Antarctopelta on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Antarctopelta'' (; meaning 'Antarctic shield') is a
 During an expedition to
During an expedition to  The
The
 Like other ankylosaurs, ''Antarctopelta oliveroi'' was a stocky,
Like other ankylosaurs, ''Antarctopelta oliveroi'' was a stocky,
 Five
Five  ''Antarctopelta'' and ''Stegouros'' have very similar caudal vertebrae, both having flattened distal centra with a prominent ventral groove. This implies that ''Antarctopelta'' also had a macuahuitl, a flat, spiked arrangement of osteoderms on the end of the tail. The name is in reference to the Aztec weapon due to its similar appearance and function. The
''Antarctopelta'' and ''Stegouros'' have very similar caudal vertebrae, both having flattened distal centra with a prominent ventral groove. This implies that ''Antarctopelta'' also had a macuahuitl, a flat, spiked arrangement of osteoderms on the end of the tail. The name is in reference to the Aztec weapon due to its similar appearance and function. The
 Ankylosaurs were a group of herbivorous, quadrupedal ornithischians with armored osteoderms adorning the dermis. Prior to the description of ''
Ankylosaurs were a group of herbivorous, quadrupedal ornithischians with armored osteoderms adorning the dermis. Prior to the description of '' In 2021, Sergio Soto-Acuña and colleagues described a new group of ankylosaurs, the
In 2021, Sergio Soto-Acuña and colleagues described a new group of ankylosaurs, the 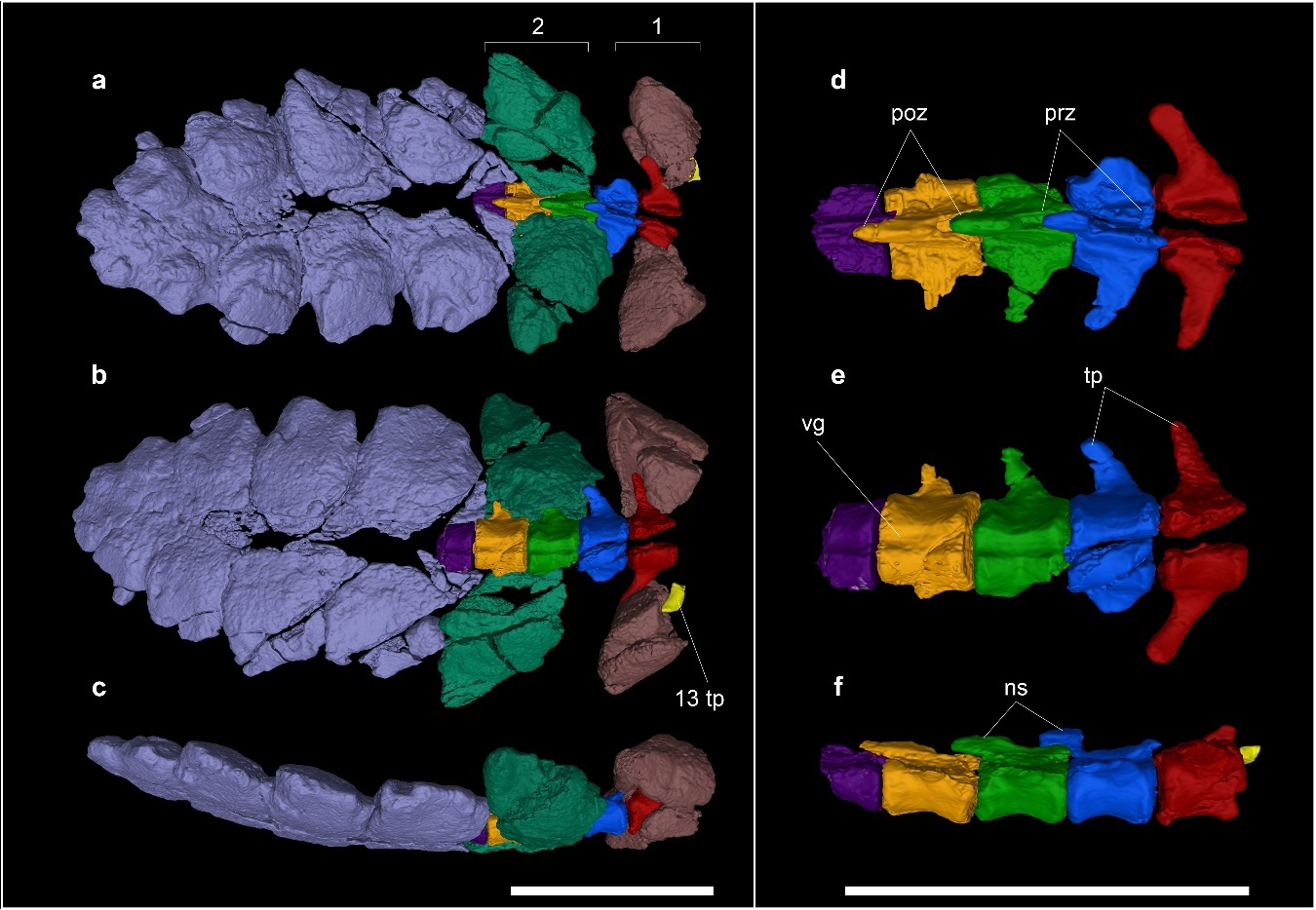
 Earlier work suggested that the holotype was a juvenile based on the fusion of bones. However, a 2019
Earlier work suggested that the holotype was a juvenile based on the fusion of bones. However, a 2019
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs ...
n dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
, a group of large, quadrupedal herbivores, that lived during the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian ( ) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age (uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage) of the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or Upper Cretaceous series (s ...
stage of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
period on what is now James Ross Island
James Ross Island () is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel.
Rising to , it is irregularly shaped and extends in a north–so ...
, Antarctica. ''Antarctopelta'' is the only known ankylosaur from Antarctica and a member of Parankylosauria
Parankylosauria is a group of Basal (phylogenetics), basal ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Cretaceous of South America, Antarctica, and Australia. It is thought the group split from other ankylosaurs during the mid-Jurassic period, despite ...
. The only described specimen was found in 1986, the first dinosaur to be found on the continent, by Argentine geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the structure, composition, and History of Earth, history of Earth. Geologists incorporate techniques from physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics, and geography to perform research in the Field research, ...
s Eduardo Olivero and Robert Scasso. The fossils were later described in 2006 by paleontologist
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
s Leonardo Salgado and Zulma Gasparini, who named the type species ''A. oliveroi'' after Olivero.
''Antarctopelta'' is a medium-sized ankylosaur, reaching or more in length, and shows characteristics of two different families, making more precise classification difficult for many years. In 2021 a nearly complete skeleton of the similar Chilean genus ''Stegouros
''Stegouros'' (, meaning "roofed tail") is an extinct genus of ankylosaurian dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Dorotea Formation of southern Chile. The genus contains a single species, ''Stegouros elengassen'', known from a semi-articulated, ne ...
'' was described. This led to the recognition of Parankylosauria, containing ''Antarctopelta'', ''Stegouros'', and ''Kunbarrasaurus
''Kunbarrasaurus'' (meaning "shield lizard") is an extinct genus of small ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Cretaceous of Australia. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''K. ieversi''.
Discovery
In November 1989, at Marathon ...
''. The head is small, with proportionally large teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
compared to other ankylosaurs and spikes above the orbits
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an physical body, object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an satellite, artificia ...
. The neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
and back vertebrae were short and circular in cross-section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture and engineering 3D
* Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
...
, whereas the tail vertebrae were elongated and flattened. Its tail likely terminated in an arrangement of spiked osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amph ...
s known as a macuahuitl, which resembled an Aztec weapon of the same name. Osteoderms were present on other parts of the body and came in six different shapes, with some being large and flat while others were tall and keeled.
It was discovered in rocks of the Gamma Member of the Snow Hill Island Formation, which bears a variety of other fossils, many of them unique as they evolved in the isolation of Antarctica after the breakup of Gondwana. ''Antarctopelta'' coexisted with the ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
dinosaur ''Trinisaura
''Trinisaura'' is a genus of ornithopod dinosaur that lived during the late Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, Upper Cretaceous, around 73 to 72 million years ago in what is now James Ross Island off the coast of northern Antarctica near Pa ...
'' in addition to a menagerie of mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Ancient Greek, Greek ' meaning 'lizard') are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains wer ...
s, plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an Order (biology), order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period (geology), Period, possibly in the Rhaetian st ...
s, and shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s.
Discovery and naming
 During an expedition to
During an expedition to James Ross Island
James Ross Island () is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel.
Rising to , it is irregularly shaped and extends in a north–so ...
off the coast of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, an incomplete skeleton of an ankylosaur
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful l ...
was discovered by Argentine
Argentines, Argentinians or Argentineans are people from Argentina. This connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural. For most Argentines, several (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their ...
geologists Eduardo Olivero and Robert Scasso in January 1986. However, excavations would not be finished for a decade due to ground frost and harsh weather conditions. Olivero and Scasso had found the specimen in strata from the Gamma Member of the Snow Hill Island Formation, which dates to the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian ( ) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age (uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage) of the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or Upper Cretaceous series (s ...
age of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
period. The material all came from a single individual, but was spread over a area and collected over several field seasons. The bones were heavily worn due to freeze-thaw weathering, causing many to become fragmented and broken. It was theorized that one of the phalanges came from a different individual, though this has been disproven. At this site, the specimen was unearthed with a tooth of the shark '' Notidanodon'', likely due to scavenging, as well as bivalves
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed by a calcified exoskeleton consis ...
. This implies that the ankylosaur died and floated out to sea, a phenomenon observed in other ankylosaurs.
 The
The holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
(specimen used as the basis for the taxon) MLP 86-X-28-1 is the only known examplar of this genus and species, and was the first dinosaur ever found in Antarctica. It consists of three isolated teeth, part of the lower jaw
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
with another tooth ''in situ
is a Latin phrase meaning 'in place' or 'on site', derived from ' ('in') and ' ( ablative of ''situs'', ). The term typically refers to the examination or occurrence of a process within its original context, without relocation. The term is use ...
'', some other skull fragments, vertebrae of the neck, back, hips and tail, some shoulder and hip bones (scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
, ilium) a thigh bone (femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
), foot and hand bones (five metapodials and two phalanges
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digit (anatomy), digital bones in the hands and foot, feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the Thumb, thumbs and Hallux, big toes have two phalanges while the other Digit (anatomy), digits have three phalanges. ...
), and numerous pieces of armor, representing approximately 15% of the skeleton.
Although the material had been known for decades and written about in three separate publications, ''Antarctopelta oliveroi'' was not named until 2006, by Argentine paleontologist
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
s Leonardo Salgado and Zulma Gasparini. It was therefore the second named genus of dinosaur from Antarctica after '' Cryolophosaurus'' in 1993, despite being discovered first. The genus name refers to its location on the continent of Antarctica and its armored nature. Antarctica is derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
words ''αντ''/''ant-'' ('opposite of') and ''αρκτος''/''arktos'' ('bear' referring to the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa M ...
, which points north). The Greek ''πελτη''/''pelte'' ('shield') is commonly used to name genera of ankylosaurs ('' Cedarpelta'' and '' Sauropelta'', for example). The single known species, ''A. oliveroi'', is named after Eduardo Olivero, who discovered the holotype, first mentioned it in print, and has worked in Antarctica for decades.
Description
herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat n ...
quadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion in which animals have four legs that are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four legs is said to be a quadruped (fr ...
protected by armor plates embedded in the skin. Although a complete skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fra ...
has not been found, the species is estimated to have reached a maximum length of from snout to tail tip. In 2010 Gregory Paul gave a higher estimation of and . The head was small, with jaws lined with small, leaf-shaped teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
. The limbs were short and about equal in length, the forefeet having five toes while the hindfeet had six.
Very little of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
is known, but all of the preserved skull fragments were heavily ossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
for protection. One bone in particular, identified as a supraorbital (brow ridge bone), bore a short spike which would have projected outwards over the eye. Other fossils likely from the quadratojugals (cheek bones), supraorbitals, and right parietal (cranium bone) were identified in 2006, though their poor condition gives little information. The leaf-shaped teeth are asymmetrical, with the majority of the denticles on the edge closest to the tip of the snout and large furrows on the cingula. Seven to eight mesial denticles are found on each ''Antarctopelta'' tooth, the highest number known from Parankylosauria
Parankylosauria is a group of Basal (phylogenetics), basal ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Cretaceous of South America, Antarctica, and Australia. It is thought the group split from other ankylosaurs during the mid-Jurassic period, despite ...
, a trait distinguishing it from the related ''Stegouros
''Stegouros'' (, meaning "roofed tail") is an extinct genus of ankylosaurian dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Dorotea Formation of southern Chile. The genus contains a single species, ''Stegouros elengassen'', known from a semi-articulated, ne ...
''. These teeth are also proportionately large compared to those of other ankylosaurs, with the largest measuring across. This compares to the much larger North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
n '' Euoplocephalus'', in body length, which had teeth averaging only across. A fragment from the left dentary
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone ...
(lower jaw bone) preserving these teeth was recovered, which has a curved tooth row like other ankylosaurs'.
Postcranium
 Five
Five cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
were found in the field, though three were molded by latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all floweri ...
and the originally material was subsequently lost. Their centra are proportionally short with amphicoelus (biconcave) ends, bearing a centrum length to height ratio of only 0.57. This is in stark contrast to genera like '' Struthiosaurus'' and '' Ankylosaurus'', which have ratios of 1.35 and 0.78 respectively. Neural canals, the area where the notochord
The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the verteb ...
would pass through, in these vertebrae are circular in cross-section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture and engineering 3D
* Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
...
and much larger than in ''Stegouros''. Two dorsal vertebrae from the synsacrum were unearthed. Two complete and one incomplete sacral vertebrae, the last of which contains parts of the sacrum, were collected as well. These vertebrae are firmly ankylosed (fused) with each other and the sacrum. Elements of the ribs
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels ...
were found attached to the sacrals as well as eight fragments from midsections of ribs. Eight caudal vertebrae
Caudal vertebrae are the vertebrae of the tail in many vertebrates. In birds, the last few caudal vertebrae fuse into the pygostyle, and in apes, including humans, the caudal vertebrae are fused into the coccyx.
In many reptiles, some of the caud ...
are preserved from the middle and distal portions of the tail. The distal caudals are associated with ossified tendons
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tension.
Tendons, like ligaments, are made of ...
on the upper and lower sides. In ankylosaurids, these tendons help to stiffen the end of the tail in support of a large, bony tail club.
 ''Antarctopelta'' and ''Stegouros'' have very similar caudal vertebrae, both having flattened distal centra with a prominent ventral groove. This implies that ''Antarctopelta'' also had a macuahuitl, a flat, spiked arrangement of osteoderms on the end of the tail. The name is in reference to the Aztec weapon due to its similar appearance and function. The
''Antarctopelta'' and ''Stegouros'' have very similar caudal vertebrae, both having flattened distal centra with a prominent ventral groove. This implies that ''Antarctopelta'' also had a macuahuitl, a flat, spiked arrangement of osteoderms on the end of the tail. The name is in reference to the Aztec weapon due to its similar appearance and function. The appendicular skeleton
The appendicular skeleton is the portion of the vertebrate endoskeleton consisting of the bones, cartilages and ligaments that support the paired appendages ( fins, flippers or limbs). In most terrestrial vertebrates (except snakes, legless li ...
is poorly known, but fragments were collected. The distal end of the left femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
(thigh bone) was found. An estimate of the femur's total length was made, with an approximation of long. Five metapodials and two phalanges
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digit (anatomy), digital bones in the hands and foot, feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the Thumb, thumbs and Hallux, big toes have two phalanges while the other Digit (anatomy), digits have three phalanges. ...
from the manus and possibly pes were also found. Ankylosaurs like ''Antarctopelta'' and ''Stegouros'' had four digits with four metapodials on the manus and pes. Some of the metapodials may be metatarsals, which are slender like those of ''Stegouros''. Fragments from the scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
(shoulderblade) and ilium were unearthed, though the former bone is notably unfused with the coracoid
A coracoid is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is n ...
. This suggests that the individual was immature, though histological analysis contradicts this.
Six different types of osteoderms were found along with the skeletal remains of ''Antarctopelta'', but very few were articulated with the skeleton, so their placement on the body is largely speculative. They included the base of what would have been a large spike. Flat oblong plates resembled the ones that guarded the neck of the nodosaurid '' Edmontonia rugosidens''. Large circular plates were found associated with smaller, polygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure made up of line segments connected to form a closed polygonal chain.
The segments of a closed polygonal chain are called its '' edges'' or ''sides''. The points where two edges meet are the polygon ...
al nodules, perhaps forming a shield over the hips as seen in '' Sauropelta''. Another type of osteoderm was oval-shaped with a keel running down the middle. A few examples of this fifth type were found ossified to the ribs, suggesting that they ran in rows along the flanks of the animal, a very typical pattern among ankylosaurs. The final group consisted mainly of small bony nodules which are often called ''ossicles'', and were probably scattered throughout the body. Several ribs were also found with these ossicles attached.
Classification
 Ankylosaurs were a group of herbivorous, quadrupedal ornithischians with armored osteoderms adorning the dermis. Prior to the description of ''
Ankylosaurs were a group of herbivorous, quadrupedal ornithischians with armored osteoderms adorning the dermis. Prior to the description of ''Stegouros
''Stegouros'' (, meaning "roofed tail") is an extinct genus of ankylosaurian dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Dorotea Formation of southern Chile. The genus contains a single species, ''Stegouros elengassen'', known from a semi-articulated, ne ...
'', it was thought that there were two main families of ankylosaur; Nodosauridae, which has no tail club, and Ankylosauridae, with tail clubs. When first described, ''Antarctopelta'' was placed at an indeterminate level within Ankylosauria but was stated to have similarities with both nodosaurids and ankylosaurids. The dentiton and osteoderms share features with nodosaurids, while it was thought to have a clubbed tail like ankylosaurids. It had been designated as Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs ...
''incertae sedis
or is a term used for a taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty ...
'' before being subjected to a phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data ...
. Later, in 2011 a phylogenetic analysis performed by Thompson and colleagues suggested that ''Antarctopelta'' was the basalmost known nodosaurid.
 In 2021, Sergio Soto-Acuña and colleagues described a new group of ankylosaurs, the
In 2021, Sergio Soto-Acuña and colleagues described a new group of ankylosaurs, the Parankylosauria
Parankylosauria is a group of Basal (phylogenetics), basal ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Cretaceous of South America, Antarctica, and Australia. It is thought the group split from other ankylosaurs during the mid-Jurassic period, despite ...
, with the description of ''Stegouros''. This clade minimally comprises ''Kunbarrasaurus
''Kunbarrasaurus'' (meaning "shield lizard") is an extinct genus of small ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Cretaceous of Australia. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''K. ieversi''.
Discovery
In November 1989, at Marathon ...
'', ''Stegouros'', and ''Antarctopelta'', all of which are small ankylosaurs from the Southern Hemisphere, the latter of which is the largest. Soto Acuña, Vargas & Kaluza supported similar results in their 2024 redescription of ''Antarctopelta'', also recovering '' Patagopelta'' as a parankylosaur. The following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
is reproduced from the phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data ...
of Soto-Acuña et al. (2021):

Paleobiology
''Antarctopelta'', based on phylogenetic bracketing and known material, probably had a macuahuitl like its relative ''Stegouros''. This structure was made up of several fused, flat osteoderms that occupied the end of the tail. The osteoderms are spiked and point outwards in a frond-like pattern, suggesting a defensive function.Histology
 Earlier work suggested that the holotype was a juvenile based on the fusion of bones. However, a 2019
Earlier work suggested that the holotype was a juvenile based on the fusion of bones. However, a 2019 histological
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at large ...
analysis by Argentine paleontologist Ignacio Cerda and colleagues found that the holotype individual was sexually mature
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans, it is related to both puberty and adulthood. ''Puberty'' is the biological process of sexual maturation, while ''adulthood'', the condition of being socially recognized as ...
. Samples from three osteoderms, a bone shaft, a metapodial, several undetermined fragments, ossified tendons, and dorsal ribs were used in the study. Based on the spacing and organization of the Outer Circumferential Layer of the bone cortex, Cerda et al. concluded that the specimen had reached sexual maturity and was close to adult maturity. During their study, the authors found that one section of bone had an abnormal bone tissue
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provi ...
that may have been caused by a tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
or other periosteal reaction. The growth patterns of the bones were not very dissimilar to those of ankylosaurs from lower latitudes. This suggests that the growth rates remained the same, despite different climatic or environmental conditions. This contrasts with hadrosaurs and ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Ancient Greek, Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivore, herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Asia and Europe, during the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, although ance ...
ns, which have varying growth rates depending on the latitude.
Paleoecology
Theholotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
skeleton was collected about from the base of the Gamma Member of the Snow Hill Island Formation. It is one of only two major dinosaur-bearing rock formations found on Antarctica, bearing all but two of the continent's named dinosaurs. The floral composition, habitat and climate are similar to modern volcanic arc
A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate, with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc ...
hes. During the time in which ''Antarctopelta'' lived, Earth's climate was much warmer and more humid than it is today and as a result Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
was without ice. The environment was mainly dominated by large dense conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
forests, cycads, and ginkgos. The animals inhabiting Antarctica at this time would still have had to endure long periods of darkness during the winter, much like in modern-day Antarctica. Despite being found in marine sediment, ''Antarctopelta'', like all ankylosaurs, lived on land. Other ankylosaurs have also been found in marine sediments, likely as a result of carcasses washing out to sea. The Antarctic Peninsula, including James Ross Island, was connected to South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
throughout this time period, allowing interchange of fauna between both continents. In fact, the recent discovery of the Chilean parankylosaurian ''Stegouros
''Stegouros'' (, meaning "roofed tail") is an extinct genus of ankylosaurian dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Dorotea Formation of southern Chile. The genus contains a single species, ''Stegouros elengassen'', known from a semi-articulated, ne ...
'' shows that these dinosaurs inhabited also South America.
In the Gamma Member, wood fragments, twigs, and leaves have been found in concretions, some being associated with dinosaur fossils like ''Antarctopelta'' itself, and were apparently transported by the same ocean currents that brought the dinosaur carcasses. From the Gamma Member, Asteraceae
Asteraceae () is a large family (biology), family of flowering plants that consists of over 32,000 known species in over 1,900 genera within the Order (biology), order Asterales. The number of species in Asteraceae is rivaled only by the Orchi ...
pollen grains were collected that are the oldest records of the family. Some of the environment may have been wet and similar to peat bogs, as evidenced by the presence of Sphagnaceae (peat mosses) and several other groups including the clubmoss ''Selaginella
''Selaginella'', also known as spikemosses or lesser clubmosses, is a genus of lycophyte. It is usually treated as the only genus in the family Selaginellaceae, with over 750 known species.
This family is distinguished from Lycopodiaceae (th ...
,'' the firmoss group Lycopodiaceae
The Lycopodiaceae (class Lycopodiopsida, order Lycopodiales) are an old family of vascular plants, including all of the core clubmosses and firmosses, comprising 17 accepted genera and about 500 known species. This family originated about 380 mi ...
, and the clade Ericaceae
The Ericaceae () are a Family (biology), family of flowering plants, commonly known as the heath or heather family, found most commonly in acidic and infertile growing conditions. The family is large, with about 4,250 known species spread acros ...
. The Gamma Member of the formation has yielded several other vertebrate remains, such as the ornithopod ''Trinisaura'', a vertebral centrum of a lithostrothian sauropod, an aquatic elasmosaurid
Elasmosauridae, often called elasmosaurs or elasmosaurids, is an extinct family of plesiosaurs that lived from the Hauterivian stage of the Early Cretaceous to the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period (c. 130 to 66 mya). The taxo ...
, and the carnivorous tylosaurine mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Ancient Greek, Greek ' meaning 'lizard') are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains wer ...
s ''Taniwhasaurus
''Taniwhasaurus'' is an extinct genus of mosasaurs (a group of extinct Marine reptile, marine lizards) that lived during the Campanian Stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Late Cretaceous. It is a member of the subfamily Tylosaurinae, a lineage of ...
'' and '' Hainosaurus.'' As for fishes and chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
, the bony fish '' Enchodus'' and '' Apateodus'', an indeterminate ichthyodectiformes
Ichthyodectiformes is an Extinction, extinct order of marine stem-teleost ray-finned fish. The order is named after the genus ''Ichthyodectes'', established by Edward Drinker Cope in 1870. Ichthyodectiforms are usually considered to be some of th ...
, and several sharks such as '' Sphenodus, Cretalamna,''Otero, R. A., Gutstein, C. S., Vargas, A., Rubilar-Rogers, D., Yury-Yañez, R., Bastías, J., & Ramírez, C. (2014). New chondrichthyans from the Upper Cretaceous (Campanian–Maastrichtian) of Seymour and James Ross islands, Antarctica. ''Journal of Paleontology'', ''88''(3), 411-420. and '' Notidanodon'' have been collected. Ammonites
Ammonoids are extinct, (typically) coiled-shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish (which comprise the clade Coleoidea) than they are to nautiluses (family N ...
, a kind of aquatic, shelled cephalopod, are also found in the layers of the Gamma Member.
See also
*Timeline of ankylosaur research
This timeline of ankylosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the History of paleontology, history of paleontology focused on the ankylosaurs, quadrupedal herbivorous dinosaurs who were protected by a covering bony plates and spik ...
* South Polar dinosaurs
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q134176 Parankylosauria Dinosaur genera Maastrichtian dinosaurs Fossil taxa described in 2006 Dinosaurs of Antarctica