|
Transition Metal Dithiocarbamate Complexes
193px, Structure of iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate). Transition metal dithiocarbamate complexes are coordination complexes containing one or more dithiocarbamate ligand, which are typically abbreviated R2dtc−. Many complexes are known. Several homoleptic derivatives have the formula M(R2dtc)n where n = 2 and 3. Ligand characteristics Dithiocarbamate anions are bidentate ligands that are classified as L-X ligand in the Covalent bond classification method. In the usual electron counting method, they are three-electron ligands. With respect to HSAB theory, they are classified as soft. Because of the pi-donor properties of the amino substituent, the two sulfur centers show enhanced basicity relative to dithiocarboxylates. This situation is represented by the zwitterionic resonance structure that depicts a positive charge on N and negative charges on both sulfurs. This N to C pi-bonding results in partial double bond character for the C-N bond. Consequently, barriers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithiocarboxylate
Dithiocarboxylic acids are organosulfur compounds with the formula . They are the dithia analogues of carboxylic acids. A closely related and better studied family of compounds are the monothiocarboxylic acids, with the formula . Dithiocarboxylic acids are about 3x more acidic than the monothiocarboxylic acids. Thus, for dithiobenzoic acid pKa = 1.92. Such compounds are commonly prepared by the reaction of carbon disulfide with a Grignard reagent: : : This reaction is comparable to the formation of carboxylic acids using a Grignard reagent and carbon dioxide. Dithiocarboxylate salts readily S-alkylate to give dithiocarboxylate esters: : Aryldithiocarboxylic acids, e.g., dithiobenzoic acid, chlorinate to give the thioacyl chlorides. Oxygen transfer to a dithiocarboxylate ester gives a sulfine Sulfinylmethane or sulfine is an organic compound with molecular formula H2CSO. It is the simplest sulfine. Sulfines are chemical compounds with the general structure XY=SO. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
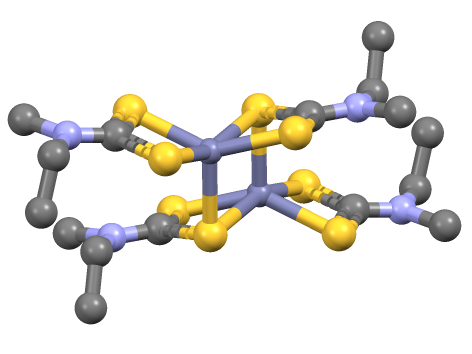
(Ru2(dtc)5)+ Isomers
Ru, ru, or RU may refer to: Russia * Russia (ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code) * Russian language (ISO 639 alpha-2 code) * .ru, the Internet country code top-level domain for Russia China * Rù (入), the entering tone in Chinese language phonetics * Rú (儒), a Chinese language term for Confucianism * Ru (surname) (茹), a Chinese surname * Ru River (汝), in Henan, China * Ru ware, a type of Chinese pottery Educational institutions * Rajasthan University in Rajasthan, India * Radboud University Nijmegen, in Nijmegen, Netherlands * Radford University, in Virginia, USA * Rai University in Gujarat, India * Rajshahi University in Bangladesh * Rama University in India * Ramkhamhaeng University in Thailand * Rangoon University in Burma * Regis University in Colorado, USA * Reykjavík University Iceland * Rhodes University in Grahamstown, South Africa * Rockefeller University in New York, USA * Rockhurst University in Missouri, USA * Roosevelt University in Chicago, Illinois, USA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate is a coordination complex of zinc with dimethyldithiocarbamate. It is a pale yellow solid that is used as a fungicide, the sulfur vulcanization of rubber, and other industrial applications. Applications Known as ziram in agriculture, it was introduced in the United States in 1960 as a broad-spectrum fungicide. It was used to address scab on apples and pears, leaf curl in peaches, and anthracnose and blight in tomatoes. In 1981, additional uses for ziram were approved, including the prevention of leaf blight and scab on almonds, shot-hole in apricots, brown rot and leaf spot in cherries, and scab and anthracnose in pecans. Ziram also began to be used on residential ornaments as a bird and mammal repellent. As a protectant fungicide, it is active on the plant’s surface where it forms a chemical barrier between the plant and a fungus. A protectant fungicide is not absorbed into the plant and must be applied prior to infection. Ziram can either be direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Bis(diethyldithiocarbamate)
Iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) is a coordination complex with the formula where Et = ethyl (). A red solid, iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) is representative of several ferrous dithiocarbamates with diverse substituents in place of ethyl. In terms of structure, the species is dimeric, consisting of a pair of pentacoordinate iron(II) centers. It is structurally related to zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate). Reactions The complex reacts with a variety of reagents with concomitant formation of mono-iron derivatives. It adds 9,10-phenanthroline (phen) to give the blue-octahedral complex . 3,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dithiete reacts to give the Fe(IV) dithiolene complex . Nitric oxide and carbon monoxide add to give the nitrosyl complex and the carbonyl complex {{chem2, Fe(S2CNEt2)2(CO)2, respectively. Related compounds * Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) References Iron compounds Iron shows the characteristic chemical properties of the transition metals, namely the abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt Tris(diethyldithiocarbamate)
Cobalt tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of cobalt with diethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Co(S2CNEt2)3 (Et = ethyl). It is a diamagnetic green solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Synthesis, structure, bonding Cobalt tris(dithiocarbamate)s are typically are prepared by air-oxidation of mixtures of dithiocarbamate salts and a cobalt(II) nitrate. Cobalt tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is an octahedral coordination complex of low-spin Co(III) with idealized D3 symmetry. The Co-S distances are 267 pm. Reactions Oxidation of Co(Et2dtc)3 occurs at mild potentials to give the cobalt(IV) derivative. Treatment of Co(Et2dtc)3 with fluoroboric acid results in the removal of 0.5 equiv of ligand giving a binuclear cation: :2Co(Et2dtc)3 + HBF4 → o2(Et2dtc)5F4 + "Et2NdtcH" See also * Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with diethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (Et = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
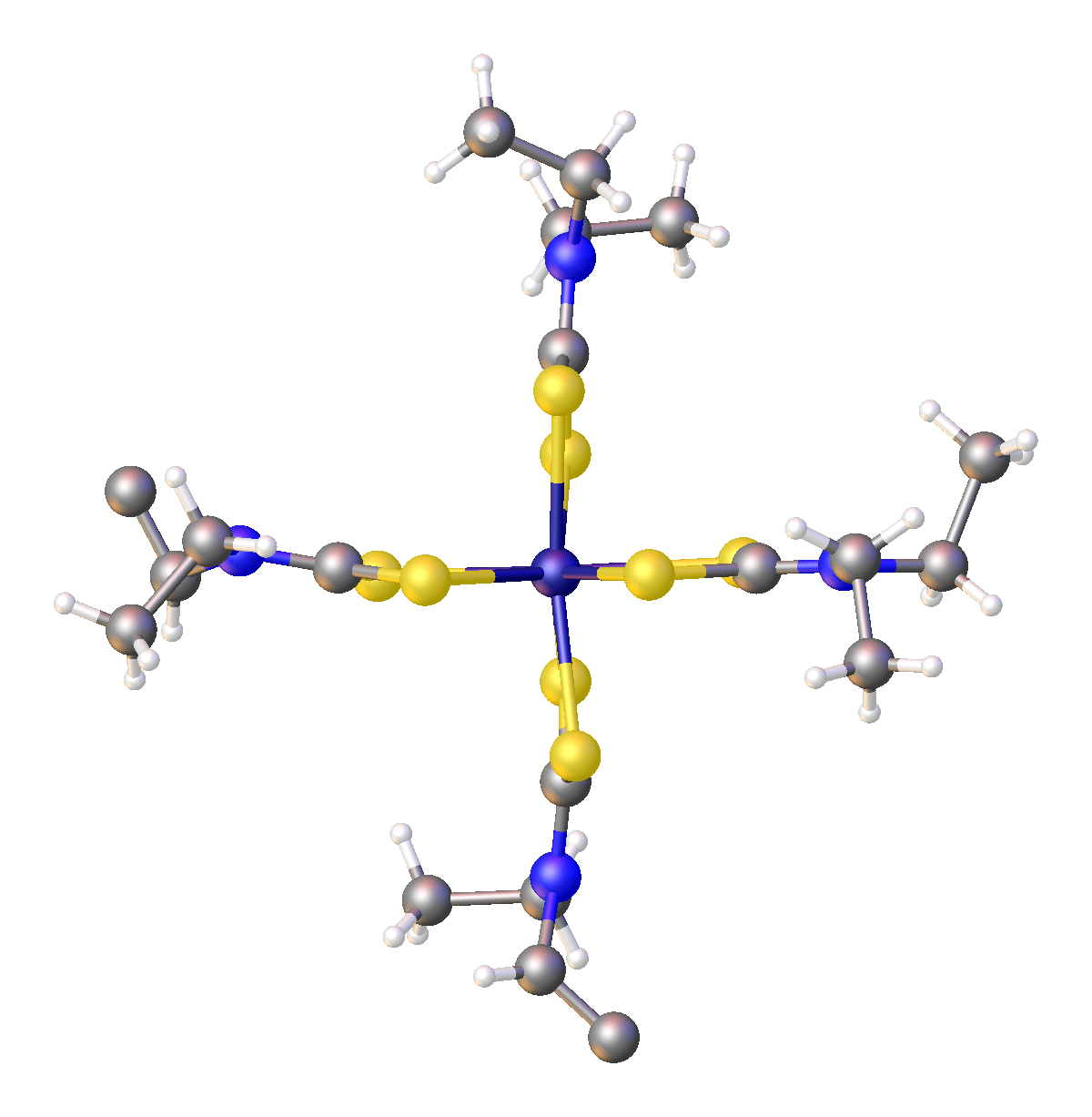
Iron Tris(diethyldithiocarbamate)
Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with diethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (Et = ethyl). It is a black solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Synthesis, structure, bonding Iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s are typically are prepared by salt metathesis reactions. Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is an octahedral coordination complex of iron(III) with idealized D3 symmetry. The phenomenon of spin crossover (SCO) was first reported in 1931 by Cambi ''et al.'' who observed anomalous magnetic behavior for the tris(N,N-dialkyldithiocarbamatoiron(III) complexes. The magnetism of these complexes are sensitive to the nature of the amine substituents as well as to temperature. This behavior is consistent with an equilibrium between two or more spin states. In the case of Fe(Et2dtc)3, X-ray crystallography reveals that the Fe-S bonds are 231 pm at 79K but 356 pm at 297 K. These data indicate a low-spin configuration at low temperatures a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel Bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex on nickel and dimethyldithiocarbamate, with the formula Ni(S2CNMe2)2 (Me = methyl). It is the prototype for a large number of square planar bis(dialkhyldithiocarbamate)s of nickel(II), which feature diverse organic substituents. Nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) has been marketed as a fungicide, and related complexes are used as stabilizers in polymers. Preparation and structure The compound precipitates as a light green solid upon combining aqueous solutions of nickel(II) salts and sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate. In terms of structure and bonding, the nickel is square planar, and the complex is diamagnetic. The structure of the closely related nickel bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) has been determined by X-ray crystallography. Oxidation of nickel bis(dieethyldithiocarbamate) gives the red-brown nickel(IV) complex .{{cite journal , last1=Mazumder , first1=Md. Motiur R. , last2=Dalpati , first2=Niharika , last3=Pokk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrakis(dimethylamido)titanium
Tetrakis(dimethylamino)titanium (TDMAT), also known as Titanium(IV) dimethylamide, is a chemical compound. The compound is generally classified as a metalorganic species, meaning that its properties are strongly influenced by the organic ligands but the compound lacks metal-carbon bonds. It is used in chemical vapor deposition to prepare titanium nitride (TiN) surfaces and in atomic layer deposition as a titanium dioxide precursor. The prefix "tetrakis" refers the presence of four of the same ligand, in this case dimethylamides. Preparation and properties Tetrakis(dimethylamino)titanium is a conventional Ti(IV) compound in the sense that it is tetrahedral and diamagnetic. Unlike the many alkoxides, the diorganoamides of titanium are monomeric and thus at least somewhat volatile. It is prepared from titanium tetrachloride (which is also tetrahedral, diamagnetic, and volatile) by treatment with lithium dimethylamide:D. C. Bradley and I. M. Thomas, "Part I. Metallo-organic Compoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiuram Disulfide
Thiuram disulfides are a class of organosulfur compounds with the formula (R2NCSS)2. Many examples are known, but popular ones include R = Me and R = Et. They are disulfides obtained by oxidation of the dithiocarbamates. These compounds are used in sulfur vulcanization of rubber as well as in the manufacture of pesticides and drugs. They are typically white or pale yellow solids that are soluble in organic solvents. Preparation, structure, reactions Thiuram disulfides are prepared by oxidizing the salts of the corresponding dithiocarbamates (e.g. sodium diethyldithiocarbamate). Typical oxidants employed include chlorine and hydrogen peroxide: : Thiuram disulfides react with Grignard reagents to give esters of dithiocarbamic acid, as in the preparation of methyl dimethyldithiocarbamate: : The compounds feature planar dithiocarbamate subunits and are linked by an S−S bond of 2.00 Å. The C(S)−N bond is short (1.33 Å), indicative of multiple bonding. The dihe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidative addition is often a step in catalytic cycles, in conjunction with its reverse reaction, reductive elimination. Role in transition metal chemistry For transition metals, oxidative reaction results in the decrease in the d''n'' to a configuration with fewer electrons, often 2e fewer. Oxidative addition is favored for metals that are (i) basic and/or (ii) easily oxidized. Metals with a relatively low oxidation state often satisfy one of these requirements, but even high oxidation state metals undergo oxidative addition, as illustrated by the oxidation of Pt(II) with chlorine: : tCl4sup>2− + Cl2 → tCl6sup>2− In classical organometallic chemistry, the formal oxidation state of the metal and the electron count of the complex both in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |