|
Invasion Of Jamaica
The Invasion of Jamaica took place in May 1655, during the 1654 to 1660 Anglo-Spanish War, when an English expeditionary force captured Spanish Jamaica. It was part of an ambitious plan by Oliver Cromwell to acquire new colonies in the Americas, known as the Western Design. Although major settlements like Santiago de la Vega, now Spanish Town, were poorly defended and quickly occupied, resistance by escaped slaves, or Jamaican Maroons, continued in the interior. The Western Design was largely a failure, but Jamaica remained in English hands, and was formally ceded by Spain in the 1670 Treaty of Madrid. The Colony of Jamaica remained a British possession until independence in 1962. Background In 1654, Oliver Cromwell and his Council of State planned a surprise attack on Spanish America. There were a number of reasons for this, including the Commonwealth's weak economic position, and finding an outlet for large numbers of disgruntled veterans from the Wars of the Three King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Spanish War (1654–60)
Anglo-Spanish War may refer to: * Hundred Years' War (1337–1453), includes the War of the Breton Succession, the Castilian Civil War, the War of the Two Peters, and the 1383–1385 Portuguese interregnum * Third Fernandine War (1381–1382) * War of the League of Cognac (1526–1530), part of the Italian Wars * Second Desmond Rebellion (1579-1583), part of the Desmond rebellions * Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), including the Spanish Armada, the English Armada and the Nine Years' War (Ireland), part of the Eighty Years' War * Dutch–Portuguese War (1601–1661), part of the Eighty Years' War * Palatinate campaign (1620–1623), part of the Thirty Years' War * Anglo-Spanish War (1625–1630), part of the Thirty Years' War ( Eighty Years' War, 1621–1648) * Anglo-Spanish War (1654–1660), part of the Franco-Spanish War * Caribbean War (1660–71), follow on from previous war, based in Caribbean. * Portuguese Restoration War (1662–1668), English support for Portug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of Caribbean islands by area, land area, after Geography of Cuba, Cuba. The island is Dominican Republic–Haiti border, divided into two separate Sovereign state, sovereign countries: the Spanish-speaking Geography of the Dominican Republic, Dominican Republic () to the east and the French language, French and Haitian Creole–speaking Geography of Haiti, Haiti () to the west. The only other divided island in the Caribbean is Saint Martin (island), Saint Martin, which is shared between France () and the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands (). At the time of the European arrival of Christopher Columbus, Hispaniola was home to the Ciguayo language, Ciguayo, Macorix language, Macorix, and Taíno Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, native pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maroons
Maroons are descendants of Africans in the Americas and islands of the Indian Ocean who escaped from slavery, through flight or manumission, and formed their own settlements. They often mixed with Indigenous peoples, eventually evolving into separate creole cultures such as the Garifuna and the Mascogos. Etymology ''Maroon'' entered English around the 1590s, from the French adjective , meaning 'feral' or 'fugitive', itself possibly from the American Spanish word , meaning 'wild, unruly' or 'runaway slave'. In the early 1570s, Sir Francis Drake's raids on the Spanish in Panama were aided by "''Symerons''", a likely misspelling of '. The linguist Leo Spitzer, writing in the journal ''Language'', says, "If there is a connection between Eng. ''maroon'', Fr. ', and Sp. ', Spain (or Spanish America) probably gave the word directly to England (or English America)." Alternatively, the Cuban philologist José Juan Arrom has traced the origins of the word ''maroon'' further t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuart Restoration
The Stuart Restoration was the reinstatement in May 1660 of the Stuart monarchy in Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland. It replaced the Commonwealth of England, established in January 1649 after the execution of Charles I, with his son Charles II of England, Charles II. The Commonwealth of England had been governed by Lord Protector Oliver Cromwell and then his son Richard Cromwell. The term is also used to describe the reign of Charles II (1660–1685), and sometimes that of his younger brother King James II, James II (1685–1688). The Protectorate After Richard Cromwell, Lord Protector from 1658 to 1659, ceded power to the Rump Parliament, Charles Fleetwood and John Lambert (general), John Lambert then dominated government for a year. On 20 October 1659, George Monck, the governor of Scotland under the Cromwells, marched south with his army from Scotland to oppose Fleetwood and Lambert. Lambert's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower Of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic citadel and castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London, England. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is separated from the eastern edge of the square mile of the City of London by the open space known as Tower Hill. It was founded toward the end of 1066 as part of the Norman Conquest. The White Tower (Tower of London), White Tower, which gives the entire castle its name, was built by William the Conqueror in 1078 and was initially a resented symbol of oppression, inflicted upon London by the new Normans, Norman ruling class. The castle was also used as a prison from 1100 (Ranulf Flambard, Bishop of Durham) until 1952 (the Kray twins), although that was not its primary purpose. A grand palace early in its history, it served as a royal residence. As a whole, the Tower is a complex of several buildings set within two concentric ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
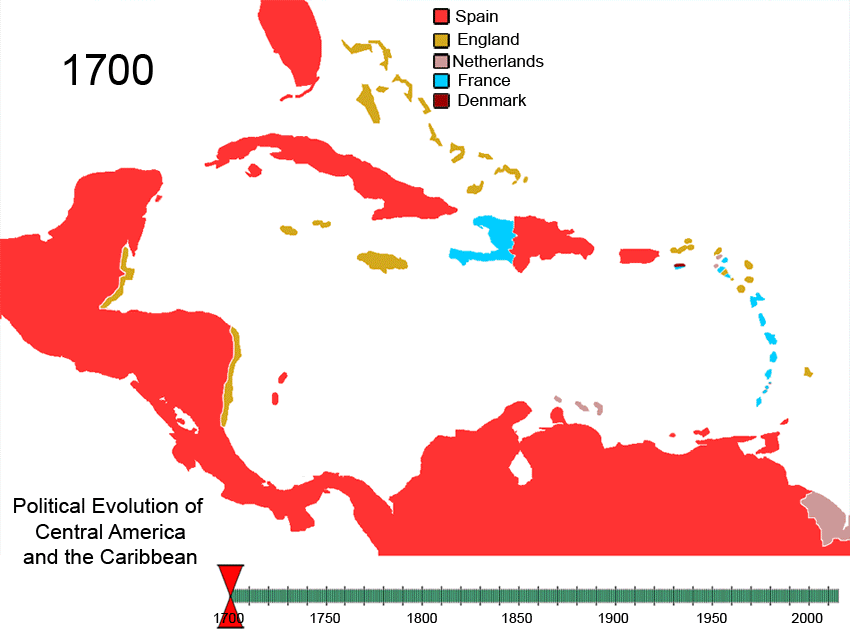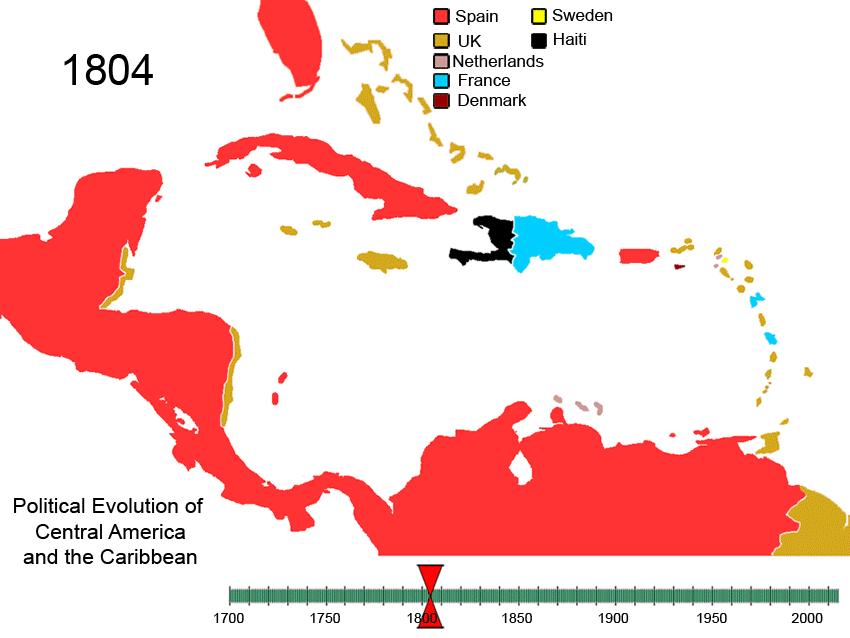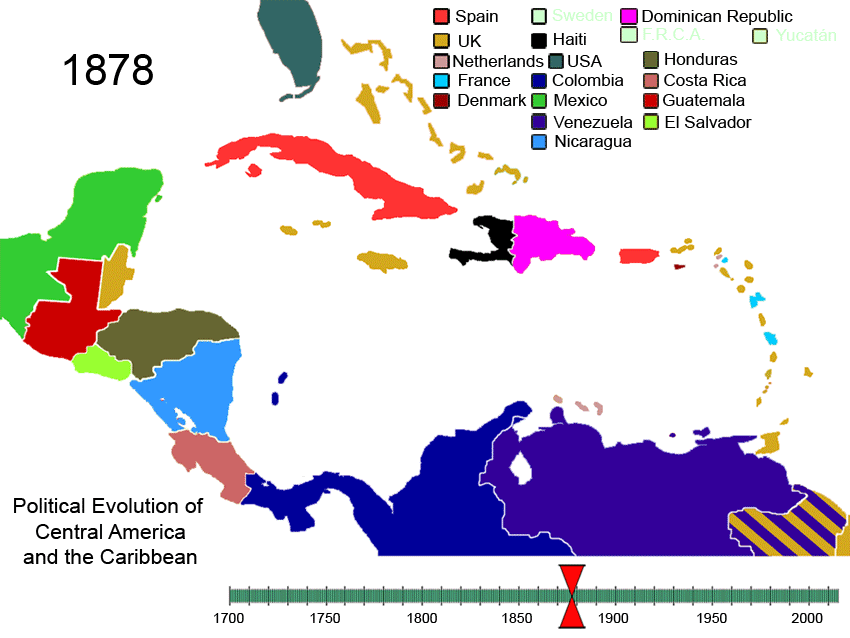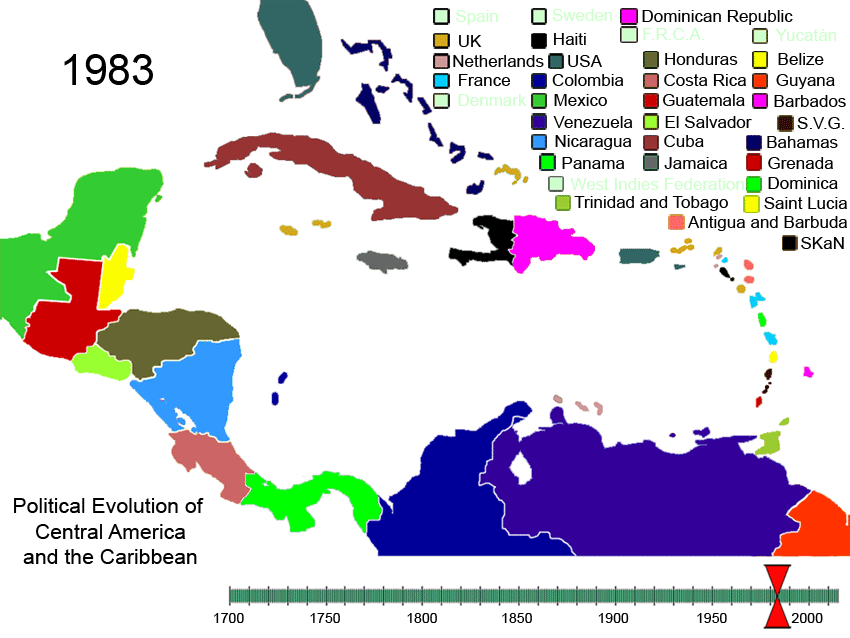
Political Evolution Of Central America And The Caribbean 1700 And On
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social status, status or resources. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Serras
Juan de Serras was one of the first Jamaican Maroon chiefs in the seventeenth century. His community was based primarily around Los Vermajales, and as a result the English called his group of Maroons the Karmahaly Maroons. It is likely that his Maroons are descended from escaped slaves Taino men and women. Fighting for the Spanish When the English captured Jamaica from the Spanish in 1655 Invasion of Jamaica, the latter freed their slaves, who then escaped into the forested mountains of the interior, and established independent communities of Free black people in Jamaica. These groups fought on the side of the Spanish in their attempts to recapture Jamaica from the English. When one group, led by Juan de Bolas, switched sides and joined the English, the Spanish gave up on their attempts to recapture the island. In contrast to de Bolas, de Serras and his men stayed loyal to the Spanish, and refused to come to terms with the English. Based in the mountains of central Jamaica, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Bolas
Juan de Bolas originally Juan Lubolo (1604?–1664) was one of the first chiefs of the Jamaican Maroons. Background When the English captured Jamaica from the Spanish in the 1655 Invasion of Jamaica, the latter freed their slaves, who fled into the mountainous forests of the interior, where they established independent communities of Free black people in Jamaica, and fought a guerrilla war against the English. It is likely that these early Spanish Maroons were descended from both escaped African slaves and Taino men and women. Juan de Bolas and his Maroon community was based primarily around the town of Lluidas Vale. The Spanish attempted to retake the Colony of Jamaica, and to this end Don Christobal de Ysasi relied on his alliance with the Spanish Maroons to secure this victory. Juan switches sides However, Governor Edward D'Oyley succeeded in persuading one of the leaders of the Spanish Maroons, Juan de Bolas, to switch sides and join the English along with his Maroon war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campeche City
San Francisco de Campeche (; , ), 19th c., also known simply as Campeche, is a city in Campeche Municipality in the List of states of Mexico, Mexican state of Campeche, on the shore of the Bay of Campeche in the Gulf of Mexico. Both the seat of the municipality and the state's capital, the city had a population of 220,389 in the 2010 census, while the municipality had a population of 259,005. The city was founded in 1540 by Spaniards, Spanish conquistadores as San Francisco de Campeche atop the pre-existing Maya civilization, Maya city of Can Pech. Little trace remains of the Pre-Columbian era, Pre-Columbian city. The city retains many of the old colonial Spanish city walls and fortifications which protected the city from piracy, pirates and buccaneers. The state of preservation and quality of its architecture earned it the status of a World Heritage Site in 1999. Campeche is (along with Quebec City) one of the only cities in North America with most of its historic old city walls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Ship Swiftsure (1621)
''Swiftsure'' was a 42-gun great ship or Second rate ship of the line of the Navy Royal of the Kingdom of England, built by William Burrell (Master Shipwright of the East India Company) at Deptford Dockyard and launched in 1621. In 1625 she was commanded by Sir Samuel Argall as the flagship of Vice-Admiral Robert Devereux for the Cadiz Expedition. In 1628 she was commanded by Captain John Burley as the flagship of the Earl of Moston in the attack on La Rochelle. Design and modification The ''Swiftsure'' was the third of the six "Great Ships" (or Second rates) to be designed and built at Deptford Dockyard for James I's navy by Burrell (as well as three Third rates and a Fourth rate). The other Second Rates were the ''Constant Reformation'', ''Victory'', ''Saint Andrew'', ''Saint George'' and ''Triumph''. The first three ships were designed with a keel length of 103 ft and a beam of 34 ft, but the ''Swiftsure'' was completed with a keel length of 106 ft and a beam of 35 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cagway Bay
Cagway Bay as the English called it following their arrival in Jamaica during the invasion of 1655 had been known to the earlier Taino and Spanish occupiers as ''Caguay'' or ''Caguaya'' bay. The bay in turn got its name from the Taino name for the sand spit now known as the Palisadoes which protects the bay or, as it is now known as, Kingston Harbour. Edward Long argued in his 1744 ''History of Jamaica'' argues that the names were "a corruption of ''caragua'', the Indian name for coratoe, or great aloe, which overspreads the adjacent Saltpan Hill". See also *Port Royal Port Royal () was a town located at the end of the Palisadoes, at the mouth of Kingston Harbour, in southeastern Jamaica. Founded in 1494 by the Spanish, it was once the largest and most prosperous city in the Caribbean, functioning as the cen ... References {{Geography of Jamaica Ports and harbours of Jamaica Bays and coves of Jamaica Kingston, Jamaica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |