|
Tehom
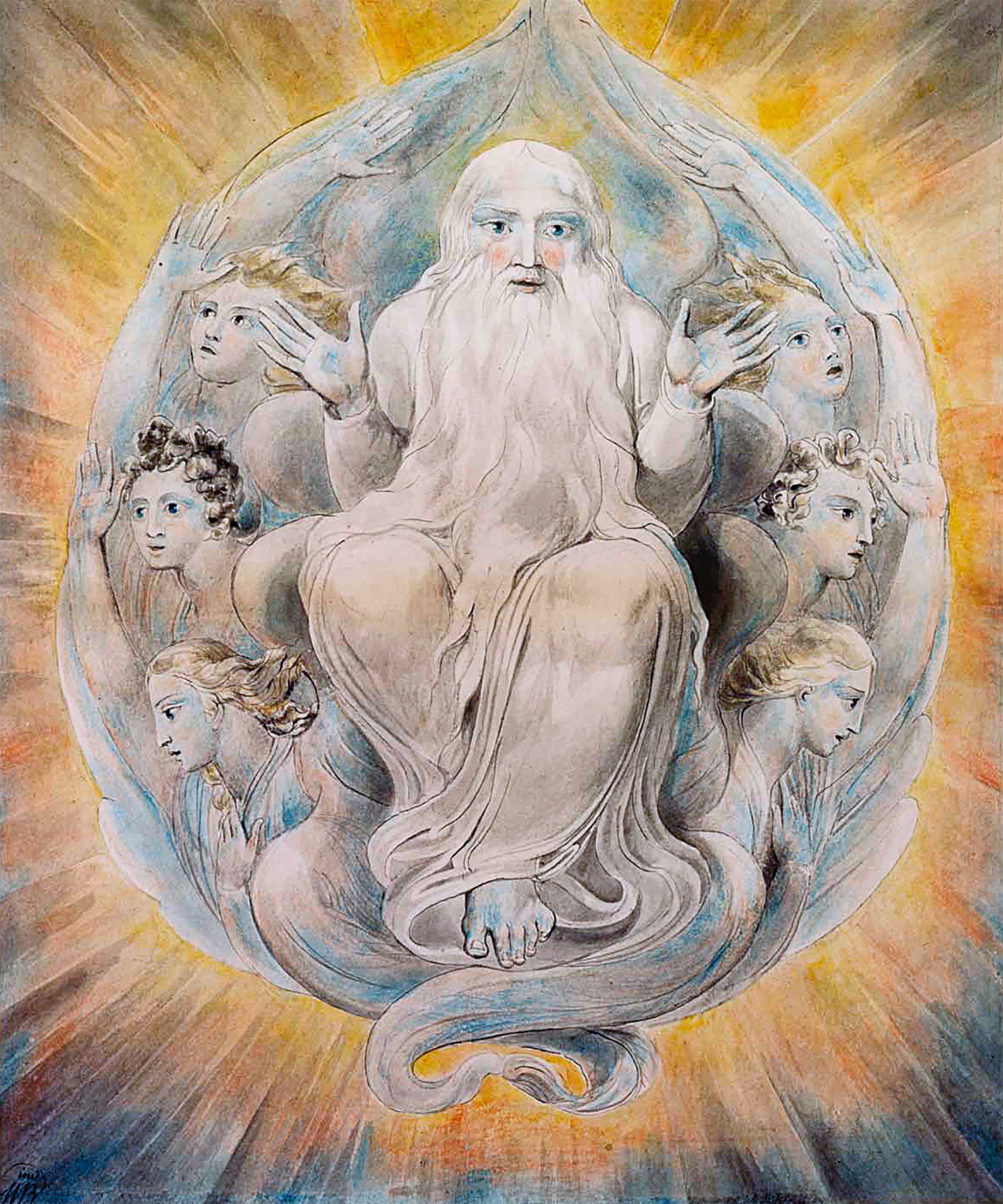
Tehom ( ''təhôm'') is a Northwest Semitic and Biblical Hebrew word meaning "the deep" or "abyss" (literally "the deeps"). It is used to describe the primeval ocean and the post- creation waters of the earth. It is a cognate of the Akkadian words '' tiāmtum'' and ''tâmtum'' as well as Ugaritic '' t-h-m'' which have similar meanings. According to a theological dictionary, ''tehom'' derives from a Semitic root which denoted the sea as a non-personified entity with mythological import. Genesis Tehom is mentioned in Genesis 1:2, where it is translated as "deep": The same word is used for the origin of Noah's flood in : Gnosticism Gnostics used Genesis 1:2 to propose that the original creator deity, called the Pléroma "Totality" or Bythós "Deep" preexisted Elohim and gave rise to such later divinities and spirits by way of emanations, progressively more distant and removed from the original form. In Mandaean cosmology, the Sea of Suf is a primordial sea in the World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abyss (religion)
In the Bible, the abyss is an unfathomably deep or boundless place. The term comes from the Greek language, Greek word ''abyssos'' (), meaning "deep, unfathomable, boundless". It is used as both an adjective and a noun. It appears in the Septuagint, which is the earliest Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible, and in the New Testament. It translates the Hebrew words ''tehom, tehóm'' (), ''ṣulā'' ( "sea-deep, deep flood") and the name of the sea monster ''rahab (term), rahab'' ( "spacious place; rage, fierceness, insolence, pride.") The Book of Jonah portrays the prophet's near death experience and his descent to the abyss. In the original sense of the Hebrew ''tehóm'', the abyss was the primordial waters or Chaos (cosmogony), chaos out of which the ordered world was created (). The term could also refer literally to the depths of the sea, the deep source of a spring or the interior of the Earth. In a later extended sense in intertestamental Jewish literature, the abyss was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Genesis Creation Narrative
The Genesis creation narrative is the creation myth of both Judaism and Christianity, told in the book of Genesis chapters 1 and 2. While the Jewish and Christian tradition is that the account is one comprehensive story, modern scholars of biblical criticism identify the account as a composite work made up of two different stories drawn from different sources. The first account, in Genesis 1:1–2:3, is from what scholars call the Priestly source (P), largely dated to the 6th century BC. In this story, Elohim (the Hebrew generic word for "god") creates the heavens and the Earth in six days, and then rests on, blesses, and sanctifies the seventh (i.e., the Biblical Sabbath). The second account, which takes up the rest of Genesis 2, is largely from the Jahwist source (J), commonly dated to the 10th or 9th centuries BC. In this story, God (now referred to by the personal name Yahweh) creates Adam, the first man, from dust and places him in the Garden of Eden. There, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wenceslas Hollar - Chaos (State 1)
Wenceslaus, Wenceslas, Wenzeslaus and Wenzslaus (and other similar names) are Latinized forms of the Czech name Václav. The other language versions of the name are , , , , , , among others. It originated as a Latin spelling for Czech rulers. It is a Slavic dithematic name (of two lexemes), derived from the Slavic words ''veli/vyache/więce/više'' ("great(er), large(r)"), and ''slava'' ("glory, fame") – both very common in Slavic names – and roughly means "greater glory". Latinised name Wenceslaus corresponds to several West Slavic, Lechitic given names, such as ''Wieceslaw'', ''Wiecejslav'', ''Wieńczysław''/''Vienceslav'', ''Vjenceslav'', ''Węzel'', ''Wacław'' and a few more. People named Wenceslaus or spelling variations thereof include: * Wenceslaus I, Duke of Bohemia (907–935 or 929), saint and subject of the Christmas carol "Good King Wenceslas" * Wenceslaus II, Duke of Bohemia (died 1192) * Wenceslaus I of Bohemia (c. 1205–1253), King of Bohemia * Wenceslaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Creator Deity
A creator deity or creator god is a deity responsible for the creation of the Earth, world, and universe in human religion and mythology. In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator. A number of monolatristic traditions separate a secondary creator from a primary transcendent being, identified as a primary creator.(2004) Sacred Books of the Hindus Volume 22 Part 2: Pt. 2, p. 67, R.B. Vidyarnava, Rai Bahadur Srisa Chandra Vidyarnava Monotheism Atenism Initiated by Pharaoh Akhenaten and Queen Nefertiti around 1330 BCE, during the New Kingdom period in ancient Egyptian history. They built an entirely new capital city ( Akhetaten) for themselves and worshippers of their sole creator god in a wilderness. His father used to worship Aten alongside other gods of their polytheistic religion. Aten, for a long time before his father's time, was revered as a god among the many gods and goddesses in Egypt. Atenism was countermanded by later pharaoh Tutankhamun, as chro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sanchuniathon
Sanchuniathon (; Ancient Greek: ; probably from , " Sakkun has given"), variant ''šknytn'' also known as Sanchoniatho the Berytian, was a Phoenician author. His three works, originally written in the Phoenician language, survive only in partial paraphrase and a summary of a Greek translation by Philo of Byblos recorded by the Christian bishop Eusebius. These few fragments comprise the most extended literary source concerning Phoenician religion in either Greek or Latin: Phoenician sources, along with all of Phoenician literature, were lost with the parchment on which they were written. The author All knowledge of Sanchuniathon and his work comes from the '' Praeparatio Evangelica'' of Eusebius (I. chs ix-x), which contains some information about him, along with the only surviving excerpts from his writing, as summarized and quoted from his purported translator, Philo of Byblos. Eusebius quotes neo-Platonist writer Porphyry as stating that Sanchuniathon of Berytus (Beiru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
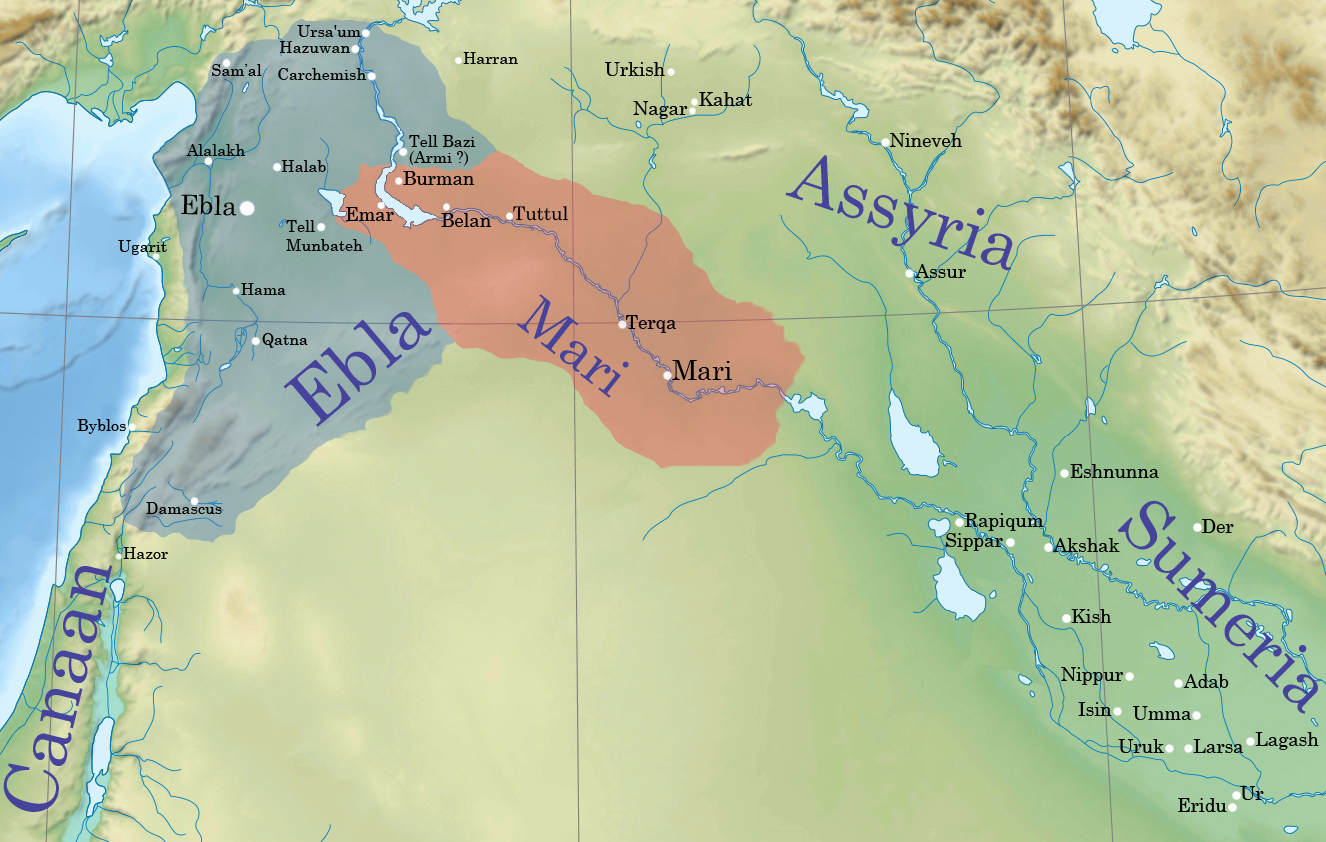
Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Ancient Near East, Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sheol
Sheol ( ; ''Šəʾōl'', Tiberian: ''Šŏʾōl'') in the Hebrew Bible is the underworld place of stillness and darkness which is death. Within the Hebrew Bible, there are few—often brief and nondescript—mentions of Sheol, seemingly describing it as a place where both the righteous and the unrighteous dead go, regardless of their moral choices in life. The implications of Sheol within the texts are therefore somewhat unclear; it may be interpreted as either a generic metaphor describing "the grave" into which all humans invariably descend, or an actual state of afterlife within Israelite thought. Though such practices are forbidden, the inhabitants of Sheol can, under some circumstances, be summoned by the living, as when the Witch of Endor calls up the spirit of Samuel for King Saul. While the Hebrew Bible appears to describe Sheol as the permanent place of the dead, in the Second Temple period (roughly 500 BC – 70 AD), a more diverse set of ideas developed. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kabbalistic
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal (). Jewish Kabbalists originally developed transmissions of the primary texts of Kabbalah within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. Kabbalists hold these teachings to define the inner meaning of both the Hebrew Bible and traditional rabbinic literature and their formerly concealed transmitted dimension, as well as to explain the significance of Jewish religious observances. Historically, Kabbalah emerged from earlier forms of Jewish mysticism, in 12th- to 13th-century al-Andalus (Spain) and in Hakhmei Provence, and was reinterpreted during the Jewish mystical renaissance in 16th-century Ottoman Palestine. The , the foundational text of Kabbalah, was author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Qlippoth
In the ''Zohar'', Lurianic Kabbalah, and Hermetic Qabalah, the ''qlippoth'' (, originally , plural of ''qəlippā''; literally "peels", "shells", or "husks"), are the representation of evil or impure spiritual forces in Jewish mysticism, the opposites of the sefirot. The realm of evil is called ''Sitra Achra'' () in Kabbalistic texts. In the Zohar The qlippoth are first mentioned in the ''Zohar'', where they are described as being created by God to function as a nutshell for holiness. The text subsequently relays an esoteric interpretation of the text of Genesis creation narrative in Genesis 1:14, which describes God creating the moon and sun to act as "luminaries" in the sky. The verse "Let there be luminaries ( ''məʾoroṯ'')," uses a defective spelling of the Hebrew plural form for "luminous body, light source" (), resulting in a written form identical to the Hebrew word for "curses." In the context of the ''Zohar'', interpreting the verse as calling the moon and sun " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location or state in the afterlife in which souls are subjected to punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history sometimes depict hells as eternal destinations, such as Christianity and Islam, whereas religions with reincarnation usually depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations, as is the case in the Indian religions. Religions typically locate hell in another dimension or under Earth's surface. Other afterlife destinations include heaven, paradise, purgatory, limbo, and the underworld. Other religions, which do not conceive of the afterlife as a place of punishment or reward, merely describe an abode of the dead, the grave, a neutral place that is located under the surface of Earth (for example, see Kur, Hades, and Sheol). Such places are sometimes equated with the English word ''hell'', though a more correct translation would be "underworld" or "world of the dead". The ancient Mesopotamian, Greek, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
World Of Darkness (Mandaeism)
In Mandaeism, the World of Darkness () is the underworld located below Tibil (Earth). It is ruled by its king Ur the Leviathan and its queen Ruha, mother of the seven planets and twelve constellations. Description The great dark Sea of Suf lies in the World of Darkness. The great dividing river of Hitpun, analogous to the river Styx in Greek mythology Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ..., separates the World of Darkness from the World of Light. Siniawis is one of the regions of the World of Darkness. The '' Ginza Rabba'' mention the Abaddons (''ebdunia'') as part of the World of Darkness. The '' Right Ginza'' mentions the existence of the "upper Abaddons" (''ebdunia ʿlaiia'') as well as the "lower Abaddons" (''ebdunia titaiia''). The World of Darkness i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sea Of Suf
A sea is a large body of salt water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the ocean, the interconnected body of seawaters that spans most of Earth. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order sections of the oceanic sea (e.g. the Mediterranean Sea), or certain large, nearly landlocked bodies of water. The salinity of water bodies varies widely, being lower near the surface and the mouths of large rivers and higher in the depths of the ocean; however, the relative proportions of dissolved salts vary little across the oceans. The most abundant solid dissolved in seawater is sodium chloride. The water also contains salts of magnesium, calcium, potassium, and mercury, among other elements, some in minute concentrations. A wide variety of organisms, including bacteria, protists, algae, plants, fungi, and animals live in various marine habitats and ecosystems throughout the seas. These range vertically from the sunlit surface and shoreline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |