|
Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome
Upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS) is a sleep disorder characterized by the narrowing of the airway that can cause disruptions to sleep. The symptoms include snoring, unrefreshing sleep, fatigue, sleepiness, chronic insomnia, and difficulty concentrating. UARS can be diagnosed by polysomnograms capable of detecting Respiratory Effort-related Arousals. It can be treated with lifestyle changes, functional orthodontics, surgery, mandibular repositioning devices or CPAP therapy. UARS is considered a variant of sleep apnea, although some scientists and doctors believe it to be a distinct disorder. History Upper airway resistance syndrome was first recognized at Stanford University in the late 1980s. The article that described it by name, along with its relationship to obstructive sleep apnea, was published in 1992 by Guilleminault et al. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of UARS are similar to those of obstructive sleep apnea, but not inherently overlapping. Fatigue, insomnia, daytim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sleep Disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder affecting an individual's sleep patterns, sometimes impacting physical, mental, social, and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sleep disorders. Sleep disorders are broadly classified into dyssomnias, parasomnias, circadian rhythm sleep disorders involving the timing of sleep, and other disorders, including those caused by medical or psychological conditions. When a person struggles to fall asleep or stay asleep without any obvious cause, it is referred to as insomnia, which is the most common sleep disorder. Other sleep disorders include sleep apnea, narcolepsy, hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness at inappropriate times), sleeping sickness (disruption of the sleep cycle due to infection), sleepwalking, and night terrors. Sleep disruptions can be caused by various issues, including teeth grinding (bruxism) and night terrors. Managing sleep disturbances that are seconda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polysomnography
Polysomnography (PSG) is a multi-parameter type of sleep study and a diagnostic tool in sleep medicine. The test result is called a polysomnogram, also abbreviated PSG. The name is derived from Greek and Latin roots: the Greek πολύς (''polus'' for "many, much", indicating many channels), the Latin ''somnus'' ("sleep"), and the Greek γράφειν (''graphein'', "to write"). Type I polysomnography is a sleep study performed overnight with the patient continuously monitored by a credentialed technologist. It records the physiological changes that occur during sleep, usually at night, though some labs can accommodate shift workers and people with circadian rhythm sleep disorders who sleep at other times. The PSG monitors many body functions, including brain activity ( EEG), eye movements ( EOG), muscle activity or skeletal muscle activation ( EMG), and heart rhythm ( ECG). After the identification of the sleep disorder sleep apnea in the 1970s, breathing functions, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
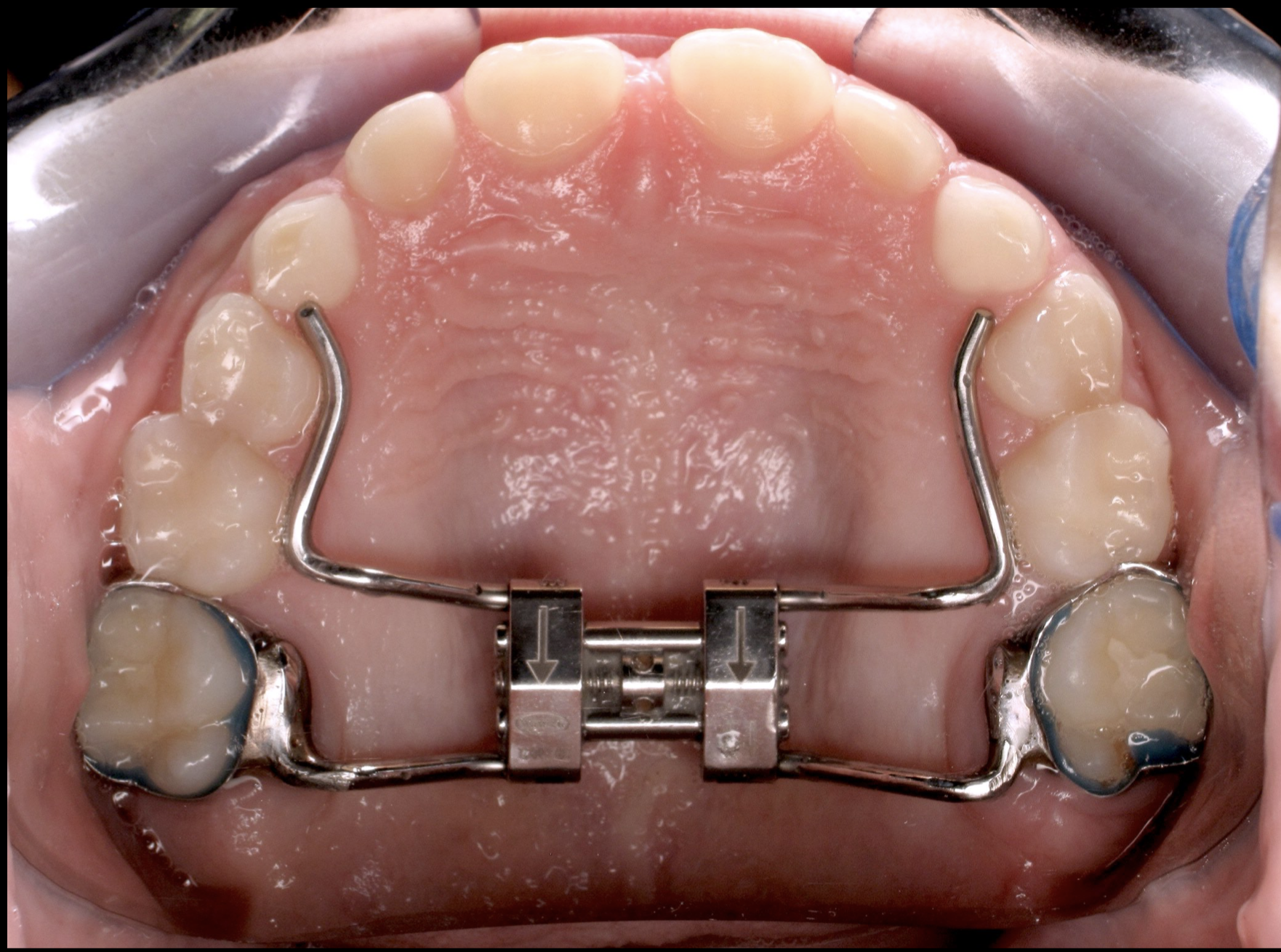
Palatal Expansion
A palatal expander is a device in the field of orthodontics which is used to widen the upper jaw (maxilla) so that the bottom and upper teeth will fit together better. This is a common orthodontic procedure. The use of an expander is most common in children and adolescents 8–18 years of age. It can also be used in adults, although expansion is more uncomfortable and takes longer in adults. A patient who would rather not wait several months for the end result achieved by a palatal expander may be able to opt for a surgical separation of the maxilla. Use of a palatal expander is most often followed by dental braces, braces to then straighten the teeth. Palate expanders are a useful tool in expanding the airway due to previous dental extractions. It is believed that expansion therapy should be started in patients either before or during their peak growth spurt. To obtain maximal skeletal changes, the therapy is typically initiated at a very early age. Expansion therapy performed af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor, sensory nerves or a dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium frequency alternating current (in the range of 350–500 kHz). RFA is generally conducted in the outpatient setting, using either a local anesthetic or twilight anesthesia. When it is delivered via catheter, it is called radiofrequency catheter ablation. Two advantages of radio frequency current (over previously used low frequency AC or pulses of DC) are that it does not directly stimulate nerves or heart muscle, and therefore can often be used without the need for general anesthesia, and that it is specific for treating the desired tissue without significant collateral damage. Due to this, RFA is an alternative for eligible patients who have comorbidities or do not want to undergo surgery. Documented benefits have led to RFA becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
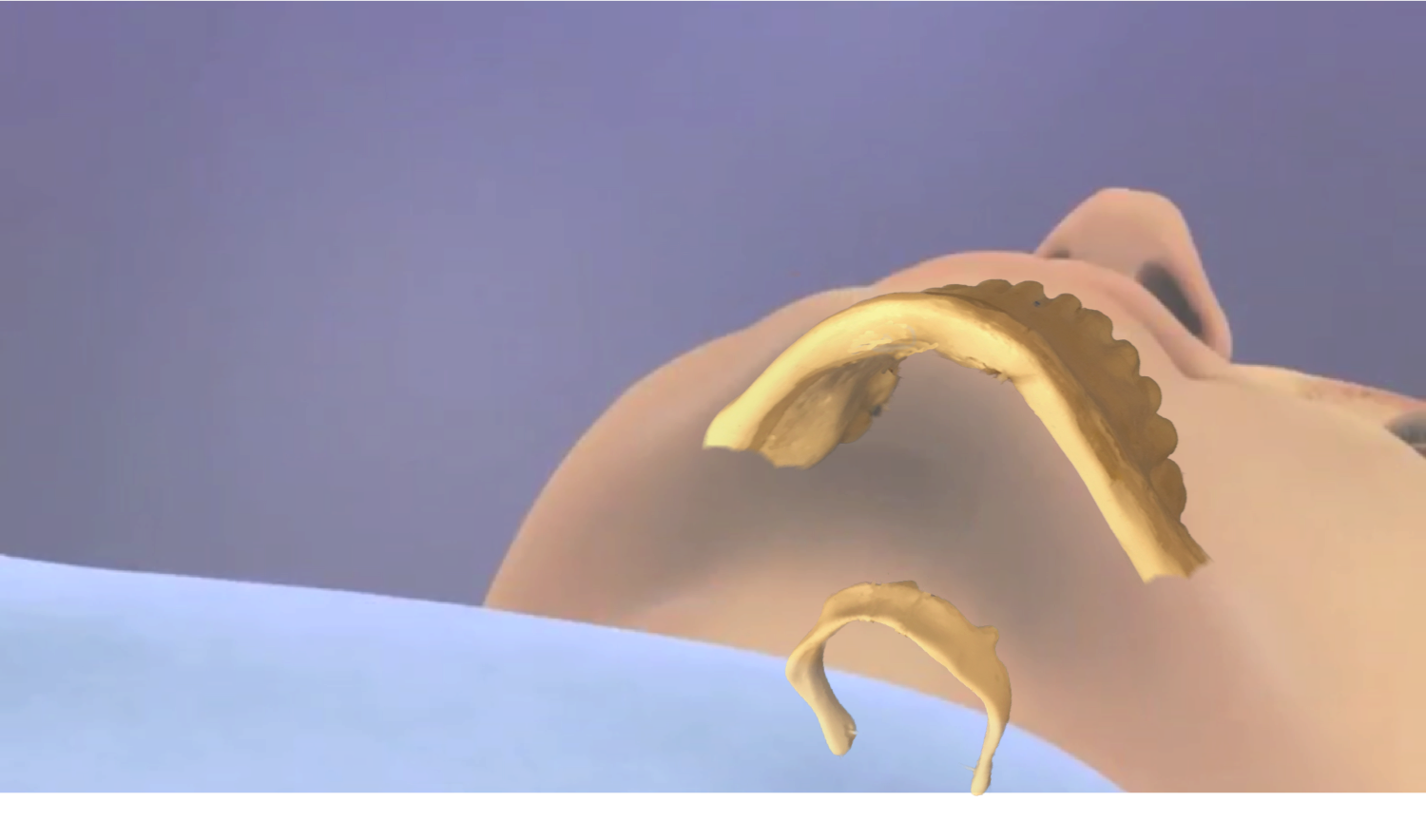
Hyoid Suspension
Hyoid suspension, also known as hyoid myotomy and suspension or hyoid advancement, is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the hyoid bone and its muscle attachments to the tongue and airway are pulled forward with the aim of increasing airway size and improving airway stability in the retrolingual and hypopharyngeal airway (airway behind and below the base of tongue). The horseshoe shaped hyoid bone sits directly below the base of tongue with the arms of the bone flanking the airway. Hyoid suspension is typically performed as a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ... (OSA). This procedure is frequently performed with a uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) which targets sites of obstruction higher in the airway. Typically, a hyoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
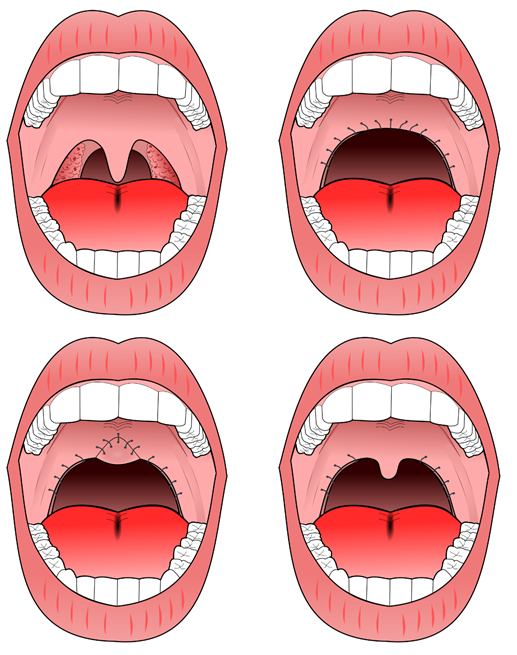
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (abbreviated as UPPP or UP3) is a type of sleep surgery, which are surgical procedures for sleep-related breathing disorders, especially obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty involves removal and/or remodeling of tissues in the throat in order to prevent obstruction of the airway during sleep. Tissues which may typically be removed include the paryngeal tonsils and the adenoid tonsil. Tissues which may typically be remodeled include the uvula (see uvulotomy), the soft palate, and parts of the pharynx. UPPP is the most common surgical procedure performed for OSA. Background OSA is one of the most common types of sleep-related breathing disorder. It involves obstruction of the upper airway during sleep. Loud snoring and apnea (periods of no breathing) followed by gasping and choking are signs of the condition. The main treatment is continuous positive airway pressure and a range of other measures such sleeping on the side and mandibular a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maxillomandibular Advancement
Maxillomandibular advancement (MMA) or orthognathic surgery, also sometimes called bimaxillary advancement (Bi-Max), or maxillomandibular osteotomy (MMO), is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery which moves the upper jaw (maxilla) and the lower jaw (mandible) forward. The procedure was first used to correct deformities of the facial skeleton to include malocclusion. In the late 1970s advancement of the lower jaw (mandibular advancement) was noted to improve sleepiness in three patients. Subsequently, maxillomandibular advancement was used for patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Currently, maxillomandibular advancement surgery is often performed simultaneously with genioglossus advancement (tongue advancement). The genioglossus advancement pulls the tongue forward in a manner that decreases the amount of tongue blockage during sleep. MMA has been demonstrated to be one of the most effective surgical treatments for sleep apnea, due to its high success rate. Nonetheless, the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Septoplasty
Septoplasty (, "septum" + , "to shape"), or alternatively submucous septal resection and septal reconstruction, is a corrective surgical procedure done to straighten a deviated nasal septum – the nasal septum being the partition between the two sides of the nasal cavity. Ideally, the septum should run down the center of the nose. When it deviates into one of the cavities, it narrows that cavity and impedes airflow. Deviated nasal septum or “crooked” internal nose can occur at childbirth or as the result of an injury or other trauma. If the wall that functions as a separator of both sides of the nose is tilted towards one side at a degree greater than 50%, it might cause difficulty breathing. Often the inferior turbinate on the opposite side enlarges, which is termed '' compensatory hypertrophy''. Deviations of the septum can lead to nasal obstruction. Most surgeries are completed in 60 minutes or less, while the recovery time could be up to several weeks. Put simply, septop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oral Appliance
The word oral may refer to: Relating to the mouth * Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid **Oral administration of medicines ** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or oral test), a practice in many schools and disciplines in which an examiner poses questions to the student in spoken form ** Oral hygiene, practices involved in cleaning the mouth and preventing disease ** Oral medication **Oral rehydration therapy, a simple treatment for dehydration associated with diarrhea **Oral sex, sexual activity involving the stimulation of genitalia by use of the mouth, tongue, teeth or throat. ** Oral stage, a human development phase in Freudian developmental psychology **Oral tradition, cultural material and tradition transmitted orally from one generation to another **Oralism, the education of deaf students through oral language by using lip reading, and mimicking of mouth shapes and breathing patterns **Speech commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Positive Airway Pressure
Positive airway pressure (PAP) is a mode of respiratory ventilation used in the treatment of sleep apnea. PAP ventilation is also commonly used for those who are critically ill in hospital with respiratory failure, in newborn infants (neonates), and for the prevention and treatment of atelectasis in patients with difficulty taking deep breaths. In these patients, PAP ventilation can prevent the need for tracheal intubation, or allow earlier extubation. Sometimes patients with neuromuscular diseases use this variety of ventilation as well. CPAP is an acronym for "continuous positive airway pressure", which was developed by Dr. George Gregory and colleagues in the neonatal intensive care unit at the University of California, San Francisco. A variation of the PAP system was developed by Professor Colin Sullivan at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney, Australia, in 1981. The main difference between BPAP and CPAP machines is that BPAP machines have two pressure settings: the pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and Developmental psychology, developmentally inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction. Impairments resulting from deficits in self-regulation such as time management, Cognitive inhibition, inhibition, task initiation, and sustained attention can include poor professional performance, relationship difficulties, and numerous health risks, collectively predisposing to a diminished Quality of life (healthcare), quality of life and a reduction in life expectancy. As a consequence, the disorder costs society hundreds of billions of US dollars each year, worldwide. It is associated with other mental disorders as well as non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment. While ADHD involves a lack of su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |