Bioorthogonal Chemistry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any  Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems. Bertozzi was awarded the
Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems. Bertozzi was awarded the
 The nucleophilic phosphine attacks the azide at the electrophilic terminal nitrogen. Through a four-membered transition state, N2 is lost to form an aza-ylide. The unstable ylide is hydrolyzed to form phosphine oxide and a primary amine. However, this reaction is not immediately bioorthogonal because hydrolysis breaks the covalent bond in the aza-ylide.
The nucleophilic phosphine attacks the azide at the electrophilic terminal nitrogen. Through a four-membered transition state, N2 is lost to form an aza-ylide. The unstable ylide is hydrolyzed to form phosphine oxide and a primary amine. However, this reaction is not immediately bioorthogonal because hydrolysis breaks the covalent bond in the aza-ylide.
 The reaction was modified to include an ester group ortho to the phosphorus atom on one of the aryl rings to direct the aza-ylide through a new path of reactivity in order to outcompete immediate hydrolysis by positioning the ester to increase local concentration. The initial nucleophilic attack on the azide is the rate-limiting step. The ylide reacts with the electrophilic ester trap through intramolecular cyclization to form a five-membered ring. This ring undergoes hydrolysis to form a stable
The reaction was modified to include an ester group ortho to the phosphorus atom on one of the aryl rings to direct the aza-ylide through a new path of reactivity in order to outcompete immediate hydrolysis by positioning the ester to increase local concentration. The initial nucleophilic attack on the azide is the rate-limiting step. The ylide reacts with the electrophilic ester trap through intramolecular cyclization to form a five-membered ring. This ring undergoes hydrolysis to form a stable

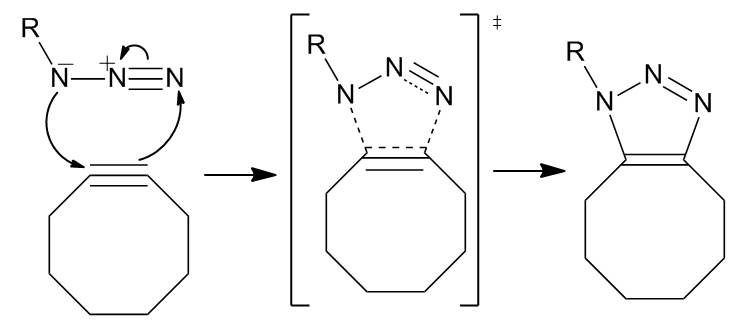 The reaction proceeds as a standard 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, a type of asynchronous, concerted
The reaction proceeds as a standard 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, a type of asynchronous, concerted
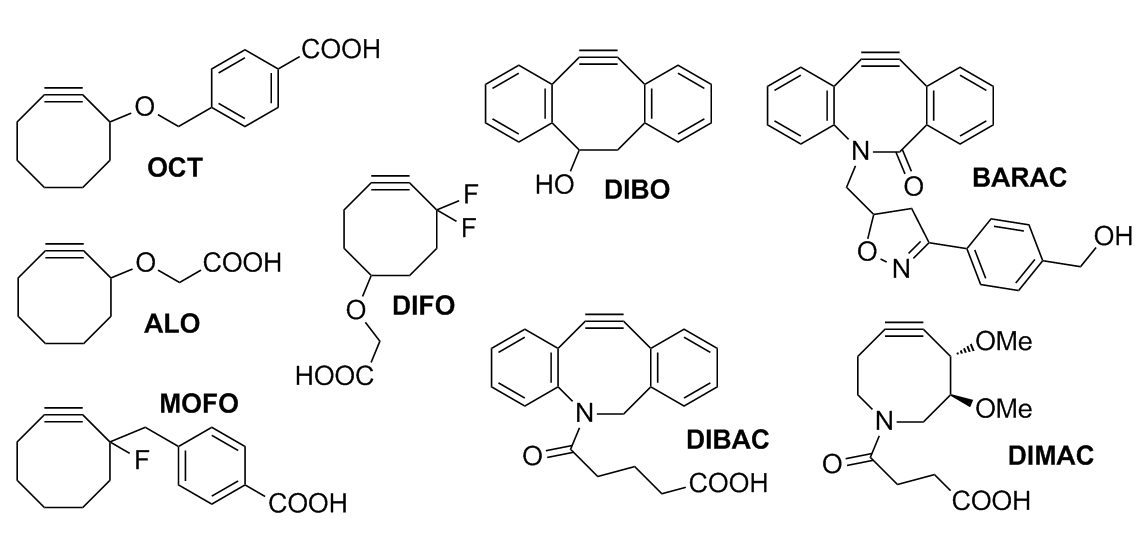 OCT was the first cyclooctyne developed for Cu-free click chemistry. While linear alkynes are unreactive at physiological temperatures, OCT was able readily react with azides in biological conditions while showing no toxicity. However, it was poorly water-soluble, and the kinetics were barely improved over the Staudinger ligation. ALO (aryl-less octyne) was developed to improve water solubility, but it still had poor kinetics.
Monofluorinated (MOFO) and difluorinated (DIFO) cyclooctynes were created to increase the rate through the addition of electron-withdrawing fluorine substituents at the
OCT was the first cyclooctyne developed for Cu-free click chemistry. While linear alkynes are unreactive at physiological temperatures, OCT was able readily react with azides in biological conditions while showing no toxicity. However, it was poorly water-soluble, and the kinetics were barely improved over the Staudinger ligation. ALO (aryl-less octyne) was developed to improve water solubility, but it still had poor kinetics.
Monofluorinated (MOFO) and difluorinated (DIFO) cyclooctynes were created to increase the rate through the addition of electron-withdrawing fluorine substituents at the
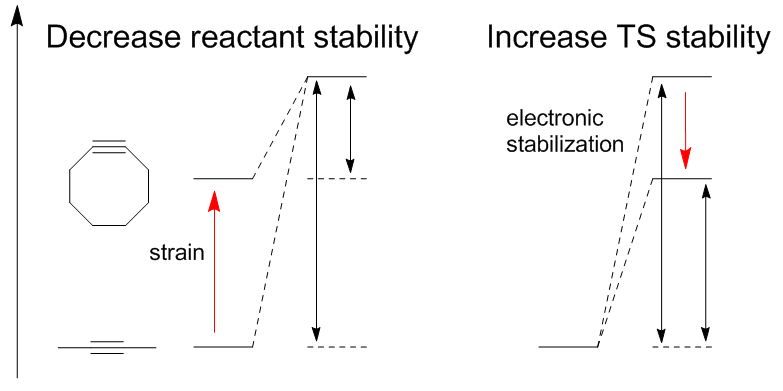 Decreasing reactant stability: Houk has proposed that differences in the energy (Ed ‡) required to distort the azide and alkyne into the transition state geometries control the barrier heights for the reaction. The activation energy (E ‡) is the sum of destabilizing distortions and stabilizing interactions (Ei ‡). The most significant distortion is in the azide functional group with lesser contribution of alkyne distortion. However, it is only the cyclooctyne that can be easily modified for higher reactivity. Calculated barriers of reaction for phenyl azide and
Decreasing reactant stability: Houk has proposed that differences in the energy (Ed ‡) required to distort the azide and alkyne into the transition state geometries control the barrier heights for the reaction. The activation energy (E ‡) is the sum of destabilizing distortions and stabilizing interactions (Ei ‡). The most significant distortion is in the azide functional group with lesser contribution of alkyne distortion. However, it is only the cyclooctyne that can be easily modified for higher reactivity. Calculated barriers of reaction for phenyl azide and  Decreasing transition state energy: Electron withdrawing groups such as fluorine increase rate by decreasing LUMO energy and the HOMO-LUMO gap. This leads to a greater charge transfer from the azide to the fluorinated cyclooctyne in the transition state, increasing interaction energy (lower negative value) and overall activation energy. The lowering of the LUMO is the result of hyperconjugation between alkyne π donor orbitals and CF σ* acceptors. These interactions provide stabilization primarily in the transition state as a result of increased donor/acceptor abilities of the bonds as they distort. NBO calculations have shown that transition state distortion increases the interaction energy by 2.8 kcal/mol.
The hyperconjugation between out-of-plane π bonds is greater because the in-plane π bonds are poorly aligned. However, transition state bending allows the in-plane π bonds to have a more antiperiplanar arrangement that facilitates interaction. Additional hyperconjugative interaction energy stabilization is achieved through an increase in the electronic population of the σ* due to the forming CN bond. Negative hyperconjugation with the σ* CF bonds enhances this stabilizing interaction.
Decreasing transition state energy: Electron withdrawing groups such as fluorine increase rate by decreasing LUMO energy and the HOMO-LUMO gap. This leads to a greater charge transfer from the azide to the fluorinated cyclooctyne in the transition state, increasing interaction energy (lower negative value) and overall activation energy. The lowering of the LUMO is the result of hyperconjugation between alkyne π donor orbitals and CF σ* acceptors. These interactions provide stabilization primarily in the transition state as a result of increased donor/acceptor abilities of the bonds as they distort. NBO calculations have shown that transition state distortion increases the interaction energy by 2.8 kcal/mol.
The hyperconjugation between out-of-plane π bonds is greater because the in-plane π bonds are poorly aligned. However, transition state bending allows the in-plane π bonds to have a more antiperiplanar arrangement that facilitates interaction. Additional hyperconjugative interaction energy stabilization is achieved through an increase in the electronic population of the σ* due to the forming CN bond. Negative hyperconjugation with the σ* CF bonds enhances this stabilizing interaction.
 Symmetrical cyclooctynes such as BCN (bicyclo .1.0onyne) form a single regioisomer upon cycloaddition and may serve to address this problem in the future.
Symmetrical cyclooctynes such as BCN (bicyclo .1.0onyne) form a single regioisomer upon cycloaddition and may serve to address this problem in the future.
 Spatial and temporal control of substrate labeling has been investigated using photoactivatable cyclooctynes. This allows equilibration of the alkyne prior to reaction in order to reduce artifacts as a result of concentration gradients. Masked cyclooctynes are unable to react with azides in the dark but become reactive alkynes upon irradiation with light.
Spatial and temporal control of substrate labeling has been investigated using photoactivatable cyclooctynes. This allows equilibration of the alkyne prior to reaction in order to reduce artifacts as a result of concentration gradients. Masked cyclooctynes are unable to react with azides in the dark but become reactive alkynes upon irradiation with light.
 Copper-free click chemistry is being explored for use in synthesizing
Copper-free click chemistry is being explored for use in synthesizing
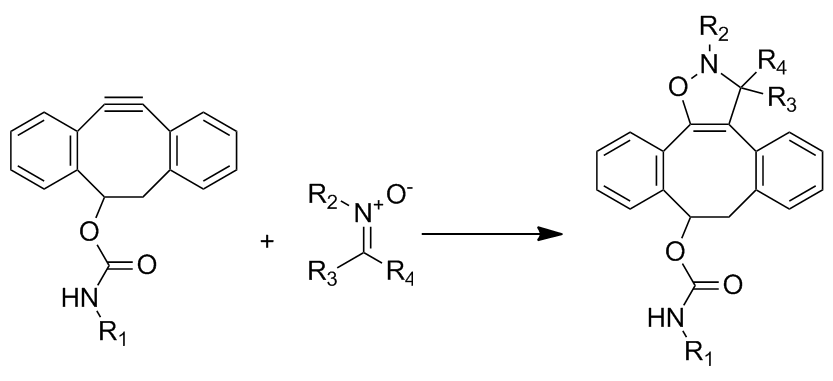 This cycloaddition between a nitrone and a cyclooctyne forms N-alkylated isoxazolines. The reaction rate is enhanced by water and is extremely fast with second order rate constants ranging from 12 to 32 M−1•s−1, depending on the substitution of the nitrone. Although the reaction is extremely fast, it faces problems in incorporating the nitrone into biomolecules through metabolic labeling. Labeling has only been achieved through post-translational peptide modification.
This cycloaddition between a nitrone and a cyclooctyne forms N-alkylated isoxazolines. The reaction rate is enhanced by water and is extremely fast with second order rate constants ranging from 12 to 32 M−1•s−1, depending on the substitution of the nitrone. Although the reaction is extremely fast, it faces problems in incorporating the nitrone into biomolecules through metabolic labeling. Labeling has only been achieved through post-translational peptide modification.
 Norbornenes were selected as dipolarophiles due to their balance between strain-promoted reactivity and stability. The drawbacks of this reaction include the cross-reactivity of the nitrile oxide due to strong electrophilicity and slow reaction kinetics.
Norbornenes were selected as dipolarophiles due to their balance between strain-promoted reactivity and stability. The drawbacks of this reaction include the cross-reactivity of the nitrile oxide due to strong electrophilicity and slow reaction kinetics.
 Ring strain and electron deficiency in the oxanorbornadiene increase reactivity towards the cycloaddition rate-limiting step. The retro-Diels Alder reaction occurs quickly afterwards to form the stable 1,2,3 triazole. Problems include poor tolerance for substituents which may change electronics of the oxanorbornadiene and low rates (second order rate constants on the order of 10−4).
Ring strain and electron deficiency in the oxanorbornadiene increase reactivity towards the cycloaddition rate-limiting step. The retro-Diels Alder reaction occurs quickly afterwards to form the stable 1,2,3 triazole. Problems include poor tolerance for substituents which may change electronics of the oxanorbornadiene and low rates (second order rate constants on the order of 10−4).
 Based on computational work by Bach, the strain energy for Z-cyclooctenes is 7.0 kcal/mol compared to 12.4 kcal/mol for cyclooctane due to a loss of two transannular interactions. E-cyclooctene has a highly twisted double bond resulting in a strain energy of 17.9 kcal/mol. As such, the highly strained trans-cyclooctene is used as a reactive dienophile. The diene is a 3,6-diaryl-s-tetrazine which has been substituted in order to resist immediate reaction with water. The reaction proceeds through an initial cycloaddition followed by a reverse Diels Alder to eliminate N2 and prevent reversibility of the reaction.
Not only is the reaction tolerant of water, but it has been found that the rate increases in aqueous media. Reactions have also been performed using norbornenes as dienophiles at second order rates on the order of 1 M−1•s−1 in aqueous media. The reaction has been applied in labeling live cells and polymer coupling.
Based on computational work by Bach, the strain energy for Z-cyclooctenes is 7.0 kcal/mol compared to 12.4 kcal/mol for cyclooctane due to a loss of two transannular interactions. E-cyclooctene has a highly twisted double bond resulting in a strain energy of 17.9 kcal/mol. As such, the highly strained trans-cyclooctene is used as a reactive dienophile. The diene is a 3,6-diaryl-s-tetrazine which has been substituted in order to resist immediate reaction with water. The reaction proceeds through an initial cycloaddition followed by a reverse Diels Alder to eliminate N2 and prevent reversibility of the reaction.
Not only is the reaction tolerant of water, but it has been found that the rate increases in aqueous media. Reactions have also been performed using norbornenes as dienophiles at second order rates on the order of 1 M−1•s−1 in aqueous media. The reaction has been applied in labeling live cells and polymer coupling.
 The reaction proceeds with an initial +1cycloaddition followed by a reversion to eliminate a thermodynamic sink and prevent reversibility. This product is stable if a tertiary amine or isocyanopropanoate is used. If a secondary or primary isocyanide is used, the produce will form an imine which is quickly hydrolyzed.
Isocyanide is a favored chemical reporter due to its small size, stability, non-toxicity, and absence in mammalian systems. However, the reaction is slow, with second order rate constants on the order of 10−2 M−1•s−1.
The reaction proceeds with an initial +1cycloaddition followed by a reversion to eliminate a thermodynamic sink and prevent reversibility. This product is stable if a tertiary amine or isocyanopropanoate is used. If a secondary or primary isocyanide is used, the produce will form an imine which is quickly hydrolyzed.
Isocyanide is a favored chemical reporter due to its small size, stability, non-toxicity, and absence in mammalian systems. However, the reaction is slow, with second order rate constants on the order of 10−2 M−1•s−1.
 Photoinduction takes place with a brief exposure to light (wavelength is tetrazole-dependent) to minimize photodamage to cells. The reaction is enhanced in aqueous conditions and generates a single regioisomer.
The transient nitrile imine is highly reactive for 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition due to a bent structure which reduces distortion energy. Substitution with electron-donating groups on phenyl rings increases the HOMO energy, when placed on the 1,3 nitrile imine and increases the rate of reaction.
Advantages of this approach include the ability to spatially or temporally control reaction and the ability to incorporate both alkenes and tetrazoles into biomolecules using simple biological methods such as genetic encoding. Additionally, the tetrazole can be designed to be fluorogenic in order to monitor progress of the reaction.
Photoinduction takes place with a brief exposure to light (wavelength is tetrazole-dependent) to minimize photodamage to cells. The reaction is enhanced in aqueous conditions and generates a single regioisomer.
The transient nitrile imine is highly reactive for 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition due to a bent structure which reduces distortion energy. Substitution with electron-donating groups on phenyl rings increases the HOMO energy, when placed on the 1,3 nitrile imine and increases the rate of reaction.
Advantages of this approach include the ability to spatially or temporally control reaction and the ability to incorporate both alkenes and tetrazoles into biomolecules using simple biological methods such as genetic encoding. Additionally, the tetrazole can be designed to be fluorogenic in order to monitor progress of the reaction.
 Quadricyclane is abiotic, unreactive with biomolecules (due to complete saturation), relatively small, and highly strained (~80 kcal/mol). However, it is highly stable at room temperature and in aqueous conditions at physiological pH. It is selectively able to react with electron-poor π systems but not simple alkenes, alkynes, or cyclooctynes.
Bis(dithiobenzil)nickel(II) was chosen as a reaction partner out of a candidate screen based on reactivity. To prevent light-induced reversion to norbornadiene, diethyldithiocarbamate is added to chelate the nickel in the product.
Quadricyclane is abiotic, unreactive with biomolecules (due to complete saturation), relatively small, and highly strained (~80 kcal/mol). However, it is highly stable at room temperature and in aqueous conditions at physiological pH. It is selectively able to react with electron-poor π systems but not simple alkenes, alkynes, or cyclooctynes.
Bis(dithiobenzil)nickel(II) was chosen as a reaction partner out of a candidate screen based on reactivity. To prevent light-induced reversion to norbornadiene, diethyldithiocarbamate is added to chelate the nickel in the product.
 These reactions are enhanced by aqueous conditions with a second order rate constant of 0.25 M−1•s−1. Of particular interest is that it has been proven to be bioorthogonal to both oxime formation and copper-free click chemistry.
These reactions are enhanced by aqueous conditions with a second order rate constant of 0.25 M−1•s−1. Of particular interest is that it has been proven to be bioorthogonal to both oxime formation and copper-free click chemistry.
chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breakin ...
that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi
Carolyn Ruth Bertozzi (born October 10, 1966) is an American chemist and Nobel laureate, known for her wide-ranging work spanning both chemistry and biology. She coined the term "bioorthogonal chemistry" for chemical reactions compatible with ...
in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation
Chemical ligation is a set of techniques used for creating long peptide or protein chains. It is the second step of a convergent approach. First, smaller peptides containing 30-50 amino acids are prepared by conventional chemical peptide synth ...
strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azide
In chemistry, azide is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula and structure . It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid . Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula , containing the azide functional group. The dominant applic ...
s and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrone
In organic chemistry, a nitrone is a functional group consisting of an ''N''-oxide of an imine. The general structure is , where R’ is not a hydrogen. A nitrone is a 1,3-dipole, and is used in 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions. Other reactions of ...
s and cyclooctynes, oxime/ hydrazone formation from aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group ...
s and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide
An isocyanide (also called isonitrile or carbylamine) is an organic compound with the functional group –. It is the isomer of the related nitrile (–C≡N), hence the prefix is ''isocyano''.IUPAC Goldboo''isocyanides''/ref> The organic fragme ...
-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.
The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
in 2022 for her development of click chemistry
In chemical synthesis, click chemistry is a class of biocompatible small molecule reactions commonly used in bioconjugation, allowing the joining of substrates of choice with specific biomolecules. Click chemistry is not a single specific reaction ...
and bioorthogonal chemistry.
Etymology
The word bioorthogonal comes from Greek ''bio-'' "living" and ''orthogōnios'' "right-angled". Thus literally a reaction that goes perpendicular to a living system, thus not disturbing it.Requirements for bioorthogonality
To be considered bioorthogonal, a reaction must fulfill a number of requirements: * Selectivity: The reaction must be selective between endogenous functional groups to avoid side reactions with biological compounds * Biological inertness: Reactive partners and resulting linkage should not possess any mode of reactivity capable of disrupting the native chemical functionality of the organism under study. * Chemical inertness: The covalent link should be strong and inert to biological reactions. * Kinetics: The reaction must be rapid so that covalent ligation is achieved prior to probe metabolism and clearance. The reaction must be fast, on the time scale of cellular processes (minutes) to prevent competition in reactions which may diminish the small signals of less abundant species. Rapid reactions also offer a fast response, necessary in order to accurately track dynamic processes. * Reaction biocompatibility: Reactions have to be non-toxic and must function in biological conditions taking into account pH, aqueous environments, and temperature. Pharmacokinetics are a growing concern as bioorthogonal chemistry expands to live animal models. * Accessible engineering: The chemical reporter must be capable of incorporation into biomolecules via some form of metabolic or protein engineering. Optimally, one of the functional groups is also very small so that it does not disturb native behavior.Staudinger ligation
TheStaudinger ligation
The Staudinger reaction is a chemical reaction of an organic azide with a phosphine or phosphite produces an iminophosphorane. The reaction was discovered by and named after Hermann Staudinger. The reaction follows this stoichiometry:
:R3P + ...
is a reaction developed by the Bertozzi group in 2000 that is based on the classic Staudinger reaction of azides with triarylphosphines. It launched the field of bioorthogonal chemistry as the first reaction with completely abiotic functional groups although it is no longer as widely used. The Staudinger ligation has been used in both live cells and live mice.
Bioorthogonality
The azide can act as a softelectrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carri ...
that prefers soft nucleophiles such as phosphines. This is in contrast to most biological nucleophiles which are typically hard nucleophiles. The reaction proceeds selectively under water-tolerant conditions to produce a stable product.
Phosphines are completely absent from living systems and do not reduce disulfide bonds despite mild reduction potential. Azides had been shown to be biocompatible in FDA-approved drugs such as azidothymidine and through other uses as cross linkers. Additionally, their small size allows them to be easily incorporated into biomolecules through cellular metabolic pathways.
Mechanism
Classic Staudinger reaction
 The nucleophilic phosphine attacks the azide at the electrophilic terminal nitrogen. Through a four-membered transition state, N2 is lost to form an aza-ylide. The unstable ylide is hydrolyzed to form phosphine oxide and a primary amine. However, this reaction is not immediately bioorthogonal because hydrolysis breaks the covalent bond in the aza-ylide.
The nucleophilic phosphine attacks the azide at the electrophilic terminal nitrogen. Through a four-membered transition state, N2 is lost to form an aza-ylide. The unstable ylide is hydrolyzed to form phosphine oxide and a primary amine. However, this reaction is not immediately bioorthogonal because hydrolysis breaks the covalent bond in the aza-ylide.
Staudinger ligation
 The reaction was modified to include an ester group ortho to the phosphorus atom on one of the aryl rings to direct the aza-ylide through a new path of reactivity in order to outcompete immediate hydrolysis by positioning the ester to increase local concentration. The initial nucleophilic attack on the azide is the rate-limiting step. The ylide reacts with the electrophilic ester trap through intramolecular cyclization to form a five-membered ring. This ring undergoes hydrolysis to form a stable
The reaction was modified to include an ester group ortho to the phosphorus atom on one of the aryl rings to direct the aza-ylide through a new path of reactivity in order to outcompete immediate hydrolysis by positioning the ester to increase local concentration. The initial nucleophilic attack on the azide is the rate-limiting step. The ylide reacts with the electrophilic ester trap through intramolecular cyclization to form a five-membered ring. This ring undergoes hydrolysis to form a stable amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is ...
bond.
Limitations
The phosphine reagents slowly undergo air oxidation in living systems. Additionally, it is likely that they are metabolized ''in vitro'' bycytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various comp ...
enzymes.
The kinetics of the reactions are slow with second order rate constants around 0.0020 M−1•s−1. Attempts to increase nucleophilic attack rates by adding electron-donating groups to the phosphines improved kinetics, but also increased the rate of air oxidation.
The poor kinetics require that high concentrations of the phosphine be used which leads to problems with high background signal in imaging applications. Attempts have been made to combat the problem of high background through the development of a fluorogenic phosphine reagents based on fluorescein
Fluorescein is an organic compound and dye based on the xanthene tricyclic structural motif, formally belonging to triarylmethine dyes family. It is available as a dark orange/red powder slightly soluble in water and alcohol. It is widely used ...
and luciferin
Luciferin (from the Latin ''lucifer'', "light-bearer") is a generic term for the light-emitting compound found in organisms that generate bioluminescence. Luciferins typically undergo an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with molecular oxygen. The resul ...
, but the intrinsic kinetics remain a limitation.
Copper-free click chemistry
Copper-free click chemistry is a bioorthogonal reaction first developed by Carolyn Bertozzi as an activated variant of an azide alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition, based on the work byKarl Barry Sharpless
Karl Barry Sharpless (born April 28, 1941) is an American chemist and a two-time Nobel laureate in Chemistry known for his work on stereoselective reactions and click chemistry.
Sharpless was awarded half of the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry ...
et al. Unlike CuAAC, Cu-free click chemistry has been modified to be bioorthogonal by eliminating a cytotoxic copper catalyst, allowing reaction to proceed quickly and without live cell toxicity. Instead of copper, the reaction is a strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloaddition (SPAAC). It was developed as a faster alternative to the Staudinger ligation, with the first generations reacting over sixty times faster. The bioorthogonality of the reaction has allowed the Cu-free click reaction to be applied within cultured cells, live zebrafish, and mice.

Copper toxicity
The classic copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition has been an extremely fast and effective click reaction for bioconjugation, but it is not suitable for use in live cells due to the toxicity of Cu(I) ions. Toxicity is due to oxidative damage from reactive oxygen species formed by the copper catalysts. Copper complexes have also been found to induce changes in cellular metabolism and are taken up by cells. There has been some development of ligands to prevent biomolecule damage and facilitate removal in ''in vitro'' applications. However, it has been found that different ligand environments of complexes can still affect metabolism and uptake, introducing an unwelcome perturbation in cellular function.Bioorthogonality
The azide group is particularly bioorthogonal because it is extremely small (favorable for cell permeability and avoids perturbations), metabolically stable, and does not naturally exist in cells and thus has no competing biological side reactions. Although azides are not the most reactive 1,3-dipole available for reaction, they are preferred for their relative lack of side reactions and stability in typical synthetic conditions. Thealkyne
\ce
\ce
Acetylene
\ce
\ce
\ce
Propyne
\ce
\ce
\ce
\ce
1-Butyne
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and n ...
is not as small, but it still has the stability and orthogonality necessary for ''in vivo'' labeling. Cyclooctynes are traditionally the most common cycloalkyne for labeling studies, as they are the smallest stable alkyne ring.
Mechanism
 The reaction proceeds as a standard 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, a type of asynchronous, concerted
The reaction proceeds as a standard 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, a type of asynchronous, concerted pericyclic
In organic chemistry, a pericyclic reaction is the type of organic reaction wherein the transition state of the molecule has a cyclic geometry, the reaction progresses in a concerted fashion, and the bond orbitals involved in the reaction overlap ...
shift. The ambivalent nature of the 1,3-dipole should make the identification of an electrophilic or nucleophilic center on the azide impossible such that the direction of the cyclic electron flow is meaningless. However, computation has shown that the electron distribution amongst nitrogens causes the innermost nitrogen atom to bear the greatest negative charge.
Regioselectivity
Although the reaction produces a regioisomeric mixture of triazoles, the lack of regioselectivity in the reaction is not a major concern for most current applications. More regiospecific and less bioorthogonal requirements are best served by copper-catalyzed Huisgen cycloaddition, especially given the synthetic difficulty (compared to the addition of a terminal alkyne) of synthesizing a strained cyclooctyne.Development of cyclooctynes
 OCT was the first cyclooctyne developed for Cu-free click chemistry. While linear alkynes are unreactive at physiological temperatures, OCT was able readily react with azides in biological conditions while showing no toxicity. However, it was poorly water-soluble, and the kinetics were barely improved over the Staudinger ligation. ALO (aryl-less octyne) was developed to improve water solubility, but it still had poor kinetics.
Monofluorinated (MOFO) and difluorinated (DIFO) cyclooctynes were created to increase the rate through the addition of electron-withdrawing fluorine substituents at the
OCT was the first cyclooctyne developed for Cu-free click chemistry. While linear alkynes are unreactive at physiological temperatures, OCT was able readily react with azides in biological conditions while showing no toxicity. However, it was poorly water-soluble, and the kinetics were barely improved over the Staudinger ligation. ALO (aryl-less octyne) was developed to improve water solubility, but it still had poor kinetics.
Monofluorinated (MOFO) and difluorinated (DIFO) cyclooctynes were created to increase the rate through the addition of electron-withdrawing fluorine substituents at the propargylic
In organic chemistry, the propargyl group is a functional group of 2-propynyl with the structure . It is an alkyl group derived from propyne ().
The term propargylic refers to a saturated position ( ''sp''3-hybridized) on a molecular framework ...
position. Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reactiv ...
is a good electron-withdrawing group in terms of synthetic accessibility and biological inertness. In particular, it cannot form an electrophilic Michael acceptor
In organic chemistry, the Michael reaction or Michael addition is a reaction between a Michael donor (an enolate or other nucleophile) and a Michael acceptor (usually an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl) to produce a Michael adduct by creating a carbon ...
that may side-react with biological nucleophiles.
DIBO (dibenzocyclooctyne) was developed as a fusion to two aryl rings, resulting in very high strain and a decrease in distortion energies. It was proposed that biaryl substitution increases ring strain and provides conjugation with the alkyne to improve reactivity. Although calculations have predicted that mono-aryl substitution would provide an optimal balance between steric clash (with azide molecule) and strain, monoarylated products have been shown to be unstable.
BARAC (biarylazacyclooctynone) followed with the addition of an amide bond which adds an sp2-like center to increase rate by distortion. Amide resonance contributes additional strain without creating additional unsaturation which would lead to an unstable molecule. Additionally, the addition of a heteroatom into the cyclooctyne ring improves both solubility and pharmacokinetics of the molecule. BARAC has sufficient rate (and sensitivity) to the extent that washing away excess probe is unnecessary to reduce background. This makes it extremely useful in situations where washing is impossible as in real-time imaging or whole animal imaging. Although BARAC is extremely useful, its low stability requires that it must be stored at 0 °C, protected from light and oxygen.
Further adjustments variations on BARAC to produce DIBAC/ADIBO were performed to add distal ring strain and reduce sterics around the alkyne to further increase reactivity. Keto-DIBO, in which the hydroxyl group has been converted to a ketone, has a three-fold increase in rate due to a change in ring conformation. Attempts to make a difluorobenzocyclooctyne (DIFBO) were unsuccessful due to the instability.
Problems with DIFO with ''in vivo'' mouse studies illustrate the difficulty of producing bioorthogonal reactions. Although DIFO was extremely reactive in the labeling of cells, it performed poorly in mouse studies due to binding with serum albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins ...
. Hydrophobicity of the cyclooctyne promotes sequestration by membranes and serum proteins, reducing bioavailable concentrations. In response, DIMAC (dimethoxyazacyclooctyne) was developed to increase water solubility, polarity, and pharmacokinetics, although efforts in bioorthogonal labeling of mouse models is still in development.
Reactivity
Computational efforts have been vital in explaining the thermodynamics and kinetics of these cycloaddition reactions which has played a vital role in continuing to improve the reaction. There are two methods for activating alkynes without sacrificing stability: decrease transition state energy or decrease reactant stability. Decreasing reactant stability: Houk has proposed that differences in the energy (Ed ‡) required to distort the azide and alkyne into the transition state geometries control the barrier heights for the reaction. The activation energy (E ‡) is the sum of destabilizing distortions and stabilizing interactions (Ei ‡). The most significant distortion is in the azide functional group with lesser contribution of alkyne distortion. However, it is only the cyclooctyne that can be easily modified for higher reactivity. Calculated barriers of reaction for phenyl azide and
Decreasing reactant stability: Houk has proposed that differences in the energy (Ed ‡) required to distort the azide and alkyne into the transition state geometries control the barrier heights for the reaction. The activation energy (E ‡) is the sum of destabilizing distortions and stabilizing interactions (Ei ‡). The most significant distortion is in the azide functional group with lesser contribution of alkyne distortion. However, it is only the cyclooctyne that can be easily modified for higher reactivity. Calculated barriers of reaction for phenyl azide and acetylene
Acetylene (systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure f ...
(16.2 kcal/mol) versus cyclooctyne (8.0 kcal/mol) results in a predicted rate increase of 106. The cyclooctyne requires less distortion energy (1.4 kcal/mol versus 4.6 kcal/mol) resulting in a lower activation energy despite smaller interaction energy.
 Decreasing transition state energy: Electron withdrawing groups such as fluorine increase rate by decreasing LUMO energy and the HOMO-LUMO gap. This leads to a greater charge transfer from the azide to the fluorinated cyclooctyne in the transition state, increasing interaction energy (lower negative value) and overall activation energy. The lowering of the LUMO is the result of hyperconjugation between alkyne π donor orbitals and CF σ* acceptors. These interactions provide stabilization primarily in the transition state as a result of increased donor/acceptor abilities of the bonds as they distort. NBO calculations have shown that transition state distortion increases the interaction energy by 2.8 kcal/mol.
The hyperconjugation between out-of-plane π bonds is greater because the in-plane π bonds are poorly aligned. However, transition state bending allows the in-plane π bonds to have a more antiperiplanar arrangement that facilitates interaction. Additional hyperconjugative interaction energy stabilization is achieved through an increase in the electronic population of the σ* due to the forming CN bond. Negative hyperconjugation with the σ* CF bonds enhances this stabilizing interaction.
Decreasing transition state energy: Electron withdrawing groups such as fluorine increase rate by decreasing LUMO energy and the HOMO-LUMO gap. This leads to a greater charge transfer from the azide to the fluorinated cyclooctyne in the transition state, increasing interaction energy (lower negative value) and overall activation energy. The lowering of the LUMO is the result of hyperconjugation between alkyne π donor orbitals and CF σ* acceptors. These interactions provide stabilization primarily in the transition state as a result of increased donor/acceptor abilities of the bonds as they distort. NBO calculations have shown that transition state distortion increases the interaction energy by 2.8 kcal/mol.
The hyperconjugation between out-of-plane π bonds is greater because the in-plane π bonds are poorly aligned. However, transition state bending allows the in-plane π bonds to have a more antiperiplanar arrangement that facilitates interaction. Additional hyperconjugative interaction energy stabilization is achieved through an increase in the electronic population of the σ* due to the forming CN bond. Negative hyperconjugation with the σ* CF bonds enhances this stabilizing interaction.
Regioselectivity
Although regioselectivity is not a great issue in the current imaging applications of copper-free click chemistry, it is an issue that prevents future applications in fields such as drug design or peptidomimetics. Currently most cyclooctynes react to form regioisomeric mixtures. Computation analysis has found that while gas phase regioselectivity is calculated to favor 1,5 addition over 1,4 addition by up to 2.9 kcal/mol in activation energy, solvation corrections result in the same energy barriers for both regioisomers. While the 1,4 isomer in the cycloaddition of DIFO is disfavored by its larger dipole moment, solvation stabilizes it more strongly than the 1,5 isomer, eroding regioselectivity. Symmetrical cyclooctynes such as BCN (bicyclo .1.0onyne) form a single regioisomer upon cycloaddition and may serve to address this problem in the future.
Symmetrical cyclooctynes such as BCN (bicyclo .1.0onyne) form a single regioisomer upon cycloaddition and may serve to address this problem in the future.
Applications
The most widespread application of copper-free click chemistry is in biological imaging in live cells or animals using an azide-tagged biomolecule and a cyclooctyne bearing an imaging agent. Fluorescent keto and oxime variants of DIBO are used in fluoro-switch click reactions in which the fluorescence of the cyclooctyne is quenched by the triazole that forms in the reaction. On the other hand,coumarin
Coumarin () or 2''H''-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula . Its molecule can be described as a benzene molecule with two adjacent hydrogen atoms replaced by a lactone-like chain , forming a second six-membered ...
-conjugated cyclooctynes such as coumBARAC have been developed such that the alkyne suppresses fluorescence while triazole formation increases the fluorescence quantum yield The quantum yield (Φ) of a radiation-induced process is the number of times a specific event occurs per photon absorbed by the system.
Applications
Fluorescence spectroscopy
The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the ratio of the numb ...
by ten-fold.
 Spatial and temporal control of substrate labeling has been investigated using photoactivatable cyclooctynes. This allows equilibration of the alkyne prior to reaction in order to reduce artifacts as a result of concentration gradients. Masked cyclooctynes are unable to react with azides in the dark but become reactive alkynes upon irradiation with light.
Spatial and temporal control of substrate labeling has been investigated using photoactivatable cyclooctynes. This allows equilibration of the alkyne prior to reaction in order to reduce artifacts as a result of concentration gradients. Masked cyclooctynes are unable to react with azides in the dark but become reactive alkynes upon irradiation with light.
 Copper-free click chemistry is being explored for use in synthesizing
Copper-free click chemistry is being explored for use in synthesizing PET imaging
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, ...
agents which must be made quickly with high purity and yield in order to minimize isotopic decay before the compounds can be administered. Both the high rate constants and the bioorthogonality of SPAAC are amenable to PET chemistry.
A company called Shasqi
Shasqi is a biotechnology company based in San Francisco, California. The company is known for developing click chemistry-based therapies to treat cancer. Their targeting approach is designed to activate powerful cancer therapies at the desired ...
is applying click chemistry to cancer therapeutics and evaluating the lead candidate in cancer patients in a Phase 2 trial.
Other bioorthogonal reactions
Nitrone dipole cycloaddition
Copper-free click chemistry has been adapted to use nitrones as the 1,3-dipole rather than azides and has been used in the modification of peptides. This cycloaddition between a nitrone and a cyclooctyne forms N-alkylated isoxazolines. The reaction rate is enhanced by water and is extremely fast with second order rate constants ranging from 12 to 32 M−1•s−1, depending on the substitution of the nitrone. Although the reaction is extremely fast, it faces problems in incorporating the nitrone into biomolecules through metabolic labeling. Labeling has only been achieved through post-translational peptide modification.
This cycloaddition between a nitrone and a cyclooctyne forms N-alkylated isoxazolines. The reaction rate is enhanced by water and is extremely fast with second order rate constants ranging from 12 to 32 M−1•s−1, depending on the substitution of the nitrone. Although the reaction is extremely fast, it faces problems in incorporating the nitrone into biomolecules through metabolic labeling. Labeling has only been achieved through post-translational peptide modification.
Norbornene cycloaddition
1,3 dipolar cycloadditions have been developed as a bioorthogonal reaction using anitrile oxide
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The prefix ''cyano-'' is used interchangeably with the term ''nitrile'' in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including meth ...
as a 1,3-dipole and a norbornene
Norbornene or norbornylene or norcamphene is a highly strained bridged cyclic hydrocarbon. It is a white solid with a pungent sour odor. The molecule consists of a cyclohexene ring with a methylene bridge between carbons 1 and 4. The molecule carr ...
as a dipolarophile. Its primary use has been in labeling DNA and RNA in automated oligonucleotide synthesizers, and polymer crosslinking in the presence of living cells.
 Norbornenes were selected as dipolarophiles due to their balance between strain-promoted reactivity and stability. The drawbacks of this reaction include the cross-reactivity of the nitrile oxide due to strong electrophilicity and slow reaction kinetics.
Norbornenes were selected as dipolarophiles due to their balance between strain-promoted reactivity and stability. The drawbacks of this reaction include the cross-reactivity of the nitrile oxide due to strong electrophilicity and slow reaction kinetics.
Oxanorbornadiene cycloaddition
The oxanorbornadiene cycloaddition is a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition followed by a retro-Diels Alder Diels is the last name of several people:
* Rudolf Diels (1900–1957), German politician
* Otto Diels (1876–1954), German scientist noted for his work on the Diels–Alder reaction
* Ludwig Diels
Dr. Friedrich Ludwig Emil Diels (24 September 1 ...
reaction to generate a triazole-linked conjugate with the elimination of a furan molecule. Preliminary work has established its usefulness in peptide labeling experiments, and it has also been used in the generation of SPECT
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, or less commonly, SPET) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is ...
imaging compounds. More recently, the use of an oxanorbornadiene was described in a catalyst-free room temperature "iClick" reaction, in which a model amino acid is linked to the metal moiety, in a novel approach to bioorthogonal reactions.
 Ring strain and electron deficiency in the oxanorbornadiene increase reactivity towards the cycloaddition rate-limiting step. The retro-Diels Alder reaction occurs quickly afterwards to form the stable 1,2,3 triazole. Problems include poor tolerance for substituents which may change electronics of the oxanorbornadiene and low rates (second order rate constants on the order of 10−4).
Ring strain and electron deficiency in the oxanorbornadiene increase reactivity towards the cycloaddition rate-limiting step. The retro-Diels Alder reaction occurs quickly afterwards to form the stable 1,2,3 triazole. Problems include poor tolerance for substituents which may change electronics of the oxanorbornadiene and low rates (second order rate constants on the order of 10−4).
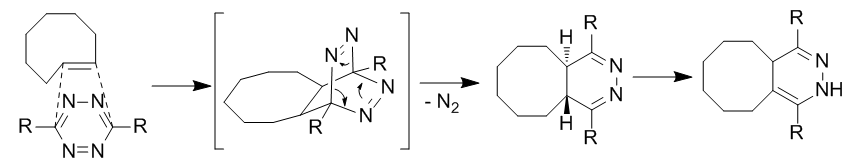
Tetrazine ligation
The tetrazine ligation is the reaction of a trans-cyclooctene and an s- tetrazine in an inverse-demand Diels Alder reaction followed by a retro-Diels Alder reaction to eliminate nitrogen gas. The reaction is extremely rapid with a second order rate constant of 2000 M−1–s−1 (in 9:1 methanol/water) allowing modifications of biomolecules at extremely low concentrations. Based on computational work by Bach, the strain energy for Z-cyclooctenes is 7.0 kcal/mol compared to 12.4 kcal/mol for cyclooctane due to a loss of two transannular interactions. E-cyclooctene has a highly twisted double bond resulting in a strain energy of 17.9 kcal/mol. As such, the highly strained trans-cyclooctene is used as a reactive dienophile. The diene is a 3,6-diaryl-s-tetrazine which has been substituted in order to resist immediate reaction with water. The reaction proceeds through an initial cycloaddition followed by a reverse Diels Alder to eliminate N2 and prevent reversibility of the reaction.
Not only is the reaction tolerant of water, but it has been found that the rate increases in aqueous media. Reactions have also been performed using norbornenes as dienophiles at second order rates on the order of 1 M−1•s−1 in aqueous media. The reaction has been applied in labeling live cells and polymer coupling.
Based on computational work by Bach, the strain energy for Z-cyclooctenes is 7.0 kcal/mol compared to 12.4 kcal/mol for cyclooctane due to a loss of two transannular interactions. E-cyclooctene has a highly twisted double bond resulting in a strain energy of 17.9 kcal/mol. As such, the highly strained trans-cyclooctene is used as a reactive dienophile. The diene is a 3,6-diaryl-s-tetrazine which has been substituted in order to resist immediate reaction with water. The reaction proceeds through an initial cycloaddition followed by a reverse Diels Alder to eliminate N2 and prevent reversibility of the reaction.
Not only is the reaction tolerant of water, but it has been found that the rate increases in aqueous media. Reactions have also been performed using norbornenes as dienophiles at second order rates on the order of 1 M−1•s−1 in aqueous media. The reaction has been applied in labeling live cells and polymer coupling.
+1Cycloaddition
This isocyanide click reaction is a +1cycloaddition followed by a retro-Diels Alder elimination of N2. The reaction proceeds with an initial +1cycloaddition followed by a reversion to eliminate a thermodynamic sink and prevent reversibility. This product is stable if a tertiary amine or isocyanopropanoate is used. If a secondary or primary isocyanide is used, the produce will form an imine which is quickly hydrolyzed.
Isocyanide is a favored chemical reporter due to its small size, stability, non-toxicity, and absence in mammalian systems. However, the reaction is slow, with second order rate constants on the order of 10−2 M−1•s−1.
The reaction proceeds with an initial +1cycloaddition followed by a reversion to eliminate a thermodynamic sink and prevent reversibility. This product is stable if a tertiary amine or isocyanopropanoate is used. If a secondary or primary isocyanide is used, the produce will form an imine which is quickly hydrolyzed.
Isocyanide is a favored chemical reporter due to its small size, stability, non-toxicity, and absence in mammalian systems. However, the reaction is slow, with second order rate constants on the order of 10−2 M−1•s−1.
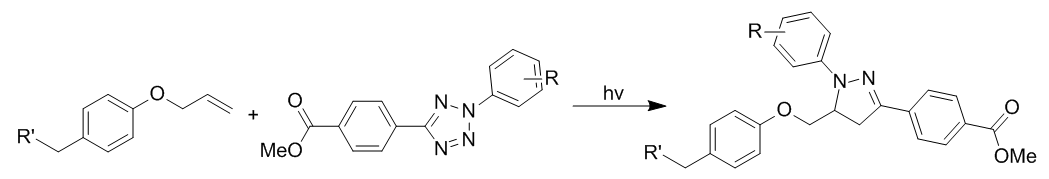
Tetrazole photoclick chemistry
Photoclick chemistry utilizes a photoinduced cycloelimination to release N2. This generates a short-lived 1,3 nitrile imine intermediate via the loss of nitrogen gas, which undergoes a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition with an alkene to generate pyrazoline cycloadducts. Photoinduction takes place with a brief exposure to light (wavelength is tetrazole-dependent) to minimize photodamage to cells. The reaction is enhanced in aqueous conditions and generates a single regioisomer.
The transient nitrile imine is highly reactive for 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition due to a bent structure which reduces distortion energy. Substitution with electron-donating groups on phenyl rings increases the HOMO energy, when placed on the 1,3 nitrile imine and increases the rate of reaction.
Advantages of this approach include the ability to spatially or temporally control reaction and the ability to incorporate both alkenes and tetrazoles into biomolecules using simple biological methods such as genetic encoding. Additionally, the tetrazole can be designed to be fluorogenic in order to monitor progress of the reaction.
Photoinduction takes place with a brief exposure to light (wavelength is tetrazole-dependent) to minimize photodamage to cells. The reaction is enhanced in aqueous conditions and generates a single regioisomer.
The transient nitrile imine is highly reactive for 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition due to a bent structure which reduces distortion energy. Substitution with electron-donating groups on phenyl rings increases the HOMO energy, when placed on the 1,3 nitrile imine and increases the rate of reaction.
Advantages of this approach include the ability to spatially or temporally control reaction and the ability to incorporate both alkenes and tetrazoles into biomolecules using simple biological methods such as genetic encoding. Additionally, the tetrazole can be designed to be fluorogenic in order to monitor progress of the reaction.
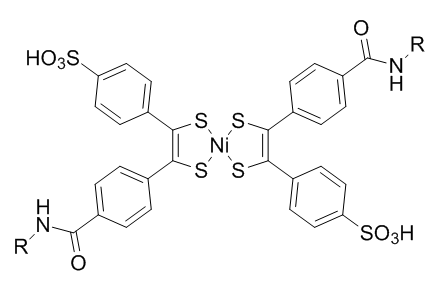
Quadricyclane ligation
The quadricyclane ligation utilizes a highly strained quadricyclane to undergo +2+2cycloaddition with π systems. Quadricyclane is abiotic, unreactive with biomolecules (due to complete saturation), relatively small, and highly strained (~80 kcal/mol). However, it is highly stable at room temperature and in aqueous conditions at physiological pH. It is selectively able to react with electron-poor π systems but not simple alkenes, alkynes, or cyclooctynes.
Bis(dithiobenzil)nickel(II) was chosen as a reaction partner out of a candidate screen based on reactivity. To prevent light-induced reversion to norbornadiene, diethyldithiocarbamate is added to chelate the nickel in the product.
Quadricyclane is abiotic, unreactive with biomolecules (due to complete saturation), relatively small, and highly strained (~80 kcal/mol). However, it is highly stable at room temperature and in aqueous conditions at physiological pH. It is selectively able to react with electron-poor π systems but not simple alkenes, alkynes, or cyclooctynes.
Bis(dithiobenzil)nickel(II) was chosen as a reaction partner out of a candidate screen based on reactivity. To prevent light-induced reversion to norbornadiene, diethyldithiocarbamate is added to chelate the nickel in the product.
 These reactions are enhanced by aqueous conditions with a second order rate constant of 0.25 M−1•s−1. Of particular interest is that it has been proven to be bioorthogonal to both oxime formation and copper-free click chemistry.
These reactions are enhanced by aqueous conditions with a second order rate constant of 0.25 M−1•s−1. Of particular interest is that it has been proven to be bioorthogonal to both oxime formation and copper-free click chemistry.
Uses
Bioorthogonal chemistry is an attractive tool for pretargeting experiments innuclear imaging
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitting ...
and radiotherapy.
References
{{Branches of chemistry Chemical reactions