|
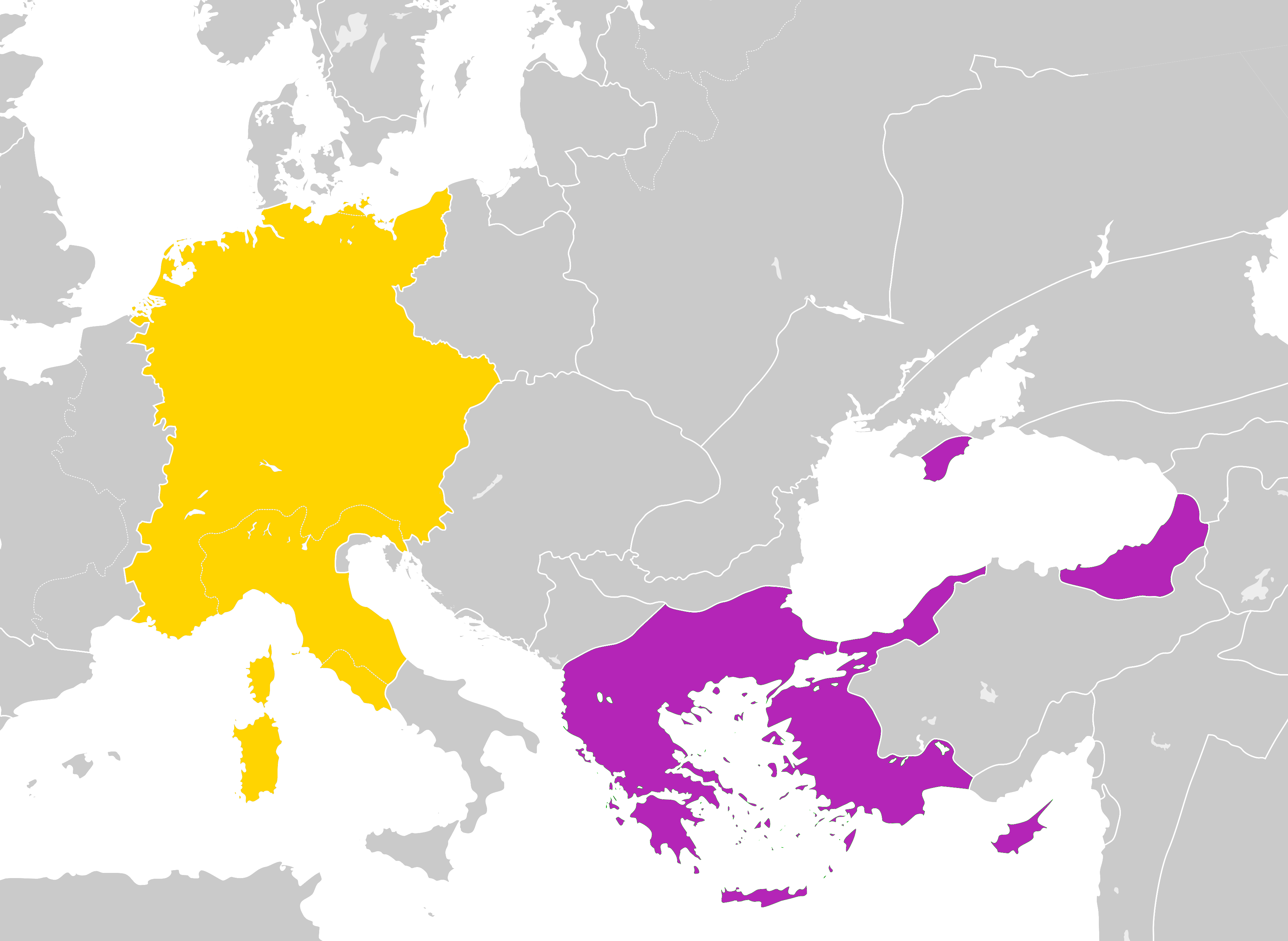
Peace Of Zsitvatorok
The Peace of Zsitvatorok (or Treaty of Sitvatorok) was a peace treaty which ended the 13-year Long Turkish War between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy on 11 November 1606. The treaty was part of a system of peace treaties which put an end to the anti-Habsburg uprising of Stephen Bocskai (1604–1606). The treaty was negotiated between 24 October and 11 November 1606 ''ad Situa Torock'', at the former mouth of the Žitava River (Hungarian: ''Zsitva''), which flows into the Danube in Royal Hungary (today part of Slovakia). Kenneth Meyer Setton, ''The Papacy and the Levant, 1204–1571'', Volume IV: The Sixteenth Century from Julius III to Pius V (Philadelphia: American Philosophical Society, 1984), p. 1097, n. 191. This location would later become the small settlement of Žitavská Tôňa (Hungarian: ''Zsitvatorok''), a part of the municipality of Radvaň nad Dunajom (Hungarian: ''Dunaradvány''). The peace was signed for a term of 20 years and has been interpreted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Turkish Language
Ottoman Turkish (, ; ) was the standardized register (sociolinguistics), register of the Turkish language in the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed extensively, in all aspects, from Arabic and Persian language, Persian. It was written in the Ottoman Turkish alphabet. Ottoman Turkish was largely unintelligible to the less-educated lower-class and to rural Turks, who continued to use ("raw/vulgar Turkish"; compare Vulgar Latin and Demotic Greek), which used far fewer foreign loanwords and is the basis of the modern standard. The Tanzimat, Tanzimât era (1839–1876) saw the application of the term "Ottoman" when referring to the language ( or ); Modern Turkish uses the same terms when referring to the language of that era ( and ). More generically, the Turkish language was called or "Turkish". History Historically, Ottoman Turkish was transformed in three eras: * (Old Ottoman Turkish): the version of Ottoman Turkish used until the 16th century. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1606 Establishments In Europe
Sixteen or 16 may refer to: *16 (number) *one of the years 16 BC, AD 16, 1916, 2016 Films * ''Pathinaaru'' or ''Sixteen'', a 2010 Tamil film * ''Sixteen'' (1943 film), a 1943 Argentine film directed by Carlos Hugo Christensen * ''Sixteen'' (2013 Indian film), a 2013 Hindi film * ''Sixteen'' (2013 British film), a 2013 British film by director Rob Brown Music *The Sixteen, an English choir *16 (band), a sludge metal band * Sixteen (Polish band), a Polish band Albums * ''16'' (Robin album), a 2014 album by Robin * 16 (Madhouse album), a 1987 album by Madhouse * ''Sixteen'' (album), a 1983 album by Stacy Lattisaw *''Sixteen'' , a 2005 album by Shook Ones * ''16'', a 2020 album by Wejdene Songs * "16" (Sneaky Sound System song), 2009 * "Sixteen" (Thomas Rhett song), 2017 * "Sixteen" (Ellie Goulding song), 2019 *"Six7een", by Hori7on, 2023 *"16", by Craig David from ''Following My Intuition'', 2016 *"16", by Green Day from ''39/Smooth'', 1990 *"16", by Highly Suspect from ''MC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of the Turkic peoples, Turkic khanates that succeeded the empire of the Golden Horde. Established by Hacı I Giray in 1441, it was regarded as the direct heir to the Golden Horde and to Cumania, Desht-i-Kipchak. In 1783, violating the 1774 Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (which had guaranteed non-interference of both Russia and the Ottoman Empire in the affairs of the Crimean Khanate), the Annexation of the Crimean Khanate by the Russian Empire, Russian Empire annexed the khanate. Among the European powers, only France came out with an open protest against this act, due to the longstanding Franco-Ottoman alliance. Naming and geography The Crimean Khans, considering their state as the heir and legal successor of the Golden Horde and Desht-i Kipcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Lewis
Bernard Lewis, (31 May 1916 – 19 May 2018) was a British-American historian specialized in Oriental studies. He was also known as a public intellectual and political commentator. Lewis was the Cleveland E. Dodge Professor Emeritus of Near Eastern Studies at Princeton University. Lewis's expertise was in the history of Islam and the interaction between Islam and the West. Lewis served as a soldier in the British Army in the Royal Armoured Corps and Intelligence Corps during the Second World War before being seconded to the Foreign Office. After the war, he returned to the School of Oriental and African Studies at the University of London and was appointed to the new chair in Near and Middle Eastern history. In 2007, Lewis was called "the West's leading interpreter of the Middle East". Others have said Lewis's approach is essentialist and generalizing to the Muslim world, as well as his tendency to restate hypotheses that were challenged by more recent research. On a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (; ), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on , in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kaynardzha, Bulgaria and Cuiugiuc, Romania) between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, ending the Russo-Turkish war (1768–1774), Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774 with major concessions to Russia. The concessions to Russia were not merely territorial; not only was the Crimea Khanate (not Crimea proper) ceded, but Russia also gained the right to construct a Russian Orthodox church in Constantinople, claiming to be the protector of the Rum millet, Orthodox Christians in the Ottoman Empire. This was a pretext for frequent and numerous interventions in the decades to follow. Ottoman Christians started to feel more empowered as European and Christian powers demonstrated their rising influence and political power. Access to Europe's political networks, markets and educational institutions created a class privilege for Ottoman Christians, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine The Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter III. Under her long reign, inspired by the ideas of the Enlightenment, Russia experienced a renaissance of culture and sciences, which led to the founding of many new cities, universities, and theatres, along with large-scale immigration from the rest of Europe and the recognition of Russia as one of the great powers of Europe. In her accession to power and her rule of the empire, Catherine often relied on her noble favourites, most notably Count Grigory Orlov and Grigory Potemkin. Assisted by highly successful generals such as Alexander Suvorov and Pyotr Rumyantsev, and admirals such as Samuel Greig and Fyodor Ushakov, she governed at a time when the Russian Empire was expanding rapidly by conquest and diplomacy. In the south, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Problem Of Two Emperors
The problem of two emperors or two-emperor problem (deriving from the German term ''Zweikaiserproblem'', ) is the historiographical term for the historical contradiction between the idea of the universal empire, that there was only ever one true emperor at any one given time, and the truth that there were often multiple individuals who claimed the position simultaneously. The term is primarily used in regards to medieval European history and often refers to in particular the long-lasting dispute between the Byzantine emperors in Constantinople and the Holy Roman emperors in modern-day Germany and Austria as to which monarch represented the legitimate Roman emperor. In the view of medieval Christians, the Roman Empire was indivisible and its emperor held a somewhat hegemonic position even over Christians who did not live within the formal borders of the empire. Since the collapse of the Western Roman Empire during late antiquity, the Byzantine Empire (which represented its survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padishah
Padishah (; ) is a superlative sovereign title of Persian origin. A form of the word is known already from Middle Persian (or Pahlavi) as ''pātaxšā(h)'' or ''pādixšā(y)''. Middle Persian ''pād'' may stem from Avestan ''paiti'', and is akin to Pati (title). ''Xšāy'' 'to rule' and ''xšāyaθiya'' 'king' are both from Old Persian. It was adopted by several monarchs claiming the highest rank, roughly equivalent to the ancient Persian notion of " Great King", and later adopted by post- Achaemenid and the Mughal emperors of India. However, in some periods it was used more generally for autonomous Muslim rulers, as in the '' Hudud al-'Alam'' of the 10th century, where even some petty princes of Afghanistan are called ''pādshā(h)''/''pādshāʼi''/''pādshāy''. The rulers on the following thrones – the first two effectively commanding major West Asian empires – were styled Padishah: * The Shahanshah of Iran, originating mainly with the Safavids * The Padishah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-day siege which had begun on 6 April. The attacking Army of the classical Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Army, which significantly outnumbered Constantinople's defenders, was commanded by the 21-year-old List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Sultan Mehmed the Conqueror, Mehmed II (later nicknamed "the Conqueror"), while the Byzantine army (Palaiologan era), Byzantine army was led by List of Byzantine emperors, Emperor Constantine XI Palaiologos. After conquering the city, Mehmed II made Constantinople the new Ottoman capital, replacing Edirne, Adrianople. The fall of Constantinople and of the Byzantine Empire was a watershed of the Late Middle Ages, marking the effective end of the Roman Empire, a state which began in roughly 27 BC and had la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar (title)
Caesar ( English language, English Caesars; Latin ; in Greek: ) is a title of imperial character. It derives from the ''cognomen'' of Julius Caesar. The change from being a surname to a title used by the Roman emperors can be traced to AD 68, following the fall of the Julio-Claudian dynasty. When used on its own, the title denoted heirs apparent, who would later adopt the title ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' on accession. The title remained an essential part of the style of the emperors, and became the word for "emperor" in some languages, such as German () and Slavic (). Origins The first known individual to bear the ''cognomen'' of "Caesar" was Sextus Julius Caesar (praetor 208 BC), Sextus Julius Caesar, who is likewise believed to be the common ancestor of all subsequent Julii Caesares. Sextus's great-grandson was the dictator Julius Caesar, Gaius Julius Caesar, who seized control of the Roman Republic following his Caesar's civil war, war against the Roman Senate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the northeast, Afghanistan to the east, Pakistan to the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. With a Ethnicities in Iran, multi-ethnic population of over 92 million in an area of , Iran ranks 17th globally in both List of countries and dependencies by area, geographic size and List of countries and dependencies by population, population. It is the List of Asian countries by area, sixth-largest country entirely in Asia and one of the world's List of mountains in Iran, most mountainous countries. Officially an Islamic republic, Iran is divided into Regions of Iran, five regions with Provinces of Iran, 31 provinces. Tehran is the nation's Capital city, capital, List of cities in Iran by province, largest city and financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |