English Regency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Regency era of
 The plays of
The plays of

The Bare-knuckle Era. Retrieved 3 July 2022. Boxing was in fact illegal but local authorities, who were often involved on the gambling side of the sport, would turn a blind eye. In any case, the huge crowds that attended championship bouts were almost impossible to police. Like
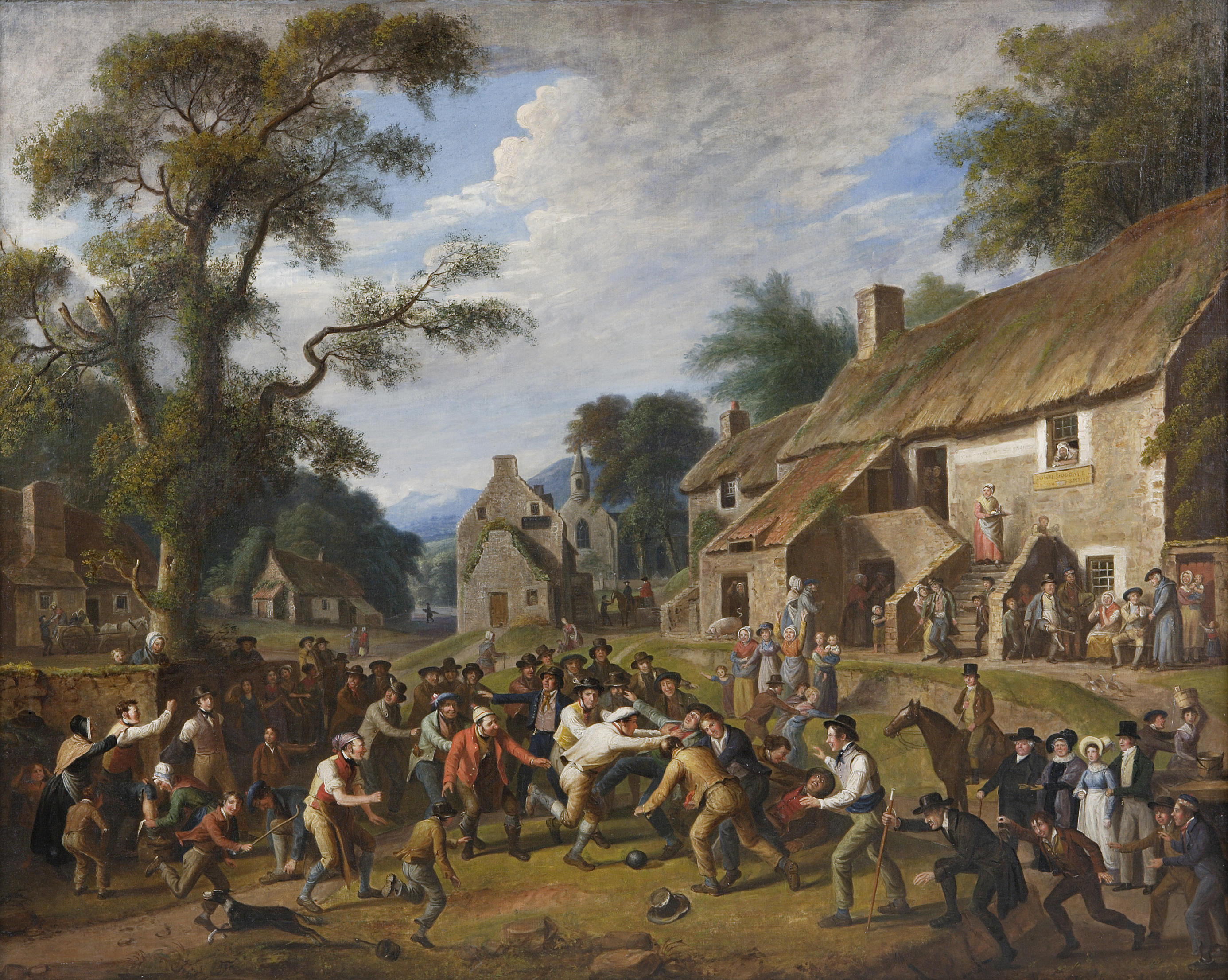
 ; 1815:Napoleon I of France defeated by the Hundred Days, Seventh Coalition at the Battle of Waterloo. Napoleon was exiled to St. Helena. The English Corn Laws restricted corn imports. Sir Humphry Davy patented the Miner's safety lamp, miners' safety lamp. John Loudon Macadam's Macadam, road construction method adopted.
; 1816: Income tax abolished. A "year without a summer" followed a 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora, volcanic eruption in Indonesia.
; 1815:Napoleon I of France defeated by the Hundred Days, Seventh Coalition at the Battle of Waterloo. Napoleon was exiled to St. Helena. The English Corn Laws restricted corn imports. Sir Humphry Davy patented the Miner's safety lamp, miners' safety lamp. John Loudon Macadam's Macadam, road construction method adopted.
; 1816: Income tax abolished. A "year without a summer" followed a 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora, volcanic eruption in Indonesia.
 * The Adelphi Theatre
* Almack's
* Angelo's, a fencing parlor
* Apsley House
* Argyll Rooms
* Astley's Amphitheatre
* Attingham Park
* Bank of England
* Bath, Somerset
* Bond Street
* Brighton Pavilion
* Brighton and Hove
* Brooks's
* Burlington Arcade
* Bury St Edmunds
* Carlton House, London
*Chalk Farm Tavern
* Chapel Royal, St. James's
* Cheltenham, Gloucestershire
* Circulating libraries, 1801–1825
* Covent Garden
* Custom Office, London Docks
* Doncaster Racecourse, Doncaster Races
* Drury Lane
* Floris of London
* Fortnum & Mason
* Gretna Green
* Gentleman Jackson's Saloon, a pugilist's parlor by bare-knuckle champion John Jackson (English boxer), John Jackson
* Hatchard's
* Haymarket Theatre, Little Theatre, Haymarket
* His Majesty's Theatre, London, His Majesty's Theatre
* Hertford House
* Holland House
* Houses of Parliament
* Hyde Park, London
* Jermyn Street
* Kensington Gardens
* King of Clubs (Whig club), King of Clubs
* Lansdowne House
* List of gentlemen's clubs in London
* Lloyd's of London
* London Docks
* London Institution
* London Post Office
* Lyme Regis
* Marshalsea, closed in 1811, new site opened in 1811 where White Lion Prison had been. Primarily a debtors' prison, also housed seditionists and political prisoners
* Mayfair, London
* Newgate Prison
*
* The Adelphi Theatre
* Almack's
* Angelo's, a fencing parlor
* Apsley House
* Argyll Rooms
* Astley's Amphitheatre
* Attingham Park
* Bank of England
* Bath, Somerset
* Bond Street
* Brighton Pavilion
* Brighton and Hove
* Brooks's
* Burlington Arcade
* Bury St Edmunds
* Carlton House, London
*Chalk Farm Tavern
* Chapel Royal, St. James's
* Cheltenham, Gloucestershire
* Circulating libraries, 1801–1825
* Covent Garden
* Custom Office, London Docks
* Doncaster Racecourse, Doncaster Races
* Drury Lane
* Floris of London
* Fortnum & Mason
* Gretna Green
* Gentleman Jackson's Saloon, a pugilist's parlor by bare-knuckle champion John Jackson (English boxer), John Jackson
* Hatchard's
* Haymarket Theatre, Little Theatre, Haymarket
* His Majesty's Theatre, London, His Majesty's Theatre
* Hertford House
* Holland House
* Houses of Parliament
* Hyde Park, London
* Jermyn Street
* Kensington Gardens
* King of Clubs (Whig club), King of Clubs
* Lansdowne House
* List of gentlemen's clubs in London
* Lloyd's of London
* London Docks
* London Institution
* London Post Office
* Lyme Regis
* Marshalsea, closed in 1811, new site opened in 1811 where White Lion Prison had been. Primarily a debtors' prison, also housed seditionists and political prisoners
* Mayfair, London
* Newgate Prison
*


 For more names see Newman (1997).
* Rudolph Ackermann
* Arthur Aikin
* Henry Addington, 1st Viscount Sidmouth
* William Arden, 2nd Baron Alvanley
* Elizabeth Armistead
*
For more names see Newman (1997).
* Rudolph Ackermann
* Arthur Aikin
* Henry Addington, 1st Viscount Sidmouth
* William Arden, 2nd Baron Alvanley
* Elizabeth Armistead
*
File:Neckclothitania-1818.gif, "Neckclothitania", 1818
File:Astley's Amphitheatre Microcosm edited.jpg, Astley's Amphitheatre, 1808–1811
File:Brighton Pavilion from Views of the Royal Pavilion (1826) edited.jpg, Brighton Pavilion, 1826
File:CarltonHouseFacade.jpg, Carlton House, Pall Mall, London
File:Microcosm of London Plate 089 - Vauxhall Garden edited.jpg, Vauxhall Gardens, 1808–1811
File:Church of All Souls-2.jpg, Church of All Souls, architect John Nash, 1823
File:Regent's Canal Limehouse1823.jpg, Regent's Canal, Limehouse, 1823
File:Frost Fair of 1814 by Luke Clenell.jpg, Frost Fair, Thames River, 1814
File:Burlington Arcade by Thomas Hosmer Shepherd 1827-28.JPG, The Piccadilly entrance to the Burlington Arcade, 1819
File:Princess Charlotte Augusta of Wales and Leopold I after George Dawe.jpg, Princess Charlotte Augusta of Wales and Prince Leopold of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, 1817
File:Morning-dress-Ackermanns-ca1820.png, Morning dress, Ackermann, 1820
File:Humphry Repton01.jpg, Water at Wentworth, Humphry Repton, 1752–1818
File:Hanover Square Horwood 1819.jpg, Hanover Square, Horwood Map, 1819
File:BrummellDighton1805.jpg, Beau Brummell, 1805
File:Battle of Waterloo 1815.PNG, ''The Battle of Waterloo (painting, Sadler II), Battle of Waterloo'', 1815
File:Almack's Assembly Rooms inside.jpg, Almack's Assembly Room, 1805–1825
File:James Sadler - 12 Aug 1811 ascent.jpg, Balloon ascent, James Sadler, 1811
File:Rowlandson - The Anatomist.JPG, The Anatomist, Thomas Rowlandson, 1811
File:Regent's Park London from 1833 Schmollinger map.jpg, Regent's Park, Schmollinger map, 1833
File:National Gallery at 100 Pall Mall.jpg, 100 Pall Mall, former location of National Gallery, 1824–1834
File:Cognocenti-Antique-Gillray.jpeg, Cognocenti, Gillray Cartoon, 1801
File:Custom Office London Dock.jpg, Custom Office, London Docks, 1811–1843
File:London Dock Custom and Excise 1820.jpg, Customs and Excise, London Docks, 1820
File:Mailcoach.jpg, Mail coach, 1827
File:Assassination-of-spencer-perceval.jpg, Assassination of Spencer Perceval, 1812
File:The Trial of Queen Caroline 1820 by Sir George Hayter.jpg, ''The Trial of Queen Caroline'' by George Hayter, 1823
File:Microcosm of London Plate 062 - Pillory, Charing Cross edited.jpg, The pillory at Charing Cross, Ackermann's ''Microcosm of London'', 1808–1811
File:Covent Garden Theatre 1827-28.jpg, Covent Garden Theatre, 1827–1828
Knafla, David, Crime, punishment, and reform in Europe, Greenwood Publishing, 2003
* Lapp, Robert Keith. ''Contest for Cultural Authority – Hazlitt, Coleridge, and the Distresses of the Regency''. Detroit: Wayne State UP, 1999. * Marriott, J. A. R. ''England Since Waterloo'' (1913
online
* Morgan, Marjorie. ''Manners, Morals, and Class in England, 1774–1859.'' New York: St. Martin's Press, 1994. * Morrison, Robert. ''The Regency Years: During Which Jane Austen Writes, Napoleon Fights, Byron Makes Love, and Britain Becomes Modern''. 2019, New York: W. W. Norton, London: Atlantic Book
online review
*
online review
904pp; 1121 short articles on Britain by 250 experts. * Parissien, Steven. ''George IV Inspiration of the Regency.'' New York: St. Martin's P, 2001. * Pilcher, Donald. ''The Regency Style: 1800–1830'' (London: Batsford, 1947). * Rendell, Jane. ''The pursuit of pleasure: gender, space & architecture in Regency London'' (Bloomsbury, 2002). * Joanna Richardson, Richardson, Joanna. ''The Regency''. London: Collins, 1973. * Webb, R.K. ''Modern England: from the 18th century to the present'' (1968
online
widely recommended university textbook * Wellesley, Lord Gerald. "Regency Furniture", ''The Burlington Magazine for Connoisseurs'' 70, no. 410 (1937): 233–241. * White, R.J. ''Life in Regency England'' (Batsford, 1963).
online
Greenwood's Map of London, 1827
Results of the 1801 and 1811 Census of London
''The European Magazine and London Review'', 1818, p. 50
The Bluestocking Archive
End of an Era: 1815–1830
Regency Style Furniture
{{Authority control Regency era, Regency London, * 1810s in the United Kingdom George III George IV History of the United Kingdom by period Historical eras Architecture of London Regency (government) 1820 in the United Kingdom 1830s in the United Kingdom
British history
The history of the British Isles began with its sporadic human habitation during the Palaeolithic from around 900,000 years ago. The British Isles has been continually occupied since the early Holocene, the current geological epoch, which star ...
is commonly understood as the years between and 1837, although the official regency
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
for which it is named only spanned the years 1811 to 1820. King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...
first suffered debilitating illness in the late 1780s, and relapsed into his final mental illness in 1810. By the Regency Act 1811, his eldest son George, Prince of Wales, was appointed Prince Regent
A prince regent or princess regent is a prince or princess who, due to their position in the line of succession, rules a monarchy as regent in the stead of a monarch, e.g., as a result of the sovereign's incapacity (minority or illness) or ab ...
to discharge royal functions. When George III died in 1820, the Prince Regent succeeded him as George IV. In terms of periodisation, the longer timespan is roughly the final third of the Georgian era
The Georgian era was a period in British history from 1714 to , named after the House of Hanover, Hanoverian kings George I of Great Britain, George I, George II of Great Britain, George II, George III and George IV. The definition of the Geor ...
(1714–1837), encompassing the last 25 years or so of George III's reign, including the official Regency, and the complete reigns of both George IV and his brother and successor William IV. It ends with the accession of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
in June 1837 and is followed by the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the ...
(1837–1901).
Although the Regency era is remembered as a time of refinement and culture, that was the preserve of the wealthy few, especially those in the Prince Regent's own social circle. For the masses, poverty was rampant as urban population density rose due to industrial labour migration. City dwellers lived in increasingly larger slum
A slum is a highly populated Urban area, urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are p ...
s, a state of affairs severely aggravated by the combined impact of war, economic collapse, mass unemployment, a bad harvest in 1816 (the " Year Without a Summer"), and an ongoing population boom. Political response to the crisis included the Corn Laws, the Peterloo Massacre
The Peterloo Massacre took place at St Peter's Field, Manchester, Lancashire, England, on Monday 16 August 1819. Eighteen people died and 400–700 were injured when the cavalry of the Yeomen charged into a crowd of around 60,000 people who ...
, and the Representation of the People Act 1832
The Representation of the People Act 1832 (also known as the Reform Act 1832, Great Reform Act or First Reform Act) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (indexed as 2 & 3 Will. 4. c. 45), enacted by the Whig government of Pri ...
. Led by William Wilberforce, there was increasing support for the abolitionist cause during the Regency era, culminating in passage of the Slave Trade Act 1807
The Slave Trade Act 1807 ( 47 Geo. 3 Sess. 1. c. 36), or the Abolition of Slave Trade Act 1807, was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom prohibiting the Atlantic slave trade in the British Empire. Although it did not automatica ...
and the Slavery Abolition Act 1833
The Slavery Abolition Act 1833 ( 3 & 4 Will. 4. c. 73) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which abolished slavery in the British Empire by way of compensated emancipation. The act was legislated by Whig Prime Minister Charl ...
.
The longer timespan recognises the wider social and cultural aspects of the Regency era, characterised by the distinctive fashions, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
and style of the period. The first 20 years to 1815 were overshadowed by the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
. Throughout the whole period, the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
gathered pace and achieved significant progress by the coming of the railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
s and the growth of the factory system. The Regency era overlapped with Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
and many of the major artists, musicians, novelists and poets of the Romantic movement were prominent Regency figures, such as Jane Austen
Jane Austen ( ; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for #List of works, her six novels, which implicitly interpret, critique, and comment on the English landed gentry at the end of the 18th century ...
, William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake has become a seminal figure in the history of the Romantic poetry, poetry and visual art of the Roma ...
, Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-kno ...
, John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romanticism, Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedha ...
, John Keats, John Nash, Ann Radcliffe, Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European literature, European and Scottish literature, notably the novels ''Ivanhoe'' (18 ...
, Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley ( , ; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an History of science fiction# ...
, Percy Bysshe Shelley
Percy Bysshe Shelley ( ; 4 August 1792 – 8 July 1822) was an English writer who is considered one of the major English Romantic poets. A radical in his poetry as well as in his political and social views, Shelley did not achieve fame durin ...
, J. M. W. Turner and William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poetry, Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romanticism, Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Balla ...
.
Legislative background
George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...
(1738–1820) became King of Great Britain on 25 October 1760 when he was 22 years old, succeeding his grandfather George II. George III had himself been the subject of legislation to provide for a regency
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
when Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
passed the Minority of Successor to Crown Act 1751 following the death of his father Frederick, Prince of Wales, on 31 March 1751. George became heir apparent
An heir apparent is a person who is first in the order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person. A person who is first in the current order of succession but could be displaced by the birth of a more e ...
at the age of 12 and he would have succeeded as a minor if his grandfather had died before 4 June 1756, George's 18th birthday. As a contingency, the Act provided for his mother, Augusta, Dowager Princess of Wales, to be appointed regent and discharge most but not all royal functions.
In 1761, George III married Princess Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz and over the following years they had 15 children (nine sons and six daughters). The eldest was Prince George, born on 12 August 1762 as heir apparent. He was named Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
soon after his birth. By 1765, three infant children led the order of succession and Parliament again passed a Regency Act as contingency. The Minority of Heir to the Crown Act 1765 provided for either Queen Charlotte or Princess Augusta to act as regent if necessary. George III had a long episode of mental illness in the summer of 1788. Parliament proposed the Regency Bill 1789 which was passed by the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
. Before the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
could debate it, the King recovered and the Bill was withdrawn. Had it been passed into law, the Prince of Wales would have become the regent in 1789.
The King's mental health continued to be a matter of concern but, whenever he was of sound mind, he opposed any further moves to implement a Regency Act. Finally, following the death on 2 November 1810 of his youngest daughter, Princess Amelia, he became permanently insane. Parliament passed the Care of King During his Illness, etc. Act 1811, commonly known as the Regency Act 1811. The King was suspended from his duties as head of state and the Prince of Wales assumed office as Prince Regent on 5 February 1811. At first, Parliament restricted some of the Regent's powers, but the constraints expired one year after the passage of the Act. The Regency ended when George III died on 29 January 1820 and the Prince Regent succeeded him as George IV.
After George IV died in 1830, a further Regency Act was passed by Parliament. George IV was succeeded by his brother William IV. His wife, Queen Adelaide, was 37 and there were no surviving legitimate children. The heir presumptive was Princess Victoria of Kent, aged eleven. The new Act provided for her mother, Victoria, Dowager Duchess of Kent to become regent in the event of William's death before 24 May 1837, the young Victoria's 18th birthday. The Act made allowance for Adelaide having another child, either before or after William's death. If the latter scenario had arisen, Victoria would have become Queen only temporarily until the new monarch was born. Adelaide had no more children and, as it happened, William died on 20 June 1837, just four weeks after Victoria was 18.
Perceptions
Periodisation terminology
Officially, the Regency began on 5 February 1811 and ended on 29 January 1820 but the "Regency era", as such, is generally perceived to have been much longer. The term is commonly, though loosely, applied to the period from until the accession ofQueen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
on 20 June 1837. The Regency Era is a sub-period of the longer Georgian era
The Georgian era was a period in British history from 1714 to , named after the House of Hanover, Hanoverian kings George I of Great Britain, George I, George II of Great Britain, George II, George III and George IV. The definition of the Geor ...
(1714–1837), both of which were followed by the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the ...
(1837–1901). The latter term had contemporaneous usage although some historians give it an earlier startpoint, typically the enactment of the Great Reform Act
The Representation of the People Act 1832 (also known as the Reform Act 1832, Great Reform Act or First Reform Act) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (indexed as 2 & 3 Will. 4. c. 45), enacted by the Whig government of Pri ...
on 7 June 1832.
Social, economic and political counterpoints
The Prince Regent himself was one of the leading patrons of thearts
The arts or creative arts are a vast range of human practices involving creativity, creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. The arts encompass diverse and plural modes of thought, deeds, and existence in an extensive ...
and architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
. He ordered the costly building and refurbishing of the exotic Brighton Pavilion, the ornate Carlton House, and many other public works and architecture. This all required considerable expense which neither the Regent himself nor HM Treasury
His Majesty's Treasury (HM Treasury or HMT), and informally referred to as the Treasury, is the Government of the United Kingdom’s economic and finance ministry. The Treasury is responsible for public spending, financial services policy, Tax ...
could afford. The Regent's extravagance was pursued at the expense of the common people.
While the Regency is noted for its elegance and achievements in the fine arts and architecture, there was a concurrent need for social, political and economic change. The country was enveloped in the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
until June 1815 and the conflict heavily impacted commerce at home and internationally. There was mass unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
and, in 1816, an exceptionally bad harvest
Harvesting is the process of collecting plants, animals, or fish (as well as fungi) as food, especially the process of gathering mature crops, and "the harvest" also refers to the collected crops. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulses fo ...
. In addition, the country underwent a population boom and the combination of these factors resulted in rampant poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
. Apart from the national unity government
A national unity government, government of national unity (GNU), or national union government is a broad coalition government consisting of all parties (or all major parties) in the legislature, usually formed during a time of war or other na ...
led by William Grenville from February 1806 to March 1807, all governments from December 1783 to November 1830 were formed and led by Tories. Their responses to the national crisis included the Peterloo Massacre
The Peterloo Massacre took place at St Peter's Field, Manchester, Lancashire, England, on Monday 16 August 1819. Eighteen people died and 400–700 were injured when the cavalry of the Yeomen charged into a crowd of around 60,000 people who ...
in 1819 and the various Corn Laws. The Whig government of Earl Grey passed the Great Reform Act
The Representation of the People Act 1832 (also known as the Reform Act 1832, Great Reform Act or First Reform Act) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (indexed as 2 & 3 Will. 4. c. 45), enacted by the Whig government of Pri ...
in 1832.
Essentially, England during the Regency era was a stratified society in which political power and influence lay in the hands of the landed class. Their fashionable locales were worlds apart from the slum
A slum is a highly populated Urban area, urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are p ...
s in which the majority of people existed. The slum districts were known as rookeries, a notorious example being St Giles in London. These were places where alcoholism, gambling, prostitution, thievery and violence prevailed.Low, Donald A. (1999). ''The Regency Underworld'', p. x. Gloucestershire: Sutton. The population boom, comprising an increase from just under a million in 1801 to one and a quarter million by 1820, heightened the crisis. Robert Southey drew a comparison between the squalor of the slums and the glamour of the Regent's circle:
The squalor that existed beneath the glamour and gloss of Regency society provided sharp contrast to the Prince Regent's social circle. Poverty was addressed only marginally. The formation of the Regency after the retirement ofGeorge III George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...saw the end of a more pious and reserved society, and gave birth of a more frivolous, ostentatious one. This change was influenced by the Regent himself, who was kept entirely removed from the machinations of politics and military exploits. This did nothing to channel his energies in a more positive direction, thereby leaving him with the pursuit of pleasure as his only outlet, as well as his sole form of rebellion against what he saw as disapproval and censure in the form of his father.
The arts
Architecture
Regent's Park and London Zoo
In the 1810s, the Prince Regent proposed the conversion of Crown land inMarylebone
Marylebone (usually , also ) is an area in London, England, and is located in the City of Westminster. It is in Central London and part of the West End. Oxford Street forms its southern boundary.
An ancient parish and latterly a metropo ...
and St Pancras into a pleasure garden. The design work was initially assigned to the architect John Nash but it was the father and son partnership of James and Decimus Burton who had the majority of input to the project. Landscaping continued through the 1820s and Regent's Park
Regent's Park (officially The Regent's Park) is one of the Royal Parks of London. It occupies in north-west Inner London, administratively split between the City of Westminster and the London Borough of Camden, Borough of Camden (and historical ...
was finally opened to the public in 1841.
The Zoological Society of London (ZSL) was founded in 1826 by Sir Stamford Raffles and Sir Humphry Davy. They obtained land alongside the route of the Regent's Canal through the northern perimeter of Regent's Park, between the City of Westminster
The City of Westminster is a London borough with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in Greater London, England. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It contains a large par ...
and the London Borough of Camden
The London Borough of Camden () is a London boroughs, borough in Inner London, England. Camden Town Hall, on Euston Road, lies north of Charing Cross. The borough was established on 1 April 1965 from the former Metropolitan boroughs of the Cou ...
. Following the death of Raffles soon afterwards, the 3rd Marquess of Lansdowne assumed responsibility for the project and supervised construction of the first animal houses. At first, the zoo was used for scientific purposes only with admittance restricted to Fellows of the ZSL which, in 1829, was granted a Royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
by George IV. The zoo was not opened to the public until 1847, after it became necessary to raise funds.
Literature
Jane Austen
Jane Austen ( ; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for #List of works, her six novels, which implicitly interpret, critique, and comment on the English landed gentry at the end of the 18th century ...
, Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-kno ...
, Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European literature, European and Scottish literature, notably the novels ''Ivanhoe'' (18 ...
and others were the most prominent writers of the Regency era. However, the time period also produced some of the 19th century's most prolific writers such as Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English novelist, journalist, short story writer and Social criticism, social critic. He created some of literature's best-known fictional characters, and is regarded by ...
, Charlotte Brontë
Charlotte Nicholls (; 21 April 1816 – 31 March 1855), commonly known as Charlotte Brontë (, commonly ), was an English novelist and poet, the eldest of the three Brontë family, Brontë sisters who survived into adulthood and whose novel ...
, and Benjamin Disraeli
Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield (21 December 1804 – 19 April 1881) was a British statesman, Conservative Party (UK), Conservative politician and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a ...
. Especially popular forms of literature at this time were novels and poetry, such as Lord Byron's ''The Regent's Bomb.''
Music
Wealthy households staged their own music events by relying on family members who could sing or play an instrument. For the vast majority of people, street performers provided their sole access to music of any kind. However, the upper class enjoyed music such as Ludwig van Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 30, Felix Mendelssohn's Violin Sonata in F major, MWV Q 7, and much more. Especially popular composers of the time included Beethoven, Rossini, Liszt, and Mendelssohn.Painting
The most prominent landscape painters wereJohn Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romanticism, Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedha ...
and J. M. W. Turner. Notable portrait painters include Thomas Lawrence
Sir Thomas Lawrence (13 April 1769 – 7 January 1830) was an English people, English portrait painter and the fourth president of the Royal Academy. A child prodigy, he was born in Bristol and began drawing in Devizes, where his father was a ...
and Martin Archer Shee
Sir Martin Archer Shee (23 December 1769 – 13 August 1850) was an Irish portrait painter. He also served as the president of the Royal Academy.
Early life
He was born in Dublin, of an old Irish Roman Catholic family, the son of Martin Shee ...
, both Presidents of the Royal Academy
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House in Piccadilly London, England. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its ...
. The National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of more than 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current di ...
was established in London in 1824.
Theatre
 The plays of
The plays of William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
were very popular throughout the period. The performers wore modern dress, however, rather than 16th-century costumes.
London had three patent theatres at Covent Garden
Covent Garden is a district in London, on the eastern fringes of the West End, between St Martin's Lane and Drury Lane. It is associated with the former fruit-and-vegetable market in the central square, now a popular shopping and tourist sit ...
, Drury Lane
Drury Lane is a street on the boundary between the Covent Garden and Holborn areas of London, running between Aldwych and High Holborn. The northern part is in the borough of London Borough of Camden, Camden and the southern part in the City o ...
and the Haymarket. Other prominent theatres were the Theatre Royal, Bath and the Crow Street Theatre in Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
. The playwright and politician Richard Brinsley Sheridan controlled the Drury Lane Theatre until it burned down in 1809.
Media
Among the popular newspapers, pamphlets and other publications of the era were: * '' Ackermann's Repository'' * ''The Gentleman's Magazine
''The Gentleman's Magazine'' was a monthly magazine founded in London, England, by Edward Cave in January 1731. It ran uninterrupted for almost 200 years, until 1907, ceasing publication altogether in 1922. It was the first to use the term ''m ...
''
* ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its si ...
''
* ''The Observer
''The Observer'' is a British newspaper published on Sundays. First published in 1791, it is the world's oldest Sunday newspaper.
In 1993 it was acquired by Guardian Media Group Limited, and operated as a sister paper to ''The Guardian'' ...
''
* '' Cobbett's Weekly Political Register''
* '' La Belle Assemblée''
Science and technology
In 1814, ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its si ...
'' adopted steam printing. Using this method, it could print 1,100 sheets every hour, five and a half times the prior rate of 200 per hour. The faster speed of printing enabled the rise of the " silver fork novels" which depicted the lives of the rich and aristocratic. Publishers used these as a way of spreading gossip
Gossip is idle talk or rumor, especially about the personal or private affairs of others; the act is also known as dishing or tattling.
Etymology
The word is from Old English ''godsibb'', from ''god (word), god'' and ''sibb'', the term for the ...
and scandal
A scandal can be broadly defined as the strong social reactions of outrage, anger, or surprise, when accusations or rumours circulate or appear for some reason, regarding a person or persons who are perceived to have transgressed in some way a ...
, often clearly hinting at identities. The novels were popular during the later years of the Regency era.
Sport and recreation
Women's activities
During the Regency era and well into the succeeding Victorian era, society women were discouraged from exertion although many did take the opportunity to pursue activities such as dancing, riding and walking that were recreational rather than competitive. Depending on a lady's rank, she may be expected to be proficient in reading and writing, mathematics, dancing, music, sewing, and embroidery. In '' Pride and Prejudice'', the Bennet sisters are frequently out walking and it is at aball
A ball is a round object (usually spherical, but sometimes ovoid) with several uses. It is used in ball games, where the play of the game follows the state of the ball as it is hit, kicked or thrown by players. Balls can also be used for s ...
where Elizabeth meets Mr Darcy. There was a contemporary belief that people had limited energy levels with women, as the "weaker sex", being most at risk of over-exertion because their menstruation cycles caused periodic energy reductions.
Balls
One of the most common activities among the upper class was attending and hosting balls, house parties, and more. These often included dancing, food, and gossip. The food generally served included items such as white soup made with veal stock, almonds and cream, cold meats, salads, etc.Bare-knuckle boxing

Bare-knuckle boxing
Bare-knuckle boxing (also known as bare-knuckle or bare-knuckle fighting) is a full-contact combat sport based on punching without any form of padding on the hands. The sport as it is known today originated in 17th-century England and, although ...
, also known as prizefighting, was a popular sport through the 18th and 19th centuries. The Regency era has been called "the peak of British boxing" because the champion fighter in Britain was also, in effect, the world champion. Britain's only potential rival was the United States, where organised boxing began .''Encyclopaedia Britannica''The Bare-knuckle Era. Retrieved 3 July 2022. Boxing was in fact illegal but local authorities, who were often involved on the gambling side of the sport, would turn a blind eye. In any case, the huge crowds that attended championship bouts were almost impossible to police. Like
cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
and horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance activity, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its bas ...
, boxing attracted gamblers. The sport needed the investment provided by gambling, but there was a seamier side in that many fights were fixed.
At one time, prizefighting was "anything goes" but the champion boxer Jack Broughton
John "Jack" Broughton ( – 8 January 1789) was an English people, English Bare-knuckle boxing, bare-knuckle boxer. He was the first person to codify a set of boxing rules; prior to this the "rules" that existed were very loosely defined and t ...
proposed a set of rules in 1743 that were observed throughout the Regency era until they were superseded by the London Prize Ring Rules
The London Prize Ring Rules were a list of boxing rules published in 1838 and revised in 1853. These rules were based on those drafted by England's Jack Broughton in 1743 (known as the Broughton Rules) and governed the conduct of prizefighting ...
in 1838. Broughton's rules were a reaction to "bar room brawling" as they restricted fighters to use of the fists only. A round ended when a fighter was grounded and the rules prohibited the hitting of a downed opponent. He was helped to his corner and then had thirty seconds in which to "step up to the mark", which was a line drawn for that purpose so that the fighters squared off less than a yard apart. The next round would then begin. A fighter who failed to step up and square off was declared the loser. Contests continued until one fighter could not step up.
There were no weight divisions and so a heavyweight
Heavyweight is a weight class in combat sports and professional wrestling.
Boxing Professional
Male boxers who weigh over are considered heavyweights by 2 of the 4 major professional boxing organizations: the International Boxing Federation an ...
always had a natural advantage over smaller fighters. Even so, the first British champion of the Regency era was Daniel Mendoza, a middleweight
Middleweight is a weight class in combat sports.
Boxing Professional
In professional boxing, the middleweight division is contested above and up to .
Early boxing history is less than exact, but the middleweight designation seems to have beg ...
who had successfully claimed the vacant title in 1792. He held it until he was defeated by the heavyweight Gentleman John Jackson in April 1795. Other Regency era champions were famous fighters like Jem Belcher, Hen Pearce, John Gully, Tom Cribb, Tom Spring, Jem Ward and James Burke. Gully went on to become a successful racehorse
Horse racing is an equestrian performance activity, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its bas ...
owner and, representing the Pontefract constituency, a Member
Member may refer to:
* Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon
* Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set
* In object-oriented programming, a member of a class
** Field (computer science), entries in ...
of the first post-Reform Parliament from December 1832 to July 1837. Cribb was the first fighter to be acclaimed world champion after he twice defeated the American Tom Molineaux in 1811.
Cricket
Marylebone Cricket Club
The Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) is a cricket club founded in 1787 and based since 1814 at Lord's, Lord's Cricket Ground, which it owns, in St John's Wood, London, England. The club was the governing body of cricket from 1788 to 1989 and retain ...
, widely known as MCC, was founded in 1787 and became cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
's governing body. In 1788, the club drafted and published a revised version of the sport's rules. MCC had considerable influence throughout the Regency era and its ground, Lord's
Lord's Cricket Ground, commonly known as Lord's, is a cricket List of Test cricket grounds, venue in St John's Wood, Westminster. Named after its founder, Thomas Lord, it is owned by Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) and is the home of Middlesex C ...
, became cricket's premier venue. There were in fact three Lord's grounds. The first, opened in 1787 when the club was formed, was on the site of Dorset Square in Marylebone
Marylebone (usually , also ) is an area in London, England, and is located in the City of Westminster. It is in Central London and part of the West End. Oxford Street forms its southern boundary.
An ancient parish and latterly a metropo ...
, hence the name of the club.Warner, p. 18. The lease was terminated in 1811 because of a rental dispute and the club took temporary lease of a second ground in St John's Wood
St John's Wood is a district in the London Borough of Camden, London Boroughs of Camden and the City of Westminster, London, England, about 2.5 miles (4 km) northwest of Charing Cross. Historically the northern part of the Civil Parish#An ...
. This was in use for only three seasons until the land was requisitioned because it was on the proposed route of the Regent's Canal. MCC moved to a nearby site on which they established their present ground.
Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-kno ...
played for Harrow School
Harrow School () is a Public school (United Kingdom), public school (English boarding school for boys) in Harrow on the Hill, Greater London, England. The school was founded in 1572 by John Lyon (school founder), John Lyon, a local landowner an ...
in the first Eton v Harrow match at Lord's in 1805. The match became an annual event in the social calendar.
Lord's staged the first Gentlemen v Players
Gentlemen v Players was a long-running series of cricket matches that began in July 1806 and was abolished in January 1963. It was a match between a team consisting of amateurs (the Gentlemen) and a team consisting of professionals (the Players ...
match in 1806. This fixture provides another illustration of the class divide in Regency society as it matched a team of well-to-do amateurs (Gentlemen) against a team of working-class
The working class is a subset of employees who are compensated with wage or salary-based contracts, whose exact membership varies from definition to definition. Members of the working class rely primarily upon earnings from wage labour. Most c ...
professionals (Players). The first match featured Billy Beldham and William Lambert, who have been recognised as the outstanding professionals of the period, and Lord Frederick Beauclerk as the outstanding amateur player. The 1821 match ended prematurely after the Gentlemen team, well behind in the contest, conceded defeat. This had been billed as the "Coronation Match" because it celebrated the accession of the Prince Regent as King George IV and the outcome was described by the sports historian Sir Derek Birley as "a suitably murky affair".
Football
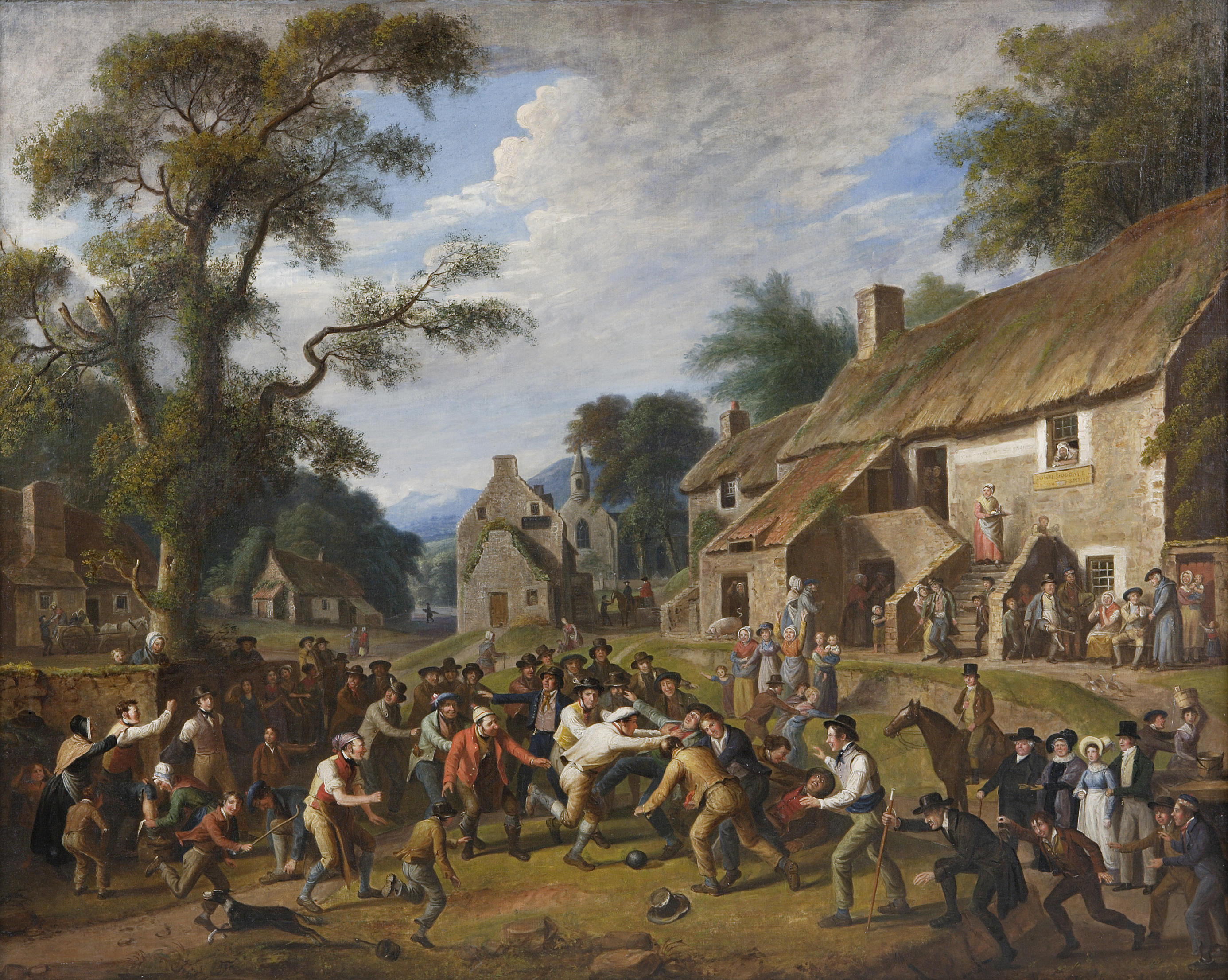
Football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
in Great Britain had long been a no-holds-barred pastime with an unlimited number of players on opposing teams which might comprise whole parishes or villages. The playing area was an undefined stretch of land between the two places. The ball
A ball is a round object (usually spherical, but sometimes ovoid) with several uses. It is used in ball games, where the play of the game follows the state of the ball as it is hit, kicked or thrown by players. Balls can also be used for s ...
, as such, was often a pig's bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
that had been inflated and the object of the exercise was to move the ball by any means possible to a distant target such as a church in the opposing village. The contests were typically arranged to take place on feast days like Shrove Tuesday
Shrove Tuesday (also known as Pancake Tuesday or Pancake Day) is the final day of Shrovetide, which marks the end of the pre-Lenten season. Lent begins the following day with Ash Wednesday. Shrove Tuesday is observed in many Christian state, Ch ...
. By the beginning of the 19th century, efforts were being made in the English public schools to transform this mob football into an organised team sport. The earliest-known versions of football code rules were written at Eton College
Eton College ( ) is a Public school (United Kingdom), public school providing boarding school, boarding education for boys aged 13–18, in the small town of Eton, Berkshire, Eton, in Berkshire, in the United Kingdom. It has educated Prime Mini ...
(1815) and Aldenham School (1825).
Horse racing
Horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance activity, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its bas ...
had been very popular since the years after the Restoration when Charles II was a frequent visitor to Newmarket Racecourse
Newmarket Racecourse is a British Thoroughbred horse racing venue in Newmarket, Suffolk, Newmarket, Suffolk, comprising two individual racecourses: the Rowley Mile and the July Course. Newmarket is often referred to as the headquarters of ...
. In the Regency era, the five classic races had all been inaugurated and have been run annually since 1814. These races are the St Leger Stakes (first run in 1776), The Oaks (1779), the Epsom Derby (1780), the 2,000 Guineas Stakes (1809) and the 1,000 Guineas Stakes (1814).
National Hunt racing
National Hunt Racing, also known as Jump Racing, is a form of horse racing particular to many European countries, including, but not limited to: France, horse racing in Great Britain, Great Britain and horse racing in Ireland, Ireland. Jump Racin ...
began in 18th century Ireland and developed in England through the Regency era. There are tentative references to races held between 1792 and 1810. The first definitely recorded hurdle race took place on Durdham Down, near Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
, in 1821. The first officially recognised steeplechase was over a cross-country route in Bedfordshire on 8 March 1830.
Aintree Racecourse
Aintree Racecourse is a horse racing, racecourse in Aintree, Merseyside, England, near to Liverpool. The racecourse is the venue for the Grand National steeplechase (horse racing), steeplechase, which takes place annually in April over three da ...
held its first meeting on 7 July 1829. On 29 February 1836, a race called the Grand Liverpool Steeplechase was held. One of its organisers was Captain Martin Becher who rode The Duke to victory. The infamous sixth fence at Aintree is called Becher's Brook. The 1836 race, which became an annual event, is recognised by some as the first Grand National
The Grand National is a National Hunt horse race held annually at Aintree Racecourse in Aintree, Merseyside, England. First run in 1839, it ...
, but there are historical uncertainties about the three races between 1836 and 1838 so they are officially regarded as precursors to the Grand National. Some sources insist they were held on Old Racecourse Farm in nearby Maghull but this is impossible as that course closed in 1835. The first official Grand National was the 1839 race.
Rowing and sailing
Rowing andsailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ...
had become popular pastimes among the wealthier citizens. The Boat Race, a rowing event between the Cambridge University Boat Club and the Oxford University Boat Club, was first held in 1829 at the instigation of Charles Merivale and Charles Wordsworth, who were students at Cambridge and Oxford, respectively. Wordsworth was a nephew of William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poetry, Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romanticism, Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Balla ...
. The first race was at Henley-on-Thames and the contest later became an annual event on the River Thames in London. In sailing, the first Cowes Week regatta was held on the Solent in August 1826.
Track and field athletics
Track and field competitions in the modern sense were first recorded in the early 19th century. They are known to have been held by schools, colleges, army and navy bases, social clubs and the like, often as a challenge to a rival establishment. In the public schools, athletics competitions were conceived as human equivalents of horse racing or fox hunting with runners known as "hounds" and named as if they were racehorses. The Shrewsbury School, Royal Shrewsbury School Hunt, established in 1819, is the world's oldest running club. The school organised Paper Chase (game), paper chase races in which the hounds followed a trail of paper shreds left by two "foxes". The oldest running race of the modern era is Shrewsbury's Annual Steeplechase (athletics), Steeplechase (cross-country), first definitely recorded in 1834.Events
; 1811:George Augustus Frederick, Prince of Wales, began his nine-year tenure as Prince regent, regent and became known as ''The Prince Regent''. This sub-period of theGeorgian era
The Georgian era was a period in British history from 1714 to , named after the House of Hanover, Hanoverian kings George I of Great Britain, George I, George II of Great Britain, George II, George III and George IV. The definition of the Geor ...
began the formal Regency. The Duke of Wellington held off the French at Fuentes de Oñoro and Battle of Albuera, Albuhera in the Peninsular War. The Prince Regent held the Carlton House Fête at 9:00 p.m. 19 June 1811, at Carlton House, London, Carlton House in celebration of his assumption of the Regency. Luddite uprisings. Glasgow weavers riot.
; 1812: Assassination of Spencer Perceval, Prime Minister Spencer Perceval was assassinated in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons. The final shipment of the Elgin Marbles arrived in England. Sarah Siddons retired from the stage. Shipping and territory disputes started the War of 1812 between the United Kingdom and the United States. The British were victorious over French armies at the Battle of Salamanca. Gas company (Gas Light and Coke Company) founded. Charles Dickens, English writer and social critic of the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the ...
, was born on 7 February 1812.
; 1813: '' Pride and Prejudice'' by Jane Austen
Jane Austen ( ; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for #List of works, her six novels, which implicitly interpret, critique, and comment on the English landed gentry at the end of the 18th century ...
was published. William Hedley's Puffing Billy (locomotive), Puffing Billy, an early steam locomotive, ran on smooth rails. Quakers, Quaker prison reformer Elizabeth Fry started her ministry at Newgate Prison. Robert Southey became Poet Laureate.
; 1814: Invasion of France by allies led to the Treaty of Paris (1814), Treaty of Paris, ended one of the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
. Napoleon abdicated and was exiled to Elba. The Duke of Wellington was honoured at Burlington House in London. British soldiers Burning of Washington, burn the White House. Last River Thames Frost Fair was held, which was the last time the river froze. Gas lighting introduced in London streets. ; 1815:Napoleon I of France defeated by the Hundred Days, Seventh Coalition at the Battle of Waterloo. Napoleon was exiled to St. Helena. The English Corn Laws restricted corn imports. Sir Humphry Davy patented the Miner's safety lamp, miners' safety lamp. John Loudon Macadam's Macadam, road construction method adopted.
; 1816: Income tax abolished. A "year without a summer" followed a 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora, volcanic eruption in Indonesia.
; 1815:Napoleon I of France defeated by the Hundred Days, Seventh Coalition at the Battle of Waterloo. Napoleon was exiled to St. Helena. The English Corn Laws restricted corn imports. Sir Humphry Davy patented the Miner's safety lamp, miners' safety lamp. John Loudon Macadam's Macadam, road construction method adopted.
; 1816: Income tax abolished. A "year without a summer" followed a 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora, volcanic eruption in Indonesia. Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley ( , ; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an History of science fiction# ...
wrote ''Frankenstein''. William Cobbett published his newspaper as a pamphlet. The British returned Indonesia to the Dutch. Regent's Canal, London, phase one of construction. Beau Brummell escaped his creditors by fleeing to France.
; 1817: Antonin Carême created a spectacular feast for the Prince Regent at the Royal Pavilion in Brighton. The death of Princess Charlotte of Wales (1796–1817), Princess Charlotte, the Prince Regent's daughter, from complications of childbirth changed Obstetrics, obstetrical practices. Elgin Marbles shown at the British Museum. Captain Bligh died.
; 1818: Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Queen Charlotte died at Kew. Manchester cotton spinners went on strike. Riot in Stanhope, County Durham between lead miners and the Bishop of Durham's men over Weardale game rights. Piccadilly Circus constructed in London. ''Frankenstein'' published. Emily Brontë born.
; 1819:Peterloo Massacre
The Peterloo Massacre took place at St Peter's Field, Manchester, Lancashire, England, on Monday 16 August 1819. Eighteen people died and 400–700 were injured when the cavalry of the Yeomen charged into a crowd of around 60,000 people who ...
. Princess Alexandrina Victoria (future Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
) was christened in Kensington Palace. ''Ivanhoe'' by Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European literature, European and Scottish literature, notably the novels ''Ivanhoe'' (18 ...
was published. Sir Stamford Raffles, a British administrator, founded Singapore. First steam-propelled vessel (the SS Savannah, SS ''Savannah'') crossed the Atlantic and arrived in Liverpool from Savannah, Georgia.
; 1820: Death of George III and the accession of ''The Prince Regent'' as George IV. The House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
passed a bill to grant George IV a divorce from Caroline of Brunswick, Queen Caroline, but because of public pressure, the bill was dropped. John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romanticism, Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedha ...
began work on ''The Hay Wain''. Cato Street Conspiracy failed. Royal Astronomical Society founded. ''Venus de Milo'' discovered.
Places
The following is a list of places associated with the Regency era: * The Adelphi Theatre
* Almack's
* Angelo's, a fencing parlor
* Apsley House
* Argyll Rooms
* Astley's Amphitheatre
* Attingham Park
* Bank of England
* Bath, Somerset
* Bond Street
* Brighton Pavilion
* Brighton and Hove
* Brooks's
* Burlington Arcade
* Bury St Edmunds
* Carlton House, London
*Chalk Farm Tavern
* Chapel Royal, St. James's
* Cheltenham, Gloucestershire
* Circulating libraries, 1801–1825
* Covent Garden
* Custom Office, London Docks
* Doncaster Racecourse, Doncaster Races
* Drury Lane
* Floris of London
* Fortnum & Mason
* Gretna Green
* Gentleman Jackson's Saloon, a pugilist's parlor by bare-knuckle champion John Jackson (English boxer), John Jackson
* Hatchard's
* Haymarket Theatre, Little Theatre, Haymarket
* His Majesty's Theatre, London, His Majesty's Theatre
* Hertford House
* Holland House
* Houses of Parliament
* Hyde Park, London
* Jermyn Street
* Kensington Gardens
* King of Clubs (Whig club), King of Clubs
* Lansdowne House
* List of gentlemen's clubs in London
* Lloyd's of London
* London Docks
* London Institution
* London Post Office
* Lyme Regis
* Marshalsea, closed in 1811, new site opened in 1811 where White Lion Prison had been. Primarily a debtors' prison, also housed seditionists and political prisoners
* Mayfair, London
* Newgate Prison
*
* The Adelphi Theatre
* Almack's
* Angelo's, a fencing parlor
* Apsley House
* Argyll Rooms
* Astley's Amphitheatre
* Attingham Park
* Bank of England
* Bath, Somerset
* Bond Street
* Brighton Pavilion
* Brighton and Hove
* Brooks's
* Burlington Arcade
* Bury St Edmunds
* Carlton House, London
*Chalk Farm Tavern
* Chapel Royal, St. James's
* Cheltenham, Gloucestershire
* Circulating libraries, 1801–1825
* Covent Garden
* Custom Office, London Docks
* Doncaster Racecourse, Doncaster Races
* Drury Lane
* Floris of London
* Fortnum & Mason
* Gretna Green
* Gentleman Jackson's Saloon, a pugilist's parlor by bare-knuckle champion John Jackson (English boxer), John Jackson
* Hatchard's
* Haymarket Theatre, Little Theatre, Haymarket
* His Majesty's Theatre, London, His Majesty's Theatre
* Hertford House
* Holland House
* Houses of Parliament
* Hyde Park, London
* Jermyn Street
* Kensington Gardens
* King of Clubs (Whig club), King of Clubs
* Lansdowne House
* List of gentlemen's clubs in London
* Lloyd's of London
* London Docks
* London Institution
* London Post Office
* Lyme Regis
* Marshalsea, closed in 1811, new site opened in 1811 where White Lion Prison had been. Primarily a debtors' prison, also housed seditionists and political prisoners
* Mayfair, London
* Newgate Prison
* Newmarket Racecourse
Newmarket Racecourse is a British Thoroughbred horse racing venue in Newmarket, Suffolk, Newmarket, Suffolk, comprising two individual racecourses: the Rowley Mile and the July Course. Newmarket is often referred to as the headquarters of ...
* The Old Bailey
* Old Bond Street
* Opera House
* Pall Mall, London
* Pantheon, London, The Pantheon
* Ranelagh Gardens
* Regent's Park
Regent's Park (officially The Regent's Park) is one of the Royal Parks of London. It occupies in north-west Inner London, administratively split between the City of Westminster and the London Borough of Camden, Borough of Camden (and historical ...
* Regent Street
* Royal Circus
* Royal Opera House
* Royal Parks of London
* Rundell and Bridge jewellery firm
* Savile Row
* Somerset House
* St George's, Hanover Square
* St. James's
* Sydney Gardens, Bath
* Temple of Concord, St. James's Park
* Tattersalls
* The Thames Tunnel
* Tunbridge Wells
* Vauxhall Gardens
* West End of London
*West India Docks
* Watier's
* White's
* Waterloo Bridge
Notable people


 For more names see Newman (1997).
* Rudolph Ackermann
* Arthur Aikin
* Henry Addington, 1st Viscount Sidmouth
* William Arden, 2nd Baron Alvanley
* Elizabeth Armistead
*
For more names see Newman (1997).
* Rudolph Ackermann
* Arthur Aikin
* Henry Addington, 1st Viscount Sidmouth
* William Arden, 2nd Baron Alvanley
* Elizabeth Armistead
* Jane Austen
Jane Austen ( ; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for #List of works, her six novels, which implicitly interpret, critique, and comment on the English landed gentry at the end of the 18th century ...
* Charles Babbage
* Joseph Banks
* Richard Barry, 7th Earl of Barrymore
* Henry Bathurst, 3rd Earl Bathurst
* William Beechey
* William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake has become a seminal figure in the history of the Romantic poetry, poetry and visual art of the Roma ...
* Beau Brummell
* Mary Brunton
* Lord Frederick Beauclerk
* Henrietta Ponsonby, Countess of Bessborough
* Marguerite Gardiner, Countess of Blessington
* Junius Brutus Booth
* Bow Street Runners
* Marc Isambard Brunel
* Caroline of Brunswick
* Frances Burney
* James Burton (property developer), James Burton
* Decimus Burton
* Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824) was an English poet. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest poets of the United Kingdom. Among his best-kno ...
* George Campbell, 6th Duke of Argyll
* Amelia Stewart, Viscountess Castlereagh
* Robert Stewart, 2nd Marquess of Londonderry, Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh
* George Canning
* George Cayley
* Georgiana Cavendish, Duchess of Devonshire
* Francis Leggatt Chantrey
* Princess Charlotte Augusta of Wales
* John Clare
* Mary Anne Clarke
* William Cobbett
* Samuel Taylor Coleridge
* Patrick Colquhoun
* John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romanticism, Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedha ...
* Elizabeth Conyngham, Marchioness Conyngham
* Tom Cribb
*John Wilson Croker
* George Cruikshank
* John Dalton
* Humphry Davy
* John Disney (archaeologist), John Disney
* David Douglas (botanist), David Douglas
* Maria Edgeworth
* Pierce Egan
* Thomas Bruce, 7th Earl of Elgin
* Grace Elliott
* Maria Fitzherbert
* Elizabeth Fry
* David Garrick
* George IV of the United Kingdom, Prince of Wales, Prince Regent then King
* James Gillray
* Frederick Robinson, 1st Viscount Goderich
* William Grenville, 1st Baron Grenville
* Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey
* Emma, Lady Hamilton
* William Harcourt, 3rd Earl Harcourt
* Ann Hatton
* William Hazlitt
* William Hedley
* James Henry Leigh Hunt, Leigh Hunt
* Isabella Ingram-Seymour-Conway, Marchioness of Hertford
* Washington Irving
* John Jackson (English boxer), John Jackson
* Edward Jenner
* Sarah Villiers, Countess of Jersey, Sarah, Countess of Jersey
* Dorothea Jordan
* Edmund Kean
* Charles Kemble
* John Philip Kemble
* Stephen Kemble
* Michael Kelly (tenor), Michael Kelly
* John Keats
* Lady Caroline Lamb
* Charles Lamb (writer), Charles Lamb
* Emily Lamb, Countess Cowper
* Thomas Lawrence (painter), Sir Thomas Lawrence, PRA
* Dorothea Lieven, Princess Lieven
* Mary Linwood
* Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool
* Hudson Lowe
* Ada Lovelace, Ada Byron Lovelace
* William Macready
* John Loudon McAdam
* Lord Melbourne
* Thomas Moore
* Hannah More
* John Nash
* Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson
* Elizabeth O'Neill (actress), Elizabeth O'Neill
* William II of the Netherlands, William, Prince of Orange
* George Ormerod
* Henry Paget, 1st Marquess of Anglesey
* Thomas Paine
* John Palmer (postal innovator), John Palmer, Royal Mail
* Sir Robert Peel
* Spencer Perceval
* Thomas Phillips
* William Pitt the Younger
* Jane Porter
* Hermann, Fürst von Pückler-Muskau
* Thomas De Quincey
* Thomas Raikes (dandy), Thomas Raikes
* Humphry Repton
* Samuel Rogers
* Thomas Rowlandson
* James Sadler (balloonist), James Sadler
* Sir Walter Scott, Walter Scott
* Richard Sharp (politician), Richard "Conversation" Sharp
* Martin Archer Shee
Sir Martin Archer Shee (23 December 1769 – 13 August 1850) was an Irish portrait painter. He also served as the president of the Royal Academy.
Early life
He was born in Dublin, of an old Irish Roman Catholic family, the son of Martin Shee ...
* Percy Bysshe Shelley
Percy Bysshe Shelley ( ; 4 August 1792 – 8 July 1822) was an English writer who is considered one of the major English Romantic poets. A radical in his poetry as well as in his political and social views, Shelley did not achieve fame durin ...
* Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley ( , ; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an History of science fiction# ...
* Richard Brinsley Sheridan
* Sarah Siddons
* John Soane
* Adam Sedgwick
* Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh
* John Wedgwood (horticulturist), John Wedgwood
* Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington
*Richard Wellesley, 1st Marquess Wellesley
* Amelia Stewart, Viscountess Castlereagh
* Thomas Telford
* Benjamin Thompson, Count Rumford
* Joseph Mallord William Turner
* Henry Vassall-Fox, 3rd Baron Holland
* Benjamin West
* William Wilberforce
* Harriette Wilson
* William Hyde Wollaston
* Mary Wollstonecraft
* William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poetry, Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romanticism, Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Balla ...
* Jeffry Wyattville
* Thomas Young (scientist), Thomas Young
Gallery
See also
* Regency architecture * 1795–1820 in Western fashion, Regency fashions * Regency dance * Régence, the period of the early 18th-century regency in France * Society of Dilettanti * Era of Good Feelings, for the United StatesReferences
Sources
* Bowman, Peter James. ''The Fortune Hunter: A German Prince in Regency England.'' Oxford: Signal Books, 2010. * David, Saul. ''Prince of Pleasure The Prince of Wales and the Making of the Regency''. New York: Atlantic Monthly Press, 1998. * *Knafla, David, Crime, punishment, and reform in Europe, Greenwood Publishing, 2003
* Lapp, Robert Keith. ''Contest for Cultural Authority – Hazlitt, Coleridge, and the Distresses of the Regency''. Detroit: Wayne State UP, 1999. * Marriott, J. A. R. ''England Since Waterloo'' (1913
online
* Morgan, Marjorie. ''Manners, Morals, and Class in England, 1774–1859.'' New York: St. Martin's Press, 1994. * Morrison, Robert. ''The Regency Years: During Which Jane Austen Writes, Napoleon Fights, Byron Makes Love, and Britain Becomes Modern''. 2019, New York: W. W. Norton, London: Atlantic Book
online review
*
online review
904pp; 1121 short articles on Britain by 250 experts. * Parissien, Steven. ''George IV Inspiration of the Regency.'' New York: St. Martin's P, 2001. * Pilcher, Donald. ''The Regency Style: 1800–1830'' (London: Batsford, 1947). * Rendell, Jane. ''The pursuit of pleasure: gender, space & architecture in Regency London'' (Bloomsbury, 2002). * Joanna Richardson, Richardson, Joanna. ''The Regency''. London: Collins, 1973. * Webb, R.K. ''Modern England: from the 18th century to the present'' (1968
online
widely recommended university textbook * Wellesley, Lord Gerald. "Regency Furniture", ''The Burlington Magazine for Connoisseurs'' 70, no. 410 (1937): 233–241. * White, R.J. ''Life in Regency England'' (Batsford, 1963).
Crime and punishment
* Emsley, Clive. ''Crime and society in England: 1750–1900'' (2013). * Innes, Joanna and John Styles. "The Crime Wave: Recent Writing on Crime and Criminal Justice in Eighteenth-Century England" ''Journal of British Studies'' 25#4 (1986), pp. 380–435 . * Low, Donald A. ''The Regency Underworld''. Gloucestershire: Sutton, 1999. * Morgan, Gwenda, and Peter Rushton. ''Rogues, Thieves And the Rule of Law: The Problem of Law Enforcement in North-East England, 1718–1820'' (2005).Primary sources
* Simond, Louis. ''Journal of a tour and residence in Great Britain, during the years 1810 and 1811'online
External links
Greenwood's Map of London, 1827
Results of the 1801 and 1811 Census of London
''The European Magazine and London Review'', 1818, p. 50
The Bluestocking Archive
End of an Era: 1815–1830
Regency Style Furniture
{{Authority control Regency era, Regency London, * 1810s in the United Kingdom George III George IV History of the United Kingdom by period Historical eras Architecture of London Regency (government) 1820 in the United Kingdom 1830s in the United Kingdom