous crinoids, brittle stars and starfish have two gonads in each arm. While the ancestors of modern echinoderms are believed to have had one genital aperture, many organisms have multiple gonopores through which eggs or sperm may be released.
Regeneration
 Many echinoderms have great powers of regeneration. Many species routinely autotomize and regenerate arms and viscera. Sea cucumbers often discharge parts of their internal organs if they perceive themselves to be threatened, regenerating them over the course of several months. Sea urchins constantly replace spines lost through damage, while sea stars and sea lilies readily lose and regenerate their arms. In most cases, a single severed arm cannot grow into a new starfish in the absence of at least part of the disc. However, in a few species a single arm can survive and develop into a complete individual, and arms are sometimes intentionally detached for the purpose of
Many echinoderms have great powers of regeneration. Many species routinely autotomize and regenerate arms and viscera. Sea cucumbers often discharge parts of their internal organs if they perceive themselves to be threatened, regenerating them over the course of several months. Sea urchins constantly replace spines lost through damage, while sea stars and sea lilies readily lose and regenerate their arms. In most cases, a single severed arm cannot grow into a new starfish in the absence of at least part of the disc. However, in a few species a single arm can survive and develop into a complete individual, and arms are sometimes intentionally detached for the purpose of asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the f ...
. During periods when they have lost their digestive tracts, sea cucumbers live off stored nutrients and absorb dissolved organic matter directly from the water.
The regeneration of lost parts involves both epimorphosis and morphallaxis. In epimorphosis stem cells, either from a reserve pool or those produced by dedifferentiation, form a blastema and generate new tissues. Morphallactic regeneration involves the movement and remodelling of existing tissues to replace lost parts. Direct transdifferentiation of one type of tissue to another during tissue replacement is also observed.
Reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Echinoderms become sexually mature after approximately two to three years, depending on the species and the environmental conditions. Almost all species have separate male and female sexes, though some are hermaphroditic. The eggs and sperm cells are typically released into open water, where fertilisation takes place. The release of sperm and eggs is synchronised in some species, usually with regard to the lunar cycle. In other species, individuals may aggregate during the reproductive season, increasing the likelihood of successful fertilisation. Internal fertilisation has been observed in three species of sea star, three brittle stars and a deep-water sea cucumber. Even at abyssal depths, where no light penetrates, echinoderms often synchronise their reproductive activity. Some echinoderms brood their eggs. This is especially common in cold water species where planktonic larvae might not be able to find sufficient food. These retained eggs are usually few in number and are supplied with large yolks to nourish the developing embryos. In starfish, the female may carry the eggs in special pouches, under her arms, under her arched body, or even in her cardiac stomach. Many brittle stars are hermaphrodites; they often brood their eggs, usually in special chambers on their oral surfaces, but sometimes in the ovary or coelom. In these starfish and brittle stars, development is usually direct to the adult form, without passing through a bilateral larval stage. A few sea urchins and one species of sand dollar carry their eggs in cavities, or near their anus, holding them in place with their spines. Some sea cucumbers use their buccal tentacles to transfer their eggs to their underside or back, where they are retained. In a very small number of species, the eggs are retained in the coelom where they develop viviparously, later emerging through ruptures in the body wall. In some crinoids, the embryos develop in special breeding bags, where the eggs are held until sperm released by a male happens to find them.Asexual reproduction
 One species of seastar, '' Ophidiaster granifer'', reproduces asexually by parthenogenesis. In certain other asterozoans, adults reproduce asexually until they mature, then reproduce sexually. In most of these species, asexual reproduction is by transverse fission with the disc splitting in two. Both the lost disc area and the missing arms regrow, so an individual may have arms of varying lengths. During the period of regrowth, they have a few tiny arms and one large arm, and are thus often known as "comets".
Adult sea cucumbers reproduce asexually by transverse fission. '' Holothuria parvula'' uses this method frequently, splitting into two a little in front of the midpoint. The two halves each regenerate their missing organs over a period of several months, but the missing genital organs are often very slow to develop.
The larvae of some echinoderms are capable of asexual reproduction. This has long been known to occur among starfish and brittle stars, but has more recently been observed in a sea cucumber, a sand dollar and a sea urchin. This may be by autotomising parts that develop into secondary larvae, by budding, or by splitting transversely. Autotomised parts or buds may develop directly into fully formed larvae, or may pass through a
One species of seastar, '' Ophidiaster granifer'', reproduces asexually by parthenogenesis. In certain other asterozoans, adults reproduce asexually until they mature, then reproduce sexually. In most of these species, asexual reproduction is by transverse fission with the disc splitting in two. Both the lost disc area and the missing arms regrow, so an individual may have arms of varying lengths. During the period of regrowth, they have a few tiny arms and one large arm, and are thus often known as "comets".
Adult sea cucumbers reproduce asexually by transverse fission. '' Holothuria parvula'' uses this method frequently, splitting into two a little in front of the midpoint. The two halves each regenerate their missing organs over a period of several months, but the missing genital organs are often very slow to develop.
The larvae of some echinoderms are capable of asexual reproduction. This has long been known to occur among starfish and brittle stars, but has more recently been observed in a sea cucumber, a sand dollar and a sea urchin. This may be by autotomising parts that develop into secondary larvae, by budding, or by splitting transversely. Autotomised parts or buds may develop directly into fully formed larvae, or may pass through a gastrula
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells), or in mammals, the blastocyst, is reorganized into a two-layered or three-layered e ...
or even a blastula stage. New larvae can develop from the preoral hood (a mound like structure above the mouth), the side body wall, the postero-lateral arms, or their rear ends.
Cloning is costly to the larva both in resources and in development time. Larvae undergo this process when food is plentiful or temperature conditions are optimal. Cloning may occur to make use of the tissues that are normally lost during metamorphosis. The larvae of some sand dollars clone themselves when they detect dissolved fish mucus, indicating the presence of predators. Asexual reproduction produces many smaller larvae that escape better from planktivorous fish, implying that the mechanism may be an anti-predator adaptation.
Larval development
 Development begins with a bilaterally symmetrical embryo, with a coeloblastula developing first. Gastrulation marks the opening of the "second mouth" that places echinoderms within the deuterostomes, and the mesoderm, which will host the skeleton, migrates inwards. The secondary body cavity, the coelom, forms by the partitioning of three body cavities. The larvae are often
Development begins with a bilaterally symmetrical embryo, with a coeloblastula developing first. Gastrulation marks the opening of the "second mouth" that places echinoderms within the deuterostomes, and the mesoderm, which will host the skeleton, migrates inwards. The secondary body cavity, the coelom, forms by the partitioning of three body cavities. The larvae are often plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
ic, but in some species the eggs are retained inside the female, while in some the female broods the larvae.
The larvae pass through several stages, which have specific names derived from the taxonomic names of the adults or from their appearance. For example, a sea urchin has an 'echinopluteus' larva while a brittle star has an 'ophiopluteus' larva. A starfish has a ' bipinnaria' larva, which develops into a multi-armed ' brachiolaria' larva. A sea cucumber's larva is an 'auricularia' while a crinoid's is a 'vitellaria'. All these larvae are bilaterally symmetrical and have bands of cilia with which they swim; some, usually known as 'pluteus' larvae, have arms. When fully developed, they settle on the seabed to undergo metamorphosis, and the larval arms and gut degenerate. The left-hand side of the larva develops into the oral surface of the juvenile, while the right side becomes the aboral surface. At this stage, the pentaradial symmetry develops.
A plankton-eating larva, living and feeding in the water column, is considered to be the ancestral larval type for echinoderms, but in extant echinoderms, some 68% of species develop using a yolk-feeding larva. The provision of a yolk-sac means that smaller numbers of eggs are produced, the larvae have a shorter development period and a smaller dispersal potential, but a greater chance of survival.
Distribution and habitat
Echinoderms are globally distributed in almost all depths, latitudes and environments in the ocean. Living echinoderms are known from between 0 to over 10,000 meters. Adults are mainly benthic, living on the seabed, whereas larvae are often pelagic, living as plankton in the open ocean. Some holothuroid adults such as '' Pelagothuria'' are pelagic. In the fossil record, some crinoids were pseudo-planktonic, attaching themselves to floating logs and debris. Some Paleozoic taxa displayed this life mode, before competition from organisms such as barnacles restricted the extent of the behaviour.Mode of life
Locomotion
Feeding
The modes of feeding vary greatly between the different echinoderm taxa. Crinoids and some brittle stars tend to be passive filter-feeders, enmeshing suspended particles from passing water. Most sea urchins are grazers; sea cucumbers are deposit feeders; and the majority of starfish are active hunters. Crinoids catch food particles using the tube feet on their outspread pinnules, move them into the ambulacral grooves, wrap them in mucus, and convey them to the mouth using the cilia lining the grooves. The exact dietary requirements of crinoids have been little researched, but in the laboratory, they can be fed with diatoms. Basket stars are suspension feeders, raising their branched arms to collect zooplankton, while other brittle stars use several methods of feeding. Some are suspension feeders, securing food particles with mucus strands, spines or tube feet on their raised arms. Others are scavengers and detritus feeders. Others again are voraciouscarnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they ar ...
s and able to lasso their waterborne prey with a sudden encirclement by their flexible arms. The limbs then bend under the disc to transfer the food to the jaws and mouth.
Many sea urchins feed on algae, often scraping off the thin layer of algae covering the surfaces of rocks with their specialised mouthparts known as Aristotle's lantern. Other species devour smaller organisms, which they may catch with their tube feet. They may also feed on dead fish and other animal matter. Sand dollars may perform suspension feeding and feed on phytoplankton, detritus, algal pieces and the bacterial layer surrounding grains of sand.
Sea cucumbers are often mobile deposit or suspension feeders, using their buccal podia to actively capture food and then stuffing the particles individually into their buccal cavities. Others ingest large quantities of sediment, absorb the organic matter and pass the indigestible mineral particles through their guts. In this way they disturb and process large volumes of substrate, often leaving characteristic ridges of sediment on the seabed. Some sea cucumbers live infaunally in burrows, anterior-end down and anus on the surface, swallowing sediment and passing it through their gut. Other burrowers live anterior-end up and wait for detritus to fall into the entrances of the burrows or rake in debris from the surface nearby with their buccal podia.
Nearly all starfish are detritus feeders or carnivores, though a few are suspension feeders. Small fish landing on the upper surface may be captured by pedicilaria and dead animal matter may be scavenged but the main prey items are living invertebrates, mostly bivalve molluscs. To feed on one of these, the starfish moves over it, attaches its tube feet and exerts pressure on the valves by arching its back. When a small gap between the valves is formed, the starfish inserts part of its stomach into the prey, excretes digestive enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s and slowly liquefies the soft body parts. As the adductor muscle of the bivalve relaxes, more stomach is inserted and when digestion is complete, the stomach is returned to its usual position in the starfish with its now liquefied bivalve meal inside it. Other starfish evert the stomach to feed on sponges, sea anemones, corals, detritus and algal films.
Antipredator defence
Despite their low nutrition value and the abundance of indigestible calcite, echinoderms are preyed upon by many organisms, includingbony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
, shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s, eider ducks, gulls, crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
s, gastropod molluscs, other echinoderms, sea otters, Arctic foxes and humans. Larger starfish prey on smaller ones; the great quantity of eggs and larva that they produce form part of the zooplankton, consumed by many marine creatures. Crinoids, on the other hand, are relatively free from predation.
Antipredator defences include the presence of spines, toxins (inherent or delivered through the tube feet), and the discharge of sticky entangling threads by sea cucumbers. Although most echinoderm spines are blunt, those of the crown-of-thorns starfish are long and sharp and can cause a painful puncture wound as the epithelium covering them contains a toxin. Because of their catch connective tissue, which can change rapidly from a flaccid to a rigid state, echinoderms are very difficult to dislodge from crevices. Some sea cucumbers have a cluster of cuvierian tubules which can be ejected as long sticky threads from their anus to entangle and permanently disable an attacker. Sea cucumbers occasionally defend themselves by rupturing their body wall and discharging the gut and internal organs. Starfish and brittle stars may undergo autotomy when attacked, detaching an arm; this may distract the predator for long enough for the animal to escape. Some starfish species can swim away from danger.
Ecology
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s, while the larvae are a major component of the plankton. Among the ecological roles of adults are the grazing of sea urchins, the sediment processing of heart urchins, and the suspension and deposit feeding of crinoids and sea cucumbers. Some sea urchins can bore into solid rock, destabilising rock faces and releasing nutrients into the ocean. Coral reefs are also bored into in this way, but the rate of accretion of carbonate material is often greater than the erosion produced by the sea urchin. Echinoderms sequester about 0.1 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide per year as calcium carbonate, making them important contributors in the global carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycl ...
.
Echinoderms sometimes have large population swings which can transform ecosystems. In 1983, for example, the mass mortality of the tropical sea urchin '' Diadema antillarum'' in the Caribbean caused a change from a coral-dominated reef system to an alga-dominated one. Sea urchins are among the main herbivores on reefs and there is usually a fine balance between the urchins and the kelp and other algae on which they graze. A diminution of the numbers of predators (otters, lobsters and fish) can result in an increase in urchin numbers, causing overgrazing of kelp forests, resulting in an alga-denuded " urchin barren". On the Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system, composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
, an unexplained increase in the numbers of crown-of-thorns starfish (''Acanthaster planci''), which graze on living coral tissue, has greatly increased coral mortality and reduced coral reef biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
.
Taxonomy and evolution
The characteristics of adult echinoderms are the possession of a water vascular system with externaltube feet
Tube or tubes may refer to:
* Tube (2003 film), ''Tube'' (2003 film), a 2003 Korean film
* "Tubes" (Peter Dale), performer on the Soccer AM#Tubes, Soccer AM television show
* Tube (band), a Japanese rock band
* Tube & Berger, the alias of dance/e ...
and a stereom endoskeleton.
Stereom is a calcareous material consisting of ossicles connected by a mesh of collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
fibres, which is unique to this phylum.
Phylogeny
Echinoderm phylogeny has long been a contentious subject. While the relationships among extant taxa are well-understood, there is no broadly accepted consensus regarding the phylum's origins or the relationships among its extinct groups. Echinoderm evolution shows a high degree of homoplasy, meaning that many features have evolved multiple times independently. This means that many features initially assumed to indicate a genetic connection do not, in fact, do so, which has obscured the true relationships of various groups.External phylogeny
Echinoderms arebilateria
Bilateria () is a large clade of animals characterised by bilateral symmetry during embryonic development. This means their body plans are laid around a longitudinal axis with a front (or "head") and a rear (or "tail") end, as well as a left� ...
ns, meaning that their ancestors were mirror-symmetric. Among the bilaterians, they belong to the deuterostome division, meaning that the blastopore, the first opening to form during embryo development, becomes the anus instead of the mouth.
Echinoderms are the sister group of the Hemichordata, with which they form the crown group Ambulacraria. Two taxa of uncertain placement, Vetulocystida and '' Yanjiahella'', have each been proposed as either stem-group echinoderms or stem-group ambulacrarians. Vetulocystids have also been proposed as stem-group chordates, while ''Yanjiahella'' has also been proposed to be a stem-group hemichordate.
The Ambulacrarian context of the echinoderms is shown below, simplified from Li et al. 2023, with the possible ambulacrarian placements of the uncertain taxa shown with dashed lines and question marks:
Internal phylogeny: extant classes
The extant echinoderms consist of the Crinoidea and the Eleutherozoa, the latter of which is divided into the Asterozoa and the Echinozoa.Internal phylogeny: total group
The lack of a consensuscladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
phylogeny incorporating extinct echinoderm groups has resulted in the continued use of terms from Linnaean taxonomies, even when the named taxa are known to be paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
and/or polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage that includes organisms with mixed evolutionary origin but does not include their most recent common ancestor. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as Homoplasy, homoplasies ...
.
=Linnaean taxonomies
= Three taxonomies introduced nearly all of the traditional subphyla and class divisions that continue to be referenced in cladistic work: * F. A. Bather produced the earliest widely referenced classification of both fossil and extant echinoderms in 1900, using a two-subphylum system. * In 1966, the '' Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology'', rejected Bather's classification, replacing it with a new four-subphylum scheme that had been previously proposed by H. B. Fell. * James Sprinkle which added a fifth subphylum to the ''Treatise'' taxonomy in 1973. His later class-level taxonomy of the five subphyla was the most recent approach cited in an early cladistic re-assessment of the phylum. Other proposed classes not included at that rank in any of the above taxonomies include: * Cryptosyringida * Somasteroidea * Stenuroidea * Coronoidea * Concentricycloidea There are also several common alternative names involving homalozoans: * Carpoidea for Homalozoa, giving rise to the term "carpoids" * Cincta as either the senior synonym of or sole order within Homostelea * Soluta as either the senior synonym of or sole order within Homoiostelea * Calcichordata , a subphylum effectively identical to Stylophora that was central to the now-disproven calcichordate hypothesis=Cladograms
= According to 2024 review, there are two main schools of thought regarding echinoderm phylogeny: One that sees pentaradiality as a plesiomorphic trait of the phylum, and another that considers it a derived trait (apomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel Phenotypic trait, character or character state that has evolution, evolved from its ancestral form (or Plesiomorphy and symplesiomorphy, plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy sh ...
).
Note that neither cladogram shown below includes all of the traditional classes, or even all of the classes mentioned in accompanying text.
; Pentaradiality as a plesiomorphy
Supporters of pentaradiality as an initial condition of the phylum note that radial forms are the first uncontested echinoderms to appear in the fossil record. They also define homologies of echinoderm anatomy based on a division of the skeleton into two parts: those that are or are not associated with the water vascular system.
The following cladogram is based on David & Mooi (1999) and David, Lefebvre, Mooi, and Parsley (2000):
In this theory, the controversial Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
fossil '' Arkarua'' is tentatively placed as the sister to all other echinoderms. Helicoplacoidea and Edrioasteroidea join it in the stem group. Pelmatozoa, Eocrinoidea, and Cystoidea are shown to be paraphyletic while Homalozoa is polyphyletic.
; Pentaradiality as an apomorphy
Those who find pentaradiality to be derived incorporate the recently discovered fossils '' Ctenoimbricata'' (seen as a possible sister to all other echinoderms) and '' Helicocystis'' (seen as bridging the triradial helicoplacoids and the pentaradial crown group). They cite research indicating that the early appearance of pentaradial forms is likely due to an incomplete fossil record, as well as multiple studies showing non-radial forms as an early stem group, to argue that this is phylogeny represents an emerging consensus. They reject ''Arkarua'' as an echinoderm due to its lack of stereom and possession of true pentaradiality instead of the 2-1-2 pseudo-pentaradiality seen in all early forms.
The following cladogram is based on Rahman & Zamora (2024), incorporating class and subphylum names from the text:
Here, Homalozoa (with uncertain placement of Stylophora) is shown to be a paraphyletic assemblage along the stem group, followed by Helicoplacoidea and then '' Helicocystis'' as the sister of the crown group. The details of Blastozoa vs Crinozoa are not addressed, as they are represented only by the classes Eocrinoidea and Crinoidea, respectively, and the overall nature of Pelmatozoa remains unresolved. The four-way polytomy including the Eleutherozoa and Crinoidea shows either '' Camptostroma'' or '' Gogia'' or both could prove to be outside of the crown group.
Fossil history
Echinoderms have a rich fossil record due to their mineralized endoskeletons.Possible early echinoderms
The three oldest known candidate echinoderms all lack stereom and other echinoderm apomorphies, making their inclusion in the phylum controversial. The oldest potential echinoderm
The oldest potential echinoderm fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
is '' Arkarua'' from the late Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
of Australia ''circa'' 555 Ma. These fossils are disc-like, with radial ridges on the rim and a five-pointed central depression marked with radial lines. However, the fossils have no stereom or internal structure indicating a water vascular system, so they cannot be conclusively identified. Additionally, all known early pentaradial echinoderms are pseudo-pentaradial in a 2-1-2 pattern, with true pentaradiality as seen in ''Arkarua'' not seen until the emergence of the Eleutherozoa.
The next possible echinoderms are the vetulocystids, which date to the early to mid Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
, 541–501 Ma. While the youngest vetulocystid, ''Thylacocercus'', displays some characteristics that could be interemediate between older vetulocystids and '' Yanjiahella'', its discoverers consider vetulocystids more likely to be stem ambulacrarians than stem echinoderms.
 '' Yanjiahella'', from the Fortunian (''circa'' 539–529 Ma), is unlike the older fossils in that it has a plated theca, albeit one without evidence of stereom. To some, this is a reason to place it as a stem ambulacrarian or stem hemichordate. Others argue that absence of evidence for stereom is not evidence of absence, and consider a stem echinoderm position more likely.
'' Yanjiahella'', from the Fortunian (''circa'' 539–529 Ma), is unlike the older fossils in that it has a plated theca, albeit one without evidence of stereom. To some, this is a reason to place it as a stem ambulacrarian or stem hemichordate. Others argue that absence of evidence for stereom is not evidence of absence, and consider a stem echinoderm position more likely.
Echinoderms in the Cambrian and Ordovician
The first universally accepted echinoderms appear in the Lower Cambrian period; asterozoans appeared in theOrdovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
, while the crinoids were a dominant group in the Paleozoic.
It is hypothesised that the ancestor of all echinoderms was a simple, motile, bilaterally symmetrical animal with a mouth, gut and anus. This ancestral organism adopted an attached mode of life with suspension feeding, and developed radial symmetry. Even so, the larvae of all echinoderms are bilaterally symmetrical, and all develop radial symmetry at metamorphosis. Like their ancestor, the starfish and crinoids still attach themselves to the seabed while changing to their adult form.
The first known echinoderms were non-motile, but evolved into animals able to move freely. These soon developed endoskeletal plates with stereom structure, and external ciliary grooves for feeding. The Paleozoic echinoderms were globular, attached to the substrate and were orientated with their oral surfaces facing upwards. These early echinoderms had ambulacral grooves extending down the side of the body, fringed on either side by brachioles, like the pinnules of a modern crinoid. Eventually, the mobile eleutherozoans reversed their orientation to become mouth-downward. Before this happened, the podia probably had a feeding function, as they do in the crinoids today. The locomotor function of the podia came later, when the re-orientation of the mouth brought the podia into contact with the substrate for the first time.
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
of Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
Use by humans
As food and medicine

 In 2019, 129,052 tonnes of echinoderms were harvested. The majority of these were sea cucumbers (59,262 tonnes) and sea urchins (66,341 tonnes). These are used mainly for food, but also in
In 2019, 129,052 tonnes of echinoderms were harvested. The majority of these were sea cucumbers (59,262 tonnes) and sea urchins (66,341 tonnes). These are used mainly for food, but also in traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medicine, alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. A large share of its claims are pseudoscientific, with the majority of treatments having no robust evidence ...
. Sea cucumbers are considered a delicacy in some countries of southeast Asia; as such, they are in imminent danger of being over-harvested. Popular species include the pineapple roller '' Thelenota ananas'' (''susuhan'') and the red sea cucumber '' Holothuria edulis''. These and other species are colloquially known as ''bêche de mer'' or ''trepang'' in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
. The sea cucumbers are boiled for twenty minutes and then dried both naturally and later over a fire which gives them a smoky tang. In China, they are used as a basis for gelatinous soups and stews. Both male and female gonads of sea urchins are consumed, particularly in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. The taste is described as soft and melting, like a mixture of seafood and fruit. Sea urchin breeding trials have been undertaken to try to compensate for overexploitation.
In research
Because of their robust larval growth, sea urchins are widely used in research, particularly asmodel organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Mo ...
s in developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and di ...
and ecotoxicology. '' Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'' and '' Arbacia punctulata'' are used for this purpose in embryological studies. The large size and the transparency of the eggs enables the observation of sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
cells in the process of fertilising ova. The arm regeneration potential of brittle stars is being studied in connection with understanding and treating neurodegenerative diseases in humans. Genomic data relevant to echinoderm model organisms are collected in Echinobase. Currently, there are four species of echinoderms fully supported (gene pages, BLAST, JBrowse tracks, genome downloads) including '' Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'' (purple sea urchin), '' Lytechinus variegatus'' (green sea urchin), '' Patiria miniata'' (bat star) and '' Acanthaster planci'' (crown-of-thorns sea star). Partially supported species (no gene pages) include '' Lytechinus pictus'' (painted sea urchin), '' Asterias rubens'' (sugar star) and '' Anneissia japonica'' (feather star crinoid).
Other uses
The calcareous tests or shells of echinoderms are used as a source of lime by farmers in areas wherelimestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
is unavailable and some are used in the manufacture of fish meal. 4,000 tons of the animals are used annually for these purposes. This trade is often carried out in conjunction with shellfish farmers, for whom the starfish pose a major threat by eating their cultured stock. Other uses for the starfish they recover include the manufacture of animal feed, composting and the preparation of dried specimens for the arts and craft trade.
See also
*References
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
echinobase.org
The Echinoid Directory
from the Natural History Museum
Echinodermata
from the Tree of Life Web Project
Echinoderms of the North Sea
{{Authority control Aquatic invertebrates Extant Cambrian first appearances Marine animals