17th-century disestablishments in Europe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 17th century lasted from January 1,  By the end of the century, Europeans were masters of
By the end of the century, Europeans were masters of
 * 1605– 1627: The reign of Mughal emperor
* 1605– 1627: The reign of Mughal emperor
UST.edu.ph. Retrieved December 21, 2008. * 1611: The first publication of the * 1613: The
* 1613: The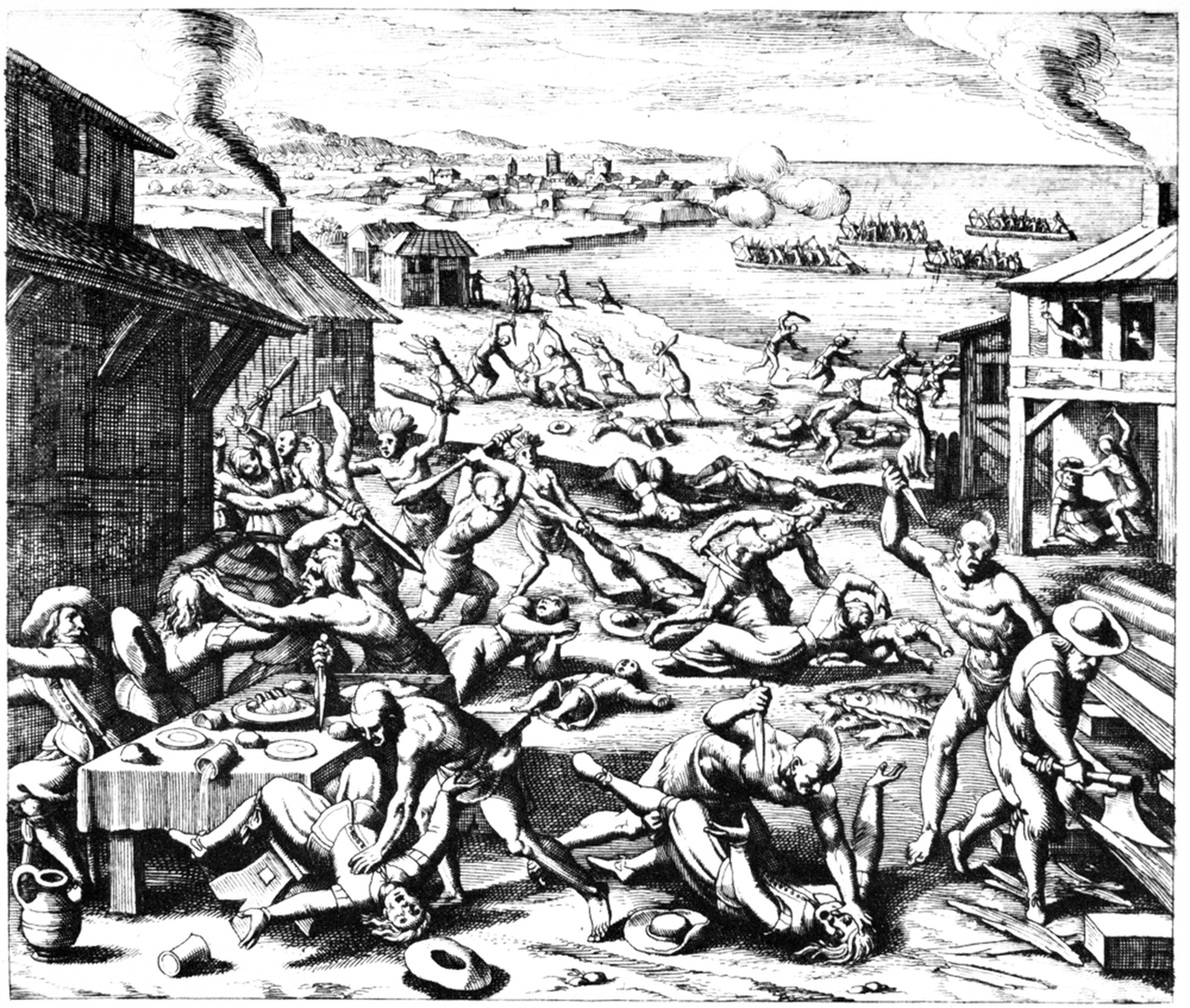  *
*  * 1648– 1653: Fronde civil war in
* 1648– 1653: Fronde civil war in
 * 1672– 1678:
* 1672– 1678: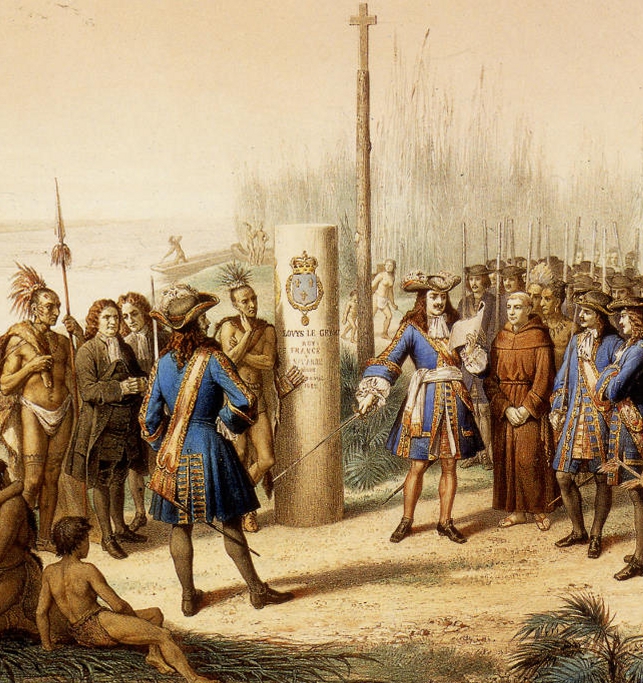  * 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of
* 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of 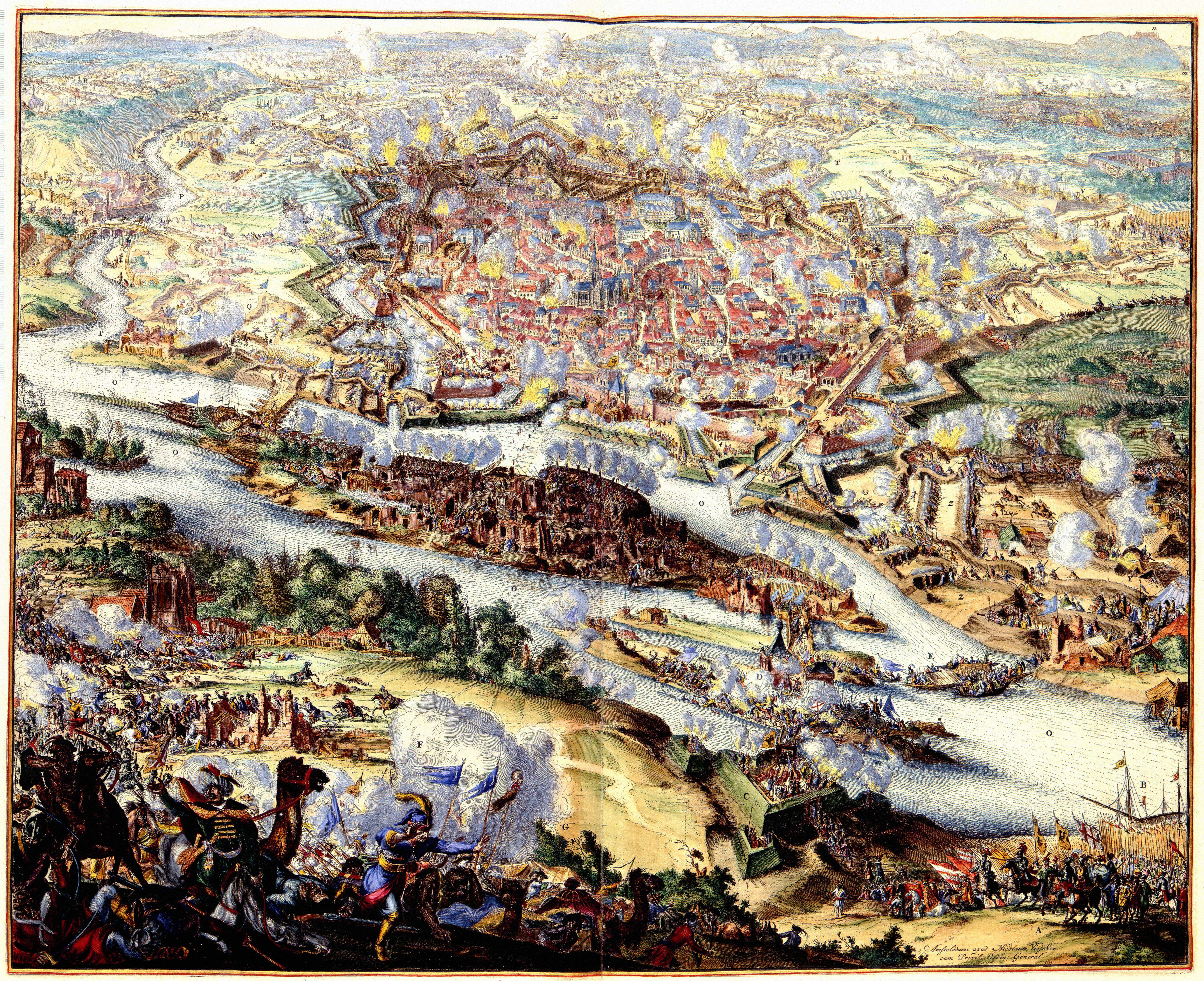 * 1689: Bill of Rights gains royal consent.
* 1689:
* 1689: Bill of Rights gains royal consent.
* 1689:
Famine in Scotland: The 'Ill Years' of the 1690s
'".
File:Albrecht Wallenstein.jpeg, Catholic general Albrecht von Wallenstein (1583–1634), supreme commander of the armies of the Imperial Army during the
 * Chang, Chun-shu, and Shelley Hsueh-lun Chang. ''Crisis and Transformation in Seventeenth-Century China'' (1998).
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of event
* Chang, Chun-shu, and Shelley Hsueh-lun Chang. ''Crisis and Transformation in Seventeenth-Century China'' (1998).
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of event
online free
* Reid, A. J. S. ''Trade and State Power in 16th & 17th Century Southeast Asia'' (1977). * Spence, J. D. ''The Death of Woman Wang: Rural Life in China in the 17th Century'' (1978).
in JSTOR
* Ogg, David. ''Europe in the Seventeenth Century'' (6th ed. 1965). * Rowbotham, Sheila. ''Hidden from history: Rediscovering women in history from the 17th century to the present'' (1976). * Trevor-Roper, Hugh R. "The general crisis of the 17th century." '' Past & Present'' 16 (1959): 31–64.
Vistorica
Timelines of 17th century events, science, culture and persons {{Authority control 2nd millennium Centuries Early modern period
1601
This Epoch (reference date)#Computing, epoch is the beginning of the 400-year Gregorian leap-year cycle within which digital files first existed; the last year of any such cycle is the only leap year whose year number is divisible by 100.
Jan ...
(represented by the Roman numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, eac ...
MDCI), to December 31, 1700 (MDCC).
It falls into the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age
The Spanish Golden Age (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Siglo de Oro'', , "Golden Century"; 1492 – 1681) was a period of literature and the The arts, arts in Spain that coincided with the political rise of the Spanish Empire under the Catholic M ...
, the Dutch Golden Age
The Dutch Golden Age ( ) was a period in the history of the Netherlands which roughly lasted from 1588, when the Dutch Republic was established, to 1672, when the '' Rampjaar'' occurred. During this period, Dutch trade, scientific development ...
, the French '' Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
, the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
, and according to some historians, the General Crisis.
From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
of Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility
The French nobility () was an Aristocracy, aristocratic social class in France from the France in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages until its abolition on 23 June 1790 during the French Revolution.
From 1808 to 1815 during the First French Empire, ...
was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily kept under surveillance. With domestic peace assured, Louis XIV caused the borders of France to be expanded. It was during this century that the English monarch
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers Constitutional monarchy, regula ...
became increasingly involved in conflicts with the Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
- this would culminate in the English civil war and an end to the dominance of the English monarchy. By the end of the century, Europeans were masters of
By the end of the century, Europeans were masters of logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , the ...
s, electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
, the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
and microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
, calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
, universal gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation describes gravity as a force by stating that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct proportionality, proportional to the product ...
, Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body re ...
, air pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The Standard atmosphere (unit), standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , whi ...
, and calculating machines
A mechanical calculator, or calculating machine, is a mechanical device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic automatically, or a simulation like an analog computer or a slide rule. Most mechanical calculators were comparable in si ...
due to the work of the first scientists of the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
, including Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
, Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best know ...
, René Descartes
René Descartes ( , ; ; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and Modern science, science. Mathematics was paramou ...
, Pierre Fermat, Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal (19June 162319August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic Church, Catholic writer.
Pascal was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. His earliest ...
, Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, Alchemy, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the foun ...
, Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution ...
, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch art, science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " ...
, Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist ("natural philosopher"), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist, and architect. He is credited as one of the first scientists to investigate living ...
, Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
, and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (or Leibnitz; – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat who is credited, alongside Sir Isaac Newton, with the creation of calculus in addition to ...
. It was also a period of development of culture in general (especially theater, music, visual arts and philosophy). Some of the greatest inventions took place in this century.
It was during this period that the European colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale colonization of the Americas, involving a number of European countries, took place primarily between the late 15th century and the early 19th century. The Norse explored and colonized areas of Europe a ...
began in earnest, including the exploitation of the silver deposits, which resulted in bouts of inflation as wealth was drawn into Europe. Also during this period, there would be a more intense European presence in Southeast Asia and East Asia (such as the colonization of Taiwan). These foreign elements would contribute to a revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...
in Ayutthaya. While the Mataram Sultanate and the Aceh Sultanate would be the major powers of the region, especially during the first half of the century.
In the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
, the gunpowder empires – the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal – grew in strength as well. The southern half of India would see the decline of the Deccan Sultanates
The Deccan sultanates is a historiographical term referring to five late medieval to early modern Persianate Indian Muslim kingdoms on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range. They were created from the disintegrati ...
and extinction of the Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
. The Dutch would colonize Ceylon and endure hostilities with Kandy
Kandy (, ; , ) is a major city located in the Central Province, Sri Lanka, Central Province of Sri Lanka. It was the last capital of the Sinhalese monarchy from 1469 to 1818, under the Kingdom of Kandy. The city is situated in the midst of ...
. The end of the 17th century saw the first major surrender of Ottoman territory in Europe when the Treaty of Karlowitz ceded most of Hungary to the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
in 1699.
In Japan, Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 – 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Gr ...
established the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
at the beginning of the century, beginning the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
; the isolationist Sakoku
is the most common name for the isolationist foreign policy of the Japanese Tokugawa shogunate under which, during the Edo period (from 1603 to 1868), relations and trade between Japan and other countries were severely limited, and almost all ...
policy began in the 1630s and lasted until the 19th century. In China, the collapsing Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
was challenged by a series of conquests led by the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
warlord Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing, was the founding khan of the Jurchen people, Jurchen-led Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty.
As the leader of the House of Aisin-Gi ...
, which were consolidated by his son Hong Taiji and finally consummated by his grandson, the Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661), also known by his temple name Emperor Shizu of Qing, personal name Fulin, was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China pro ...
, founder of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
. Qing China
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty ...
spent decades of this century with economic problems (results of civil wars between the Qing and former Ming dynasty loyalists), only recovering well at the end of the century.
The greatest military conflicts of the century were the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, Dutch–Portuguese War
The Dutch–Portuguese War (; ) was a global armed conflict involving Dutch forces, in the form of the Dutch East India Company, the Dutch West India Company, and their allies, against the Iberian Union, and after 1640, the Portuguese Empire. Beg ...
, the Great Turkish War, the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
, Mughal–Safavid Wars, and the Qing annexation of the Ming.
Events
1601–1650
*1601
This Epoch (reference date)#Computing, epoch is the beginning of the 400-year Gregorian leap-year cycle within which digital files first existed; the last year of any such cycle is the only leap year whose year number is divisible by 100.
Jan ...
: 4th Spanish Armada; in the Battle of Kinsale, England defeats Irish and Spanish forces, driving the Gaelic aristocracy out of Ireland and destroying the Gaelic clan system.
* 1601
This Epoch (reference date)#Computing, epoch is the beginning of the 400-year Gregorian leap-year cycle within which digital files first existed; the last year of any such cycle is the only leap year whose year number is divisible by 100.
Jan ...
– 1603: The Russian famine of 1601–1603 kills perhaps one-third of Russia.
* 1602: Matteo Ricci produces the Map of the Myriad Countries of the World (坤輿萬國全圖, ''Kūnyú Wànguó Quántú''), a world map that will be used throughout East Asia for centuries.
* 1602: The Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
(VOC) is established by merging competing Dutch trading companies.Ricklefs (1991), page 28 Its success contributes to the Dutch Golden Age
The Dutch Golden Age ( ) was a period in the history of the Netherlands which roughly lasted from 1588, when the Dutch Republic was established, to 1672, when the '' Rampjaar'' occurred. During this period, Dutch trade, scientific development ...
.
* 1603: Elizabeth I of England
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudor. Her eventful reign, and its effect on history ...
dies and is succeeded by her cousin King James VI of Scotland
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
, uniting the crowns of Scotland and England.
* 1603: Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 – 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Gr ...
takes the title of ''shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military rulers of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, except during parts of the Kamak ...
'', establishing the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
. This begins the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
, which will last until 1868.
* 1603: In Nagasaki
, officially , is the capital and the largest Cities of Japan, city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
Founded by the Portuguese, the port of Portuguese_Nagasaki, Nagasaki became the sole Nanban trade, port used for tr ...
, the Portuguese Jesuit missionary João Rodrigues publishes '' Nippo Jisho'', the first dictionary of Japanese to a European (Portuguese) language.
* 1605: The King of Gowa, a Makassarese kingdom in South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi () is a Provinces of Indonesia, province in the South Peninsula, Sulawesi, southern peninsula of Sulawesi, Indonesia. The Selayar Islands archipelago to the south of Sulawesi is also part of the province. The capital and largest ci ...
, converts to Islam. * 1605– 1627: The reign of Mughal emperor
* 1605– 1627: The reign of Mughal emperor Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
after the death of emperor Akbar.
* 1606: The Long Turkish War between the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
is ended with the Peace of Zsitvatorok—Austria abandons Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
.
* 1606: Treaty of Vienna ends an anti-Habsburg uprising in Royal Hungary.
* 1606: Willem Janszoon captained the first recorded European landing on the Australian continent, sailing from Bantam, Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, in the '' Duyfken''.
* 1607: Flight of the Earls
On 14 September ld Style and New Style dates, O.S. 4 September1607, Irish earls Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone, and Rory O'Donnell, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell, permanently departed Rathmullan in Ireland for mainland Europe, accompanied by their fa ...
(the fleeing of most of the native Gaelic aristocracy
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense Economy, economic, Politics, political, and soc ...
) occurs from County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county of the Republic of Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster and is the northernmost county of Ireland. The county mostly borders Northern Ireland, sharing only a small b ...
in the west of Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
in Ireland.
* 1607: Iskandar Muda becomes the Sultan of Aceh
Aceh ( , ; , Jawi script, Jawoë: ; Van Ophuijsen Spelling System, Old Spelling: ''Atjeh'') is the westernmost Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is located on the northern end of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capit ...
for 30 years. He will launch a series of naval conquests that will transform Aceh into a great power in the western Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago is the archipelago between Mainland Southeast Asia and Australia, and is also called Insulindia or the Indo-Australian Archipelago. The name was taken from the 19th-century European concept of a Malay race, later based ...
.
* 1610: The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
army defeats combined Russian–Swedish forces at the Battle of Klushino and conquers Moscow.
* 1610: King Henry IV of France is assassinated by François Ravaillac.
* 1611: The Pontifical and Royal University of Santo Tomas
The University of Santo Tomas (UST; ), officially the Pontifical and Royal University of Santo Tomas, The Catholic University of the Philippines or colloquially as ''Ustê'' (), is a Private university, private Catholic school, Catholic researc ...
, the oldest existing university in Asia, is established by the Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers (, abbreviated OP), commonly known as the Dominican Order, is a Catholic Church, Catholic mendicant order of pontifical right that was founded in France by a Castilians, Castilian priest named Saint Dominic, Dominic de Gu ...
in ManilaHistory of USTUST.edu.ph. Retrieved December 21, 2008. * 1611: The first publication of the
King James Bible
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version (AV), is an Early Modern English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by ...
.
* 1612: The first Cotswold Olympic Games, an annual public celebration of games and sports begins in the Cotswolds
The Cotswolds ( ) is a region of central South West England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper River Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and the Vale of Evesham. The area is defined by the bedroc ...
, England.
* 1613: The Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles (), also known as Smuta (), was a period of political crisis in Tsardom of Russia, Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Feodor I of Russia, Feodor I, the last of the Rurikids, House of Rurik, and ended in 1613 wit ...
in Russia ends with the establishment of the House of Romanov
The House of Romanov (also transliterated as Romanoff; , ) was the reigning dynasty, imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after Anastasia Romanovna married Ivan the Terrible, the first crowned tsar of all Russi ...
, which rules until 1917.
* 1613–1617
Events
January–March
* January 5
**Pocahontas and Tomocomo of the Powhatan Algonquian tribe, in the Virginia colony of America, meet King James I of England as his guests, at the Banqueting House at Whitehall.
**'' The Mad L ...
: Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
is invaded by the Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
dozens of times.in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
 * 1613: The
* 1613: The Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
is forced to evacuate Gresik due to the Mataram siege in neighboring Surabaya
Surabaya is the capital city of East Java Provinces of Indonesia, province and the List of Indonesian cities by population, second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. Located on the northeastern corner of Java island, on the Madura Strai ...
. The dutch negotiates with Mataram and is allowed to set up a trading post in Jepara.
* 1614– 1615: The Siege of Osaka
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict charact ...
(last major threat to Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
) ends.
* 1616: The last remaining Moriscos (Moors who had nominally converted to Christianity) in Spain are expelled.
* 1616: English poet and playwright William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
dies.
* 1618: The Defenestration of Prague.
* 1618: The Bohemian Revolt precipitates the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, which devastates Europe in the years 1618–48.
* 1618: The Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
s start invading China. Their conquest eventually topples the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
.
* 1619: European slaving reaches America when the first Africans are brought to the present-day United States.
* 1619: The Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
storm Jayakarta and withstand a months-long siege by the combined English, Bantenese and Jayakartan forces. They are relieved by Jan Pieterszoon Coen and a fleet of ships from Ambon. The dutch destroys Jayakarta and builds its new headquarters, Batavia, on top of it.
* 1620–1621
Events
January–March
* January 12 – Şehzade Mehmed, the 15-year old half-brother of Ottoman Sultan Osman II, is put to death by hanging on Osman's orders. Before dying, Mehmed prays aloud that Osman's reign as Sultan be r ...
: Polish–Ottoman War over Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
.
* 1620: Bethlen Gabor allies with the Ottomans and an invasion of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
takes place. The Polish suffer a disaster at Cecora on the River Prut.
* 1620: The Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English sailing ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, reac ...
sets sail from Plymouth, England to what became the Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on t ...
in New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
. *
* 1621
Events
January–March
* January 12 – Şehzade Mehmed, the 15-year old half-brother of Ottoman Sultan Osman II, is put to death by hanging on Osman's orders. Before dying, Mehmed prays aloud that Osman's reign as Sultan be r ...
: The Battle of Chocim: Poles and Cossacks
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic languages, East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borde ...
under Jan Karol Chodkiewicz
Jan Karol Chodkiewicz (; 1561 – 24 September 1621) was a Polish–Lithuanian identity, Polish–Lithuanian military commander of the Grand Ducal Lithuanian Army, who was from 1601 Field Hetman of Lithuania, and from 1605 Grand Hetman of Lit ...
defeat the Ottomans.
* 1622: Jamestown massacre: Algonquian natives kill 347 English settlers outside Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent British colonization of the Americas, English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James River, about southwest of present-day Willia ...
(approximately one-third of the colony's population) and burn the Henricus settlement.
* 1624–1642
Events
January–March
* January 4 – King Charles I of England, accompanied by soldiers, arrives at a session of the Long Parliament and attempts to arrest his chief opponents, the Five Members, John Hampden, Arthur Haselri ...
: As chief minister, Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, 1st Duke of Richelieu (9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), commonly known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a Catholic Church in France, French Catholic prelate and statesman who had an outsized influence in civil and religi ...
centralises power in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
.
* 1626: St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican completed.
* 1627: Aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius''; or ; pl.: aurochs or aurochsen) is an extinct species of Bovini, bovine, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of t ...
go extinct.
* 1628
Events
January–March
* January 19 – (26 Jumada al-Awwal 1037 Islamic calendar, A.H.) The reign of Shahryar Mirza, Salef-ud-din Muhammad Shahryar as the Mughal Emperor, Shahryar Mirza, comes to an end a little more than tw ...
– 1629: Sultan Agung of Mataram launches a failed campaign to conquer Dutch Batavia.
* 1629: Abbas I, the Safavids king, died.
* 1629: Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, 1st Duke of Richelieu (9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), commonly known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a Catholic Church in France, French Catholic prelate and statesman who had an outsized influence in civil and religi ...
allies with Swedish Protestant forces in the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
to counter Ferdinand II's expansion.
* 1630: Birth of Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the ...
at Shivneri fort, in present day Maharashtra, India, who later founded Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
in year 1674.
* 1631: Mount Vesuvius erupts.
* 1632
Events
January–March
* January 8 – University of Amsterdam is established at the site of the Athenaeum Illustre of Amsterdam.
* January 31 – The dissection of a body for the benefit of medical students is carried o ...
: Battle of Lützen, death of king of Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
Gustav II Adolf.
* 1632
Events
January–March
* January 8 – University of Amsterdam is established at the site of the Athenaeum Illustre of Amsterdam.
* January 31 – The dissection of a body for the benefit of medical students is carried o ...
: Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal ( ; ; ) is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India. It was commissioned in 1631 by the fifth Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor, Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his belo ...
building work started in Agra, India.
* 1633
Events
January–March
* January 20 – Galileo Galilei, having been summoned to Rome on orders of Pope Urban VIII, leaves for Florence for his journey. His carriage is halted at Ponte a Centino at the border of Tuscany, wher ...
: Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
arrives in Rome for his trial before the Inquisition
The Inquisition was a Catholic Inquisitorial system#History, judicial procedure where the Ecclesiastical court, ecclesiastical judges could initiate, investigate and try cases in their jurisdiction. Popularly it became the name for various med ...
.
* 1633
Events
January–March
* January 20 – Galileo Galilei, having been summoned to Rome on orders of Pope Urban VIII, leaves for Florence for his journey. His carriage is halted at Ponte a Centino at the border of Tuscany, wher ...
–1639
Events
January–March
* January 19 – Hämeenlinna () is granted privileges, after it separates from the Vanaja parish, as its own city in Tavastia.
*c. January – The first printing press in British North America is ...
: Japan transforms into "locked country".
* 1634: Battle of Nördlingen results in Catholic victory.
* 1636: Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
is founded in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
* 1637: Shimabara Rebellion
The , also known as the or , was an rebellion, uprising that occurred in the Shimabara Domain of the Tokugawa shogunate in Japan from 17 December 1637 to 15 April 1638.
Matsukura Katsuie, the ''daimyō'' of the Shimabara Domain, enforced unpo ...
of Japanese Christians, rōnin
In feudal Japan to early modern Japan (1185–1868), a ''rōnin'' ( ; , , 'drifter' or 'wandering man', ) was a samurai who had no lord or master and in some cases, had also severed all links with his family or clan. A samurai became a ''rō ...
and peasants against Edo.
* 1637: The first opera house, Teatro San Cassiano, opens in Venice.
* 1637: Qing dynasty attacked the Joseon dynasty.
* 1639
Events
January–March
* January 19 – Hämeenlinna () is granted privileges, after it separates from the Vanaja parish, as its own city in Tavastia.
*c. January – The first printing press in British North America is ...
: Naval Battle of the Downs – Republic of the United Provinces fleet decisively defeats a Spanish fleet in English waters.
* 1639
Events
January–March
* January 19 – Hämeenlinna () is granted privileges, after it separates from the Vanaja parish, as its own city in Tavastia.
*c. January – The first printing press in British North America is ...
: Disagreements between the Farnese and Barberini Pope Urban VIII
Pope Urban VIII (; ; baptised 5 April 1568 – 29 July 1644), born Maffeo Vincenzo Barberini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 6 August 1623 to his death, in July 1644. As pope, he expanded the papal terri ...
escalate into the Wars of Castro
The Wars of Castro were a series of conflicts during the mid-17th century revolving around the ancient city of Castro (located in present-day Lazio, Italy), which eventually resulted in the city's destruction on 2 September 1649. The conflict ...
and last until 1649.
* 1639
Events
January–March
* January 19 – Hämeenlinna () is granted privileges, after it separates from the Vanaja parish, as its own city in Tavastia.
*c. January – The first printing press in British North America is ...
– 1651: Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, then separate entities in a personal union un ...
, civil wars throughout Scotland, Ireland, and England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
.
* 1640– 1668: The Portuguese Restoration War led to the end of the Iberian Union
The Iberian Union is a historiographical term used to describe the period in which the Habsburg Spain, Monarchy of Spain under Habsburg dynasty, until then the personal union of the crowns of Crown of Castile, Castile and Crown of Aragon, Aragon ...
.
* 1641
Events
January–March
* January 4 – The stratovolcano Mount Parker (Philippines), Mount Parker in the Philippines has a major eruption.
* January 14 – Battle of Malacca (1641), The Battle of Malacca concludes with the D ...
: The Irish Rebellion, by Irish Catholics who wanted an end to discrimination, greater self-governance, and reverse ownership of the plantations of Ireland.
* 1641
Events
January–March
* January 4 – The stratovolcano Mount Parker (Philippines), Mount Parker in the Philippines has a major eruption.
* January 14 – Battle of Malacca (1641), The Battle of Malacca concludes with the D ...
: René Descartes
René Descartes ( , ; ; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and Modern science, science. Mathematics was paramou ...
publishes ''Meditationes de prima philosophia'' Meditations on First Philosophy.
* 1642
Events
January–March
* January 4 – King Charles I of England, accompanied by soldiers, arrives at a session of the Long Parliament and attempts to arrest his chief opponents, the Five Members, John Hampden, Arthur Haselri ...
: Beginning of English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
, conflict will end in 1649 with the execution of King Charles I, the abolition of the monarchy and the establishment of the supremacy of Parliament over the king.
* 1643: L'incoronazione di Poppea
''L'incoronazione di Poppea'' (Stattkus-Verzeichnis, SV 308, ''The Coronation of Poppaea'') is an Italian List of operas by Claudio Monteverdi, opera by Claudio Monteverdi. It was Monteverdi's last opera, with a libretto by Giovanni Francesco Buse ...
, Monterverdi
* 1644
It is one of eight years (CE) to contain each Roman numeral once (1000(M)+500(D)+100(C)+(-10(X)+50(L))+(-1(I)+5(V)) = 1644).
Events
January–March
* January 22 – The Royalist Oxford Parliament is first assembled by King Cha ...
: The Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
conquer China ending the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
. The subsequent Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
rules until 1912.
* 1644
It is one of eight years (CE) to contain each Roman numeral once (1000(M)+500(D)+100(C)+(-10(X)+50(L))+(-1(I)+5(V)) = 1644).
Events
January–March
* January 22 – The Royalist Oxford Parliament is first assembled by King Cha ...
– 1674: The Mauritanian Thirty-Year War.
* 1645– 1669: Ottoman war with Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
. The Ottomans invade Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
and capture Canea.
* 1647– 1652: The Great Plague of Seville.
* 1648: The Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
ends the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
and the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the w ...
and marks the ends of Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
as major European powers. * 1648– 1653: Fronde civil war in
* 1648– 1653: Fronde civil war in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
.
* 1648– 1657: The Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising, also known as the Cossack–Polish War, Khmelnytsky insurrection, or the National Liberation War, was a Cossack uprisings, Cossack rebellion that took place between 1648 and 1657 in the eastern territories of the Poli ...
– a Cossack rebellion in Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
which turned into a Ukrainian war of liberation from Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
.
* 1648– 1667: The Deluge wars leave Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
in ruins.
* 1648– 1669: The Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
capture Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
from the Venetians after the Siege of Candia.
* 1649: King Charles I is executed for high treason, the first and only English king to be subjected to legal proceedings in a High Court of Justice
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal (England and Wales), Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Courts of England and Wales, Senior Cour ...
and put to death.
* 1649– 1653: The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland.
1651–1700
* 1651:English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
ends with the Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Worcester
The Battle of Worcester took place on 3 September 1651 in and around the city of Worcester, England and was the last major battle of the 1642 to 1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A Parliamentarian army of around 28,000 under Oliver Cromwell def ...
.
* 1656–1661
Events
January–March
* January 6 – The Fifth Monarchists, led by Thomas Venner, unsuccessfully attempt to seize control of London; George Monck's regiment defeats them.
* January 29 – The Rokeby baronets, a Br ...
: Mehmed Köprülü is Grand Vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Soko ...
.
* 1655–1661
Events
January–March
* January 6 – The Fifth Monarchists, led by Thomas Venner, unsuccessfully attempt to seize control of London; George Monck's regiment defeats them.
* January 29 – The Rokeby baronets, a Br ...
: The Northern Wars
"Northern Wars" is a term used for a series of wars fought in northern Europe, northern and northeastern Europe from the 16th to the 18th century, primarily between the territorial rivals of the Swedish Empire, Tsardom of Russia, Poland–Lithuani ...
cement Sweden's rise as a Great Power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
.
* 1657 : Sambhaji, the second King of Maratha Empire and eldest son of King Shivaji was born at Purandar Fort on 14 May.
* 1658
Events
January–March
* January 13 – Edward Sexby, who had plotted against Oliver Cromwell, dies in the Tower of London.
* January 30 – The " March Across the Belts" (''Tåget över Bält''), Sweden's use of winter w ...
: After his father Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the ...
completes the Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal ( ; ; ) is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India. It was commissioned in 1631 by the fifth Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor, Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his belo ...
, his son Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
deposes him as ruler of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
.
* 1659: King Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the ...
killed Adil Shahi dynasty's general Afzal Khan at Pratapgad fort on 9 November.
* 1660
Events
January–March
* January 1
** At daybreak, English Army Colonel George Monck, with two brigades of troops from his Scottish occupational force, fords the River Tweed at Coldstream in Scotland to cross the Anglo-Scottish ...
: The Commonwealth of England
The Commonwealth of England was the political structure during the period from 1649 to 1660 when Kingdom of England, England and Wales, later along with Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, were governed as a republi ...
ends and the monarchy is brought back during the English Restoration
The Stuart Restoration was the reinstatement in May 1660 of the Stuart monarchy in Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland. It replaced the Commonwealth of England, established in January 164 ...
.
* 1660
Events
January–March
* January 1
** At daybreak, English Army Colonel George Monck, with two brigades of troops from his Scottish occupational force, fords the River Tweed at Coldstream in Scotland to cross the Anglo-Scottish ...
: The Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
is founded.
* 1660
Events
January–March
* January 1
** At daybreak, English Army Colonel George Monck, with two brigades of troops from his Scottish occupational force, fords the River Tweed at Coldstream in Scotland to cross the Anglo-Scottish ...
: The Bruneian Civil War begins
* 1661
Events
January–March
* January 6 – The Fifth Monarchists, led by Thomas Venner, unsuccessfully attempt to seize control of London; George Monck's regiment defeats them.
* January 29 – The Rokeby baronets, a Br ...
: The reign of the Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 165420 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, personal name Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign of 61 ...
of China begins.
* 1663: Ottoman war against Habsburg Hungary.
* 1664: The Battle of St. Gotthard: count Raimondo Montecuccoli
Raimondo Montecuccoli (; 21 February 1609 – 16 October 1680) was an Italian-born professional soldier, military theorist, and diplomat, who served the Habsburg monarchy.
Experiencing the Thirty Years' War from scratch as a simple footsoldier, ...
defeats the Ottomans. The Peace of Vasvar – intended to keep the peace for 20 years.
* 1665: Maratha
The Marathi people (; Marathi: , ''Marāṭhī lōk'') or Marathis (Marathi: मराठी, ''Marāṭhī'') are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are native to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-A ...
King Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the ...
signed the Treaty of Purandar with Mughal general Jai Singh I after Battle of Purandar.
* 1665: Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist ("natural philosopher"), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist, and architect. He is credited as one of the first scientists to investigate living ...
discovers cells using a microscope.
* 1665: Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
defeats the Kongo Empire at the Battle of Mbwila.
* 1665– 1667: The Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War, began on 4 March 1665, and concluded with the signing of the Treaty of Breda (1667), Treaty of Breda on 31 July 1667. It was one in a series of Anglo-Dutch Wars, naval wars between Kingdom of England, England and the D ...
fought between England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and the United Provinces.
* 1666: The Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London was a major conflagration that swept through central London from Sunday 2 September to Wednesday 5 September 1666, gutting the medieval City of London inside the old London Wall, Roman city wall, while also extendi ...
.
* 1666: Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the ...
visited Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
at Agra Fort and forced him into house arrest. Shivaji later escaped and returned to the Maratha kingdom.
* 1667: The Raid on the Medway during the Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War, began on 4 March 1665, and concluded with the signing of the Treaty of Breda (1667), Treaty of Breda on 31 July 1667. It was one in a series of Anglo-Dutch Wars, naval wars between Kingdom of England, England and the D ...
.
* 1667– 1668: The War of Devolution
The War of Devolution took place from May 1667 to May 1668. In the course of the war, Kingdom of France, France occupied large parts of the Spanish Netherlands and County of Burgundy, Franche-Comté, both then provinces of the Holy Roman Empire ...
: France invades the Netherlands. The Peace of Aix-la-Chapelle (1668) brings this to a halt.
* 1667– 1699: The Great Turkish War halts the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
's expansion into Europe.
* 1672–1673
Events
January–March
* January 22 – Impersonator Mary Carleton is hanging, hanged at Newgate Prison in London, for multiple thefts and returning from penal transportation.
* February 10 – Molière's ''comédie-ballet ...
: Ottoman campaign to help the Ukrainian Cossacks. John Sobieski defeats the Ottomans at the second battle of Khotyn (1673)
The Battle of Khotyn or Battle of Chocim, also known as the Hotin War, took place on 11 November 1673 in Khotyn, where the forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth under the Hetmans of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Grand Hetman ...
.
* 1672– 1674: The Third Anglo-Dutch War fought between England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and the United Provinces
* 1672–1676
Events
January–March
* January 29 – Feodor III of Russia, Feodor III becomes Tsar of Russia.
* January 31 – Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, the oldest institution of higher education in Central America, is f ...
: Polish–Ottoman War.Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, 1672 to 1678, was primarily fought by Kingdom of France, France and the Dutch Republic, with both sides backed at different times by a variety of allies. Related conflicts include the 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and ...
.
* 1673
Events
January–March
* January 22 – Impersonator Mary Carleton is hanging, hanged at Newgate Prison in London, for multiple thefts and returning from penal transportation.
* February 10 – Molière's ''comédie-ballet ...
: The Bruneian Civil War ends with Muhiyiddin winning the war.
* 1674: Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the ...
founded the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
and crowned himself as first Chatrapati of the empire.
* 1676
Events
January–March
* January 29 – Feodor III of Russia, Feodor III becomes Tsar of Russia.
* January 31 – Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, the oldest institution of higher education in Central America, is f ...
– 1681: Russia and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
commence the Russo-Turkish Wars
The Russo-Turkish wars ( ), or the Russo-Ottoman wars (), began in 1568 and continued intermittently until 1918. They consisted of twelve conflicts in total, making them one of the longest series of wars in the history of Europe. All but four of ...
.
* 1678: The Treaty of Nijmegen ends various interconnected wars among France, the Dutch Republic, Spain, Brandenburg, Sweden, Denmark, the Prince-Bishopric of Münster, and the Holy Roman Empire. * 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of
* 1680: The Pueblo Revolt drives the Spanish out of New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
until 1692.
* 1680: Prince Sambhaji crowned himself as the second '' Chatrapati'' of Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
20 July.
*1682
Events
January–March
* January 7 – The Republic of Genoa forbids the unauthorized printing of newspapers and all handwritten newssheets; the ban is lifted after three months.
* January 12 – Scottish minister James Ren ...
: French explorer Robert La Salle claims all the land east of the Mississippi River.
* 1683: China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
conquers the Kingdom of Tungning and annexes Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
.
* 1683: The Ottoman Empire is defeated in the second Siege of Vienna.
* 1683– 1699: The Great Turkish War leads to the conquest of most of Ottoman Hungary
Ottoman Hungary () encompassed the parts of the Kingdom of Hungary which were under the rule of the Ottoman Empire from the occupation of Buda in 1541 until the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The territory was incorporated into the empire, under ...
by the Habsburgs.
* 1687: Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
publishes '' Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica''.
* 1688: The Siege of Derry, the first major event in the Williamite War in Ireland
The Williamite War in Ireland took place from March 1689 to October 1691. Fought between Jacobitism, Jacobite supporters of James II of England, James II and those of his successor, William III of England, William III, it resulted in a Williamit ...
.
* 1688: Siamese revolution of 1688 ousted French influence and virtually severed all ties with the West until the 19th century.
* 1688– 1689: The Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also known as the Revolution of 1688, was the deposition of James II and VII, James II and VII in November 1688. He was replaced by his daughter Mary II, Mary II and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange ...
starts with the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
invading England, England becomes a constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
.
* 1688– 1691: The War of the Two Kings in Ireland.
* 1688– 1697: The Grand Alliance sought to stop French expansion during the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
.
* 1689: The Battle of Killiecrankie is fought between Jacobite and Williamite forces in Highland Perthshire
Perthshire (Scottish English, locally: ; ), officially the County of Perth, is a Shires of Scotland, historic county and registration county in central Scotland. Geographically it extends from Strathmore, Angus and Perth & Kinross, Strathmore ...
.
* 1689: The Karposh rebellion is crushed in present-day North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
, Skopje is retaken by the Ottoman Turks. Karposh is killed, and the rebels are defeated. * 1689: Bill of Rights gains royal consent.
* 1689:
* 1689: Bill of Rights gains royal consent.
* 1689: John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) – 28 October 1704 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.)) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of the Enlightenment thi ...
publishes ''Two Treatises of Government
''Two Treatises of Government'' (full title: ''Two Treatises of Government: In the Former, The False Principles, and Foundation of Sir Robert Filmer, and His Followers, Are Detected and Overthrown. The Latter Is an Essay Concerning The True O ...
'' and '' A Letter Concerning Toleration.''
* 1690: The Battle of the Boyne in Ireland.
* 1692
Events
January–March
* January 24 – At least 75 residents of what is now York, Maine are killed in the Raid on York (1692), Candlemas Massacre, carried out by French soldiers led by missionary Louis-Pierre Thury, along with a ...
: Port Royal in Jamaica is struck by an earthquake and a tsunami. Approximately 2,000 people die and 2,300 are injured.
* 1692
Events
January–March
* January 24 – At least 75 residents of what is now York, Maine are killed in the Raid on York (1692), Candlemas Massacre, carried out by French soldiers led by missionary Louis-Pierre Thury, along with a ...
– 1694: Famine in France kills two million.
* 1693: College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (abbreviated as W&M) is a public university, public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. Founded in 1693 under a royal charter issued by King William III of England, William III and Queen ...
is founded in Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an Independent city (United States), independent city in Virginia, United States. It had a population of 15,425 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Located on the Virginia Peninsula, Williamsburg is in the northern par ...
, by a royal charter.
* 1694: The Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
is established.
* 1695: The Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
nearly bans the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
in response to pirate Henry Every's capture of the trading ship '' Ganj-i-Sawai''.
* 1696– 1697: Famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
in Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
wipes out almost one-third of the population.Karen J. Cullen (2010). "Famine in Scotland: The 'Ill Years' of the 1690s
'".
Edinburgh University Press
Edinburgh University Press is a scholarly publisher of academic books and journals, based in Edinburgh, Scotland.
History
Edinburgh University Press was founded in the 1940s and became a wholly owned subsidiary of the University of Edinburgh ...
. p. 20.
* 1697– 1699: Grand Embassy of Peter the Great to Western Europe.
* 1699: Thomas Savery demonstrates his first steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
to the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
.
Gallery
Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, whil ...
File:Jan Pieterszoon Coen.jpg, Jan Pieterszoon Coen (1587–1629), the founder of Batavia, was an officer of the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
(VOC), holding two terms as its Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies
The governor-general of the Dutch East Indies (, ) represented Dutch rule in the Dutch East Indies between 1610 and Dutch recognition of the independence of Indonesia in 1949. Occupied by Japanese forces between 1942 and 1945, followed by the ...
File:René Descartes i samtal med Sveriges drottning, Kristina.jpg, René Descartes
René Descartes ( , ; ; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and Modern science, science. Mathematics was paramou ...
(1596–1650) with Queen Christina of Sweden
Christina (; 18 December ld Style and New Style dates, O.S. 8 December1626 – 19 April 1689), a member of the House of Vasa, was Monarchy of Sweden, Queen of Sweden from 1632 until her abdication in 1654. Her conversion to Catholicism and ...
(1626–1689)
File:Cardinal Mazarin by Pierre Mignard (Musée Condé).jpg, Cardinal Mazarin (1602–1661), who served as the chief minister
A chief minister is an elected or appointed head of government of – in most instances – a sub-national entity, for instance an administrative subdivision or federal constituent entity. Examples include a state (and sometimes a union ter ...
to the kings of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I, king of the Fra ...
Louis XIII and Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
File:Aurangzeb-portrait.jpg, Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
(1618–1707), who ruled over almost the entire Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
for a period of 49 years
File:Shivaji British Museum.jpg, Chhatrapati Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the ...
(1630–1680) founder of Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
is widely regarded as one of the greatest Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
rulers
File:Portrait of the Kangxi Emperor in Court Dress.jpg, Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 165420 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, personal name Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign of 61 ...
(1661–1722) one of the most influential emperors of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
File:Tokugawa Ieyasu2.JPG, ''Shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military rulers of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, except during parts of the Kamak ...
'' Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 – 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Gr ...
was the founder of Japan's final shogunate, which lasted well into the 19th century
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
Major changes in philosophy and science take place, often characterized as theScientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
.
* Banknote
A banknote or bank notealso called a bill (North American English) or simply a noteis a type of paper money that is made and distributed ("issued") by a bank of issue, payable to the bearer on demand. Banknotes were originally issued by commerc ...
s reintroduced in Europe.
* Ice cream
Ice cream is a frozen dessert typically made from milk or cream that has been flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as Chocolate, cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit, such as strawberries or peaches. Food ...
.
* Tea and coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
become popular in Europe.
* Central Banking
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
in France and modern Finance by Scottish economist John Law.
* Minaret
A minaret is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer (''adhan'') from a muezzin, but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can h ...
s, Jamé Mosque of Isfahan, Isfahan
Isfahan or Esfahan ( ) is a city in the Central District (Isfahan County), Central District of Isfahan County, Isfahan province, Iran. It is the capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is located south of Tehran. The city ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
(Iran), are built.
* 1604: Supernova SN 1604 is observed in the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
.
* 1605: Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best know ...
starts investigating elliptical orbits of planets.
* 1605: Johann Carolus of Germany publishes the 'Relation', the first newspaper.
* 1608: Refracting telescope
A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens (optics), lens as its objective (optics), objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptrics, dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope d ...
s first appear. Dutch spectacle-maker Hans Lippershey
Hans Lipperhey ( – buried 29 September 1619), also known as Johann Lippershey or simply Lippershey, was a Germany, German-Netherlands, Dutch Glasses, spectacle-maker. He is commonly associated with the invention of the telescope, because he was ...
tries to obtain a patent on one, spreading word of the invention.
* 1610: The Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula in the Milky Way situated south of Orion's Belt in the Orion (constellation), constellation of Orion, and is known as the middle "star" in the "sword" of Orion. It ...
is identified by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc of France.
* 1610: Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
and Simon Marius observe Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
's Galilean moons
The Galilean moons (), or Galilean satellites, are the four largest moons of Jupiter. They are, in descending-size order, Ganymede (moon), Ganymede, Callisto (moon), Callisto, Io (moon), Io, and Europa (moon), Europa. They are the most apparent m ...
.
* 1611: King James Bible
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version (AV), is an Early Modern English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by ...
or 'Authorized Version' first published.
* 1612: The first flintlock
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking lock (firearm), ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism its ...
musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually dis ...
likely created for Louis XIII of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
by gunsmith
A gunsmith is a person who repairs, modifies, designs, or builds guns. The occupation differs from an armorer, who usually replaces only worn parts in standard firearms. Gunsmiths do modifications and changes to a firearm that may require a very ...
Marin Bourgeois.
* 1614: John Napier
John Napier of Merchiston ( ; Latinisation of names, Latinized as Ioannes Neper; 1 February 1550 – 4 April 1617), nicknamed Marvellous Merchiston, was a Scottish landowner known as a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer. He was the 8 ...
introduces the logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , the ...
to simplify calculations.
* 1616: Niccolò Zucchi describes experiments with a bronze parabolic mirror trying to make a reflecting telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternati ...
.
* 1620: Cornelis Drebbel, funded by James I of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 unti ...
, builds the first 'submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
' made of wood and greased leather.
* 1623: The third English dictionary, ''English Dictionarie'', is published by Henry Cockeram, listing difficult words with definitions.
* 1628
Events
January–March
* January 19 – (26 Jumada al-Awwal 1037 Islamic calendar, A.H.) The reign of Shahryar Mirza, Salef-ud-din Muhammad Shahryar as the Mughal Emperor, Shahryar Mirza, comes to an end a little more than tw ...
: William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions to anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, pulmonary and systemic circulation ...
publishes and elucidates his earlier discovery of the circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
.
* 1637: Dutch Bible published.
* 1637: Teatro San Cassiano, the first public opera house, opened in Venice.
* 1637: Pierre de Fermat
Pierre de Fermat (; ; 17 August 1601 – 12 January 1665) was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he is recognized for his d ...
formulates his so-called Last Theorem, unsolved until 1995.
* 1637: Although Chinese naval mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive weapon placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Similar to anti-personnel mine, anti-personnel and other land mines, and unlike purpose launched naval depth charges, they are ...
s were earlier described in the 14th century '' Huolongjing'', the ''Tian Gong Kai Wu'' book of Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
scholar Song Yingxing describes naval mines wrapped in a lacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity.
Asian lacquerware, which may be c ...
bag and ignited by an ambusher pulling a rip cord on the nearby shore that triggers a steel-wheel flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
mechanism.
* 1642
Events
January–March
* January 4 – King Charles I of England, accompanied by soldiers, arrives at a session of the Long Parliament and attempts to arrest his chief opponents, the Five Members, John Hampden, Arthur Haselri ...
: Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal (19June 162319August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic Church, Catholic writer.
Pascal was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. His earliest ...
invents the mechanical calculator called Pascal's calculator.
* 1642
Events
January–March
* January 4 – King Charles I of England, accompanied by soldiers, arrives at a session of the Long Parliament and attempts to arrest his chief opponents, the Five Members, John Hampden, Arthur Haselri ...
: Mezzotint
Mezzotint is a monochrome printmaking process of the intaglio (printmaking), intaglio family. It was the first printing process that yielded half-tones without using line- or dot-based techniques like hatching, cross-hatching or stipple. Mezzo ...
engraving introduces grey tones to printed images.
* 1643: Evangelista Torricelli
Evangelista Torricelli ( ; ; 15 October 160825 October 1647) was an Italian people, Italian physicist and mathematician, and a student of Benedetto Castelli. He is best known for his invention of the barometer, but is also known for his advances i ...
of Italy invents the mercury barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis ...
.
* 1645: Giacomo Torelli of Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
, Italy invents the first rotating stage.
* 1651: Giovanni Riccioli renames the lunar maria.
* 1656: Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution ...
describes the true shape of the rings of Saturn.
* 1657: Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution ...
develops the first functional pendulum clock based on the learnings of Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
.
* 1659: Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution ...
first to observe surface details of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
.
* 1662: Christopher Merret
Christopher Merret FRSFRCP(16 February 1614/1615 – 19 August 1695), also spelt Merrett, was an English physician and scientist. He was the first to document the deliberate addition of sugar for the production of sparkling wine
Sparkli ...
presents first paper on the production of sparkling wine.
* 1663: James Gregory publishes designs for a reflecting telescope.
* 1669: The first known operational reflecting telescope is built by Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
.
* 1676
Events
January–March
* January 29 – Feodor III of Russia, Feodor III becomes Tsar of Russia.
* January 31 – Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, the oldest institution of higher education in Central America, is f ...
: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch art, science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " ...
discovers Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
.
* 1676
Events
January–March
* January 29 – Feodor III of Russia, Feodor III becomes Tsar of Russia.
* January 31 – Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, the oldest institution of higher education in Central America, is f ...
: First measurement of the speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time i ...
.
* 1679: Binary system developed by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (or Leibnitz; – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat who is credited, alongside Sir Isaac Newton, with the creation of calculus in addition to ...
.
* 1684: Calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
independently developed by both Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz and Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His book (''Mathe ...
and used to formulate classical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics inv ...
.
References
Further reading
 * Chang, Chun-shu, and Shelley Hsueh-lun Chang. ''Crisis and Transformation in Seventeenth-Century China'' (1998).
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of event
* Chang, Chun-shu, and Shelley Hsueh-lun Chang. ''Crisis and Transformation in Seventeenth-Century China'' (1998).
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973); highly detailed outline of eventonline free
* Reid, A. J. S. ''Trade and State Power in 16th & 17th Century Southeast Asia'' (1977). * Spence, J. D. ''The Death of Woman Wang: Rural Life in China in the 17th Century'' (1978).
Focus on Europe
* Clark, George. ''The Seventeenth Century'' (2nd ed. 1945). * Hampshire, Stuart. ''The Age of Reason the 17th Century Philosophers, Selected, with Introduction and Interpretive Commentary'' (1961). * * Lewitter, Lucian Ryszard. "Poland, the Ukraine and Russia in the 17th Century." '' The Slavonic and East European Review'' (1948): 157–171in JSTOR
* Ogg, David. ''Europe in the Seventeenth Century'' (6th ed. 1965). * Rowbotham, Sheila. ''Hidden from history: Rediscovering women in history from the 17th century to the present'' (1976). * Trevor-Roper, Hugh R. "The general crisis of the 17th century." '' Past & Present'' 16 (1959): 31–64.
External links
Vistorica
Timelines of 17th century events, science, culture and persons {{Authority control 2nd millennium Centuries Early modern period