Bermuda is a
British Overseas Territory
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs) or alternatively referred to as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are the fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom that, ...
in the
North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of
North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, about to the west-northwest.
Bermuda is an
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
consisting of
181 islands, although the most significant islands are connected by bridges and appear to form one landmass. It has a land area of . Bermuda has a tropical climate, with warm winters and hot summers. Its climate also exhibits
oceanic
Oceanic may refer to:
*Of or relating to the ocean
*Of or relating to Oceania
**Oceanic climate
**Oceanic languages
**Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)"
Places
* Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, ...
features similar to other coastal areas in the
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
with warm, moist air from the ocean ensuring relatively high humidity and stabilising temperatures. Bermuda is prone to severe weather from
recurving tropical cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its ...
; however, it receives some protection from a coral reef and its position north of the
Main Development Region, which limits the direction and severity of approaching storms.
Bermuda is named after Spanish explorer
Juan de Bermúdez
Juan de Bermúdez (; ; born , died ) was a Spanish navigator of the 16th century, and the namesake for the island country Bermuda.
Early life
Juan Bermúdez was born in Palos de la Frontera, Province of Huelva, Crown of Castile.
Voyages
In 150 ...
, who discovered the archipelago in 1503. The islands have been permanently inhabited since 1612 when an
English settlement
''English Settlement'' is the fifth studio album and first double album by the English rock band XTC, released 12 February 1982 on Virgin Records. It marked a turn towards the more pastoral pop songs that would dominate later XTC releases, wi ...
was established at
St. George's, which is also the territory's largest settlement. Forming part of
British America
British America collectively refers to various British colonization of the Americas, colonies of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and its predecessors states in the Americas prior to the conclusion of the American Revolutionary War in 1 ...
, Bermuda was governed under
Royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
by the
Somers Isles Company
The Somers Isles Company (fully, the Company of the City of London for the Plantacion of The Somers Isles or the Company of The Somers Isles) was formed in 1615 to operate the English colony of the Somers Isles, also known as Bermuda, as a commer ...
until 1684, when it became a
crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony governed by Kingdom of England, England, and then Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain or the United Kingdom within the English overseas possessions, English and later British Empire. There was usua ...
. The first
enslaved Africans
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were once commonplace in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the rest of the Ancient history, ancient and Post-classical history, medieval world. When t ...
were taken to Bermuda in 1616. The Somers Isles Company ensured a steady flow of free but
indentured servants
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract called an "indenture", may be entered voluntarily for a prepaid lump sum, as payment for some good or ser ...
until 1684, and most tobacco farms owned by overseas ''adventurers'' were sold to the tenants or other occupants after Bermuda-grown tobacco became steadily less profitable following the 1620s, becoming family farms that switched from growing tobacco for export to producing food (initially for local consumption). Consequently, a
plantation economy did not develop and the slave trade largely ceased by the end of the 17th century. The economy instead became maritime-focused, with the colony serving as a base for merchants,
privateers
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign o ...
and the
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, giving its name to the
Bermuda rig
Bermuda rig, Bermudian rig, or Marconi rig is a type of sailing rig that uses a triangular sail set abaft (behind) the mast. It is the typical configuration for most modern sailboats. Whilst commonly seen in sloop-rigged vessels, Bermuda rig is ...
and
Bermuda sloop
The Bermuda sloop is a historical type of fore-and-aft rigged single-masted sailing vessel developed on the islands of Bermuda in the 17th century. Such vessels originally had gaff rigs with quadrilateral sails, but evolved to use the Bermuda ri ...
. It became an
imperial fortress
Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury, Lord Salisbury described Malta, Gibraltar, Bermuda, and Halifax as Imperial fortresses at the 1887 Colonial Conference, though by that point they had been so designated for decades. Later histor ...
, the most important British naval and military base in the western hemisphere with vast funds lavished on its
Royal Naval Dockyard and
military defences until the 1950s. Tourism has been
a significant contributor to Bermuda's economy since the 19th century and after World War II, the territory became a prominent
offshore financial centre and
tax haven
A tax haven is a term, often used pejoratively, to describe a place with very low tax rates for Domicile (law), non-domiciled investors, even if the official rates may be higher.
In some older definitions, a tax haven also offers Bank secrecy, ...
.
Divided into
nine parishes, Bermuda is a self-governing
parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of the legisl ...
with a
bicameral parliament
Bicameralism is a type of legislature that is divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single ...
located in the capital
Hamilton
Hamilton may refer to:
* Alexander Hamilton (1755/1757–1804), first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
* ''Hamilton'' (musical), a 2015 Broadway musical by Lin-Manuel Miranda
** ''Hamilton'' (al ...
. The
House of Assembly
House of Assembly is a name given to the legislature or lower house of a bicameral parliament. In some countries this may be at a subnational level.
Historically, in British Crown colonies as the colony gained more internal responsible g ...
dates from 1620, making it one of the world's oldest legislatures. The
premier
Premier is a title for the head of government in central governments, state governments and local governments of some countries. A second in command to a premier is designated as a deputy premier.
A premier will normally be a head of govern ...
is the head of government and is formally appointed by the
governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
, who is nominated by the British government as the representative of the
King
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
. The United Kingdom is responsible for foreign affairs and defence. An
independence referendum
An independence referendum is a type of referendum in which the residents of a territory decide whether the territory should become an Independence, independent sovereign state. An independence referendum that results in a vote for independenc ...
was held in 1995 with a large majority voting against independence. As of 2019, Bermuda had a population of around 64,000 people, making it the second-most populous of the British Overseas Territories.
Black Bermudians, a diverse population primarily of any mixture of African, European, and Native
American ancestry
In the demography of the United States, some people self-identify their ancestral origin or descent as "American", rather than the more common officially recognized racial and ethnic groups that make up the bulk of the American people. The ...
, make up around 50% of the population, while
White Bermudians
White Bermudians are Bermudians whose ancestry lies within the continent of Europe, most notably the British Isles and Portugal. At the 2016 census the number of Bermudians who identify as white was 19,466 or 31 percent of the total population ...
, primarily of British, Irish and Portuguese descent, make up 30% of the population. There are smaller groups from other races or identifying as mixed race and about 30% of the population is not Bermudian by birth. The last remaining territory in the former
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
(following the 1867
Confederation of Canada
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation, called the Dominion of Canada, on July 1, 1867. This process ...
and the
Colony of Newfoundland
Newfoundland was an English overseas possessions, English, and later British, colony established in 1610 on the Newfoundland (island), island of Newfoundland. That followed decades of sporadic English settlement on the island, which was at first ...
becoming the
Dominion of Newfoundland
Newfoundland was a British dominion in eastern North America, today the modern Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It included the island of Newfoundland, and Labrador on the continental mainland. Newfoundland was one of the orig ...
in 1907), Bermuda has
a distinct dialect of English and has historically had strong ties with other English-speaking countries in the Americas, including the United States, Canada, and the
Commonwealth Caribbean
The Commonwealth Caribbean refers to a group of English-speaking world, English-speaking sovereign states in the Caribbean, including both island states and mainland countries in the Americas, that are members of the Commonwealth of Nations and ...
. It is an associate member of the
Caribbean Community
The Caribbean Community (abbreviated as CARICOM or CC) is an intergovernmental organisation that is a Political association, political and economic union of 15 member states (14 nation-states and one dependency) and five associated members thro ...
.
Etymology
Bermuda is named after the Spanish sailor
Juan de Bermúdez
Juan de Bermúdez (; ; born , died ) was a Spanish navigator of the 16th century, and the namesake for the island country Bermuda.
Early life
Juan Bermúdez was born in Palos de la Frontera, Province of Huelva, Crown of Castile.
Voyages
In 150 ...
, who discovered the islands in 1505,
while sailing for
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
from a provisioning voyage to
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
in the ship ''La Garça''.
History
Discovery

Bermuda was discovered in the early 1500s by Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez.
Bermuda had no
Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology)
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often populari ...
population when it was discovered, nor during initial British settlement a century later. It was mentioned in ''
Legatio Babylonica
In 1501–1502, Peter Martyr d'Anghiera, an Italian humanist, was sent on a diplomatic mission to Mamluk Egypt by Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, in order to convince Sultan Qansuh al-Ghuri not to retaliate against his Christian ...
'', published in 1511 by historian
Pedro Mártir de Anglería, and was included on Spanish charts of that year.
Both Spanish and Portuguese ships used the islands as a replenishment spot to take on fresh meat and water. Shipwrecked Portuguese mariners are now thought to have been responsible for the 1543 inscription on
Portuguese Rock
Rock music and its subgenres are very popular in Portugal. The history of the Portuguese rock and roll, rock music scene spans several decades.
History
1950s to 1970s
In the late 1950s, singer Joaquim Costa was one of the first rock artists, but ...
, previously called Spanish Rock. Legends arose of spirits and devils, now thought to have stemmed from the calls of raucous birds (most likely the
Bermuda petrel
The Bermuda petrel (''Pterodroma cahow'') is a gadfly petrel. Commonly known in Bermuda as the cahow, a name derived from its eerie cries, this nocturnal ground-nesting seabird is the national bird of Bermuda, pictured on Bermudian currency. Berm ...
, or ''cahow'') and loud nocturnal noises from introduced wild hogs. With its frequent storm-racked conditions and dangerous reefs, the archipelago became known as the "Isle of Devils". Neither Spain nor Portugal attempted to settle it.
Settlement by the British
For the next century, the island was frequently visited but not settled. The English began to focus on the New World, initially settling in
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, starting British colonisation in North America, establishing a colony at
Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent British colonization of the Americas, English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James River, about southwest of present-day Willia ...
in 1607. Two years later, a
flotilla
A flotilla (from Spanish, meaning a small ''flota'' ( fleet) of ships), or naval flotilla, is a formation of small warships that may be part of a larger fleet.
Composition
A flotilla is usually composed of a homogeneous group of the same cla ...
of seven ships left England with several hundred settlers, food, and supplies to relieve the Jamestown colony. However, the flotilla was broken up by a storm and the flagship, the ''
Sea Venture
''Sea Venture'' was a seventeenth-century English sailing ship, part of the Third Supply mission flotilla to the Jamestown Colony in 1609. She was the 300 ton flagship of the London Company. During the voyage to Virginia, ''Sea Venture'' encount ...
'', drove onto Bermuda's reef to prevent her sinking, resulting in the survival of all her passengers and crew.
The settlers were unwilling to move on, having now heard about the true conditions in Jamestown from the sailors, and made multiple attempts to rebel and stay in Bermuda. They argued that they had a right to stay and establish their own government. The new settlement became a prison labour camp, and built two ships, the ''Deliverance'' and the ''Patience''.
[
]
In 1612, the English began settlement of the archipelago, officially named Virgineola, with arrival of the ship the ''Plough''. New London (renamed St. George's Town) was settled that year and designated as the colony's first capital.
It is the oldest continuously inhabited English town in the
New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
.
[ In 1616 and 1620 acts were passed banning the hunting of certain birds and young ]tortoise
Tortoises ( ) are reptiles of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines (Latin for "tortoise"). Like other turtles, tortoises have a shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, and like o ...
s. The archipelago's limited land area and resources led to the creation of what may be the earliest conservation laws of the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
.
Slavery in Bermuda
In 1615, the colony, which had been renamed the Somers Isles in commemoration of Sir George Somers
Sir George Somers (before 24 April 1554 – 9 November 1610) was an English privateer and naval hero, knighted for his achievements and the Admiral of the Virginia Company of London. He achieved renown as part of an expedition led by ...
, was passed on to the Somers Isles Company
The Somers Isles Company (fully, the Company of the City of London for the Plantacion of The Somers Isles or the Company of The Somers Isles) was formed in 1615 to operate the English colony of the Somers Isles, also known as Bermuda, as a commer ...
. As Bermudians settled the Carolina Colony
The Province of Carolina was a colony of the Kingdom of England (1663–1707) and later the Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1712) that existed in North America and the Caribbean from 1663 until the Carolinas were partitioned into North and Sou ...
and contributed to establishing other English colonies in the Americas, several other locations were named after the archipelago. During this period the first slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
were held and trafficked to the islands. These were a mixture of native Africans
The ethnic groups of Africa number in the thousands, with each ethnicity generally having their own language (or dialect of a language) and culture. The ethnolinguistic groups include various Afroasiatic, Khoisan, Niger-Congo, and Nilo-Sahara ...
who were trafficked to the Americas via the African slave trade
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were once commonplace in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the rest of the ancient and medieval world. When the trans-Saharan slave trade, Red Sea s ...
and Native Americans who were enslaved from the new world colonies.
Civil War
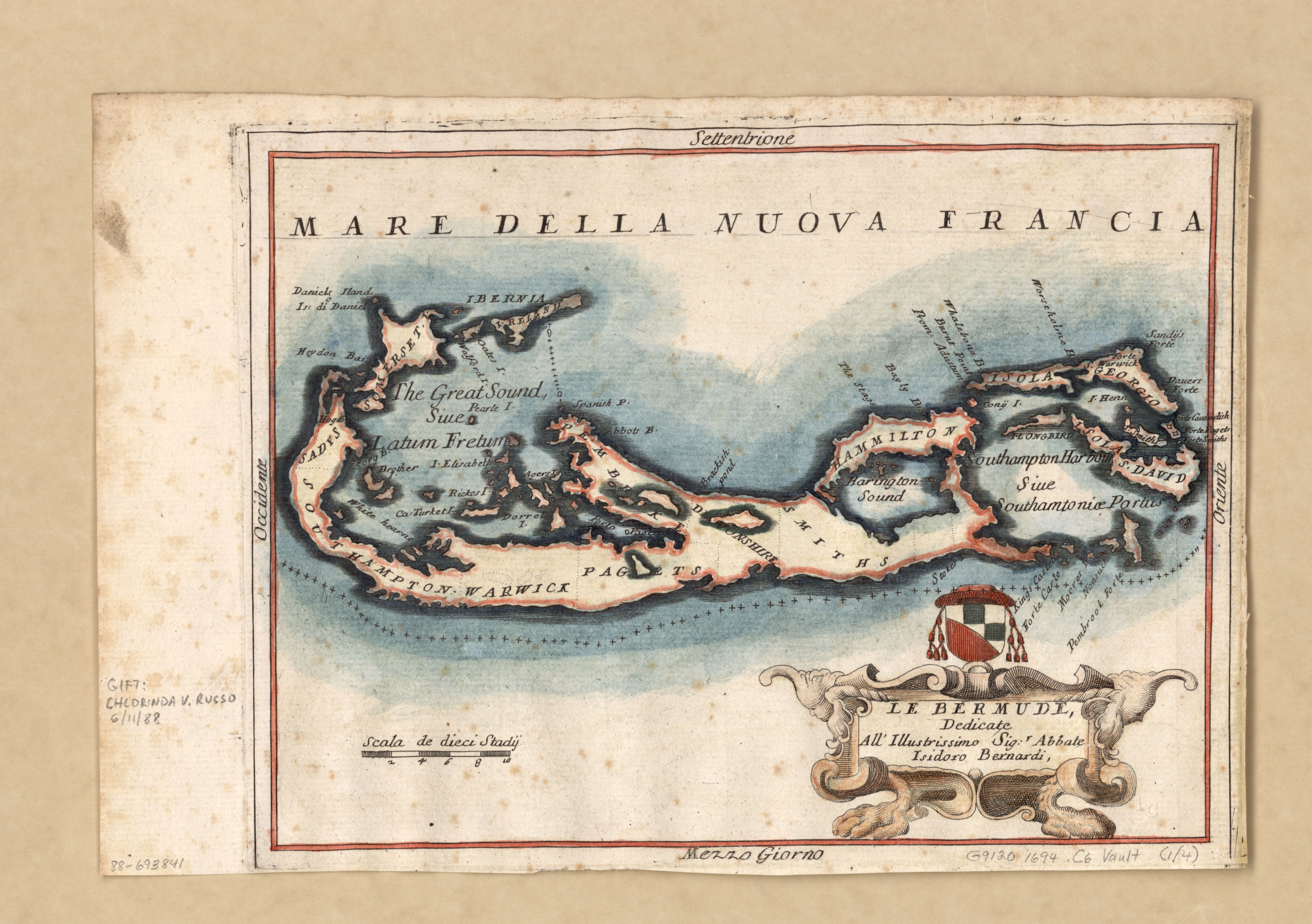 In 1649, the
In 1649, the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
was taking place and King Charles I was beheaded in Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London, England. The road forms the first part of the A roads in Zone 3 of the Great Britain numbering scheme, A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea, London, Chelsea. It ...
, London. The conflict spilled over into Bermuda, where most of the colonists developed a strong sense of devotion to the Crown. The royalists ousted the Somers Isles Company's Governor and elected John Trimingham as their leader (see Governor of Bermuda
The governor of Bermuda (officially Governor and Commander-in-Chief of the Somers Isles (alias the Islands of Bermuda)) is the representative of the British monarch in the British overseas territory of Bermuda.
For the purposes of this arti ...
). Bermuda's civil war was ended by militias, and dissenters were pushed to settle The Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of ...
under William Sayle
Captain William Sayle ( 1590 – 1671) was a prominent English landholder who was Governor of Bermuda in 1643 and again in 1658. As an Independent in religion and politics, and an adherent of Oliver Cromwell, he was dissatisfied with life in Ber ...
.
The rebellious royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gove ...
colonies of Bermuda, Virginia, Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
and Antigua
Antigua ( ; ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the local population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the most populous island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua ...
, were the subjects of an Act of the Rump Parliament of England. The royalist colonies were also threatened with invasion. The Government of Bermuda eventually reached an agreement with the Parliament of England which retained the status quo in Bermuda. In 1655 fifty-four Bermudians became the first English subjects to permanently settle on the Island of Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
, followed by a further (200) Bermudians in 1658, following Cromwell's Invasion of Jamaica
The Invasion of Jamaica took place in May 1655, during the 1654 to 1660 Anglo-Spanish War, when an English expeditionary force captured Spanish Jamaica. It was part of an ambitious plan by Oliver Cromwell to acquire new colonies in the Americ ...
.
Later 17th century
 In the 17th century, the Somers Isles Company suppressed shipbuilding, as it needed Bermudians to farm to generate income from the land. The Virginia colony, however, far surpassed Bermuda in quality and quantity of tobacco produced. Bermudians began to turn to maritime trades relatively early in the 17th century, but the Somers Isles Company used all its authority to suppress turning away from agriculture. This interference led to islanders demanding, and receiving, revocation of the company's charter in 1684, and the company was dissolved.
In the 17th century, the Somers Isles Company suppressed shipbuilding, as it needed Bermudians to farm to generate income from the land. The Virginia colony, however, far surpassed Bermuda in quality and quantity of tobacco produced. Bermudians began to turn to maritime trades relatively early in the 17th century, but the Somers Isles Company used all its authority to suppress turning away from agriculture. This interference led to islanders demanding, and receiving, revocation of the company's charter in 1684, and the company was dissolved.Juniperus bermudiana
''Juniperus bermudiana'' is a species of juniper endemic to Bermuda. This species is most commonly known as Bermuda cedar, but is also referred to as Bermuda juniper ( Bermudians refer to it simply as ''cedar''). Historically, this tree formed w ...
'', called Bermuda cedar). Establishing effective control over the Turks Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands (abbreviated TCI; and ) are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and no ...
, Bermudians deforested their landscape to begin the salt trade. It became the world's largest and remained the cornerstone of Bermuda's economy for the next century. Bermudians also vigorously pursued whaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales for their products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that was important in the Industrial Revolution. Whaling was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16t ...
, privateering
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since Piracy, robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sover ...
, and the merchant trade.
Some islanders, especially in St David's
St Davids or St David's (, , "Saint David, David's Welsh toponymy, house”) is a St David's Cathedral, cathedral City status in the United Kingdom, city in Pembrokeshire, Wales. It lies on the River Alun, Pembrokeshire, River Alun and is ...
, still trace their ancestry to Native Americans, and others are unaware that they have such ancestry. Hundreds of Native Americans were shipped to Bermuda. The best-known examples were the Algonquian peoples
The Algonquians are one of the most populous and widespread North American indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous American groups, consisting of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. They historically were prominent along the East ...
such as Pequots, Wampanoags, Podunks, Nipmucks, Narragansetts and others who were exiled from the New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
colonies and sold into slavery in the seventeenth century, notably in the aftermaths of the Pequot War
The Pequot War was an armed conflict that took place in 1636 and ended in 1638 in New England, between the Pequot nation and an alliance of the colonists from the Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, and Saybrook colonies and their allies from the Na ...
and King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1678 between a group of indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodland ...
; some are believed to have been brought from as far away as Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
.
The American War of Independence
Bermuda's ambivalence towards the American rebellion changed in September 1774, when the Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislature, legislative bodies, with some executive function, for the Thirteen Colonies of British America, Great Britain in North America, and the newly declared United States before, during, and after ...
resolved to ban trade with Great Britain, Ireland, and the West Indies after 10 September 1775. Such an embargo would mean the collapse of their inter-colonial commerce, famine and civil unrest. Lacking political channels with Great Britain, the Tucker Family met in May 1775 with eight other parishioners and resolved to send delegates to the Continental Congress in July, aiming for an exemption from the ban. Henry Tucker noted a clause in the ban which allowed the exchange of American goods for military supplies. The clause was confirmed by Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
when Tucker met with the Pennsylvania Committee of Safety. Independently, others confirmed this business arrangement with Peyton Randolph
Peyton Randolph (September 10, 1721 – October 22, 1775) was an American politician and planter who was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father of the United States. Born into Virginia's Randolph family of Virginia, wealthies ...
, the Charlestown Committee of Safety, and George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
.George James Bruere
Lieutenant-Colonel George James Bruere ( – 10 September 1780) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator who served as governor of Bermuda from 1764 until his death in 1780. Of all Bermuda's governors since 1612, his term of office ...
slept, and loaded onto these boats. As a consequence, on 2 October the Continental Congress exempted Bermuda from their trade ban, and Bermuda acquired a reputation for disloyalty. Later that year, the British Parliament passed the Prohibitory Act
The Prohibitory Act 1775 ( 16 Geo. 3. c. 5) was British legislation in late 1775 that cut off all trade between the Thirteen Colonies and England and removed the colonies from the King's protection. In essence, it was a declaration of economic ...
to prohibit trade with the American rebelling colonies and sent HMS ''Scorpion'' to keep watch over the island. The island's forts were stripped of cannons. Yet, wartime trade of contraband continued along well-established family connections. With 120 boats by 1775, Bermuda continued to trade with St. Eustatius until 1781 and provided salt to North American ports.[
In June 1776, HMS ''Nautilus'' secured the island, followed by in September. Yet, the two British captains seemed more intent on capturing prize money, causing a severe food shortage on the island until the departure of ''Nautilus'' in October. After France's entry into the war in 1778, Henry Clinton refortified the island under the command of Major William Sutherland. As a result, 91 French and American ships were captured in the winter of 1778–1779, bringing the population once again to the brink of starvation. Bermudian trade was severely hampered by the combined efforts of the Royal Navy, the British garrison and loyalist privateers, such that famine struck the island in 1779.][
Upon the death of George Bruere in 1780, the governorship passed to his son, George Jr., an active loyalist. Under his leadership, smuggling was stopped, and the Bermudian colonial government was populated with like-minded loyalists. Even Henry Tucker abandoned trading with the United States, because of the presence of multiple privateers.][
'']The Bermuda Gazette
''The Bermuda Gazette'' was a Bermudian English-language weekly newspaper
Weekly newspaper is a general-news or Current affairs (news format), current affairs publication that is issued once or twice a week in a wide variety broadsheet, mag ...
'', Bermuda's first newspaper, began publishing in 1784.Joseph Stockdale
Joseph Stockdale (died 10 October 1803) was the publisher of Bermuda's first newspaper, ''The Bermuda Gazette'', a Bermudian English-language weekly newspaper
Weekly newspaper is a general-news or Current affairs (news format), current affai ...
, had been given financial incentive to move to Bermuda with his family and establish the newspaper. He also provided other printing services and operated Bermuda's first local postal service. The ''Bermuda Gazette'' was sold by subscription and delivered to subscribers, with Stockdale's employee also delivering mail for a fee.
19th century
After the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
, the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
began improving the harbours on the Bermudas. In 1811, work began on the large Royal Naval Dockyard on Ireland Island
Ireland Island is the north-westernmost island in the chain which comprises Bermuda. It forms a long finger of land pointing northeastwards from the main island, the last link in a chain which also includes Boaz Island and Somerset Island. ...
, which was to serve as the islands' principal naval base guarding the western Atlantic Ocean shipping lanes. To guard the dockyard, the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
built the Bermuda Garrison
The Bermuda Garrison was the military establishment maintained on the British Overseas Territory and Imperial fortress of Bermuda by the regular British Army and its local-service militia and voluntary reserves from 1701 to 1957. The garrison ev ...
, and heavily fortified the archipelago.
During the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
between Britain and the United States, the British attacks on Washington, D.C., and the Chesapeake Chesapeake most often refers to:
*Chesapeake people, a Native American tribe also known as the Chesepian
*Chesapeake Bay
*Delmarva Peninsula, also known as the Chesapeake Peninsula
Chesapeake may also refer to:
Populated places In Virginia
* ...
were planned and launched from Bermuda, where the headquarters of the Royal Navy's North American Station
The North America and West Indies Station was a formation or command of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy stationed in North American waters from 1745 to 1956, with main bases at the Imperial fortresses of Bermuda and Halifax, Nova Scotia. The ...
had recently been moved from Halifax, Nova Scotia
Halifax is the capital and most populous municipality of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Nova Scotia, and the most populous municipality in Atlantic Canada. As of 2024, it is estimated that the population of the H ...
.
In 1816, James Arnold, the son of Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold (#Brandt, Brandt (1994), p. 4June 14, 1801) was an American-born British military officer who served during the American Revolutionary War. He fought with distinction for the American Continental Army and rose to the rank of ...
, fortified Bermuda's Royal Naval Dockyard against possible US attacks. Today, the National Museum of Bermuda
The National Museum of Bermuda, previously the Bermuda Maritime Museum from its opening in 1974 until 2009 (legislatively formalised in 2013), explores the maritime and island history of Bermuda. The maritime museum is located within the grounds ...
, which incorporates Bermuda's Maritime Museum, occupies the Keep of the Royal Naval Dockyard.
Due to its proximity to the southeastern US coast, Bermuda was frequently used during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
as a stopping point base for the Confederate States
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States from 1861 to 1865. It comprised eleven U.S. states th ...
' blockade runners
A blockade runner is a merchant vessel used for evading a naval blockade of a port or strait. It is usually light and fast, using stealth and speed rather than confronting the blockaders in order to break the blockade. Blockade runners usual ...
on their runs to and from the Southern states, and England, to evade Union naval vessels on blockade patrol.
Anglo-Boer War
During the Anglo-Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic an ...
(1899–1902), 5,000 Boer
Boers ( ; ; ) are the descendants of the proto Afrikaans-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled the Dutch ...
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
were housed on five islands of Bermuda. They were located according to their views of the war. "Bitterenders" (), who refused to pledge allegiance to the British Crown, were interned on Darrell's Island and closely guarded. Other islands such as Morgan's Island held 884 men, including 27 officers; Tucker's Island held 809 Boer prisoners, Burt's Island 607, and Ports Island held 35. Hinson's Island housed underage prisoners. The camp cemetery is on Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
.
''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' reported an attempted mutiny by Boer prisoners of war en route to Bermuda and that martial law was enacted on Darrell's Island.
The most famous escapee was the Boer prisoner of war Captain Fritz Joubert Duquesne
Frederick "Fritz" Joubert Duquesne ( ; sometimes Du Quesne; 21 September 187724 May 1956) was a South African Boer and German soldier, big-game hunter, journalist, and spy. Many of the claims Duquesne made about himself are in dispute; over hi ...
, who was serving a life sentence for "conspiracy against the British government and on (the charge of) espionage". On the night of 25 June 1902, Duquesne slipped out of his tent, worked his way over a barbed-wire fence, swam past patrol boats and bright spotlights, through storm-swept waters, using the distant Gibbs Hill Lighthouse for navigation until he arrived ashore on the main island. He settled in the U.S. and later became a spy for Germany in both World Wars. In 1942, Col. Duquesne was arrested by the FBI
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
for leading the Duquesne Spy Ring
The Duquesne Spy Ring is the largest espionage case in the United States history that ended in convictions. A total of 33 members of a Nazi German espionage network, headed by Frederick "Fritz" Duquesne, were convicted after a lengthy investigat ...
, which to this day remains the largest espionage case uncovered in the history of the United States.
20th and 21st centuries

 In the early 20th century Bermuda became a popular destination for American, Canadian and British tourists arriving by sea. The US
In the early 20th century Bermuda became a popular destination for American, Canadian and British tourists arriving by sea. The US Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act
The Tariff Act of 1930, also known as the Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act, was a protectionist trade measure signed into law in the United States by President Herbert Hoover on June 17, 1930. Named after its chief congressional sponsors, Senator Reed ...
of 1930, which enacted protectionist trade tariffs
A tariff or import tax is a duty imposed by a national government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods or raw materials and is ...
on goods imported into the US, led to the demise of Bermuda's once-thriving agricultural export trade to America and encouraged development of tourism as an alternative source of income. The island was one of the centres for illegal alcohol smuggling during the era of Prohibition in the United States
The Prohibition era was the period from 1920 to 1933 when the United States prohibited the production, importation, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages. The alcohol industry was curtailed by a succession of state legislatures, an ...
(1920–1933).Bermuda Railway
The Bermuda Railway was a common carrier line that operated in Bermuda for a brief period (31 October 1931 – 1 May 1948). In its 17 years of existence, the railway provided frequent passenger and freight service over its length spanni ...
, which was abandoned in 1948. The right of way is now the Bermuda Railway Trail.
In 1930, after several failed attempts, a Stinson Detroiter
The Stinson Detroiter was a six-seat cabin airliner for passengers or freight designed and built by the Stinson Aircraft Company, Stinson Aircraft Syndicate, later the ''Stinson Aircraft Corporation''. Two distinct designs used the Detroiter nam ...
seaplane
A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of takeoff, taking off and water landing, landing (alighting) on water.Gunston, "The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary", 2009. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their tech ...
flew to Bermuda from New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
: It was the first aeroplane ever to reach the islands. In 1936, Deutsche Luft Hansa
''Deutsche Luft Hansa A.G.'' (from 1933 styled as ''Deutsche Lufthansa'' and also known as ''Luft Hansa'', ''Lufthansa'', or DLH) was a German airline. It served as flag carrier of the country during the later years of the Weimar Republic and t ...
began to experiment with seaplane flights from Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
via the Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
with continuation flights to New York City.
In 1937, Imperial Airways
Imperial Airways was an early British commercial long-range airline, operating from 1924 to 1939 and principally serving the British Empire routes to South Africa, India, Australia and the Far East, including Malaya and Hong Kong. Passengers ...
and Pan American Airways
Pan American World Airways, originally founded as Pan American Airways and more commonly known as Pan Am, was an airline that was the principal and largest international air carrier and unofficial overseas flag carrier of the United States for ...
began operating scheduled flying boat
A flying boat is a type of seaplane with a hull, allowing it to land on water. It differs from a floatplane in having a fuselage that is purpose-designed for flotation, while floatplanes rely on fuselage-mounted floats for buoyancy.
Though ...
airline services from New York and Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
to Darrell's Island, Bermuda
Darrell's Island is a small island within the Great Sound of Bermuda. It lies in the southeast of the sound, and is in the north of Warwick Parish. The island is owned by the Bermuda Government.
Early history
The 1621 version of Richard No ...
. In World War II, the Hamilton Princess Hotel became a censorship centre. All mail, radio and telegraphic traffic bound for Europe, the US and the Far East was intercepted and analysed by 1,200 censors, of British Imperial Censorship, part of British Security Coordination
British Security Co-ordination (BSC) was a covert organisation set up in New York City by the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6) in May 1940 upon the authorisation of the Prime Minister, Winston Churchill.
Its purpose was to investigate ...
(BSC), before being routed to their destination. With BSC working closely with the FBI, the censors were responsible for the discovery and arrest of a number of Axis spies operating in the US, including the Joe K ring.
In 1948, a regularly scheduled commercial airline service began to operate, using land-based aeroplanes landing at Kindley Field
Kindley Air Force Base was a United States Air Force base in Bermuda from 1948–1970, having been operated from 1943 to 1948 by the United States Army Air Forces as ''Kindley Field''.
History
World War II
Prior to American entry into th ...
(now L.F. Wade International Airport), helping tourism to reach a peak in the 1960s and 1970s. By the end of the 1970s, however, international business had supplanted tourism as the dominant sector of Bermuda's economy.
The Royal Naval Dockyard and its attendant military garrison remained important to Bermuda's economy until the mid-20th century. In addition to considerable building work, the armed forces needed to source food and other materials from local vendors. Beginning in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, US military installations were also located in Bermuda, including a naval air station
A Naval Air Station (NAS) is a military air base, and consists of a permanent land-based operations locations for the military aviation division of the relevant branch of a navy (Naval aviation). These bases are typically populated by squadron ...
, and submarine base
A submarine base is a military base that shelters submarines and their personnel. Examples of present-day submarine bases include HMNB Clyde, Île Longue (the base for France's Force océanique stratégique), Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay, N ...
. The American military presence lasted until 1995.Richard Sharples
Sir Richard Christopher Sharples, (6 August 1916 – 10 March 1973) was a British politician and Governor of Bermuda who was shot dead by assassins linked to a small militant Bermudian Black Power group called the Black Beret Cadre. The former ...
, was assassinated by local Black Power
Black power is a list of political slogans, political slogan and a name which is given to various associated ideologies which aim to achieve self-determination for black people. It is primarily, but not exclusively, used in the United States b ...
militants during a period of civil unrest.2020 Summer Olympics
The officially the and officially branded as were an international multi-sport event that was held from 23 July to 8 August 2021 in Tokyo, Japan, with some of the preliminary sporting events beginning on 21 July 2021. Tokyo ...
, Bermuda became the smallest overseas territory to earn a gold medal, as Flora Duffy
Dame Flora Jane Duffy (born 30 September 1987) is a Bermudian professional triathlete. She won a gold medal at the 2020 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, Bermuda's first gold medal. She also competed in the Beijing, London, and Rio de Janeiro Olympics ...
won Bermuda's first ever Olympic gold medal in the women's triathlon.
Geography
 Bermuda is a group of low-forming volcanoes in the Atlantic Ocean, in the west of the
Bermuda is a group of low-forming volcanoes in the Atlantic Ocean, in the west of the Sargasso Sea
The Sargasso Sea () is a region of the Atlantic Ocean bounded by four currents forming an ocean gyre. Unlike all other regions called seas, it is the only one without land boundaries. It is distinguished from other parts of the Atlantic Oc ...
, roughly east-southeast of Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras is a cape located at a pronounced bend in Hatteras Island, one of the barrier islands of North Carolina.
As a temperate barrier island, the landscape has been shaped by wind, waves, and storms. There are long stretches of beach ...
on the Outer Banks
The Outer Banks (frequently abbreviated OBX) are a string of barrier islands and spits off the coast of North Carolina and southeastern Virginia, on the east coast of the United States. They line most of the North Carolina coastline, separatin ...
of North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, United States which is the nearest landmass.Cape Sable Island
Cape Sable Island, locally referred to as Cape Island, is a small Canada, Canadian island at the southernmost point of the Nova Scotia peninsula. It is sometimes confused with Sable Island. Historically, the Argyle, Nova Scotia region was known ...
, Nova Scotia Canada which is north of Bermuda. It is also located south-southwest of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon ( ), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, located near the Canada, Canadian prov ...
(France), north-northeast of Havana
Havana (; ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.[Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...](_bl ...<br></span></div>, <div class=)
, north of the British Virgin Islands, and north of San Juan San Juan, Spanish for Saint John (disambiguation), Saint John, most commonly refers to:
* San Juan, Puerto Rico
* San Juan, Argentina
* San Juan, Metro Manila, a highly urbanized city in the Philippines
San Juan may also refer to:
Places Arge ...
, Puerto Rico.
The territory consists of 181 islands, with a total area of .[ The territory's tallest peak is Town Hill on Main Island at tall.]Bermuda Triangle
The Bermuda Triangle, also known as the Devil's Triangle, is a loosely defined region in the North Atlantic Ocean, roughly bounded by Florida, Bermuda, and Puerto Rico. Since the mid-20th century, it has been the focus of an urban legend sug ...
, a region of sea in which, according to legend, a number of aircraft and boats have disappeared under unexplained or mysterious circumstances.
Main sights
Bermuda's pink sand beaches and clear, cerulean
The color cerulean (American English) or caerulean (British English, Commonwealth English), is a variety of the hue of blue that may range from a light azure blue to a more intense sky blue. Cerulean may also be mixed with the hue of green. ...
blue ocean waters are popular with tourists. A number of Bermuda's hotels are located along the south shore of the island. In addition to its beaches, there are a number of sightseeing attractions. Historic St. George's is a designated World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. Scuba
Scuba, originally SCUBA, often expanded to scuba set, is any self contained underwater breathing apparatus, a source of breathing gas used for underwater diving which is carried by the diver.
Scuba may also refer to:
* Scuba diving, swimming unde ...
divers can explore a number of wrecks
''Wrecks'' is a one-man play by Neil LaBute, that was commissioned and produced by the Everyman Palace Theatre in Cork, Ireland. The play was a part of the city's Capital of Culture programme in 2005.LaBute, Neil''Wrecks'Wrecks: And Other Play ...
and coral reefs
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
...
in relatively shallow water (typically in depth), with virtually unlimited visibility. A number of nearby reefs are readily accessible from shore by snorkellers, especially at Church Bay.
Bermuda's most popular visitor attraction is the Royal Naval Dockyard, which includes the National Museum of Bermuda. Other attractions include the Bermuda Aquarium, Museum and Zoo, Bermuda Underwater Exploration Institute, the Botanical Gardens and Masterworks Museum of Bermuda Art, lighthouses, and the Crystal Caves with stalactites
A stalactite (, ; , ) is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is ca ...
and underground saltwater pools. Somerset Bridge is the world's smallest drawbridge, and Horseshoe Bay and Warwick Long Bay are among the beautiful beaches in Bermuda.
Non-residents are prohibited from driving cars on the island. Public transport and taxis are available or visitors can rent scooters for use as private transport.[
]
Geology
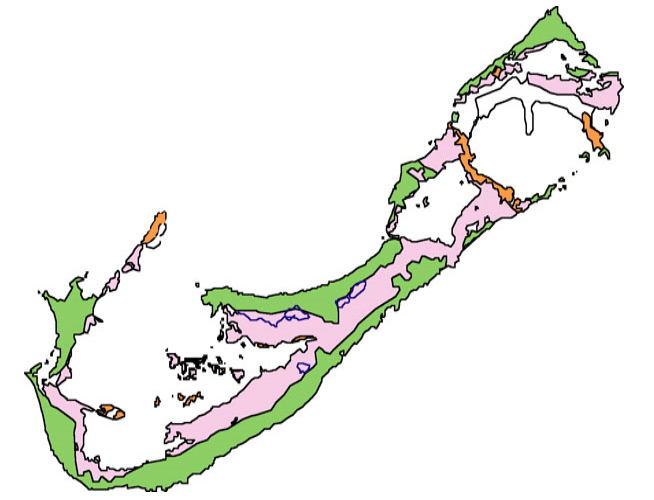 Bermuda consists of over 150
Bermuda consists of over 150 limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
islands, but especially five main islands, along the southern margin of the Bermuda Platform, one of three topographic highs found on the Bermuda Pedestal. This Bermuda Pedestal sits atop the Bermuda Rise, a mid-basin swell surrounded by abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between . Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. They ...
s. The Bermuda Pedestal is one of four topographic highs aligned roughly from North-East to South-West. The others, all submerged, are ''Bowditch Seamount'' to the north-east, and ''Challenger Bank'' and ''Argus Bank'' to the south-west. Initial uplift of this rise occurred in the Middle to Late Eocene
The Priabonian is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS's geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age or the upper stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Eocene epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), Series. It spans ...
and concluded by the Late Oligocene
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the pro ...
, when it subsided below sea level. The volcanic rocks associated with this rise are tholeiitic lavas and intrusive lamprophyre
Lamprophyres () are uncommon, small-volume ultrapotassic igneous rocks primarily occurring as dikes, lopoliths, laccoliths, stocks, and small intrusions. They are alkaline silica- undersaturated mafic or ultramafic rocks with high magnesium o ...
sheets, which form a volcanic basement, on average, below the island carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
surface.aeolian processes
Aeolian processes, also spelled eolian, pertain to wind activity in the study of geology and weather and specifically to the wind's ability to shape the surface of the Earth (or other planets). Winds may erosion, erode, transport, and deposit ...
, with a karst terrain. These eolianite
Eolianite or aeolianite is any rock formed by the lithification of sediment deposited by aeolian processes; that is, the wind. In common use, however, the term refers specifically to the most common form of eolianite: coastal limestone consisting ...
s are actually the type locality, and formed during interglaciation
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene in ...
s (i.e., the upper levels of the limestone cap, formed primarily by calcium-secreting algae, was broken down into sand by wave action during interglaciation when the seamount was submerged, and during glaciation, when the top of the seamount was above sea level, that sand was blown into dunes and fused together into a limestone sandstone), and are laced by red paleosol
In Earth science, geoscience, paleosol (''palaeosol'' in Great Britain and Australia) is an ancient soil that formed in the past. The definition of the term in geology and paleontology is slightly different from its use in soil science.
In geo ...
s, also referred to as geosols or terra rossas, indicative of Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
n atmospheric dust and forming during glacial stage
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and gr ...
s. The stratigraphic column
A stratigraphic column is a representation used in geology and its subfield of stratigraphy to describe the vertical location of rock units in a particular area. A typical stratigraphic column shows a sequence of sedimentary rocks, with the oldest ...
starts with the Walsingham Formation, overlain by the Castle Harbour Geosol, the Lower and Upper Town Hill Formations separated by the Harbour Road Geosol, the Ord Road Geosol, the Belmont Formation, the Shore Hills Geosol, the Rocky Bay Formation, and the Southampton Formation.[
The older ]eolianite
Eolianite or aeolianite is any rock formed by the lithification of sediment deposited by aeolian processes; that is, the wind. In common use, however, the term refers specifically to the most common form of eolianite: coastal limestone consisting ...
ridges (older Bermuda) are more rounded and subdued compared to the outer coastline (Younger Bermuda). Thus, post deposition morphology includes chemical erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
, with inshore water bodies demonstrating that much of Bermuda is partially drowned Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
karst
Karst () is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone and Dolomite (rock), dolomite. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. Ther ...
. The Walsingham Formation is a clear example, constituting the cave district around Castle Harbour. The Upper Town Hill Formation forms the core of the Main Island, and prominent hills such as Town Hill, Knapton Hill, and St. David's Lighthouse, while the highest hills, Gibbs Hill Lighthouse, are due to the Southampton Formation.[
Bermuda has two major ]aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
s, the Langton Aquifer located within the Southampton, Rocky Bay and Belmont Formations, and the Brighton Aquifer located within the Town Hill Formation. Four freshwater lenses
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), ...
occur in Bermuda, with the Central Lens being the largest on Main Island, containing an area of and a thickness greater than .[
]
Climate
Bermuda has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: ''Cfa''), bordering closely on the tropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southeast Florida, United States ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: ''Af''). Bermuda's oceanic influence results in a more moderate climate, more similar to the western coast of Europe than on the eastern coast of North America, characterised by high relative humidity that moderates temperature, ensuring generally mild winters and summers.
Bermuda is warmed by the nearby Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude (North Carolin ...
. The islands may experience modestly cooler temperatures in January, February, and March verage [
]
Bermuda lies within the Main Development Region, and is often directly in the path of hurricanes[
File:1904 view of eastern Hamilton Harbour and Paget Parish from Fort Hamilton, Prospect Camp, Bermuda.jpg, 1904 view across Hamilton Harbour from Fort Hamilton of cedar-cloaked hills in Paget Parish
File:Bermuda wv.jpg, Residential suburb near the old St. George's Garrison, Bermuda, St. George's Garrison, with "Town Cut Battery" or "Gate's Fort" on the shore of the Town Cut, and St. George's, Bermuda, St. George's Town and its St. George's Harbour, Bermuda, harbour in the background
File:.jpgOfficers of 3rd Battalion, The Royal Fusiliers (City of London Regiment), at Battalion Training at Tucker's Town, Bermuda, 1905.jpg, Officers of 3rd Battalion, The Royal Fusiliers (City of London Regiment), at Battalion Training at Tucker's Town, Bermuda, 1905. Bermuda's climate means heavier temperate uniforms were by armed forces and police personnel and are worn for much of the year.
File:Battalion Training at Tucker's Town Bermuda of the 3rd Battalion Royal Fusiliers.jpg, Battalion Training at Tucker's Town Bermuda of the 3rd Battalion Royal Fusiliers, wearing lightweight khaki drills, intended as a warm climate uniform, as a summer uniform
]
Flora and fauna
 When discovered, Bermuda was uninhabited by humans and mostly dominated by forests of Juniperus bermudiana, Bermuda cedar, with mangrove marshes along its shores. Forest cover is around 20% of the total land area, equivalent to 1,000 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, which was unchanged from 1990.
Only 165 of the island's current 1,000 vascular plant species are considered indigenous (ecology), native; fifteen of those, including the eponymous cedar, are endemism, endemic. The tropical climate of Bermuda allowed settlers to introduce multiple non-native species of trees and plants to the island.
When discovered, Bermuda was uninhabited by humans and mostly dominated by forests of Juniperus bermudiana, Bermuda cedar, with mangrove marshes along its shores. Forest cover is around 20% of the total land area, equivalent to 1,000 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, which was unchanged from 1990.
Only 165 of the island's current 1,000 vascular plant species are considered indigenous (ecology), native; fifteen of those, including the eponymous cedar, are endemism, endemic. The tropical climate of Bermuda allowed settlers to introduce multiple non-native species of trees and plants to the island.Bermuda petrel
The Bermuda petrel (''Pterodroma cahow'') is a gadfly petrel. Commonly known in Bermuda as the cahow, a name derived from its eerie cries, this nocturnal ground-nesting seabird is the national bird of Bermuda, pictured on Bermudian currency. Berm ...
or cahow, which was rediscovered in 1951 after having been thought extinct since the 1620s. The cahow is important as an example of a Lazarus taxon, Lazarus species, hence the government has a programme to protect it, including restoration of its habitat areas. Another well-known species includes the white-tailed tropicbird, locally known as the longtail. These birds come inland to breed around February to March and are Bermudians' first sign of incoming spring.
The Bermuda rock lizard (or Bermuda rock skink) was long thought to have been the only indigenous non-bird land vertebrate of Bermuda, discounting the marine turtles that lay their eggs on its beaches. However, scientists have recently discovered through genetic DNA studies that a species of turtle, the diamondback terrapin, previously thought to have been introduced to the archipelago, actually pre-dated the arrival of humans.
Only three bee species have been recorded on Bermuda. The western honey bee ''Western honey bee, Apis mellifera'' was introduced by English colonists around 1616, marking the beginning of beekeeping's cultural significance on the island. A second species, the sweat bee ''Lasioglossum semiviridie'', was last recorded in 1922. Recent DNA analysis has revealed that the leafcutter bee ''Megachile pruina'' in Bermuda constitutes a unique evolutionary lineage, distinct from ''M. pruina'' populations in the United States.
Demographics
 Bermuda's 2016 Census put its population at 63,779 and, with an area of , it has a calculated population density of .
Bermuda's 2016 Census put its population at 63,779 and, with an area of , it has a calculated population density of .
Languages
The predominant language in Bermuda is Bermudian English.Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
, Madeira, and the Cape Verde Islands and their descendants.
Religion
Christianity is the largest religion on Bermuda.
Politics
 Bermuda is an British Overseas Territory, Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom, and the Government of the United Kingdom is the sovereign government.
Bermuda is an British Overseas Territory, Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom, and the Government of the United Kingdom is the sovereign government.[
Defence and foreign affairs are the responsibility of the United Kingdom, which also retains responsibility to ensure good government and must approve any changes to the Constitution of Bermuda. Bermuda is Britain's oldest overseas territory. Although the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament retains ultimate legislative authority over the territory, in 1620, a Royal Proclamation granted Bermuda limited self-governance, delegating to the ]House of Assembly
House of Assembly is a name given to the legislature or lower house of a bicameral parliament. In some countries this may be at a subnational level.
Historically, in British Crown colonies as the colony gained more internal responsible g ...
of the Parliament of Bermuda the internal legislation of the colony. The Parliament of Bermuda is the fifth oldest legislature in the world, behind the Sejm of Poland, the Parliament of England, the Tynwald of the Isle of Man, and the Althing of Iceland.
 The Constitution of Bermuda came into force in 1968 and has been amended several times since then.
The Constitution of Bermuda came into force in 1968 and has been amended several times since then.House of Assembly
House of Assembly is a name given to the legislature or lower house of a bicameral parliament. In some countries this may be at a subnational level.
Historically, in British Crown colonies as the colony gained more internal responsible g ...
, or lower house, has 36 members, elected by the eligible voting populace in secret ballot to represent geographically defined constituencies.
Nationality and citizenship
 Historically, English (later British) colonials shared the same citizenship as those born within that part of the sovereign territory of the Kingdom of England (including the Principality of Wales) that lay within the Island of Britain (although Magna Carta had effectively created English citizenship, citizens were still termed 'subjects of the King of England' or 'English subjects'. With the Acts of Union 1707, 1707 union of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland, this was replaced with 'British Subject', which encompassed citizens throughout the sovereign territory of the British Government, including its colonies, though not the British protectorates). With no Representative government, representation at the sovereign or national level of government, British colonials were therefore not consulted, or required to give their consent, to a series of Acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom between 1968 and 1982, which were to limit their rights and ultimately change their citizenship.
When several colonies had been elevated before the Second World War to Dominion status, collectively forming the old Commonwealth of Nations#Adoption and formalisation of the Commonwealth, British Commonwealth (as distinct from the United Kingdom and its dependent colonies), their citizens remained British Subjects, and in theory, any British Subject born anywhere in the World had the same basic right to enter, reside, and work in the United Kingdom as a British Subject born in the United Kingdom whose parents were also both British Subjects born in the United Kingdom (although a number of governmental policies and practices acted to thwart the free exercise of these rights by various groups of colonials, including Greek Cypriots).
When the Dominions and an increasing number of colonies began choosing complete independence from the United Kingdom after the Second World War, the Commonwealth was transformed into a community of independent nations, or Commonwealth realms, each recognising the British monarch as its own head of state (creating separate monarchies with the same person occupying all of the separate Thrones; the exception being republican India).
'British Subject' was replaced by the British Nationality Act 1948 with 'Citizen of the United Kingdom and Colonies' for the residents of the United Kingdom and its colonies, as well as for the Crown Dependencies. However, as it was desired to retain free movement for all Commonwealth Citizens throughout the Commonwealth, 'British Subject' was retained as a blanket nationality shared by Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies (the 'British realm') as well as the citizens of the various other Commonwealth realms.
Historically, English (later British) colonials shared the same citizenship as those born within that part of the sovereign territory of the Kingdom of England (including the Principality of Wales) that lay within the Island of Britain (although Magna Carta had effectively created English citizenship, citizens were still termed 'subjects of the King of England' or 'English subjects'. With the Acts of Union 1707, 1707 union of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland, this was replaced with 'British Subject', which encompassed citizens throughout the sovereign territory of the British Government, including its colonies, though not the British protectorates). With no Representative government, representation at the sovereign or national level of government, British colonials were therefore not consulted, or required to give their consent, to a series of Acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom between 1968 and 1982, which were to limit their rights and ultimately change their citizenship.
When several colonies had been elevated before the Second World War to Dominion status, collectively forming the old Commonwealth of Nations#Adoption and formalisation of the Commonwealth, British Commonwealth (as distinct from the United Kingdom and its dependent colonies), their citizens remained British Subjects, and in theory, any British Subject born anywhere in the World had the same basic right to enter, reside, and work in the United Kingdom as a British Subject born in the United Kingdom whose parents were also both British Subjects born in the United Kingdom (although a number of governmental policies and practices acted to thwart the free exercise of these rights by various groups of colonials, including Greek Cypriots).
When the Dominions and an increasing number of colonies began choosing complete independence from the United Kingdom after the Second World War, the Commonwealth was transformed into a community of independent nations, or Commonwealth realms, each recognising the British monarch as its own head of state (creating separate monarchies with the same person occupying all of the separate Thrones; the exception being republican India).
'British Subject' was replaced by the British Nationality Act 1948 with 'Citizen of the United Kingdom and Colonies' for the residents of the United Kingdom and its colonies, as well as for the Crown Dependencies. However, as it was desired to retain free movement for all Commonwealth Citizens throughout the Commonwealth, 'British Subject' was retained as a blanket nationality shared by Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies (the 'British realm') as well as the citizens of the various other Commonwealth realms.Sea Venture
''Sea Venture'' was a seventeenth-century English sailing ship, part of the Third Supply mission flotilla to the Jamestown Colony in 1609. She was the 300 ton flagship of the London Company. During the voyage to Virginia, ''Sea Venture'' encount ...
) in 1612, when it received its Third Royal Charter from James VI and I, King James I, amending the boundaries of the Virginia Colony, First Colony of Virginia far enough across the Atlantic to include Bermuda. The citizenship rights guaranteed to settlers by King James I in the original Royal Charter of 10 April 1606, thereby applied to Bermudians:
These rights were confirmed in the Royal Charter granted to the London Company's spin-off, the Somers Isles, Company of the City of London for the Plantacion of The Somers Isles, in 1615 on Bermuda being separated from Virginia:
Bermuda is not the only territory whose citizenship rights were laid down in a Royal Charter. In regards to Saint Helena, St. Helena, Tim Beaumont, Lord Beaumont of Whitley in the House of Lords debate on the British Overseas Territories Bill on 10 July 2001, stated:
Some Conservative Party backbenchers stated that it was the unpublished intention of the Conservative British Government to return to a single citizenship for the United Kingdom and all of the remaining territories once Hong Kong had been handed over to China. Whether this was so will never be known as by 1997 the Labour Party was in Government. The Labour Party had declared prior to the election that the colonies had been ill-treated by the British Nationality Act 1981, and it had made a pledge to return to a single citizenship for the United Kingdom and the remaining territories part of its election manifesto. Other matters took precedence, however, and this commitment was not acted upon during Labour's first term in Government. The House of Lords, in which multiple former colonial Governors sat (including former Governor of Bermuda Lord Waddington), lost patience and tabled and passed its own bill, then handed it down to the House of Commons to confirm in 2001. As a result, the British Dependent Territories were renamed the British Overseas Territory, British Overseas Territories in 2002 (the term 'dependent territory' had caused much ire in the former colonies, especially well-heeled and self-reliant Bermuda, as it implied not only that British Dependent Territories Citizens were 'other than British', but that their relationship to Britain and to 'real British people' was both inferior and parasitic).[#refFAC, House of Commons Foreign Affairs Committee Overseas Territories Report, pp. 145–47]
At the same time, although Labour had promised a return to a single citizenship for the United Kingdom, Crown dependencies, and all remaining territories, British Dependent Territories Citizenship, renamed British Overseas Territories Citizenship, remained the default citizenship for the territories, other than the Falkland Islands and Gibraltar (for which British Citizenship is still the default citizenship). The bars to residence and work in the United Kingdom that had been raised against holders of British Dependent Territories Citizenship by The British Nationality Act 1981 were, however, removed, and British Citizenship was made attainable by simply obtaining a second British passport with the citizenship recorded as British Citizen (requiring a change to passport legislation as prior to 2002, it had been illegal to possess two British Passports).
In March 2021, the government implemented a new visa policy towards foreigners, through which residency can be obtained by way of investing at least $2.5 million in "real estate, Bermuda government bonds, a contribution to the island's debt relief fund or the Bermuda Trust Fund, and charity", among other options. According to the Labour Minister, Jason Hayward, this step had to be taken to relieve some of the country's debt resulting from the Covid pandemic.
Administrative divisions
 Bermuda is divided into nine Parish (administrative division), parishes and two incorporated municipalities.
Bermuda is divided into nine Parish (administrative division), parishes and two incorporated municipalities.Hamilton
Hamilton may refer to:
* Alexander Hamilton (1755/1757–1804), first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
* ''Hamilton'' (musical), a 2015 Broadway musical by Lin-Manuel Miranda
** ''Hamilton'' (al ...
(city)
* St. George's, Bermuda, St George's (town)
Bermuda's two informal villages are:
* Flatts Village, Bermuda, Flatts Village
* Somerset Village, Bermuda, Somerset Village
Jones Village in Warwick, Cashew City (St. George's), Claytown (Hamilton), Middle Town (Pembroke), and Tucker's Town (St. George's) are neighbourhoods (the original settlement at Tucker's Town was replaced with a golf course in the 1920s and the few houses in the area today are mostly on the water's edge of Castle Harbour or the adjacent peninsula); Dandy Town and North Village are sports clubs, and Harbour View Village is a small public housing development.
International relations
As a British Overseas Territory, Bermuda does not have a seat in the General Assembly of the United Nations, United Nations; it is represented by Britain in matters of Foreign and Commonwealth Office, foreign affairs.Sargasso Sea
The Sargasso Sea () is a region of the Atlantic Ocean bounded by four currents forming an ocean gyre. Unlike all other regions called seas, it is the only one without land boundaries. It is distinguished from other parts of the Atlantic Oc ...
.
In 2013 and 2017 Bermuda chaired the United Kingdom Overseas Territories Association.
Asylum offer to four former Guantánamo detainees
On 11 June 2009, four Uyghur people, Uyghurs who had been held in the United States Guantánamo Bay detention camp, in Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, were transferred to Bermuda.
British North America, British West Indies and the Caribbean Community
The British Government originally grouped Bermuda with North America (given its proximity, and Bermuda having been established as an extension of the Colony of Virginia, and with Carolina Colony
The Province of Carolina was a colony of the Kingdom of England (1663–1707) and later the Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1712) that existed in North America and the Caribbean from 1663 until the Carolinas were partitioned into North and Sou ...
, the nearest landfall, having been settled from Bermuda). After the acknowledgement by the British Government of the independence of Thirteen Colonies, thirteen continental colonies (including Virginia and the Carolinas) in 1783, Bermuda was generally grouped regionally by the British Government with The Maritimes and Newfoundland and Labrador (and more widely, as part of British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
), substantially nearer to Bermuda than is the Caribbean.
From 1783 through 1801, the British Empire, including British North America, was administered by the Home Office and by the Home Secretary, then from 1801 to 1854 by the War Office (which became the ''War and Colonial Office'') and Secretary of State for War and Colonies (as the Secretary of State for War was renamed). From 1824, the British Empire was divided by the War and Colonial Office into four administrative departments, including ''North America'', the ''West Indies'', ''Mediterranean and Africa'', and ''Eastern Colonies'', of which the North American department included Bermuda. The Colonial Office and War Office, the Secretary of State for the Colonies and the Secretary of State for War, were all separated in 1854.Colony of Newfoundland
Newfoundland was an English overseas possessions, English, and later British, colony established in 1610 on the Newfoundland (island), island of Newfoundland. That followed decades of sporadic English settlement on the island, which was at first ...
became the Dominion of Newfoundland
Newfoundland was a British dominion in eastern North America, today the modern Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It included the island of Newfoundland, and Labrador on the continental mainland. Newfoundland was one of the orig ...
, leaving the Imperial fortress of Bermuda as the sole remaining British North American colony.
Bermuda, with a land mass totalling less than 21 square miles and a population of 17,535, could hardly constitute an Imperial administrative region on its own. By 1908, the Colonial Office included two departments (one overseeing dominion and British protectorate, protectorate business, the other colonial): The Crown Colonies Department was made up of a West Indian Division that included Bermuda, as well as Jamaica, Turks Islands, British Honduras, British Guiana, Bahamas, Bermuda, Trinidad, Barbados, Windward Islands, Leeward Islands, Falkland Islands, and St. Helena.
 Following Canadian confederation in 1867, the British political, naval and military hierarchy in Bermuda became increasingly separated from that of the Canadian Government (the
Following Canadian confederation in 1867, the British political, naval and military hierarchy in Bermuda became increasingly separated from that of the Canadian Government (the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
headquarters for the North America and West Indies Station had spent summers at Halifax, Nova Scotia, and winters at Bermuda, but settled at Bermuda year round with the Royal Naval Dockyard, Halifax finally being transferred to the Royal Canadian Navy in 1907, and the Bermuda Garrison
The Bermuda Garrison was the military establishment maintained on the British Overseas Territory and Imperial fortress of Bermuda by the regular British Army and its local-service militia and voluntary reserves from 1701 to 1957. The garrison ev ...
had been placed under the military Commander-in-Chief America in New York during the American War of Independence, and had been part of the Nova Scotia Command thereafter, but became the separate ''Bermuda Command'' from the 1860s with the Major-General or Lieutenant-General appointed as Commander-in-Chief of Bermuda also filling the civil role of Governor of Bermuda
The governor of Bermuda (officially Governor and Commander-in-Chief of the Somers Isles (alias the Islands of Bermuda)) is the representative of the British monarch in the British overseas territory of Bermuda.
For the purposes of this arti ...
), and Bermuda was increasingly perceived by the British Government as in, or at least grouped for convenience with, the British West Indies (although the established Church of England in Bermuda, which from 1825 to 1839 had been attached to the See of Nova Scotia) remained part of the Diocese of Newfoundland, Diocese of Newfoundland and Bermuda until 1879, when the Synod of the Church of England in Bermuda was formed and a Diocese of Bermuda became separate from the Diocese of Newfoundland, but continued to be grouped under the ''Bishop of Newfoundland and Bermuda'' until 1919, when Newfoundland and Bermuda each received its own bishop. Newfoundland attained Dominion status in 1907, leaving the nearest other territories to Bermuda that were still within the Commonwealth realm, British Realm (a term which replaced ''Dominion'' in 1952 as the dominions and a number of colonies moved towards full political independence) as the British colonies in the British West Indies.
Other denominations also at one time included Bermuda with Nova Scotia or Canada. Following the separation of the Church of England from the Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic worship was outlawed in England (subsequently ''Britain'') and its colonies, including Bermuda, until the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1791, and operated thereafter under restrictions until the Twentieth Century. Once Roman Catholic worship was established, Bermuda formed part of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Halifax-Yarmouth, Archdiocese of Halifax, Nova Scotia until 1953, when it was separated to become the Roman Catholic Diocese of Hamilton in Bermuda, Apostolic Prefecture of Bermuda Islands.Caribbean Community
The Caribbean Community (abbreviated as CARICOM or CC) is an intergovernmental organisation that is a Political association, political and economic union of 15 member states (14 nation-states and one dependency) and five associated members thro ...
(CARICOM) in July 2003.
CARICOM is a socio-economic bloc of nations in or near the Caribbean Sea established in 1973. Other outlying member states include the Co-operative Republic of Guyana and the Republic of Suriname in South America, and Belize in Central America. The Turks and Caicos Islands, an associate member of CARICOM, and the Commonwealth of The Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of ...
, a full member of CARICOM, are in the Atlantic, but close to the Caribbean. Other nearby nations or territories, such as the United States, are not members (although the US Commonwealth of Puerto Rico has observer status, and the United States Virgin Islands announced in 2007 that they would seek ties with CARICOM). Bermuda has minimal trade with the Caribbean region, and little in common with it economically, being roughly from the Caribbean Sea; it joined CARICOM primarily to strengthen cultural links with the region.
Among some scholars, "the Caribbean" can be a socio-historical category, commonly referring to a cultural zone characterised by the legacy of slavery (a characteristic Bermuda shared with the Caribbean and the US) and the plantation system (which did not exist in Bermuda). It embraces the islands and parts of the neighbouring continent, and may be extended to include the Caribbean Diaspora overseas.[Norman Girvan, Girvan, Norman (2001), In ''New Caribbean Thought'', Folke Lindahl and Brian Meeks (eds), UWI Press, pp. 3 ff]
Google Books
The PLP, which was the party in government when the decision was made to join CARICOM, has been dominated for decades by West Indians and their descendants. The prominent roles of West Indians among Bermuda's black politicians and labour activists predated party politics in Bermuda, as exemplified by E. F. Gordon. The late PLP leader, Dame Lois Browne-Evans (whose parents and grandparents emigrated to Bermuda from Nevis and St. Kitts in 1914), and her Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidadian-born husband, John Evans (who co-founded the ''West Indian Association of Bermuda'' in 1976),
Police
Law enforcement in Bermuda is provided chiefly by the Bermuda Police Service and is also supported with the Customs Department and Immigration Department. During certain times the Royal Bermuda Regiment can be called in to assist law enforcement personnel.
Military and defence

 A former Imperial fortress British Overseas Territory, colony once known as "the Gibraltar of the West" and "Fortress Bermuda", defence of Bermuda, as part of the British sovereign state, is the responsibility of the British Government.
For the first two centuries of settlement, the most potent armed force operating from Bermuda was its merchant shipping fleet, which turned to
A former Imperial fortress British Overseas Territory, colony once known as "the Gibraltar of the West" and "Fortress Bermuda", defence of Bermuda, as part of the British sovereign state, is the responsibility of the British Government.
For the first two centuries of settlement, the most potent armed force operating from Bermuda was its merchant shipping fleet, which turned to privateering
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since Piracy, robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sover ...
at every opportunity. The Bermuda government maintained a local (infantry) militia and fortified coastal artillery batteries manned by volunteer artillerymen. Bermuda tended toward the Royalist side during the English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, English Civil War, being the first of six colonies to recognise Charles II of England, Charles II as King on the execution of his father, Charles I of England, Charles I, in 1649, and was one of those targeted by the Rump Parliament in An Act for prohibiting Trade with the Barbadoes, Virginia, Bermuda and Antego, which was passed on 30 October 1650. With control of the "army" (the militia and coastal artillery), the colony's Royalists deposed the Governor, Captain Thomas Turner, elected John Trimingham to replace him, and exiled a number of its Parliamentary leaning Independent (religion), Independents to settle the Bahamas under William Sayle
Captain William Sayle ( 1590 – 1671) was a prominent English landholder who was Governor of Bermuda in 1643 and again in 1658. As an Independent in religion and politics, and an adherent of Oliver Cromwell, he was dissatisfied with life in Ber ...
as the Eleutheran Adventurers. Bermuda's barrier reef, coastal artillery batteries and militia provided a defence too powerful for the fleet sent in 1651 by Parliament under the command of Admiral Sir George Ayscue to capture the Royalist colonies. The Parliamentary Navy was consequently forced to blockade Bermuda for several months 'til the Bermudians negotiated a peace.
After the American Revolutionary War, Bermuda was established as the Western Atlantic headquarters of the ''North America Station'' (later called the North America and West Indies Station, and later still the ''America and West Indies Station'' as it absorbed other stations) of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
. Once the Royal Navy established a base and dockyard defended by regular soldiers, however, the militias were disbanded following the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
. At the end of the 19th century, the colony raised volunteer units to form a reserve for the Bermuda Garrison, military garrison.
Due to its isolated location in the North Atlantic Ocean, Bermuda was vital to the Allies' war effort during both world wars of the 20th century, serving as a marshalling point for trans-Atlantic convoys, as well as a naval air base. By the Second World War, both the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm and the Royal Air Force were operating Seaplane bases on Bermuda.
In May 1940, the US requested base rights in Bermuda from the United Kingdom, but British Prime Minister Winston Churchill was initially unwilling to accede to the American request without getting something in return. In September 1940, as part of the Destroyers for Bases Agreement, the UK granted the US base rights in Bermuda. Bermuda and Dominion of Newfoundland, Newfoundland were not originally included in the agreement, but both were added to it, with no war material received by the UK in exchange. One of the terms of the agreement was that the airfield the US Army built would be used jointly by the US and the UK (which it was for the duration of the war, with RAF Transport Command relocating there from Royal Air Force, Bermuda, 1939-1945, Darrell's Island in 1943). The US Army established the Bermuda Base Command in 1941 to co-ordinate its USAAF, air, anti-aircraft, and United States Army Coast Artillery Corps, coast artillery assets during the war. The US Navy operated a submarine base
A submarine base is a military base that shelters submarines and their personnel. Examples of present-day submarine bases include HMNB Clyde, Île Longue (the base for France's Force océanique stratégique), Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay, N ...
on Ordnance Island, Bermuda, Ordnance Island from 1942 through 1945.seaplane
A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of takeoff, taking off and water landing, landing (alighting) on water.Gunston, "The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary", 2009. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their tech ...
base until the mid-1960s, was designated as the Naval Air Station Bermuda Annex. It provided optional anchorage and dockage facilities for transiting US Navy, US Coast Guard and NATO vessels, depending on size. An additional US Navy compound known as Naval Facility Bermuda (NAVFAC Bermuda), a submarine-detecting SOSUS station, was located to the west of the Annex near a Canadian Forces communications facility in the Tudor Hill area; it was converted from a US Army coast artillery bunker in 1954 and operated until 1995. Although leased for 99 years, US forces withdrew in 1995, as part of the wave of base closures following the end of the Cold War.
Canada, which had operated a war-time naval base, HMCS Somers Isles, HMCS ''Somers Isles'', on the old Royal Navy base at Convict Bay, St George's, also established a radio-listening post at Daniel's Head in the West End of the islands during this time.
In the 1950s, after the end of World War II, the Royal Naval dockyard and the military garrison were closed. A small Royal Navy supply base, HMS Malabar (shore establishment), HMS ''Malabar'', continued to operate within the dockyard area, supporting transiting Royal Navy ships and submarines until it, too, was closed in 1995, along with the American and Canadian bases.
 Bermudians served in the British armed forces during both World War I and World War II. After the latter, Major-General Glyn Gilbert, Glyn Charles Anglim Gilbert, Bermuda's highest-ranking soldier, was instrumental in developing the Royal Bermuda Regiment. A number of other Bermudians and their descendants had preceded him into senior ranks, including Bahamian-born Admiral James Gambier, 1st Baron Gambier, Lord Gambier, and Bermudian-born Royal Marines Brigadier A. John Harvey. When promoted to brigadier at age 38, following his wounding at the Allied invasion of Sicily, Harvey became the youngest-ever Royal Marine Brigadier. The Cenotaph in front of the Cabinet Building (in Hamilton) was erected in tribute to Bermuda's Great War dead (the tribute was later extended to Bermuda's Second World War dead) and is the site of the annual Remembrance Day commemoration.
Today, the only military unit remaining in Bermuda, other than Bermuda Sea Cadet Corps, naval and army cadet corps, is the Royal Bermuda Regiment, an amalgam of the voluntary units originally formed toward the end of the 19th century. Although the Regiment's predecessors were voluntary units, until 2018 the modern body was formed primarily by conscription: balloted males were required to serve for three years, two months part-time, once they turn 18. Conscription was abolished 1 July 2018.
In early 2020 the Royal Bermuda Regiment formed the Bermuda Coast Guard. Its 24-hour on-duty service includes search and rescue, counter-narcotics operations, border control, and protection of Bermuda's maritime interests. The Bermuda Coast Guard will interact with the rest of the Royal Bermuda Regiment and the Bermuda Police Service.
Bermudians served in the British armed forces during both World War I and World War II. After the latter, Major-General Glyn Gilbert, Glyn Charles Anglim Gilbert, Bermuda's highest-ranking soldier, was instrumental in developing the Royal Bermuda Regiment. A number of other Bermudians and their descendants had preceded him into senior ranks, including Bahamian-born Admiral James Gambier, 1st Baron Gambier, Lord Gambier, and Bermudian-born Royal Marines Brigadier A. John Harvey. When promoted to brigadier at age 38, following his wounding at the Allied invasion of Sicily, Harvey became the youngest-ever Royal Marine Brigadier. The Cenotaph in front of the Cabinet Building (in Hamilton) was erected in tribute to Bermuda's Great War dead (the tribute was later extended to Bermuda's Second World War dead) and is the site of the annual Remembrance Day commemoration.
Today, the only military unit remaining in Bermuda, other than Bermuda Sea Cadet Corps, naval and army cadet corps, is the Royal Bermuda Regiment, an amalgam of the voluntary units originally formed toward the end of the 19th century. Although the Regiment's predecessors were voluntary units, until 2018 the modern body was formed primarily by conscription: balloted males were required to serve for three years, two months part-time, once they turn 18. Conscription was abolished 1 July 2018.
In early 2020 the Royal Bermuda Regiment formed the Bermuda Coast Guard. Its 24-hour on-duty service includes search and rescue, counter-narcotics operations, border control, and protection of Bermuda's maritime interests. The Bermuda Coast Guard will interact with the rest of the Royal Bermuda Regiment and the Bermuda Police Service.
Economy
Banking and other financial services now form the largest sector of the economy at about 85% of GDP, with tourism being the second largest industry at 5%.[ Industrial and agriculture activities occur; however, these are on a limited scale and Bermuda is heavily reliant on imports.]
1890s to 1920s: economy severely affected by lily virus
Early Lilium longiflorum, Easter Lily bulb exports to New York—then vital financially for Bermuda—became badly diseased from the late 19th century to the mid-1920s. Lawrence Ogilvie, the Bermuda Department of Agriculture plant pathologist saved the industry by identifying the problem as a virus (not aphid damage as previously thought) and instituting controls in the fields and packing houses. Exports showed a marked improvement: from 23 cases of lily bulbs in 1918, to 6,043 cases in 1927 from the 204 lily fields then in existence. Still in his 20s at the time, Ogilvie was professionally honoured by an article in Nature (journal), ''Nature'' magazine.
Currency
In 1970, the country switched its currency from the Bermudian pound to the Bermudian dollar, which is Fixed exchange rate, pegged at par with the US dollar. US notes and coins are used interchangeably with Bermudian notes and coins within the islands for most practical purposes; however, banks levy an exchange rate fee for the purchase of US dollars with Bermudian dollars for those going out of the islands for external purposes. The Bermuda Monetary Authority is the issuing authority for all banknotes and coins and regulates financial institutions.
Finance
Bermuda is an offshore financial centre, which results from its minimal standards of business regulation/laws and direct taxation on personal or corporate income. It has one of the highest consumption taxes in the world and taxes all imports in lieu of an income tax system. Bermuda's consumption tax is equivalent to local income tax to local residents and funds government and infrastructure expenditures. The local tax system depends upon import duties, payroll taxes and consumption taxes. Foreign private individuals cannot easily open bank accounts or subscribe to mobile phone or internet services.
Having no corporate income tax, Bermuda is a popular Tax haven, tax avoidance location. Google, for example, is known to have shifted over $10 billion in revenue to its Bermuda subsidiary using the Double Irish arrangement, Double Irish and Dutch Sandwich tax avoidance strategies, reducing its 2011 tax liability by $2 billion. The Bermuda Black Hole is another tax avoidance method in which untaxed profits end up in Bermuda.
Large numbers of leading international insurance companies operate in Bermuda. Those internationally owned and operated businesses that are physically based in Bermuda (around four hundred) are represented by the Association of Bermuda International Companies (ABIC). In total, over 15,000 exempted or international companies are currently registered with the Registrar of Companies in Bermuda, most of which hold no office space or employees.
The Bermuda Stock Exchange (BSX) specialises in listing and trading of capital market instruments such as equities, debt issues, funds (including hedge fund structures) and depository receipt programmes. The BSX is a full member of the World Federation of Exchanges and is located in an OECD member nation. It also has Approved Stock Exchange status under Australia's Foreign Investment Fund (FIF) taxation rules and Designated Investment Exchange status by the UK's Financial Services Authority.
Four banks operate in Bermuda, having consolidated total assets of $24.3 billion (March 2014).
Tourism
 Tourism is Bermuda's second-largest industry, with the island attracting over half a million visitors annually, of whom more than 80% are from the United States.
Tourism is Bermuda's second-largest industry, with the island attracting over half a million visitors annually, of whom more than 80% are from the United States.
Housing
The affordability of housing became a prominent issue during Bermuda's business peak in 2005 but has softened with the decline of Bermuda's real estate prices. The World Factbook lists the average cost of a house in June 2003 as $976,000,
Education
The Bermuda Education Act 1996 requires that only three categories of schools can operate in the Bermuda Education system:
* An ''aided school'' has all or a part of its property vested in a body of trustees or board of governors and is partially maintained by public funding or, since 1965 and the desegregation of schools, has received a grant-in-aid out of public funds.
* A ''maintained school'' has the whole of its property belonging to the Government and is fully maintained by public funds.
* A ''private school'', not maintained by public funds and which has not, since 1965 and the desegregation of schools, received any capital grant-in-aid out of public funds. The private school sector consists of six traditional private schools, two of which are religious schools, and the remaining four are secular with one of these being a single-gender school and another a Montessori method, Montessori school. Also, within the private sector there are a number of home schools, which must be registered with the government and receive minimal government regulation. The only boys' school opened its doors to girls in the 1990s, and in 1996, one of the aided schools became a private school.
Prior to 1950, the Bermuda school system was racially segregated. When the desegregation of schools was enacted in 1965, two of the formerly maintained "white" schools and both single-sex schools opted to become private schools. The rest became part of the public school system and were either aided or maintained.
There are 38 schools in the Bermuda Public School System, including 10 preschools, 18 primary schools, 5 middle schools, 2 senior schools (The Berkeley Institute and Cedarbridge Academy), 1 school for students with physical and cognitive challenges, and 1 for students with behavioural problems. There is one aided primary school, two aided middle schools, and one aided senior school. Since 2010, Portuguese has been taught as an optional foreign language in the Bermudian school system.
For higher education, the Bermuda College offers various associate degrees and other certificate programmes. Bermuda does not have any Bachelor-level colleges or universities. Bermuda's graduates usually attend Bachelor-level universities in the United States, Canada and the United Kingdom.
In May 2009, the Bermudian Government's application was approved to become a contributory member of the University of the West Indies (UWI). Bermuda's membership enabled Bermudian students to enter the university at an agreed-upon subsidised rate by 2010. UWI also agreed that its University of the West Indies Open Campus, Open Campus (online degree courses) would become open to Bermudian students in the future, with Bermuda becoming the 13th country to have access to the Open Campus. In 2010, it was announced that Bermuda would be an "associate contributing country" due to local Bermudian laws.
Culture
 Bermuda's culture is a mixture of the various sources of its population: Native American, Spanish-Caribbean, English, Irish, and Scots cultures were evident in the 17th century, and became part of the dominant British culture. English is the primary and official language. Due to 160 years of immigration from Portuguese Atlantic islands (primarily the
Bermuda's culture is a mixture of the various sources of its population: Native American, Spanish-Caribbean, English, Irish, and Scots cultures were evident in the 17th century, and became part of the dominant British culture. English is the primary and official language. Due to 160 years of immigration from Portuguese Atlantic islands (primarily the Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
, though also from Madeira and the Cape Verde Islands), a portion of the population also speaks Portuguese language, Portuguese. There are strong British influences, together with African diaspora, Afro-Caribbean ones.
The first notable, and historically important, book credited to a Bermudian was ''Mary Prince#Publication of The History of Mary Prince, The History of Mary Prince'', a slave narrative by Mary Prince. The book was published in 1831 at the height of Great Britain's abolitionist movement. Graham Ingham, Ernest Graham Ingham, an expatriate author, published his books at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. The novelist Brian Burland (1931– 2010) achieved a degree of success and acclaim internationally. More recently, Angela Barry has won critical recognition for her published fiction.
Arts
West Indian musicians introduced calypso music when Bermuda's tourist industry was expanded with the increase of visitors brought by post-Second World War aviation. Local icons the The Talbot Brothers of Bermuda, Talbot Brothers performed calypso music for a number of decades both in Bermuda and the United States, and appeared on the ''Ed Sullivan Show''. While calypso appealed more to tourists than to the local residents, reggae has been embraced by a number of Bermudians since the 1970s with the influx of Jamaicans, Jamaican immigrants.
 Noted Bermudian musicians include tenor, operatic tenor Gary Burgess; jazz pianist Lance Hayward; singer-songwriter and poet, Heather Nova, and her brother Mishka (musician), Mishka, reggae musician; classical musician and conductor Kenneth Amis; and more recently, dancehall artist Collie Buddz.
The dances of the Gombey dancers, seen at multiple events, are strongly influenced by African, Caribbean and British cultural traditions.
Alfred Birdsey was one of the more famous and talented watercolourists, known for his impressionistic landscapes of
Noted Bermudian musicians include tenor, operatic tenor Gary Burgess; jazz pianist Lance Hayward; singer-songwriter and poet, Heather Nova, and her brother Mishka (musician), Mishka, reggae musician; classical musician and conductor Kenneth Amis; and more recently, dancehall artist Collie Buddz.
The dances of the Gombey dancers, seen at multiple events, are strongly influenced by African, Caribbean and British cultural traditions.
Alfred Birdsey was one of the more famous and talented watercolourists, known for his impressionistic landscapes of Hamilton
Hamilton may refer to:
* Alexander Hamilton (1755/1757–1804), first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
* ''Hamilton'' (musical), a 2015 Broadway musical by Lin-Manuel Miranda
** ''Hamilton'' (al ...
, St. George's, Bermuda, St George's, and the surrounding sailboats, homes, and bays of Bermuda. Hand-carved cedar sculptures are another speciality. In 2010, his sculpture ''We Arrive'' was unveiled in Barr's Bay Park, overlooking Hamilton Harbour, Bermuda, Hamilton Harbour, to commemorate the freeing of slaves in 1835 from the American brig ''Enterprise (slave ship), Enterprise''.
Local resident Tom Butterfield founded the Masterworks Museum of Bermuda Art in 1986, initially featuring works about Bermuda by artists from other countries. He began with pieces by American artists, such as Winslow Homer, Charles Demuth, and Georgia O'Keeffe, who had lived and worked on Bermuda. In 2008, the museum opened its new building, constructed within the Bermuda Botanical Gardens, Botanical Gardens.
Bermuda hosts an annual international film festival, which shows multiple independent films. One of the founders is film producer and director Arthur Rankin Jr., co-founder of the Rankin/Bass production company.
Sport
 Many sports popular today were formalised by British Public school (United Kingdom), public schools and universities in the 19th century. These schools produced the civil servants and military and naval officers required to build and maintain the British Empire, and team sports were considered a vital tool for training their students to think and act as part of a team. Former public schoolboys continued to pursue these activities, and founded organisations such as the Football Association (FA).
Bermuda's role as the primary Royal Navy base in the Western Hemisphere ensured that the naval and military officers quickly introduced the newly formalised sports to Bermuda, including cricket, association football, rugby football, and even Lawn tennis, tennis and Rowing (sport), rowing.
Bermuda national cricket team, Bermuda's national cricket team participated in the Cricket World Cup 2007 in the West Indies but were knocked out of the World Cup. The Bermuda national football team managed to qualify to the 2019 CONCACAF Gold Cup, the country's first ever major football competition. In 2007, Bermuda hosted the 25th PGA Grand Slam of Golf. This 36-hole event was held on 16–17 October 2007, at the Mid Ocean Club in Tucker's Town. This season-ending tournament is limited to four golfers: the winners of the Masters Tournament, Masters, U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open, The Open Championship and PGA Championship. The event returned to Bermuda in 2008 and 2009. One-armed Bermudian golfer Quinn Talbot was both the United States National Amputee Golf Champion for five successive years and the British World One-Arm Golf Champion.
Many sports popular today were formalised by British Public school (United Kingdom), public schools and universities in the 19th century. These schools produced the civil servants and military and naval officers required to build and maintain the British Empire, and team sports were considered a vital tool for training their students to think and act as part of a team. Former public schoolboys continued to pursue these activities, and founded organisations such as the Football Association (FA).
Bermuda's role as the primary Royal Navy base in the Western Hemisphere ensured that the naval and military officers quickly introduced the newly formalised sports to Bermuda, including cricket, association football, rugby football, and even Lawn tennis, tennis and Rowing (sport), rowing.
Bermuda national cricket team, Bermuda's national cricket team participated in the Cricket World Cup 2007 in the West Indies but were knocked out of the World Cup. The Bermuda national football team managed to qualify to the 2019 CONCACAF Gold Cup, the country's first ever major football competition. In 2007, Bermuda hosted the 25th PGA Grand Slam of Golf. This 36-hole event was held on 16–17 October 2007, at the Mid Ocean Club in Tucker's Town. This season-ending tournament is limited to four golfers: the winners of the Masters Tournament, Masters, U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open, The Open Championship and PGA Championship. The event returned to Bermuda in 2008 and 2009. One-armed Bermudian golfer Quinn Talbot was both the United States National Amputee Golf Champion for five successive years and the British World One-Arm Golf Champion.
 The Government announced in 2006 that it would provide substantial financial support to Bermuda's cricket and Bermuda national football team, football teams. Football did not become popular with Bermudians until after the Second World War. Bermuda's most prominent footballers are Clyde Best, Shaun Goater, Kyle Lightbourne, Reggie Lambe, Sam Nusum and Nahki Wells. In 2006, the Bermuda Hogges were formed as the nation's first professional football team to raise the standard of play for the Bermuda national football team. The team played in the United Soccer Leagues Second Division but folded in 2013.
Sailing, fishing and Equestrianism, equestrian sports are popular with both residents and visitors alike. The prestigious Bermuda Race, Newport–Bermuda Yacht Race is a more than 100-year-old tradition, with boats racing between Newport, Rhode Island, and Bermuda. In 2007, the 16th biennial Marion, Massachusetts, Marion-Bermuda yacht race occurred. A sport unique to Bermuda is racing the Bermuda Fitted Dinghy. International One Design racing also originated in Bermuda.
At the Bermuda at the 2004 Summer Olympics, 2004 Summer Olympics, Bermuda competed in sailing, athletics, swimming, diving, triathlon and equestrian events. In those Olympics, Bermuda's Katura Horton-Perinchief made history by becoming the first black female diver to compete in the Olympic Games. Bermuda has had two Olympic medallists, Clarence Hill (boxer), Clarence Hill – who won a bronze medal in boxing – and
The Government announced in 2006 that it would provide substantial financial support to Bermuda's cricket and Bermuda national football team, football teams. Football did not become popular with Bermudians until after the Second World War. Bermuda's most prominent footballers are Clyde Best, Shaun Goater, Kyle Lightbourne, Reggie Lambe, Sam Nusum and Nahki Wells. In 2006, the Bermuda Hogges were formed as the nation's first professional football team to raise the standard of play for the Bermuda national football team. The team played in the United Soccer Leagues Second Division but folded in 2013.
Sailing, fishing and Equestrianism, equestrian sports are popular with both residents and visitors alike. The prestigious Bermuda Race, Newport–Bermuda Yacht Race is a more than 100-year-old tradition, with boats racing between Newport, Rhode Island, and Bermuda. In 2007, the 16th biennial Marion, Massachusetts, Marion-Bermuda yacht race occurred. A sport unique to Bermuda is racing the Bermuda Fitted Dinghy. International One Design racing also originated in Bermuda.
At the Bermuda at the 2004 Summer Olympics, 2004 Summer Olympics, Bermuda competed in sailing, athletics, swimming, diving, triathlon and equestrian events. In those Olympics, Bermuda's Katura Horton-Perinchief made history by becoming the first black female diver to compete in the Olympic Games. Bermuda has had two Olympic medallists, Clarence Hill (boxer), Clarence Hill – who won a bronze medal in boxing – and Flora Duffy
Dame Flora Jane Duffy (born 30 September 1987) is a Bermudian professional triathlete. She won a gold medal at the 2020 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, Bermuda's first gold medal. She also competed in the Beijing, London, and Rio de Janeiro Olympics ...
, who won a gold medal in triathlon. It is tradition for Bermuda to march in the Opening Ceremony in Bermuda shorts, regardless of the summer or winter Olympic celebration. Bermuda also competes in the biennial Island Games, which it hosted in 2013.
In 1998, Bermuda established its own basketball association.
Healthcare
The Bermuda Hospitals Board operates the King Edward VII Memorial Hospital, located in Paget Parish, and the Mid-Atlantic Wellness Institute, located in Devonshire Parish. Boston's Lahey Medical Center has an established visiting specialists program on the island which provides Bermudians and expats with access to specialists regularly on the island. There were about 6,000 hospital admissions, 30,000 emergency department attendances and 6,300 outpatient procedures in 2017.
Unlike the other territories that still remain under British rule, Bermuda does not have National health insurance, national healthcare. Employers must provide a healthcare plan and pay for up to 50% of the cost for each employee.
COVID-19 pandemic
The Minister for Health during the COVID-19 pandemic in Bermuda, COVID-19 pandemic was Kim Wilson (politician), Kim Wilson, who led the territory's approach with "an abundance of caution".
See also
* Culture of Bermuda#Notable cultural figures, Notable cultural people of Bermuda
* Economy of Bermuda
* History of Bermuda#Notable historical figures, Notable historical people of Bermuda
* Index of Bermuda-related articles
* Sports and recreation in Bermuda#Notable sporting figures, Notable sporting people of Bermuda
* Outline of Bermuda
* Places of interest in Bermuda
* Politics of Bermuda#Notable political figures, Notable political people of Bermuda
* Telecommunications in Bermuda
Explanatory notes
References
Citations
General and cited references
*
*
*
*
Further reading
* Anonymous, but probably written by John Smith (1580–1631): ''The Historye of the Bermudaes or Summer Islands''. University of Cambridge Press, 2010. .
* Boultbee, Paul G., and David F. Raine. ''Bermuda''. Oxford: ABC-Clio Press, 1998.
* Connell, John. (1994)
"Britain's Caribbean colonies: The End of the Era of Decolonisation?"
''The Journal of Commonwealth & Comparative Politics'', 32(1), 87–106. .
*
External links
* of the Government of Bermuda
Bermuda Tourism
Bermuda Guide
Bermuda Parliament
Bermuda Chamber of commerce
(archived 26 September 2006)
*
{{Coord, 32.32, N, 64.74, W, type:country_region:BM, display=title
Bermuda,
Volcanoes of Bermuda,
1612 establishments in North America
1612 establishments in the British Empire
Archipelagoes of the Atlantic Ocean
Bermuda Triangle
British North America
British Overseas Territories
Calderas of North America
Dependent territories in North America
English colonization of the Americas
English-speaking countries and territories
Island countries
Islands of North America by dependent territory
Islands of the North Atlantic Ocean
Northern America
Pre-Holocene volcanism
States and territories established in 1612
 Bermuda was discovered in the early 1500s by Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez. Bermuda had no
Bermuda was discovered in the early 1500s by Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez. Bermuda had no  In 1649, the
In 1649, the  In the 17th century, the Somers Isles Company suppressed shipbuilding, as it needed Bermudians to farm to generate income from the land. The Virginia colony, however, far surpassed Bermuda in quality and quantity of tobacco produced. Bermudians began to turn to maritime trades relatively early in the 17th century, but the Somers Isles Company used all its authority to suppress turning away from agriculture. This interference led to islanders demanding, and receiving, revocation of the company's charter in 1684, and the company was dissolved.
Bermudians rapidly abandoned agriculture for shipbuilding, replanting farmland with the native juniper trees (''
In the 17th century, the Somers Isles Company suppressed shipbuilding, as it needed Bermudians to farm to generate income from the land. The Virginia colony, however, far surpassed Bermuda in quality and quantity of tobacco produced. Bermudians began to turn to maritime trades relatively early in the 17th century, but the Somers Isles Company used all its authority to suppress turning away from agriculture. This interference led to islanders demanding, and receiving, revocation of the company's charter in 1684, and the company was dissolved.
Bermudians rapidly abandoned agriculture for shipbuilding, replanting farmland with the native juniper trees (''
 In the early 20th century Bermuda became a popular destination for American, Canadian and British tourists arriving by sea. The US
In the early 20th century Bermuda became a popular destination for American, Canadian and British tourists arriving by sea. The US  Bermuda is a group of low-forming volcanoes in the Atlantic Ocean, in the west of the
Bermuda is a group of low-forming volcanoes in the Atlantic Ocean, in the west of the  Bermuda consists of over 150
Bermuda consists of over 150  When discovered, Bermuda was uninhabited by humans and mostly dominated by forests of Juniperus bermudiana, Bermuda cedar, with mangrove marshes along its shores. Forest cover is around 20% of the total land area, equivalent to 1,000 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, which was unchanged from 1990.
Only 165 of the island's current 1,000 vascular plant species are considered indigenous (ecology), native; fifteen of those, including the eponymous cedar, are endemism, endemic. The tropical climate of Bermuda allowed settlers to introduce multiple non-native species of trees and plants to the island. Today, multiple types of palm trees, fruit trees, and bananas grow on Bermuda, though the cultivated coconut palms are considered non-native and may be removed. The country contains the Bermuda subtropical conifer forests terrestrial ecoregion.
The only Indigenous (ecology), indigenous mammals of Bermuda are five species of bat, all of which are also found in the eastern United States: the silver-haired bat ''Lasionycteris noctivagans'', eastern red bat ''Lasiurus borealis'', hoary bat ''Lasiurus cinereus'', Seminole bat ''Lasiurus seminolus,'' and tricolored bat ''Perimyotis subflavus''. Other commonly known fauna of Bermuda include its national bird, the
When discovered, Bermuda was uninhabited by humans and mostly dominated by forests of Juniperus bermudiana, Bermuda cedar, with mangrove marshes along its shores. Forest cover is around 20% of the total land area, equivalent to 1,000 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, which was unchanged from 1990.
Only 165 of the island's current 1,000 vascular plant species are considered indigenous (ecology), native; fifteen of those, including the eponymous cedar, are endemism, endemic. The tropical climate of Bermuda allowed settlers to introduce multiple non-native species of trees and plants to the island. Today, multiple types of palm trees, fruit trees, and bananas grow on Bermuda, though the cultivated coconut palms are considered non-native and may be removed. The country contains the Bermuda subtropical conifer forests terrestrial ecoregion.
The only Indigenous (ecology), indigenous mammals of Bermuda are five species of bat, all of which are also found in the eastern United States: the silver-haired bat ''Lasionycteris noctivagans'', eastern red bat ''Lasiurus borealis'', hoary bat ''Lasiurus cinereus'', Seminole bat ''Lasiurus seminolus,'' and tricolored bat ''Perimyotis subflavus''. Other commonly known fauna of Bermuda include its national bird, the  Bermuda's 2016 Census put its population at 63,779 and, with an area of , it has a calculated population density of . As of July 2018, the population is estimated to be 71,176.
The racial makeup of Bermuda was 52% Dark skin, Black, 31% White skin, White, 9% multiracial, 4% Asian people, Asian, and 4% other races, these numbers being based on self-identification recorded by the 2016 census. The majority of those who answered "Black" may have any mixture of black, white or other ancestry. Native-born Bermudians made up 70% of the population, compared to 30% non-natives.
The island experienced large-scale immigration over the 20th century, especially after World War II. About 64% of the population identified themselves with Bermudian ancestry in 2010, which was an increase from the 51% who did so in the 2000 census. Those identifying with British ancestry dropped by 1% to 11% - although those born in the United Kingdom remain the largest non-native group at 3,942 people. The number of people born in Canada declined by 13%. 13% of the population reported West Indian ancestry and the number increased by 538. A significant segment of the population is of Portuguese ancestry (25%), the result of immigration over the past 160 years, of whom 79% have residency status. In June 2018, Premier Edward David Burt announced that 4 November 2019 'will be declared a public holiday to mark the 170th anniversary of the arrival of the first Portuguese immigrants in Bermuda' due to the significant impact that Portuguese immigration has had on the territory. Those first immigrants arrived from Madeira aboard the vessel the Golden Rule on 4 November 1849.
There are also several thousand expatriate workers, principally from the United Kingdom, Canada, the West Indies, South Africa, and the United States, who reside in Bermuda. They are primarily engaged in specialised professions such as accounting, finance, and insurance. Others are employed in various trades, such as hotels, restaurants, construction, and landscaping services. Despite the high cost of living, the high salaries offer expatriates several benefits by moving to Bermuda and working for a period of time. Of the total workforce of 38,947 people in 2005, government employment figures stated that 11,223 (29%) were non-Bermudians.
Bermuda's 2016 Census put its population at 63,779 and, with an area of , it has a calculated population density of . As of July 2018, the population is estimated to be 71,176.
The racial makeup of Bermuda was 52% Dark skin, Black, 31% White skin, White, 9% multiracial, 4% Asian people, Asian, and 4% other races, these numbers being based on self-identification recorded by the 2016 census. The majority of those who answered "Black" may have any mixture of black, white or other ancestry. Native-born Bermudians made up 70% of the population, compared to 30% non-natives.
The island experienced large-scale immigration over the 20th century, especially after World War II. About 64% of the population identified themselves with Bermudian ancestry in 2010, which was an increase from the 51% who did so in the 2000 census. Those identifying with British ancestry dropped by 1% to 11% - although those born in the United Kingdom remain the largest non-native group at 3,942 people. The number of people born in Canada declined by 13%. 13% of the population reported West Indian ancestry and the number increased by 538. A significant segment of the population is of Portuguese ancestry (25%), the result of immigration over the past 160 years, of whom 79% have residency status. In June 2018, Premier Edward David Burt announced that 4 November 2019 'will be declared a public holiday to mark the 170th anniversary of the arrival of the first Portuguese immigrants in Bermuda' due to the significant impact that Portuguese immigration has had on the territory. Those first immigrants arrived from Madeira aboard the vessel the Golden Rule on 4 November 1849.
There are also several thousand expatriate workers, principally from the United Kingdom, Canada, the West Indies, South Africa, and the United States, who reside in Bermuda. They are primarily engaged in specialised professions such as accounting, finance, and insurance. Others are employed in various trades, such as hotels, restaurants, construction, and landscaping services. Despite the high cost of living, the high salaries offer expatriates several benefits by moving to Bermuda and working for a period of time. Of the total workforce of 38,947 people in 2005, government employment figures stated that 11,223 (29%) were non-Bermudians.
 Bermuda is an British Overseas Territory, Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom, and the Government of the United Kingdom is the sovereign government. Executive authority in Bermuda is vested in the British monarch (currently Charles III) and is exercised on his behalf by the governor of Bermuda. The governor is appointed by the king on the advice of the British Government. Since January 2025, the governor is Andrew Murdoch (diplomat), Andrew Murdoch; he was sworn in on 23 January 2025. There is also a deputy governor (currently Tom Oppenheim).
Defence and foreign affairs are the responsibility of the United Kingdom, which also retains responsibility to ensure good government and must approve any changes to the Constitution of Bermuda. Bermuda is Britain's oldest overseas territory. Although the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament retains ultimate legislative authority over the territory, in 1620, a Royal Proclamation granted Bermuda limited self-governance, delegating to the
Bermuda is an British Overseas Territory, Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom, and the Government of the United Kingdom is the sovereign government. Executive authority in Bermuda is vested in the British monarch (currently Charles III) and is exercised on his behalf by the governor of Bermuda. The governor is appointed by the king on the advice of the British Government. Since January 2025, the governor is Andrew Murdoch (diplomat), Andrew Murdoch; he was sworn in on 23 January 2025. There is also a deputy governor (currently Tom Oppenheim).
Defence and foreign affairs are the responsibility of the United Kingdom, which also retains responsibility to ensure good government and must approve any changes to the Constitution of Bermuda. Bermuda is Britain's oldest overseas territory. Although the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament retains ultimate legislative authority over the territory, in 1620, a Royal Proclamation granted Bermuda limited self-governance, delegating to the  The Constitution of Bermuda came into force in 1968 and has been amended several times since then. The head of government is the premier of Bermuda; a cabinet is nominated by the premier and appointed officially by the governor. The legislative branch consists of a bicameral parliament modelled on the Westminster system. The Senate of Bermuda, Senate is the upper house, consisting of 11 members appointed by the governor on the advice of the premier and the leader of the opposition. The
The Constitution of Bermuda came into force in 1968 and has been amended several times since then. The head of government is the premier of Bermuda; a cabinet is nominated by the premier and appointed officially by the governor. The legislative branch consists of a bicameral parliament modelled on the Westminster system. The Senate of Bermuda, Senate is the upper house, consisting of 11 members appointed by the governor on the advice of the premier and the leader of the opposition. The  Historically, English (later British) colonials shared the same citizenship as those born within that part of the sovereign territory of the Kingdom of England (including the Principality of Wales) that lay within the Island of Britain (although Magna Carta had effectively created English citizenship, citizens were still termed 'subjects of the King of England' or 'English subjects'. With the Acts of Union 1707, 1707 union of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland, this was replaced with 'British Subject', which encompassed citizens throughout the sovereign territory of the British Government, including its colonies, though not the British protectorates). With no Representative government, representation at the sovereign or national level of government, British colonials were therefore not consulted, or required to give their consent, to a series of Acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom between 1968 and 1982, which were to limit their rights and ultimately change their citizenship.
When several colonies had been elevated before the Second World War to Dominion status, collectively forming the old Commonwealth of Nations#Adoption and formalisation of the Commonwealth, British Commonwealth (as distinct from the United Kingdom and its dependent colonies), their citizens remained British Subjects, and in theory, any British Subject born anywhere in the World had the same basic right to enter, reside, and work in the United Kingdom as a British Subject born in the United Kingdom whose parents were also both British Subjects born in the United Kingdom (although a number of governmental policies and practices acted to thwart the free exercise of these rights by various groups of colonials, including Greek Cypriots).
When the Dominions and an increasing number of colonies began choosing complete independence from the United Kingdom after the Second World War, the Commonwealth was transformed into a community of independent nations, or Commonwealth realms, each recognising the British monarch as its own head of state (creating separate monarchies with the same person occupying all of the separate Thrones; the exception being republican India).
'British Subject' was replaced by the British Nationality Act 1948 with 'Citizen of the United Kingdom and Colonies' for the residents of the United Kingdom and its colonies, as well as for the Crown Dependencies. However, as it was desired to retain free movement for all Commonwealth Citizens throughout the Commonwealth, 'British Subject' was retained as a blanket nationality shared by Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies (the 'British realm') as well as the citizens of the various other Commonwealth realms. The inflow of people of colour to the United Kingdom in the 1940s and 1950s from both the remaining colonies and newly independent Commonwealth nations was responded to with a backlash that led to the passing of the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1962, which restricted the rights of Commonwealth nationals to enter, reside and work in the United Kingdom. This Act also allowed certain colonials (primarily ethnic-Indians in African colonies) to retain Citizenship of the United Kingdom and Colonies if their colonies became independent, which was intended as a measure to ensure these people did not become Statelessness, stateless if they were denied the citizenship of their newly independent nation.
Many ethnic-Indians from former African colonies (notably Kenya) subsequently relocated to the United Kingdom, in response to which the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1968 was rapidly passed, stripping all British Subjects (including Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies) who were not born in the United Kingdom, and who did not have a Citizen of the United Kingdom and Colonies parent or grandparent born in the United Kingdom or some other qualification (such as existing residence status), of the rights to freely enter, reside and work in the United Kingdom.
Although the 1968 Act was intended primarily to bar immigration of specific British passport holders from Commonwealth countries in Africa, it amended the wording of the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1962 in such a way as to apply to all Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies who were not specifically excepted, including most colonials.
This was followed by the Immigration Act 1971, which effectively divided Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies into two types, although their citizenship remained the same: Patrials, who were those from (or with a specified qualifying connection to) the United Kingdom itself, who retained the rights of free entry, abode, and work in the United Kingdom; and those born in the colonies (or in foreign countries to British Colonial parents), from whom those rights were denied.
The British Nationality Act 1981, which entered into force on 1 January 1983, abolished British Subject status, and stripped colonials of their full British Citizenship of the United Kingdom and Colonies, replacing it with British Dependent Territories Citizenship, which entailed no right of abode or to work anywhere. This left Bermudians and most other erstwhile British colonials as British nationals without the rights of British citizenship.
The exceptions were the Gibraltarians (permitted to retain British Citizenship to also retain Citizenship of the European Union) and the Falkland Islands, Falkland Islanders, who were permitted to retain the same new British Citizenship that became the default citizenship for those from the United Kingdom and the Crown Dependencies.
The stripping of citizens' birthrights from Bermudians by the British Government in 1968 and 1971, and the change of their citizenship in 1983, violated the rights granted them by Royal Charters at the founding of the colony. Bermuda (fully The Somers Isles or Islands of Bermuda) had been settled by the London Company (which had been in occupation of the archipelago since the 1609 wreck of the
Historically, English (later British) colonials shared the same citizenship as those born within that part of the sovereign territory of the Kingdom of England (including the Principality of Wales) that lay within the Island of Britain (although Magna Carta had effectively created English citizenship, citizens were still termed 'subjects of the King of England' or 'English subjects'. With the Acts of Union 1707, 1707 union of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland, this was replaced with 'British Subject', which encompassed citizens throughout the sovereign territory of the British Government, including its colonies, though not the British protectorates). With no Representative government, representation at the sovereign or national level of government, British colonials were therefore not consulted, or required to give their consent, to a series of Acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom between 1968 and 1982, which were to limit their rights and ultimately change their citizenship.
When several colonies had been elevated before the Second World War to Dominion status, collectively forming the old Commonwealth of Nations#Adoption and formalisation of the Commonwealth, British Commonwealth (as distinct from the United Kingdom and its dependent colonies), their citizens remained British Subjects, and in theory, any British Subject born anywhere in the World had the same basic right to enter, reside, and work in the United Kingdom as a British Subject born in the United Kingdom whose parents were also both British Subjects born in the United Kingdom (although a number of governmental policies and practices acted to thwart the free exercise of these rights by various groups of colonials, including Greek Cypriots).
When the Dominions and an increasing number of colonies began choosing complete independence from the United Kingdom after the Second World War, the Commonwealth was transformed into a community of independent nations, or Commonwealth realms, each recognising the British monarch as its own head of state (creating separate monarchies with the same person occupying all of the separate Thrones; the exception being republican India).
'British Subject' was replaced by the British Nationality Act 1948 with 'Citizen of the United Kingdom and Colonies' for the residents of the United Kingdom and its colonies, as well as for the Crown Dependencies. However, as it was desired to retain free movement for all Commonwealth Citizens throughout the Commonwealth, 'British Subject' was retained as a blanket nationality shared by Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies (the 'British realm') as well as the citizens of the various other Commonwealth realms. The inflow of people of colour to the United Kingdom in the 1940s and 1950s from both the remaining colonies and newly independent Commonwealth nations was responded to with a backlash that led to the passing of the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1962, which restricted the rights of Commonwealth nationals to enter, reside and work in the United Kingdom. This Act also allowed certain colonials (primarily ethnic-Indians in African colonies) to retain Citizenship of the United Kingdom and Colonies if their colonies became independent, which was intended as a measure to ensure these people did not become Statelessness, stateless if they were denied the citizenship of their newly independent nation.
Many ethnic-Indians from former African colonies (notably Kenya) subsequently relocated to the United Kingdom, in response to which the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1968 was rapidly passed, stripping all British Subjects (including Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies) who were not born in the United Kingdom, and who did not have a Citizen of the United Kingdom and Colonies parent or grandparent born in the United Kingdom or some other qualification (such as existing residence status), of the rights to freely enter, reside and work in the United Kingdom.
Although the 1968 Act was intended primarily to bar immigration of specific British passport holders from Commonwealth countries in Africa, it amended the wording of the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1962 in such a way as to apply to all Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies who were not specifically excepted, including most colonials.
This was followed by the Immigration Act 1971, which effectively divided Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies into two types, although their citizenship remained the same: Patrials, who were those from (or with a specified qualifying connection to) the United Kingdom itself, who retained the rights of free entry, abode, and work in the United Kingdom; and those born in the colonies (or in foreign countries to British Colonial parents), from whom those rights were denied.
The British Nationality Act 1981, which entered into force on 1 January 1983, abolished British Subject status, and stripped colonials of their full British Citizenship of the United Kingdom and Colonies, replacing it with British Dependent Territories Citizenship, which entailed no right of abode or to work anywhere. This left Bermudians and most other erstwhile British colonials as British nationals without the rights of British citizenship.
The exceptions were the Gibraltarians (permitted to retain British Citizenship to also retain Citizenship of the European Union) and the Falkland Islands, Falkland Islanders, who were permitted to retain the same new British Citizenship that became the default citizenship for those from the United Kingdom and the Crown Dependencies.
The stripping of citizens' birthrights from Bermudians by the British Government in 1968 and 1971, and the change of their citizenship in 1983, violated the rights granted them by Royal Charters at the founding of the colony. Bermuda (fully The Somers Isles or Islands of Bermuda) had been settled by the London Company (which had been in occupation of the archipelago since the 1609 wreck of the  Bermuda is divided into nine Parish (administrative division), parishes and two incorporated municipalities.
Bermuda's nine parishes are:
* Devonshire Parish, Devonshire
* Hamilton Parish, Hamilton
* Paget Parish, Paget
* Pembroke Parish, Pembroke
* Sandys Parish, Sandys
* Smith's Parish, Smith's
* Southampton Parish, Bermuda, Southampton
* St. George's Parish, Bermuda, St George's
* Warwick Parish, Warwick
Bermuda's two incorporated municipalities are:
*
Bermuda is divided into nine Parish (administrative division), parishes and two incorporated municipalities.
Bermuda's nine parishes are:
* Devonshire Parish, Devonshire
* Hamilton Parish, Hamilton
* Paget Parish, Paget
* Pembroke Parish, Pembroke
* Sandys Parish, Sandys
* Smith's Parish, Smith's
* Southampton Parish, Bermuda, Southampton
* St. George's Parish, Bermuda, St George's
* Warwick Parish, Warwick
Bermuda's two incorporated municipalities are:
*  Following Canadian confederation in 1867, the British political, naval and military hierarchy in Bermuda became increasingly separated from that of the Canadian Government (the
Following Canadian confederation in 1867, the British political, naval and military hierarchy in Bermuda became increasingly separated from that of the Canadian Government (the 
 A former Imperial fortress British Overseas Territory, colony once known as "the Gibraltar of the West" and "Fortress Bermuda", defence of Bermuda, as part of the British sovereign state, is the responsibility of the British Government.
For the first two centuries of settlement, the most potent armed force operating from Bermuda was its merchant shipping fleet, which turned to
A former Imperial fortress British Overseas Territory, colony once known as "the Gibraltar of the West" and "Fortress Bermuda", defence of Bermuda, as part of the British sovereign state, is the responsibility of the British Government.
For the first two centuries of settlement, the most potent armed force operating from Bermuda was its merchant shipping fleet, which turned to  Bermudians served in the British armed forces during both World War I and World War II. After the latter, Major-General Glyn Gilbert, Glyn Charles Anglim Gilbert, Bermuda's highest-ranking soldier, was instrumental in developing the Royal Bermuda Regiment. A number of other Bermudians and their descendants had preceded him into senior ranks, including Bahamian-born Admiral James Gambier, 1st Baron Gambier, Lord Gambier, and Bermudian-born Royal Marines Brigadier A. John Harvey. When promoted to brigadier at age 38, following his wounding at the Allied invasion of Sicily, Harvey became the youngest-ever Royal Marine Brigadier. The Cenotaph in front of the Cabinet Building (in Hamilton) was erected in tribute to Bermuda's Great War dead (the tribute was later extended to Bermuda's Second World War dead) and is the site of the annual Remembrance Day commemoration.
Today, the only military unit remaining in Bermuda, other than Bermuda Sea Cadet Corps, naval and army cadet corps, is the Royal Bermuda Regiment, an amalgam of the voluntary units originally formed toward the end of the 19th century. Although the Regiment's predecessors were voluntary units, until 2018 the modern body was formed primarily by conscription: balloted males were required to serve for three years, two months part-time, once they turn 18. Conscription was abolished 1 July 2018.
In early 2020 the Royal Bermuda Regiment formed the Bermuda Coast Guard. Its 24-hour on-duty service includes search and rescue, counter-narcotics operations, border control, and protection of Bermuda's maritime interests. The Bermuda Coast Guard will interact with the rest of the Royal Bermuda Regiment and the Bermuda Police Service.
Bermudians served in the British armed forces during both World War I and World War II. After the latter, Major-General Glyn Gilbert, Glyn Charles Anglim Gilbert, Bermuda's highest-ranking soldier, was instrumental in developing the Royal Bermuda Regiment. A number of other Bermudians and their descendants had preceded him into senior ranks, including Bahamian-born Admiral James Gambier, 1st Baron Gambier, Lord Gambier, and Bermudian-born Royal Marines Brigadier A. John Harvey. When promoted to brigadier at age 38, following his wounding at the Allied invasion of Sicily, Harvey became the youngest-ever Royal Marine Brigadier. The Cenotaph in front of the Cabinet Building (in Hamilton) was erected in tribute to Bermuda's Great War dead (the tribute was later extended to Bermuda's Second World War dead) and is the site of the annual Remembrance Day commemoration.
Today, the only military unit remaining in Bermuda, other than Bermuda Sea Cadet Corps, naval and army cadet corps, is the Royal Bermuda Regiment, an amalgam of the voluntary units originally formed toward the end of the 19th century. Although the Regiment's predecessors were voluntary units, until 2018 the modern body was formed primarily by conscription: balloted males were required to serve for three years, two months part-time, once they turn 18. Conscription was abolished 1 July 2018.
In early 2020 the Royal Bermuda Regiment formed the Bermuda Coast Guard. Its 24-hour on-duty service includes search and rescue, counter-narcotics operations, border control, and protection of Bermuda's maritime interests. The Bermuda Coast Guard will interact with the rest of the Royal Bermuda Regiment and the Bermuda Police Service.
 Tourism is Bermuda's second-largest industry, with the island attracting over half a million visitors annually, of whom more than 80% are from the United States. Other significant sources of visitors are from Canada and the United Kingdom. However, the sector is vulnerable to external shocks, such as the 2008 recession.
Tourism is Bermuda's second-largest industry, with the island attracting over half a million visitors annually, of whom more than 80% are from the United States. Other significant sources of visitors are from Canada and the United Kingdom. However, the sector is vulnerable to external shocks, such as the 2008 recession.
 Bermuda's culture is a mixture of the various sources of its population: Native American, Spanish-Caribbean, English, Irish, and Scots cultures were evident in the 17th century, and became part of the dominant British culture. English is the primary and official language. Due to 160 years of immigration from Portuguese Atlantic islands (primarily the
Bermuda's culture is a mixture of the various sources of its population: Native American, Spanish-Caribbean, English, Irish, and Scots cultures were evident in the 17th century, and became part of the dominant British culture. English is the primary and official language. Due to 160 years of immigration from Portuguese Atlantic islands (primarily the  Noted Bermudian musicians include tenor, operatic tenor Gary Burgess; jazz pianist Lance Hayward; singer-songwriter and poet, Heather Nova, and her brother Mishka (musician), Mishka, reggae musician; classical musician and conductor Kenneth Amis; and more recently, dancehall artist Collie Buddz.
The dances of the Gombey dancers, seen at multiple events, are strongly influenced by African, Caribbean and British cultural traditions.
Alfred Birdsey was one of the more famous and talented watercolourists, known for his impressionistic landscapes of
Noted Bermudian musicians include tenor, operatic tenor Gary Burgess; jazz pianist Lance Hayward; singer-songwriter and poet, Heather Nova, and her brother Mishka (musician), Mishka, reggae musician; classical musician and conductor Kenneth Amis; and more recently, dancehall artist Collie Buddz.
The dances of the Gombey dancers, seen at multiple events, are strongly influenced by African, Caribbean and British cultural traditions.
Alfred Birdsey was one of the more famous and talented watercolourists, known for his impressionistic landscapes of  Many sports popular today were formalised by British Public school (United Kingdom), public schools and universities in the 19th century. These schools produced the civil servants and military and naval officers required to build and maintain the British Empire, and team sports were considered a vital tool for training their students to think and act as part of a team. Former public schoolboys continued to pursue these activities, and founded organisations such as the Football Association (FA).
Bermuda's role as the primary Royal Navy base in the Western Hemisphere ensured that the naval and military officers quickly introduced the newly formalised sports to Bermuda, including cricket, association football, rugby football, and even Lawn tennis, tennis and Rowing (sport), rowing.
Bermuda national cricket team, Bermuda's national cricket team participated in the Cricket World Cup 2007 in the West Indies but were knocked out of the World Cup. The Bermuda national football team managed to qualify to the 2019 CONCACAF Gold Cup, the country's first ever major football competition. In 2007, Bermuda hosted the 25th PGA Grand Slam of Golf. This 36-hole event was held on 16–17 October 2007, at the Mid Ocean Club in Tucker's Town. This season-ending tournament is limited to four golfers: the winners of the Masters Tournament, Masters, U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open, The Open Championship and PGA Championship. The event returned to Bermuda in 2008 and 2009. One-armed Bermudian golfer Quinn Talbot was both the United States National Amputee Golf Champion for five successive years and the British World One-Arm Golf Champion.
Many sports popular today were formalised by British Public school (United Kingdom), public schools and universities in the 19th century. These schools produced the civil servants and military and naval officers required to build and maintain the British Empire, and team sports were considered a vital tool for training their students to think and act as part of a team. Former public schoolboys continued to pursue these activities, and founded organisations such as the Football Association (FA).
Bermuda's role as the primary Royal Navy base in the Western Hemisphere ensured that the naval and military officers quickly introduced the newly formalised sports to Bermuda, including cricket, association football, rugby football, and even Lawn tennis, tennis and Rowing (sport), rowing.
Bermuda national cricket team, Bermuda's national cricket team participated in the Cricket World Cup 2007 in the West Indies but were knocked out of the World Cup. The Bermuda national football team managed to qualify to the 2019 CONCACAF Gold Cup, the country's first ever major football competition. In 2007, Bermuda hosted the 25th PGA Grand Slam of Golf. This 36-hole event was held on 16–17 October 2007, at the Mid Ocean Club in Tucker's Town. This season-ending tournament is limited to four golfers: the winners of the Masters Tournament, Masters, U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open, The Open Championship and PGA Championship. The event returned to Bermuda in 2008 and 2009. One-armed Bermudian golfer Quinn Talbot was both the United States National Amputee Golf Champion for five successive years and the British World One-Arm Golf Champion.
 The Government announced in 2006 that it would provide substantial financial support to Bermuda's cricket and Bermuda national football team, football teams. Football did not become popular with Bermudians until after the Second World War. Bermuda's most prominent footballers are Clyde Best, Shaun Goater, Kyle Lightbourne, Reggie Lambe, Sam Nusum and Nahki Wells. In 2006, the Bermuda Hogges were formed as the nation's first professional football team to raise the standard of play for the Bermuda national football team. The team played in the United Soccer Leagues Second Division but folded in 2013.
Sailing, fishing and Equestrianism, equestrian sports are popular with both residents and visitors alike. The prestigious Bermuda Race, Newport–Bermuda Yacht Race is a more than 100-year-old tradition, with boats racing between Newport, Rhode Island, and Bermuda. In 2007, the 16th biennial Marion, Massachusetts, Marion-Bermuda yacht race occurred. A sport unique to Bermuda is racing the Bermuda Fitted Dinghy. International One Design racing also originated in Bermuda.
At the Bermuda at the 2004 Summer Olympics, 2004 Summer Olympics, Bermuda competed in sailing, athletics, swimming, diving, triathlon and equestrian events. In those Olympics, Bermuda's Katura Horton-Perinchief made history by becoming the first black female diver to compete in the Olympic Games. Bermuda has had two Olympic medallists, Clarence Hill (boxer), Clarence Hill – who won a bronze medal in boxing – and
The Government announced in 2006 that it would provide substantial financial support to Bermuda's cricket and Bermuda national football team, football teams. Football did not become popular with Bermudians until after the Second World War. Bermuda's most prominent footballers are Clyde Best, Shaun Goater, Kyle Lightbourne, Reggie Lambe, Sam Nusum and Nahki Wells. In 2006, the Bermuda Hogges were formed as the nation's first professional football team to raise the standard of play for the Bermuda national football team. The team played in the United Soccer Leagues Second Division but folded in 2013.
Sailing, fishing and Equestrianism, equestrian sports are popular with both residents and visitors alike. The prestigious Bermuda Race, Newport–Bermuda Yacht Race is a more than 100-year-old tradition, with boats racing between Newport, Rhode Island, and Bermuda. In 2007, the 16th biennial Marion, Massachusetts, Marion-Bermuda yacht race occurred. A sport unique to Bermuda is racing the Bermuda Fitted Dinghy. International One Design racing also originated in Bermuda.
At the Bermuda at the 2004 Summer Olympics, 2004 Summer Olympics, Bermuda competed in sailing, athletics, swimming, diving, triathlon and equestrian events. In those Olympics, Bermuda's Katura Horton-Perinchief made history by becoming the first black female diver to compete in the Olympic Games. Bermuda has had two Olympic medallists, Clarence Hill (boxer), Clarence Hill – who won a bronze medal in boxing – and