chromates on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of
Potassium-chromate-sample.jpg,
Chromates react with
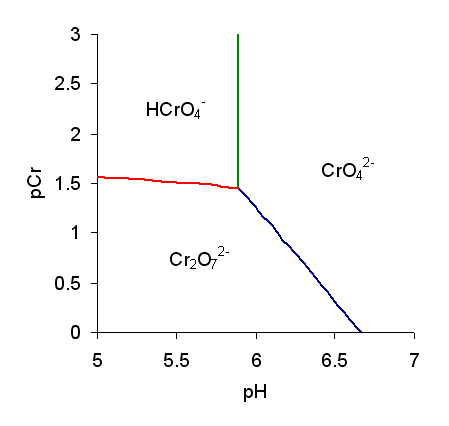 The chromate ion is the predominant species in alkaline solutions, but dichromate can become the predominant ion in acidic solutions.
Further condensation reactions can occur in strongly acidic solution with the formation of trichromates, , and tetrachromates, . All poly oxyanions of chromium(VI) have structures made up of tetrahedral units sharing corners.
The hydrogen chromate ion, , is a weak acid:
:; p''K''a ≈ 5.9
It is also in equilibrium with the dichromate ion:
:
This equilibrium does not involve a change in hydrogen ion concentration, which would predict that the equilibrium is independent of pH. The red line on the predominance diagram is not quite horizontal due to the simultaneous equilibrium with the chromate ion. The hydrogen chromate ion may be protonated, with the formation of molecular
The chromate ion is the predominant species in alkaline solutions, but dichromate can become the predominant ion in acidic solutions.
Further condensation reactions can occur in strongly acidic solution with the formation of trichromates, , and tetrachromates, . All poly oxyanions of chromium(VI) have structures made up of tetrahedral units sharing corners.
The hydrogen chromate ion, , is a weak acid:
:; p''K''a ≈ 5.9
It is also in equilibrium with the dichromate ion:
:
This equilibrium does not involve a change in hydrogen ion concentration, which would predict that the equilibrium is independent of pH. The red line on the predominance diagram is not quite horizontal due to the simultaneous equilibrium with the chromate ion. The hydrogen chromate ion may be protonated, with the formation of molecular
 Approximately of
Approximately of
 The primary chromium ore is the mixed metal oxide
The primary chromium ore is the mixed metal oxide
National Pollutant Inventory - Chromium(VI) and compounds fact sheetDemonstration of chromate-dichromate equilibrium
{{Chromates and dichromates Oxidizing agents Transition metal oxyanions Oxometallates
chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
in the +6 oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
and are moderately strong oxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In ot ...
s. In an aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in wat ...
solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible.
Chemical properties
Potassium chromate
Potassium chromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Potassium, K2Chromate ion, CrO4. This yellow solid is the potassium salt of the Chromate ion, chromate anion. It is a common laboratory chemical, whereas sodium chromate is important ...
Potassium-dichromate-sample.jpg, Potassium dichromate
hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
, giving products in which peroxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of Chemical compound, compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined ...
, , replaces one or more oxygen atoms. In acid solution the unstable blue peroxo complex Chromium(VI) oxide peroxide, , is formed; it is an uncharged covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
molecule, which may be extracted into ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R� ...
. Addition of pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom . It is a highly flammable, weak ...
results in the formation of the more stable complex .
Acid–base properties
In aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate anions exist in achemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both the Reagent, reactants and Product (chemistry), products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time, so that there is no observable chan ...
.
:
The predominance diagram shows that the position of the equilibrium depends on both pH and the analytical concentration of chromium.pCr is equal to the negative of the decimal logarithm of the molar concentration
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. Specifically, It is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular, of a so ...
of chromium. Thus, when pCr = 2, the chromium concentration is 10−2 mol/L.
 The chromate ion is the predominant species in alkaline solutions, but dichromate can become the predominant ion in acidic solutions.
Further condensation reactions can occur in strongly acidic solution with the formation of trichromates, , and tetrachromates, . All poly oxyanions of chromium(VI) have structures made up of tetrahedral units sharing corners.
The hydrogen chromate ion, , is a weak acid:
:; p''K''a ≈ 5.9
It is also in equilibrium with the dichromate ion:
:
This equilibrium does not involve a change in hydrogen ion concentration, which would predict that the equilibrium is independent of pH. The red line on the predominance diagram is not quite horizontal due to the simultaneous equilibrium with the chromate ion. The hydrogen chromate ion may be protonated, with the formation of molecular
The chromate ion is the predominant species in alkaline solutions, but dichromate can become the predominant ion in acidic solutions.
Further condensation reactions can occur in strongly acidic solution with the formation of trichromates, , and tetrachromates, . All poly oxyanions of chromium(VI) have structures made up of tetrahedral units sharing corners.
The hydrogen chromate ion, , is a weak acid:
:; p''K''a ≈ 5.9
It is also in equilibrium with the dichromate ion:
:
This equilibrium does not involve a change in hydrogen ion concentration, which would predict that the equilibrium is independent of pH. The red line on the predominance diagram is not quite horizontal due to the simultaneous equilibrium with the chromate ion. The hydrogen chromate ion may be protonated, with the formation of molecular chromic acid
Chromic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is also a jargon for a solution formed by the addition of sulfuric acid to aqueous solutions of dichromate. It consists at least in part of chromium trioxide.
The term "chromic ...
, , but the p''K''a for the equilibrium
:
is not well characterized. Reported values vary between about −0.8 and 1.6.
The dichromate ion is a somewhat weaker base than the chromate ion:
:, p''K''a = 1.18
The p''K''a value for this reaction shows that it can be ignored at pH > 4.
Oxidation–reduction properties
The chromate and dichromate ions are fairly strongoxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In ot ...
s. Commonly three electrons are added to a chromium atom, reducing it to oxidation state +3. In acid solution the aquated ion is produced.
: ''ε''0 = 1.33 V
In alkaline solution chromium(III) hydroxide is produced. The redox potential shows that chromates are weaker oxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In ot ...
in alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The ...
solution than in acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
solution..
: ''ε''0 = −0.13 V
Applications
 Approximately of
Approximately of hexavalent chromium
Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is any chemical compound that contains the element chromium in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). It has been identified as carcinogenic, which is of concern since approximately of ...
, mainly sodium dichromate, were produced in 1985. Chromates and dichromates are used in chrome plating
Chrome plating (less commonly chromium plating) is a technique of electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. A chrome plated part is called ''chrome'', or is said to have been ''chromed''. The chromium layer can be decorativ ...
to protect metals from corrosion and to improve paint adhesion. Chromate and dichromate salts of heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals is a controversial and ambiguous term for metallic elements with relatively h ...
, lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium (el ...
s and alkaline earth metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group (periodic table), group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar p ...
s are only very slightly soluble in water and are thus used as pigments. The lead-containing pigment chrome yellow was used for a very long time before environmental regulations discouraged its use. When used as oxidizing agents or titrants in a redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is t ...
chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
, chromates and dichromates convert into trivalent chromium, , salts of which typically have a distinctively different blue-green color.
Natural occurrence and production
 The primary chromium ore is the mixed metal oxide
The primary chromium ore is the mixed metal oxide chromite
Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of Iron, FeChromium, Cr2Oxygen, O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The ...
, , found as brittle metallic black crystals or granules. Chromite ore is heated with a mixture of calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
and sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash, sal soda, and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water ...
in the presence of air. The chromium is oxidized to the hexavalent form, while the iron forms iron(III) oxide, :
:
Subsequent leaching of this material at higher temperatures dissolves the chromates, leaving a residue of insoluble iron oxide. Normally the chromate solution is further processed to make chromium metal, but a chromate salt may be obtained directly from the liquor.
Chromate containing minerals are rare. Crocoite, , which can occur as spectacular long red crystals, is the most commonly found chromate mineral. Rare potassium chromate minerals and related compounds are found in the Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert () is a desert plateau located on the Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of South America, in the north of Chile. Stretching over a strip of land west of the Andes Mountains, it covers an area of , which increases to if the barre ...
. Among them is lópezite – the only known dichromate mineral.
As chromate is isostructural to sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
, sulfate and chromate minerals can form solid solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogeneous mixture of two compounds in solid state and having a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solutio ...
s such as hashemite
The Hashemites (), also House of Hashim, are the Dynasty, royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Hejaz, Hejaz (1916–1925), Arab Kingdom of Syria, Syria (1920), and Kingd ...
, and chromate minerals are often listed alongside sulfate mineral
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal Vein (geology), veins and as ...
s in mineral classification schemes such as Nickel-Strunz classification.
Toxicity
Hexavalent chromium
Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is any chemical compound that contains the element chromium in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). It has been identified as carcinogenic, which is of concern since approximately of ...
compounds can be toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
and carcinogenic
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and Biological agent, biologic agent ...
(IARC Group 1
IARC group 1 Carcinogens are substances, chemical mixtures, and exposure circumstances which have been classified as carcinogenic to humans by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). This category is used when there is sufficien ...
). Inhaling particles of hexavalent chromium compounds can cause lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged ...
. Also positive associations have been observed between exposure to chromium (VI)
Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is any chemical compound that contains the element chromium in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). It has been identified as carcinogenic, which is of concern since approximately of ...
compounds and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
of the nose
A nose is a sensory organ and respiratory structure in vertebrates. It consists of a nasal cavity inside the head, and an external nose on the face. The external nose houses the nostrils, or nares, a pair of tubes providing airflow through the ...
and nasal sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired skeletal pneumaticity, air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the Ethmoid sinus, ethmoidal sinuses a ...
. The use of chromate compounds in manufactured goods is restricted in the EU (and by market commonality the rest of the world) by EU Parliament directive on the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive (2002/95/EC).
See also
*Chromate conversion coating
Chromate conversion coating or alodine coating is a type of conversion coating used to passivate steel, aluminium, zinc, cadmium, copper, silver, titanium, magnesium, and tin alloys. The coating serves as a corrosion inhibitor, as a pri ...
Notes
References
External links
National Pollutant Inventory - Chromium(VI) and compounds fact sheet
{{Chromates and dichromates Oxidizing agents Transition metal oxyanions Oxometallates