Digestive System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The human digestive system consists of the
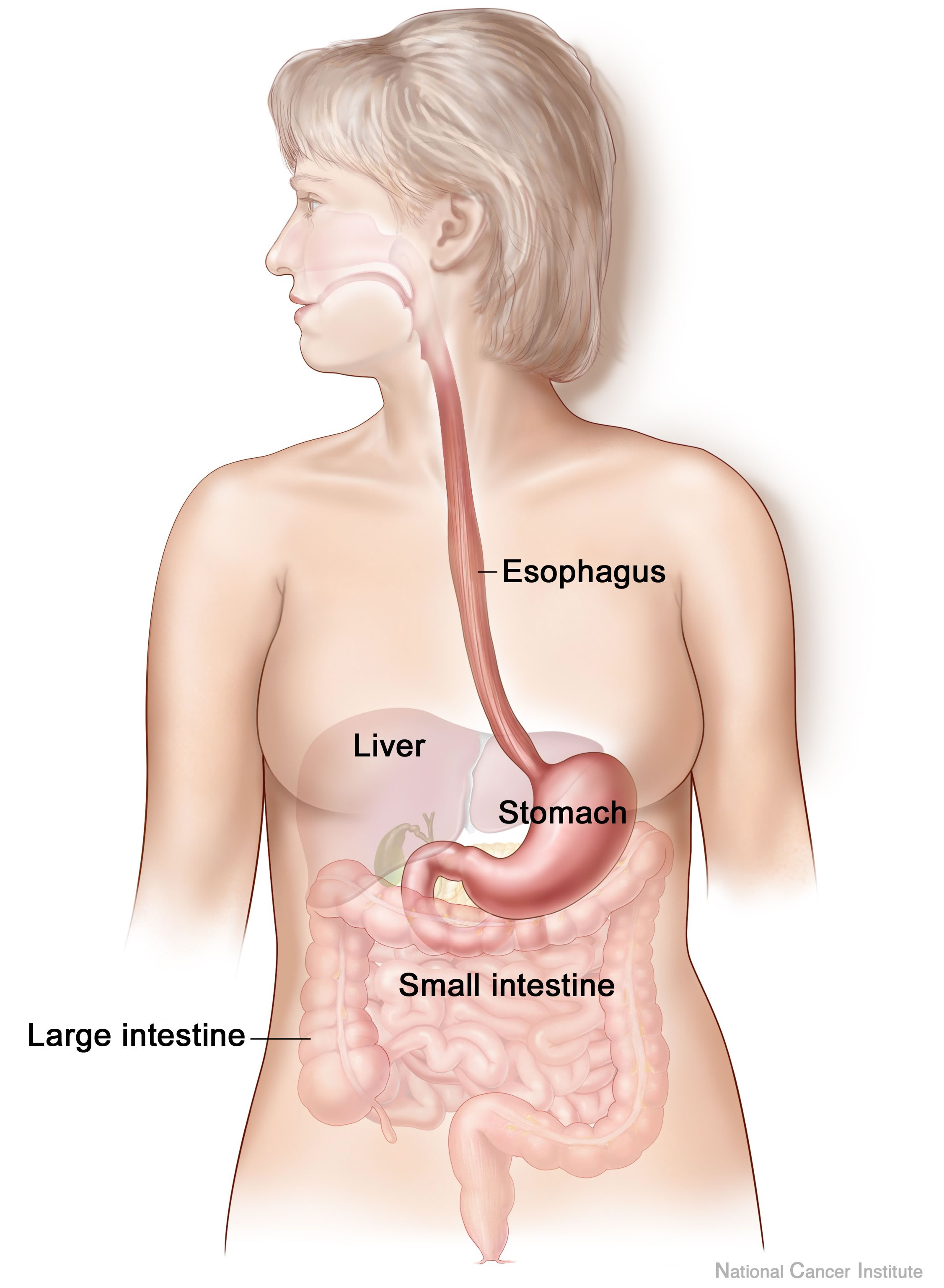 There are several organs and other components involved in the digestion of food. The organs known as the accessory digestive organs are the liver,
There are several organs and other components involved in the digestion of food. The organs known as the accessory digestive organs are the liver,
 The
The
 There are three pairs of main salivary glands and between 800 and 1,000 minor salivary glands, all of which mainly serve the digestive process, and also play an important role in the maintenance of dental health and general mouth lubrication, without which speech would be impossible. The main glands are all
There are three pairs of main salivary glands and between 800 and 1,000 minor salivary glands, all of which mainly serve the digestive process, and also play an important role in the maintenance of dental health and general mouth lubrication, without which speech would be impossible. The main glands are all
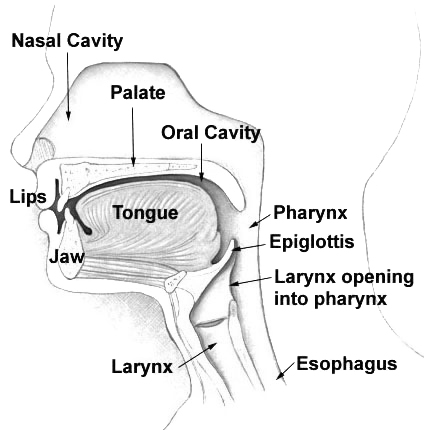 Food enters the mouth where the first stage in the digestive process takes place, with the action of the tongue and the secretion of saliva. The tongue is a fleshy and muscular sensory organ, and the first sensory information is received via the taste buds in the
Food enters the mouth where the first stage in the digestive process takes place, with the action of the tongue and the secretion of saliva. The tongue is a fleshy and muscular sensory organ, and the first sensory information is received via the taste buds in the

 The
The
 The
The
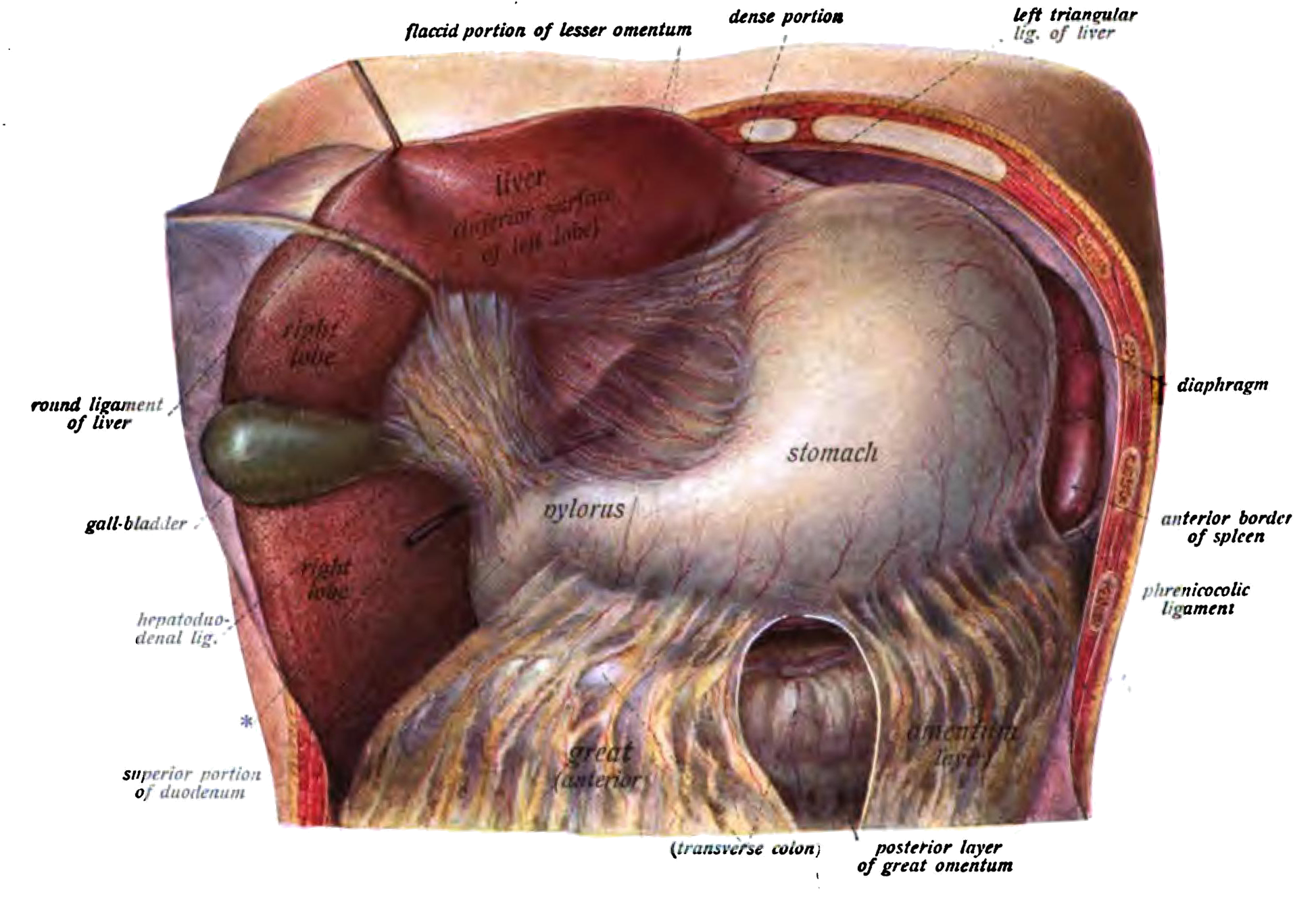 The gallbladder is a hollow part of the
The gallbladder is a hollow part of the

 The pancreas is a major organ functioning as an accessory digestive gland in the digestive system. It is both an
The pancreas is a major organ functioning as an accessory digestive gland in the digestive system. It is both an
 Partially digested food starts to arrive in the
Partially digested food starts to arrive in the  When the digested food particles are reduced enough in size and composition, they can be absorbed by the intestinal wall and carried to the bloodstream. The first receptacle for this chyme is the duodenal bulb. From here it passes into the first of the three sections of the small intestine, the duodenum (the next section is the
When the digested food particles are reduced enough in size and composition, they can be absorbed by the intestinal wall and carried to the bloodstream. The first receptacle for this chyme is the duodenal bulb. From here it passes into the first of the three sections of the small intestine, the duodenum (the next section is the
 The
The
 In the
In the
 The digestive system is supplied by the
The digestive system is supplied by the

 In the early 11th century the Islamic medical philosopher
In the early 11th century the Islamic medical philosopher
gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase
The nervous system, and endocrine system collaborate in the digestive system to control gastric secretions, and motility associated with the movement of food throughout the gastrointestinal tract, including peristalsis, and segmentation contract ...
, and the intestinal phase
The nervous system, and endocrine system collaborate in the digestive system to control gastric secretions, and motility associated with the movement of food throughout the gastrointestinal tract, including peristalsis, and segmentation contraction ...
.
The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, ...
, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
. Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus
Bolus may refer to:
Geography
* Bolus, Iran, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran
* Bolus, or Baulus, an Anatolian village on the site of ancient Berissa
Medicine
* Bolus (digestion), a ball-shaped mass moving through the digestive tract
* Bolus ...
which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the stomach.
The second stage of digestion begins in the stomach with the gastric phase. Here the food is further broken down by mixing with gastric acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
until it passes into the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
, the first part of the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
.
The third stage begins in the duodenum with the intestinal phase, where partially digested food is mixed with a number of enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s produced by the pancreas. Digestion is helped by the chewing of food carried out by the muscles of mastication
There are four classical muscles of mastication. During mastication, three muscles of mastication (''musculi masticatorii'') are responsible for adduction of the jaw, and one (the lateral pterygoid) helps to abduct it. All four move the jaw late ...
, the tongue, and the teeth, and also by the contractions of peristalsis, and segmentation. Gastric acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
, and the production of mucus in the stomach, are essential for the continuation of digestion.
Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
s that begins in the esophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoi ...
. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ( ...
are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon of the large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being r ...
. The waste products of digestion (feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a rela ...
) are defecated from the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
via the anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
.
Components
 There are several organs and other components involved in the digestion of food. The organs known as the accessory digestive organs are the liver,
There are several organs and other components involved in the digestion of food. The organs known as the accessory digestive organs are the liver, gall bladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, althoug ...
and pancreas. Other components include the mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
, salivary glands, tongue, teeth and epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food i ...
.
The largest structure of the digestive system is the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
(GI tract). This starts at the mouth and ends at the anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
, covering a distance of about nine metres.
A major digestive organ is the stomach. Within its mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
are millions of embedded gastric glands. Their secretions are vital to the functioning of the organ.
Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
which is the longest part of the GI tract.
The largest part of the GI tract is the colon or large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being r ...
. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste matter is stored prior to defecation
Defecation (or defaecation) follows digestion, and is a necessary process by which organisms eliminate a solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material known as feces from the digestive tract via the anus. The act has a variety of names ranging ...
.
There are many specialised cells of the GI tract. These include the various cells of the gastric glands, taste cells, pancreatic duct cell
Centroacinar cells are spindle-shaped cells in the exocrine pancreas. They represent an extension of the intercalated duct into each pancreatic acinus. These cells are commonly known as duct cells, and secrete an aqueous bicarbonate solution u ...
s, enterocytes and microfold cells.
Some parts of the digestive system are also part of the excretory system, including the large intestine.
Mouth
 The
The mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
is the first part of the upper gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
and is equipped with several structures that begin the first processes of digestion. These include salivary glands, teeth and the tongue. The mouth consists of two regions; the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. The vestibule is the area between the teeth, lips and cheeks, and the rest is the oral cavity proper. Most of the oral cavity is lined with oral mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been des ...
, a mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
that produces a lubricating mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
, of which only a small amount is needed. Mucous membranes vary in structure in the different regions of the body but they all produce a lubricating mucus, which is either secreted by surface cells or more usually by underlying glands. The mucous membrane in the mouth continues as the thin mucosa which lines the bases of the teeth. The main component of mucus is a glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as g ...
called mucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins ( glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in m ...
and the type secreted varies according to the region involved. Mucin is viscous, clear, and clinging. Underlying the mucous membrane in the mouth is a thin layer of smooth muscle tissue
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit m ...
and the loose connection to the membrane gives it its great elasticity. It covers the cheeks, inner surfaces of the lips, and floor of the mouth, and the mucin produced is highly protective against tooth decay
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
.
The roof of the mouth is termed the palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly s ...
and it separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. The palate is hard at the front of the mouth since the overlying mucosa is covering a plate of bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
; it is softer and more pliable at the back being made of muscle and connective tissue, and it can move to swallow food and liquids. The soft palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. ...
ends at the uvula
The palatine uvula, usually referred to as simply the uvula, is a conic projection from the back edge of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fibers. It also cont ...
. The surface of the hard palate
The hard palate is a thin horizontal bony plate made up of two bones of the facial skeleton, located in the roof of the mouth. The bones are the palatine process of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of palatine bone. The hard palate spans th ...
allows for the pressure needed in eating food, to leave the nasal passage clear. The opening between the lips is termed the oral fissure, and the opening into the throat is called the fauces.
At either side of the soft palate are the palatoglossus muscles which also reach into regions of the tongue. These muscles raise the back of the tongue and also close both sides of the fauces to enable food to be swallowed. Mucus helps in the mastication of food in its ability to soften and collect the food in the formation of the bolus.
Salivary glands
 There are three pairs of main salivary glands and between 800 and 1,000 minor salivary glands, all of which mainly serve the digestive process, and also play an important role in the maintenance of dental health and general mouth lubrication, without which speech would be impossible. The main glands are all
There are three pairs of main salivary glands and between 800 and 1,000 minor salivary glands, all of which mainly serve the digestive process, and also play an important role in the maintenance of dental health and general mouth lubrication, without which speech would be impossible. The main glands are all exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of ...
s, secreting via ducts. All of these glands terminate in the mouth. The largest of these are the parotid gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the m ...
s—their secretion is mainly serous
In physiology, serous fluid or serosal fluid (originating from the Medieval Latin word ''serosus'', from Latin ''serum'') is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent and of a benign nature. The f ...
. The next pair are underneath the jaw, the submandibular gland
The paired submandibular glands (historically known as submaxillary glands) are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. They each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimula ...
s, these produce both serous fluid
In physiology, serous fluid or serosal fluid (originating from the Medieval Latin word ''serosus'', from Latin ''serum'') is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent and of a benign nature. The fl ...
and mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
. The serous fluid is produced by serous glands in these salivary glands which also produce lingual lipase. They produce about 70% of the oral cavity saliva. The third pair are the sublingual glands located underneath the tongue and their secretion is mainly mucous with a small percentage of saliva.
Within the oral mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been des ...
, and also on the tongue, palates, and floor of the mouth, are the minor salivary glands; their secretions are mainly mucous and they are innervated by the facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of ta ...
( CN7).Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 157 The glands also secrete amylase a first stage in the breakdown of food acting on the carbohydrate in the food to transform the starch content into maltose. There are other serous glands on the surface of the tongue that encircle taste bud
Taste buds contain the taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, the chee ...
s on the back part of the tongue and these also produce lingual lipase. Lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually tr ...
is a digestive enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
of lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids incl ...
s (fats). These glands are termed Von Ebner's glands which have also been shown to have another function in the secretion of histatin
Histatins are histidine-rich (cationic) antimicrobial proteins found in saliva. Histatin's involvement in antimicrobial activities makes histatin part of the innate immune system.
Histatin was first discovered (isolated) in 1988, with functions th ...
s which offer an early defense (outside of the immune system) against microbes in food, when it makes contact with these glands on the tongue tissue. Sensory information can stimulate the secretion of saliva providing the necessary fluid for the tongue to work with and also to ease swallowing of the food.
=Saliva
=Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
moistens and softens food, and along with the chewing action of the teeth, transforms the food into a smooth bolus
Bolus may refer to:
Geography
* Bolus, Iran, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran
* Bolus, or Baulus, an Anatolian village on the site of ancient Berissa
Medicine
* Bolus (digestion), a ball-shaped mass moving through the digestive tract
* Bolus ...
. The bolus is further helped by the lubrication provided by the saliva in its passage from the mouth into the esophagus. Also of importance is the presence in saliva of the digestive enzymes amylase and lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually tr ...
. Amylase starts to work on the starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
in carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
s, breaking it down into the simple sugars
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
of maltose
}
Maltose ( or ), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the tw ...
and dextrose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, usin ...
that can be further broken down in the small intestine. Saliva in the mouth can account for 30% of this initial starch digestion. Lipase starts to work on breaking down fats. Lipase is further produced in the pancreas where it is released to continue this digestion of fats. The presence of salivary lipase is of prime importance in young babies whose pancreatic lipase has yet to be developed.
As well as its role in supplying digestive enzymes, saliva has a cleansing action for the teeth and mouth. It also has an immunological
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there ...
role in supplying antibodies to the system, such as immunoglobulin A
Immunoglobulin A (Ig A, also referred to as sIgA in its secretory form) is an antibody that plays a role in the immune function of mucous membranes. The amount of IgA produced in association with mucosal membranes is greater than all other t ...
. This is seen to be key in preventing infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
s of the salivary glands, importantly that of parotitis
Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary gland
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, ...
.
Saliva also contains a glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as g ...
called haptocorrin which is a binding protein to vitamin B12. It binds with the vitamin in order to carry it safely through the acidic content of the stomach. When it reaches the duodenum, pancreatic enzymes break down the glycoprotein and free the vitamin which then binds with intrinsic factor
Intrinsic factor (IF), cobalamin binding intrinsic factor, also known as gastric intrinsic factor (GIF), is a glycoprotein produced by the parietal cells (in humans) or chief cells (in rodents) of the stomach. It is necessary for the absorption o ...
.
Tongue
 Food enters the mouth where the first stage in the digestive process takes place, with the action of the tongue and the secretion of saliva. The tongue is a fleshy and muscular sensory organ, and the first sensory information is received via the taste buds in the
Food enters the mouth where the first stage in the digestive process takes place, with the action of the tongue and the secretion of saliva. The tongue is a fleshy and muscular sensory organ, and the first sensory information is received via the taste buds in the papillae
Papilla (Latin, 'nipple') or papillae may refer to:
In animals
* Papilla (fish anatomy), in the mouth of fish
* Basilar papilla, a sensory organ of lizards, amphibians and fish
* Dental papilla, in a developing tooth
* Dermal papillae, part of ...
on its surface. If the taste is agreeable, the tongue will go into action, manipulating the food in the mouth which stimulates the secretion of saliva from the salivary glands. The liquid quality of the saliva will help in the softening of the food and its enzyme content will start to break down the food whilst it is still in the mouth. The first part of the food to be broken down is the starch of carbohydrates (by the enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
amylase in the saliva).
The tongue is attached to the floor of the mouth by a ligamentous band called the frenum and this gives it great mobility for the manipulation of food (and speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
); the range of manipulation is optimally controlled by the action of several muscles and limited in its external range by the stretch of the frenum. The tongue's two sets of muscles, are four intrinsic muscles
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location.
Types
There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, ...
that originate in the tongue and are involved with its shaping, and four extrinsic muscles originating in bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
that are involved with its movement.
=Taste
=
Taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste recepto ...
is a form of chemoreception that takes place in the specialised taste receptor
A taste receptor or tastant is a type of cellular receptor which facilitates the sensation of taste. When food or other substances enter the mouth, molecules interact with saliva and are bound to taste receptors in the oral cavity and other loca ...
s, contained in structures called taste buds
Taste buds contain the taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, the chee ...
in the mouth. Taste buds are mainly on the upper surface (dorsum) of the tongue. The function of taste perception is vital to help prevent harmful or rotten foods from being consumed. There are also taste buds on the epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food i ...
and upper part of the esophagus. The taste buds are innervated by a branch of the facial nerve the chorda tympani
The chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve that originates from the taste buds in the front of the tongue, runs through the middle ear, and carries taste messages to the brain. It joins the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) inside the facia ...
, and the glossopharyngeal nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Be ...
. Taste messages are sent via these cranial nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and ...
to the brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
. The brain can distinguish between the chemical qualities of the food. The five basic tastes are referred to as those of saltiness
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor ...
, sourness, bitterness, sweetness, and umami
Umami ( from ja, 旨味 ), or savoriness, is one of the five basic tastes. It has been described as savory and is characteristic of broths and cooked meats.
People taste umami through taste receptors that typically respond to glutamates and ...
. The detection of saltiness and sourness enables the control of salt and acid balance. The detection of bitterness warns of poisons—many of a plant's defences are of poisonous compounds that are bitter. Sweetness guides to those foods that will supply energy; the initial breakdown of the energy-giving carbohydrates by salivary amylase creates the taste of sweetness since simple sugars are the first result. The taste of umami is thought to signal protein-rich food. Sour tastes are acidic which is often found in bad food. The brain has to decide very quickly whether the food should be eaten or not. It was the findings in 1991, describing the first olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, i ...
receptors that helped to prompt the research into taste. The olfactory receptors are located on cell surfaces in the nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next pass ...
which bind to chemicals enabling the detection of smells. It is assumed that signals from taste receptors work together with those from the nose, to form an idea of complex food flavours.
Teeth
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, te ...
are complex structures made of materials specific to them. They are made of a bone-like material called dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by e ...
, which is covered by the hardest tissue in the body— enamel. Teeth have different shapes to deal with different aspects of mastication
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, th ...
employed in tearing and chewing pieces of food into smaller and smaller pieces. This results in a much larger surface area for the action of digestive enzymes.
The teeth are named after their particular roles in the process of mastication—incisors
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wh ...
are used for cutting or biting off pieces of food; canines, are used for tearing, premolars
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth ...
and molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
are used for chewing and grinding. Mastication of the food with the help of saliva and mucus results in the formation of a soft bolus which can then be swallowed to make its way down the upper gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
to the stomach.
The digestive enzymes in saliva also help in keeping the teeth clean by breaking down any lodged food particles.
Epiglottis
 The
The epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food i ...
is a flap of elastic cartilage
Elastic cartilage, fibroelastic cartilage or yellow fibrocartilage is a type of cartilage present in the pinnae (auricles) of the ear giving it shape, provides shape for the lateral region of the external auditory meatus, medial part of the aud ...
attached to the entrance of the larynx. It is covered with a mucous membrane and there are taste buds on its lingual surface which faces into the mouth. Its laryngeal surface faces into the larynx. The epiglottis functions to guard the entrance of the glottis
The glottis is the opening between the vocal folds (the rima glottidis). The glottis is crucial in producing vowels and voiced consonants.
Etymology
From Ancient Greek ''γλωττίς'' (glōttís), derived from ''γλῶττα'' (glôtta), ...
, the opening between the vocal folds
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech ...
. It is normally pointed upward during breathing with its underside functioning as part of the pharynx, but during swallowing, the epiglottis folds down to a more horizontal position, with its upper side functioning as part of the pharynx. In this manner it prevents food from going into the trachea and instead directs it to the esophagus, which is behind. During swallowing, the backward motion of the tongue forces the epiglottis over the glottis' opening to prevent any food that is being swallowed from entering the larynx which leads to the lungs; the larynx is also pulled upwards to assist this process. Stimulation of the larynx by ingested matter produces a strong cough reflex The cough reflex occurs when stimulation of cough receptors in the respiratory tract by dust or other foreign particles produces a cough, which causes rapidly moving air which usually remove the foreign material before it reaches the lungs. This typ ...
in order to protect the lungs.
Pharynx
Thepharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
is a part of the conducting zone
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
of the respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
and also a part of the digestive system. It is the part of the throat immediately behind the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal ...
at the back of the mouth and above the esophagus and larynx. The pharynx is made up of three parts. The lower two parts—the oropharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
and the laryngopharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
are involved in the digestive system. The laryngopharynx connects to the esophagus and it serves as a passageway for both air and food. Air enters the larynx anteriorly but anything swallowed has priority and the passage of air is temporarily blocked. The pharynx is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of the vagus nerve. Muscles in the pharynx push the food into the esophagus. The pharynx joins the esophagus at the oesophageal inlet which is located behind the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
.
Esophagus
The esophagus, commonly known as the foodpipe or gullet, consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is continuous with the laryngopharynx. It passes through the posteriormediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
in the thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the ...
and enters the stomach through a hole in the thoracic diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the ...
—the esophageal hiatus, at the level of the tenth thoracic vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervica ...
(T10). Its length averages 25 cm, varying with an individual's height. It is divided into cervical, thoracic
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
and abdominal
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso ...
parts. The pharynx joins the esophagus at the esophageal inlet which is behind the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
.
At rest the esophagus is closed at both ends, by the upper and lower esophageal sphincters. The opening of the upper sphincter is triggered by the swallowing reflex
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing is ...
so that food is allowed through. The sphincter also serves to prevent back flow from the esophagus into the pharynx. The esophagus has a mucous membrane and the epithelium which has a protective function is continuously replaced due to the volume of food that passes inside the esophagus. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus. The epiglottis folds down to a more horizontal position to direct the food into the esophagus, and away from the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from th ...
.
Once in the esophagus, the bolus travels down to the stomach via rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscles known as peristalsis. The lower esophageal sphincter is a muscular sphincter surrounding the lower part of the esophagus. The gastroesophageal junction between the esophagus and the stomach is controlled by the lower esophageal sphincter, which remains constricted at all times other than during swallowing and vomiting to prevent the contents of the stomach from entering the esophagus. As the esophagus does not have the same protection from acid as the stomach, any failure of this sphincter can lead to heartburn.
Diaphragm
Thediaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
is an important part of the body's digestive system. The muscular diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There ...
from the abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is th ...
where most of the digestive organs are located. The suspensory muscle attaches the ascending duodenum to the diaphragm. This muscle is thought to be of help in the digestive system in that its attachment offers a wider angle to the duodenojejunal flexure
The duodenojejunal flexure or duodenojejunal junction is the border between the duodenum and the jejunum.
Structure
The ascending portion of the duodenum ascends on the left side of the aorta, as far as the level of the upper border of the secon ...
for the easier passage of digesting material. The diaphragm also attaches to, and anchors the liver at its bare area. The esophagus enters the abdomen through a hole in the diaphragm at the level of T10 T10 may refer to:
Aircraft
* AmeriPlanes Mitchell Wing T-10, an American ultralight aircraft
* Auster T.10, a British observation aircraft
* Carmier Dupoy T.10, a French sport plane
* Sukhoi T-10, a Soviet prototype jet fighter
Anatomy
* T ...
.
Stomach
The stomach is a major organ of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive system. It is a consistently J-shaped organ joined to the esophagus at its upper end and to the duodenum at its lower end.Gastric acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
(informally ''gastric juice''), produced in the stomach plays a vital role in the digestive process, and mainly contains hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dig ...
and sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35 ...
. A peptide hormone
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the former. These hormones have an effect on the endocrine system of animals, including ...
, gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gastrin ...
, produced by G cell
In anatomy, the G cell or gastrin cell, is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within the pyloric glands of the stomach antrum ...
s in the gastric glands, stimulates the production of gastric juice which activates the digestive enzymes. Pepsinogen
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, w ...
is a precursor enzyme (zymogen
In biochemistry, a zymogen (), also called a proenzyme (), is an inactive precursor of an enzyme. A zymogen requires a biochemical change (such as a hydrolysis reaction revealing the active site, or changing the configuration to reveal the acti ...
) produced by the gastric chief cell
A gastric chief cell (or peptic cell, or gastric zymogenic cell) is a type of gastric gland cell that releases pepsinogen and gastric lipase. It is the cell responsible for secretion of chymosin in ruminant animals. The cell stains basophilic ...
s, and gastric acid activates this to the enzyme pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, ...
which begins the digestion of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s. As these two chemicals would damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by innumerable gastric glands in the stomach, to provide a slimy protective layer against the damaging effects of the chemicals on the inner layers of the stomach.
At the same time that protein is being digested, mechanical churning occurs through the action of peristalsis, waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption into the cells of the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of anim ...
. Gastric lipase secreted by the chief cells in the fundic glands in the gastric mucosa of the stomach, is an acidic lipase, in contrast with the alkaline pancreatic lipase. This breaks down fats to some degree though is not as efficient as the pancreatic lipase.
The pylorus
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pylori ...
, the lowest section of the stomach which attaches to the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
via the pyloric canal, contains countless glands which secrete digestive enzymes including gastrin. After an hour or two, a thick semi-liquid called chyme is produced. When the pyloric sphincter
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pylori ...
, or valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes further with digestive enzymes from the pancreas, and then passes through the small intestine, where digestion continues.
The parietal cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of ...
s in the fundus of the stomach, produce a glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as g ...
called intrinsic factor
Intrinsic factor (IF), cobalamin binding intrinsic factor, also known as gastric intrinsic factor (GIF), is a glycoprotein produced by the parietal cells (in humans) or chief cells (in rodents) of the stomach. It is necessary for the absorption o ...
which is essential for the absorption of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It ...
. Vitamin B12 (cobalamin), is carried to, and through the stomach, bound to a glycoprotein secreted by the salivary glands - transcobalamin I also called haptocorrin, which protects the acid-sensitive vitamin from the acidic stomach contents. Once in the more neutral duodenum, pancreatic enzymes break down the protective glycoprotein. The freed vitamin B12 then binds to intrinsic factor which is then absorbed by the enterocytes in the ileum.
The stomach is a distensible organ and can normally expand to hold about one litre of food. This expansion is enabled by a series of gastric folds in the inner walls of the stomach. The stomach of a newborn baby will only be able to expand to retain about 30 ml.
Spleen
Thespleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
is the largest lymphoid organ in the body but has other functions. It breaks down both red and white blood cells
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
that are ''spent''. This is why it is sometimes known as the 'graveyard of red blood cells'. A product of this ''digestion'' is the pigment bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the ...
, which is sent to the liver and secreted in the bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver b ...
. Another product is iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, which is used in the formation of new blood cells in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoieti ...
. Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion ...
treats the spleen solely as belonging to the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoi ...
, though it is acknowledged that the full range of its important functions is not yet understood.
Liver
 The
The liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
is the second largest organ (after the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
) and is an accessory digestive gland which plays a role in the body's metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
. The liver has many functions some of which are important to digestion. The liver can detoxify various metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, ...
s; synthesise protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s and produce biochemical
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology ...
s needed for digestion. It regulates the storage of glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
which it can form from glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, usi ...
(glycogenesis
Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis, in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. This process is activated during rest periods following the Cori cycle, in the liver, and also activated by insulin in r ...
). The liver can also synthesise glucose from certain amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s. Its digestive functions are largely involved with the breaking down of carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
s. It also maintains protein metabolism in its synthesis and degradation. In lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids incl ...
metabolism it synthesises cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membr ...
. Fats are also produced in the process of lipogenesis
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat. Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty acid and triglyceride synt ...
. The liver synthesises the bulk of lipoproteins. The liver is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen and below the diaphragm to which it is attached at one part, the bare area of the liver. This is to the right of the stomach and it overlies the gall bladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, althoug ...
. The liver synthesises bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
Primary ...
s and lecithin
Lecithin (, from the Greek ''lekithos'' "yolk") is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic – they attract both water and fatty substances (and so a ...
to promote the digestion of fat.
Bile
Bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver b ...
produced by the liver is made up of water (97%), bile salt
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
Primary ...
s, mucus and pigments
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compou ...
, 1% fats and inorganic salts. Bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the ...
is its major pigment. Bile acts partly as a surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, fo ...
which lowers the surface tension between either two liquids or a solid and a liquid and helps to emulsify the fats in the chyme. Food fat is dispersed by the action of bile into smaller units called micelle
A micelle () or micella () (plural micelles or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloidal suspension (also known as associated col ...
s. The breaking down into micelles creates a much larger surface area for the pancreatic enzyme, lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually tr ...
to work on. Lipase digests the triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and '' glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as ...
s which are broken down into two fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s and a monoglyceride
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two differe ...
. These are then absorbed by villi on the intestinal wall. If fats are not absorbed in this way in the small intestine problems can arise later in the large intestine which is not equipped to absorb fats. Bile also helps in the absorption of vitamin K
Vitamin K refers to structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulat ...
from the diet.
Bile is collected and delivered through the common hepatic duct. This duct joins with the cystic duct to connect in a common bile duct
The common bile duct, sometimes abbreviated as CBD, is a duct in the gastrointestinal tract of organisms that have a gallbladder. It is formed by the confluence of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct and terminates by uniting with pancr ...
with the gallbladder.
Bile is stored in the gallbladder for release when food is discharged into the duodenum and also after a few hours.
Gallbladder
 The gallbladder is a hollow part of the
The gallbladder is a hollow part of the biliary tract
The biliary tract, (biliary tree or biliary system) refers to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and ...
that sits just beneath the liver, with the gallbladder body resting in a small depression. It is a small organ where the bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver b ...
produced by the liver is stored, before being released into the small intestine. Bile flows from the liver through the bile duct
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates.
Bile is required for the digestion of food and is secreted by the liver into passages that carry bile toward the hepatic duct. It ...
s and into the gall bladder for storage. The bile is released in response to cholecystokinin
Cholecystokinin (CCK or CCK-PZ; from Greek ''chole'', "bile"; ''cysto'', "sac"; ''kinin'', "move"; hence, ''move the bile-sac (gallbladder)'') is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat an ...
(CCK) a peptide hormone
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the former. These hormones have an effect on the endocrine system of animals, including ...
released from the duodenum. The production of CCK (by endocrine cells of the duodenum) is stimulated by the presence of fat in the duodenum.
It is divided into three sections, a fundus, body and neck. The neck tapers and connects to the biliary tract via the cystic duct, which then joins the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct
The common bile duct, sometimes abbreviated as CBD, is a duct in the gastrointestinal tract of organisms that have a gallbladder. It is formed by the confluence of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct and terminates by uniting with pancr ...
. At this junction is a mucosal fold called ''Hartmann's pouch'', where gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
s commonly get stuck. The muscular layer
The muscular layer (muscular coat, muscular fibers, muscularis propria, muscularis externa) is a region of muscle in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis. The Latin ...
of the body is of smooth muscle tissue that helps the gallbladder contract, so that it can discharge its bile into the bile duct. The gallbladder needs to store bile in a natural, semi-liquid form at all times. Hydrogen ions secreted from the inner lining of the gallbladder keep the bile acidic enough to prevent hardening. To dilute the bile, water and electrolytes from the digestion system are added. Also, salts attach themselves to cholesterol molecules in the bile to keep them from crystallising. If there is too much cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile, or if the gallbladder doesn't empty properly the systems can fail. This is how gallstones form when a small piece of calcium gets coated with either cholesterol or bilirubin and the bile crystallises and forms a gallstone. The main purpose of the gallbladder is to store and release bile, or ''gall''. Bile is released into the small intestine in order to help in the digestion of fats by breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones. After the fat is absorbed, the bile is also absorbed and transported back to the liver for reuse.
Pancreas

 The pancreas is a major organ functioning as an accessory digestive gland in the digestive system. It is both an
The pancreas is a major organ functioning as an accessory digestive gland in the digestive system. It is both an endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid ...
and an exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of ...
. The endocrine part secretes insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
when the blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
becomes high; insulin moves glucose from the blood into the muscles and other tissues for use as energy. The endocrine part releases glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to trea ...
when the blood sugar is low; glucagon allows stored sugar to be broken down into glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, usi ...
by the liver in order to re-balance the sugar levels. The pancreas produces and releases important digestive enzymes in the pancreatic juice that it delivers to the duodenum. The pancreas lies below and at the back of the stomach. It connects to the duodenum via the pancreatic duct
The pancreatic duct, or duct of Wirsung (also, the major pancreatic duct due to the existence of an accessory pancreatic duct), is a duct joining the pancreas to the common bile duct. This supplies it with pancreatic juice from the exocrine panc ...
which it joins near to the bile duct's connection where both the bile and pancreatic juice can act on the chyme that is released from the stomach into the duodenum. Aqueous pancreatic secretions from pancreatic duct cell
Centroacinar cells are spindle-shaped cells in the exocrine pancreas. They represent an extension of the intercalated duct into each pancreatic acinus. These cells are commonly known as duct cells, and secrete an aqueous bicarbonate solution u ...
s contain bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate ( IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioch ...
ions which are alkaline and help with the bile to neutralise the acidic chyme that is churned out by the stomach.
The pancreas is also the main source of enzymes for the digestion of fats and proteins. Some of these are released in response to the production of CKK in the duodenum. (The enzymes that digest polysaccharides, by contrast, are primarily produced by the walls of the intestines.) The cells are filled with secretory granules containing the precursor digestive enzymes. The major protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the form ...
s, the pancreatic enzymes which work on proteins, are trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen
Chymotrypsinogen is an inactive precursor (zymogen) of chymotrypsin, a digestive enzyme which breaks proteins down into smaller peptides. Chymotrypsinogen is a single polypeptide chain consisting of 245 amino acid residues. It is synthesized in the ...
. Elastase is also produced. Smaller amounts of lipase and amylase are secreted. The pancreas also secretes phospholipase A2
The enzyme phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4, PLA2, systematic name phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase) catalyse the cleavage of fatty acids in position 2 of phospholipids, hydrolyzing the bond between the second fatty acid “tail” and the gly ...
, lysophospholipase
The enzyme lysophospholipase (EC 3.1.1.5) catalyzes
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged af ...
, and cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membr ...
esterase
An esterase is a hydrolase enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis.
A wide range of different esterases exist that differ in their substrate specificity, their protein structure ...
. The precursor zymogens, are inactive variants of the enzymes; which avoids the onset of pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic p ...
caused by autodegradation. Once released in the intestine, the enzyme enteropeptidase present in the intestinal mucosa activates trypsinogen by cleaving it to form trypsin; further cleavage results in chymotripsin.
Lower gastrointestinal tract
The lower gastrointestinal tract (GI), includes thesmall intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
and all of the large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being r ...
. The intestine is also called the bowel or the gut. The lower GI starts at the pyloric sphincter of the stomach and finishes at the anus. The small intestine is subdivided into the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
, the jejunum
The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine in humans and most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. Its lining is specialised for the absorption by enterocytes of small nutrient molecules which have been previou ...
and the ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine m ...
. The cecum marks the division between the small and large intestine. The large intestine includes the rectum and anal canal
The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional segm ...
.
Small intestine
 Partially digested food starts to arrive in the
Partially digested food starts to arrive in the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
as semi-liquid chyme, one hour after it is eaten. The stomach is half empty after an average of 1.2 hours. After four or five hours the stomach has emptied.
In the small intestine, the pH becomes crucial; it needs to be finely balanced in order to activate digestive enzymes. The chyme is very acidic, with a low pH, having been released from the stomach and needs to be made much more alkaline. This is achieved in the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
by the addition of bile from the gall bladder combined with the bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate ( IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioch ...
secretions from the pancreatic duct and also from secretions of bicarbonate-rich mucus from duodenal glands known as Brunner's glands. The chyme arrives in the intestines having been released from the stomach through the opening of the pyloric sphincter
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pylori ...
. The resulting alkaline fluid mix neutralises the gastric acid which would damage the lining of the intestine. The mucus component lubricates the walls of the intestine.
 When the digested food particles are reduced enough in size and composition, they can be absorbed by the intestinal wall and carried to the bloodstream. The first receptacle for this chyme is the duodenal bulb. From here it passes into the first of the three sections of the small intestine, the duodenum (the next section is the
When the digested food particles are reduced enough in size and composition, they can be absorbed by the intestinal wall and carried to the bloodstream. The first receptacle for this chyme is the duodenal bulb. From here it passes into the first of the three sections of the small intestine, the duodenum (the next section is the jejunum
The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine in humans and most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. Its lining is specialised for the absorption by enterocytes of small nutrient molecules which have been previou ...
and the third is the ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine m ...
). The duodenum is the first and shortest section of the small intestine. It is a hollow, jointed C-shaped tube connecting the stomach to the jejunum. It starts at the duodenal bulb and ends at the suspensory muscle of duodenum. The attachment of the suspensory muscle to the diaphragm is thought to help the passage of food by making a wider angle at its attachment.
Most food digestion takes place in the small intestine. Segmentation contractions act to mix and move the chyme more slowly in the small intestine allowing more time for absorption (and these continue in the large intestine). In the duodenum, pancreatic lipase is secreted together with a co-enzyme, colipase
Colipase, abbreviated CLPS, is a protein co-enzyme required for optimal enzyme activity of pancreatic lipase. It is secreted by the pancreas in an inactive form, procolipase, which is activated in the intestinal lumen by trypsin. Its function i ...
to further digest the fat content of the chyme. From this breakdown, smaller particles of emulsified fats called chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (8 ...
s are produced. There are also digestive cells called enterocytes lining the intestines (the majority being in the small intestine). They are unusual cells in that they have villi on their surface which in turn have innumerable microvilli
Microvilli (singular: microvillus) are microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that increase the surface area for diffusion and minimize any increase in volume, and are involved in a wide variety of functions, including absorption, secretion, ...
on their surface. All these villi make for a greater surface area, not only for the absorption of chyme but also for its further digestion by large numbers of digestive enzymes present on the microvilli.
The chylomicrons are small enough to pass through the enterocyte villi and into their lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
capillaries called lacteals. A milky fluid called chyle, consisting mainly of the emulsified fats of the chylomicrons, results from the absorbed mix with the lymph in the lacteals. Chyle is then transported through the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoi ...
to the rest of the body.
The suspensory muscle marks the end of the duodenum and the division between the upper gastrointestinal tract and the lower GI tract. The digestive tract continues as the jejunum which continues as the ileum. The jejunum, the midsection of the small intestine contains circular folds, flaps of doubled mucosal membrane which partially encircle and sometimes completely encircle the lumen of the intestine. These folds together with villi serve to increase the surface area of the jejunum enabling an increased absorption of digested sugars, amino acids and fatty acids into the bloodstream. The circular folds also slow the passage of food giving more time for nutrients to be absorbed.
The last part of the small intestine is the ileum. This also contains villi and vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It ...
; bile acids and any residue nutrients are absorbed here. When the chyme is exhausted of its nutrients the remaining waste material changes into the semi-solids called feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a rela ...
, which pass to the large intestine, where bacteria in the gut flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut ...
further break down residual proteins and starches.
Transit time through the small intestine is an average of 4 hours. Half of the food residues of a meal have emptied from the small intestine by an average of 5.4 hours after ingestion. Emptying of the small intestine is complete after an average of 8.6 hours.
Cecum
 The
The cecum
The cecum or caecum is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix, to which it is joined). The w ...
is a pouch marking the division between the small intestine and the large intestine. It lies below the ileocecal valve
The ileocecal valve (ileal papilla, ileocaecal valve, Tulp's valve, Tulpius valve, Bauhin's valve, ileocecal eminence, valve of Varolius or colic valve) is a sphincter muscle valve that separates the small intestine and the large intestine. Its ...
in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen. The cecum receives chyme from the last part of the small intestine, the ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine m ...
, and connects to the ascending colon
''Ascending'' is a science fiction novel by the Canadian writer James Alan Gardner, published in 2001 by HarperCollins Publishers under its various imprints.HarperCollins, Avon, HarperCollins Canada, SFBC/Avon; paperback edition 2001, Eos Books. ...
of the large intestine. At this junction there is a sphincter or valve, the ileocecal valve which slows the passage of chyme from the ileum, allowing further digestion. It is also the site of the appendix
Appendix, or its plural form appendices, may refer to:
__NOTOC__ In documents
* Addendum, an addition made to a document by its author after its initial printing or publication
* Bibliography, a systematic list of books and other works
* Index (pub ...
attachment.
Large intestine
 In the
In the large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being r ...
, the passage of the digesting food in the colon is a lot slower, taking from 30 to 40 hours until it is removed by defecation
Defecation (or defaecation) follows digestion, and is a necessary process by which organisms eliminate a solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material known as feces from the digestive tract via the anus. The act has a variety of names ranging ...
. The colon mainly serves as a site for the fermentation of digestible matter by the gut flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut ...
. The time taken varies considerably between individuals. The remaining semi-solid waste is termed feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a rela ...
and is removed by the coordinated contractions of the intestinal walls, termed peristalsis, which propels the excreta forward to reach the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
and exit via defecation from the anus. The wall has an outer layer of longitudinal muscles, the taeniae coli, and an inner layer of circular muscles. The circular muscle keeps the material moving forward and also prevents any back flow of waste. Also of help in the action of peristalsis is the basal electrical rhythm that determines the frequency of contractions. The taeniae coli can be seen and are responsible for the bulges ( haustra) present in the colon. Most parts of the GI tract are covered with serous membranes and have a mesentery
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines ...
. Other more muscular parts are lined with adventitia.
Blood supply
 The digestive system is supplied by the
The digestive system is supplied by the celiac artery
The celiac () artery (also spelled ''coeliac''), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in ...
. The celiac artery is the first major branch from the abdominal aorta
In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta (of the thorax).
Structure
The abdominal aorta begins at the level of the diaphragm ...
, and is the only major artery that nourishes the digestive organs.
There are three main divisions – the left gastric artery, the common hepatic artery and the splenic artery
In human anatomy, the splenic artery or lienal artery is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen. It branches from the celiac artery, and follows a course superior to the pancreas. It is known for its tortuous path to the sp ...
.
The celiac artery supplies the liver, stomach, spleen and the upper 1/3 of the duodenum (to the sphincter of Oddi) and the pancreas with oxygenated blood. Most of the blood is returned to the liver via the portal venous system
In the circulatory system of animals, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed pools into another capillary bed through veins, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessels that connect them are con ...
for further processing and detoxification before returning to the systemic circulation
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
via the hepatic veins
In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava (as opposed to the hepatic portal vein which conveys blood from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver). There are usually thre ...
.
The next branch from the abdominal aorta is the superior mesenteric artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the ...
, which supplies the regions of the digestive tract derived from the midgut, which includes the distal 2/3 of the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, appendix, ascending colon, and the proximal 2/3 of the transverse colon.
The final branch which is important for the digestive system is the inferior mesenteric artery
In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery, often abbreviated as IMA, is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the an ...
, which supplies the regions of the digestive tract derived from the hindgut, which includes the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and the anus above the pectinate line.
Blood flow to the digestive tract reaches its maximum 20–40 minutes after a meal and lasts for 1.5–2 hours.
Nerve supply
Theenteric nervous system
The enteric nervous system (ENS) or intrinsic nervous system is one of the main divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract. It is capable o ...
consists of some one hundred million neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, electrically excitable cell (biology), cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous ...
s that are embedded in the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesot ...
, the lining of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
extending from the esophagus to the anus. These neurons are collected into two plexus
In neuroanatomy, a plexus (from the Latin term for "braid") is a branching network of vessels or nerves. The vessels may be blood vessels (veins, capillaries) or lymphatic vessels. The nerves are typically axons outside the central nervous sy ...
es - the myenteric (or Auerbach's) plexus that lies between the longitudinal and the smooth muscle layers, and the submucosal (or Meissner's) plexus that lies between the circular smooth muscle layer and the mucosa.
Parasympathetic innervation to the ascending colon
''Ascending'' is a science fiction novel by the Canadian writer James Alan Gardner, published in 2001 by HarperCollins Publishers under its various imprints.HarperCollins, Avon, HarperCollins Canada, SFBC/Avon; paperback edition 2001, Eos Books. ...
is supplied by the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and rig ...
. Sympathetic innervation
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the ...
is supplied by the splanchnic nerves
The splanchnic nerves are paired visceral nerves (nerves that contribute to the innervation of the internal organs), carrying fibers of the autonomic nervous system (visceral efferent fibers) as well as sensory fibers from the organs (visceral a ...
that join the celiac ganglia. Most of the digestive tract is innervated by the two large celiac ganglia, with the upper part of each ganglion joined by the greater splanchnic nerve and the lower parts joined by the lesser splanchnic nerve. It is from these ganglia that many of the gastric plexuses arise.
Development
Early inembryonic development
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
, the embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
has three germ layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three pr ...
s and abuts a yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is fa ...
. During the second week of development, the embryo grows and begins to surround and envelop portions of this sac. The enveloped portions form the basis for the adult gastrointestinal tract. Sections of this foregut
The foregut is the anterior part of the alimentary canal, from the mouth to the duodenum at the entrance of the bile duct. Beyond the stomach, the foregut is attached to the abdominal walls by mesentery. The foregut arises from the endoderm, devel ...
begin to differentiate into the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, such as the esophagus, stomach, and intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
s.
During the fourth week of development, the stomach rotates. The stomach, originally lying in the midline of the embryo, rotates so that its body is on the left. This rotation also affects the part of the gastrointestinal tube immediately below the stomach, which will go on to become the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
. By the end of the fourth week, the developing duodenum begins to spout a small outpouching on its right side, the hepatic diverticulum
The hepatic diverticulum (or liver bud) is a primordial cellular extension of the embryonic foregut endoderm that gives rise to the parenchyma of the liver and the bile duct. It typically differentiates from the endoderm in the third or fourth we ...
, which will go on to become the biliary tree. Just below this is a second outpouching, known as the ''cystic diverticulum'', that will eventually develop into the gallbladder.
Clinical significance
Each part of the digestive system is subject to a wide range of disorders many of which can becongenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities c ...
. Mouth diseases can also be caused by pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
ic bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, virus
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and ...
es, fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
and as a side effect of some medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field an ...
s. Mouth diseases include tongue diseases and salivary gland diseases. A common gum
Gum may refer to:
Types of gum
* Adhesive
* Bubble gum
* Chewing gum
* Gum (botany), sap or other resinous material associated with certain species of the plant kingdom
** Gum arabic, made from the sap of ''Acacia senegal'', an Old World tree s ...
disease in the mouth is gingivitis which is caused by bacteria in plaque. The most common viral infection of the mouth is gingivostomatitis
Stomatitis is inflammation of the mouth and lips. It refers to any inflammatory process affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips, with or without oral ulceration.
In its widest meaning, stomatitis can have a multitude of different cau ...
caused by herpes simplex
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected.
Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold ...
. A common fungal
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
infection is candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth ...
commonly known as ''thrush'' which affects the mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
s of the mouth.
There are a number of esophageal diseases such as the development of Schatzki rings that can restrict the passageway, causing difficulties in swallowing. They can also completely block the esophagus.
Stomach diseases are often chronic conditions and include gastroparesis
Gastroparesis (gastro- from Ancient Greek γαστήρ – gaster, "stomach"; and -paresis, πάρεσις – "partial paralysis"), also called delayed gastric emptying, is a medical disorder consisting of weak muscular contractions ( peristalsis) ...
, gastritis
Gastritis is inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain (see dyspepsia). Other poss ...
, and peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines ...
s.
A number of problems including malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
and anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
can arise from malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety ...
, the abnormal absorption of nutrients in the GI tract. Malabsorption can have many causes ranging from infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
, to enzyme deficiencies such as exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is the inability to properly digest food due to a lack of digestive enzymes made by the pancreas. EPI is found in humans afflicted with cystic fibrosis and Shwachman–Diamond syndrome, and is common in ...
. It can also arise as a result of other gastrointestinal diseases such as coeliac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barl ...
. Coeliac disease is an autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
disorder of the small intestine. This can cause vitamin deficiencies due to the improper absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. The small intestine can also be obstructed by a volvulus
A volvulus is when a loop of intestine twists around itself and the mesentery that supports it, resulting in a bowel obstruction. Symptoms include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, vomiting, constipation, and bloody stool. Onset of symptoms m ...
, a loop of intestine that becomes twisted enclosing its attached mesentery
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines ...
. This can cause mesenteric ischemia
Intestinal ischemia is a medical condition in which injury to the large or small intestine occurs due to not enough blood supply. It can come on suddenly, known as acute intestinal ischemia, or gradually, known as chronic intestinal ischemia. Th ...
if severe enough.
A common disorder of the bowel is diverticulitis
Diverticulitis, specifically colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches— diverticula—which can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdomin ...
. Diverticula
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false.
In medicine, t ...
are small pouches that can form inside the bowel wall, which can become inflamed to give diverticulitis. This disease can have complications if an inflamed diverticulum bursts and infection sets in. Any infection can spread further to the lining of the abdomen (peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesot ...
) and cause potentially fatal peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or ...
.
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension, ...
is a common chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as wel ...
(IBD), which can affect any part of the GI tract, but it mostly starts in the terminal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine m ...
.
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood ( hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, an ...
an ulcerative form of colitis
Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine ( colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.
In a medical context, the label ''colitis'' (without qualification ...
, is the other major inflammatory bowel disease which is restricted to the colon and rectum. Both of these IBDs can give an increased risk of the development of colorectal cancer. Ulcerative colitis is the most common of the IBDs
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms ma ...
(IBS) is the most common of the functional gastrointestinal disorders
Functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGID), also known as disorders of gut–brain interaction, include a number of separate idiopathic disorders which affect different parts of the gastrointestinal tract and involve visceral hypersensitivity ...
. These are idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin. From Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approximately "a disease of its own kind ...
disorders that the Rome process has helped to define.
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by '' Giardia duodenalis'' (also known as ''G. lamblia'' and ''G. intestinalis''). Infected individuals who experience symptoms (about 10% have no symptoms) may have diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight l ...
is a disease of the small intestine caused by a protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the e ...
parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of lif ...
''Giardia lamblia
''Giardia duodenalis'', also known as ''Giardia intestinalis'' and ''Giardia lamblia'', is a flagellated parasitic microorganism of the genus ''Giardia'' that colonizes the small intestine, causing a diarrheal condition known as giardiasis. The ...
''. This does not spread but remains confined to the lumen of the small intestine. It can often be asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered as ...
, but as often can be indicated by a variety of symptoms. Giardiasis is the most common pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
parasitic infection in humans.
There are diagnostic tools mostly involving the ingestion of barium sulphate to investigate disorders of the GI tract. These are known as upper gastrointestinal series that enable imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
of the pharynx, larynx, oesophagus, stomach and small intestine and lower gastrointestinal series
A lower gastrointestinal series is a medical procedure used to examine and diagnose problems with the human colon of the large intestine. Radiographs (X-ray pictures) are taken while barium sulfate, a radiocontrast agent, fills the colon via a ...
for imaging of the colon.
In pregnancy
Gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during preg ...
can predispose for certain digestive disorders. Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and o ...
can develop in the mother as a result of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
and while this often presents with few symptoms it can lead to pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease ...
.
History

 In the early 11th century the Islamic medical philosopher
In the early 11th century the Islamic medical philosopher Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islam ...
wrote extensively on many subjects including medicine. Forty of these treatises on medicine survive, and in the most famous one titled the ''Canon of Medicine'' he discusses "rising gas". Avicenna believed that digestive system dysfunction was responsible for the overproduction of gas in the gastrointestinal tract. He suggested lifestyle changes and a compound of herbal drugs for its treatment.
In 1497 Alessandro Benedetti
Alessandro Benedetti (1450?–1512) was born in Parma, traveled and worked extensively in Greece and Crete, and worked as surgeon general of the Venetian army. His “Anatomice, or The History of the Human Body” is a descriptive anatomy in the ...
viewed the stomach as an unclean organ separated off by the diaphragm. This view of the stomach and intestines as being base organs was generally held until the mid-17th century.
In the Renaissance of the 16th century Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially re ...
produced some early drawings of the stomach and intestines. He thought that the digestive system aided the respiratory system. Andreas Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius (Latinized from Andries van Wezel) () was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, '' De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ...
provided some early anatomical drawings of the abdominal organs in the 16th century.
In the middle of the 17th century a Flemish physician Jan Baptist van Helmont
Jan Baptist van Helmont (; ; 12 January 1580 – 30 December 1644) was a chemist, physiologist, and physician from Brussels. He worked during the years just after Paracelsus and the rise of iatrochemistry, and is sometimes considered t ...
offered the first chemical account of digestion which was later described as being very close to the later conceptualised enzyme.
In 1653 William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and prope ...
described the intestines in terms of their length, their blood supply, the mesenteries, and fat (adenylyl cyclase).
In 1823 William Prout
William Prout FRS (; 15 January 1785 – 9 April 1850) was an English chemist, physician, and natural theologian. He is remembered today mainly for what is called Prout's hypothesis.
Biography
Prout was born in Horton, Gloucestershire in 1 ...
discovered hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dig ...
in the gastric juice. In 1895 Ivan Pavlov
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov ( rus, Ива́н Петро́вич Па́влов, , p=ɪˈvan pʲɪˈtrovʲɪtɕ ˈpavləf, a=Ru-Ivan_Petrovich_Pavlov.ogg; 27 February 1936), was a Russian and Soviet experimental neurologist, psychologist and physiol ...
described its secretion as being stimulated by a neurologic reflex with the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and rig ...
having a crucial role. Black in the 19th century suggested an association of histamine with this secretion. In 1916 Popielski described histamine as a gastric secretagogue of hydrochloric acid.
William Beaumont
William Beaumont (November 21, 1785 – April 25, 1853) was a surgeon in the U.S. Army who became known as the "Father of Gastric Physiology" following his research on human digestion.
was an army surgeon who in 1825 was able to observe digestion as it took place in the stomach. This was made possible by experiments on a man with a stomach wound that did not fully heal leaving an opening into the stomach. The churning motion of the stomach was described among other findings.
In the 19th century it was accepted that chemical processes were involved in the process of digestion. Physiological research into secretion and the gastrointestinal tract was pursued with experiments undertaken by Claude Bernard, Rudolph Heidenhain and Ivan Pavlov.
The rest of the 20th century was dominated by research into enzymes. The first to be discovered was secretin
Secretin is a hormone that regulates water homeostasis throughout the body and influences the environment of the duodenum by regulating secretions in the stomach, pancreas, and liver. It is a peptide hormone produced in the S cells of the duoden ...
by Ernest Starling
Ernest Henry Starling (17 April 1866 – 2 May 1927) was a British physiologist who contributed many fundamental ideas to this subject. These ideas were important parts of the British contribution to physiology, which at that time led the world. ...
in 1902, with ensuing results from John Edkins in 1905 who first suggested gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gastrin ...
with its structure being determined in 1964. Andre Latarjet and Lester Dragstedt found a role for acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
in the digestive system. In 1972 H2 receptor agonists were described by J. Black, that block the action of histamine and decrease the production of hydrochloric acid. In 1980 proton pump inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitor ...
s were described by Sachs. In 1983 the role of ''Helicobacter pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is th ...
'' in the formation of ulcers was described by Barry Marshall
Barry James Marshall (born 30 September 1951) is an Australian physician, Nobel Prize Laureate in Physiology or Medicine, Professor of Clinical Microbiology and Co-Director of the Marshall Centre at the University of Western Australia. Marsh ...
, and Robin Warren
John Robin Warren (born 11 June 1937, in Adelaide) is an Australian pathologist, Nobel Laureate and researcher who is credited with the 1979 re-discovery of the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'', together with Barry Marshall. The duo proved ...
.
Art historians have often noted that banqueters on iconographic records of ancient Mediterranean societies almost always appear to be lying down on their left sides. One possible explanation could lie in the anatomy of the stomach and in the digestive mechanism. When lying on the left, the food has room to expand because the curvature of the stomach is enhanced in that position.
See also
*Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood ( hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, an ...
* Abdominal internal oblique muscle
References
{{Authority control Organ systems Metabolism