Alvin Hansen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alvin Harvey Hansen (August 23, 1887 – June 6, 1975) was an American economist who taught at the
at JSTOR
* Hansen, Alvin H. (1941). ''Fiscal Policy and Business Cycles'' * Hansen, Alvin H. (1949). ''Monetary Theory and Fiscal Policy''. New York: McGraw-Hill. * Hansen, Alvin H. (1953). '' A Guide To Keynes'', including th
Preface
New York: McGraw-Hill. * Hansen, Alvin H. (1964). ''Business Cycles and National Income''. London: AllenUnin.
University of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota Twin Cities (historically known as University of Minnesota) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint ...
and was later a chair professor of economics at Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
. Often referred to as "the American Keynes", he was a widely read popular author on economic issues, and an influential advisor to the government on economic policy
''Economic Policy'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Oxford University Press, Oxford Academic on behalf of the Centre for Economic Policy Research, the Center for Economic Studies (University of Munich), and the Paris Scho ...
. Hansen helped create the Council of Economic Advisors and the Social Security
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance ...
system. He is best remembered today for introducing Keynesian economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomics, macroeconomic theories and Economic model, models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongl ...
in the United States in the 1930s and 40s.
More effectively than anyone else, he explicated, extended, domesticated, and popularized the ideas embodied in Keynes's '' The General Theory.'' He helped develop with John Hicks
Sir John Richard Hicks (8 April 1904 – 20 May 1989) was a British economist. He is considered one of the most important and influential economists of the twentieth century. The most familiar of his many contributions in the field of economics ...
the IS–LM model (or Hicks–Hansen model), a mathematical representation of Keynesian macroeconomic theory. In 1967, Paul McCracken, chairman of the President's Council of Economic Advisers, saluted Hansen stating: "It is certainly a statement of fact that you have influenced the nation's thinking about economic policy more profoundly than any other economist in this century."
Early life and education
Hansen was born in Viborg,South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state, state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Dakota people, Dakota Sioux ...
on August 23, 1887, the son of Niels Hansen, a farmer, and Marie Bergitta Nielsen. Graduating from the nearby Yankton College (closed in 1984) in 1910 with a major in English, he enrolled in the University of Wisconsin-Madison
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Uni ...
in 1913 to study economics under Richard Ely and John R. Commons, from whom he learned to use economics to address pressing social problems. Upon completion of the coursework for the PhD in 1916. Hansen married Mabel Lewis: they had two children.
Academic career
He taught atBrown University
Brown University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Providence, Rhode Island, United States. It is the List of colonial colleges, seventh-oldest institution of higher education in the US, founded in 1764 as the ' ...
while writing his doctoral dissertation, "Cycles of Prosperity and Depression". Upon completion of the dissertation in 1918 (published in 1921), he moved back west to the University of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota Twin Cities (historically known as University of Minnesota) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint ...
in 1919, where he rose quickly through the ranks of a full teacher in 1923. Subsequently, his ''Business Cycle Theory'' (1927) and his introductory text ''Principles of Economics'' (1928, with Frederic Garver) brought him to the attention of the wider economics profession. His ''Economic Stabilization in an Unbalanced World'' (1932), written with the help of a Guggenheim grant that funded travel in Europe during 1928–1929, established Hansen in the broader circle of public affairs. He was elected as a Fellow of the American Statistical Association in 1932. He also worked for the Economic and Financial Organization of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
.
In 1937 he received an invitation to occupy the new Lucius N. Littauer Chair of political Economy at Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
. His first book at Harvard posed the question ''Full Recovery or Stagnation?'' (1938) sketched the outlines of what came to be called the " secular stagnation thesis".
Later, his ''America's Role in the World Economy'' (1945) and ''Economic Policy and Full Employment'' (1947) made this case to a wider public.
Hansen was appointment as special economic adviser to Marriner Eccles at the Federal Reserve Board in 1940 and he was in charge until 1945.
After retiring from active teaching in 1956, he wrote ''The American Economy'' (1957), ''Economic Issues of the 1960s and Problems'' (1964), and ''The Dollar and the International Monetary System'' (1965).
He died in Alexandria, Virginia on June 6 of 1975 at the age of 87 years.
Theories
His most outstanding contribution to economic theory was the joint development, withJohn Hicks
Sir John Richard Hicks (8 April 1904 – 20 May 1989) was a British economist. He is considered one of the most important and influential economists of the twentieth century. The most familiar of his many contributions in the field of economics ...
, of the so-called IS–LM model, also known as the "Hicks–Hansen synthesis." The IS–LM diagram claims to show the relationship between the investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broade ...
-saving
Saving is income not spent, or deferred Consumption (economics), consumption. In economics, a broader definition is any income not used for immediate consumption. Saving also involves reducing expenditures, such as recurring Cost, costs.
Methods ...
(IS) curve and the liquidity preference- money supply (LM) curve. It is used in mainstream economics
Mainstream economics is the body of knowledge, theories, and models of economics, as taught by universities worldwide, that are generally accepted by economists as a basis for discussion. Also known as orthodox economics, it can be contrasted to ...
literature and textbooks to illustrate how monetary and fiscal policy can influence GDP.
Hansen's book of 1938, ''Full Recovery or Stagnation''. based in Keynes's ''General Theory'', presents his thesis for both growth and employment being stagnant if there is no economic state intervention to stimulate demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a goods, good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. In economics "demand" for a commodity is not the same thing as "desire" for it. It refers to both the desi ...
.
Hansen presented evidence on several occasions before the U.S. Congress to oppose the use of unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
as the main means of fighting inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
. He advocated instead that inflation could be controlled by changes in interest- and tax-rates as well as controls on prices and wages.
Lately, theories of economic stagnation have become more associated with Hansen's ideas than with those of Keynes.
Keynesianism
Hansen, in his review of ''The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money
''The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money'' is a book by English economist John Maynard Keynes published in February 1936. It caused a profound shift in economic thought, giving macroeconomics a central place in economic theory and ...
'', was skeptical of John Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist and philosopher whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originall ...
's propositions, but by December 1938, in his presidential address to the American Economic Association
The American Economic Association (AEA) is a learned society in the field of economics, with approximately 23,000 members. It publishes several peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Economic Literature, American Economic Review, an ...
, he embraced Keynesian theories of the need for government intervention in periods of economic recession. Soon after his arrival at Harvard in 1937, Hansen's famous graduate seminar on fiscal policy began inspiring graduate students such as Paul Samuelson
Paul Anthony Samuelson (May 15, 1915 – December 13, 2009) was an American economist who was the first American to win the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. When awarding the prize in 1970, the Swedish Royal Academies stated that he "h ...
and James Tobin
James Tobin (March 5, 1918 – March 11, 2002) was an American economist who served on the Council of Economic Advisers and consulted with the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, and taught at Harvard University, Harvard and Yale Uni ...
(both of whom would go on to win the Economics Nobel) to further develop and popularize Keynesian economics. Hansen's 1941 book, ''Fiscal Policy and Business Cycles'', was the first major work in the United States to entirely support Keynes's analysis of the causes of the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
. Hansen used that analysis to argue for Keynesian deficit spending
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit, the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budg ...
.
Hansen's best known contribution to economics was his and John Hicks
Sir John Richard Hicks (8 April 1904 – 20 May 1989) was a British economist. He is considered one of the most important and influential economists of the twentieth century. The most familiar of his many contributions in the field of economics ...
's development of the IS–LM model, also known as the "Hicks–Hansen synthesis." The framework claims to graphically represent the investment-savings (IS) curve and the liquidity-money supply (LM) curve as an illustration of how fiscal and monetary policies can be employed to alter national income.
Hansen's 1938 book, ''Full Recovery or Stagnation'', was based on Keynesian ideas and was an extended argument that there would be long-term employment stagnation without government demand-side intervention.
Paul Samuelson
Paul Anthony Samuelson (May 15, 1915 – December 13, 2009) was an American economist who was the first American to win the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. When awarding the prize in 1970, the Swedish Royal Academies stated that he "h ...
was Hansen's most famous student. Samuelson credited Hansen's ''Full Recovery or Stagnation?'' (1938) as the main inspiration for his famous multiplier-accelerator model of 1939. Leeson (1997) shows that while Hansen and Sumner Slichter continued to be regarded as leading exponents of Keynesian economics, their gradual abandonment of a commitment to price stability contributed to the development of a Keynesianism that conflicted with positions of Keynes himself.
Stagnation
In the late 1930s, Hansen argued that "secular stagnation" had set in so the American economy would never grow rapidly again because all the growth ingredients had played out, including technological innovation and population growth. The only solution, he argued, was constant, large-scale deficit spending by the federal government. The thesis was highly controversial, as critics, such as George Terborgh, attacked Hansen as a "pessimist" and a "defeatist." Hansen replied that secular stagnation was just another name for Keynes's underemployment equilibrium. However, the sustained economic growth, beginning in 1940, undercut Hansen's predictions and his stagnation model was forgotten.
Economic cycles
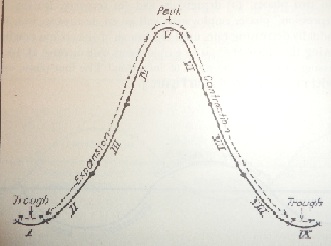
One of the most important contribution to the economic theory by Alvin Hansen are the economic cycles. In his book ''Business Cycles and National Income'', he defines the cycle as a fluctuation in: employment, output, and prices. The cycle is divided in two phases: expansion, extending from trough to peak; and contraction, extending from peak to trough. For Hansen, there exist stable and unstable economic cycles. The instability is caused by displacement due to external shocks. Hansen claims that the business-cycle analysis must take into consideration technical progress, the money market, and expectations.Public policy
Hansen argued that the American economy during theGreat Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
was not going through a particularly severe business cycle
Business cycles are intervals of general expansion followed by recession in economic performance. The changes in economic activity that characterize business cycles have important implications for the welfare of the general population, governmen ...
but through the exhaustion of a longer-term progressive dynamic. What Hansen had in mind was not just counter-cyclical public spending to stabilize employment but rather major projects such as rural electrification, slum clearance
Slum clearance, slum eviction or slum removal is an urban renewal strategy used to transform low-income settlements with poor reputation into another type of development or housing. This has long been a strategy for redeveloping urban communities; ...
, and natural resource development conservation, all with a view of opening up new investment opportunities for the private sector and so, restoring the economic dynamism needed to the system as a whole.''American National Biography'', New York: Oxford UP, 1999
Hansen trained and arguably influenced numerous students, many of whom later held government posts, and he served on numerous governmental committees dealing with economic issues. The American Economic Association
The American Economic Association (AEA) is a learned society in the field of economics, with approximately 23,000 members. It publishes several peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Economic Literature, American Economic Review, an ...
awarded him its Walker Medal in 1967.
Hansen frequently testified before Congress. He advocated against using unemployment to control inflation. He argued that inflation could be managed by timely changes in tax rates and the money supply, and by effective wage and price controls. He also advocated fiscal and other stimuli to ward off the stagnation that he thought was endemic to mature, industrialized economies. Hansen was not without his critics, however; journalist John T. Flynn, for example, argued that Hansen's policies were ''de facto'' fascism, sharing alarming similarities with the economic policy of Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who, upon assuming office as Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister, became the dictator of Fascist Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 un ...
, the dictator of Italy.
During the Roosevelt and Truman presidencies, Hansen served on government commissions and as consultant to the Federal Reserve Board, the United States Department of the Treasury
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the Treasury, national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States. It is one of 15 current United States federal executive departments, U.S. government departments.
...
and the National Security Resources Board. In 1935, he helped create the US Social Security system and, in 1946, he assisted in the drafting of the Full Employment Act, which, among other things, created the Council of Economic Advisors.
Between 1939 and 1945, he served as co-rapporteur to the economic and financial group of the Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank focused on Foreign policy of the United States, U.S. foreign policy and international relations. Founded in 1921, it is an independent and nonpartisan 501(c)(3) nonprofit organi ...
's '' War and Peace Studies'' project, along with Chicago economist Jacob Viner.
Hansen's advocacy (with Luther Gulick) during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
of Keynesian policies to promote post-war full employment helped persuade Keynes to assist in the development of plans for the international economy. Donald Markwell, ''John Maynard Keynes and International Relations: Economic Paths to War and Peace'', Oxford University Press, 2006.
References
Primary sources
* Hansen, Alvin H. (1939). "Economic Progress and Declining Population Growth," ''American Economic Review'' (29) Marchat JSTOR
* Hansen, Alvin H. (1941). ''Fiscal Policy and Business Cycles'' * Hansen, Alvin H. (1949). ''Monetary Theory and Fiscal Policy''. New York: McGraw-Hill. * Hansen, Alvin H. (1953). '' A Guide To Keynes'', including th
Preface
New York: McGraw-Hill. * Hansen, Alvin H. (1964). ''Business Cycles and National Income''. London: AllenUnin.
Secondary sources
* Barber, William J. "The Career of Alvin H. Hansen in the 1920s and 1930s: a Study in Intellectual Transformation." ''History of Political Economy'' 1987 19(2): 191–205. * Leeson, Robert. "The Eclipse of the Goal of Zero Inflation." ''History of Political Economy'' 1997 29(3): 445–496. Fulltext: in Ebsco. deals with Hansen and Sumner Slichter * Donald Markwell, ''John Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist and philosopher whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originall ...
and International Relations: Economic Paths to War and Peace'', Oxford University Press (2006).
* Miller, John E. "From South Dakota Farm to Harvard Seminar: Alvin H. Hansen, America's Prophet of Keynesianism" ''Historian'' (2002) 64(3–4): 603–622.
* Rosenof, Theodore. ''Economics in the Long Run: New Deal Theorists and Their Legacies, 1933–1993'' (1997)
* Seligman, Ben B., ''Main Currents in Modern Economics'', 1962.
* ''American National Biography''. New York: Oxford UP, 1999. Print.
Special issues of journals
* ''Quarterly Journal of Economics'' vol 90 # 1 (1976) pp. 1–37, online at JSTOR and/or in most college libraries. * "Alvin Hansen on Economic Progress and Declining Population Growth" in ''Population and Development Review'', Vol. 30, 2004External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hansen, Alvin 1887 births 1975 deaths University of Wisconsin–Madison College of Letters and Science alumni Brown University faculty University of Minnesota faculty Harvard University faculty 20th-century American economists Fellows of the Econometric Society American people of Danish descent Neo-Keynesian economists Yankton College alumni People from Viborg, South Dakota Fellows of the American Statistical Association Presidents of the American Economic Association Mathematicians from South Dakota Distinguished fellows of the American Economic Association Economists from South Dakota