|
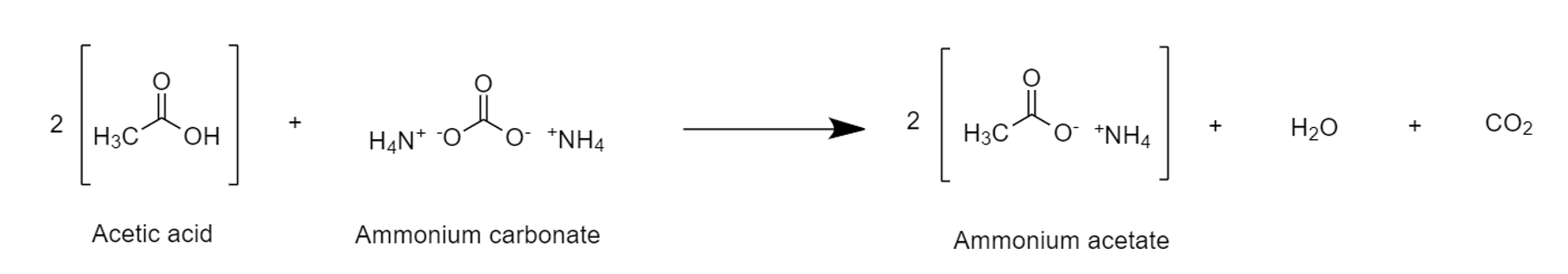
Solvolysis
In chemistry, solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution (S1/S2) or elimination reaction, elimination where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characteristic of S1 reactions, solvolysis of a chirality (chemistry), chiral reactant affords the racemate. Sometimes however, the stereochemical course is complicated by intimate ion pairs, whereby the leaving anion remains close to the carbocation, effectively shielding it from an attack by the nucleophile. Particularly fast reactions can occur by neighbour group participation, with nonclassical ions as intermediates or transition states. Examples For certain nucleophiles, solvolysis reactions are classified. Solvolysis involving water (molecule), water is called hydrolysis. Related terms are alcoholysis (Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols) and specifically methanolysis (methanol), acetolysis, ammonolysis (ammonia), and aminolysis (alkyl amines). Glycolysis is however an older term for the multistep conversion of glucose to pyruvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonclassical Ion
Nonclassical carbocations are stabilized by charge delocalization from contributions of neighbouring or bonds, which can form bridged intermediates or transition states. Nonclassical ions have been extensively studied with the 2-norbornyl system, which as “naked” ion unambiguously exhibit such a bridged structure. The landmark of nonclassical ions are unexpectedly fast solvolysis rates and large differences between epimeric esters. Such behaviour is not restricted to 2-norbornyl esters, as has been shown with some cyclopentyl and steroidal esters with the tosyloxy leaving group. Substitution reactions of secondary esters occur by SN2- or SN1-like mechanisms. Only in highly polar solvents such as hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) of low nucleophilicity one can expect a nearly same uniform SN1-like mechanism. The solvolysis of several cyclopentyl and steroidal esters show that large solvolysis rates and differences between epimers can occur which surpass those of the 2-norbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholysis
In chemistry, solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution (S1/S2) or elimination where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characteristic of S1 reactions, solvolysis of a chiral reactant affords the racemate. Sometimes however, the stereochemical course is complicated by intimate ion pairs, whereby the leaving anion remains close to the carbocation, effectively shielding it from an attack by the nucleophile. Particularly fast reactions can occur by neighbour group participation, with nonclassical ions as intermediates or transition states. Examples For certain nucleophiles, solvolysis reactions are classified. Solvolysis involving water is called hydrolysis. Related terms are alcoholysis (alcohols) and specifically methanolysis (methanol), acetolysis, ammonolysis (ammonia), and aminolysis (alkyl amines). Glycolysis is however an older term for the multistep conversion of glucose to pyruvate. Hydrolysis While solvolysis often refers to an organic chemistry context ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intimate Ion Pair
In chemistry, the intimate ion pair concept, introduced by Saul Winstein, describes the interactions between a cation, anion and surrounding solvent molecules. In ordinary aqueous solutions of inorganic salts, an ion is completely solvated and shielded from the counterion. In less polar solvents, two ions can still be connected to some extent. In a ''tight'', ''intimate'', or ''contact'' ion pair, there are no solvent molecules between the two ions. When solvation increases, ionic bonding decreases and a ''loose'' or ''solvent-shared'' ion pair results. The ion pair concept explains stereochemistry in solvolysis. The concept of intimate ion pairs is used to explain the slight tendency for inversion of stereochemistry during an S1 reaction. It is proposed that solvent or other ions in solution may assist in the removal of a leaving group to form a carbocation which reacts in an S1 fashion; similarly, the leaving group may associate loosely with the cationic intermediate. The as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminolysis
In chemistry, aminolysis (/am·i·nol·y·sis/) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule is Chemical decomposition, lysed (split into two parts) by reacting with ammonia () or an amine (any molecule containing a nitrogen atom with a lone pair, :N). The case where the reaction involves ammonia may be more specifically referred to as ammonolysis. Reactions Alkyl group An example of an aminolysis reaction is the replacement of a halogen in an alkyl group () by an amine () and the elimination of hydrogen halide (HX). :R-X + R'-NH2 -> R-NH-R' + HX Synthesis of peptides Another common example is the reaction of a primary amine or secondary amine with a carboxylic acid or with a carboxylic acid derivative to form an amide. This reaction is widely used, especially in the synthesis of peptides. On the simple addition of an amine to a carboxylic acid, a salt of the organic acid and base is obtained. To overcome this, the carboxylic acid first needs to be "activated". This is usually do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth ( botany), the formation of igneous rocks ( geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded ( ecology), the properties of the soil on the moon ( cosmochemistry), how medications work ( pharmacology), and how to collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture. Key concepts Many inorganic compounds are ionic compounds, consisting of cations and anions joined by ionic bonding. Examples of salts (which are ionic compounds) are magnesium chloride MgCl2, which consists of magnesium cations Mg2+ and chloride anions Cl−; or sodium oxide Na2O, which consists of sodium cations Na+ and oxide anions O2−. In any salt, the proportions of the ions are such that the electric charges cancel out, so that the bulk compound is ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex (chemistry)
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane (Me3B) is a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Chloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving a yellow color. The anhydrous material is important commercially. It has a low melting and boiling point. It is mainly produced and consumed in the production of aluminium metal, but large amounts are also used in other areas of the chemical industry. The compound is often cited as a Lewis acid. It is an example of an inorganic compound that reversibly changes from a polymer to a monomer at mild temperature. Structure Anhydrous adopts three structures, depending on the temperature and the state (solid, liquid, gas). Solid has a sheet-like layered structure with cubic close-packed chloride ions. In this framework, the Al centres exhibit octahedral coordination geometry. In contrast, has a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Ions In Aqueous Solution
A metal ion in aqueous solution or aqua ion is a cation, dissolved in water, of chemical formula (H2O)nsup>z+. The solvation number, ''n'', determined by a variety of experimental methods is 4 for Li+ and Be2+ and 6 for most elements in periods 3 and 4 of the periodic table. Lanthanide and actinide aqua ions have higher solvation numbers (often 8 to 9), with the highest knowm being 11 for Ac3+. The strength of the bonds between the metal ion and water molecules in the primary solvation shell increases with the electrical charge, ''z'', on the metal ion and decreases as its ionic radius, ''r'', increases. Aqua ions are subject to hydrolysis. The logarithm of the first hydrolysis constant is proportional to ''z''2/''r'' for most aqua ions. The aqua ion is associated, through hydrogen bonding with other water molecules in a secondary solvation shell. Water molecules in the first hydration shell exchange with molecules in the second solvation shell and molecules in the bulk liquid. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |