Exit Wound on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Penetrating trauma is an
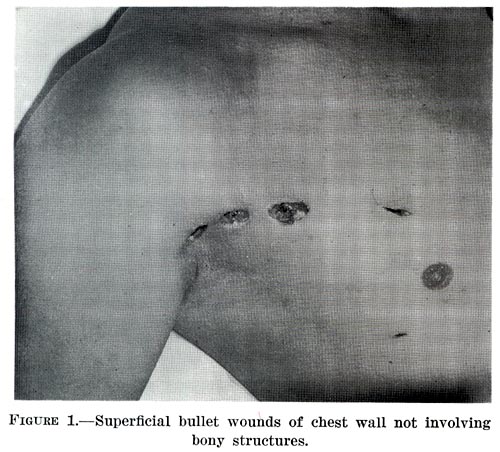 As a missile passes through tissue, it decelerates, dissipating and transferring
As a missile passes through tissue, it decelerates, dissipating and transferring
 Most penetrating injuries are chest wounds and have a mortality rate (death rate) of under 10%. Penetrating
Most penetrating injuries are chest wounds and have a mortality rate (death rate) of under 10%. Penetrating
open wound
A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying diseas ...
injury
Injury is physiological damage to the living tissue of any organism, whether in humans, in other animals, or in plants.
Injuries can be caused in many ways, including mechanically with penetration by sharp objects such as teeth or with ...
that occurs when an object pierces the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
and enters a tissue of the body, creating a deep but relatively narrow entry wound
A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying diseas ...
. In contrast, a blunt or ''non-penetrating'' trauma may have some deep damage, but the overlying skin is not necessarily broken and the wound is still closed to the outside environment. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out the path it entered, or pass through the full thickness of the tissues and exit from another area.
A penetrating injury in which an object enters the body or a structure and passes all the way through an exit wound is called a perforating trauma, while the term ''penetrating trauma'' implies that the object does not perforate wholly through. In gunshot wound
A gunshot wound (GSW) is a penetrating injury caused by a projectile (e.g. a bullet) shot from a gun (typically a firearm). Damage may include bleeding, bone fractures, organ damage, wound infection, and loss of the ability to move part of ...
s, perforating trauma is associated with an entrance wound and an often larger exit wound.
Penetrating trauma can be caused by a foreign object or by fragments of a broken bone. Usually occurring in violent crime
A violent crime, violent felony, crime of violence or crime of a violent nature is a crime in which an offender or perpetrator uses or threatens to use harmful Force (law), force upon a victim. This entails both crimes in which the violence, vio ...
or armed combat
Combat ( French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict between multiple combatants with the intent to harm the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is resorted to either as a method of ...
, penetrating injuries are commonly caused by gunshots and stabbing
A stabbing is penetrating trauma, penetration or rough contact with a sharp or pointed object at close range. ''Stab'' connotes purposeful action, as by an Assassination, assassin or murderer, but it is also possible to accidentally stab oneself ...
s.
Penetrating trauma can be serious because it can damage internal organs and presents a risk of shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses
Healthcare
* Acute stress reaction, also known as psychological or mental shock
** Shell shock, soldiers' reaction to battle trauma
* Circulatory shock, a medical emergency
** Cardiogenic shock, resulting from ...
and infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
. The severity of the injury varies widely depending on the body parts involved, the characteristics of the penetrating object, and the amount of energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
transmitted to the tissues. Assessment may involve X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s or CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
s, and treatment may involve surgery, for example to repair damaged structures or to remove foreign objects. Following penetrating trauma, spinal motion restriction
Spinal precautions, also known as spinal immobilization and spinal motion restriction, are efforts to prevent movement of the bones of the spine in those with a risk of a spine injury. This is done as an effort to prevent injury to the spinal cor ...
is associated with worse outcomes and therefore it should not be done routinely.
Mechanism
 As a missile passes through tissue, it decelerates, dissipating and transferring
As a missile passes through tissue, it decelerates, dissipating and transferring kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.
In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Rober ...
to the tissues. The velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical q ...
of the projectile is a more important factor than its mass in determining how much damage is done; kinetic energy increases with the square of the velocity. In addition to injury caused directly by the object that enters the body, penetrating injuries may be associated with secondary injuries, due for example to a blast injury
A blast injury is a complex type of physical trauma resulting from direct or indirect exposure to an explosion. Blast injuries occur with the detonation of high-order explosives as well as the deflagration of low order explosives. These injuri ...
.
The path of a projectile can be estimated by imagining a line from the entrance wound to the exit wound, but the actual trajectory may vary due to ricochet
A ricochet ( ; ) is a rebound, bounce, or skip off a surface, particularly in the case of a projectile. Most ricochets are caused by accident and while the force of the deflection decelerates the projectile, it can still be energetic and almost ...
or differences in tissue density. In a cut, the discolouration and the swelling of the skin from a blow happens because of the ruptured blood vessels and escape of blood and fluid and other injuries that interrupt the circulation.
Cavitation
Permanent
Low-velocity items, such as knives and swords, are usually propelled by a person's hand, and usually do damage only to the area that is directly contacted by the object. The space left by tissue that is destroyed by the penetrating object as it passes through forms a cavity; this is called permanent cavitation.Temporary
High-velocity objects are usuallyprojectile
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found ...
s such as bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. They are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax; and are made in various shapes and constru ...
s from high-powered rifles, such as assault rifle
An assault rifle is a select fire rifle that uses an intermediate cartridge, intermediate-rifle cartridge and a Magazine (firearms), detachable magazine.C. Taylor, ''The Fighting Rifle: A Complete Study of the Rifle in Combat'', F.A. Moyer '' ...
sDaniel Limmer and Michael F. O'Keefe. 2005. ''Emergency Care'' 10th ed. Edward T. Dickinson, Ed. Pearson, Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. Pages 189-190. or sniper rifle
A sniper rifle is a high-precision, long range shooting, long-range rifle. Requirements include high accuracy, reliability, mobility, concealment, and optics, for anti-personnel weapon, anti-personnel, anti-materiel rifle, anti-materiel and sur ...
s. Bullets classed as medium-velocity projectiles include those from handgun
A handgun is a firearm designed to be usable with only one hand. It is distinguished from a long gun, long barreled gun (i.e., carbine, rifle, shotgun, submachine gun, or machine gun) which typically is intended to be held by both hands and br ...
s, shotgun
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, peppergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge (firearms), cartridge known as a shotshell, which discharges numerous small ...
s, and submachine gun
A submachine gun (SMG) is a magazine (firearms), magazine-fed automatic firearm, automatic carbine designed to fire handgun cartridges. The term "submachine gun" was coined by John T. Thompson, the inventor of the Thompson submachine gun, to descri ...
s. In addition to causing damage to the tissues they contact, medium- and high-velocity projectiles cause a secondary cavitation injury: as the object enters the body, it creates a pressure wave
Longitudinal waves are waves which oscillate in the direction which is parallel to the direction in which the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal w ...
which forces tissue out of the way, creating a cavity which can be much larger than the object itself; this is called "temporary cavitation". The temporary cavity is the radial stretching of tissue around the bullet's wound track, which momentarily leaves an empty space caused by high pressures surrounding the projectile that accelerate material away from its path.
The characteristics of the tissue injured also help determine the severity of the injury; for example, the denser the tissue, the greater the amount of energy transmitted to it. Skin, muscles, and intestines absorb energy and so are resistant to the development of temporary cavitation, while organs such as the liver, spleen, kidney, and brain, which have relatively low tensile strength, are likely to split or shatter because of temporary cavitation. Flexible elastic soft tissues, such as muscle, intestine, skin, and blood vessels, are good energy absorbers and are resistant to tissue stretch. If enough energy is transferred, the liver may disintegrate. Temporary cavitation can be especially damaging when it affects delicate tissues such as the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, as occurs in penetrating head trauma.
Location
Head
Whilepenetrating head trauma
A penetrating head injury, or open head injury, is a head injury in which the dura mater, the outer layer of the meninges, is breached.University of Vermont College of Medicine"Neuropathology: Trauma to the CNS."Accessed through web archive on Aug ...
accounts for only a small percentage of all traumatic brain injuries
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumat ...
(TBI), it is associated with a high mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
, and only a third of people with penetrating head trauma
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inj ...
survive long enough to arrive at a hospital. Injuries from firearms are the leading cause of TBI-related deaths. Penetrating head trauma can cause cerebral contusion
Cerebral contusion (), a form of traumatic brain injury, is a bruise of the brain tissue.
Like bruises in other tissues, cerebral contusion can be associated with multiple microhemorrhages, small blood vessel leaks into brain tissue. Contusion ...
s and lacerations, intracranial hematoma
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) refers to any form of bleeding within the skull. It can result from trauma, vascular abnormalities, hypertension, or other medical conditions. ICH is broadly categorized into several subtypes based on the locati ...
s, pseudoaneurysm
A pseudoaneurysm, also known as a false aneurysm, is a locally contained hematoma outside an artery or the heart due to damage to the vessel wall. The injury passes through all three layers of the arterial wall, causing a leak, which is contai ...
s, and arteriovenous fistula
An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein. It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arteri ...
s. The prognosis for penetrating head injuries varies widely.
Penetrating facial trauma
Facial trauma, also called maxillofacial trauma, is any physical trauma to the face. Facial trauma can involve soft tissue injury, soft tissue injuries such as burns, lacerations and bruises, or bone fracture, fractures of the facial bones such ...
can pose a risk to the airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory ...
and breathing
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into ( inhalation) and out of ( exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxy ...
; airway obstruction can occur later due to swelling or bleeding. Penetrating eye trauma can cause the globe of the eye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
to rupture or vitreous humor
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humo ...
to leak from it, and presents a serious threat to eyesight.
Chest
 Most penetrating injuries are chest wounds and have a mortality rate (death rate) of under 10%. Penetrating
Most penetrating injuries are chest wounds and have a mortality rate (death rate) of under 10%. Penetrating chest trauma
A chest injury, also known as chest trauma, is any form of physical injury to the chest including the ribs, heart and lungs. Chest injuries account for 25% of all deaths from traumatic injury. Typically chest injuries are caused by blunt mechanism ...
can injure vital organs such as the heart and lungs and can interfere with breathing and circulation. Lung injuries that can be caused by penetrating trauma include pulmonary laceration
A pulmonary laceration is a chest injury in which lung tissue is torn or cut.
An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung,
while pulmonary contus ...
(a cut or tear) pulmonary contusion
A pulmonary contusion, also known as a lung contusion, is a bruise of the lung, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, ...
(a bruise), hemothorax
A hemothorax (derived from hemo- lood+ thorax hest plural ''hemothoraces'') is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may inc ...
(an accumulation of blood in the chest cavity outside of the lung), pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and dyspnea, shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is ...
(an accumulation of air in the chest cavity) and hemopneumothorax
Hemopneumothorax, or haemopneumothorax, is the condition of having both air (pneumothorax) and blood (hemothorax) in the chest cavity. A hemothorax, pneumothorax, or the combination of both can occur due to an injury to the lung or chest.
Cause
T ...
(accumulation of both blood and air). Sucking chest wound
A pneumothorax is collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is formed by ...
s and tension pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is formed b ...
may result.
Penetrating trauma can also cause injuries to the heart and circulatory system. When the heart is punctured, it may bleed profusely into the chest cavity if the membrane around it (the pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ...
) is significantly torn, or it may cause pericardial tamponade
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade (), is a compression of the heart due to pericardial effusion (the build-up of pericardial fluid in the sac around the heart). Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically include those ...
if the pericardium is not disrupted.
In pericardial tamponade, blood escapes from the heart but is trapped within the pericardium, so pressure builds up between the pericardium and the heart, compressing the latter and interfering with its pumping. Fractures of the ribs commonly produce penetrating chest trauma when sharp bone ends pierce tissues.
Abdomen
Penetratingabdominal trauma
Abdominal trauma is an injury to the abdomen. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, tenderness (medicine), tenderness, rigidity, and bruise, bruising of the external abdomen. Complications may include blood loss and infection.
Diagnosis ma ...
(PAT) typically arises from stabbings, ballistic injuries (shootings), or industrial accidents. PAT can be life-threatening because abdominal organs, especially those in the retroperitoneal space
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the spatium, anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum ...
, can bleed profusely, and the space can hold a large volume of blood. If the pancreas is injured, it may be further injured by its own secretion
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mec ...
s, in a process called ''autodigestion''. Injuries of the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, common because of the size and location of the organ, present a serious risk for shock because the liver tissue is delicate and has a large blood supply and capacity. The intestines, taking a large part of the lower abdomen, are also at risk of perforation
A perforation is a small hole in a thin material or web. There is usually more than one perforation in an organized fashion, where all of the holes collectively are called a ''perforation''. The process of creating perforations is called perfor ...
.
People with penetrating abdominal trauma may have signs of hypovolemic shock
Hypovolemic shock is a form of Shock (circulatory), shock caused by severe hypovolemia (insufficient blood volume or extracellular fluid in the body). It can be caused by severe dehydration or blood loss. Hypovolemic shock is a medical emergency ...
(insufficient blood in the circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
) and peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and covering of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One pa ...
(an inflammation of the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesotheli ...
, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contain Organ (anatomy), organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roo ...
). Penetration may abolish or diminish bowel sounds due to bleeding, infection, and irritation, and injuries to arteries may cause bruit
Bruit, also called vascular murmur, is the abnormal sound generated by turbulent flow of blood in an artery due to either an area of partial obstruction or a localized high rate of blood flow through an unobstructed artery.
The bruit may be hea ...
s (a distinctive sound similar to heart murmur
Heart murmurs are unique heart sounds produced when blood flows across a heart valve or blood vessel. This occurs when turbulent blood flow creates a sound loud enough to hear with a stethoscope. The sound differs from normal heart sounds by th ...
s) to be audible. Percussion of the abdomen may reveal hyperresonance (indicating air in the abdominal cavity) or dullness (indicating a buildup of blood). The abdomen may be distended or tender, signs which indicate an urgent need for surgery.
The standard management of penetrating abdominal trauma was for many years mandatory laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a surgical incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy.
Origins and history
The first successful laparotomy was performed without ...
. A greater understanding of mechanisms of injury, outcomes from surgery, improved imaging and interventional radiology has led to more conservative operative strategies being adopted.
Assessment and treatment
Assessment can be difficult because much of the damage is often internal and not visible. The patient is thoroughly examined. X-ray andCT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
ning may be used to identify the type and location of potentially lethal injuries. Sometimes before an X-ray is performed on a person with penetrating trauma from a projectile, a paper clip is taped over entry and exit wounds to show their location on the film. The patient is given intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
fluids to replace lost blood. Surgery may be required; impale
Impalement, as a method of torture and execution, is the penetration of a human by an object such as a stake, pole, spear, or hook, often by the complete or partial perforation of the torso. It was particularly used in response to "crimes again ...
d objects are secured into place so that they do not move and cause further injury, and they are removed in an operating room
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man ...
. If the location of the injury is not obvious, a surgical operation called an exploratory laparotomy
An exploratory laparotomy is a general surgical operation where the abdomen is opened and the abdominal organs are examined for injury or disease. It is the standard of care in various blunt and penetrating trauma situations in which there may b ...
may be required to look for internal damage to the organs in the abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
. Foreign bodies such as bullets may be removed, but they may also be left in place if the surgery necessary to get them out would cause more damage than would leaving them. Wounds are debrided to remove tissue that cannot survive and other material that presents risk for infection.
Negative pressure wound therapy is no more effective in preventing wound infection than standard care when used on open traumatic wounds.
History
Before the 17th century, medical practitioners poured hot oil into wounds in order to cauterize damaged blood vessels, but the French surgeonAmbroise Paré
Ambroise Paré (; – 20 December 1590) was a French barber surgeon who served in that role for kings Henry II, Francis II, Charles IX and Henry III. He is considered one of the fathers of surgery and modern forensic pathology and a pione ...
challenged the use of this method in 1545. Paré was the first to propose controlling bleeding using ligature Ligature may refer to:
Language
* Ligature (writing), a combination of two or more letters into a single symbol (typography and calligraphy)
* Ligature (grammar), a morpheme that links two words
Medicine
* Ligature (medicine), a piece of suture us ...
.
During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and po ...
was used during surgery to reduce pain and allow more time for operations. Due in part to the lack of sterile technique
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgical. The modern day notion of asepsis is deri ...
in hospitals, infection was the leading cause of death for wounded soldiers.
In World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, doctors began replacing patients' lost fluid with salt solutions. With World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
came the idea of blood bank
A blood bank is a center where blood gathered as a result of blood donation is stored and preserved for later use in blood transfusion. The term "blood bank" typically refers to a department of a hospital usually within a clinical pathology labora ...
ing, having quantities of donated blood available to replace lost fluids. The use of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s also came into practice in World War II.
See also
*Aortic dissection
Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of agonizing ches ...
* Ballistic trauma
A gunshot wound (GSW) is a penetrating trauma, penetrating injury caused by a projectile (e.g. a bullet) Shooting, shot from a gun (typically a firearm). Damage may include bleeding, bone fractures, organ (anatomy), organ damage, wound infectio ...
* Blunt splenic trauma
Blunt splenic trauma occurs when a significant impact to the spleen from some outside source (i.e. automobile accident) damages or ruptures the spleen. Treatment varies depending on severity, but often consists of embolism or splenectomy.
Signs ...
* Blunt trauma personal protective equipment
* Geriatric trauma
* Pediatric trauma
* Stab wound
A stab wound is a specific form of penetrating trauma to the skin that results from a knife or a similar pointed object. While stab wounds are typically known to be caused by knives, they can also occur from a variety of implements, including br ...
* Transmediastinal gunshot wound
References
External links
{{Authority control Medical emergencies Traumatology Injuries Trauma types