CIM-10 Bomarc on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Boeing CIM-10 BOMARC (Boeing Michigan Aeronautical Research Center) (IM-99 Weapon System prior to September 1962) was a supersonic
The Boeing CIM-10 BOMARC (Boeing Michigan Aeronautical Research Center) (IM-99 Weapon System prior to September 1962) was a supersonic
 The operational IM-99A missiles were based horizontally in semi-hardened shelters, nicknamed "coffins". After the launch order, the shelter's roof would slide open, and the missile raised to the vertical. After the missile was supplied with fuel for the booster rocket, it would be launched by the Aerojet General LR59-AJ-13 booster. After sufficient speed was reached, the Marquardt RJ43-MA-3 ramjets would ignite and propel the missile to its cruise speed of Mach 2.8 at an altitude of .
When the Bomarc was within of the target, its own Westinghouse AN/DPN-34 radar guided the missile to the interception point. The maximum range of the IM-99A was , and it was fitted with either a conventional high-explosive or a 10 kiloton W-40 nuclear fission warhead.
The Bomarc relied on the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE), an automated control system used by NORAD for detecting, tracking and intercepting enemy
The operational IM-99A missiles were based horizontally in semi-hardened shelters, nicknamed "coffins". After the launch order, the shelter's roof would slide open, and the missile raised to the vertical. After the missile was supplied with fuel for the booster rocket, it would be launched by the Aerojet General LR59-AJ-13 booster. After sufficient speed was reached, the Marquardt RJ43-MA-3 ramjets would ignite and propel the missile to its cruise speed of Mach 2.8 at an altitude of .
When the Bomarc was within of the target, its own Westinghouse AN/DPN-34 radar guided the missile to the interception point. The maximum range of the IM-99A was , and it was fitted with either a conventional high-explosive or a 10 kiloton W-40 nuclear fission warhead.
The Bomarc relied on the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE), an automated control system used by NORAD for detecting, tracking and intercepting enemy
 In September 1958 Air Research & Development Command decided to transfer the Bomarc program from its testing at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station to a new facility on Santa Rosa Island, immediately south of Eglin AFB
In September 1958 Air Research & Development Command decided to transfer the Bomarc program from its testing at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station to a new facility on Santa Rosa Island, immediately south of Eglin AFB
 In the era of the intercontinental ballistic missiles the Bomarc, designed to intercept relatively slow manned bombers, had become a useless asset. The remaining Bomarc missiles were used by all armed services as high-speed target drones for tests of other air-defense missiles. The Bomarc A and Bomarc B targets were designated as CQM-10A and CQM-10B, respectively.
Following the accident, the McGuire complex has never been sold or converted to other uses and remains in Air Force ownership, making it the most intact site of the eight in the US. It has been nominated to the National Register of Historic Sites. Although a number of IM-99/CIM-10 Bomarcs have been placed on public display, because of concerns about the possible environmental hazards of the thoriated magnesium structure of the airframe several have been removed from public view.Young, Gord
In the era of the intercontinental ballistic missiles the Bomarc, designed to intercept relatively slow manned bombers, had become a useless asset. The remaining Bomarc missiles were used by all armed services as high-speed target drones for tests of other air-defense missiles. The Bomarc A and Bomarc B targets were designated as CQM-10A and CQM-10B, respectively.
Following the accident, the McGuire complex has never been sold or converted to other uses and remains in Air Force ownership, making it the most intact site of the eight in the US. It has been nominated to the National Register of Historic Sites. Although a number of IM-99/CIM-10 Bomarcs have been placed on public display, because of concerns about the possible environmental hazards of the thoriated magnesium structure of the airframe several have been removed from public view.Young, Gord
"Cold War relic on the move."
'
 * XF-99 (experimental for booster research)
* XF-99A/XIM-99A (experimental for ramjet research)
* YF-99A/YIM-99A (service-test)
* IM-99A/CIM-10A (initial production)
* IM-99B/CIM-10B ("advanced""IM-99A Bases Manual". ''Boeing: Pilotless Aircraft Division'' (Seattle, Washington), 12 March 1959.)
* CQM-10A (target drone developed from CIM-10A)"Factsheets : Boeing XF-99."
* XF-99 (experimental for booster research)
* XF-99A/XIM-99A (experimental for ramjet research)
* YF-99A/YIM-99A (service-test)
* IM-99A/CIM-10A (initial production)
* IM-99B/CIM-10B ("advanced""IM-99A Bases Manual". ''Boeing: Pilotless Aircraft Division'' (Seattle, Washington), 12 March 1959.)
* CQM-10A (target drone developed from CIM-10A)"Factsheets : Boeing XF-99."
''Nationalmuseum.af.mil''. Retrieved: 18 September 2013. * CQM-10B (target drone developed from CIM-10B)
File:6th Air Defense Missile Squadron - ADC - Emblem.png, 6th ADMS
File:22d Air Defense Missile Squadron - ADC - Emblem.png, 22d ADMS
File:26th Air Defense Missile Squadron - ADC - Emblem.png, 26th ADMS
File:30th Air Defense Missile Squadron - ADC - Emblem.png, 30th ADMS
File:35th Air Defense Missile Squadron - ADC - Emblem.png, 35th ADMS
File:37th Air Defense Missile Squadron - ADC - Emblem.png, 37th ADMS
File:46th Air Defense Missile Squadron - ADC - Emblem.png, 46th ADMS
File:74th Air Defense Missile Squadron - ADC - Emblem.png, 74th ADMS
File:4751st_Air_Defense_Squadron_-_ADC_-_Emblem.png, 4751st ADMS
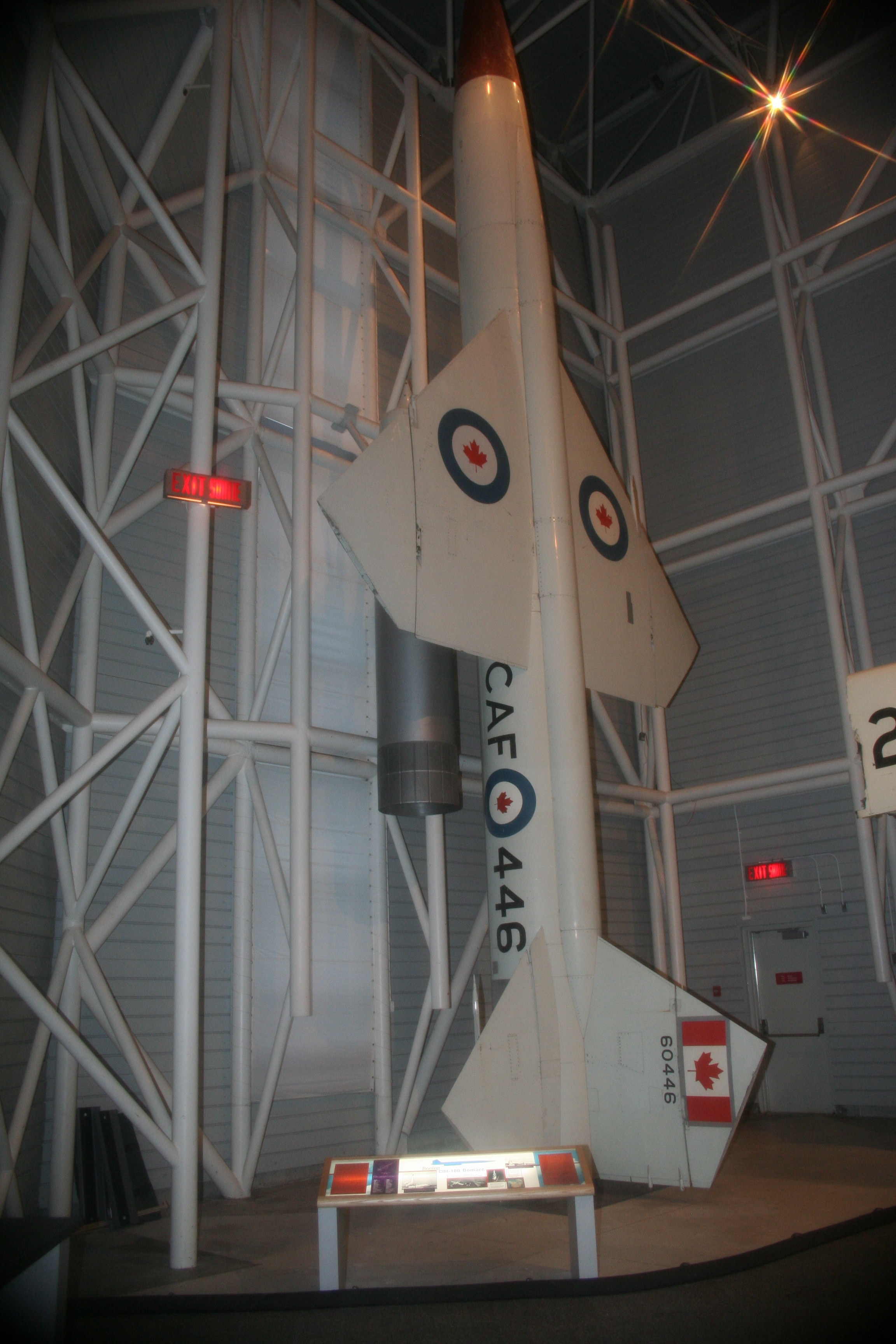
File:Rcaf 446 squadorn BOMARC.png, RCAF 446 Sqdn
File:Rcaf 447 squadorn BOMARC.png, RCAF 447 Squdn
 Below is a list of museums or sites which have a Bomarc missile on display:
*
Below is a list of museums or sites which have a Bomarc missile on display:
*
Bomarc Records
, ''Rate Your Music'' and a moderately successful Canadian pop group, The Beau Marks.
RCAF 446 SAM Squadron
Bomarc Video Clip
– Oral history: Les Earnest talks about air defense system called SAGE and a ground-to-air missile called BOMARC. {{DEFAULTSORT:Cim-10 Bomarc Cold War surface-to-air missiles of the United States Nuclear anti-aircraft weapons Ramjet-powered aircraft Nuclear weapons of Canada Nuclear weapons of the United States Military equipment introduced in the 1950s
 The Boeing CIM-10 BOMARC (Boeing Michigan Aeronautical Research Center) (IM-99 Weapon System prior to September 1962) was a supersonic
The Boeing CIM-10 BOMARC (Boeing Michigan Aeronautical Research Center) (IM-99 Weapon System prior to September 1962) was a supersonic ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an as ...
powered long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) used during the Cold War for the air defense of North America. In addition to being the first operational long-range SAM and the first operational pulse doppler aviation radar,Tactical missile aerodynamics, Volume 141. P17. Michael J. Hemsch, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1992 it was the only SAM deployed by the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
.
Stored horizontally in a launcher shelter with a movable roof, the missile was erected, fired vertically using rocket boosters to high altitude, and then tipped over into a horizontal Mach 2.5 cruise powered by ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an as ...
engines. This lofted trajectory allowed the missile to operate at a maximum range as great as 430 mi (700 km). Controlled from the ground for most of its flight, when it reached the target area it was commanded to begin a dive, activating an onboard active radar homing seeker for terminal guidance In the field of weaponry, terminal guidance refers to any guidance system that is primarily or solely active during the "terminal phase", just before the weapon impacts its target. The term is generally used in reference to missile guidance system ...
. A radar proximity fuse detonated the warhead, either a large conventional explosive or the W40 nuclear warhead.
The Air Force originally planned for a total of 52 sites covering most of the major cities and industrial regions in the US. The US Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
was deploying their own systems at the same time, and the two services fought constantly both in political circles and in the press. Development dragged on, and by the time it was ready for deployment in the late 1950s, the nuclear threat had moved from manned bombers to the intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). By this time the Army had successfully deployed the much shorter range Nike Hercules
The Nike Hercules, initially designated SAM-A-25 and later MIM-14, was a surface-to-air missile (SAM) used by U.S. and NATO armed forces for medium- and high-altitude long-range air defense. It was normally armed with the W31 nuclear warhead, bu ...
that they claimed filled any possible need through the 1960s, in spite of Air Force claims to the contrary.
As testing continued, the Air Force reduced its plans to sixteen sites, and then again to eight with an additional two sites in Canada. The first US site was declared operational in 1959, but with only a single working missile. Bringing the rest of the missiles into service took years, by which time the system was obsolete. Deactivations began in 1969 and by 1972 all Bomarc sites had been shut down. A small number were used as target drones, and only a few remain on display today.
Design and development
Bomarc A
In 1946, Boeing started to study surface-to-air guided missiles under theUnited States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
project MX-606. By 1950, Boeing had launched more than 100 test rockets in various configurations, all under the designator XSAM-A-1 GAPA (Ground-to-Air Pilotless Aircraft). Because these tests were very promising, Boeing received a USAF contract in 1949 to develop a pilotless interceptor (a term then used by the USAF for air-defense guided missiles) under project MX-1599.Gibson 1996, pp. 200–201.
The MX-1599 missile was to be a ramjet-powered, nuclear-armed long-range surface-to-air missile to defend the Continental United States from high-flying bombers. The Michigan Aerospace Research Center (MARC) was added to the project soon afterward, and this gave the new missile its name Bomarc (for Boeing and MARC). In 1951, the USAF decided to emphasize its point of view that missiles were nothing else than pilotless aircraft by assigning aircraft designators to its missile projects, and anti-aircraft missiles received F-for-Fighter designations. The Bomarc became the F-99.
Test flights of XF-99 test vehicles began in September 1952 and continued through early 1955. The XF-99 tested only the liquid-fueled booster rocket, which would accelerate the missile to ramjet ignition speed. In February 1955, tests of the XF-99A propulsion test vehicles began. These included live ramjets, but still had no guidance system or warhead. The designation YF-99A had been reserved for the operational test vehicles. In August 1955, the USAF discontinued the use of aircraft-like type designators for missiles, and the XF-99A and YF-99A became XIM-99A and YIM-99A, respectively. Originally the USAF had allocated the designation IM-69, but this was changed (possibly at Boeing's request to keep number 99) to IM-99 in October 1955.
In October 1957, the first YIM-99A production-representative prototype flew with full guidance, and succeeded to pass the target within destructive range. In late 1957, Boeing received the production contract for the IM-99A Bomarc A interceptor missile, and in September 1959, the first IM-99A squadron became operational.
The IM-99A had an operational radius of and was designed to fly at Mach 2.5–2.8 at a cruising altitude of . It was long and weighed . Its armament was either a conventional warhead or a W40 nuclear warhead (7–10 kiloton
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. The is a unit of energy defined by that convention to be , which is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a ...
yield). A liquid-fuel rocket engine boosted the Bomarc to Mach 2, when its Marquardt RJ43-MA-3 ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an as ...
engines, fueled by 80-octane gasoline, would take over for the remainder of the flight. This was the same model of engine used to power the Lockheed X-7, the Lockheed AQM-60 Kingfisher drone used to test air defenses, and the Lockheed D-21 launched from the back of an M-21, although the Bomarc and Kingfisher engines used different materials due to the longer duration of their flights.
Operational units
 The operational IM-99A missiles were based horizontally in semi-hardened shelters, nicknamed "coffins". After the launch order, the shelter's roof would slide open, and the missile raised to the vertical. After the missile was supplied with fuel for the booster rocket, it would be launched by the Aerojet General LR59-AJ-13 booster. After sufficient speed was reached, the Marquardt RJ43-MA-3 ramjets would ignite and propel the missile to its cruise speed of Mach 2.8 at an altitude of .
When the Bomarc was within of the target, its own Westinghouse AN/DPN-34 radar guided the missile to the interception point. The maximum range of the IM-99A was , and it was fitted with either a conventional high-explosive or a 10 kiloton W-40 nuclear fission warhead.
The Bomarc relied on the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE), an automated control system used by NORAD for detecting, tracking and intercepting enemy
The operational IM-99A missiles were based horizontally in semi-hardened shelters, nicknamed "coffins". After the launch order, the shelter's roof would slide open, and the missile raised to the vertical. After the missile was supplied with fuel for the booster rocket, it would be launched by the Aerojet General LR59-AJ-13 booster. After sufficient speed was reached, the Marquardt RJ43-MA-3 ramjets would ignite and propel the missile to its cruise speed of Mach 2.8 at an altitude of .
When the Bomarc was within of the target, its own Westinghouse AN/DPN-34 radar guided the missile to the interception point. The maximum range of the IM-99A was , and it was fitted with either a conventional high-explosive or a 10 kiloton W-40 nuclear fission warhead.
The Bomarc relied on the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE), an automated control system used by NORAD for detecting, tracking and intercepting enemy bomber aircraft
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an airc ...
. SAGE allowed for remote launching of the Bomarc missiles, which were housed in a constant combat-ready basis in individual launch shelters in remote areas. At the height of the program, there were 14 Bomarc sites located in the US and two in Canada.
Bomarc B
The liquid-fuel booster of the Bomarc A had several drawbacks. It took two minutes to fuel before launch, which could be a long time in high-speed intercepts, and its hypergolic propellants (hydrazine and nitric acid) were very dangerous to handle, leading to several serious accidents. As soon as high-thrust solid-fuel rockets became a reality in the mid-1950s, the USAF began to develop a new solid-fueled Bomarc variant, the IM-99B Bomarc B. It used aThiokol
Thiokol (variously Thiokol Chemical Corporation(/Company), Morton Thiokol Inc., Cordant Technologies Inc., Thiokol Propulsion, AIC Group, ATK Thiokol, ATK Launch Systems Group; finally Orbital ATK before becoming part of Northrop Grumman) was an ...
XM51 booster, and also had improved Marquardt RJ43-MA-7 (and finally the RJ43-MA-11) ramjets. The first IM-99B was launched in May 1959, but problems with the new propulsion system delayed the first fully successful flight until July 1960, when a supersonic MQM-15A Regulus II drone was intercepted. Because the new booster took up less space in the missile, more ramjet fuel could be carried, increasing the range to . The terminal homing system was also improved, using the world's first pulse Doppler search radar, the Westinghouse AN/DPN-53. All Bomarc Bs were equipped with the W-40 nuclear warhead. In June 1961, the first IM-99B squadron became operational, and Bomarc B quickly replaced most Bomarc A missiles. On 23 March 1961, a Bomarc B successfully intercepted a Regulus II cruise missile flying at , thus achieving the highest interception in the world up to that date.
Boeing built 570 Bomarc missiles between 1957 and 1964, 269 CIM-10A, 301 CIM-10B.
 In September 1958 Air Research & Development Command decided to transfer the Bomarc program from its testing at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station to a new facility on Santa Rosa Island, immediately south of Eglin AFB
In September 1958 Air Research & Development Command decided to transfer the Bomarc program from its testing at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station to a new facility on Santa Rosa Island, immediately south of Eglin AFB Hurlburt Field
Hurlburt Field is a United States Air Force installation located in Okaloosa County, Florida, immediately west of the town of Mary Esther. It is part of the greater Eglin Air Force Base reservation and is home to Headquarters Air Force Spe ...
on the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
. To operate the facility and to provide training and operational evaluation in the missile program, Air Defense Command established the 4751st Air Defense Wing (Missile) (4751st ADW) on 15 January 1958. The first launch from Santa Rosa took place on 15 January 1959.
Operational history
In 1955, to support a program which called for 40 squadrons of BOMARC (120 missiles to a squadron for a total of 4,800 missiles), ADC reached a decision on the location of these 40 squadrons and suggested operational dates for each. The sequence was as follows: ... l. McGuire 1/60 2. Suffolk 2/60 3. Otis 3/60 4.Dow
Dow or DOW may refer to:
Business
* Dow Jones Industrial Average, or simply the Dow, a stock market index
* Dow Inc., an American commodity chemical company
** Dow Chemical Company, a subsidiary, an American multinational chemical corporation
...
4/60 5. Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Fall ...
1/61 6. Plattsburgh 1/61 7. Kinross
Kinross (, gd, Ceann Rois) is a burgh in Perth and Kinross, Scotland, around south of Perth and around northwest of Edinburgh. It is the traditional county town of the historic county of Kinross-shire.
History
Kinross's origins are conn ...
2/61 8. K.I. Sawyer 2/61 9. Langley 2/61 10. Truax 3/61 11. Paine
Paine may refer to:
Geography
* Paine, Chile
*Paine College, a defunct Historically Black college in Augusta, Georgia
*Paine Field, an airport in Everett, Washington, United States
*Paine Lake, a lake in Minnesota
* Paine River, a waterstream loca ...
3/61 12. Portland 3/61 ... At the end of 1958, ADC plans called for construction of the following BOMARC bases in the following order: l. McGuire 2. Suffolk 3. Otis 4. Dow 5. Langley 6. Truax 7. Kinross 8. Duluth
, settlement_type = City
, nicknames = Twin Ports (with Superior), Zenith City
, motto =
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top: urban Duluth skyline; Minnesota ...
9. Ethan Allen 10. Niagara Falls 11. Paine 12. Adair 13. Travis 14. Vandenberg 15. San Diego 16. Malmstrom 17. Grand Forks 18. Minot 19. Youngstown 20. Seymour-Johnson 21. Bunker Hill 22. Sioux Falls 23. Charleston 24. McConnell 25. Holloman 26. McCoy 27. Amarillo
Amarillo ( ; Spanish for " yellow") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the seat of Potter County. It is the 14th-most populous city in Texas and the largest city in the Texas Panhandle. A portion of the city extends into Randall Cou ...
28. Barksdale 29. Williams.
United States
The first USAF operational Bomarc squadron was the 46th Air Defense Missile Squadron (ADMS), organized on 1 January 1959 and activated on 25 March. The 46th ADMS was assigned to the New York Air Defense Sector at McGuire Air Force Base, New Jersey. The training program, under the 4751st Air Defense Wing used technicians acting as instructors and was established for a four-month duration. Training included missile maintenance; SAGE operations and launch procedures, including the launch of an unarmed missile at Eglin. In September 1959 the squadron assembled at their permanent station, the Bomarc site near McGuire AFB, and trained for operational readiness. The first Bomarc-A were used at McGuire on 19 September 1959 with Kincheloe AFB getting the first operational IM-99Bs. While several of the squadrons replicated earlier fighter interceptor unit numbers, they were all new organizations with no previous historical counterpart. ADC's initial plans called for some 52 Bomarc sites around the United States with 120 missiles each but as defense budgets decreased during the 1950s the number of sites dropped substantially. Ongoing development and reliability problems didn't help, nor did Congressional debate over the missile's usefulness and necessity. In June 1959, the Air Force authorized 16 Bomarc sites with 56 missiles each; the initial five would get the IM-99A with the remainder getting the IM-99B. However, in March 1960, HQ USAF cut deployment to eight sites in the United States and two in Canada.Bomarc incident
Within a year of operations, a Bomarc A with a nuclear warhead caught fire atMcGuire AFB
McGuire AFB/McGuire, the common name of the McGuire unit of Joint Base McGuire-Dix-Lakehurst, is a United States Air Force base in Burlington County, New Jersey, United States, approximately south-southeast of Trenton. McGuire is under the ju ...
on 7 June 1960 after its on-board helium tank exploded. While the missile's explosives did not detonate, the heat melted the warhead and released plutonium, which the fire crews spread. The Air Force and the Atomic Energy Commission cleaned up the site and covered it with concrete. This was the only major incident involving the weapon system. The site remained in operation for several years following the fire. Since its closure in 1972, the area has remained off limits, primarily due to low levels of plutonium contamination. Between 2002 and 2004, 21,998 cubic yards of contaminated debris and soils were shipped to what was then known as Envirocare
EnergySolutions (stylized as Energy''Solutions''), headquartered in Salt Lake City, Utah, is one of the largest processors of low level waste (LLW) in America, making it also one of the world's largest nuclear waste processors. It was formed in 20 ...
, located in Utah.
Modification and deactivation
In 1962, the US Air Force started using modified A-models as drones; following the October 1962 tri-service redesignation of aircraft and weapons systems they became CQM-10As. Otherwise the air defense missile squadrons maintained alert while making regular trips to Santa Rosa Island for training and firing practice. After the inactivation of the 4751st ADW(M) on 1 July 1962 and transfer of Hurlburt to Tactical Air Command for air commando operations the 4751st Air Defense Squadron (Missile) remained at Hurlburt and Santa Rosa Island for training purposes. In 1964, the liquid-fueled Bomarc-A sites and squadrons began to be deactivated. The sites at Dow and Suffolk County closed first. The remainder continued to be operational for several more years while the government started dismantling the air defense missile network. Niagara Falls was the first BOMARC B installation to close, in December 1969; the others remained on alert through 1972. In April 1972, the last Bomarc B in U.S. Air Force service was retired at McGuire and the 46th ADMS inactivated and the base was deactivated."Cold War relic on the move."
'
North Bay Nugget
The ''North Bay Nugget'' is a newspaper published in North Bay, Ontario, Canada. The paper is currently owned by Postmedia.
The paper was launched in 1907 as the ''Cobalt Nugget'', during the silver boom at Cobalt, Ontario. It was acquired by b ...
'', 12 September 2009. Retrieved: 24 December 2009.
Russ Sneddon, director of the Air Force Armament Museum
The Air Force Armament Museum is a military aviation museum adjacent to Eglin Air Force Base in Valparaiso, Florida, dedicated to the display of Air Force armament. It is supported by the private, non-profit Air Force Armament Museum Foundation.
...
, Eglin Air Force Base, Florida provided information about missing CIM-10 exhibit airframe serial 59–2016, one of the museum's original artifacts from its founding in 1975 and donated by the 4751st Air Defense Squadron at Hurlburt Field
Hurlburt Field is a United States Air Force installation located in Okaloosa County, Florida, immediately west of the town of Mary Esther. It is part of the greater Eglin Air Force Base reservation and is home to Headquarters Air Force Spe ...
, Eglin Auxiliary Field 9, Eglin AFB. As of December 2006, the suspect missile was stored in a secure compound behind the Armaments Museum. In December 2010, the airframe was still on premises, but partly dismantled.
Canada
The Bomarc Missile Program was highly controversial in Canada. The Progressive Conservative government ofPrime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
John Diefenbaker
John George Diefenbaker ( ; September 18, 1895 – August 16, 1979) was the 13th prime minister of Canada, serving from 1957 to 1963. He was the only Progressive Conservative party leader between 1930 and 1979 to lead the party to an electi ...
initially agreed to deploy the missiles, and shortly thereafter controversially scrapped the Avro Arrow
The Avro Canada CF-105 Arrow was a delta-winged interceptor aircraft designed and built by Avro Canada. The CF-105 held the promise of Mach 2 speeds at altitudes exceeding and was intended to serve as the Royal Canadian Air Force's (RCAF) p ...
, a supersonic manned interceptor aircraft, arguing that the missile program made the Arrow unnecessary.
Initially, it was unclear whether the missiles would be equipped with nuclear warheads. By 1960 it became known that the missiles were to have a nuclear payload, and a debate ensued about whether Canada should accept nuclear weapons.
Ultimately, the Diefenbaker government decided that the Bomarcs should not be equipped with nuclear warheads.
The dispute split the Diefenbaker Cabinet, and led to the collapse of the government in 1963. The Official Opposition and Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world. The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left.
__TOC__ Active liberal parties
This is a li ...
leader Lester B. Pearson
Lester Bowles "Mike" Pearson (23 April 1897 – 27 December 1972) was a Canadian scholar, statesman, diplomat, and politician who served as the 14th prime minister of Canada from 1963 to 1968.
Born in Newtonbrook, Ontario (now part of ...
originally was against nuclear missiles, but reversed his personal position and argued in favor of accepting nuclear warheads.
He won the 1963 election, largely on the basis of this issue, and his new Liberal government proceeded to accept nuclear-armed Bomarcs, with the first being deployed on 31 December 1963."Special to The Star: Canada's Bomarcs get atom warheads." ''The Toronto Daily Star,'' 2 January 1964, pp. 1, 4. When the nuclear warheads were deployed, Pearson's wife, Maryon, resigned her honorary membership in the anti-nuclear weapons group, Voice of Women.
Canadian operational deployment of the Bomarc involved the formation of two specialized Surface/Air Missile squadrons. The first to begin operations was No. 446 SAM Squadron at RCAF Station North Bay, which was the command and control center for both squadrons. With construction of the compound and related facilities completed in 1961, the squadron received its Bomarcs in 1961, without nuclear warheads. The squadron became fully operational from 31 December 1963, when the nuclear warheads arrived, until disbanding on 31 March 1972. All the warheads were stored separately and under control of Detachment 1 of the USAF 425th Munitions Maintenance Squadron at Stewart Air Force Base. During operational service, the Bomarcs were maintained on stand-by, on a 24-hour basis, but were never fired, although the squadron test-fired the missiles at Eglin AFB, Florida on annual winter retreats.Nicks et al. 1997, pp. 84–85.
No. 447 SAM Squadron operating out of RCAF Station La Macaza, Quebec, was activated on 15 September 1962 although warheads were not delivered until late 1963. The squadron followed the same operational procedures as No. 446, its sister squadron. With the passage of time the operational capability of the 1950s-era Bomarc system no longer met modern requirements; the Department of National Defence deemed that the Bomarc missile defense was no longer a viable system, and ordered both squadrons to be stood down in 1972. The bunkers and ancillary facilities remain at both former sites.Nicks et al. 1997, pp. 85–87.
Variants
 * XF-99 (experimental for booster research)
* XF-99A/XIM-99A (experimental for ramjet research)
* YF-99A/YIM-99A (service-test)
* IM-99A/CIM-10A (initial production)
* IM-99B/CIM-10B ("advanced""IM-99A Bases Manual". ''Boeing: Pilotless Aircraft Division'' (Seattle, Washington), 12 March 1959.)
* CQM-10A (target drone developed from CIM-10A)"Factsheets : Boeing XF-99."
* XF-99 (experimental for booster research)
* XF-99A/XIM-99A (experimental for ramjet research)
* YF-99A/YIM-99A (service-test)
* IM-99A/CIM-10A (initial production)
* IM-99B/CIM-10B ("advanced""IM-99A Bases Manual". ''Boeing: Pilotless Aircraft Division'' (Seattle, Washington), 12 March 1959.)
* CQM-10A (target drone developed from CIM-10A)"Factsheets : Boeing XF-99."''Nationalmuseum.af.mil''. Retrieved: 18 September 2013. * CQM-10B (target drone developed from CIM-10B)
Operators
; / *Royal Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; french: Aviation royale canadienne, ARC) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environm ...
from 1955 to 1968 / Canadian Forces
}
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; french: Forces armées canadiennes, ''FAC'') are the unified military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air elements referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Forc ...
from 1968 to 1972
: 446 SAM Squadron
__NOTOC__
Year 446 ( CDXLVI) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aetius and Symmachus (or, less frequently, year 1199 ' ...
: 28 IM-99B, CFB North Bay
Canadian Forces Base North Bay, also CFB North Bay, is an air force base located at the City of North Bay, Ontario about north of Toronto. The base is subordinate to 1 Canadian Air Division, Winnipeg, Manitoba, and is the centre for North Ame ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
1962–1972
:: Bomarc site located at
: 447 SAM Squadron
__NOTOC__
Year 447 ( CDXLVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Calepius and Ardabur (or, less frequently, year 1200 ...
: 28 IM-99B, La Macaza, Quebec ( La Macaza – Mont Tremblant International Airport) 1962–1972
:: Bomarc site located at (Approximately)
;
*United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
Air (later Aerospace) Defense Command
: 6th Air Defense Missile Squadron
The 6th Air Defense Missile Squadron was an air defense unit of the United States Air Force. It was assigned to the New York Air Defense Sector of Aerospace Defense Command, at Suffolk County Air Force Base, New York, where it was inactivated on ...
, 56 IM-99A
:: Activated on 1 February 1959
:: Assigned to: New York Air Defense Sector
:: Inactivated 15 December 1964
:: Stationed at: Suffolk County Air Force Base Missile Annex
The Suffolk County Air Force Base Missile Annex ( SAGE codename "BED") is a Formerly Used Defense Site (NY29799F12240/C02NY0714) on Long Island () that was a CIM-10 Bomarc missile complex during the Cold War, west of Suffolk County Air Force B ...
, New York
::: Bomarc site located 3 miles SW at
: 22d Air Defense Missile Squadron
The 22d Air Defense Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 20th Air Division of Aerospace Defense Command, stationed near Langley Air Force Base, Virginia, where it was inactivated on 31 October ...
: 28 IM-99A/28 IM-99B
:: Activated on 15 September 1959
:: Assigned to: Washington Air Defense Sector
The Washington Air Defense Sector (WaADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command (ADC) 26th Air Division, being stationed at Fort Lee Air Force Station (AFS), Virginia. It w ...
:: Reassigned to: 33d Air Division
The 33rd Air Division (33d AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, assigned to First Air Force, being stationed at Fort Lee Air Force Station, Virginia. It was inactivated on ...
, 1 April 1966
:: Reassigned to: 20th Air Division
The 20th Air Division is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Tactical Air Command at Tyndall Air Force Base, Florida where it was inactivated on 1 March 1983.
During most of the division's history it ...
, 19 November 1969
:: Inactivated: 31 October 1972
:: Stationed at: Langley AFB
Langley Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in Hampton, Virginia, adjacent to Newport News. It was one of thirty-two Air Service training camps established after the entry of the United States into World War I in April 1 ...
, Virginia
::: Bomarc site located 3 miles WNW at
: 26th Air Defense Missile Squadron
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number.
In mathematics
Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second small ...
: 28 IM-99A/28 IM-99B
:: Activated 1 March 1959
:: Assigned to: Boston Air Defense Sector
:: Reassigned to: 35th Air Division
The 35th Air Division (35th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, assigned to First Air Force, at Hancock Field, New York. It was inactivated on 19 November 1969.
History
...
, 1 April 1966
:: Reassigned to: 21st Air Division
The 21st Air Division (21st AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Tactical Air Command, being stationed at Griffiss Air Force Base, New York. It was inactivated on 23 September 1983.
History World W ...
, 19 November 1969
:: Inactivated: 30 April 1972
:: Stationed at: Otis Air Force Base BOMARC site, Massachusetts
::: Bomarc site located 1 mile NNW at
: 30th Air Defense Missile Squadron
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
: 28 IM-99A
:: Activated on 1 June 1959
:: Assigned to Bangor Air Defense Sector
The Bangor Air Defense Sector (BaADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command 26th Air Division, being stationed at Topsham Air Force Station, Maine. It was inactivated on 1 ...
:: Inactivated: 15 December 1964
:: Stationed at Dow AFB, Maine
::: Bomarc site located 4 mils NNE at
: 35th Air Defense Missile Squadron Military units
*35th Fighter Wing, an air combat unit of the United States Air Force
*35th Infantry Division (United States), a formation of the National Guard since World War I
*35th Infantry Regiment (United States), a regiment created on 1 July 1 ...
: 56 IM-99B
:: Activated 1 June 1960
:: Assigned to Syracuse Air Defense Sector
:: Reassigned to: Detroit Air Defense Sector
The Detroit Air Defense Sector (DEADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command (ADC) 26th Air Division at Custer Air Force Station (AFS), Michigan. It was inactivated on 1 Apri ...
, 4 September 1963
:: Reassigned to: 34th Air Division
The 34th Air Division (34th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command at Custer Air Force Station, Michigan. It was inactivated on 31 December 1969.
History
Assigned to Air De ...
, 1 April 1966
:: Reassigned to: 35th Air Division
The 35th Air Division (35th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, assigned to First Air Force, at Hancock Field, New York. It was inactivated on 19 November 1969.
History
...
, 15 September 1969
:: Inactivated: 31 December 1969
:: Stationed at: Niagara Falls Air Force Missile Site
The Niagara Falls Air Force Missile Site was a Cold War USAF launch complex for Boeing CIM-10 Bomarc surface-to-air missiles. It was operated by the 35th Air Defense Missile Squadron. Equipped only IM-99Bs (46 missiles: solid-state, solid-fuel ...
, New York
::: Bomarc site located at
: 37th Air Defense Missile Squadron 37th may refer to:
* 37th (Howitzer) Brigade Royal Field Artillery, a brigade of the Royal Field Artillery which served in the First World War
*37th (North Hampshire) Regiment of Foot, raised in Ireland in February 1702
*37th (Northern Ontario) Bat ...
: 28 IM-99B
:: Activated 1 March 1960
:: Assigned to 30th Air Division
The 30th Air Division (30th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, assigned to Tenth Air Force, being stationed at Sioux City Municipal Airport, Iowa. It was inactivated on ...
:: Reassigned to: Sault Sainte Marie Air Defense Sector
The Sault Sainte Marie Air Defense Sector (SsmADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the 30th Air Division, being stationed at K.I. Sawyer Air Force Base, Michigan.
History
SsmADS was establi ...
, 1 April 1960
:: Reassigned to: Duluth Air Defense Sector
The Duluth Air Defense Sector (DUADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command 29th Air Division, being stationed at Duluth Airport, Minnesota. It was inactivated on 1 April 19 ...
, 1 October 1963
:: Reassigned to: 29th Air Division
The 29th Air Division (29th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, being stationed at Duluth International Airport, Minnesota. It was inactivated on 15 November 1969.
History
...
, 1 April 1966
:: Reassigned to: 23d Air Division, 19 November 1969
:: Inactivated 31 July 1972
:: Stationed at: Kincheloe AFB, Michigan
::: Bomarc site located 19 miles NW at Raco
: 46th Air Defense Missile Squadron: 28 IM-99A/56 IM-99B
:: Activated 1 January 1959
:: Assigned to New York Air Defense Sector
:: Reassigned to: 21st Air Division
The 21st Air Division (21st AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Tactical Air Command, being stationed at Griffiss Air Force Base, New York. It was inactivated on 23 September 1983.
History World W ...
, 1 April 1966
:: Reassigned to: 35th Air Division
The 35th Air Division (35th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, assigned to First Air Force, at Hancock Field, New York. It was inactivated on 19 November 1969.
History
...
, 1 December 1957
:: Reassigned to: 21st Air Division
The 21st Air Division (21st AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Tactical Air Command, being stationed at Griffiss Air Force Base, New York. It was inactivated on 23 September 1983.
History World W ...
, 19 November 1969
:: Inactivated 31 October 1972
:: Stationed at: McGuire AFB
McGuire AFB/McGuire, the common name of the McGuire unit of Joint Base McGuire-Dix-Lakehurst, is a United States Air Force base in Burlington County, New Jersey, United States, approximately south-southeast of Trenton. McGuire is under the ju ...
, New Jersey
::: Bomarc site located 4 miles ESE at
: 74th Air Defense Missile Squadron: 28 IM-99B
:: Activated 1 April 1960
:: Assigned to Duluth Air Defense Sector
The Duluth Air Defense Sector (DUADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command 29th Air Division, being stationed at Duluth Airport, Minnesota. It was inactivated on 1 April 19 ...
:: Reassigned to: 29th Air Division
The 29th Air Division (29th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, being stationed at Duluth International Airport, Minnesota. It was inactivated on 15 November 1969.
History
...
, 1 April 1966
:: Reassigned to: 23d Air Division, 19 November 1969
:: Inactivated 30 April 1972
:: Stationed at: Duluth International Airport
: ''For the United States Air Force use of this facility, see Duluth Air National Guard Base.''
Duluth International Airport is a city-owned public-use joint civil-military airport located five nautical miles (9 km) northwest of the centra ...
, Minnesota
::: Bomarc site located 10 miles NE at
: 4751st Air Defense Missile Squadron
The 4751st Air Defense Missile Squadron is a discontinued United States Air Force unit. It was last active with Air Defense, Tactical Air Command (ADTAC), based at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. It was inactivated on 30 September 1979.
History
...
:: Activated 15 January 1959
:: Assigned to 73d Air Division (Weapons)
:: Reassigned to: 32d Air Division
The 32d Air Division (32d AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. It was last active with Air Defense Command, assigned to First Air Force at Gunter Air Force Base, Alabama, where it was inactivated on 31 December 1969.
The di ...
, 1 October 1959
:: Reassigned to: Montgomery Air Defense Sector
The Southeast Air Defense Sector (SEADS), was a unit of the US Air Force located at Tyndall Air Force Base near Panama City, Florida. It provided air defense and surveillance of the southeastern region of the US. SEADS closed in winter 2005, ...
, 1 July 1962
:: Reassigned to: Air Defense, Tactical Air Command
Air Defense, Tactical Air Command (ADTAC) was a Named Unit of the United States Air Force, and operated at the Numbered Air Force echelon of Tactical Air Command. It was responsible for the air defense of the United States, and was last statione ...
, 1 September 1979
:: Inactivated 30 September 1979
:: Stationed at: Eglin Auxiliary Field #9 (Hurlburt Field), Florida
::: Bomarc site located on Santa Rosa Island at
::: Bomarc site located at Eglin Auxiliary Field #5 (Piccolo Field) at
* Air Force Systems Command
:: Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the statio ...
, Florida
::: Launch Complex 4 (LC-4) was used for Bomarc testing and development launches 2 February 1956 – 15 April 1960 (17 Launches).
:: Vandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg Sp ...
, California
::: Two launch sites, BOM-1 and BOM-2 were used by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
for Bomarc launches against aerial targets. The first launch taking place on 25 August 1966. The last two launches occurred on 14 July 1982. BOM1 49 launches; BOM2 38 launches.
Locations under construction but not activated. Each site was programmed for 28 IM-99B missiles:
* Camp Adair
Camp Adair was a United States Army division training facility established north of Corvallis, Oregon, operating from 1942 to 1946. During its peak period of use, the camp was home to approximately 40,000 persons — enough to have constituted ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
* Charleston AFB, South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
* Ethan Allen AFB, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
* Paine Field, Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
* Travis AFB
Travis Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base under the operational control of the Air Mobility Command (AMC), located three miles (5 km) east of the central business district of the city of Fairfield, in Solano County, California ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
* Truax Field, Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
* Vandenberg AFB
Vandenberg Space Force Base , previously Vandenberg Air Force Base, is a United States Space Force Base in Santa Barbara County, California. Established in 1941, Vandenberg Space Force Base is a space launch base, launching spacecraft from th ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
Reference for BOMARC units and locations:
Surviving missiles
 Below is a list of museums or sites which have a Bomarc missile on display:
*
Below is a list of museums or sites which have a Bomarc missile on display:
* Air Force Armament Museum
The Air Force Armament Museum is a military aviation museum adjacent to Eglin Air Force Base in Valparaiso, Florida, dedicated to the display of Air Force armament. It is supported by the private, non-profit Air Force Armament Museum Foundation.
...
, Eglin Air Force Base, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
* Air Force Space & Missile Museum, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the statio ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
. It is on display Hangar C.
* Alberta Aviation Museum
The Alberta Aviation Museum is an aviation museum located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. The museum is located on-site at the former Edmonton City Centre (Blatchford Field) Airport on the southwest corner of the field (11410 Kingsway Avenue).
...
, Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
, Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, Canada
* Canada Aviation and Space Museum, Ottawa, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, Canada
* Hill Aerospace Museum
Hill Aerospace Museum is a military aviation museum located at Hill Air Force Base in Roy, Utah. It is dedicated to the history of the base and aviation in Utah.
History
Preparations for a museum began in 1984, when ground was broken on an "Ae ...
, Hill Air Force Base, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
* Historical Electronics Museum, Linthicum, Maryland
Linthicum is a census-designated place (CDP) and unincorporated community in Anne Arundel County, Maryland, United States. The population was 10,324 at the 2010 census. It is located directly north of Baltimore–Washington International Thurgood ...
(display of AN/DPN-53, the first airborne pulse-doppler radar, used in the Bomarc)
* Illinois Soldiers & Sailors Home, Quincy, Illinois
* Keesler Air Force Base, Biloxi, Mississippi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in and one of two county seats of Harrison County, Mississippi, United States (the other being the adjacent city of Gulfport). The 2010 United States Census recorded the population as 44,054 and in 2019 the estimated popu ...
* Museum of Aviation, Robins Air Force Base
Robins Air Force Base is a major United States Air Force installation located in Houston County, Georgia, United States. The base is located just east of the city of Warner Robins, south-southeast of Macon and approximately south-southeast o ...
, Warner Robins, Georgia
Warner Robins (typically ) is a city in the U.S. state of Georgia, located in Houston and Peach counties in the central part of the state. It is currently Georgia's eleventh-largest incorporated city, with an estimated population of 80,308 in t ...
* National Museum of Nuclear Science & History
The National Museum of Nuclear Science & History (formerly named National Atomic Museum) is a national repository of nuclear science information chartered by the 102nd United States Congress under Public Law 102-190, and located in unincorporated ...
, Kirtland Air Force Base, Albuquerque, New Mexico
* National Museum of the United States Air Force
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB) is a United States Air Force base and census-designated place just east of Dayton, Ohio, in Greene and Montgomery counties. It includes both Wright and Patterson Fields, which were originally Wilbur Wr ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
* Octave Chanute Aerospace Museum (former Chanute Air Force Base), Rantoul, Illinois; the museum closed on December 30, 2015
* Peterson Air and Space Museum, Peterson Air Force Base
Peterson Space Force Base, previously Peterson Air Force Base, Peterson Field, and Army Air Base, Colorado Springs, is a U.S. Space Force Base that shares an airfield with the adjacent Colorado Springs Municipal Airport and is home to the N ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
* Strategic Air and Space Museum, Ashland, Nebraska
Ashland is a city in Saunders County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 2,453 at the 2010 census.
History
Ashland is located at the site of a low-water limestone ledge along the bottom of Salt Creek, an otherwise mud-bottomed stream ...
* U.S. Air Force History and Traditions Museum, Lackland Air Force Base
Lackland Air Force Base is a United States Air Force (USAF) base located in Bexar County, Texas. The base is under the jurisdiction of the 802d Mission Support Group, Air Education and Training Command (AETC) and an enclave of the city of S ...
, San Antonio, Texas
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, subdivision_t ...
* Vandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg Sp ...
( Space and Missile Heritage Center), California. Bomarc not for public access.
Impact on popular music
The Bomarc missile captured the imagination of the American and Canadian popular music industry, giving rise to a pop music group, the Bomarcs (composed mainly of servicemen stationed on a Florida radar site that tracked Bomarcs), a record label, Bomarc Records,, ''Rate Your Music'' and a moderately successful Canadian pop group, The Beau Marks.
See also
References
Bibliography
* Clearwater, John. ''Canadian Nuclear Weapons: The Untold Story of Canada's Cold War Arsenal''. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Dundern Press, 1999. . * Clearwater, John. ''U.S. Nuclear Weapons in Canada''. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Dundern Press, 1999. . * Cornett, Lloyd H. Jr. and Mildred W. Johnson. ''A Handbook of Aerospace Defense Organization 1946–1980''. Peterson Air Force Base, Colorado: Office of History, Aerospace Defense Center, 1980. No ISBN. * Gibson, James N. ''Nuclear Weapons of the United States: An Illustrated History''. Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing Ltd., 1996. . * Jenkins, Dennis R. and Tony R. Landis. ''Experimental & Prototype U.S. Air Force Jet Fighters''. North Branch, Minnesota: Specialty Press, 2008. . * Nicks, Don, John Bradley and Chris Charland. ''A History of the Air Defence of Canada 1948–1997''. Ottawa, Ontario, Canada: Commander Fighter Group, 1997. . * ''Pedigree of Champions: Boeing Since 1916, Third Edition''. Seattle, Washington: The Boeing Company, 1969. * Winkler, David F. ''Searching the Skies: The Legacy of the United States Cold War Defense Radar Program''. Langley Air Force Base, Virginia: United States Air Force Headquarters Air Combat Command, 1997. .External links
RCAF 446 SAM Squadron
Bomarc Video Clip
– Oral history: Les Earnest talks about air defense system called SAGE and a ground-to-air missile called BOMARC. {{DEFAULTSORT:Cim-10 Bomarc Cold War surface-to-air missiles of the United States Nuclear anti-aircraft weapons Ramjet-powered aircraft Nuclear weapons of Canada Nuclear weapons of the United States Military equipment introduced in the 1950s