|
Szeged
Szeged ( , ; see also other alternative names) is the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat of Csongrád-Csanád county. The University of Szeged is one of the most distinguished universities in Hungary. The Szeged Open Air (Theatre) Festival (first held in 1931) is one of the main attractions, held every summer and celebrated as the Day of the City on 21 May. Etymology The name ''Szeged'' might come from an old Hungarian word for 'corner' (), pointing to the turn of the river Tisza that flows through the city. Others say it derives from the Hungarian word which means 'island'. Others still contend that means 'dark blond' () – a reference to the color of the water where the rivers Tisza and Maros merge. The city has its own name in a number of foreign languages, usually by adding a suffix ''-in'' to the Hungarian name: Romanian ; German or ; Serbo-Croatian /; Greek (''Partiskon''); It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szeged002
Szeged ( , ; see also other alternative names) is the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat of Csongrád-Csanád county. The University of Szeged is one of the most distinguished universities in Hungary. The Szeged Open Air (Theatre) Festival (first held in 1931) is one of the main attractions, held every summer and celebrated as the Day of the City on 21 May. Etymology The name ''Szeged'' might come from an old Hungarian word for 'corner' (), pointing to the turn of the river Tisza that flows through the city. Others say it derives from the Hungarian word which means 'island'. Others still contend that means 'dark blond' () – a reference to the color of the water where the rivers Tisza and Maros merge. The city has its own name in a number of foreign languages, usually by adding a suffix ''-in'' to the Hungarian name: Romanian ; German or ; Serbo-Croatian /; Greek (''Partiskon''); Italia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szeged Town Hall In Winter 2009 (1)
Szeged ( , ; see also other alternative names) is the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat of Csongrád-Csanád county. The University of Szeged is one of the most distinguished universities in Hungary. The Szeged Open Air (Theatre) Festival (first held in 1931) is one of the main attractions, held every summer and celebrated as the Day of the City on 21 May. Etymology The name ''Szeged'' might come from an old Hungarian word for 'corner' (), pointing to the turn of the river Tisza that flows through the city. Others say it derives from the Hungarian word which means 'island'. Others still contend that means 'dark blond' () – a reference to the color of the water where the rivers Tisza and Maros merge. The city has its own name in a number of foreign languages, usually by adding a suffix ''-in'' to the Hungarian name: Romanian ; German or ; Serbo-Croatian /; Greek (''Partiskon''); Italia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
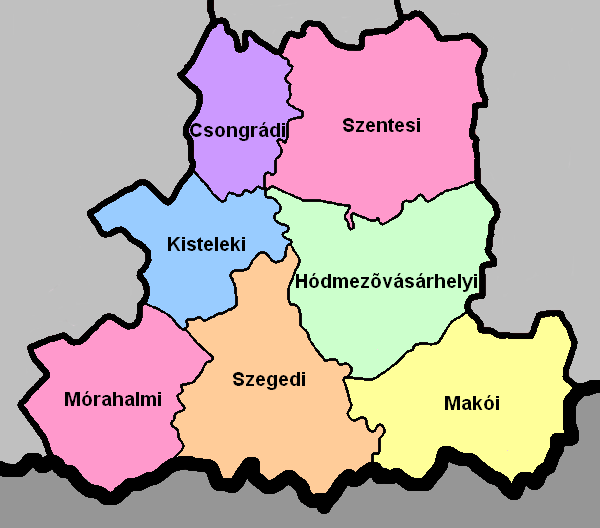
Szeged District
Szeged ( hu, Szegedi járás; sr, Сегедински округ, Segedinski okrug; german: Kreis Szegedin) is a district in southern part of Csongrád County. ''Szeged'' is also the name of the town where the district seat is found. The district is located in the Southern Great Plain Statistical Region. Geography Szeged District borders with Kistelek District to the northwest, Hódmezővásárhely District to the northeast, Makó District to the east, the Serbian districts of North Banat to the east and North Bačka to the south, Mórahalom District to the west. The number of the inhabited places in Szeged District is 13. Municipalities The district has 1 urban county, 1 town, 1 large village and 10 villages. (ordered by population, as of 1 January 2012) The bolded municipalities are cities, ''italics'' municipality is large village. Demographics In 2011, it had a population of 204,263 and the population density was 276/km². Ethnicity Besides the Hungarian maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Csongrád-Csanád County
Csongrád-Csanád ( hu, Csongrád-Csanád megye ) is the name of an administrative county (comitatus or ''megye'') in southern Hungary, straddling the river Tisza, on the border with Serbia and Romania. It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Bács-Kiskun County, Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County and Békés. The administrative centre of Csongrád-Csanád county is Szeged. The county is also part of the Danube–Criș–Mureș–Tisa Euroregion. History On October 3, 2017, the Hungarian Parliament passed a resolution to rename Csongrád County to Csongrád-Csanád County, which took effect on June 4, 2020. The resolution was submitted by János Lázár, then-Minister of the Prime Minister's Office, who called the renaming symbolic as more than a dozen settlements in the area still share Csanád County's identity. Geography This county has a total area of – 4,58% of Hungary. The area of Csongrád-Csanád County is flat. It has a high number of sunshine hours and excellent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns Of Hungary
Hungary has 3,152 municipalities as of July 15, 2013: 346 towns (Hungarian term: ''város'', plural: ''városok''; the terminology doesn't distinguish between cities and towns – the term town is used in official translations) and 2,806 villages (Hungarian: ''község'', plural: ''községek'') of which 126 are classified as large villages (Hungarian: ''nagyközség'', plural: ''nagyközségek''). The number of towns can change, since villages can be elevated to town status by act of the President. The capital Budapest has a special status and is not included in any county while 23 of the towns are so-called urban counties (''megyei jogú város'' – town with county rights). All county seats except Budapest are urban counties. Four of the cities (Budapest, Miskolc, Győr, and Pécs) have agglomerations, and the Hungarian Statistical Office distinguishes seventeen other areas in earlier stages of agglomeration development. The largest city is the capital, Budapest, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Hungary
Districts of Hungary are the second-level divisions of Hungary after counties. They replaced the 175 subregions of Hungary in 2013. Altogether, there are 174 districts in the 19 counties, and there are 23 districts in Budapest. Districts of the 19 counties are numbered by Arabic numerals and named after the district seat, while districts of Budapest are numbered by Roman numerals and named after the historical towns and neighbourhoods. In Hungarian, the districts of the capital and the rest of the country hold different titles. The districts of Budapest are called ''kerületek'' (lit. district, pl.) and the districts of the country are called ''járások.'' By county Baranya County Bács-Kiskun County Békés County Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County Csongrád-Csanád County Fejér County Győr-Moson-Sopron County Hajdú-Bihar County Heves County Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County Komárom-Esztergom County Nógrád County Pest County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbs In Hungary
The Serbs in Hungary ( hu, Magyarországi szerbek, sr, Срби у Мађарској / ) are recognized as an ethnic minority, numbering 7,210 people or 0.1% of the total population (2011 census). The number of Serbs in Hungary has drastically diminished; in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries large Serb communities existed throughout Hungary, notably in Buda (western Budapest), Baja, Szentendre and Szeged. The Serb community in the territory of present-day Hungary has its origin in migrations from the territory of medieval Serbian states during and after the Ottoman conquest of these states. Matthias Corvinus and his successors are known to have welcomed Serbs from the other side of the Danube, giving the exiled military commanders fiefdoms to rule and defend from the Ottomans. After the dissolution of Austro-Hungarian monarchy in 1918 and after new borders were defined by the Treaty of Trianon in 1920, only a small fraction of ethnic Serbs remained within the borders of post-Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City With County Rights
A city with county rights (or urban county, Hungarian: ''megyei jogú város'', MJV) is a level of administrative subdivision in Hungary. Since 1994 all county seats are automatically awarded this status, and since 2012 this is the only way a new city may become a city with county rights. However, all cities that achieved this rank before 2012 have retained their status and there is no law that provides for the revocation of this title. As such, cities like Hódmezővásárhely or Dunaújváros that are not county seats are still cities with county rights. From 2006 until 2022, there were 23 cities with county rights. Since May 2022, there are 25 cities with county rights. Before 1950, the former so-called cities with municipal rights ''(törvényhatósági jogú város)'' had a similar status as the present urban counties. Budapest is not considered an urban county and has a special status among the other Hungarian cities. Every city with county rights is allowed to be subdivide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In Hungary
The Catholic Church in Hungary or Hungarian Catholic Church ( hu, Magyar Katolikus Egyház) is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. According to a 2019 survey by Eurobarometer, 62% of Hungarians consider themselves Catholics. The country is divided into 12 dioceses including 4 archdioceses. In addition, there is a territorial abbey and a separate sui juris particular Church for those who adhere to the Byzantine Rite known as the Hungarian Greek Catholic Church. History From early times to the accession of St. Stephen (997) Since the early times the territory of the former Kingdom of Hungary were inhabited by many peoples followed by several waves of migrations until the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin. At about the same time, under their leader Árpád ( 845 – 907), they began once more expeditions to the countries west of them in order to recon the neighboring environments and secure their n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Free City
Royal free city or free royal city (Latin: libera regia civitas) was the official term for the most important cities in the Kingdom of Hungary from the late 12th centuryBácskai Vera – Nagy Lajos: Piackörzetek, piacközpontok és városok Magyarországon 1828-ban. Budapest, 1984. until the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. These cities were granted certain privileges by the king to rule out the possibility of the control of the Hungarian nobility, hence "royal", and exercised some self-government in relation to their internal affairs, hence "free". From the late 14th century, the elected envoys of the Royal free cities participated in the sessions of the Hungarian parliament, thus they became part of the legislature. The list include also cities in the Kingdom of Croatia and the Banate of Bosnia, which were part of the Lands of the Hungarian Crown. The term "royal free city" in the languages of the kingdom is: * la, Libera regia civitas * hu, Szabad királyi város *german: Kö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Urban Areas In Hungary
This is a list of the most populous urban areas in Hungary, based on official data of the Hungarian Central Statistical Office (KSH) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Methodology The functional urban areas identified with the methodology described in the book ''Redefining “urban”: A new way to measure metropolitan areas'' (OECD Publishing, 2012) are here listed by size, according to four different classes: * Small urban areas (population between 50,000 and 200,000) * Medium-sized urban areas (population between 200,000 and 500,000) * Metropolitan areas (population between 500,000 and 1.5 million) * Large metropolitan areas (population above 1.5 million) List of most populous urban areas See also * List of cities and towns of Hungary * Regions of Hungary * Counties of Hungary References External links {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Cities And Towns In Hungary Hungary Demographics of Hungary Hungary Urban areas An urban area, bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographics Of Hungary
Population This article is about the demographic features of the population of Hungary, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. Hungary's population has been slowly declining since 1980.The population composition at the foundation of Hungary (895) depends on the size of the arriving Hungarian population and the size of the Slavic (and remains of Avar-Slavic) population at the time. One source mentions 200 000 Slavs and 400 000 Hungarians, while other sources often don't give estimates for both, making comparison more difficult. The size of the Hungarian population around 895 is often estimated between 120 000 and 600 000, with a number of estimates in the 400-600 000 range.Edgar C. Polomé, Essays on Germanic religion, Institute for the Study of Man, 1989, p. 15/ref> Other sources only mention a fighting force of 25 000 Magyar warriors used in the attack, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_of_Hungary.png)


