|
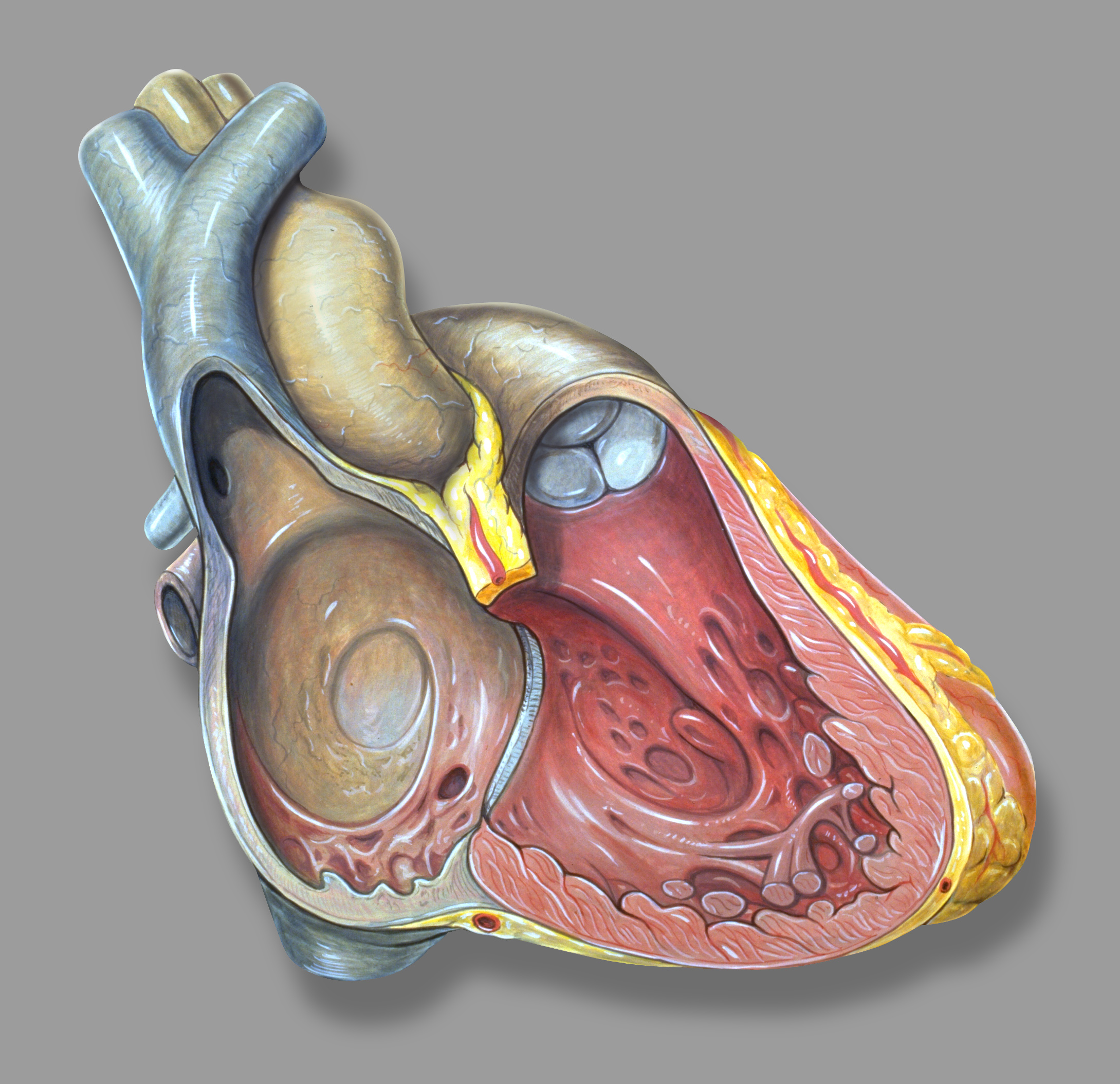
Sinoatrial Nodal Artery
The sinoatrial nodal artery, sinoatrial nodal artery or sinoatrial artery is an artery of the heart which supplies the sinoatrial node, the natural pacemaker center of the heart. It is usually a branch of the right coronary artery. It passes between the right atrium, and the opening of the superior vena cava. Anatomy Origin It arises from the right coronary artery in around 60% of individuals, from the left circumflex coronary artery in about 40% of individuals, and in less than 1% of humans, the artery has an anomalous origin directly from the coronary sinus, descending aorta, or distal right coronary artery. The origin of the sinoatrial node artery is not related to coronary artery dominance, which means the side (right or left) that provides the circulation to the back of the heart. In contrast, the atrioventricular nodal branch, that is the artery that brings blood to the atrioventricular node, depends on coronary artery dominance. Course In more than 50% of human hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
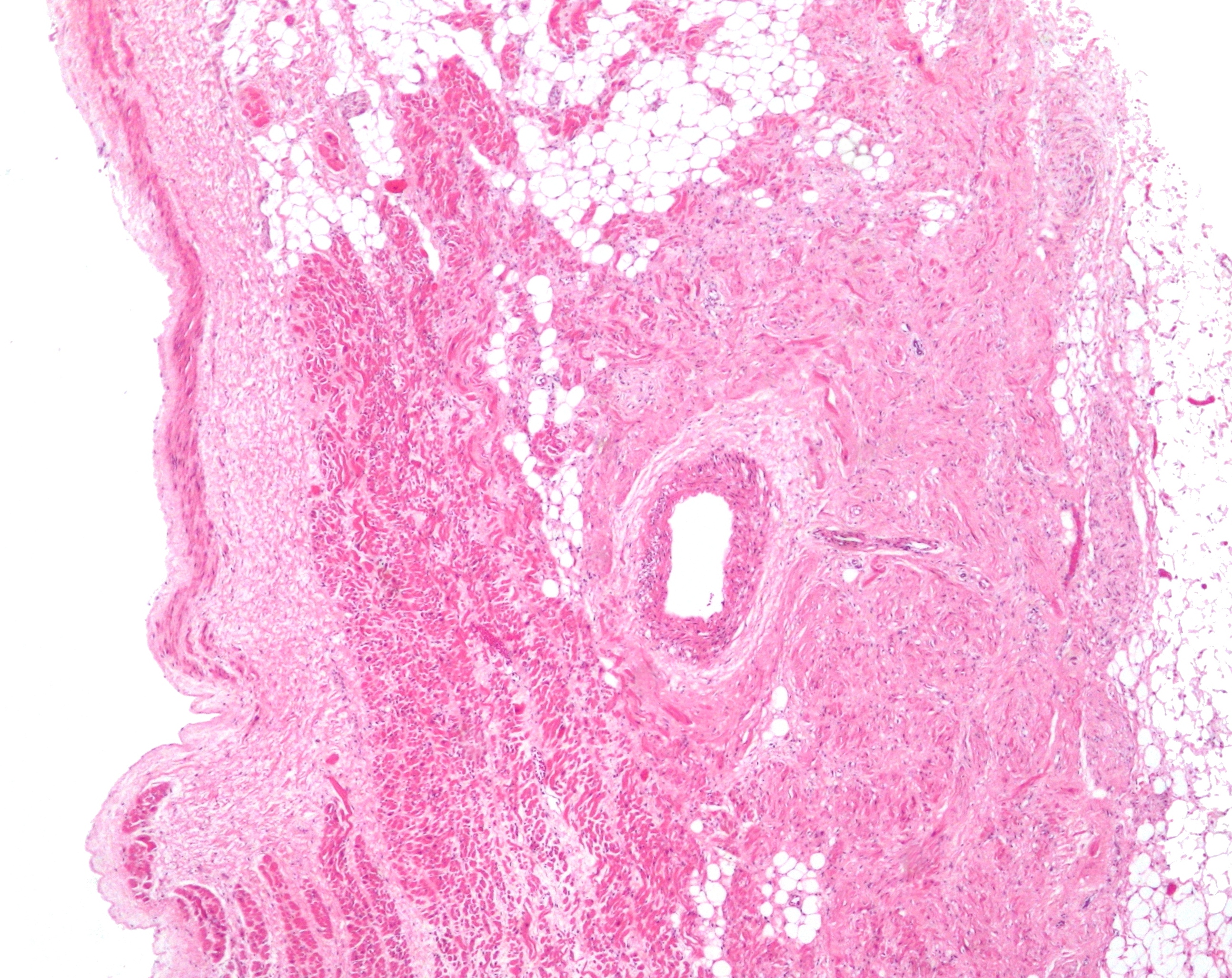
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Sinus
The coronary sinus () is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begins at the junction of the great cardiac vein, and oblique vein of the left atrium. It receives multiple tributaries. It passes across the backside of the heart along a groove between left atrium and left ventricle, then drains into the right atrium at the orifice of the coronary sinus (which is usually guarded by the valve of coronary sinus). Structure Origin The coronary sinus arises upon the posterior aspect of the heart between the left atrium, and left ventricle. The coronary sinus commences at the union of the great cardiac vein, and the oblique vein of the left atrium. The origin of the coronary sinus is marked by the Vieussens valve of the coronary sinus which is situated at the endpoint of the great cardiac vein. Cour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SA Artery From LCx Volume Rendererd
Sa, SA, S.A. or s.a. may refer to: Arts, media and entertainment Music * Initialism for "soprano and alto", voice types for which a piece of music is written * SA (Samurai Attack), a Japanese punk rock band * SA Martinez, a vocalist and DJ for the band 311 * Soziedad Alkoholika, a Spanish punk rock band * ''SA'', a 2018 album by Jonathan Richman * Strike Anywhere, a hardcore punk band from Richmond, Virginia Other media * ''Sa'' (film), a 2016 Indian film * ''S.A'' (manga), a manga series by Maki Minami * ''Something Awful'', a comedy website * Star Awards, an annual Singaporean television award ceremony * ''Subterranean Animism'', a video game from the Touhou series by ZUN * Siragadikka Aasai (TV series), an Indian TV series Language and writing * Sa (cuneiform), a cuneiform sign * sa (hieroglyph), an Egyptian hieroglyph meaning "protection" * Sa (kana) (さ and サ), characters (kana) in the two Japanese syllabaries * Saa language, spoken in Vanuatu * Sanskrit (ISO 639-1 code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablation Of Atrial Fibrillation
Ablation ( – removal) is the removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosive processes, or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, including spacecraft material for ascent and atmospheric reentry, ice and snow in glaciology, biological tissues in medicine and passive fire protection materials. Artificial intelligence In artificial intelligence (AI), especially machine learning, ablation is the removal of a component of an AI system. The term is by analogy with biology: removal of components of an organism. Biology Biological ablation is the removal of a biological structure or functionality. Genetic ablation is another term for gene silencing, in which gene expression is abolished through the alteration or deletion of genetic sequence information. In cell ablation, individual cells in a population or culture are destroyed or removed. Both can be used as experimental tools, as in loss-of-function experiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Atrial Appendage
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle, the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, previously known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. Auricles in this modern terminology are distinguished by having thicker muscu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approximately 15 mm long, 3 mm wide, and 1 mm thick, located directly below and to the side of the superior vena cava. These cells produce an electrical impulse known as a cardiac action potential that travels through the electrical conduction system of the heart, causing it to contract. In a healthy heart, the SA node continuously produces action potentials, setting the rhythm of the heart (sinus rhythm), and so is known as the heart's natural pacemaker. The rate of action potentials produced (and therefore the heart rate) is influenced by the nerves that supply it. Structure The sinoatrial node is an oval-shaped structure that is approximately 15 mm long, 3 mm wide, and 1 mm thick, located directly below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Atrium
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle, the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, previously known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. Auricles in this modern terminology are distinguished by having thicker mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interatrial Septum
The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart. Structure The interatrial septum is a that lies between the left atrium and right atrium of the human heart. The interatrial septum lies at angle of 65 degrees from right posterior to left anterior because right atrium is located at the right side of the body while left atrium is located at the left side of the body. The interatrial septum represents the posterior wall of the right atrium. Development The interatrial septum forms during the first and second months of fetal development. Formation of the septum occurs in several stages. The first is the development of the septum primum, a crescent-shaped piece of tissue forming the initial divider between the right and left atria. Because of its crescent shape, the septum primum does not fully occlude the space between the left and right atria; the opening that remains is called the ostium primum. During fetal development, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrioventricular Node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of the interatrial septum near the opening of the coronary sinus, and conducts the normal electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles. The AV node is quite compact (~1 x 3 x 5 mm).Full Size Picture triangle of-Koch.jpg Retrieved on 2008-12-22 Structure Location The AV node lies at the lower back section of the i ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descending Aorta
In human anatomy, the descending aorta is part of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The descending aorta begins at the aortic arch and runs down through the chest and abdomen. The descending aorta anatomically consists of two portions or segments, the thoracic and the abdominal aorta, in correspondence with the two great cavities of the trunk in which it is situated. Within the abdomen, the descending aorta branches into the two common iliac arteries which serve the pelvis and eventually legs. The ductus arteriosus connects to the junction between the pulmonary artery and the descending aorta in foetal life. This artery later regresses as the ligamentum arteriosum. The descending aorta has important functions within the body. The descending aorta transports oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. See also * Abbott artery References External links * – "Left side of the mediastinum The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Circumflex Coronary Artery
The circumflex branch of left coronary artery (also known as the left circumflex artery or circumflex artery) is a branch of the left coronary artery. It winds around the left side of the heart along the atrioventricular groove (coronary sulcus). It supplies the posterolateral portion of the left ventricle. In a minority of individuals, the left circumflex artery gives rise to the posterior interventricular artery, in which cases such a heart is deemed left dominant. Anatomy The left circumflex artery follows the left part of the coronary sulcus, running first to the left and then to the right, reaching nearly as far as the posterior longitudinal sulcus. There have been multiple anomalies described, for example the left circumflex having an aberrant course from the right coronary artery. Branches The circumflex artery curves to the left around the heart within the coronary sulcus, giving rise to one or more left marginal arteries (also called obtuse marginal branches) as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Vena Cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein that receives venous return from the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm. Venous return from the lower half, below the diaphragm, flows through the inferior vena cava. The SVC is located in the anterior right superior mediastinum. It is the typical site of central venous access via a central venous catheter or a peripherally inserted central catheter. Mentions of "the cava" without further specification usually refer to the SVC. Structure The superior vena cava is formed by the left and right brachiocephalic veins, which receive blood from the upper limbs, head and neck, behind the lower border of the first right costal cartilage. It passes vertically downwards behind the first intercostal space and receives the azygos vei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |