Dentistry Procedures on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of
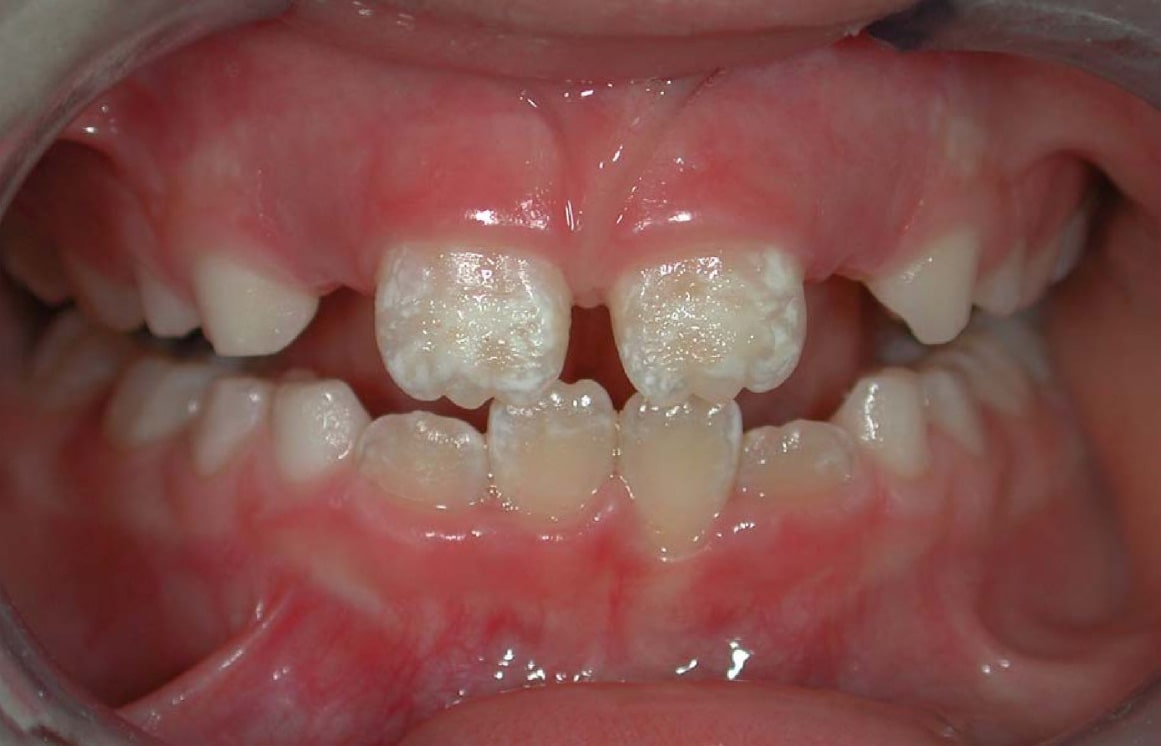 Dentists also encourage the prevention of oral diseases through proper
Dentists also encourage the prevention of oral diseases through proper
 John M. Harris started the world's first dental school in Bainbridge, Ohio, and helped to establish dentistry as a health profession. It opened on 21 February 1828, and today is a dental museum. The first dental college, Baltimore College of Dental Surgery, opened in Baltimore, Maryland, US in 1840. The second in the United States was the Ohio College of Dental Surgery, established in Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1845. The Philadelphia College of Dental Surgery followed in 1852. In 1907,
John M. Harris started the world's first dental school in Bainbridge, Ohio, and helped to establish dentistry as a health profession. It opened on 21 February 1828, and today is a dental museum. The first dental college, Baltimore College of Dental Surgery, opened in Baltimore, Maryland, US in 1840. The second in the United States was the Ohio College of Dental Surgery, established in Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1845. The Philadelphia College of Dental Surgery followed in 1852. In 1907,

 Tooth decay was low in pre-agricultural societies, but the advent of
Tooth decay was low in pre-agricultural societies, but the advent of  The first book focused solely on dentistry was the "Artzney Buchlein" in 1530, and the first dental textbook written in English was called "Operator for the Teeth" by Charles Allen in 1685.
In the United Kingdom, there was no formal qualification for the providers of dental treatment until 1859 and it was only in 1921 that the practice of dentistry was limited to those who were professionally qualified. The Royal Commission on the National Health Service in 1979 reported that there were then more than twice as many registered dentists per 10,000 population in the UK than there were in 1921.
The first book focused solely on dentistry was the "Artzney Buchlein" in 1530, and the first dental textbook written in English was called "Operator for the Teeth" by Charles Allen in 1685.
In the United Kingdom, there was no formal qualification for the providers of dental treatment until 1859 and it was only in 1921 that the practice of dentistry was limited to those who were professionally qualified. The Royal Commission on the National Health Service in 1979 reported that there were then more than twice as many registered dentists per 10,000 population in the UK than there were in 1921.
 Fauchard was the pioneer of dental prosthesis, and he invented many methods to replace lost teeth. He suggested that substitutes could be made from carved blocks of ivory or
Fauchard was the pioneer of dental prosthesis, and he invented many methods to replace lost teeth. He suggested that substitutes could be made from carved blocks of ivory or

medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition (the development and arrangement of teeth) as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental doctor, dental physician, dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in provi ...
.
The history of dentistry is almost as ancient as the history of humanity and civilization, with the earliest evidence dating from 7000 BC to 5500 BC. Dentistry is thought to have been the first specialization in medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
which has gone on to develop its own accredited degree with its own specializations. Dentistry is often also understood to subsume the now largely defunct medical specialty
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (pediatrics), cancer (oncology), ...
of stomatology (the study of the mouth and its disorders and diseases) for which reason the two terms are used interchangeably in certain regions. However, some specialties such as oral and maxillofacial surgery (facial reconstruction) may require both medical and dental degrees to accomplish. In European history, dentistry is considered to have stemmed from the trade of barber surgeons.
Dental treatments are carried out by a dental team, which often consists of a dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental doctor, dental physician, dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in provi ...
and dental auxiliaries (such as dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and dental therapists). Most dentists either work in private practices (primary care
Primary care is a model of health care that supports first-contact, accessible, continuous, comprehensive, and coordinated person-focused care. It aims to optimise population health and reduce disparities across the groups by ensuring equitable ...
), dental hospitals, or ( secondary care) institutions (prisons, armed forces bases, etc.).
The modern movement of evidence-based dentistry calls for the use of high-quality scientific research and evidence to guide decision-making such as in manual tooth conservation, use of fluoride water treatment and fluoride toothpaste, dealing with oral diseases such as tooth decay and periodontitis, as well as systematic diseases such as osteoporosis, diabetes, celiac disease, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, and HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
which could also affect the oral cavity. Other practices relevant to evidence-based dentistry include radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide treatment within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but tod ...
of the mouth to inspect teeth deformity or oral malaises, haematology (study of blood) to avoid bleeding complications during dental surgery, cardiology
Cardiology () is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery di ...
(due to various severe complications arising from dental surgery with patients with heart disease), etc.
Terminology
The term dentistry comes from ''dentist'', which comes from French ''dentiste'', which comes from the French and Latin words for tooth. The term for the associated scientific study of teeth is odontology (from ) – the study of the structure, development, and abnormalities of the teeth.Dental treatment
Dentistry usually encompasses practices related to the oral cavity. According to theWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, oral diseases are major public health problems due to their high incidence and prevalence across the globe, with the disadvantaged affected more than other socio-economic groups.
The majority of dental treatments are carried out to prevent or treat the two most common oral diseases, which are dental caries (tooth decay) and periodontal disease (gum disease or pyorrhea). Common treatments involve the restoration of teeth, extraction or surgical removal of teeth, scaling and root planing, endodontic root canal treatment, and cosmetic dentistry.
By nature of their general training, dentists, without specialization, can carry out the majority of dental treatments such as restorative (fillings, crowns, bridges), prosthetic ( dentures), endodontic (root canal) therapy, periodontal (gum) therapy, and extraction of teeth, as well as performing examinations, radiographs (x-rays), and diagnosis. Dentists can also prescribe medications used in the field such as antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s, sedatives, and any other drugs used in patient management. Depending on their licensing boards, general dentists may be required to complete additional training to perform sedation, dental implants, etc.
 Dentists also encourage the prevention of oral diseases through proper
Dentists also encourage the prevention of oral diseases through proper hygiene
Hygiene is a set of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
and regular, twice or more yearly, checkups for professional cleaning and evaluation. Oral infections and inflammations may affect overall health, and conditions in the oral cavity may be indicative of systemic diseases, such as osteoporosis, diabetes, celiac disease or cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. Many studies have also shown that gum disease is associated with an increased risk of diabetes, heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
, and preterm birth. The concept that oral health can affect systemic health and disease is referred to as "oral-systemic health".
Education and licensing
 John M. Harris started the world's first dental school in Bainbridge, Ohio, and helped to establish dentistry as a health profession. It opened on 21 February 1828, and today is a dental museum. The first dental college, Baltimore College of Dental Surgery, opened in Baltimore, Maryland, US in 1840. The second in the United States was the Ohio College of Dental Surgery, established in Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1845. The Philadelphia College of Dental Surgery followed in 1852. In 1907,
John M. Harris started the world's first dental school in Bainbridge, Ohio, and helped to establish dentistry as a health profession. It opened on 21 February 1828, and today is a dental museum. The first dental college, Baltimore College of Dental Surgery, opened in Baltimore, Maryland, US in 1840. The second in the United States was the Ohio College of Dental Surgery, established in Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1845. The Philadelphia College of Dental Surgery followed in 1852. In 1907, Temple University
Temple University (Temple or TU) is a public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related research university in Philadelphia, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. It was founded in 1884 by the Baptist ministe ...
accepted a bid to incorporate the school.
Studies show that dentists who graduated from different countries, or even from different dental schools in one country, may make different clinical decisions for the same clinical condition. For example, dentists that graduated from Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
i dental schools may recommend the removal of asymptomatic impacted third molar (wisdom teeth) more often than dentists that graduated from Latin American or Eastern European dental schools.
In the United Kingdom, the first dental schools, the London School of Dental Surgery and the Metropolitan School of Dental Science, both in London, opened in 1859. The British Dentists Act of 1878 and the 1879 Dentists Register limited the title of "dentist" and "dental surgeon" to qualified and registered practitioners. The 1879 register is referred to as the "Dental Register". However, others could legally describe themselves as "dental experts" or "dental consultants". The practice of dentistry in the United Kingdom became fully regulated with the 1921 Dentists Act, which required the registration of anyone practising dentistry. The British Dental Association, formed in 1880 with Sir John Tomes as president, played a major role in prosecuting dentists practising illegally. Dentists in the United Kingdom are now regulated by the General Dental Council.
Dentists in many countries complete between five and eight years of post-secondary education before practising. Though not mandatory, many dentists choose to complete an internship or residency focusing on specific aspects of dental care after they have received their dental degree. In a few countries, to become a qualified dentist one must usually complete at least four years of postgraduate study; Dental degree
A number of professional degrees in dentistry are offered by dental schools in various countries around the world.
Degrees
Dental degrees may include:
Bachelor's degree
* Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS)
* Bachelor's degree of Dentistry (BDS ...
s awarded around the world include the Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) and Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD) in North America (US and Canada), and the Bachelor of Dental Surgery/Baccalaureus Dentalis Chirurgiae (BDS, BDent, BChD, BDSc) in the UK and current and former British Commonwealth countries.
All dentists in the United States undergo at least three years of undergraduate studies, but nearly all complete a bachelor's degree. This schooling is followed by four years of dental school to qualify as a " Doctor of Dental Surgery" (DDS) or " Doctor of Dental Medicine" (DMD). Specialization in dentistry is available in the fields of Anesthesiology, Dental Public Health, Endodontics, Oral Radiology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Oral Medicine, Orofacial Pain, Pathology, Orthodontics, Pediatric Dentistry (Pedodontics), Periodontics, and Prosthodontics.
Specialties
Some dentists undertake further training after their initial degree in order to specialize. Exactly which subjects are recognized by dental registration bodies varies according to location. Examples include: *Anesthesiology
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative medicine, perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critica ...
– the specialty of dentistry that deals with the advanced use of general anesthesia, sedation and pain management to facilitate dental procedures.
* Cosmetic dentistry – focuses on improving the appearance of the mouth, teeth and smile.
* Dental public health – the study of epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent dise ...
and social health policies relevant to oral health.
* Endodontics
Endodontics () is the Specialty (dentistry), dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.
Overview
Endodontics encompasses the study (practice) of the basic and clinical sciences of normal dental pulp, the etiolo ...
(also called ''endodontology'') – root canal therapy and study of diseases of the dental pulp and periapical tissues.
* Forensic odontology – the gathering and use of dental evidence in law. This may be performed by any dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental doctor, dental physician, dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in provi ...
with experience or training in this field. The function of the forensic dentist is primarily documentation and verification of identity.
* Geriatric dentistry or ''geriodontics'' – the delivery of dental care to older adults involving the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of problems associated with normal aging and age-related diseases as part of an interdisciplinary team with other health care professionals.
* Oral and maxillofacial pathology – the study, diagnosis, and sometimes the treatment of oral and maxillofacial related diseases.
* Oral and maxillofacial radiology – the study and radiologic interpretation of oral and maxillofacial diseases.
* Oral and maxillofacial surgery (also called ''oral surgery'') – extractions, implants, and surgery of the jaws, mouth and face.The scope of oral and maxillofacial surgery is variable. In some countries, both a medical and dental degree is required for training, and the scope includes head and neck oncology and craniofacial deformity.
* Oral biology – research in dental and craniofacial biology
* Oral implantology – the replacement of extracted teeth with dental implants.
* Oral medicine – the clinical evaluation and diagnosis of oral mucosal diseases
* Orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics – the straightening of teeth and modification of midface and mandibular growth.
* Pediatric dentistry (also called ''pedodontics'') – dentistry for children
* Periodontology (also called ''periodontics'') – the study and treatment of diseases of the periodontium
The periodontium () is the specialized tissues that both surround and support the teeth, maintaining them in the maxillary and mandibular bones. Periodontics is the dental specialty that relates specifically to the care and maintenance of the ...
(non-surgical and surgical) as well as placement and maintenance of dental implants
* Prosthodontics (also called ''prosthetic dentistry'') – dentures, bridges and the restoration of implants.
** Some prosthodontists super-specialize in maxillofacial prosthetics, which is the discipline originally concerned with the rehabilitation of patients with congenital facial and oral defects such as cleft lip and palate or patients born with an underdeveloped ear ( microtia). Today, most maxillofacial prosthodontists return function and esthetics to patients with acquired defects secondary to surgical removal of head and neck tumors, or secondary to trauma from war or motor vehicle accidents.
* Special needs dentistry (also called ''special care dentistry'') – dentistry for those with developmental and acquired disabilities.
* Sports dentistry – the branch of sports medicine
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the ...
dealing with prevention and treatment of dental injuries and oral diseases associated with sports and exercise. The sports dentist works as an individual consultant or as a member of a sports medicine
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the ...
team.
* Veterinary dentistry – the field of dentistry applied to the care of animals. It is a specialty of veterinary medicine
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, medical diagnosis, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in non-human animals. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all a ...
.
History

 Tooth decay was low in pre-agricultural societies, but the advent of
Tooth decay was low in pre-agricultural societies, but the advent of farming
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
society about 10,000 years ago correlated with an increase in tooth decay (cavities). An infected tooth from Italy partially cleaned with flint tools, between 13,820 and 14,160 years old, represents the oldest known dentistry, although a 2017 study suggests that 130,000 years ago the Neanderthals
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
already used rudimentary dentistry tools. In Italy evidence dated to the Paleolithic, around 13,000 years ago, points to bitumen used to fill a tooth and in Neolithic Slovenia, 6500 years ago, beeswax was used to close a fracture in a tooth. The Indus valley has yielded evidence of dentistry being practised as far back as 7000 BC, during the Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
. The Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
site of Mehrgarh (now in Pakistan's south western province of Balochistan) indicates that this form of dentistry involved curing tooth related disorders with bow drill
A bow drill is a simple hand-operated type of tool, consisting of a rod (the ''spindle'' or ''drill shaft'') that is set in rapid rotary motion by means of a cord wrapped around it, kept taut by a bow and arrow, bow which is pushed back and forth ...
s operated, perhaps, by skilled bead-crafters. The reconstruction of this ancient form of dentistry showed that the methods used were reliable and effective. The earliest dental filling, made of beeswax, was discovered in Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
and dates from 6500 years ago. Dentistry was practised in prehistoric Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, as evidenced by a skull which had a dental abscess lanced from the root of a tooth dating back to around 2500 BC. The practice of dentistry dates back thousands of years, with evidence of dental procedures such as tooth extraction and fillings found in ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and the Greeks. One notable historical figure is Pierre Fauchard, often referred to as the 'father of modern dentistry,' who wrote the first comprehensive book on the subject in 1728.
An ancient Sumerian text describes a " tooth worm" as the cause of dental caries. Evidence of this belief has also been found in ancient India, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Japan, and China. The legend of the worm is also found in the '' Homeric Hymns'', and as late as the 14th century AD the surgeon Guy de Chauliac still promoted the belief that worms cause tooth decay.
Recipes for the treatment of toothache, infections and loose teeth are spread throughout the Ebers Papyrus, Kahun Papyri, Brugsch Papyrus, and Hearst papyrus of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
. The Edwin Smith Papyrus, written in the 17th century BC but which may reflect previous manuscripts from as early as 3000 BC, discusses the treatment of dislocated or fractured jaws. In the 18th century BC, the Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed during 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organized, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian language, Akkadi ...
referenced dental extraction twice as it related to punishment. Examination of the remains of some ancient Egyptians and Greco-Romans reveals early attempts at dental prosthetics. However, it is possible the prosthetics were prepared after death for aesthetic reasons.
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
scholars Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
and Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
wrote about dentistry, including the eruption pattern of teeth, treating decayed teeth and gum disease, extracting teeth with forceps
Forceps (: forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forcep ...
, and using wires to stabilize loose teeth and fractured jaws. Use of dental appliances, bridges and dentures was applied by the Etruscans in northern Italy, from as early as 700 BC, of human or other animal teeth fastened together with gold bands. The Romans had likely borrowed this technique by the 5th century BC. The Phoenicians crafted dentures during the 6th–4th century BC, fashioning them from gold wire and incorporating two ivory teeth. In ancient Egypt, Hesy-Ra is the first named "dentist" (greatest of the teeth). The Egyptians bound replacement teeth together with gold wire. Roman medical writer Cornelius Celsus wrote extensively of oral diseases as well as dental treatments such as narcotic-containing emollients and astringents. The earliest dental amalgams were first documented in a Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
medical text written by the Chinese physician Su Kung in 659, and appeared in Germany in 1528.
During the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.
This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign o ...
Dentistry was discussed in several famous books of medicine such as The Canon in medicine written by Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
and Al-Tasreef by Al-Zahrawi
Abū al-Qāsim Khalaf ibn al-'Abbās al-Zahrāwī al-Ansari (; c. 936–1013), popularly known as al-Zahrawi (), Latinisation of names, Latinised as Albucasis or Abulcasis (from Arabic ''Abū al-Qāsim''), was an Arabs, Arab physician, su ...
who is considered the greatest surgeon of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, Avicenna said that jaw fracture should be reduced according to the occlusal guidance of the teeth; this principle is still valid in modern times. Al-Zahrawi invented over 200 surgical tools that resemble the modern kind.
Historically, dental extractions have been used to treat a variety of illnesses. During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and throughout the 19th century, dentistry was not a profession in itself, and often dental procedures were performed by barbers or general physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Med ...
s. Barbers usually limited their practice to extracting teeth which alleviated pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
and associated chronic tooth infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
. Instruments used for dental extractions date back several centuries. In the 14th century, Guy de Chauliac most probably invented the dental pelican (resembling a pelican's beak) which was used to perform dental extractions up until the late 18th century. The pelican was replaced by the dental key which, in turn, was replaced by modern forceps in the 19th century.
 The first book focused solely on dentistry was the "Artzney Buchlein" in 1530, and the first dental textbook written in English was called "Operator for the Teeth" by Charles Allen in 1685.
In the United Kingdom, there was no formal qualification for the providers of dental treatment until 1859 and it was only in 1921 that the practice of dentistry was limited to those who were professionally qualified. The Royal Commission on the National Health Service in 1979 reported that there were then more than twice as many registered dentists per 10,000 population in the UK than there were in 1921.
The first book focused solely on dentistry was the "Artzney Buchlein" in 1530, and the first dental textbook written in English was called "Operator for the Teeth" by Charles Allen in 1685.
In the United Kingdom, there was no formal qualification for the providers of dental treatment until 1859 and it was only in 1921 that the practice of dentistry was limited to those who were professionally qualified. The Royal Commission on the National Health Service in 1979 reported that there were then more than twice as many registered dentists per 10,000 population in the UK than there were in 1921.
Modern dentistry
It was between 1650 and 1800 that the science of modern dentistry developed. The English physician Thomas Browne in his '' A Letter to a Friend'' ( pub. 1690) made an early dental observation with characteristic humour: The French surgeon Pierre Fauchard became known as the "father of modern dentistry". Despite the limitations of the primitive surgical instruments during the late 17th and early 18th century, Fauchard was a highly skilled surgeon who made remarkable improvisations of dental instruments, often adapting tools from watchmakers, jewelers and even barbers, that he thought could be used in dentistry. He introduced dental fillings as treatment for dental cavities. He asserted thatsugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
-derived acids like tartaric acid were responsible for dental decay, and also suggested that tumors surrounding the teeth and in the gums could appear in the later stages of tooth decay.
 Fauchard was the pioneer of dental prosthesis, and he invented many methods to replace lost teeth. He suggested that substitutes could be made from carved blocks of ivory or
Fauchard was the pioneer of dental prosthesis, and he invented many methods to replace lost teeth. He suggested that substitutes could be made from carved blocks of ivory or bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
. He also introduced dental braces, although they were initially made of gold, he discovered that the teeth position could be corrected as the teeth would follow the pattern of the wires. Waxed linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong and absorbent, and it dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. Lin ...
or silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
threads were usually employed to fasten the braces. His contributions to the world of dental science consist primarily of his 1728 publication Le chirurgien dentiste or The Surgeon Dentist. The French text included "basic oral anatomy and function, dental construction, and various operative and restorative techniques, and effectively separated dentistry from the wider category of surgery".
After Fauchard, the study of dentistry rapidly expanded. Two important books, ''Natural History of Human Teeth'' (1771) and ''Practical Treatise on the Diseases of the Teeth'' (1778), were published by British surgeon John Hunter. In 1763, he entered into a period of collaboration with the London-based dentist James Spence. He began to theorise about the possibility of tooth transplants from one person to another. He realised that the chances of a successful tooth transplant (initially, at least) would be improved if the donor tooth was as fresh as possible and was matched for size with the recipient. These principles are still used in the transplantation of internal organs. Hunter conducted a series of pioneering operations, in which he attempted a tooth transplant. Although the donated teeth never properly bonded with the recipients' gums, one of Hunter's patients stated that he had three which lasted for six years, a remarkable achievement for the period.
Major advances in science were made in the 19th century, and dentistry evolved from a trade to a profession. The profession came under government regulation by the end of the 19th century. In the UK, the Dentist Act was passed in 1878 and the British Dental Association formed in 1879. In the same year, Francis Brodie Imlach was the first ever dentist to be elected President of the Royal College of Surgeons (Edinburgh), raising dentistry onto a par with clinical surgery for the first time.
Hazards in modern dentistry
Long term occupational noise exposure can contribute to permanent hearing loss, which is referred to as noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) and tinnitus. Noise exposure can cause excessive stimulation of the hearing mechanism, which damages the delicate structures of the inner ear. NIHL can occur when an individual is exposed to sound levels above 90 dBA according to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Regulations state that the permissible noise exposure levels for individuals is 90 dBA. For the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health ( NIOSH), exposure limits are set to 85 dBA. Exposures below 85 dBA are not considered to be hazardous. Time limits are placed on how long an individual can stay in an environment above 85 dBA before it causes hearing loss. OSHA places that limitation at 8 hours for 85 dBA. The exposure time becomes shorter as the dBA level increases. Within the field of dentistry, a variety of cleaning tools are used including piezoelectric and sonic scalers, and ultrasonic scalers and cleaners. While a majority of the tools do not exceed 75 dBA, prolonged exposure over many years can lead to hearing loss or complaints of tinnitus. Few dentists have reported using personal hearing protective devices, which could offset any potential hearing loss or tinnitus.Evidence-based dentistry
There is a movement in modern dentistry to place a greater emphasis on high-quality scientific evidence in decision-making. Evidence-based dentistry (EBD) uses current scientific evidence to guide decisions. It is an approach to oral health that requires the application and examination of relevant scientific data related to the patient's oral and medical health. Along with the dentist's professional skill and expertise, EBD allows dentists to stay up to date on the latest procedures and patients to receive improved treatment. A new paradigm for medical education designed to incorporate current research into education and practice was developed to help practitioners provide the best care for their patients. It was first introduced by Gordon Guyatt and the Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group at McMaster University inOntario, Canada
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
in the 1990s. It is part of the larger movement toward evidence-based medicine
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients. It means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available exte ...
and other evidence-based practices
Evidence-based practice is the idea that occupational practices ought to be based on scientific evidence. The movement towards evidence-based practices attempts to encourage and, in some instances, require professionals and other decision-makers ...
, especially since a major part of dentistry involves dealing with oral and systemic diseases. Other issues relevant to the dental field in terms of evidence-based research and evidence-based practice include population oral health, dental clinical practice, tooth morphology etc.
Digitalization of dentistry
Like other medical disciplines, dentistry is strongly influenced by the digital transformation of healthcare. Processes are changing fundamentally, affecting the effectiveness and accuracy of patient treatment. Various technologies are being used in dentistry, including CAD/CAM systems in combination with 3D printing, artificial intelligence (AI), and electronic health records. The degree of implementation of such technologies varies significantly across dental practices. Research shows that larger dental centers are adopting digital solutions more rapidly. Younger dentists, as well as those who regularly participate in digital training programs, show a higher willingness to implement new technologies. However, financial constraints and the lack of comprehensive training opportunities for the digitalization of dentistry currently represent major barriers to implementation.
Ethical and medicolegal issues
Dentistry is unique in that it requires dental students to have competence-based clinical skills that can only be acquired through supervised specialized laboratory training and direct patient care. This necessitates the need for a scientific and professional basis of care with a foundation of extensive research-based education. According to some experts, the accreditation of dental schools can enhance the quality and professionalism of dental education.See also
* Dental aerosol * Dental instrument * Dental public health * Domestic healthcare: ** Dentistry in ancient Rome ** Dentistry in Canada ** Dentistry in the Philippines ** Dentistry in Israel ** Dentistry in the United Kingdom ** Dentistry in the United States * Eco-friendly dentistry * Geriatric dentistry * List of dental organizations * Pediatric dentistry * Sustainable dentistry * Veterinary dentistryNotes
References
External links
{{Authority control