Brain Aneurysm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm, is a cerebrovascular disorder characterized by a localized dilation or ballooning of a
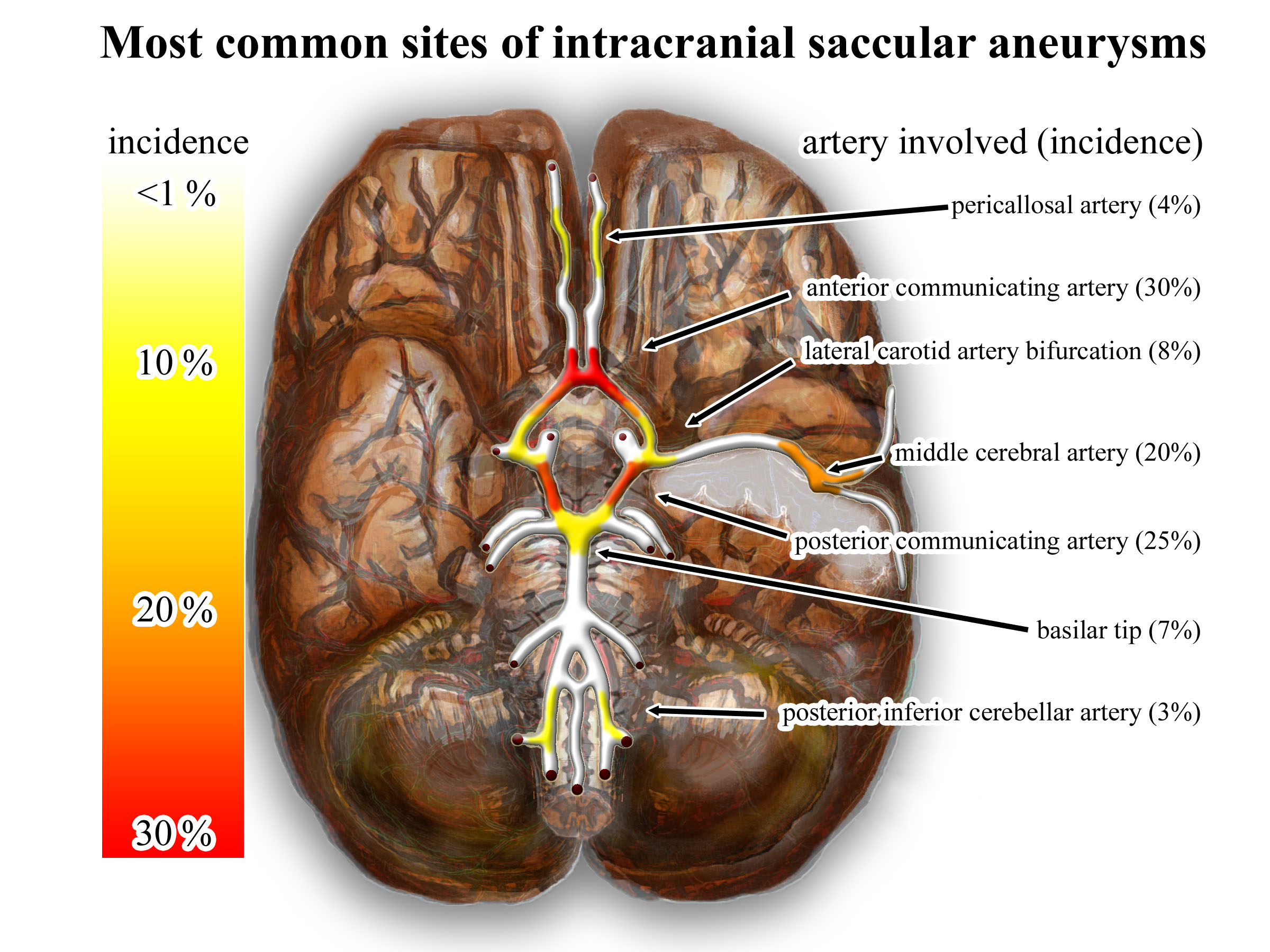 Saccular aneurysms are almost always the result of hereditary weaknesses in blood vessels and typically occur within the arteries of the circle of Willis, in order of frequency affecting the following arteries:
* Anterior communicating artery
* Posterior communicating artery
*
Saccular aneurysms are almost always the result of hereditary weaknesses in blood vessels and typically occur within the arteries of the circle of Willis, in order of frequency affecting the following arteries:
* Anterior communicating artery
* Posterior communicating artery
*
 Once suspected, intracranial aneurysms can be diagnosed radiologically using magnetic resonance or CT angiography. But these methods have limited sensitivity for diagnosis of small aneurysms, and often cannot be used to specifically distinguish them from infundibular dilations without performing a formal angiogram. The determination of whether an aneurysm is ruptured is critical to diagnosis. Lumbar puncture (LP) is the gold standard technique for determining aneurysm rupture (
Once suspected, intracranial aneurysms can be diagnosed radiologically using magnetic resonance or CT angiography. But these methods have limited sensitivity for diagnosis of small aneurysms, and often cannot be used to specifically distinguish them from infundibular dilations without performing a formal angiogram. The determination of whether an aneurysm is ruptured is critical to diagnosis. Lumbar puncture (LP) is the gold standard technique for determining aneurysm rupture (
 Emergency treatment for individuals with a ruptured cerebral aneurysm generally includes restoring deteriorating respiration and reducing
Emergency treatment for individuals with a ruptured cerebral aneurysm generally includes restoring deteriorating respiration and reducing
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cerebral Aneurysm Cerebrovascular diseases Neurosurgery
blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
in the brain due to a weakness in the vessel wall. These aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward :wikt:bulge, bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also b ...
s can occur in any part of the brain but are most commonly found in the arteries of the cerebral arterial circle. The risk of rupture varies with the size and location of the aneurysm, with those in the posterior circulation being more prone to rupture.
Cerebral aneurysms are classified by size into small, large, giant, and super-giant, and by shape into saccular (berry), fusiform, and microaneurysms. Saccular aneurysms are the most common type and can result from various risk factors, including genetic conditions, hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, and drug abuse
Substance misuse, also known as drug misuse or, in older vernacular, substance abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder, differing definitions ...
.
Symptoms of an unruptured aneurysm are often minimal, but a ruptured aneurysm can cause severe headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
s, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, vision impairment
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
, and loss of consciousness, leading to a subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid (brain), arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the human brain, brain. Symptoms may include a thunderclap headache, severe heada ...
. Treatment options include surgical clipping and endovascular coiling, both aimed at preventing further bleeding.
Diagnosis typically involves imaging techniques such as CT or MR angiography
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to image blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography is used to generate images of arteries (and less commonly veins) in order to evaluate ...
and lumbar puncture to detect subarachnoid hemorrhage. Prognosis depends on factors like the size and location of the aneurysm and the patient’s age and health, with larger aneurysms having a higher risk of rupture and poorer outcomes.
Advances in medical imaging have led to increased detection of unruptured aneurysms, prompting ongoing research into their management and the development of predictive tools for rupture risk.
Classification
Cerebral aneurysms are classified both by size and shape. Small aneurysms have a diameter of less than 15 mm. Larger aneurysms include those classified as large (15 to 25 mm), giant (25 to 50 mm) (0.98 inches to 1.97 inches), and super-giant (over 50 mm).Berry (saccular) aneurysms
Saccular aneurysms, also known as berry aneurysms, appear as a round outpouching and are the most common form of cerebral aneurysm. Causes include connective tissue disorders, polycystic kidney disease, arteriovenous malformations, untreatedhypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, tobacco smoking, cocaine and amphetamines, intravenous drug abuse (can cause infectious mycotic aneurysms), alcoholism, heavy caffeine intake, head trauma, and infection in the arterial wall from bacteremia
Bloodstream infections (BSIs) are infections of blood caused by blood-borne pathogens. The detection of microbes in the blood (most commonly accomplished by blood cultures) is always abnormal. A bloodstream infection is different from sepsis, wh ...
(mycotic aneurysms).
Fusiform aneurysms
Fusiform dolichoectatic aneurysms represent a widening of a segment of an artery around the entire blood vessel, rather than just arising from a side of an artery's wall. They have an estimated annual risk of rupture between 1.6 and 1.9 percent.Microaneurysms
Microaneurysms, also known as Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms, typically occur in smallblood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s (less than 300 micrometre
The micrometre (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American English), also commonly known by the non-SI term micron, is a uni ...
diameter), most often the lenticulostriate vessels of the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
, and are associated with chronic hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
. Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms are a common cause of intracranial hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) refers to any form of Hemorrhage, bleeding Internal bleeding, within the Human skull, skull. It can result from trauma, vascular abnormalities, hypertension, or other medical conditions. ICH is broadly categorized ...
.
Signs and symptoms
A small, unchanging aneurysm will produce few, if any, symptoms. Before a larger aneurysm ruptures, the individual may experience such symptoms as a sudden and unusually severe headache,nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, vision impairment, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, and loss of consciousness, or no symptoms at all.
Subarachnoid bleed
If an aneurysm ruptures, blood leaks into the space around the brain. This is called asubarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid (brain), arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the human brain, brain. Symptoms may include a thunderclap headache, severe heada ...
. Onset is usually sudden without prodrome, classically presenting as a " thunderclap headache" worse than previous headaches. Symptoms of a subarachnoid hemorrhage differ depending on the site and size of the aneurysm. Symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm can include:
* a sudden severe headache that can last from several hours to days
* nausea and vomiting
* drowsiness, confusion and/or loss of consciousness
* visual abnormalities
* meningism
* dizziness
Almost all aneurysms rupture at their apex. This leads to hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space and sometimes in brain parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
. Minor leakage from aneurysm may precede rupture, causing warning headaches. About 60% of patients die immediately after rupture. Larger aneurysms have a greater tendency to rupture, though most ruptured aneurysms are less than 10 mm in diameter.
Microaneurysms
A ruptured microaneurysm may cause anintracerebral hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as hemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into Intraparenchymal hemorrhage, the tissues of the brain (i.e. the parenchyma), into its Intraventricular hemorrhage, ventricles, or into both. An ICH is ...
, presenting as a focal neurological deficit.
Rebleeding, hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with n ...
(the excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
), vasospasm (spasm, or narrowing, of the blood vessels), or multiple aneurysms may also occur. The risk of rupture from a cerebral aneurysm varies according to the size of an aneurysm, with the risk rising as the aneurysm size increases.
Vasospasm
Vasospasm, referring to blood vessel constriction, can occur secondary to subarachnoid hemorrhage following a ruptured aneurysm. This is most likely to occur within 21 days and is seen radiologically within 60% of such patients. The vasospasm is thought to be secondary to theapoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
of inflammatory cells such as macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s and neutrophil
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in differe ...
s that become trapped in the subarachnoid space. These cells initially invade the subarachnoid space from the circulation in order to phagocytose the hemorrhaged red blood cells. Following apoptosis, it is thought there is a massive degranulation of vasoconstrictors, including endothelins and free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabolic disorders
Metabolism
...
s, that cause the vasospasm.
Risk factors
Intracranial aneurysms may result from diseases acquired during life, or from genetic conditions.Hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
, and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
are associated with the development of brain aneurysms. Cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
use has also been associated with the development of intracranial aneurysms.
Other acquired associations with intracranial aneurysms include head trauma and infections.
Genetic associations
Coarctation of the aorta is also a known risk factor, as is arteriovenous malformation. Genetic conditions associated with connective tissue disease may also be associated with the development of aneurysms. This includes: *autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common, life-threatening Genetic disorder, inherited human disorders and the most common hereditary kidney disease. It is associated with large interfamilial and intrafamilia ...
,
* neurofibromatosis type I,
* Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
,
* multiple endocrine neoplasia type I,
* pseudoxanthoma elasticum,
* hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and
* Ehlers-Danlos syndrome types II and IV.
Specific genes have also had reported association with the development of intracranial aneurysms, including perlecan, elastin
Elastin is a protein encoded by the ''ELN'' gene in humans and several other animals. Elastin is a key component in the extracellular matrix of gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly Elasticity (physics), elastic and present in connective ...
, collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
type 1 A2, endothelial nitric oxide synthase, endothelin receptor A and cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor. Recently, several genetic loci have been identified as relevant to the development of intracranial aneurysms. These include 1p34–36, 2p14–15, 7q11, 11q25, and 19q13.1–13.3.
Pathophysiology
Aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward :wikt:bulge, bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also b ...
means an outpouching of a blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
wall that is filled with blood. Aneurysms occur at a point of weakness in the vessel wall. This can be because of acquired disease or hereditary factors. The repeated trauma of blood flow against the vessel wall presses against the point of weakness and causes the aneurysm to enlarge. As described by the law of Young-Laplace, the increasing area increases tension against the aneurysmal walls, leading to enlargement. In addition, a combination of computational fluid dynamics and morphological indices have been proposed as reliable predictors of cerebral aneurysm rupture.
Both high and low wall shear stress
Shear stress (often denoted by , Greek alphabet, Greek: tau) is the component of stress (physics), stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross secti ...
of flowing blood can cause aneurysm and rupture. However, the mechanism of action is still unknown. It is speculated that low shear stress causes growth and rupture of large aneurysms through inflammatory response while high shear stress causes growth and rupture of small aneurysm through mural response (response from the blood vessel wall). Other risk factors that contributes to the formation of aneurysm are: cigarette smoking, hypertension, female gender, family history of cerebral aneurysm, infection, and trauma. Damage to structural integrity of the arterial wall by shear stress causes an inflammatory response with the recruitment of T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s, macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s, and mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s. The inflammatory mediators are: interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 6, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha), MMP1
Interstitial collagenase, also known as fibroblast collagenase and matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MMP1'' gene. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to 11q, chromosome 11q2 ...
, MMP2, MMP9, prostaglandin E2, complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the humoral, innate immune system and enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inf ...
, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and angiotensin II
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the ...
. However, smooth muscle cells from the tunica media
The tunica media (Neo-Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the internal elastic lamina of the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside.
Artery
The ...
layer of the artery moved into the tunica intima
The tunica intima (Neo-Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (biology), tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelium, endothelial cells (and macrophages in areas of disturbed blood flo ...
, where the function of the smooth muscle cells changed from contractile function into pro-inflammatory function. This causes the fibrosis of the arterial wall, with reduction of number of smooth muscle cells, abnormal collagen synthesis, resulting in a thinning of the arterial wall and the formation of aneurysm and rupture. No specific gene loci has been identified to be associated with cerebral aneurysms.
Generally, aneurysms larger than 7 mm in diameter should be treated because they are prone for rupture. Meanwhile, aneurysms less than 7 mm arise from the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
and posterior communicating artery and are more easily ruptured when compared to aneurysms arising from other locations.
Saccular aneurysms
 Saccular aneurysms are almost always the result of hereditary weaknesses in blood vessels and typically occur within the arteries of the circle of Willis, in order of frequency affecting the following arteries:
* Anterior communicating artery
* Posterior communicating artery
*
Saccular aneurysms are almost always the result of hereditary weaknesses in blood vessels and typically occur within the arteries of the circle of Willis, in order of frequency affecting the following arteries:
* Anterior communicating artery
* Posterior communicating artery
* Middle cerebral artery
The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral artery, cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches an ...
* Internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
* Tip of basilar artery
Saccular aneurysms tend to have a lack of tunica media
The tunica media (Neo-Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the internal elastic lamina of the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside.
Artery
The ...
and elastic lamina around their dilated locations (congenital), with a wall of sac made up of thickened hyalinized intima and adventitia. In addition, some parts of the brain vasculature are inherently weak—particularly areas along the circle of Willis, where small communicating vessels link the main cerebral vessels. These areas are particularly susceptible to saccular aneurysms. Approximately 25% of patients have multiple aneurysms, predominantly when there is a familial pattern.
Diagnosis
 Once suspected, intracranial aneurysms can be diagnosed radiologically using magnetic resonance or CT angiography. But these methods have limited sensitivity for diagnosis of small aneurysms, and often cannot be used to specifically distinguish them from infundibular dilations without performing a formal angiogram. The determination of whether an aneurysm is ruptured is critical to diagnosis. Lumbar puncture (LP) is the gold standard technique for determining aneurysm rupture (
Once suspected, intracranial aneurysms can be diagnosed radiologically using magnetic resonance or CT angiography. But these methods have limited sensitivity for diagnosis of small aneurysms, and often cannot be used to specifically distinguish them from infundibular dilations without performing a formal angiogram. The determination of whether an aneurysm is ruptured is critical to diagnosis. Lumbar puncture (LP) is the gold standard technique for determining aneurysm rupture (subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid (brain), arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the human brain, brain. Symptoms may include a thunderclap headache, severe heada ...
). Once an LP is performed, the CSF is evaluated for RBC count, and presence or absence of xanthochromia.
Treatment
 Emergency treatment for individuals with a ruptured cerebral aneurysm generally includes restoring deteriorating respiration and reducing
Emergency treatment for individuals with a ruptured cerebral aneurysm generally includes restoring deteriorating respiration and reducing intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
. Currently there are two treatment options for securing intracranial aneurysms: surgical clipping or endovascular coiling. If possible, either surgical clipping or endovascular coiling is typically performed within the first 24 hours after bleeding to occlude the ruptured aneurysm and reduce the risk of recurrent hemorrhage.
While a large meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
found the outcomes and risks of surgical clipping and endovascular coiling to be statistically similar, no consensus has been reached. In particular, the large randomised control trial International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial appears to indicate a higher rate of recurrence when intracerebral aneurysms are treated using endovascular coiling. Analysis of data from this trial has indicated a 7% lower eight-year mortality rate with coiling, a high rate of aneurysm recurrence in aneurysms treated with coiling—from 28.6 to 33.6% within a year, a 6.9 times greater rate of late retreatment for coiled aneurysms, and a rate of rebleeding 8 times higher than surgically clipped aneurysms.
Surgical clipping
Aneurysms can be treated by clipping the base of the aneurysm with a specially designed clip. Whilst this is typically carried out bycraniotomy
A craniotomy is a surgery, surgical operation in which a bone flap is temporarily removed from the Human skull, skull to access the Human brain, brain. Craniotomies are often critical operations, performed on patients who are suffering from brain ...
, a new endoscopic endonasal approach is being trialled. Surgical clipping was introduced by Walter Dandy of the Johns Hopkins Hospital in 1937.
After clipping, a catheter angiogram or CTA can be performed to confirm complete clipping.
Endovascular coiling
Endovascular coiling refers to the insertion ofplatinum
Platinum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a density, dense, malleable, ductility, ductile, highly unreactive, precious metal, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name origina ...
coils into the aneurysm. A catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. ...
is inserted into a blood vessel, typically the femoral artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters ...
, and passed through blood vessels into the cerebral circulation and the aneurysm. Coils are pushed into the aneurysm, or released into the blood stream ahead of the aneurysm. Upon depositing within the aneurysm, the coils expand and initiate a thrombotic reaction within the aneurysm. If successful, this prevents further bleeding from the aneurysm. In the case of broad-based aneurysms, a stent may be passed first into the parent artery to serve as a scaffold for the coils.
Cerebral bypass surgery
Cerebral bypass surgery was developed in the 1960s in Switzerland by Gazi Yaşargil. When a patient has an aneurysm involving a blood vessel or a tumor at the base of the skull wrapping around a blood vessel, surgeons eliminate the problem vessel by replacing it with an artery from another part of the body.Prognosis
Outcomes depend on the size of the aneurysm. Small aneurysms (less than 7 mm) have a low risk of rupture and increase in size slowly. The risk of rupture is less than one percent for aneurysms of this size. Theprognosis
Prognosis ( Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing"; : prognoses) is a medical term for predicting the likelihood or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) ...
for a ruptured cerebral aneurysm depends on the extent and location of the aneurysm, the person's age, general health, and neurological condition. Some individuals with a ruptured cerebral aneurysm die from the initial bleeding. Other individuals with cerebral aneurysm recover with little or no neurological deficit. The most significant factors in determining outcome are the Hunt and Hess grade, and age. Generally patients with Hunt and Hess grade I and II hemorrhage on admission to the emergency room and patients who are younger within the typical age range of vulnerability can anticipate a good outcome, without death or permanent disability. Older patients and those with poorer Hunt and Hess grades on admission have a poor prognosis. Generally, about two-thirds of patients have a poor outcome, death, or permanent disability.
Increased availability and greater access to medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
has caused a rising number of asymptomatic, unruptured cerebral aneurysms to be discovered incidentally during medical imaging investigations. Unruptured aneurysms may be managed by endovascular clipping or stenting. For those subjects that underwent follow-up for the unruptured aneurysm, computed tomography angiography
Computed tomography angiography (also called CT angiography or CTA) is a computed tomography technique used for angiography—the visualization of arteries and veins—throughout the human body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, im ...
(CTA) or magnetic resonance angiography
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to image blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography is used to generate images of arteries (and less commonly veins) in order to evaluate ...
(MRA) of the brain can be done yearly. Recently, an increasing number of aneurysm features have been evaluated in their ability to predict aneurysm rupture status, including aneurysm height, aspect ratio, height-to-width ratio, inflow angle, deviations from ideal spherical or elliptical forms, and radiomics morphological features.
Epidemiology
Theprevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
of intracranial aneurysm is about 1–5% (10 million to 12 million persons in the United States) and the incidence is 1 per 10,000 persons per year in the United States (approximately 27,000), with 30- to 60-year-olds being the age group most affected. Intracranial aneurysms occur more in women, by a ratio of 3 to 2, and are rarely seen in pediatric populations.
Clinical trials
International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial
The International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) was a large multicenter prospective randomized clinical medical trial comparing the safety and efficacy of endovascular coil treatment and surgical clipping for the treatment of brain aneurysms. The study began in 1994 with the first results being published in ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'' in 2002, and the 10-year data were published again in ''The Lancet'' in early September 2005. A total of 2,143 study participants were mostly drawn from U.K. hospitals, with the rest drawn from North American and European hospitals.
The study found superior results with endovascular coil treatment compared to surgical clipping. However, subsequent studies have questioned this conclusion.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005 Feb;26(2):367-72. The study was criticized by many clinicians and was not accepted by most surgeons.Michael Forsting, Isabel Wanke, ''Intracranial Vascular Malformations and Aneurysms: From Diagnostic Work-Up to Endovascular Therapy'', Springer 2008, . Primary criticisms were related to the study's generalizability and the long-term prognosis of coil embolization.
Study design and results
ISAT sought to measure outcomes ofcerebral aneurysm
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm, is a Cerebrovascular disease, cerebrovascular disorder characterized by a localized dilation or ballooning of a blood vessel in the brain due to a weakness in the vessel wall. These a ...
patients at 2 and 12 months using a type of Rankin scale.Michael S. Horowitz, Elad I. Levy, ''Neuroendovascular surgery'', Karger Publishers, 2005, . The study was prematurely terminated in 2002 after the oversight committee determined there was increased morbidity with surgical clipping compared to endovascular coiling.
Criticism
ISAT was criticized on several factors related to the randomization of the patient population. The randomized patient population in the ISAT was younger on average; the majority had aneurysms under 10 mm and in anterior circulation compared to the population ofsubarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid (brain), arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the human brain, brain. Symptoms may include a thunderclap headache, severe heada ...
patients in the U.S. and Japan.Adnan I. Qureshi, ''Textbook of Interventional Neurology'', Ed. Adnan I. Qureshi, Alexandros L. Georgiadis, Cambridge University Press: 2011, . In response to these criticisms, a facility that participated in ISAT compared the clinical outcomes of their patients who were not selected for the study to those who were. They reported similar outcomes to the ISAT.
Subsequent analysis
Although the initial ISAT analysis appeared to favor endovascular coiling over microsurgical clipping, subsequent meta-analysis have questioned that conclusion finding higher incidences of recurrence.''See'', Raja PV, Huang J, Germanwala AV, Gailloud P, Murphy KP, Tamargo RJ. Microsurgical clipping and endovascular coiling of intracranial aneurysms: A critical review of the literature. Neurosurgery 62: 1187-1202, June 2008 A large meta-analysis fromJohns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
published in ''Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the specialty (medicine), medical specialty that focuses on the surgical treatment or rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system ...
'' concluded that "there is no clear consensus in these two studies or in the 45 observational studies included."
Updated data from the ISAT group in March 2008 shows that the higher aneurysm rate of recurrence is also associated with a higher re-bleeding rate, given that the re-bleed rate of coiled aneurysms appears to be 8 times higher than that of aneurysms treated with surgical clipping in this study.Mitchell P, Kerr R, Mendelow AD, Molyneux A. Could late rebleeding overturn the superiority of cranial aneurysm coil embolization over clip ligation seen in ISAT? Journal of Neurosurgery 108: 437-442, March 2008 The ISAT authors conclude that "when treating ruptured cerebral aneurysms, the advantage of coil embolization over clip ligation cannot be assumed for patients younger than 40 years old." Other studies have directly questioned the ISAT's conclusions. This conclusion is based on a number of methodological assumptions itself and other authors have cautioned about extending it to other patient populations.J Mocco, L. Nelson Hopkins, "International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial analysis", ''Journal of Neurosurgery'', March 2008 / Vol. 108 / No. 3 / Pages 436-436.
See also
* Interventional neuroradiology * Intradural pseudoaneurysmReferences
External links
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cerebral Aneurysm Cerebrovascular diseases Neurosurgery