Battle of Nicopolis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Nicopolis took place on 25 September 1396 and resulted in the rout of an allied Crusader army (assisted by the Venetian navy) at the hands of an Ottoman force, raising the siege of the Danubian fortress of
Nicopolis
Nicopolis () or Actia Nicopolis was the capital city of the Roman province of Epirus (Roman province), Epirus. Its site, near Preveza, Greece, still contains impressive ruins. The city was founded in 29 BC by Octavian in commemoration of his ...
and leading to the end of the Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1422. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II ...
. It is often referred to as the Crusade of Nicopolis as it was one of the last big Crusades of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, together with the Crusade of Varna in 1443–1444. By their victory at Nicopolis, the Turks discouraged the formation of European coalitions against them. They maintained their pressure on Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, tightened their control over the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, and became a greater threat to Central Europe.
Background
There were many minor crusades in the 14th century, undertaken by individual kings or knights. Most recently there had been a failed crusade againstTunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
in 1390, and there was ongoing warfare in northern Europe along the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
coast. After the Battle of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan Murad I. It was one of the largest battles of the Late Middl ...
in 1389, the Ottomans had conquered most of the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
and had reduced the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
to the area immediately surrounding Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, which they blockaded from 1394 on.
In 1393 the Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
n tsar Ivan Shishman had lost Nicopolis — his temporary capital — to the Ottomans, while his brother, Ivan Stratsimir, still held Vidin
Vidin (, ) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as of the Metropolitan of Vidin (since ...
but had been reduced to an Ottoman vassal. In the eyes of the Bulgarian boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Bulgaria, Kievan Rus' (and later Russia), Moldavia and Wallachia (and later Romania), Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. C ...
s, despots, and other independent Balkan rulers, the crusade was a great chance to reverse the course of the Ottoman conquest and take back the Balkans from Islamic rule. In addition, the front line between Islam and Christianity had been moving slowly towards the Kingdom of Hungary. The Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
was now the frontier between the two religions in Eastern Europe, and the Hungarians were in danger of being attacked themselves. The Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
feared that Ottoman control of the Balkan peninsula, which included Venetian territories like parts of Morea
Morea ( or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used by the Principality of Achaea, the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the O ...
and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, would reduce their influence over the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
, Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea (, ; or , ; , ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, ...
, and Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
. The Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
, on the other hand, feared that if the Ottomans were to gain control over River Danube and the Turkish Straits
The Turkish Straits () are two internationally significant waterways in northwestern Turkey. The Straits create a series of international passages that connect the Aegean and Mediterranean seas to the Black Sea. They consist of the Dardanelles ...
, they would eventually obtain a monopoly over the trade routes between Europe and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, where the Genoese had many important colonies like Caffa, Sinop, and Amasra
Amasra (from Greek language, Greek Amastris Ἄμαστρις, ''gen''. Ἀμάστριδος) is a small Black Sea port town in the Bartın Province, Turkey. It is the seat of Amasra District.Galata
Galata is the former name of the Karaköy neighbourhood in Istanbul, which is located at the northern shore of the Golden Horn. The district is connected to the historic Fatih district by several bridges that cross the Golden Horn, most nota ...
, located at the north of the Golden Horn
The Golden Horn ( or ) is a major urban waterway and the primary inlet of the Bosphorus in Istanbul, Turkey. As a natural estuary that connects with the Bosphorus Strait at the point where the strait meets the Sea of Marmara, the waters of the ...
in Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, to which Bayezid had laid siege in 1395.
In 1394, Pope Boniface IX
Pope Boniface IX (; ; c. 1350 – 1 October 1404, born Pietro Tomacelli) was head of the Catholic Church from 2 November 1389 to his death, in October 1404. He was the second Roman pope during the Western Schism.Richard P. McBrien, ''Lives of t ...
proclaimed a new crusade against the Turks, although the Western Schism
The Western Schism, also known as the Papal Schism, the Great Occidental Schism, the Schism of 1378, or the Great Schism (), was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 20 September 1378 to 11 November 1417, in which bishops residing ...
had split the papacy in two, with rival popes at Avignon
Avignon (, , ; or , ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rhône, the Communes of France, commune had a ...
and Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, and the days when a pope had the authority to call a crusade were long past.
The two decisive factors in the formation of the last crusade were the ongoing Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
between Richard II's England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and Charles VI's France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and the support of Philip II, Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy () was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by the Crown lands of France, French crown in 1477, and later by members of the House of Habsburg, including Holy Roman E ...
. In 1389, the war had ground to one of its periodic truces. Further, in March 1395, Richard II proposed a marriage between himself and Charles VI's daughter Isabella in the interests of peace and the two kings met in October 1396 on the borders of Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a French port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Calais is the largest city in Pas-de-Calais. The population of the city proper is 67,544; that of the urban area is 144,6 ...
to agree to the union and agree to lengthen the Truce of Leulinghem
The Truce of Leulinghem was a truce agreed to by Richard II of England, Richard II's kingdom of England and its allies, and Charles VI of France, Charles VI's kingdom of France and its allies, on 18 July 1389, ending the Caroline War of the Hund ...
. The support of Burgundy, among the most powerful of the French nobles, was also vital. In 1391, Burgundy, trying to decide between sending a crusade to either Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
or Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, sent his envoy Guy de La Trémoille to Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
and Hungary to evaluate the situation. Burgundy originally envisioned a crusade led by himself and the Dukes of Orléans
Orléans (,"Orleans"
(US) and Lancaster, though none would join the eventual crusade. It was very unlikely that defense against the Turks was considered a particularly important goal of the crusade. Burgundy's interest in sponsoring the crusade was in increasing his and his house's prestige and power and, historian Barbara Tuchman notes, "since he was the prince of self-magnification, the result was that opulent display became the dominant theme; plans, logistics, intelligence about the enemy came second, if at all."Tuchman, 545 In 1394, Burgundy extracted 120,000 livres from
 From France, it was said about 5,000 knights and squires joined, and were accompanied by 6,000 archers and foot soldiers drawn from the best volunteer and mercenary companies; totalling some 11,000 men. Next in importance were the
From France, it was said about 5,000 knights and squires joined, and were accompanied by 6,000 archers and foot soldiers drawn from the best volunteer and mercenary companies; totalling some 11,000 men. Next in importance were the
 The crusade set forth from
The crusade set forth from 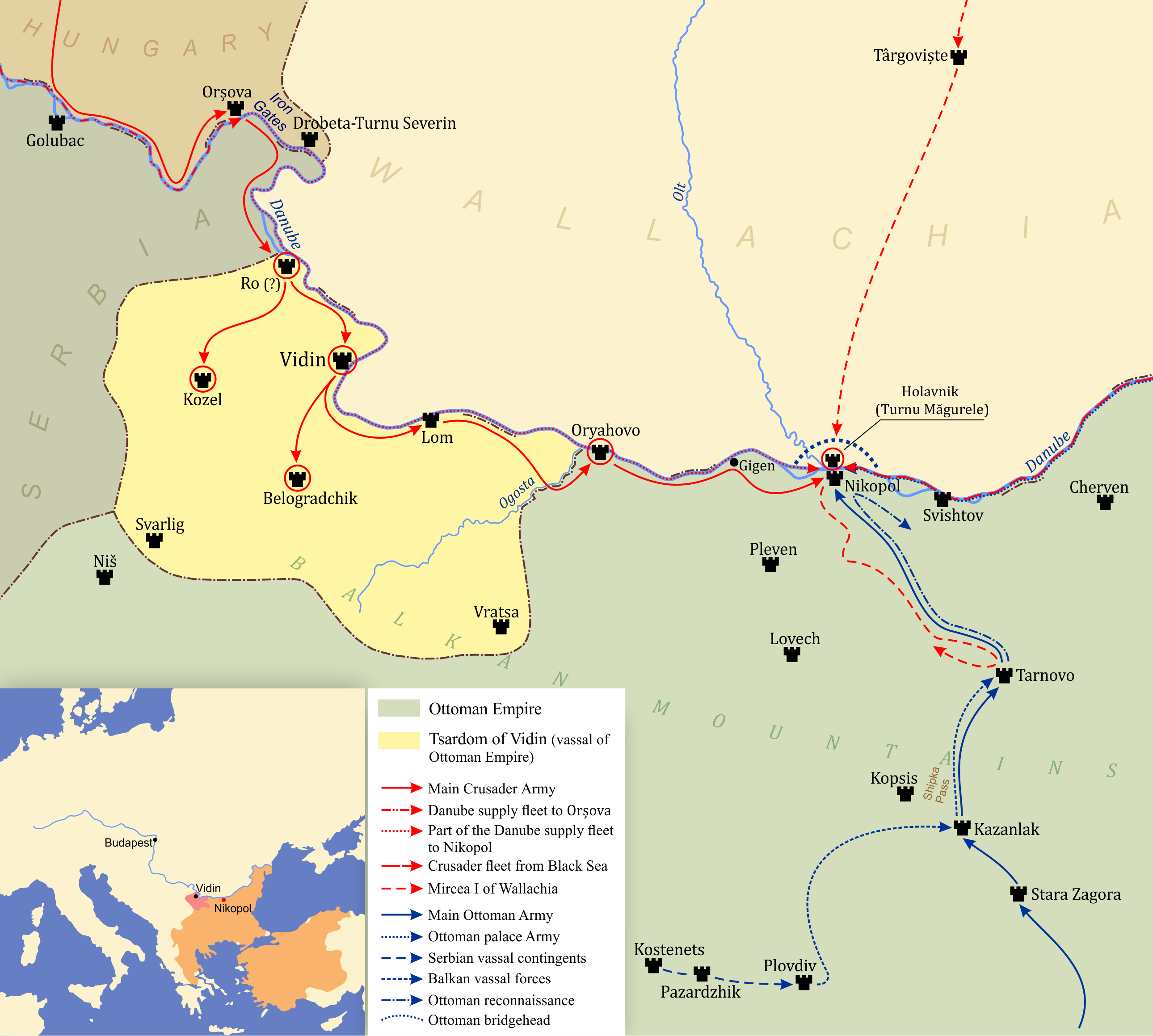 Coucy was not with the crusader body as it traveled, having been detached on a diplomatic mission to
Coucy was not with the crusader body as it traveled, having been detached on a diplomatic mission to
 Once the leaders had arrived, strategy had to be coordinated with Philibert de Naillac, Master of the Knights Hospitaller, and representatives of the Venetian fleet. Forty-four Venetian ships had carried the Hospitallers from Rhodes through the Aegean into the
Once the leaders had arrived, strategy had to be coordinated with Philibert de Naillac, Master of the Knights Hospitaller, and representatives of the Venetian fleet. Forty-four Venetian ships had carried the Hospitallers from Rhodes through the Aegean into the
 The timeline of events is hazy, but it appears that as the French were advancing up the slope, sipahis were sweeping down along the flanks in an envelopment. Accounts tell of the Hungarians and other nationalities in confused combat on the plain and of a stampede of riderless horses, which Tuchman speculates pulled free from their tethers, at the sight of which the
The timeline of events is hazy, but it appears that as the French were advancing up the slope, sipahis were sweeping down along the flanks in an envelopment. Accounts tell of the Hungarians and other nationalities in confused combat on the plain and of a stampede of riderless horses, which Tuchman speculates pulled free from their tethers, at the sight of which the
History of War: Battle of Nicopolis, 25 September 1396
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nicopolis Conflicts in 1396 Battles involving Hungary Battles involving Wallachia Battles involving Bohemia Battles of the Crusades Battles involving the Ottoman Empire 1396 in Europe Battles of the Ottoman–Hungarian Wars Battles involving Serbia in the Middle Ages Battles involving the Second Bulgarian Empire 14th century in Bulgaria 14th-century military history of Croatia Battles involving the Knights Hospitaller Military history of Bulgaria History of Pleven Province 1390s in the Ottoman Empire Massacres committed by the Ottoman Empire Death marches Battles involving the Holy Roman Empire Battles of the Crusade of Varna Prisoner of war massacres Bayezid I
(US) and Lancaster, though none would join the eventual crusade. It was very unlikely that defense against the Turks was considered a particularly important goal of the crusade. Burgundy's interest in sponsoring the crusade was in increasing his and his house's prestige and power and, historian Barbara Tuchman notes, "since he was the prince of self-magnification, the result was that opulent display became the dominant theme; plans, logistics, intelligence about the enemy came second, if at all."Tuchman, 545 In 1394, Burgundy extracted 120,000 livres from
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, sufficient to begin preparations for a crusade, and in January 1395 sent word to King Sigismund of Hungary that an official request to the King of France would be accepted.
In August, Sigismund's delegation of four knights and a bishop arrived in the court of Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
to paint a description of how "40,000" Turks were despoiling and imperiling Christian lands and beg, on Sigismund of Hungary's behalf, for help. Charles VI, having secured a peace with England through the marriage of his daughter, was able to reply that it was his responsibility to protect Christianity and punish Sultan Bayezid. French nobility responded enthusiastically to the declaration; Philip of Artois, Count of Eu
Philip of Artois (1358 – 16 June 1397), sometimes Philip I, son of John of Artois, Count of Eu, and Isabeau of Melun, was Count of Eu from 1387 until his death, succeeding his brother Robert.
Philip was an ignoble and hotheaded soldier. ...
, the Constable of France
The Constable of France (, from Latin for 'count of the stables') was lieutenant to the King of France, the first of the original five Great Officers of the Crown (along with seneschal, chamberlain, butler, and chancellor) and the commander-in ...
, and Jean Le Maingre
Jean II Le Maingre (Old French: Jehan le Meingre), also known as Boucicaut (28 August 1366 – 21 June 1421), was a French knight and military leader. Renowned for his military skill and embodiment of chivalry, he was made a marshal of France.
...
, the Marshal of France
Marshal of France (, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to General officer, generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished (1793–1804) ...
, declared participation in the crusade the duty of every "man of valor". Another major participant was John I John I may refer to:
People
Religious figures
* John I (bishop of Jerusalem)
* John Chrysostom (349 – c. 407), Patriarch of Constantinople
* John I of Antioch (died 441)
* Pope John I of Alexandria, Coptic Pope from 496 to 505
* Pope John I, P ...
, future Duke of Burgundy
Burgundy ( ; ; Burgundian: ''Bregogne'') is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. ...
and Count of Nevers at the time. He was one of the principal leaders of the French forces sent to aid in the war. John's bravery during the battle earned him the cognomen Fearless (''Sans-Peur'').
Strength of forces
According to theChronica Hungarorum
''Chronica Hungarorum'' (Latin for "Chronicle of the Hungarians") (), also known as the Thuróczy Chronicle, is the title of a 15th-century Latin-language Hungarian chronicle written by Johannes de Thurocz, Johannes Thuróczy by compiling seve ...
, King Sigismund of Hungary was so delighted at the sight of the large army gathered around him in Buda
Buda (, ) is the part of Budapest, the capital city of Hungary, that lies on the western bank of the Danube. Historically, “Buda” referred only to the royal walled city on Castle Hill (), which was constructed by Béla IV between 1247 and ...
, he exclaimed in joy: "Who would be so bold as to dare to resist us? If the enormous weight of the sky were to fall on us, with spears that we carry, we would also hold it up so that no harm would come to us."
The number of combatants is heavily contested in historical accounts. Historian Tuchman notes the Battle of Nicopolis was considered so significant that the number of combatants given by medieval chroniclers ranges as high as 400,000, with each side insisting that the enemy outnumbered them two-to-one, which for the crusaders offered some solace for their defeat and for the Turks increased the glory of their victory. The oft-given figure of 100,000 crusaders is dismissed by Tuchman, who claims that 100,000 men would have taken a month to cross the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
at Iron Gate, while the crusaders took eight days.Tuchman, 554
The closest record to a first-person account was made by Johann Schiltberger
Johann (Hans) Schiltberger (1380) was a German traveller and writer. He was born of a noble family, probably at Hollern near Lohhof halfway between Munich and Freising.
Travels
Schiltberger joined the suite of Lienhart Richartinger in 1394, ...
, a German follower of a Bavarian noble, who witnessed the battle at the age of 16 and was captured and enslaved for 30 years by the Turks before returning home, at which time he wrote a narrative of the battle estimating the crusader strength at the final battle at 17,000, though he also overestimated Turkish forces as a wildly inflated 200,000. German historians of the 19th century attempting to estimate the combatants on each side came to the figures of about 7,500–15,000 Christians and about 12,000–20,000 Turks, while noting that, from the point of logistics, it would have been impossible for the countryside around Nicopolis to have supplied food and fodder for scores of thousands of men and horses. (Medieval armies acquired supplies by taking them from the surrounding area as they marched, as opposed to using the supply lines of modern armies.)
Composition of crusader forces
 From France, it was said about 5,000 knights and squires joined, and were accompanied by 6,000 archers and foot soldiers drawn from the best volunteer and mercenary companies; totalling some 11,000 men. Next in importance were the
From France, it was said about 5,000 knights and squires joined, and were accompanied by 6,000 archers and foot soldiers drawn from the best volunteer and mercenary companies; totalling some 11,000 men. Next in importance were the Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there ...
of Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
, who were the standard bearers of Christianity in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
since the decline of Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
and Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
. Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
supplied a naval fleet for supporting action, while Hungarian envoys encouraged German princes of the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
, Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
, Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
, and other parts of the empire to join. French heralds had proclaimed the crusade in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, Navarre
Navarre ( ; ; ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre, is a landlocked foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Autonomous Community, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and New Aquitaine in France. ...
, and Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, from which individuals came to join.Tuchman, 548
The Italian city-states were too much engaged in their customary violent rivalries to participate, and the widely reported and acclaimed English participation never actually occurred. The report of 3,000 English knights comes from contemporary Antonio Fiorentino, and was taken as fact by historian Aziz S. Atiya and others following him. A thousand knights would have actually amounted to "four to six thousand men and at least twice as many horses", counting foot-soldiers and other retainers. However, there are no records of financial arrangements being made in England to send a force abroad, nor of any royal preparation needed to organize and dispatch such a force. Reports of Henry of Bolingbroke or other "son of the Duke of Lancaster" leading an English contingent must be false since the presence of Henry and every other such son, as well as almost every other significant noble in the land, is recorded at the King's wedding five months ''after'' the crusade's departure. Atiya also thought that the invocation of St. George
Saint George (;Geʽez: ጊዮርጊስ, , ka, გიორგი, , , died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to holy tradition, he was a soldier in the ...
as a war cry at Nicopolis
Nicopolis () or Actia Nicopolis was the capital city of the Roman province of Epirus (Roman province), Epirus. Its site, near Preveza, Greece, still contains impressive ruins. The city was founded in 29 BC by Octavian in commemoration of his ...
signified the presence of English soldiers, for whom George was a patron saint; but Froissart
Jean Froissart ( Old and Middle French: ''Jehan''; sometimes known as John Froissart in English; – ) was a French-speaking medieval author and court historian from the Low Countries who wrote several works, including ''Chronicles'' and ''Meli ...
, who mentions this, claims that the cry was made by the French knight Philippe d'Eu. Furthermore, there was no collection of ransom money in England to pay for captives, as there was in every other country that had sent men to the battle. Sporadic mention in contemporary accounts of the presence of "English" may be attributed to Knights Hospitaller of the English langue subgrouping, who joined their comrades for the crusade after leaving Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
(where the Hospitallers were based at the time) and sailing up the Danube. Possible reasons for the English absence include the increasing tension between the King and the Duke of Gloucester, which may have convinced the two that they had best keep their supporters close, and the antipathy caused by the long war between the English and French, resulting in the English refusing to consider putting themselves under a French-led crusade, regardless of the recently concluded peace.
Nevertheless, obviously inflated figures continue to be repeated. These include 6,000–12,000 Hungarians,GrantMadden about 11,000 French, English and Burgundian troops, about 12,000 Wallachians led by Mircea cel Batran (Mircea the Elder
Mircea the Elder (, ; 1355 – 31 January 1418) was the Voivode of Wallachia from 1386 until his death in 1418. He was the son of Radu I of Wallachia and brother of Dan I of Wallachia, after whose death he inherited the throne.
After the dea ...
) the Prince of Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
, about 6,000 Germans and nearly 15,000 Dutch, Bohemian, Spanish, Italian, Polish, Bulgarian, Scottish and Swiss troops on the land, with the naval support of Venice, Genoa and the Knights of St. John. These result in a figure of about 47,000–49,000 in total; possibly up to 120,000 or 130,000 according to numerous sources, including the Ottoman historian Şükrullah who, in the 1460s, gives the figure of the crusader army as 130,000 in his ''Behçetu't-Tevârih''.
Composition of Ottoman forces
The strength of the Ottoman forces is also estimated at 15–20,000; but inflated figures are common here as well. Numerous sources provide estimates of the size of the army as up to 60,000 including the Ottoman historian Şükrullah, who, writing in the 1460s, gives the figure of the Ottoman army as 60,000 in his ''Behçetu't-Tevârih''; alternately described as roughly half of the Crusader army. The Ottoman force also included 1,500 Serbian heavy cavalry knights under the command of PrinceStefan Lazarević
Stefan Lazarević ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Лазаревић, 1377 – 19 July 1427), also known as Stefan the Tall (), was a Serbian ruler as prince (1389–1402) and Despot (court title), despot (1402–1427). He was also a diplomat, legislat ...
, who was Sultan Bayezid's brother-in-law and vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
since the Battle of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan Murad I. It was one of the largest battles of the Late Middl ...
in 1389.
Journey
While Philip,Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy () was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by the Crown lands of France, French crown in 1477, and later by members of the House of Habsburg, including Holy Roman E ...
, had originally planned to lead the crusade along with John of Gaunt
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (6 March 1340 – 3 February 1399), was an English royal prince, military leader and statesman. He was the fourth son (third surviving) of King Edward III of England, and the father of King Henry IV. Because ...
and Louis of Orleans, all three withdrew, claiming that the peace negotiations with England required their presence, though perhaps also because none dared leave the vicinity of the throne if their chief rivals stayed. However, Burgundy retained control of the enterprise he was funding by naming 24-year-old John, Count of Nevers, the Duke's eldest son, for nominal command. Burgundy, perhaps recognizing that his son, as well as Constable d'Eu and Marshal Boucicaut, who were both under 35, lacked the necessary experience, summoned Enguerrand VII, Lord of Coucy, the most experienced warrior and statesman of the realm, and prevailed on him to be "chief counselor" to Nevers during the crusade. The ambiguity of the crusaders' command structure would prove to be crucial in the outcome. While Nevers was given a long list of "counselors", as well as another list of prominent French lords on the crusade with whom Nevers could consult "when it seemed good to him", the concept of unity of command
Command may refer to:
Computing
* Command (computing), a statement in a computer language
* command (Unix), a Unix command
* COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS
* Command key, a modifier key on A ...
was not yet embraced by medieval warriors.Tuchman, 549 Rules of discipline for the crusade were decreed at a War Council on 28 March 1396, which included the final provision, "Item, that n battlethe Count and his company claim the ''avante garde''", revealing that the chivalric code continued to require knights to prove their valor by leading the charge.Tuchman, 550
To Buda
 The crusade set forth from
The crusade set forth from Dijon
Dijon (, ; ; in Burgundian language (Oïl), Burgundian: ''Digion'') is a city in and the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Côte-d'Or Departments of France, department and of the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté Regions of France, region in eas ...
on 30 April 1396, heading to Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
by way of Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
via the upper Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
, from where they used river transport to join with Sigismund in Buda
Buda (, ) is the part of Budapest, the capital city of Hungary, that lies on the western bank of the Danube. Historically, “Buda” referred only to the royal walled city on Castle Hill (), which was constructed by Béla IV between 1247 and ...
. From there the crusader goals, though lacking details of planning, were to expel the Turks from the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
and then go to the aid of Constantinople, cross the Hellespont
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey t ...
, and march through Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
to liberate Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
and the Holy Sepulchre, before returning in triumph to Europe by sea. Arrangements were made for a fleet of Venetian vessels to blockade the Turks in the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara, also known as the Sea of Marmora or the Marmara Sea, is a small inland sea entirely within the borders of Turkey. It links the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea via the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits, separating Turkey's E ...
and for the Venetians to sail up the Danube to meet the crusaders in Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
in July.
 Coucy was not with the crusader body as it traveled, having been detached on a diplomatic mission to
Coucy was not with the crusader body as it traveled, having been detached on a diplomatic mission to Gian Galeazzo Visconti
Gian Galeazzo Visconti (16 October 1351 – 3 September 1402), was the first duke of Duchy of Milan, Milan (1395) and ruled that late-medieval city just before the dawn of the Renaissance. He also ruled Lombardy jointly with his uncle Bernabò V ...
, the Duke of Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
. Furious at French political maneuvering that had removed Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
from his influence, Gian Galeazzo had been attempting to stop the transfer of Genoese sovereignty to France and Coucy was dispatched to warn him that France would consider further interference a hostile act. The quarrel was more than political. Valentina Visconti, the wife of the Duke of Orleans and Gian Galeazzo's beloved daughter, had been exiled from Paris due to the machinations of Queen Isabeau the same month as the departure of the crusade. The Duke of Milan threatened to send knights to defend his daughter's honor but, in the wake of the disaster at Nicopolis, it was widely believed that he had relayed intelligence to Bayezid I of crusader troop movements. There is no firm evidence of this and it is likely that Gian Galeazzo became a scapegoat after the fact due to the existing animosity with France, though there remains the possibility that the Duke of Milan, who had murdered his own uncle to ensure his own power, did in fact betray the crusaders. Coucy, his diplomatic mission complete and accompanied by Henry of Bar
Henry of Bar (c. 1362 – October 1397, in Treviso, Italy) was lord of Marle, Aisne, Marle and the Marquis of Pont-à-Mousson, Marquis de Pont-à-Mousson. He was the eldest son of Robert I of Bar and Marie of Valois (1344-1404), Marie of Valois.
...
and their followers, left Milan for Venice, from where he requisitioned a ship on 17 May to take him across the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
, landing in the Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
n port of Senj
Senj is a town on the upper Adriatic coast in Croatia, in the foothills of the Mala Kapela and Velebit mountains.
The symbol of the town is the Nehaj Fortress () which was completed in 1558. For a time this was the seat of the Uskoks, who were ...
on 30 May before making his way overland to the rendezvous in Buda. Croatian forces led by Ban Nicholas II Garai moved towards Buda from the coastal town of Nin in June, following a session of the Croatian Parliament
The Croatian Parliament () or the Sabor is the Unicameralism, unicameral legislature of Croatia. Under the terms of the Constitution of Croatia, Croatian Constitution, the Sabor represents the nation, people and is vested with legislative power. ...
, and joined the royal Hungarian army led by Sigismund.
Coucy arrived well before Nevers, who had stopped in the upper Danube for receptions and festivities thrown by German princes. Nevers did not arrive in Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
until 24 June, a full month behind the crusader vanguard led by d'Eu and Boucicaut. A fleet of 70 Venetian vessels loaded with provisions was sent down the Danube, while Nevers enjoyed yet more parties thrown by his brother-in-law Leopold IV, Duke of Austria. Nevers then asked his brother-in-law for a staggering loan of 100,000 ducat
The ducat ( ) coin was used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages to the 19th century. Its most familiar version, the gold ducat or sequin containing around of 98.6% fine gold, originated in Venice in 1284 and gained wide inter ...
s, which took time to arrange, and eventually arrived in Buda in July.Tuchman, 552
Buda to Nicopolis
 Once the leaders had arrived, strategy had to be coordinated with Philibert de Naillac, Master of the Knights Hospitaller, and representatives of the Venetian fleet. Forty-four Venetian ships had carried the Hospitallers from Rhodes through the Aegean into the
Once the leaders had arrived, strategy had to be coordinated with Philibert de Naillac, Master of the Knights Hospitaller, and representatives of the Venetian fleet. Forty-four Venetian ships had carried the Hospitallers from Rhodes through the Aegean into the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara, also known as the Sea of Marmora or the Marmara Sea, is a small inland sea entirely within the borders of Turkey. It links the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea via the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits, separating Turkey's E ...
, and some continued into the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
and up the Danube without engaging in battle. The fact that the Turks, who had an inferior naval presence, did not challenge the Venetians for control of the sea is seen as evidence that Bayezid and the majority of his forces were already on the European side.
The War Council in Buda was immediately the forum of a fierce dispute. The previous year, Bayezid had declared that he would attack Hungary by May, yet he had not appeared by end of July. Hungarian scouts sent out as far as the Hellespont could find no sign of him, causing the French to proclaim that he was a coward. Sigismund of Hungary assured the crusaders that Bayezid would come, and advised that it would be wiser to let the Turks make the long march to them, rather than make the same long march to find them. This strategy was rejected by the French and their allies. Coucy, acting as spokesman, stated, "Though the Sultan's boasts be lies, that should not keep us from doing deeds of arms and pursuing our enemies, for that is the purpose for which we came." Sigismund had little choice but to acquiesce, though chroniclers also write that Coucy's speech excited jealousy in D'Eu, who felt that he should have had the honor of spokesman due to his position as Constable of France.Tuchman, 553
The crusaders began to march down the left bank of the Danube, though part of the Hungarian army veered north to gather the forces of Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
and the Mircea the Elder
Mircea the Elder (, ; 1355 – 31 January 1418) was the Voivode of Wallachia from 1386 until his death in 1418. He was the son of Radu I of Wallachia and brother of Dan I of Wallachia, after whose death he inherited the throne.
After the dea ...
-led forces of Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
. The remainder of the Hungarians brought up the rear of the crusader column. As the crusaders moved into Muslim-held territory, pillaging and mistreatment of the population reportedly grew. While crusaders had been reported to engage in periodic pillage and raping while passing through Germany, the indiscipline of the French reportedly reached new heights when they entered "schismatic" lands. Chroniclers also waxed eloquent on the immorality and blasphemy of the crusaders, writing detailed accounts of drunkard knights lying with prostitutes for days, despite writing from at best second-hand accounts. Tuchman cautions that such chroniclers were part of a contemporary tendency to blame the defeat of the crusade on the immorality of the crusaders, and that it is impossible to verify such claims.Tuchman, 553–554
At Orşova, where the Danube narrows at the Iron Gates gorge, the column crossed to the right bank using pontoons and boats over eight days. Their first target was Vidin
Vidin (, ) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as of the Metropolitan of Vidin (since ...
, previously the capital of Western Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
and then under Turkish control. The ruler of Vidin, Ivan Sratsimir of Bulgaria, having no desire to fight for his Turkish conquerors against an overwhelming force of crusaders, promptly surrendered. The only bloodshed was the execution of Turkish officers in the defending garrison, though the incident served to further convince the French that Turks were incapable of challenging the crusaders in the field.
The next target was Oryahovo (Rachowa), a strong fortress located from Vidin. Frustrated by the lack of opportunity to show their bravery in deeds of arms, the French carried out a forced march at night to reach the castle before their allies, arriving in the morning just as the Turkish forces had come out to destroy the bridge across the moat. In fierce combat the French secured the bridge but were unable to push forward until Sigismund arrived. The forces combined and managed to reach the walls before night forced the combatants to retire. The next morning the inhabitants of Oryahovo agreed to surrender to Sigismund on the assurance that their lives and property would be spared. The French promptly broke Sigismund's agreement, pillaging and massacring the town after the gates were open, and later claiming that they had taken the town by conquest because their men-at-arms had topped the walls the night before. A thousand residents, both Turkish and Bulgarian, were taken hostage and the town set ablaze. The Hungarians took the French action as a grave insult to their king, while the French accused the Hungarians of trying to rob them of the glory of victory through combat.Tuchman, 554–555Madden, p. 184
Leaving a garrison to hold Oryahovo, the crusaders continued towards Nicopolis
Nicopolis () or Actia Nicopolis was the capital city of the Roman province of Epirus (Roman province), Epirus. Its site, near Preveza, Greece, still contains impressive ruins. The city was founded in 29 BC by Octavian in commemoration of his ...
, assaulting one or two forts or settlements along the way, but bypassing one citadel from which messengers escaped to inform Bayezid of the Christian army. On 12 September the crusaders came within view of the fortress of Nicopolis on its limestone cliff.Tuchman, 555
Siege of Nicopolis
Nicopolis, located in a natural defensive position, was a key stronghold controlling the lower Danube and lines of communication to the interior. A small road ran between the cliff and river, while the fortress was actually two walled towns, the larger one on the heights on the cliff and the smaller below. Further inland from the fortified walls, the cliff sloped steeply down to the plain. Well-defended and well-supplied, the Turkish governor of Nicopolis, Doğan Bey, was certain that Bayezid would have to come to the aid of the town and was prepared to endure a long siege.Tuchman, 556 The crusaders had brought no siege machines with them, but Boucicaut optimistically stated that ladders were easily made and worth more than catapults when used by courageous men. However, the lack of siege weapons, the steep slope up to the walls and the formidable fortifications made taking the castle by force impossible. The crusaders set up positions around the town to block the exits, and with the naval blockade of the river, settled in for asiege
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict charact ...
to starve out the defenders. Nevertheless, they were convinced that the siege of the fortress would be a mere prelude to a major thrust into relieving Constantinople and did not believe that Bayezid I would arrive so speedily to give them a real battle.Madden, 185
Two weeks passed as the bored crusaders entertained themselves with feasts, games, and insulting the martial prowess of their enemy. Whether through drunkenness or carelessness, the crusaders posted no sentries, though foragers venturing away from the camps brought word of the Turks' approach. Bayezid was at this time already through Adrianople
Edirne (; ), historically known as Orestias, Adrianople, is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the Edirne Province, province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second c ...
and on a forced march through the Shipka Pass to Tirnovo.Tuchman, 556–557 His ally Stefan Lazarević
Stefan Lazarević ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Лазаревић, 1377 – 19 July 1427), also known as Stefan the Tall (), was a Serbian ruler as prince (1389–1402) and Despot (court title), despot (1402–1427). He was also a diplomat, legislat ...
of Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
joined him on the way. Sigismund had sent 500 horsemen to carry out reconnaissance in force around Tirnovo, to the south, and they brought word back that the Turks were indeed coming. Word also reached the besieged inhabitants of Nicopolis, who blew horns and cheered. Boucicaut claimed the noise of their celebration was a ruse as he believed that the Sultan would never attack; he further threatened to cut off the ears of anyone who discussed rumors of the Turks' approach as being damaging to the morale of the crusaders.
One of the few to concern himself with scouting the situation was de Coucy, who took a group of 500 knights and 500 mounted archers south. Learning of a large group of Turks approaching through a nearby pass, he separated 200 horsemen to carry out a feint retreat, drawing the pursuing Turks into an ambush where the rest of his men, waiting concealed, attacked their rear. Giving no quarter, de Coucy's men killed as many as they could and returned to the camp where his action shook the camp from its lethargy and drew the admiration of the other crusaders. Tuchman argues that it also increased the overconfidence of the French and again drew the jealousy of D'Eu, who accused Coucy of risking the army out of recklessness and attempting to steal glory and authority from Nevers.Tuchman, 558
Sigismund called a war council on the 24th, in which he and Mircea of Wallachia suggested a battle plan in which the Wallachian foot soldiers, who had experience in fighting the Turks, would be sent in the first attack to meet the Turkish vanguard; this was usually a poorly armed militia, normally used for pillage but used in battle to tire opponents before they met better quality Turkish forces. Sigismund claimed that this vanguard was not worthy of the attention of knights. Sigismund proposed that, once the shock of first clash had passed, the French form the front line to rush in, while the Hungarians and the other allies follow to support the attack and keep the sipahi
The ''sipahi'' ( , ) were professional cavalrymen deployed by the Seljuk Turks and later by the Ottoman Empire. ''Sipahi'' units included the land grant–holding ('' timar'') provincial ''timarli sipahi'', which constituted most of the arm ...
s (Turkish heavy cavalry) from sweeping around the crusaders' flanks. D'Eu denounced the proposal as demeaning to the knights, who would be forced to follow peasant footmen into battle. He reportedly stated, "To take up the rear is to dishonor us, and expose us to the contempt of all" and declared that he would claim front place as Constable and anyone in front of him would do him mortal insult. In this he was supported by Boucicaut; Nevers, reassured by the confidence of the younger French lords, was easily convinced.
With the French set on a charge, Sigismund left to make a battle plan for his own forces. Apparently within hours, he sent word to the camp that Bayezid was only six hours away. The crusaders, said to be drunk over dinner, reacted in confusion; some refused to believe the report, some rose in panic, and some hastily prepared for battle. At this point, supposedly because of a lack of spare guards, the prisoners taken at Rachowa were massacred. Even European chroniclers would later call this an act of "barbarism".Tuchman, 558–559
Battle
At daybreak on 25 September the combatants began to organize themselves under the banners of their leaders. At this point, Sigismund sent his Grand Marshal to Nevers to report that his scouts had sighted the Turkish vanguard and asked for the offensive to be postponed for two hours, when his scouts would have returned with intelligence as to the numbers and disposition of the enemy. Nevers summoned a hasty council of advisors, in which Coucy and Jean de Vienne,admiral of France
Admiral of France () is a French title of honour. It is the naval equivalent of Marshal of France and was one of the Great Officers of the Crown of France.
History
The title was created in 1270 by Louis IX of France, during the Eighth Crusad ...
and the eldest French knight on the crusade, advised obeying the wishes of the Hungarian king, which seemed wise to them. At this, D'Eu declared that Sigismund simply wished to hoard the battle honors for himself and declared his willingness to lead the charge. Coucy, who declared D'Eu's words to be a "presumption", asked for the counsel of Vienne, who noted, "When truth and reason cannot be heard, then must rule presumption."Tuchman 559 Vienne commented that if D'Eu wished to advance, the army must follow, but that it would be wiser to advance in concert with the Hungarians and other allies. D'Eu rejected any wait and the council fell into a fierce dispute, with the younger hawks charging that the elder knights were not prudent, but fearful. The argument seems to have been settled when D'Eu decided to advance.
D'Eu took control of the vanguard of the French knights, while Nevers and Coucy commanded the main body. The French knights, accompanied by their mounted archers, rode out with their backs to Nicopolis to meet the Turks, who were descending the hills to the south. The Knights Hospitaler, Germans, and other allies stayed with the Hungarian forces under Sigismund. The subsequent events are obscured by conflicting accounts. Tuchman notes, "Out of the welter of different versions, a coherent account of the movements and fortunes of the battlefield is not to be had; there is only a tossing kaleidoscope."Tuchman 559–560 The French charge crushed the untrained conscripts in the Turkish front line and advanced into the lines of trained infantry, though the knights came under heavy fire from archers and were hampered by rows of sharpened stakes designed to skewer the stomachs of their horses. Chroniclers write of horses impaled on stakes, riders dismounting, stakes being pulled up to allow horses through, and the eventual rout of the Turkish infantry, who fled behind the relative safety of the sipahis. Coucy and Vienne recommended that the French pause to reform their ranks, give themselves some rest and allow the Hungarians time to advance to a position where they could support the French. They were overruled by the younger knights who, having no idea of the size of the Turkish force, believed that they had just defeated Bayezid's entire army and insisted on pursuit.Tuchman 560
The French knights thus continued up the hill, though accounts state that more than half were on foot by this point, either because they had been unhorsed by the lines of sharpened stakes or had dismounted to pull up stakes. Struggling in their heavy armor, they reached the plateau on the top of the slope, where they had expected to find fleeing Turkish forces, but instead found themselves facing a fresh corps of sipahis, whom Bayezid had kept in reserve. As the sipahi
The ''sipahi'' ( , ) were professional cavalrymen deployed by the Seljuk Turks and later by the Ottoman Empire. ''Sipahi'' units included the land grant–holding ('' timar'') provincial ''timarli sipahi'', which constituted most of the arm ...
s surged forward in the counterattack sounding trumpets, banging kettle drums and shouting the '' Tekbir'', the French realized how desperate their situation was and some knights fled back down the slope. The rest fought on, "no frothing boar nor enraged wolf more fiercely", in the words of one contemporary chronicler. Admiral de Vienne, to whom was granted the honor as the eldest knight of carrying the French standard into battle, was wounded many times as he attempted to rally his countrymen before being struck down. Other notable knights who were slain include Jean de Carrouges, Philippe de Bar, and Odard de Chasseron. The Turks threatened to overwhelm Nevers, and his bodyguard threw themselves to the ground in submission to plead for the life of their liege lord. Notwithstanding the declaration of jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God ...
, the Turks were as interested in the riches that could be gained by ransom
Ransom refers to the practice of holding a prisoner or item to extort money or property to secure their release. It also refers to the sum of money paid by the other party to secure a captive's freedom.
When ransom means "payment", the word ...
ing noble captives as anyone else, and took Nevers prisoner. Seeing Nevers taken, the rest of the French yielded.Tuchman 560–561
 The timeline of events is hazy, but it appears that as the French were advancing up the slope, sipahis were sweeping down along the flanks in an envelopment. Accounts tell of the Hungarians and other nationalities in confused combat on the plain and of a stampede of riderless horses, which Tuchman speculates pulled free from their tethers, at the sight of which the
The timeline of events is hazy, but it appears that as the French were advancing up the slope, sipahis were sweeping down along the flanks in an envelopment. Accounts tell of the Hungarians and other nationalities in confused combat on the plain and of a stampede of riderless horses, which Tuchman speculates pulled free from their tethers, at the sight of which the Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
ns and the Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
ns concluded that the day was lost and abandoned the field. Sigismund, the Master of Rhodes, and the Germans fought to prevent the envelopment with "unspeakable massacre" on both sides. At this point, the Turks received a reinforcement of 1,500 Serbian knights under the command of Stefan Lazarević
Stefan Lazarević ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Лазаревић, 1377 – 19 July 1427), also known as Stefan the Tall (), was a Serbian ruler as prince (1389–1402) and Despot (court title), despot (1402–1427). He was also a diplomat, legislat ...
, which proved critical. Sigismund's force was overwhelmed. Convinced to flee, Sigismund and the Master managed to escape on a fisherman's boat to the Venetian ships in the Danube. Count Hermann of Cilli, governor of Habsburg Carniola
Carniola ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region still tend to identify with its traditional parts Upp ...
and a cousin of Sigismund's deceased wife, led the force that allowed the escape and would later become the king's father-in-law
A parent-in-law is a person who has a legal affinity (law), affinity with another by being the parent of the other's spouse. Many cultures and legal systems impose duties and responsibilities on persons connected by this relationship. A person i ...
. Bayezid and his vassal Stefan Lazarević recognized Nicholas II Garai, Lazarević's brother-in-law, fighting on Sigismund's side. A deal was made, and Sigismund's army surrendered, completing their defeat in detail.
Aftermath
Sigismund would later state to the Hospitaller Master, "We lost the day by the pride and vanity of these French. If they believed my advice, we had enough men to fight our enemies." ChroniclerJean Froissart
Jean Froissart ( Old and Middle French: ''Jehan''; sometimes known as John Froissart in English; – ) was a French-speaking medieval author and court historian from the Low Countries who wrote several works, including ''Chronicles'' and ''Meli ...
would declare. "Since the Battle of Roncesvalles when ll twelve peers of France were slain, Christendom received not so great a damage."Tuchman 561
Captives and ransom
Bayezid toured the battlefield later that day, hoping to find the corpse of the King of Hungary. His rage was only heightened by the discovery of the massacred prisoners from Rahovo. He ordered all of the prisoners assembled before him the following morning (26 September). The Turks recognized Jacques de Helly, a French knight who had served underMurad I
Murad I (; ), nicknamed ''Hüdavendigâr'' (from – meaning "Head of state, sovereign" in this context; 29 June 1326 – 15 June 1389) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1362 to 1389. He was the son of Orhan Gazi and Nilüfer Hatun. Mura ...
, and had him identify the chief nobles for ransom. Coucy, Bar, D'Eu, Gui de La Tremoïlle and several others were grouped with Nevers to be spared. Those judged to be under the age of 20 were taken as slaves by the Turks.Tuchman 561–562
The rest, thought to number several thousand, were bound together in groups of three or four and had their hands tied to be marched naked before the Sultan. Ordered to proceed, a group of executioners proceeded to kill each group in turn, either by decapitation
Decapitation is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and all vertebrate animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood by way of severing through the jugular vein and common c ...
or by severing their limbs from the body. Nevers and the rest of the noble captives were forced to stand beside Bayezid and watch the executions. Jean Le Maingre, called "Boucicaut", was recognized in the line, and Nevers fell to his knees before the Sultan and indicated with intertwined fingers that they were like brothers. Thus convinced that Boucicaut was worth a noble ransom, he was spared and grouped with the other high nobles. The killing continued from early morning until late afternoon, at which point Bayezid, either himself sickened by the bloodshed or convinced by his ministers that he was unnecessarily enraging Christendom against him, called off the executioners. Leaving aside the more hyperbolic account, the number of dead is said to have ranged from 300 to 3,000, though the number of dead on the battlefield was much more.See, for example, an estimate of 10,000 executed in
Of those who fled the battlefield, few survived. So many attempted to swim to the boats in the Danube that several sank from the load; afterward, those on the boats pushed away those trying to board. Many who attempted to swim all the way across the river drowned. Sigismund, fearful of Wallachian treachery, sailed to the Black Sea and Constantinople before making his way home by sea. Those Crusaders who made it across the Danube and tried to return home by land found that the land they were traveling over had already been stripped of forage by the retreating force of Wallachians. Reduced to wandering through the woods in rags and robbed of whatever possessions they had, many of the starved survivors died along the way. Perhaps the most famous of the few who reached home after this journey was Count Rupert of Bavaria (), eldest son of the future King Rupert of Germany, who arrived at his doorstep in beggar's rags and died several days later from his trials.
The captives were forced to march the 350-mile length to Gallipoli
The Gallipoli Peninsula (; ; ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles strait to the east.
Gallipoli is the Italian form of the Greek name (), meaning ' ...
, stripped of clothing down to their shirts and most without shoes, with hands tied and beaten by their captors. At Gallipoli, the noble captives were kept in the upper rooms of a tower while the 300 prisoners that were the Sultan's share of the common captives were kept below. The ship carrying Sigismund passed within half a mile of the tower as it went through the Hellespont, for which the Turks lined the captives along the shore and mockingly called out for Sigismund to come and rescue his comrades. Sigismund, while in Constantinople, had made overtures to ransom the captives, but Bayezid was aware that Hungary's wealth had been depleted in the crusade and that richer ransoms could be had from France. After two months in Gallipoli, the prisoners were transferred to Bursa
Bursa () is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the Marmara Region, Bursa is one of the industrial centers of the country. Most of ...
, the joint Ottoman capital located in Asia, where they awaited word of their ransom.Tuchman 564–566
In the first week of December, rumors of unimaginable defeat arrived in Paris. As no certain news was to be had, rumor-mongers were imprisoned in the Grand Châtelet and, if convicted of lying, sentenced to death by drowning. The King, Burgundy, Orleans and Duc de Bar all sped envoys to Venice and Hungary to bring word back. On 16 December merchant ships brought word to Venice of defeat at Nicopolis and the escape of Sigismund.Tuchman 566
Jacques de Helly, the knight who had identified the nobles after the battle, had been charged by Bayezid, under his vow to return, to inform the King of France and Duke of Burgundy of his victory and demands for ransom. On Christmas, de Helly rode into Paris and, kneeling before the king, recounted the expedition, the battle, defeat and Bayezid's massacre of the prisoners. He also carried letters from Nevers and the other noble captives. Those for whom he did not carry letters were assumed to be dead, and weeping members of the court gathered around de Helly to seek more information about loved ones. According to the Monk of St. Denis, "affliction reigned in all hearts" and Deschamps wrote of "funerals from morning to eve". 9 January was declared a day of mourning throughout France and that day "it was piteous to hear the bells toiling in all the churches in Paris."Tuchman 566–567
A delegation with rich gifts for Bayezid left Paris on 20 January 1397 to negotiate the ransoms. De Helly, bound by his oath to return, had already departed with letters for the captives. Gian Galeazzo's help became vital, as he had extensive contacts in the Ottoman court. Envoys were sent informing him of belated approval by the King allowing the fleur-de-lis
The ''fleur-de-lis'', also spelled ''fleur-de-lys'' (plural ''fleurs-de-lis'' or ''fleurs-de-lys''), is a common heraldic charge in the (stylized) shape of a lily (in French, and mean and respectively). Most notably, the ''fleur-de-lis'' ...
to be added to the Visconti escutcheon, Galeazzo's first wife having been from the French royal house, and to make every effort to gain his assistance. Meanwhile, those envoys sent in early December had reached Venice and, having learned of the fate of the captives, were attempting to make their way to Bursa. Venice, which was the French conduit to the Muslim east due to her trade network, became the center for exchange of news, cash and ransomed captives.Tuchman 568
On 13 February 1397, de Coucy, ill and perhaps suffering from battle wounds, died. Released on their own accord to seek funds in the Levant, Boucicaut and Guy de Tremoille reached Rhodes, where de Tremoille fell ill and died around Easter. French negotiators in the Sultan's court finally reached agreement on a ransom of 200,000 gold florin
The Florentine florin was a gold coin (in Italian ''Fiorino d'oro'') struck from 1252 to 1533 with no significant change in its design or metal content standard during that time.
It had 54 grains () of nominally pure or 'fine' gold with a pu ...
s in June. Comte d'Eu died on 15 June. With a down payment of 75,000, the prisoners were released on 24 June on their promise to stay in Venice until the rest of the ransom was paid. However, the nobles found it unthinkable to travel in less than their accustomed splendor and borrowed nearly as much as the ransom amount in reprovisioning themselves. Arriving in Venice in October after stopping in various islands to recover and borrow money, the financial transactions required to both provide the ransom and pay for the travel arrangements and living expenses of the nobles were tremendously complicated. A three-sided transaction between Burgundy, Sigismund and Venice took 27 years to settle. A plague outbreak in Venice required the nobles to move temporarily to Treviso
Treviso ( ; ; ) is a city and (municipality) in the Veneto region of northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Treviso and the municipality has 87.322 inhabitants (as of December 2024). Some 3,000 live within the Venetian wall ...
, but still claimed Henri de Bar.Tuchman 571–575
The last of the Crusader leaders (Nevers, Boucicaut, Guillaume de Tremoille and Jacques de la Marche), along with seven or eight other knights, re-entered France in February 1398. They were greeted by minstrels, parties and parades as they journeyed across the kingdom, though Tuchman notes, "the receptions probably represented not so much popular enthusiasm as organized joy, in which the 14th century excelled."Tuchman 575
Broader ramifications
With a historian's hindsightJohan Huizinga
Johan Huizinga (; 7 December 1872 – 1 February 1945) was a Dutch historian and one of the founders of modern cultural history.
Life
Born in Groningen as the son of Dirk Huizinga, a professor of physiology, and Jacoba Tonkens, who died two ...
remarked upon "the lamentable consequences of statecraft recklessly embarking on an enterprise of vital import in the spirit of a chivalrous adventure", though participants and contemporary chroniclers did not analyse the event in these terms.
After this defeat, Western Europe made no further moves to stop the Turkish advance in the Balkans until the 1440s. England and France soon renewed their war. Wallachia continued its stance against the Ottomans, repelling expeditions in 1397 and 1400. In 1402 Sultan Bayezid I was defeated and captured by Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeat ...
(Tamerlane), and Mircea cel Batran and the Kingdom of Hungary took advantage of the resulting anarchy to campaign against the Ottomans. The Hungarians, Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
and Wallachians were defeated at the Battle of Varna in 1444, and Constantinople finally fell
A fell (from Old Norse ''fell'', ''fjall'', "mountain"Falk and Torp (2006:161).) is a high and barren landscape feature, such as a mountain or Moorland, moor-covered hill. The term is most often employed in Fennoscandia, Iceland, the Isle of M ...
in 1453 to the Turks, followed by the Despotate of Morea
The Despotate of the Morea () or Despotate of Mystras () was a province of the Byzantine Empire which existed between the mid-14th and mid-15th centuries. Its territory varied in size during its existence but eventually grew to include almost a ...
in 1460, the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of A ...
in 1461, and the Principality of Theodoro in 1475, which brought an end to the last vestiges of the Eastern Roman Empire, as well as the final remaining pockets of Greek resistance against the Ottoman Turks in both the Balkans and Anatolia.
The Battle of Nicopolis is also widely regarded as the end of the Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1422. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II ...
, since hopes for its revival had come to an end with the defeat of the Crusaders. Its last ruler, Ivan Sratsimir of Bulgaria, was captured and killed in Bursa.
By their victory at Nicopolis, the Turks discouraged the formation of future European coalitions against them. They maintained their pressure on Constantinople, tightened their control over the Balkans, and became a greater threat to central Europe.
See also
* Leonhard ReichartingerReferences
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
History of War: Battle of Nicopolis, 25 September 1396
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nicopolis Conflicts in 1396 Battles involving Hungary Battles involving Wallachia Battles involving Bohemia Battles of the Crusades Battles involving the Ottoman Empire 1396 in Europe Battles of the Ottoman–Hungarian Wars Battles involving Serbia in the Middle Ages Battles involving the Second Bulgarian Empire 14th century in Bulgaria 14th-century military history of Croatia Battles involving the Knights Hospitaller Military history of Bulgaria History of Pleven Province 1390s in the Ottoman Empire Massacres committed by the Ottoman Empire Death marches Battles involving the Holy Roman Empire Battles of the Crusade of Varna Prisoner of war massacres Bayezid I