|
Segmental Arch
A segmental arch is a type of arch with a circular arc of less than 180 degrees. It is sometimes also called a scheme arch. The segmental arch is one of the strongest arches because it is able to resist thrust. To prevent failure, a segmental arch must have a rise that is equal to at least one-eighth the width of the span. Segmental arches with a rise that is less than one-eighth of the span width must have a permanent support or frame beneath the arch to prevent failure. As far as is known, the ancient Romans were the first to develop the segmental arch. The closed-spandrel Pont-Saint-Martin bridge in the Aosta Valley in Italy dates to 25 BC. The first open-spandrel segmental arch bridge is the Anji Bridge over the Xiao River in Hebei Province Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
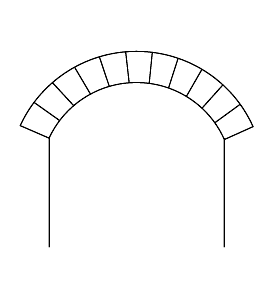
Arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent colla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent colla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer (architecture)
A springer is an architectural term for the lowest voussoir on each side of an arch. Since it is the bottom-most element of the arch, it is where the arch support terminates at the respond. It rests on the impost or pier of the arch, that is, the topmost part of the abutment An abutment is the substructure at the ends of a bridge span or dam supporting its superstructure. Single-span bridges have abutments at each end which provide vertical and lateral support for the span, as well as acting as retaining wal ..., from which the arch arises. Notes Arches and vaults {{architecturalelement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impost (architecture)
In architecture, an impost or impost block is a projecting block resting on top of a column or embedded in a wall, serving as the base for the springer or lowest voussoir of an arch. Ornamental training The imposts are left smooth or profiled, and "then express a certain separation between abutment and arch." The Byzantine fighters are high blocks, which are sometimes referred to as pulvino. The Romanesque designed the impost ornamentally or figuratively, similar to the capitals. In the Gothic period, the fighter almost completely disappeared from the calyx bud capital. The architecture of the Renaissance returns to the formation of the imposts of the ancient column orders. See also * Capital (architecture) * Abacus (architecture) In architecture, an abacus (from the Greek ''abax'', slab; or French ''abaque'', ''tailloir''; plural abacuses or abaci) is a flat slab forming the uppermost member or division of the capital of a column, above the bell. Its chief function is to . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
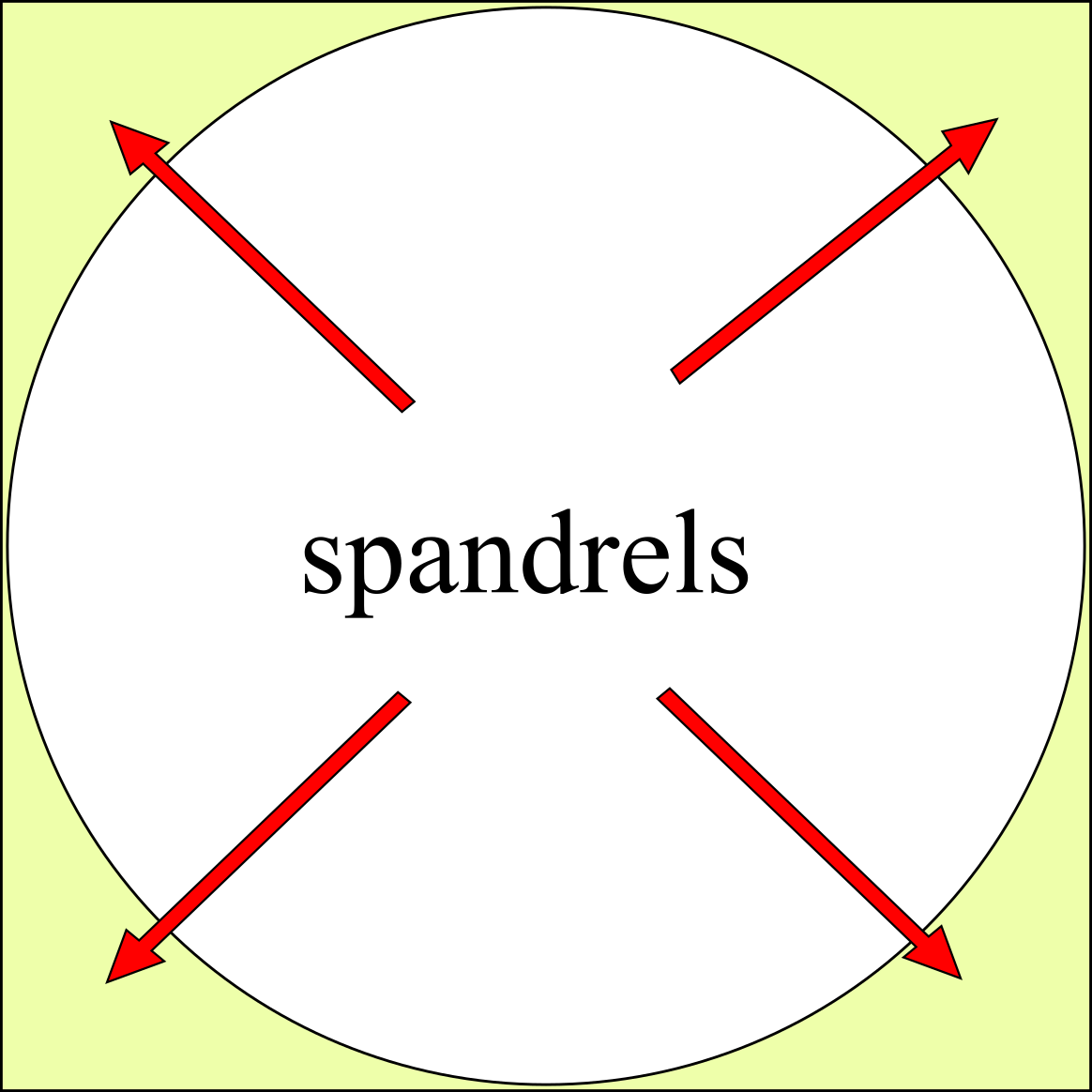
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pont-Saint-Martin (bridge)
The Pont-Saint-Martin is a Roman bridge in the Aosta Valley in Italy dating to the 1st century BC. The span is according to recent research, but frequently stated to be 35.64 m or 36.65 m. Other extant Roman bridges in the Aosta valley include the Pont d'Aël in the Cogne Valley and the Pont de Pierre (Aosta), Pont de Pierre in Aosta. See also * List of Roman bridges * Roman architecture * Roman engineering References Sources * External links * Traianus – Technical investigation of Roman public works Roman bridges in Italy Roman segmental arch bridges Deck arch bridges Stone bridges in Italy Bridges completed in the 1st century BC Bridges in Aosta Valley Pont-Saint-Martin, Aosta Valley {{Italy-bridge-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aosta Valley
, Valdostan or Valdotainian it, Valdostano (man) it, Valdostana (woman)french: Valdôtain (man)french: Valdôtaine (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = Official languages , population_blank1 = Italian French , demographics_type1 = Citizenship , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = Italian , demographics1_info1 = 95% , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-23 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €4.9 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €38,900 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Bridge
An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct (a long bridge) may be made from a series of arches, although other more economical structures are typically used today. History Possibly the oldest existing arch bridge is the Mycenaean Arkadiko Bridge in Greece from about 1300 BC. The stone corbel arch bridge is still used by the local populace. The well-preserved Hellenistic Eleutherna Bridge has a triangular corbel arch. The 4th century BC Rhodes Footbridge rests on an early voussoir arch. Although true arches were already known by the Etruscans and ancient Greeks, the Romans were – as with the vault and the dome – the first to fully realize the potential of arches for bridge construction. A list of Roman bridges compiled by the engineer Colin O'Connor featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anji Bridge
The Anji Bridge () is the world's oldest open-spandrel segmental arch bridge of stone construction.This title strictly applies only to the ''sum of attributes given'' (O’Connor, Colin: ''Roman Bridges'', Cambridge University Press 1993, , p.171): Various Roman stone pillar bridges featured wooden open-spandrel segmental arches as early as the 2nd century CE, among them Trajan's bridge, the longest bridge of the world to have been built for over a thousand years. Also, a dozen or more Roman close-spandrel stone segmental arch bridges are known from the 1st century BC onwards, such as the Ponte San Lorenzo (Padua), Alconétar Bridge and the Makestos Bridge (Turkey), the last having half-open spandrels. The 27 segmental arches of the Bridge at Limyra (300 ce) feature span to rise ratios between 5.3 and 6.5 to 1, making it an earlier example of a stone quarter circle segmental arch bridge. This leaves the Anji bridge the title of "the oldest ''open-spandrel'' stone quarter circle seg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiao River
The Xiao River ( ) is the Main Stream of the upper Xiang River located in Yongzhou, Hunan. As of 2011 Water Census of China, it has a length of from the headwaters to the confluence in the Ping Island of Yongzhou with the Xiang River West Branch (Left Branch) originating from Guangxi. With the tributaries, its drainage basin area is .As of 2011 Water Census of China, the Xiao River was identified as the Main Stem of the Upper Xiang River. 湘江源头在湖南蓝山, 湘江干流全长948公里, 流域面积94,721平方公里 - The source stream of the Xiang is in Lanshan County, the main river of the Xiang has a length of with a drainage basin area of rough , according thn.xinhuanet.como/ref> Geography The Xiao River borders to the south by the Mengzhu Mountains and Gui River of Xi River tributary, to the east by ''Yangming Mountains'' (阳明山), Chongling River and Lianjiang River of Bei River tributary, to the west by the Dupang Mountains. The tributaries of the Xiao r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)