|
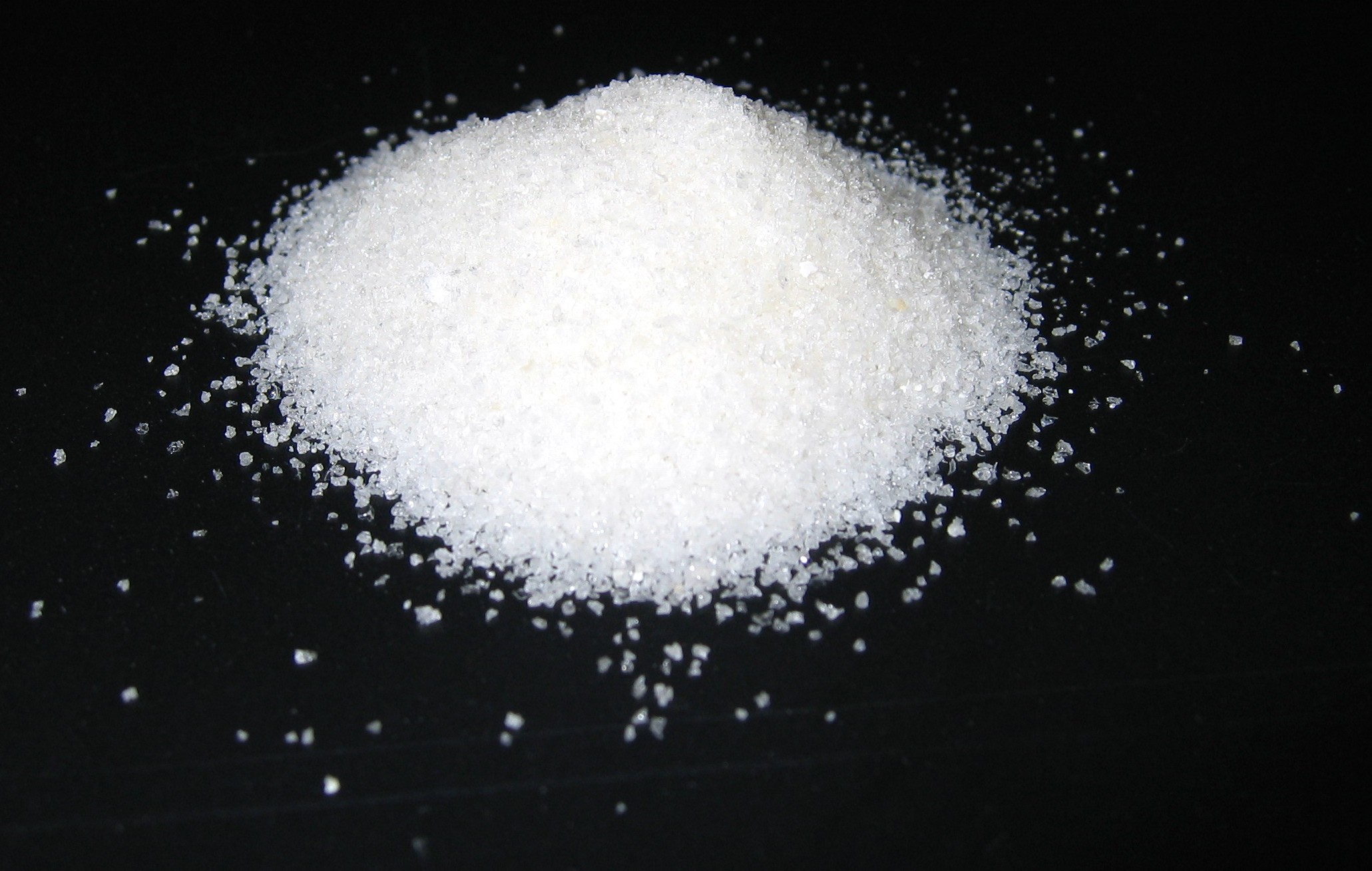
Superabsorbent Polymer
A superabsorbent polymer (SAP) (also called slush powder) is a water-absorbing hydrophilic homopolymers or copolymers that can absorb and retain extremely large amounts of a liquid relative to its own mass. Water-absorbing polymers, which are classified as hydrogels when mixed, absorb aqueous solutions through hydrogen bonding with water molecules. A SAP's ability to absorb water depends on the ionic concentration of the aqueous solution. In deionized and distilled water, a SAP may absorb 300 times its weight (from 30 to 60 times its own volume) and can become up to 99.9% liquid, and when put into a 0.9% saline solution the absorbency drops to approximately 50 times its weight. The presence of valence cations in the solution impedes the polymer's ability to bond with the water molecule. The SAP's total absorbency and swelling capacity are controlled by the type and degree of cross-linkers used to make the gel. Low-density cross-linked SAPs generally have a higher absorbent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
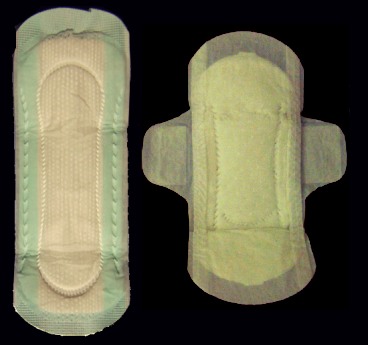
Sanitary Napkin
A menstrual pad is an absorbent item worn in the underwear when menstruating, bleeding after giving birth, recovering from gynecologic surgery, experiencing a miscarriage or abortion, or in any other situation where it is necessary to absorb a flow of blood from the vagina. A menstrual pad is a type of menstrual hygiene product that is worn externally, unlike tampons and menstrual cups, which are worn inside the vagina. Pads are generally changed by being stripped off the pants and panties, taking out the old pad, sticking the new one on the inside of the panties and pulling them back on. Pads are recommended to be changed every 3–4 hours to avoid certain bacteria that can fester in blood; this time also may differ depending on the kind worn, flow, and the time it is worn. Menstrual pads are made from a range of materials, differing depending on style, country of origin, and brand. The pads are not the same as incontinence pads, which generally have higher absorbency and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylic Acid
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: prop-2-enoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than a million tons are produced annually. History The word "acrylic" was coined in 1843, for a chemical derivative of acrolein, an acrid-smelling oil derived from glycerol. Production Acrylic acid is produced by oxidation of propylene, which is a byproduct of the production of ethylene and gasoline: : Historical methods Because acrylic acid and its esters have long been valued commercially, many other methods have been developed. Most have been abandoned for economic or environmental reasons. An early method was the hydrocarboxylation of acetylene (" Reppe chemistry"): : This method requires nickel carbonyl, high pressures of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helix, helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermentation, fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile is an organic compound with the formula and the structure . It is a colorless, volatile liquid. It has a pungent odor of garlic or onions. Its molecular structure consists of a vinyl group () linked to a nitrile (). It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics such as polyacrylonitrile. It is reactive and toxic at low doses. Acrylonitrile is one of the components of ABS plastic (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene). Structure and basic properties Acrylonitrile is an organic compound with the formula and the structure . It is a colorless, volatile liquid although commercial samples can be yellow due to impurities. It has a pungent odor of garlic or onions. Its molecular structure consists of a vinyl group () linked to a nitrile (). It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics such as polyacrylonitrile. It is reactive and toxic at low doses. Production Acrylonitrile was first synthesized by the French chemist Charle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid collection of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three- state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the secretary of agriculture, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The current secretary is Brooke Rollins, who has served since February 13, 2025. Approximately 71% of the USDA's $213 billion budget goes towards nutrition assistance programs administered by the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS). The largest component of the FNS budget is the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (formerly known as the 'Food Stamp' program), which is the cornerstone of USDA's nutrition assistance. The United States Fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluff Pulp
Fluff pulp (also called comminution pulp or fluffy pulp) is a type of chemical pulp made from long fibre softwoods. Important parameters for fluff pulp are bulk and water absorbency. History Fluff pulp was first developed for use in disposable sanitary napkins. Kotex's first advertisement for products made with wood pulp (Cellucotton) appeared in 1921. Disposable diaper producers also were early to convert to fluff pulp because of its low cost and high absorbency. Normal usage of fluff pulp in a diaper was about 55 percent. In the 1980s started the commercialization of air-laid paper, which gave better bulk, porosity, strength, softness, and water absorption properties compared with normal tissue paper. Also in the 1980s started the use of superabsorbents in diapers and reduced the need for fluff pulp and is now down to 15 grams or even less. The demand of the pulp in diapers has gone from being the absorbent of liquid to giving the products dry and wet strength. Manufacture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaculture Of Sea Sponges
Sea sponge aquaculture is the process of farming sea sponges under controlled conditions. It has been conducted in the world's oceans for centuries using a number of aquaculture techniques. There are many factors such as light, salinity, pH, dissolved oxygen and the accumulation of waste products that influence the growth rate of sponges. The benefits of sea sponge aquaculture are realised as a result of its ease of establishment, minimum infrastructure requirements and the potential to be used as a source of income for populations living in developing countries. Sea sponges are produced on a commercial scale to be used as bath sponges or to extract biologically active compounds which are found in certain sponge species. Techniques such as the rope and mesh bag method are used to culture sponges independently or within an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system setting. One of the only true sustainable sea sponges cultivated in the world occur in the region of Micronesia, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Paper
Tissue paper, or simply tissue, is a lightweight paper or light crêpe paper. Tissue can be made from recycled pulp (paper), paper pulp on a paper machine. Tissue paper is very versatile, and different kinds are made to best serve these purposes, which are hygienic tissue paper, facial tissues, paper towels, as packing material, among other (sometimes creative) uses. The use of tissue paper is common in developed nations, around 21 million tonnes in North America and 6 million in Europe, and is growing due to urbanization. As a result, the industry has often been scrutinized for deforestation. However, more companies are presently using more recycled fibres in tissue paper. Properties The key properties of tissues are absorbency, basis weight, thickness, bulk (specific volume), brightness, stretch, appearance and comfort. Production Tissue paper is produced on a Fourdrinier machine, paper machine that has a single large steam heated drying cylinder (Yankee dryer) fitted with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimberly Clark
Kimberly-Clark Corporation is an American multinational consumer goods and personal care corporation that produces mostly paper-based consumer products. The company manufactures sanitary paper products and surgical & medical instruments. Kimberly-Clark brand name products include Kleenex facial tissue, Kotex feminine hygiene products, Cottonelle, Scott and Andrex toilet paper, Wypall utility wipes, KimWipes scientific cleaning wipes and Huggies disposable diapers and baby wipes. Founded in Neenah, Wisconsin, in 1872 and based in the Las Colinas section of Irving, Texas, since 1985, the company operated its own paper mills around the world for decades, but closed the last of those in 2012. With recent annual revenues topping $18 billion per year, Kimberly-Clark is regularly listed among the Fortune 500. As of March 2020, the company had approximately 40,000 employees. History Kimberly, Clark and Co. was founded in 1872 by John A. Kimberly, Havilah Babcock, Charles B. Clark a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |