|
Bruit
Bruit, also called vascular murmur, is the abnormal sound generated by turbulent flow of blood in an artery due to either an area of partial obstruction or a localized high rate of blood flow through an unobstructed artery. The bruit may be heard (" auscultated") by securely placing the head of a stethoscope to the skin over the turbulent flow, and listening. Most bruits occur only in systole, so the bruit is intermittent and its frequency dependent on the heart rate. Anything increasing the blood flow velocity such as fever, anemia, hyperthyroidism, or physical exertion, can increase the amplitude of the bruit. Etymology It is naturalized from the French word for "noise", although another notes that and are also common, and others give only for the cardiac sense. Associated terms Describing location of a partial obstruction * Peripheral vascular disease; femoral artery stenosis * Renal artery stenosis * Stroke, carotid artery stenosis * Aortic aneurysm * Tinnitus – a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Bruit
A carotid bruit is a vascular murmur sound (bruit) heard over the carotid artery area on auscultation during systole. Associated conditions It may occur as the result of carotid artery stenosis (though some disagree); however, most carotid bruits, particularly those found in younger or asymptomatic patients, are not related to any disease and are termed "innocent carotid bruits". Many carotid bruits are discovered incidentally in an otherwise asymptomatic Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test). P ... patient. The presence of a carotid bruit alone does not necessarily indicate the presence of stenosis, and the physical examination cannot be used to estimate the degree of stenosis, if present; therefore, any bruit must be evaluated by ultrasound or imaging.DeGowin's Diagnostic Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
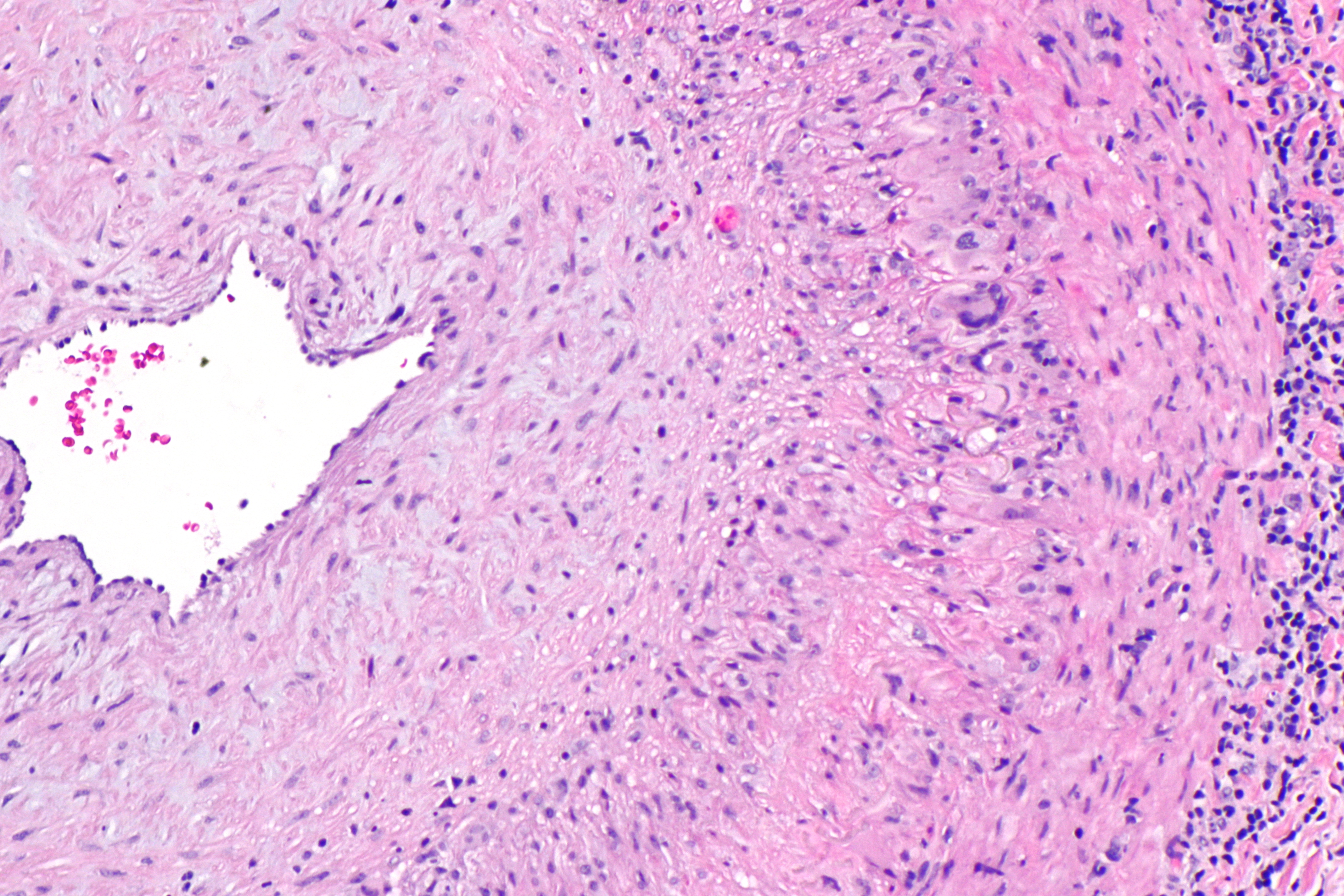
Giant-cell Arteritis
Giant cell arteritis (GCA), also called temporal arteritis, is an inflammatory autoimmune disease of large blood vessels. Symptoms may include headache, pain over the temples, flu-like symptoms, double vision, and difficulty opening the mouth. Complications can include blockage of the artery to the eye with resulting blindness, as well as aortic dissection, and aortic aneurysm. GCA is frequently associated with polymyalgia rheumatica. The cause is unknown. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the small blood vessels that supply the walls of larger arteries. This mainly affects arteries around the head and neck, though some in the chest may also be affected. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms, blood tests, and medical imaging, and confirmed by biopsy of the temporal artery. However, in about 10% of people the temporal artery is normal. Treatment is typical with high doses of steroids such as prednisone or prednisolone. Once symptoms have resolved, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. HCC most commonly occurs in those with chronic liver disease especially those with cirrhosis or fibrosis, which occur in the setting of chronic liver injury and inflammation. HCC is rare in those without chronic liver disease. Chronic liver diseases which greatly increase the risk of HCC include hepatitis infection such as (hepatitis B, hepatitis C, C or hepatitis D, D), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), alcoholic liver disease, or exposure to toxins such as aflatoxin, or pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Certain diseases, such as HFE hereditary haemochromatosis, hemochromatosis and alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency, markedly increase the risk of developing HCC. The five-year survival in those with HCC is 18%. As with any cancer, the treatment and prognosis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a non-atherosclerotic, non-inflammatory disease of the blood vessels that causes abnormal growth within the wall of an artery. FMD has been found in nearly every arterial bed in the body, although the most commonly affected are the renal and carotid arteries. There are various types of FMD, with multi-focal fibroplasia being the most common. Less common forms of the disease include focal (previously known as intimal) and adventitial fibroplasia. FMD predominantly affects middle-aged women, but it has been found in men and people of all ages. Pediatric cases of FMD are vastly different from those of the adult population, and poorly studied. The prevalence of FMD is not known; although the disease was initially thought to be rare, some studies have suggested that it may be underdiagnosed. Signs and symptoms Symptoms expressed by FMD patients are largely dependent on the vascular bed(s) affected by the disease. Patients may also be entirely asympto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by pain or stiffness, usually in the neck, shoulders, upper arms, and hips, but which may occur all over the body. Almost all cases occur in people age 50 or older. Pain and stiffness of PMR is worst in the morning and improves throughout the day, but these symptoms frequently persist to some extent throughout the day and into the evening. People who have polymyalgia rheumatica may also have temporal arteritis (giant cell arteritis), an inflammation of blood vessels in the face which can cause blindness if not treated quickly. The pain and stiffness can result in a lowered quality of life, and can lead to depression. The exact cause of PMR, including whether or not it may be an autoimmune disease, is unclear. Persons of Northern European descent are at greater risk. There is no definitive laboratory test, but C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) can be useful as non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paget's Disease Of Bone
Paget's disease of bone (commonly known as Paget's disease or, historically, osteitis deformans) is a condition involving Bone remodeling, cellular remodeling and deformity of one or more bones. The affected bones show signs of dysregulated bone remodeling at the microscopic level, specifically excessive Osteoclast, bone breakdown and subsequent disorganized new bone formation. These structural changes cause the bone to weaken, which may result in deformity, pain, bone fractures, fracture or arthritis of associated joints. The exact cause is unknown, although leading theories indicate both genetic and acquired factors (see #Causes, Causes). Paget's disease may affect any one or several bones of the body (most commonly pelvis, tibia, femur, lumbar vertebrae, and skull), but never the entire skeleton, and does not spread from bone to bone. Rarely, a bone affected by Paget's disease can transform into a Osteosarcoma, malignant bone cancer. As the disease often affects people diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goitre
A goitre (British English), or goiter (American English), is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly. Worldwide, over 90% of goitre cases are caused by iodine deficiency. The term is from the Latin ''gutturia'', meaning throat. Most goitres are not cancerous ( benign), though they may be potentially harmful. Signs and symptoms A goitre can present as a palpable or visible enlargement of the thyroid gland at the base of the neck. A goitre, if associated with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, may be present with symptoms of the underlying disorder. For hyperthyroidism, the most common symptoms are associated with adrenergic stimulation: tachycardia (increased heart rate), palpitations, nervousness, tremor, increased blood pressure and heat intolerance. Clinical manifestations are often related to hypermetabolism (increased metabolism), excessive thyroid hormone, an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graves' Disease
Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter or Basedow's disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea and unintentional weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye bulging, a condition caused by Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25 to 30% of people with the condition develop eye problems. The exact cause of the disease is unclear, but symptoms are a result of antibodies binding to receptors on the thyroid causing over-expression of thyroid hormone. Persons are more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one monozygotic twin is affected, a 30% chance exists that the other twin will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriovenous Fistula
An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein. It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arterial aneurysm. Clinical features Pathological Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is a condition where there is direct connection between arterioles and venules without intervening capillary beds, at the mucocutaneous region and internal bodily organs. Those who are affected by this conditions usually do not experience any symptoms. Difficulty in breathing is the most common symptom for those who experience symptoms. Just like berry aneurysm, a cerebral arteriovenous malformation can rupture causing subarachnoid hemorrhage. Causes The cause of this condition include * Congenital (developmental defect) * Rupture of arterial aneurysm into an adjacent vein * Penetrating injuries * Inflammatory necrosis of adjacent vessels * Complication of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Artery
The celiac () artery (also spelled coeliac in British English), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). Structure The celiac artery is the first major branch of the descending abdominal aorta, branching at a 90° angle. This occurs just below the crus of the diaphragm. This is around the first lumbar vertebra. There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches: The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries. Function The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen, and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the embry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Arcuate Ligament Syndrome
In medicine, the median arcuate ligament syndrome (MALS, also known as celiac artery compression syndrome, celiac axis syndrome, celiac trunk compression syndrome or Dunbar syndrome) is a rare condition characterized by abdominal pain attributed to compression of the celiac artery and the celiac ganglia by the median arcuate ligament. The abdominal pain may be related to meals, may be accompanied by weight loss, and may be associated with an abdominal bruit heard by a clinician. The diagnosis of MALS is one of exclusion, as many healthy patients demonstrate some degree of celiac artery compression in the absence of symptoms. Consequently, a diagnosis of MALS is typically only entertained after more common conditions have been ruled out. Once suspected, screening for MALS can be done with ultrasonography and confirmed with computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) angiography. Treatment is generally surgical, the mainstay being open or laparoscopic division, or separat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |