|
Synteny
In genetics, the term synteny refers to two related concepts: * In classical genetics, ''synteny'' describes the physical co-localization of genetic loci on the same chromosome within an individual or species. * In current biology, ''synteny'' more commonly refers to ''colinearity'', i.e. conservation of blocks of order within two sets of chromosomes that are being compared with each other. These blocks are referred to as ''syntenic blocks''. The Encyclopædia Britannica gives the following description of synteny, using the modern definition: Etymology ''Synteny'' is a neologism meaning "on the same ribbon"; Greek: ', ''syn'' "along with" + ', ''tainiā'' "band". This can be interpreted classically as "on the same chromosome", or in the modern sense of having the same order of genes on two (homologous) strings of DNA (or chromosomes). : co-localization on a chromosome The classical concept is related to genetic linkage: Linkage between two loci is established by the observat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Comparative Genomics
Comparative genomics is a branch of biological research that examines genome sequences across a spectrum of species, spanning from humans and mice to a diverse array of organisms from bacteria to chimpanzees. This large-scale holistic approach compares two or more genomes to discover the similarities and differences between the genomes and to study the biology of the individual genomes. Comparison of Whole genome sequencing, whole genome sequences provides a highly detailed view of how organisms are related to each other at the gene level. By comparing whole genome sequences, researchers gain insights into Genetics, genetic relationships between organisms and study Evolutionary biology, evolutionary changes. The major principle of comparative genomics is that common features of two organisms will often be encoded within the DNA that is evolutionarily Conserved sequence, conserved between them. Therefore, Comparative genomics provides a powerful tool for studying evolutionary chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hox Gene
Hox genes, a subset of homeobox, homeobox genes, are a gene cluster, group of related genes that Evolutionary developmental biology, specify regions of the body plan of an embryo along the craniocaudal axis, head-tail axis of animals. Hox proteins encode and specify the characteristics of 'position', ensuring that the correct structures form in the correct places of the body. For example, Hox genes in insects specify which appendages form on a segment (for example, legs, antennae, and wings in fruit flies), and Hox genes in vertebrates specify the types and shape of vertebrae that will form. In segmented animals, Hox proteins thus confer segmental or positional identity, but do not form the actual segments themselves. Studies on Hox genes in ciliated larvae have shown they are only expressed in future adult tissues. In larvae with gradual metamorphosis the Hox genes are activated in tissues of the larval body, generally in the trunk region, that will be maintained through metamorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Happy Mapping
In genetics, HAPPY Mapping, first proposed by Paul H. Dear and Peter R. Cook in 1989, is a method used to study the linkage between two or more DNA sequences. According to thSingle Molecule Genomics Group it is ''"Mapping based on the analysis of approximately HAPloid DNA samples using the PolYmerase chain reaction"''. In genomics, HAPPY mapping can be applied to assess the synteny and orientation of various DNA sequences across a particular genome - the generation of a "genomic" map. As with linkage mapping, HAPPY mapping relies on the differential probability of two or more DNA sequences being separated. In genetic mapping, the probability of a recombination event between two genetic loci on the same chromosome A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ... is directly propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BLAST (biotechnology)
In bioinformatics, BLAST (basic local alignment search tool) is an algorithm and program for comparing Primary structure, primary biological sequence information, such as the amino acid, amino-acid sequences of proteins or the nucleotides of DNA sequence, DNA and/or RNA sequences. A BLAST search enables a researcher to compare a subject protein or nucleotide sequence (called a query) with a library or database of sequences, and identify database sequences that resemble the query sequence above a certain threshold. For example, following the discovery of a previously unknown gene in the Mus musculus, mouse, a scientist will typically perform a BLAST search of the human genome to see if humans carry a similar gene; BLAST will identify sequences in the human genome that resemble the mouse gene based on similarity of sequence. Background BLAST is one of the most widely used bioinformatics programs for sequence searching. It addresses a fundamental problem in bioinformatics research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
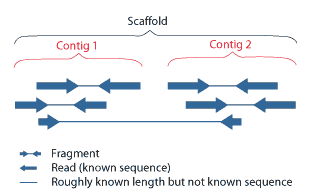
Contig
A contig (from ''contiguous'') is a set of overlapping DNA segments that together represent a consensus region of DNA.Gregory, S. ''Contig Assembly''. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 2005. In bottom-up sequencing projects, a contig refers to overlapping sequence data ( reads); in top-down sequencing projects, contig refers to the overlapping clones that form a physical map of the genome that is used to guide sequencing and assembly.Dear, P. H. ''Genome Mapping''. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 2005. . Contigs can thus refer both to overlapping DNA sequences and to overlapping physical segments (fragments) contained in clones depending on the context. Original definition of contig In 1980, Staden wrote: ''In order to make it easier to talk about our data gained by the shotgun method of sequencing we have invented the word "contig". A contig is a set of gel readings that are related to one another by overlap of their sequences. All gel readings belong to one and only one cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in question. In addition to their use for inferring phylogenetic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trait (biology)
A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotypic characteristic of an organism; it may be either inherited or determined environmentally, but typically occurs as a combination of the two.Lawrence, Eleanor (2005) ''Henderson's Dictionary of Biology''. Pearson, Prentice Hall. For example, having eye color is a ''character'' of an organism, while blue, brown and hazel versions of eye color are ''traits''. The term ''trait'' is generally used in genetics, often to describe the phenotypic expression of different combinations of alleles in different individual organisms within a single population, such as the famous purple vs. white flower coloration in Gregor Mendel's pea plants. By contrast, in systematics, the term ''character state'' is employed to describe features that represent fixed diagnostic differences among taxa, such as the absence of tails in great apes, relative to other primate groups. Definition A phenotypic trait is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enterobacteriales
Enterobacterales is an order of Gram-negative, non-spore forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria with the class Gammaproteobacteria. The type genus of this order is ''Enterobacter.'' The name Enterobacterales is derived from the Latin term ''Enterobacter'', referring the type genus of the order and the suffix "-ales", an ending used to denote an order. Together, Enterobacterales refers to an order whose nomenclatural type is the genus ''Enterobacter''. Historical Identification and Systematics Enterobacterales was proposed in 2005 under the name "Enterobacteriales". However, the name "Enterobacteriales" was not validated according to the rules of the ''International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes,'' thus it lacked standing in nomenclature, so the name was written in parentheses. "Enterobacteriales" was a monotypic order, containing only the family ''Enterobacteriaceae'', and shared its type genus ''Escherichia''.NCBEnterobacteralesaccessed 9 Mar 2013 The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hyphomicrobiales
The Hyphomicrobiale' (synonym Rhizobiales) are an order of Gram-negative Alphaproteobacteria. The rhizobia, which fix nitrogen and are symbiotic with plant roots, appear in several different families. The four families '' Nitrobacteraceae'', '' Hyphomicrobiaceae'', '' Phyllobacteriaceae'', and '' Rhizobiaceae'' contain at least several genera of nitrogen-fixing, legume-nodulating, microsymbiotic bacteria. Examples are the genera '' Bradyrhizobium'' and ''Rhizobium''. Species of the '' Methylocystaceae'' are methanotrophs; they use methanol (CH3OH) or methane (CH4) as their sole energy and carbon sources. Other important genera are the human pathogens '' Bartonella'' and ''Brucella'', as well as ''Agrobacterium,'' an important tool in genetic engineering. Taxonomy Accepted families * '' Aestuariivirgaceae'' Li ''et al''. 2019 * '' Afifellaceae'' Hördt ''et al''. 2020 * '' Ahrensiaceae'' Hördt ''et al''. 2020 * '' Alsobacteraceae'' Sun ''et al''. 2018 * '' Amorphaceae'' Hör ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brachypodium
''Brachypodium'' is a genus of plants in the grass family, widespread across much of Africa, Eurasia, and Latin America. The genus is classified in its own tribe Brachypodieae. Flimsy upright stems form tussocks. Flowers appear in compact spike-like racemes with 5-25 flowers on each short-stalked spikelet in summer. Leaves are flat or curved. According to a study published in 2010, there is evidence of ''Brachypodium'' and cattail (''Typha'' spp.) residues occurring on prehistoric human grinding tools dated 28,000 years ago from Bilancino in central Italy. Another contemporaneously published study stated that the grain residues resemble ''Brachypodium'', based on a comparison to two modern specimens: "Among these, the grains, which are slightly angular, with hardly visible centric, point-shaped hila and adequate dimensions (in the sample measuring 9–14 μm), appeared very similar to those of ''Brachypodium'' or related genera." ;Species * ''Brachypodium × ambrosii'' - Spai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |