|
Worm, Parcel And Serve
To worm, parcel and serve a rope, line is to apply a multi-layered protection against chafe and deterioration to standing rigging. It is a technique not usually used on modern small boats, but is found extensively on traditionally-rigged sailing ships. Worming, parcelling and serving —referred to collectively as "service"— is traditionally applied only to traditional twisted rope, either natural fiber or steel wire-rope, not the braided line almost exclusively used on modern vessels, but some traditional vessels now use modern high modulus braided lines (like Amsteel or AS-90) in place of wire rope (to save weight aloft) and serve the line to maintain the traditional appearance. It can be applied to the entire length of a line, such as a Shroud (sailing), shroud, or selectively, to specific parts of a line, such as over the spliced ends of a stays (nautical), stay, where the chafe on the middle section of the stay precludes complete protection. Technique Worming "Wormin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USCGC Eagle Cable Preservation Sample2
United States Coast Guard Cutter is the term used by the United States Coast Guard, U.S. Coast Guard for its ship commissioning, commissioned vessels. They are or greater in length and have a permanently assigned crew with accommodations aboard. They carry the ship prefix USCGC. History of the USCG cutters The Revenue Marine and the Revenue Cutter Service, as it was known variously throughout the late 18th and the 19th centuries, referred to its ships as Cutter (boat), cutters. The term is English in origin and refers to a specific type of vessel, namely, "a small, decked ship with one Mast (sailing), mast and bowsprit, with a Gaff rig, gaff mainsail on a Boom (sailing), boom, a square yard and topsail, and two jibs or a jib and a staysail."Peter Kemp, ed. (1976). ''The Oxford Companion to Ships & the Sea''. London: Oxford University Press. pp. 221–222. With general usage, that term came to define any vessel of the United Kingdom's HM Customs and Excise and the term was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Useful Instruction For Sailors
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rope
A rope is a group of yarns, Plying, plies, fibres, or strands that are plying, twisted or braided together into a larger and stronger form. Ropes have high tensile strength and can be used for dragging and lifting. Rope is thicker and stronger than similarly constructed cord, String (structure), string, and twine. Construction Rope may be constructed of any long, stringy, fibrous material (e.g., rattan, a natural material), but generally is constructed of certain natural fibre, natural or synthetic fibre, synthetic fibres. Synthetic fibre ropes are significantly stronger than their natural fibre counterparts, they have a higher tensile strength, they are more resistant to rotting than ropes created from natural fibres, and they can be made to float on water. But synthetic ropes also possess certain disadvantages, including slipperiness, and some can be damaged more easily by UV light. Common natural fibres for rope are Manila hemp, hemp, linen, cotton, coir, jute, straw, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
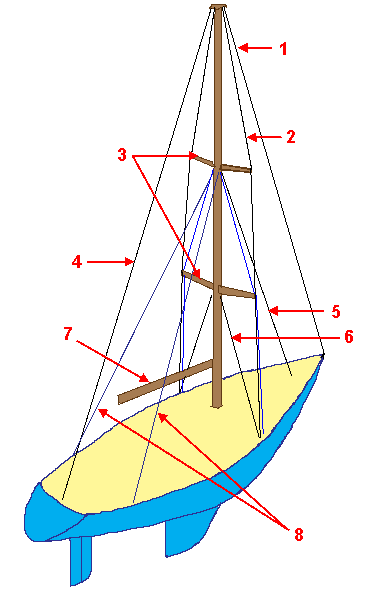
Standing Rigging
Standing rigging comprises the fixed lines, wires, or rods, which support each mast or bowsprit on a sailing vessel and reinforce those spars against wind loads transferred from the sails. This term is used in contrast to running rigging, which represents the moveable elements of rigging which adjust the position and shape of the sails. Historical development Early sailing vessels used rope of hemp or other fibers, which gave way to wire ropes of various types. Galvanized steel was common for the first half of the 20th century, continuing as an inexpensive option to its 1960s successor material—stainless steel cables and rods. In the late 20th Century, racing yachts adopted composite fiber lines for standing rigging, with the goal of reducing weight and windage aloft. Materials On modern yachts, standing rigging is often stainless steel wire, Nitronic-50 stainless steel rod or synthetic fiber Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres (in British English; see spelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shroud (sailing)
On a sailing ship, the shrouds are the standing rigging which holds the mast (sailing), mast up from side to side. There is frequently more than one shroud on each side of the boat. Usually a shroud will connect at the top of the mast, and additional shrouds might connect partway down the mast, depending on the design of the boat. Shrouds terminate at their bottom ends at the Chainplate, chain plates, which are tied into the hull. They are sometimes held outboard by Chains (nautical), channels, a ledge that keeps the shrouds clear of the gunwales.''The Lore of Ships,'' ed. by Bengt Kihlberg. Göteborg :Tre tryckare & New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston, 1963. Shrouds are attached symmetrically on both the port (nautical), port and starboard sides. For those shrouds which attach high up the mast, a structure projecting from the mast must be used to increase the angle of the shroud at the attachment point, providing more support to the mast. On most sailing boats, such structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stays (nautical)
Stays are ropes, wires, or rods on sailing Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ... vessels that run fore-and-aft along the centerline from the masts to the hull, deck, bowsprit, or to other masts which serve to stabilize the masts. A stay is part of the standing rigging and is used to hold a mast upright. It is a large strong rope, wire or rod extending from the upper end of each mast and running down towards the deck of the vessel in a midships -and- direction. The shrouds serve a similar function but extend on each side of the mast and provide support in the athwartships direction. The object of both is to prevent the masts from falling down but the stays also prevent springing, when the ship is pitching deep. Thus stays are fore and aft. Those led aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pine Tar
Pine tar is a form of wood tar produced by the high temperature carbonization of pine wood in anoxic conditions (dry distillation or destructive distillation). The wood is rapidly decomposed by applying heat and pressure in a closed container; the primary resulting products are charcoal and pine tar. Pine tar consists primarily of aromatic hydrocarbons, tar acids, and tar bases. Components of tar vary according to the pyrolytic process (e.g. method, duration, temperature) and origin of the wood (e.g. age of pine trees, type of soil, and moisture conditions during tree growth). The choice of wood, design of kiln, burning, and collection of the tar can vary. Only pine stumps and roots are used in the traditional production of pine tar. Pine tar has a long history as a wood preservative, as a wood sealant for maritime use, in roofing construction and maintenance, in soaps, and in the treatment of carbuncles and skin diseases, such as psoriasis, eczema, and rosacea. It is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction Tape
Friction tape is a type of woven Textile, cloth adhesive tape, historically made of cotton, impregnated with a rubber-based adhesive. Sticky on both sides, it is mainly used by electricians to Insulator (electricity), insulate splices in electric wires and cables. The rubber-based adhesive provides a degree of protection from liquids and corrosion, while the cloth mesh protects against punctures and abrasion. It has been supplanted by Polyvinyl chloride, PVC-based electrical tape except commonly used for over wrapping. Other uses Friction tape is commonly used to improve the grip on various sporting implements, including tennis racquets, baseball bats, and hockey sticks. It is also used similarly on the handlebars of bicycles, dirt bikes, lawnmowers, and other small machines that require gripping or steering. See also * List of adhesive tapes References Adhesive tape Dielectrics {{tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Tape
Surgical tape or medical tape is a type of pressure-sensitive adhesive tape used in medicine and first aid to hold a bandage or other dressing onto a wound. These tapes usually have a hypoallergenic adhesive which is designed to hold firmly onto skin, dressing materials, and underlying layers of tape, but to remove easily without damaging the skin. They allow air to reach the skin ("breathable"). Some breathable tapes such as kinesiology tape, and other elastic bandages with adhesive are made of cotton. Surgical tape is often white because it contains zinc oxide, which is added to help prevent infections. Tapes made of porous material, such as 3M Micropore, are widely used. History Primitive surgical tape, or ''sparadrapum'' probably consisted of strips of cloth impregnated with some type of plaster or sticky gum, which was applied over gauzes or wound dressings to hold them in place. Plaster casts over fractures were sometimes called "Spanish dressings" In the Middle Ages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serving Mallet
{{Disambiguation ...
Serving may refer to: * "Serving" (song), by Miriana Conte, Malta's entry for the Eurovision Song Contest 2025 * Serving size * Providing a non-material good, as in the work of a servant * Supplying customers with food and drink, as in the work of a food server * Service of process, the procedure for delivering a legal or administrative summons * Serving channel, a type of file sharing channel * Servitude (other) * Worm, parcel and serve, a technique for protecting rope from abrasion See also * Serve (other) * Service (other) Service may refer to: Activities * Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty * Civil service, the body of employees of a government * Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |